A Comprehensive Review of the Biology, Ecological Impacts, and Control Strategies of Eichhornia crassipes
Abstract
1. Introduction
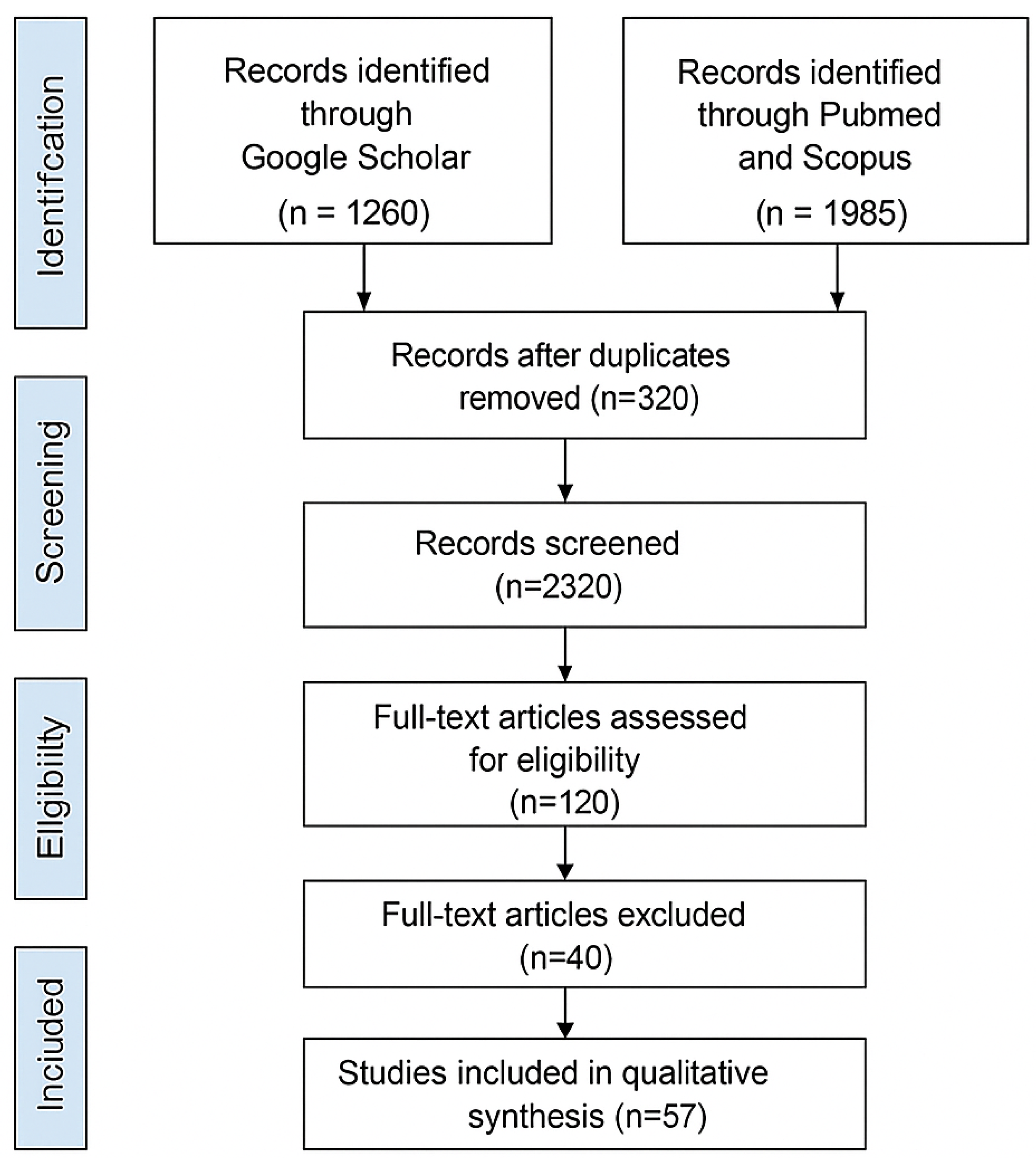
2. Methodology
3. Taxonomic and Biological Overview
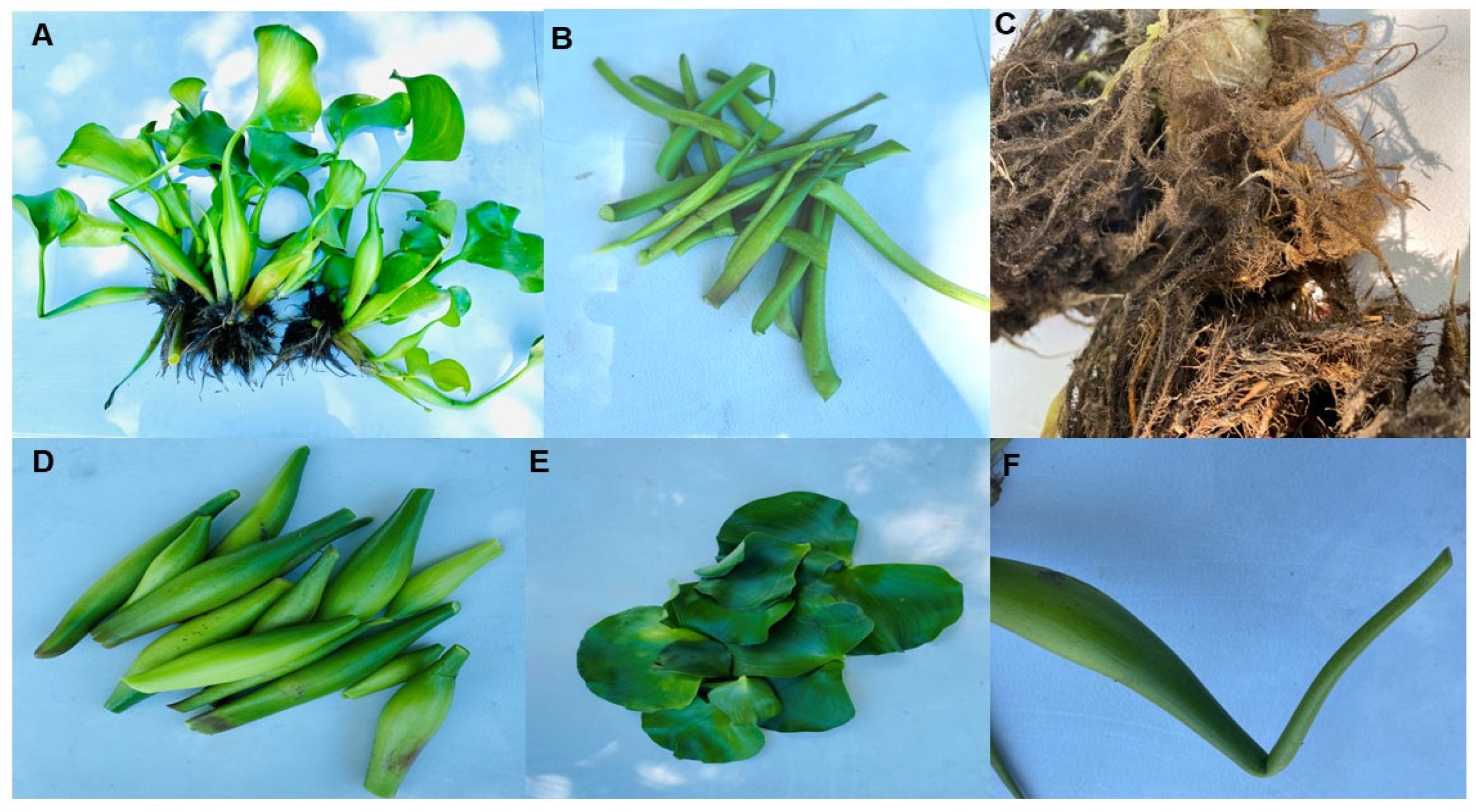
4. Morphological Characteristics of E. crassipes
4.1. Leaf Structure
4.2. Flower and Inflorescence
4.3. Petiole and Spongy Petiole
4.4. Root System
5. Reproduction and Growth
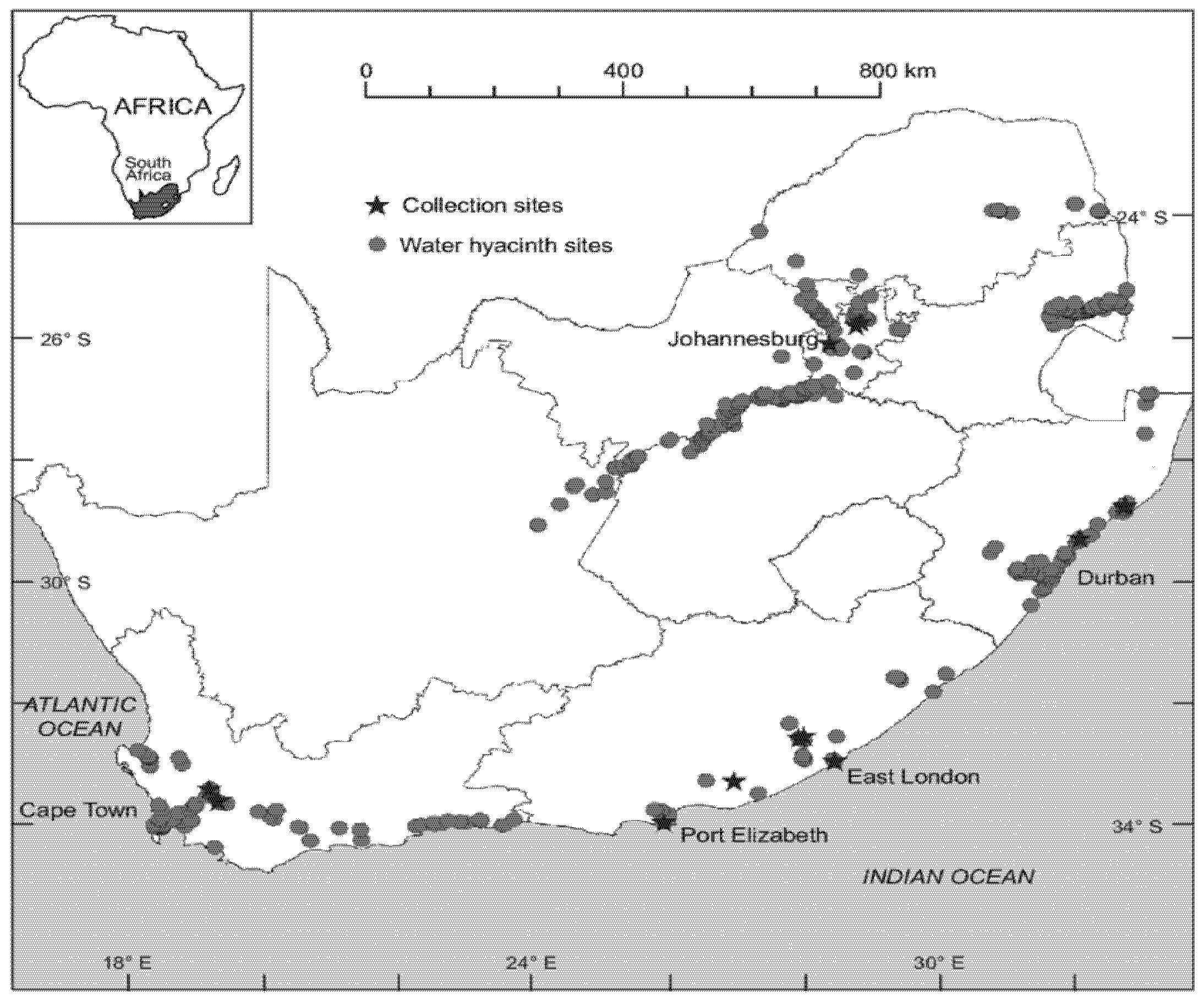
6. Global Distribution
7. Habitat Requirements and Invasion Ecology
8. Ecological and Socioeconomic Impacts
9. Control and Management Strategies
9.1. Mechanical Control
9.2. Chemical Control
9.3. Biological Control
9.4. Integrated Approaches
| Method | Description | Example | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical control | Involves physically removing weeds from bodies of water using machinery and equipment. | Machines used: weed harvester tractors, dredgers, crusher boats, destroyer boats, and mechanical mowers. For instance, tarping, digging. | [10,50] |
| Chemical control | Uses pesticides to get rid of weeds fast and efficiently. | Herbicides: triclopyr, glyphosate, and paraquat. For instance, herbicides are used to eliminate E. crassipes and Salvinia molesta. | [23,40,52] |
| Biological control | Involves using weeds’ natural enemies, like fungi and insects, to control their population. | Natural enemies: fungi (such as Aspergillus and Trichothecium species), beetles, flies, moths, and weevils. For instance, weevils are utilized against E. crassipes and Salvinia molesta, also known as Giant Salvinia. | [10,19,34,55] |
| Method | Description | Effectiveness | Limitation | Regional Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Machine and manual removal | High in small areas | Costly, labor-intensive | South Africa, India |
| Chemical | Herbicide application | Fast, effective | Environmental risks | South Africa, Nigeria, Brazil |
| Biological | Insects, fungi | Sustainable long-term | Slow implementation | South Africa, Ethiopia, USA |
| Integrated | Combined approach | Most effective overall | Requires coordination | South Africa, Kenya, China |
10. Utilization Potential
11. Discussion
12. Recommendations
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ilo, O.P.; Simatele, M.D.; Nkomo, S.P.L.; Mkhize, N.M.; Prabhu, N.G. The Benefits of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for Southern Africa: A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanda, O.I.; Ajayi, T.; Asuwaju, F.P. Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms: Uses, Challenges, Threats, and Prospects. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 3452172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.O.O.; Horn, C.N.; Almeida, R.F. Total evidence phylogeny of pontederiaceae (commelinales) sheds light on the necessity of its recircumscription and synopsis of Pontederia L. PhytoKeys 2018, 108, 25–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mqingwana, P.; Shoko, C.; Gxokwe, S.; Dube, T. Monitoring and assessing the effectiveness of the biological control implemented to address the invasion of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) in Hartbeespoort Dam, South Africa. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 36, 101295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gouveia, C.C.; Bührmann, J.H. Prediction of water hyacinth coverage on the hartbeespoort dam. S. Afri. J. Ind Eng. 2024, 35, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechassa, N.; Abate, B. Current Status of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) in Ethiopia: Achievements, Challenges, and Prospects: A Review. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Téllez, T.R.; López, E.M.D.R.; Granado, G.L.; Pérez, E.A.; López, R.M.; Guzmán, J.M.S. The Water Hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes: An Invasive Plant in the Guadiana River Basin (Spain). Aquat. Invasions 2008, 3, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceschin, S.; Abati, S.; Traversetti, L.; Spani, F.; Del Grosso, F.; Scalici, M. Effects of the Invasive Duckweed Lemna minuta on Aquatic Animals: Evidence from an Indoor Experiment. Plant Biosyst. 2019, 153, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, M.H. Biological Control of Water Hyacinth with Arthropods: A Review to 2000. In Aciar Proceedings; ACIAR: Canberra, Australia, 1998; pp. 8–20. [Google Scholar]
- Villamagna, A.M.; Murphy, B.R. Ecological and Socio-Economic Impacts of Invasive Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): A Review. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, J.A.; Jones, R.W.; Hill, M.P. Water Hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes (Pontederiaceae), Reduces Benthic Macroinvertebrate Diversity in a Protected Subtropical Lake in South Africa. Biodivers. Conserv. 2014, 23, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Sun, Q.; Xia, M.; Wen, Z.; Yao, Z. The Resource Utilization of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes [Mart.] Solms) and Its Challenges. Resources 2018, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.P.; Coetzee, J.A. Control of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes [Mart.] Solms) in South Africa: Historical Perspectives and Current Challenges. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 124, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniadie, D.; Rezkia, N.N.; Widayat, D.; Widiawan, A.; Duy, L.; Prabowo, D.P. Control of aquatic weed Eichhornia crassipes using florpyrauxifen-benzyl herbicide—Case study in Cangkuang lake (Indonesia). Water. 2023, 15, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, P.; Morais, M.C. Strategies for the Management of Aggressive Invasive Plant Species. Plants 2023, 12, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karouach, F.; Ben Bakrim, W.; Ezzariai, A.; Sobeh, M.; Kibret, M.; Yasri, A.; Hafidi, M.; Kouisni, L. A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Existing Approaches for Controlling and Managing the Proliferation of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 767871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, J.A.; Hill, M.P. The role of eutrophication in the biological control of water hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes, in South Africa. BioControl 2012, 57, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauptfleisch, K.A. A Model for Water Hyacinth Biological Control. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Witwatersrand, Faculty of Science, School of Animal, Plant and Environmental Sciences, Johannesburg, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wilgen, B.W.; De Lange, W.J. The Costs and Benefits of Biological Control of Invasive Alien Plants in South Africa. Afr. Entomol. 2011, 19, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.H.; Song, W.; Guo, J.Y. Advances in Management and Utilization of Invasive Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) in Aquatic Ecosystems–A Review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elenwo, E.I.; Akankali, J.A. The Estimation of Potential Yield of Water Hyacinth: A Tool for Environmental Management and an Economic Resource for the Niger Delta Region. J. Sustain. Dev. Stud. 2016, 9, 115–137. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.W. The Impact on Biodiversity, and Integrated Control, of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes [Mart.] Solms-Laubach) on the Lake Nsezi-Nseleni River System. Ph.D. Thesis, Rhodes University, Makhanda, South Africa, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mujere, N. Water Hyacinth: Characteristics, Problems, Control Options, and Beneficial Uses. In Impact of Water Pollution on Human Health and Environmental Sustainability; IGI Global: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 343–361. [Google Scholar]
- Degaga, A.H. Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) Biology and Its Impacts on the Ecosystem, Biodiversity, Economy, and Human Well-Being. J. Life Sci. Biomed. 2018, 8, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S. Threats, Management and Envisaged Utilizations of Aquatic Weed Eichhornia crassipes: An Overview. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2012, 11, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omofunmi, O.E.; Olaniyan, A.M.; Ebietomiye, O.T. Utilisation of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) as Fish Aggregating Device by Riverine Fisher Folks in a South West Nigeria Community. Livest. Res. Rural Dev. 2018, 30, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Ndimele, P.E. A Review on the Phytoremediation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 13, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Song, S.; Chang, S.; Liu, C.; Yu, D. Impact of eutrophication on root morphological and topological performance in free-floating invasive and native plant species. Hydrobiologia 2019, 836, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gichuki, J.; Omondi, R.; Boera, P.; Okorut, T.; Matano, A.S.; Jembe, T.; Ofulla, A. Water Hyacinth Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms-Laubach Dynamics and Succession in the Nyanza Gulf of Lake Victoria (East Africa): Implications for Water Quality and Biodiversity Conservation. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 106429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, J.A.; Hill, M.P.; Byrne, M.J.; Bownes, A. A Review of the Biological Control Programmes on Eichhornia crassipes (C. Mart.) Solms (Pontederiaceae), Salvinia molesta DS Mitch. (Salviniaceae), Pistia stratiotes L. (Araceae), Myriophyllum aquaticum (Vell.) Verdc. (Haloragaceae), and Azolla filiculoides Lam. (Azollaceae) in South Africa. Afr. Entomol. 2011, 19, 451–468. [Google Scholar]
- Hussner, A.; Stiers, I.; Verhofstad, M.J.J.M.; Bakker, E.S.; Grutters, B.M.C.; Haury, J.; Van Valkenburg, J.L.C.H.; Brundu, G.; Newman, J.; Clayton, J.S.; et al. Management and Control Methods of Invasive Alien Freshwater Aquatic Plants: A Review. Aquat. Bot. 2017, 136, 112–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaura, A.; Kamau, J.; Ombori, O. An Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Commonly Traded in Kajiado, Narok, and Nairobi Counties, Kenya: Medicinal Plant Species Traded in Kenya. East Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. 2020, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, C.D.; Saraf, S. In Vitro Sun Protection Factor Determination of Herbal Oils Used in Cosmetics. Pharmacogn. Res. 2010, 2, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.W.; Kwon, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Na, J.I.; Huh, C.H.; Choi, H.R.; Park, K.C. Molecular Mechanisms of Dermal Aging and Antiaging Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setshego, M.V.; Aremu, A.O.; Mooki, O.; Otang-Mbeng, W. Natural Resources Used as Folk Cosmeceuticals Among Rural Communities in Vhembe District Municipality, Limpopo Province, South Africa. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee, J.A.; Hill, M.P.; Julien, M.H.; Center, T.D.; Cordo, H.A. Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms-Laub. (Pontederiaceae). In Biological Control of Tropical Weeds Using Arthropods; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 183–210. [Google Scholar]
- Guna, V.; Ilangovan, M.; Anantha Prasad, M.G.; Reddy, N. Water hyacinth: A unique source for sustainable materials and products. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4478–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dersseh, M.G.; Melesse, A.M.; Tilahun, S.A.; Abate, M.; Dagnew, D.C. Water Hyacinth: Review of Its Impacts on Hydrology and Ecosystem Services—Lessons for Management of Lake Tana. In Extreme Hydrology and Climate Variability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Fan, S.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Lei, X.; Liu, C.; Yu, D. Invasion of water hyacinth and water lettuce inhibits the abundance of epiphytic algae. Divers. Distrib. 2022, 28, 1650–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.; Hill, M.P. Fungi Associated with Eichhornia crassipes in South Africa and Their Pathogenicity Under Controlled Conditions. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 37, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinty, V.; Colas, C.; Nasreddine, R.; Nehmé, R.; Piot, C.; Draye, M.; Destandau, E.; Da Silva, D.; Chatel, G. Screening and Evaluation of Dermo-Cosmetic Activities of the Invasive Plant Species Polygonum cuspidatum. Plants 2022, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndhlovu, P.T.; Mooki, O.; Mbeng, W.O.; Aremu, A.O. Plant Species Used for Cosmetic and Cosmeceutical Purposes by the Vhavenda Women in Vhembe District Municipality, Limpopo, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 122, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebashe, F.C.; Naidoo, D.; Amoo, S.O.; Masondo, N.A. Cosmeceuticals: A Newly Expanding Industry in South Africa. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ke, F.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Guan, B.; Li, K. Functional traits underlying performance variations in the overwintering of the cosmopolitan invasive plant water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) under climate warming and water drawdown. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavundza, E.J.; Street, R.; Baijnath, H. A Review of the Ethnomedicinal, Pharmacology, Cytotoxicity, and Phytochemistry of the Genus Euphorbia in Southern Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 144, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, D.; Liu, C. Response Differences of Eichhornia crassipes to Shallow Submergence and Drawdown with an Experimental Warming in Winter. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Bakrim, W.; Ezzariai, A.; Karouach, F.; Sobeh, M.; Kibret, M.; Hafidi, M.; Kouisni, L.; Yasri, A. Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms: A Comprehensive Review of Its Chemical Composition, Traditional Use, and Value-Added Products. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 842511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.P.; Coetzee, J.A. Integrated Control of Water Hyacinth in Africa 1. EPPO Bull. 2008, 38, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, J.A.; Miller, B.E.; Kinsler, D.; Sebola, K.; Hill, M.P. It’s a numbers game: Inundative biological control of water hyacinth (Pontederia crassipes), using Megamelus scutellaris (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) yields success at a high elevation, hypertrophic reservoir in South Africa. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerveira Junior, W.R.; de Carvalho, L.B. Control of Water Hyacinth: A Short Review. Environments 2019, 6, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Agidie, A.; Sahle, S.; Admas, A.; Alebachew, M. Controlling Water Hyacinth, Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms Using Some Selected Eco-Friendly Chemicals. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2018, 9, 521. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shahawy, T.G. Chemicals with a Natural Reference for Controlling Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms). J. Plant Prot. Res. 2015, 55, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodituwakku, K.A.R.K.; Yatawara, M. Phytoremediation of industrial sewage sludge with Eichhornia crassipes, Salvinia molesta and Pistia stratiotes in batch fed free water flow constructed wetlands. Bull. Environ. Contamin. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, P.W.; Gettys, L.A.; Minteer, C.R.; Foley, J.R.; Sardes, S.N. Herbivory by Biological Control Agents Improves Herbicidal Control of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). Invas. Plant Sci. Manag. 2017, 10, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, H.M.; Hayder, G. Recent Studies on Applications of Aquatic Weed Plants in Phytoremediation of Wastewater: A Review Article. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, S.; Ponraj, M.; Din, M.F.M.; Songip, A.R.; Sairan, F.M.; Chelliapan, S. The Diverse Applications of Water Hyacinth with Main Focus on Sustainable Energy and Production for New Era: An Overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Reynolds, C.; Byrne, M.; Rosman, B. A remote sensing method to monitor water, aquatic vegetation, and invasive water hyacinth at national extents. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khotsa, M.D.; Mkolo, N.M.; Motshudi, M.C.; Mphephu, M.M.; Makhafola, M.A.; Naidoo, C.M. A Comprehensive Review of the Biology, Ecological Impacts, and Control Strategies of Eichhornia crassipes. Diversity 2025, 17, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080564
Khotsa MD, Mkolo NM, Motshudi MC, Mphephu MM, Makhafola MA, Naidoo CM. A Comprehensive Review of the Biology, Ecological Impacts, and Control Strategies of Eichhornia crassipes. Diversity. 2025; 17(8):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080564
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhotsa, Matlhatse Daisy, Nqobile Monate Mkolo, Mmei Cheryl Motshudi, Mukhethwa Micheal Mphephu, Mmamudi Anna Makhafola, and Clarissa Marcelle Naidoo. 2025. "A Comprehensive Review of the Biology, Ecological Impacts, and Control Strategies of Eichhornia crassipes" Diversity 17, no. 8: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080564
APA StyleKhotsa, M. D., Mkolo, N. M., Motshudi, M. C., Mphephu, M. M., Makhafola, M. A., & Naidoo, C. M. (2025). A Comprehensive Review of the Biology, Ecological Impacts, and Control Strategies of Eichhornia crassipes. Diversity, 17(8), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080564








