Abstract
A total of 61 specimens of deep-sea chimaeras (Hydrolagus melanophasma = 41; Chimaera sp. = 20) were obtained during September 2017 as by-catch of the local fishery of the Patagonian toothfish (Dissostichus eleginoides, Pisces: Nototheniidae) along the northern Chilean coasts (≈22°20′ S) at depths ranging from 950 to 1500 m using a deep-sea longline. Nine species of metazoan parasites were found in H. melanophasma and seven in Chimaera sp. Four species were shared between both host species. Gyrocotyle sp.1 (Cestodaria) and Multicalyx elegans (Aspidogastrea) showed the higher prevalence H. melanophasma (68.3% and 65.38%, respectively), whereas Plectognathotrema hydrolagi (Digenea), Gyrocotyle sp.1 (Cestodaria), and Chimaericola sp. (Monogenea) showed higher prevalence in Chimaera sp. (90%, 55% and 55%, respectively). Beta diversity analysis reveals that the parasite communities of these two related and sympatric species are strongly differentiated. Our results suggest a strong relationship between the ancient Holocephali, which harbor ancient parasites belonging to Rugogasteridae and Multicalycidae (Aspidogastrea), and two Cestodaria species. Chimaera spp. are also parasitized by some highly specific monogeneans, such as Chimaericola spp. Our results demonstrate the differences in the parasite community structures—both of ecto- and endoparasites—of two related and sympatric hosts.
1. Introduction
Without doubt, the deep sea—encompassing depths from 200 to 11,000 m—is the largest biotope on earth and remains largely unexplored [1]. Its biodiversity is still poorly understood, and the ecological relationships among the species inhabiting this environment remain almost unknown [2,3]
Despite the low values of primary production in the deep sea, important marine resources inhabit this environment, including the Patagonian toothfish Dissostichus eleginoides in the southern hemisphere [3]. Consequently, as coastal fisheries collapse, the deep-sea region may offer new resources [4]. It is therefore critical to possess not only clear and adequate knowledge of these potential new resources but also a sound understanding of the biodiversity of these ecosystems [5,6].
Parasites are an important component of any ecosystem, with the number of such species potentially being higher than that of the free-living species; for instance, the number of helminth species infecting vertebrates is at least 50% higher than the number of their hosts [7]. Parasites are also important because of the role they play in ecosystems, regulating the abundance or density of host populations, stabilizing food webs, and structuring host communities [8], as well as potentially providing critical information regarding ecology and phylogenetic information of the host species [9]. Data regarding the parasite fauna harbored by deep-sea fishes are available for less than 10% of the ichthyofauna that inhabit these ecosystems [6,10,11]. The economic and logistical difficulties in accessing hosts that inhabit these ecosystems are the main reasons explaining the scarcity of knowledge regarding the parasite fauna of deep-sea fishes. An alternative is to study host species from the by-catch of deep-sea commercial fisheries, providing additional opportunities for sampling [11].
Knowledge regarding the parasite community of Holocephali is particularly scarce. The class includes 55 species in six genera and three families [12]. Except for the three species of Callorynchus, which are restricted to shallow waters in the southern hemisphere [13], and Hydrolagus colliei, the remaining species are considered deep-sea fishes [14]. Quantitative data regarding metazoan parasites have been gathered for only four species: Chimaera monstrosa from Norway [15], Callorhynchus capensis from South Africa [13], Hydrolagus affinis from Greenland [16], and Callorhynchus callorhinchus from Perú and Central Chile [17,18]. Although at least 54 parasitic species have been specifically recorded for 18 species of Chimaera, at least 17 additional taxa have been reported at the generic or higher taxonomic level (see Table S1 in the Supplementary Materials).
For the Southeastern Pacific Ocean (SEPO hereafter), eight species of Holocephali are known [12]; however, quantitative data regarding metazoan parasites have been obtained only for the shallow-water C. callorhinchus. Two species of shortnose chimaeras are commonly caught as by-catch in the deep-sea fishery (>1000 m) of the Patagonian tooth fish D. eleginoides in Northern Chile: the Eastern Pacific Black Ghostshark Hydrolagus melanophasma—with a wide geographic range along the Eastern Pacific Ocean, from Baja California, Mexico, to Valdivia, Chile [12]—and Chimaera sp.
Our goal is to report, for the first time, the compositions of the metazoan parasite communities of two deep-sea Holocephali from the SEPO, as well as to quantitatively describe the characteristics of these communities and evaluate the similarity/differences (in terms of alpha and beta diversities) between them.
2. Materials and Methods
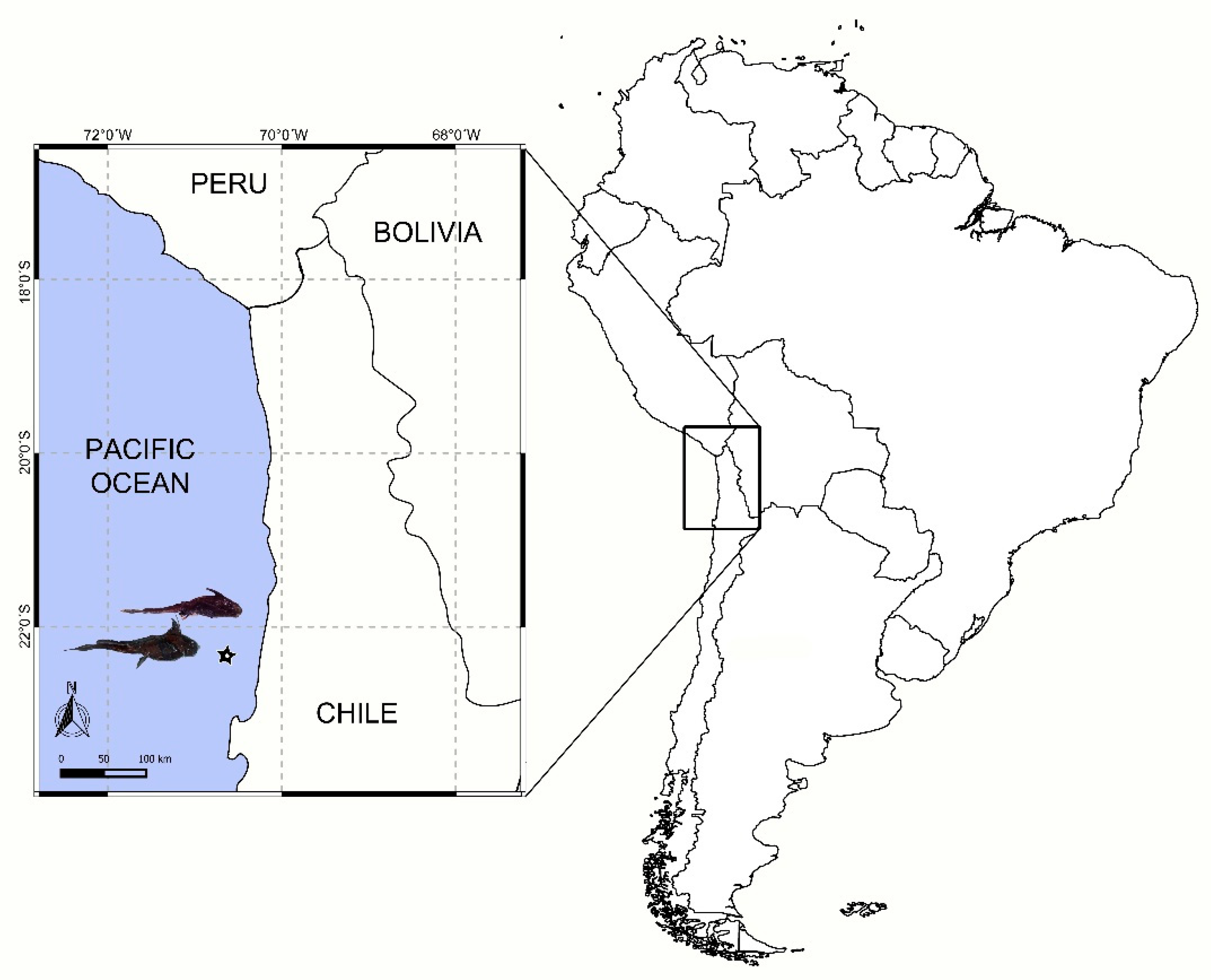
A total of 61 deep-sea chimaera specimens (H. melanophasma = 41; Chimaera sp. = 20) were obtained as by-catch of the local fishery of the Patagonian toothfish (D. eleginoides) along the Northern Chilean coast (22°20′ S, 70°37′ W), using a deep-sea longline at depths ranging from 950 to 1500 m (Figure 1), during September 2017. Chimaeras were captured, stored in individual bags, and immediately frozen (−18 °C) on board, then transported to the laboratory for parasitological analyses.
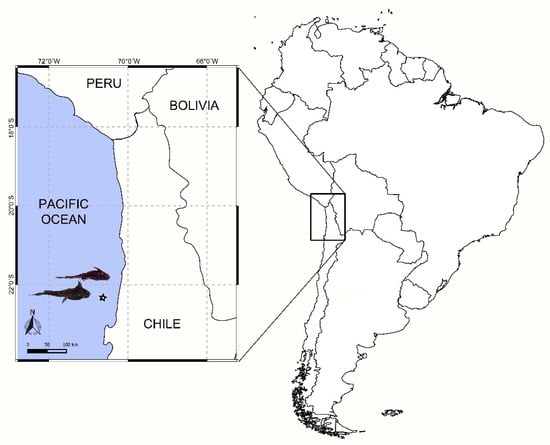
Figure 1.
Approximate position (star) where samples were obtained.
After thawing, the chimaeras were measured (total length to the nearest 1.0 cm), dissected, and examined for metazoan ectoparasites and endoparasites. All specimens were examined first for ectoparasites, including the skin, gills, and mouth cavity and then for endoparasites. All viscera, including heart and blood vessels (arterial cone and branchial artery), were examined. To count endoparasites, each visceral organ was dissected separately and washed under running water. All material retained on a 0.3 mm mesh was examined under a LEICA M 125 stereoscope with an incorporated LEICA MC120 HD camera (Heerbrugg, Switzerland). Parasites were sorted by species for each host individual, fixed in AFA (alcohol/formalin/acetic acid), and preserved in 70% alcohol. Nematoda were cleaned with Amann’s lactophenol. Monogenea, Digenea, and Cestoda were stained (acetic carmine), cleaned with clove oil (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), and mounted in Eukitt medium (O. Kindler Freiburg GmbH, Germany) [19]. Copepoda and Isopoda were stored in ethanol (70%) and dissected for taxonomic purposes. Parasites were identified to the lowest taxonomic level possible. Prevalence and mean intensity of infection were calculated [20].
Potential relationships between total length and richness (both raw data and log n + 1) were explored (Pearson’s correlation coefficient). Due to the small sample size, the relationship between host size and mean intensity of infection was estimated for those parasite species with prevalence higher than 20%, ensuring at least eight values (for a given species) for the intensity of infection for specimens of H. melanophasma and six values for specimens of Chimaera sp. Diversity indices (alpha and beta diversity) were compared between the two host species with non-parametric (richness, Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney) and parametric (Shannon diversity, Pielou’s J evenness, ANOVA) tests.
Shannon diversity was estimated using the following formula
where H′ = Shannon diversity index, and pi = proportion of individuals of species i.
H′ = −∑(pilnpi)
Pielou’s J evenness was calculated as
where J = Pielou’s evenness, and LnS = log of the number of species.
J = H’/LnS
Differential analysis of alpha diversity was performed to evaluate the significance of differences in the richness, diversity, and evenness of metazoan parasites at infracommunity and community component levels [20]. The significance of differences in diversity at the community component level was graphically evaluated via principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) on a similitude matrix, using Primer 6.0 [21]. Multivariate discriminant analysis (MDA) at the infracommunity level was used to test whether metazoan parasite communities could be suitable tools for discriminating between host species [22,23]. All statistical analyses were performed with the Minitab 17 statistical software.
3. Results
The total length of specimens of H. melanophasma ranged from 88 to 117 cm (mean = 104 cm; SD = 8.1), and the total length of Chimaera sp. ranged from 75 to 115 cm (mean = 84 cm; SD = 8.8).
A total of 228 parasites belonging to nine species were obtained from H. melanophasma (just two specimens were devoid of parasites), whereas 2085 parasites belonging to seven species were obtained from Chimaera sp.; notably, 100% of these hosts were parasitized (Table 1).

Table 1.
Site of infection, prevalence (P), and mean intensity of infection (MI ± SD) of metazoan parasites found in two species of shortnose chimaeras from deep waters in Northern Chile.
Richness was not correlated with total length for both H. melanophasma and Chimaera sp. (p > 0.10 for all correlations). In a similar way, the significance of the correlation coefficient (r) for the relationship between the intensity of infection for selected parasite species and host size was always >0.05.
At the infracommunity level, mean richness did not differ significantly between host species (W = 680, p = 0.082), whereas diversity (H’ Shannon Index) and evenness (J’ index) differed significantly (F17,26 = 9.08 and 26.4, respectively; p < 0.001 for both comparisons) (Table 2). At the community component level, diversity differed significantly (“t” test = 19.22, estimated gl = 231, p < 0.001).

Table 2.
Diversity indices at infracommunity and community component levels for metazoan parasites in two shortnose chimaeras from Northern Chile.
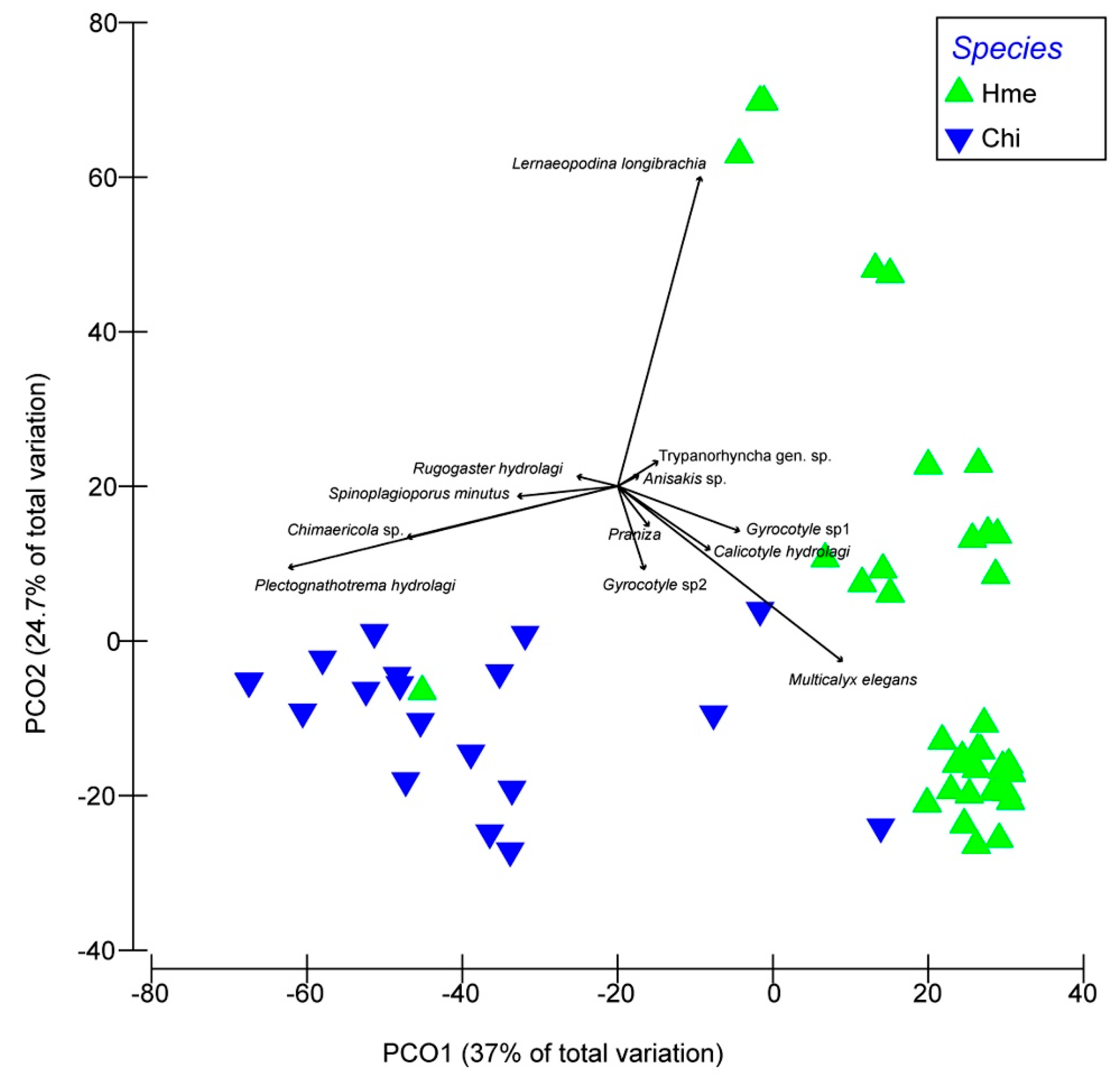
The results of principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) on the similarity matrix showed that the two species could be well identified according to the intensity of infection (Figure 2); the same conclusion was reached according to the multivariate discriminant analysis, with 100% of H. melanophasma specimens and 85% of Chimaera sp. specimens classified correctly (Table 3). Specifically, the Chimaera sp. were closely associated with two species of digenea (S. minutus and P. hydrology) and the monogenea Chimaericola sp., whereas H. melanophasma was associated with the copepod L. longibrachia as well as the Aspidogastrean M. elegans.
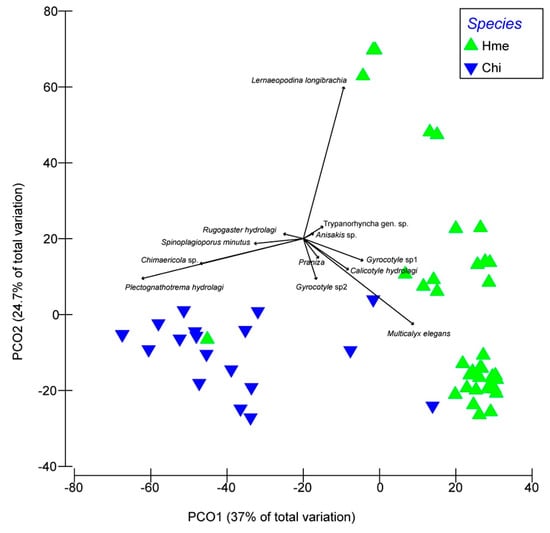
Figure 2.
Principal component analysis based on metazoan parasite infracommunities from two species of shortnose chimaeras from Northern Chile. Hme: Hydrolagus melanophasma; Chi: Chimaera sp.

Table 3.
Classification matrix (cases in row categories classified into columns) for two host species based on metazoan parasite communities.
4. Discussion
Hosts were caught using the same fishing gear (deep-sea longline), on the same date and at the same locality. Accordingly, the differences in the number of hosts obtained suggest differences in their relative abundance—as similarly described for two deep-sea shark species also caught as by-catch of the Patagonian tooth fish in Northern Chile [22].
This is the first report regarding parasite communities of two sympatric deep-sea chimaera species—H. melanophasma and Chimaera sp.—associated with the deep waters of the Atacama Trench.
Chimaeras (Holocephali) are a small and enigmatic subclass of ancient Chondrichthyes, which hypothetically diverged from a common ancestor with the elasmobranch about 413 Ma [24]. To date, 55 Holocephalan species are recognized, while metazoan parasites (under a taxonomic approach) have only been reported for 18 species (see Supplementary Materials, Table S1 and Figure S1). Quantitative analyses of metazoan parasite communities (sample size > 30) have been performed for just three species: the shallow-water Callorhynchus callorhinchus from Chile and Perú [17,18], Callorhynchus capensis from South Africa [13], and the deep-water Chimaera monstrosa from Norway [15].
Holocephalans are the only host group for the unique and non-segmented Gyrocotyle spp. (Gyrocotylidae: Cestodaria), which represent a sister group of the true tapeworms (Eucestoda) [25] and, like their host, are considered to be “living fossils” of a vanished past [26]. Holocephalans are also unique hosts for some ectoparasites—such as members of Chimaericolidae (Monogenea: Polyophistocotylea) [24], which includes five species in two genera, and members of the genus Callorhynchocotyle (Monogenea: Hexabothriidae), which includes five species [27]. The four species of the primitive copepod Vanbenedenia (Lernaeopodidae) are parasites of Chimaeras [28]. Multicalyx—a genus of the family Multicalycidae (Aspidogastrea)—are parasites of Holocephali and Elasmobranchii [29], while the two species of Rugogaster (Rugogasteridae: Aspidogastrea) are also specific parasites of Chimaeridae [30].
Gyrocotylidae is considered a group of distinct species that are mostly host-specific to Holocephali and cannot be distinguished by morphology [25]. Our data suggest the presence of two morphotypes of Gyrocotyle, which were found in both host species.
While the differences in richness between the host species were not significant, there were clear differences in their parasite species composition. The main differences include the presence of two species of digenea in Chimaera sp., one of which—Plectognatotrema hydrolagi (Zoogonidae), with prevalence of 90% and mean intensity of infection of 101.5—has been described from the shallow-water Hydrolagus colliei obtained off the coast of Oregon (USA) [30]. No quantitative studies regarding metazoan parasites of holocephalans have reported this species. Quantitative data for Spinoplagioporus minutus (Acanthocolpidae) parasitizing C. mostrosa were provided with the original description of the species [31], with a prevalence of 100% and an abundance ranging from 1 to 283 specimens in the host C. monstrosa from the Barent Sea. The species has also been registered from Chimaera phantasma [6]. The second intermediate hosts for members of Acanthocolpidae and Zoogonidae are bivalves [32,33]. The presence of both species of digenea—which are trophically transmitted—suggests that Chimaera sp. predate on invertebrates (bivalves) that are not a component of the diet of H. melanophasma, thus avoiding predatory competition for diet between these sympatric species. Unfortunately, data regarding the diets of deep-sea chimaeras are almost absent.
Recently, it has been suggested that the main force shaping the parasite community structure in teleost marine fish is age, for which total length can serve as a surrogate [34]. Our results showed an opposite picture: without exception, all relationships between richness, intensity of infection, and host size were non-significant. The expected positive relationship between richness and size (age) can be explained by the accumulation of long-lived encysted larval parasitic stages with age and/or an increased consumption rate of prey in longer-lived fish; however, this can only occur if colonization is higher than mortality [34]. According to the composition of the parasite community for both host species in this study, it is evident that larval stages are scarce; in particular, 6.1% of the total number of parasites in H. melanophasma were larval stages of Anisakis sp. (Nematoda) and Trypanorhyncha gen. sp. (Eucestoda), whereas Chimaera sp. harbored only adult parasites. Larval cestodes have been considered as “incidental parasites” in Chimaerids [15]. The absence of larval stages of metazoan parasites strongly suggests a higher trophic level (at least for Chimaera sp.), as reported for C. monstrosa [35].
Our results strongly suggest a strong component of the evolutionary history of the host on the characteristic of the parasite fauna of the ancient Holocephali, including not only ancient parasites belonging to Rugogasteridae and Multicalycidae (Aspidogastrea) but also the unsegmented member of Gyrocotylidae. Holocephali are also parasitized by highly specific monogeneans, such as Chimaericola spp., Callorhynchicola, and Callorhynchocotyle, which are all parasites of Chimaeridae, while the last genus is also a parasite of Callorhinchidae. In a similar way, while other species are parasites of Holocephali, members of some genera (i.e., Plectognathotrema) are also parasites of teleosts. Vanbenedenia species are also specific parasites of Holocephali, whereas the observed larval forms (Anisakis sp. Trypanorhyncha gen. sp.) and caligids copepods (Caligus spp.) are non-specific and can also be found as parasites of teleosts. In summary, there exist ancient parasite species that are specific to some ancient Holocephalans, as indicated by the results of the multivariate analysis in this study.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d17090601/s1. Table S1. Recorded metazoan parasites from Chimaeriformes. Figure S1. Pictures of parasites found in Chimaera sp. and Hydrolagus melanophasma (not identified at the species level).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.E.O., L.A.Ñ. and R.E.; methodology, M.E.O., L.A.Ñ. and J.F.E.-N.; formal analysis, M.E.O., L.A.Ñ., R.E. and J.F.E.-N.; investigation, M.E.O., L.A.Ñ., R.E. and J.F.E.-N.; resources, M.E.O., R.E. and J.F.E.-N.; data curation, L.A.Ñ.; writing—original draft preparation, M.E.O. and L.A.Ñ.; writing—review and editing, M.E.O., L.A.Ñ., J.F.E.-N. and R.E.; funding acquisition, M.E.O. and R.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by MINEDUC-UA project ANT 1855 and Plan de Fortalecimiento Universidades Estatales—Chile RED21992 (MEO). Additional support was provided by Instituto Milenio de Oceanografia IMO-Chile Grant AIM23-0003 (Agencia Nacional de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica de Chile) to R.E. J.F.E.-N. was supported by the SECIHTI (Secretaría de Ciencia, Humanidades, Tecnología e Innovación) postdoctoral fellowship “Estancias Posdoctorales por México, Modalidad Académica” (CVU 351170).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, as the fishes were obtained as commercial by-catch from local fishermen. The considered fishes are not subject to conservation measures.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the lab work of Florence Nono-Almeida, as well as the kind support of Dani Manzo, captain, and the crews of the artisanal fishing boat “Huayca.”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Korostelev, N.B.; Frey, P.H.; Orlov, A.M. Using Different Hard Structures to Estimate the Age of Deep-Sea Fishes: A Case Study of the Pacific Flatnose, Antimora microlepis (Moridae, Gadiformes, Teleostei). Fish. Res. 2020, 232, 105731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drazen, J.C.; Sutton, T.T. Dining in the Deep: The Feeding Ecology of Deep-Sea Fishes. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 337–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamford, C.C.G.; Hollyman, P.R.; Abreu, J.; Darby, C.; Collins, M.A. Spatial, temporal, and demographic variability in patagonian toothfish (Dissostichus eleginoides) spawning from twenty-five years of fishery data at South Georgia. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2024, 203, 104199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norse, E.A.; Brooke, S.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Clark, M.R.; Ekeland, I.; Froese, R.; Gjerde, K.M.; Haedrich, R.L.; Heppell, S.S.; Morato, T.; et al. Sustainability of deep-sea fisheries. Mar. Policy 2012, 36, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, C.W.; Foley, N.S.; Tinch, R.; van den Hove, S. Services from the deep: Steps towards valuation of deep-sea goods and services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 2, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimpel, S.; Busch, M.W.; Kellermanns, E.; Kleinertz, S.; Palm, H.W. Metazoan deep-sea fish parasites. In Acta Biologica Benrodis; Natur & Wissen: Solingen, Germany, 2009; 384p. [Google Scholar]
- Dobson, A.; Lafferty, K.D.; Kuris, A.M.; Hechinger, R.F.; Jetz, W. Homage to Linnaeus: How many parasites? How many hosts? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11482–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.E.; Siwertsson, A.; Lafferty, K.D.; Kuris, A.M.; Soldanova, M.; Morton, D.; Primicerio, R.; Amundsen, P.A. Parasites alter food-web topology of a subarctic lake food web and its pelagic and benthic compartments. Oecologia 2024, 204, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, A.; Ingram, T.; Randhawa, H.S. Role of ecology and phylogeny in determining tapeworm assemblages in skates (Rajiformes). J. Helminthol. 2019, 93, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimpel, S.; Palm, H.W.; Busch, M.W.; Kellermanns, E.; Rückert, S. Fish parasites in the Arctic deep-sea: Poor diversity in pelagic fish species vs. heavy parasite load in a demersal fish. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2006, 53, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espínola-Novelo, J.F.; Oliva, M.E. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Parasite Communities: Implications for Fish Stock Identification. Fishes 2021, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. (Eds.) FishBase. Chimaera Linnaeus. 1758. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=105733 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Morris, T.C.; Ploeg, J.; Awa, S.B.; Lingen, C.; Reed, C.C. Parasite community structure as a predictor of host population structure: An example using Callorhinchus capensis. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 8, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, J.G.; Miya, M.; Lam, K.; Tay, B.-H.; Danks, J.A.; Bell, J.; Walker, T.I.; Venkatesh, B. Evolutionary Origin and Phylogeny of the Modern Holocephalans (Chondrichthyes: Chimaeriformes): A Mitogenomic Perspective. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2576–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieske, H. A survey of the metazoan parasites of the rabbit-fish, Chimaera mostrosa L. (Holocephali). Neth. J. Sea Res. 1968, 4, 32–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsbakk, E.; Aspholm, P.E.; Berg, V.; Hareide, N.R.; Berland, B. Some parasites of the small-eyed rabbitfish, Hydrolagus affinis (Capello, 1867) (Holocephali), caught in deep waters off SW Greenland. Sarsia 2002, 87, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, C.; Minaya, D.; Iannacone, J. Community of metazoan parasites of the cockfish Callorhinchus callorynchus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Chimaeriformes: Callorhinchidae) from artisanal fishing in Pisco, Ica, Peru. Rev. Mus. Argent. Cienc. Nat. 2021, 24, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, J.C.; Villalba, C.S.; Alviña, A. Parásitos del pejegallo, Callorhinchus callorhynchus, en Chile: Aspectos biológicos y sistemáticos. Biol. Pesq. 1986, 15, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ñacari, L.A.; Oliva, M.E. Metazoan parasites of deep-sea fishes from the South Eastern Pacific: Exploring the role of ecology and host phylogeny. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 115, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Primer v6: User Manual/Tutorial. Primer-E; Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Plymouth, UK, 2006; 193p. [Google Scholar]
- Espínola-Novelo, J.F.; Escribano, R.; Oliva, M.E. Metazoan parasite communities of two deep-sea elasmobranchs: The southern lanternshark, Etmopterus granulosus and the largenose catshark, Apristurus nasutus, in the Southeastern Pacific Ocean. Parasite 2018, 25, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouiche, I.; Neifar, L.; Gey, D.; Justine, J.-L.; Tazerouti, F. Holocephalocotyle monstrosae n. gen. n. sp. (Monogenea, Monocotylidae) from the olfactory rosette of the rabbit fish, Chimaera monstrosa (Holocephali, Chimaeridae) in deep waters off Algeria. Parasite 2019, 26, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, R.A.; Waeschenbach, A.; Littlewood, D.T.J.; Halvorsen, O.; Olson, P.D. Molecular circumscription of new species of Gyrocotyle Diesing, 1850 (Cestoda) from deep-sea chimaeriform holocephalans in the North Atlantic. Syst. Parasitol. 2020, 97, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barčák, D.; Fan, C.-K.; Sonko, P.; Kuchta, R.; Scholz, T.; Orosová, M.; Chen, H.-W.; Oros, M. Hidden diversity of the most basal tapeworms (Cestoda, Gyrocotylidea), the enigmatic parasites of holocephalans (Chimaeriformes). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, A.; Ogawa, K.; Taniuchi, T.; Hirose, H. Two new species of hexabothriid monogeneans from the ginzame Chimaera phantasma and shortspine spurdog Squalus mitsukurii. Syst. Parasitol. 2006, 65, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldewage, W.H. A new species of Vanbenedenia Maim, 1860 (Copepoda: Lernaeopodidae) from the Southern Indian Ocean. Syst. Parasitol. 1993, 26, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoney, D.A.; Burreson, E.M. Revision of the Multicalycidae (Aspidocotylea) with Comments on Postlarval Development. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1988, 55, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Amato, J.F.R.; Pereira, J. A new species of Rugogaster (Aspidobothrea: Rugogastridae) parasite of the elephant fish, Callorhinchus callorhynchus (Callorhinchidae), from the estuary of the La Plata River, Coasts of Uruguay and Argentina. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. 1995, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, R.E.; Hanson, A.W.; Pratt, I. Plectognathotrema hydrolagi sp. n. (Trematoda Cephaloporidaqe) from the ratfish (Hydrolagus colliei). J. Parasitol. 1970, 56, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyansky, Y.I. Two new species of digenetic trematodes from fish in northern Atlantic. Parazitologicheskii Sbornik 1952, 14, 266–280. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kremnev, G.; Gonchar, A.; Krapivin, V.; Uryadova, A.; Miroliubov, A.; Krupenko, A. Life cycle truncation in Digenea, a case study of Neophasis spp. (Acanthocolpidae). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2021, 15, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremnev, G.; Gonchar, A.; Uryadova, A.; Krapivin, V.; Skobkina, O.; Gubler, A.; Krupenko, D. No Tail No Fail: Life Cycles of the Zoogonidae (Digenea). Diversity 2023, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinola-Novelo, J.F.; González, M.T.; Pacheco, A.S.; Luque, J.L.; Oliva, M.E. Testing for deterministic succession in metazoan parasite communities of marine fish. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albo-Puigserver, M.; Navarro, J.; Coll, M.; Aguzzi, J.; Cardona, L.; Sáez-Liante, R. Feeding ecology and trophic position of three sympatric demersal chondrichthyans in the northwestern Mediterranean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 524, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).