DNA Metabarcoding Reveals Seasonal Variations in Crop-Foraging Behavior of Wild Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3. Statistical Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Sequencing Data
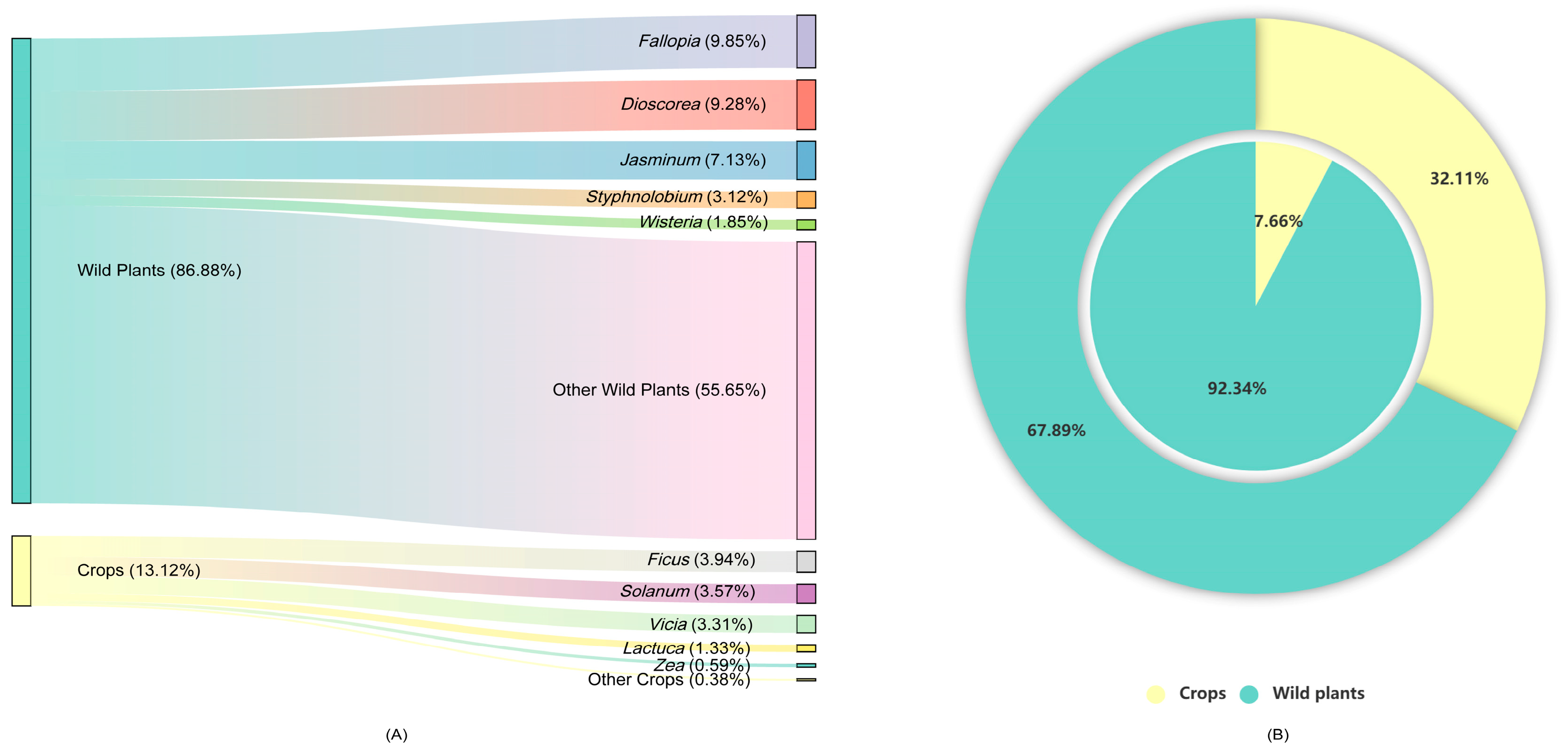
3.2. Seasonal Dietary Composition and Variations
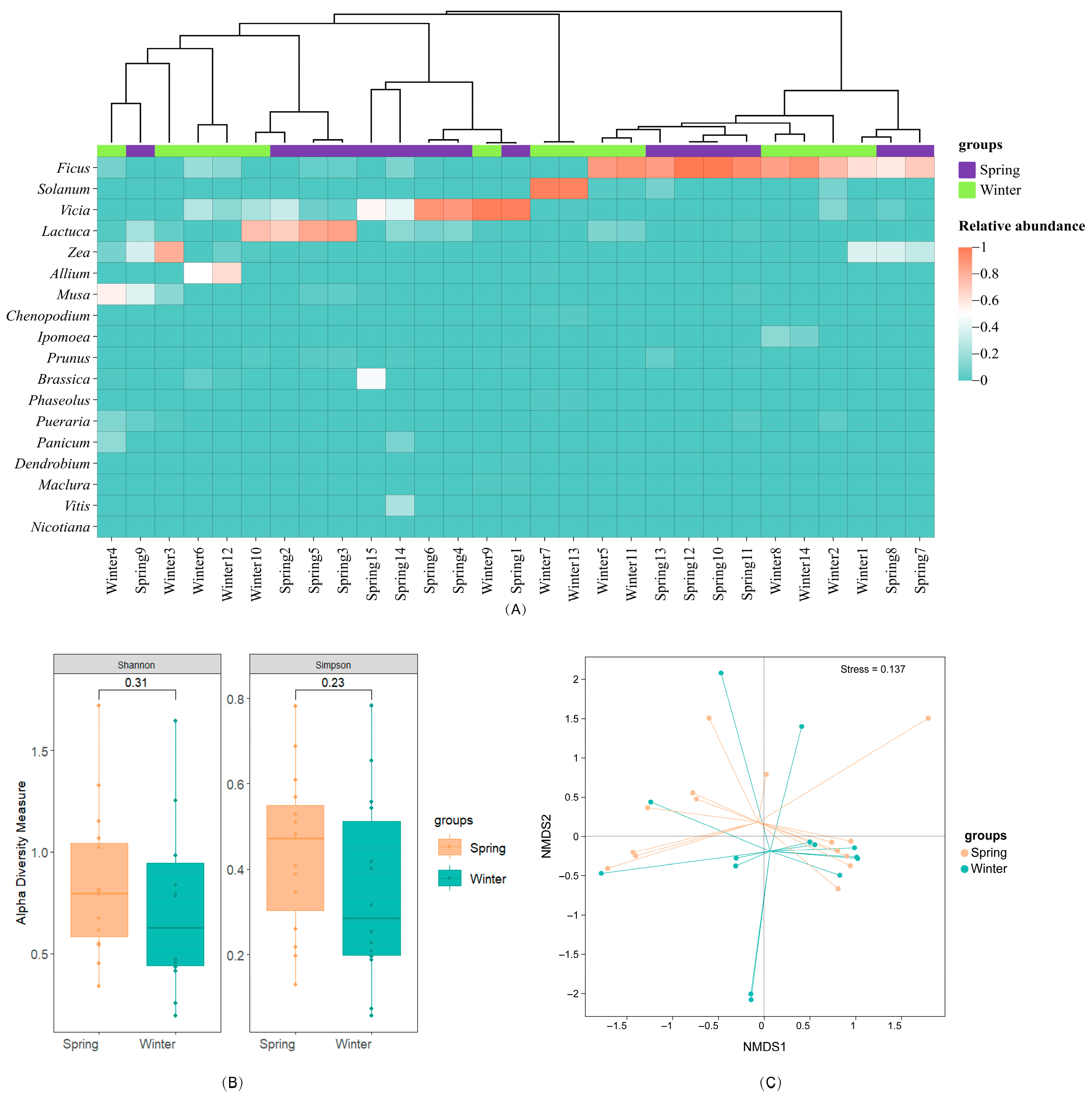
3.3. Analysis of Seasonal Foraging Diversity for Crops
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, S.T.; Hou, R.; Garber, P.A.; Raubenheimer, D.; Righini, N.; Ji, W.H.; Jay, O.; He, S.J.; Wu, F.; Li, F.F.; et al. Nutrient-specific compensation for seasonal cold stress in a free-ranging temperate colobine monkey. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 2170–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodice, P.G.R.; Roby, D.D.; Turco, K.R.; Suryan, R.M.; Irons, D.B.; Piatt, J.F.; Shultz, M.T.; Roseneau, D.G.; Kettle, A.B.; Anthony, J.A.M. Assessing the nutritional stress hypothesis: Relative influence of diet quantity and quality on seabird productivity. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 325, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, R.; Orben, R.A.; Suryan, R.M.; Irons, D.B.; Roby, D.D.; Harding, A.M.; Young, R.C.; Benoit-Bird, K.; Ladd, C.; Renner, H.; et al. Foraging responses of black-legged kittiwakes to prolonged food-shortages around colonies on the Bering Sea shelf. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tian, J.; Lu, J. Genetic structure and recent population demographic history of Taihangshan macaque (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis), North China. Integr. Zool. 2023, 18, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priston, N.E.C.; McLennan, M.R. Managing Humans, Managing Macaques: Human–Macaque Conflict in Asia and Africa. In The Macaque Connection: Cooperation and Conflict Between Humans and Macaques; Radhakrishna, S., Huffman, M.A., Sinha, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 225–250. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, B.K. The Mammals of Sri Lanka. J. Mammal. 2015, 96, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pebsworth, P.; Radhakrishna, S. Using conditioned taste aversion to reduce human-nonhuman primate conflict: A comparison of four potentially illness-inducing drugs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2020, 225, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Radhakrishna, S. The Hand That Feeds the Monkey: Mutual Influence of Humans and Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta) in the Context of Provisioning. Int. J. Primatol. 2018, 39, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu, K.; Mekonnen, A.; Bekele, A.; Fashing, P.J. Diet and activity patterns of Arsi geladas in low-elevation disturbed habitat south of the Rift Valley at Indetu, Ethiopia. Primates 2018, 59, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.K.; Ridley, A.; Kaplin, B.A.; Grueter, C.C. A comparison of fecal sampling and direct feeding observations for quantifying the diet of a frugivorous primate. Curr. Zool. 2020, 66, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, J.A.; Urakawa, H.; Frisk, M.G.; Newton, A.L.; Manz, M.; Fogg, M.; McMullen, C.; Crawford, L.; Shipley, O.N. DNA metabarcoding of cloacal swabs provides insight into diets of highly migratory sharks in the Mid-Atlantic Bight. J. Fish Biol. 2023, 103, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, L.E.; Cuff, J.P.; Bedmar, S.; McDonald, R.; Symondson, W.O.C.; Chadwick, E.A. Otterly delicious: Spatiotemporal variation in the diet of a recovering population of Eurasian otters (Lutra lutra) revealed through DNA metabarcoding and morphological analysis of prey remains. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumm, Y.R.; Masello, J.F.; Vreugdenhil-Rowlands, J.; Fischer, D.; Hillerich, K.; Quillfeldt, P. Diet composition of wild columbiform birds: Next-generation sequencing of plant and metazoan DNA in faecal samples. Sci. Nat. 2023, 110, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawes, J.E.; Calouro, A.M.; Peres, C.A. Sampling Effort in Neotropical Primate Diet Studies: Collective Gains and Underlying Geographic and Taxonomic Biases. Int. J. Primatol. 2013, 34, 1081–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertoldi, C.; Schmidt, J.B.; Thomsen, P.M.; Nielsen, L.B.; de Jonge, N.; Iacolina, L.; Muro, F.; Nielsen, K.T.; Pagh, S.; Lauridsen, T.L.; et al. Comparing DNA metabarcoding with faecal analysis for diet determination of the Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra) in Vejlerne, Denmark. Mammal Res. 2021, 66, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassea-Pérez, E.; Schramm, Y.; Heckel, G.; Chong-Robles, J.; Lago-Lestón, A. Metabarcoding analysis of the Pacific harbor seal diet in Mexico. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivathsan, A.; Sha, J.C.; Vogler, A.P.; Meier, R. Comparing the effectiveness of metagenomics and metabarcoding for diet analysis of a leaf-feeding monkey (Pygathrix nemaeus). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Yang, X.; Peng, C.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Su, H. Winter Dietary Analysis Reveals the Foraging Differences of Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) in Different Regions of a Karst Mountainous Area. Animals 2023, 13, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Wang, C.; Meng, B.; Xie, B.; Cao, H.; Su, H.; Zhang, M. The Food Niche Overlap and Interspecific Relationship between the Sympatric Tibetan Macaque and Grey Snub-Nosed Monkey. Animals 2023, 13, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portugal-Baranda, T.; Mougeot, F.; Ortiz-Santaliestra, M.E.; Madeira, M.J.; Fernández-Vizcaíno, E.; Cabodevilla, X. Metabarcoding reveals seasonal variations in the consumption of crops and weeds by wild Red-legged Partridge Alectoris rufa. J. Ornithol. 2024, 165, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, H.; Ran, J.; Luo, J.; Chen, M.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Yan, Y.; Huang, X. Analysis of winter diet in Guizhou golden monkey (Rhinopithecus brelichi) using DNA metabarcoding data. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, H.; Xu, N.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Xu, R.; Liu, H. Molecular diet analysis of common cranes (Grus grus) under supplementary feeding based on fecal DNA metabarcoding. Ecosphere 2023, 14, e4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechin, A.; Boyarskikh, U.; Kel, A.; Filipenko, M. cutPrimers: A New Tool for Accurate Cutting of Primers from Reads of Targeted Next Generation Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2017, 24, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Shao, Q.; Grueter, C.C.; Wang, Z.; Lu, J.; Raubenheimer, D. Dietary diversity of an ecological and macronutritional generalist primate in a harsh high-latitude habitat, the Taihangshan macaque (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis). Am. J. Primatol. 2019, 81, e22965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doorn, A.C.; O’Riain, M.J.; Swedell, L. The effects of extreme seasonality of climate and day length on the activity budget and diet of semi-commensal chacma baboons (Papio ursinus) in the Cape Peninsula of South Africa. Am. J. Primatol. 2010, 72, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agetsuma, N. Foraging strategies of yakushima macaques(Macaca fuscata yakui). Int. J. Primatol. 1995, 16, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, N. Feeding rate as valuable information in primate feeding ecology. Primates 2009, 50, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Lu, J. Seasonal variations in activity budget of adult female rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) at Mt. Taihangshan area, Jiyuan, China: Effects of diet and temperature. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2015, 35, 138–146. [Google Scholar]
- Balkrishna, A.; Rohela, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Arya, V.; Thakur, P.; Oleksak, P.; Krejcar, O.; Verma, R.; Kumar, D.; et al. Mechanistic Insight into Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Potential of Jasminum Species: A Herbal Approach for Disease Management. Plants 2021, 10, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, E.; McLachlan, C.; Oketch-Rabah, H.; Calderón, A.I. United States Pharmacopeia comprehensive safety review of Styphnolobium japonicum flower and flower bud. Phytother. Res. PTR 2022, 36, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Tian, J.; Shao, Q.; Lu, J. DNA metabarcoding reveals the seasonal variation of dietary composition of Taihangshan macaque (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis), Jiyuan, north China. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e11256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, S.; Baral, S.; Garber, P.A.; Basnet, H.; Katuwal, H.B.; Gurung, S.; Rai, D.; Gaire, R.; Sharma, B.; Pun, T.; et al. Identifying the environmental and anthropogenic causes, distribution, and intensity of human rhesus macaque conflict in Nepal. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, N. Determinants of the dramatic seasonal changes in the intake of energy and protein by Japanese monkeys in a cool temperate forest. Am. J. Primatol. 1997, 41, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, S.; Garber, P.A.; Somasundaram, D.; Katuwal, H.B.; Ren, B.; Huang, C.; Li, M. Factors affecting the crop raiding behavior of wild rhesus macaques in Nepal: Implications for wildlife management. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, E.P.; Priston, N.E. Macaques in farms and folklore: Exploring the human-nonhuman primate interface in Sulawesi, Indonesia. Am. J. Primatol. 2010, 72, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Shi, G.; Cao, H.; He, M.; Su, H. DNA Metabarcoding Reveals Seasonal Variations in Crop-Foraging Behavior of Wild Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta). Diversity 2025, 17, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080517
Wang Y, Li H, Shi G, Cao H, He M, Su H. DNA Metabarcoding Reveals Seasonal Variations in Crop-Foraging Behavior of Wild Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta). Diversity. 2025; 17(8):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080517
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yun, Hongjia Li, Gongyuan Shi, Heqin Cao, Manfang He, and Haijun Su. 2025. "DNA Metabarcoding Reveals Seasonal Variations in Crop-Foraging Behavior of Wild Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta)" Diversity 17, no. 8: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080517
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, H., Shi, G., Cao, H., He, M., & Su, H. (2025). DNA Metabarcoding Reveals Seasonal Variations in Crop-Foraging Behavior of Wild Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta). Diversity, 17(8), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17080517





