Abstract
Species co-occurrence is closely linked to complex environmental changes and biological interactions in ecosystems. Freshwater ecosystems are among the most endangered ecosystems in the world, highly sensitive to environmental change, and rich in biodiversity. Clarifying the mechanisms of co-occurrence of zooplankton and phytoplankton, which are the basis of freshwater ecosystems, can provide important insights into ecosystem stability. We employed the Hierarchical Modeling of Species Communities (HMSC) within Joint Species Distribution Models (JSDMs) to fit the abundance data of zooplankton and phytoplankton dominant species sampled in April (spring) and July (summer) 2023 in Shengjin Lake to understand their co-occurrence pattern in typical Yangtze-connected lakes. Due to biotic interactions, rotifers primarily exhibit a positive co-occurrence pattern with one diatom and one cyanobacterium, while copepods mainly show a negative co-occurrence pattern with one diatom and one cyanobacterium. Only one rotifer and one chlorophyta mainly display a positive co-occurrence pattern, mainly driven by shared environmental preferences in that they are more likely to co-occur in areas with lower transparency, lower total phosphorus (TP) levels, and relatively higher pH levels. These findings show that the co-occurrence mechanisms of zooplankton and phytoplankton differ under the influence of biotic interactions and environmental factors, neither of which can be overlooked. These findings may provide important implications for the management of zooplankton and phytoplankton, the fundamental components of wetland ecosystems.
1. Introduction
Understanding the ecological processes that drive species associations is crucial for elucidating the mechanisms that maintain biodiversity and ecosystem stability in freshwater systems [1]. One of the main goals of ecology is to identify the factors that determine the distribution of species [2]. Among these, environmental factors and potential interactions between species are emphasized. Therefore, it is essential to quantify species associations and their responses to environmental change in real communities to understand how to preserve community structure and ecosystem services in freshwater systems.
Currently, the academic community primarily relies on two theories to explain the patterns of species co-occurrence. On one hand, abiotic factors, such as climate and hydrological conditions, can act as filters, selecting species that can adapt to specific environmental conditions (abiotic filtering). Habitat specialist species tend to co-occur more frequently with other species that share similar habitat preferences [3,4]. On the other hand, biotic factors, such as competition and predation, can limit the presence of certain species in specific areas (biotic filtering) [5,6]. Stephanie emphasized the importance of multiple biotic interactions in phytoplankton communities [7]. Inoue emphasizes the necessity of simultaneously considering environmental factors and species co-occurrence in the modeling of species distributions and the assembly of riverine communities [8]. Previously, a common method for assessing whether and how biological interactions affect the co-occurrence of species was species distribution modeling (SDM) [4]. However, for a disproportionately high number of species associations in rich communities, this approach may be less efficient in its estimation. In recent years, Joint Species Distribution Models (JSDMs) have become one of the main methods for quantifying species associations and their responses to environmental changes in real communities, and are an effective tool for capturing the effects of biotic and abiotic interactions in communities. JSDMs allow for the simultaneous modeling of multiple species and the estimation of residual correlations between species co-occurrences that are not explained by environmental variables [9,10].
Freshwater ecosystems, characterized by their rich biodiversity and complex ecological networks, are highly fragile. Phytoplankton and zooplankton form a foundational component of these systems and are highly sensitive to environmental changes. They are influenced by a variety of environmental factors, including transparency, nutrients, pH, and temperature, etc. [11]. Specifically, transparency and the nitrogen and phosphorus components of nutrients are closely related to the growth and distribution of phytoplankton [12]. For zooplankton, pH, phosphorus, nitrogen, dissolved oxygen, conductivity, etc., are closely related to their communities [13]. Additionally, different species have varying preferences for water with different pH levels [14,15]. Temperature also affects their growth and reproduction by influencing enzyme activity [16]. Beyond these environmental factors, there are complex biotic interactions between phytoplankton and zooplankton that may affect their co-occurrence. As primary producers, phytoplankton supply oxygen and nutrients to the water body through photosynthesis [17]. Zooplankton, including rotifers, cladocerans, and copepods, act as primary consumers and play a crucial role in the transfer of energy and nutrients between primary producers and higher trophic levels [18]. They primarily feed on small algae, bacteria, and organic detritus and also serve as an important food source for fish and other large aquatic organisms [19]. The relationship between phytoplankton and zooplankton is interdependent and extends beyond simple predation to include complex ecological processes such as competition and symbiosis [20,21]. Research should focus on determining whether their co-occurrence is driven by environmental factors or biotic interactions and what co-occurrence patterns emerge under their influence. This knowledge is of great significance for maintaining the species diversity of phytoplankton and zooplankton [22].
Influenced by the dynamics of hydrological connectivity, nutrient inputs, and water level fluctuations, the connected lakes of the Yangtze River accumulate plankton from both rivers and lakes through water exchange, forming a transitional community where both widespread and endemic species are present [23,24,25]. During the flood season, the nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients carried by the river may stimulate the proliferation of phytoplankton such as cyanobacteria and diatoms [26], but strong water currents can also scour some plankton [25]. In the dry season, the reduced water flow is conducive to the accumulation of plankton, but nutrient limitations may inhibit growth [26]. In addition to these natural factors, human activities have exacerbated the fragility of such ecosystems [27]. For example, eutrophication in some lakes can lead to changes in dominant algal species, potentially disrupting the balance of the plankton community and the health of the water body [28,29]. However, past research has primarily focused on the individual distribution patterns of other species and the effects of environmental factors on plankton community structure [30,31,32,33]. The co-occurrence relationship between zooplankton and phytoplankton and the factors influencing it remain unclear.
Shengjin Lake is a typical Yangtze-connected lake, where plankton species and quantities are richer and interspecific relationships are more complex. In this study, we quantified zooplankton and phytoplankton dominant species abundance and environmental factor data for April and July in Shengjin Lake, and used JSDMs to explore co-occurrence relationships among zooplankton. We investigated the drivers influencing species co-occurrence and examined the co-occurrence patterns of species under the influence of both biotic and abiotic factors [34]. Due to biotic interactions, we predict that rotifers and phytoplankton will mainly exhibit a positive co-occurrence pattern, as rotifers primarily feed on phytoplankton, organic debris, and bacteria [35]. Cladocerans and copepods are expected to exhibit a negative co-occurrence pattern with phytoplankton, as they are larger in size and have extensive and complex feeding. Under the influence of environmental factors, some species may co-occur due to their common environmental preferences [36]. This study investigates the co-occurrence mechanisms of zooplankton and phytoplankton to reflect the stability of the aquatic ecosystem in Shengjin Lake, providing a scientific basis for the protection of the typical middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River aquatic ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Shengjin Lake, situated in the southern part of Chizhou City, Anhui Province (30.24–31.86° N, 116.92–117.94° E), is a crucial ecological barrier in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River [37]. Covering a total area of approximately 333.4 km2 with a maximum water area of up to 1.45 × 104 ha, it represents a vast freshwater ecosystem [37]. As a permanent freshwater lake with a subtropical monsoon climate, Shengjin Lake experiences an average annual rainfall of 1600 mm and an average annual temperature of 16 °C, providing ample moisture and favorable conditions for the growth of plankton [37,38]. During the period 1850–2000, total nitrogen levels in Shengjin Lake have continued to increase, indicating increasing trophic levels in the lake. The current trophic state is generally mild to moderately eutrophic [39,40,41].
Due to its geographical location and ecological environment, Shengjin Lake serves as a habitat for a multitude of flora and fauna, offering diverse living conditions for plankton and playing a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity. It holds significant status in domestic ecological conservation and has been listed in the Ramsar Convention, highlighting its importance in global ecological protection [42]. The water level of Shengjin Lake fluctuates markedly, with April (spring) and July (summer) corresponding to the low-water season and the flood season, respectively [43,44]. These seasonal variations create a diverse range of habitats suitable for zooplankton and phytoplankton with different ecological niches. Additionally, the abundance and biodiversity of zooplankton and phytoplankton are generally higher during both periods, making it an ideal time for species statistics and analysis (Figure 1).
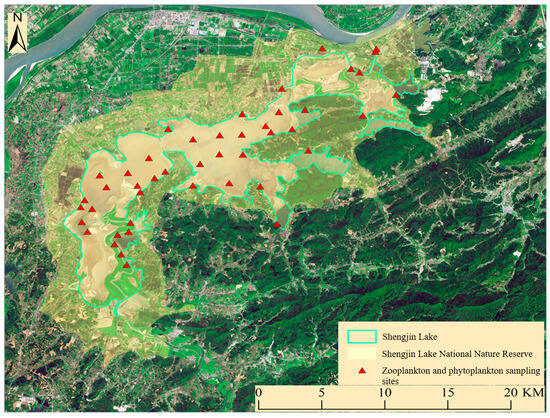
Figure 1.
Shengjin Lake National Nature Reserve and zooplankton and phytoplankton sampling sites in April and July 2023.
2.2. Data Collection
In April and July 2023, we conducted field surveys and sample collection in the main lake area of Shengjin Lake. Considering the surface area of the lake, connectivity, and the dispersal characteristics of plankton, we established a total of 44 sampling sites across the open water, lake inlets, and lake edges. Specifically, there were 18 sites on the open water, 10 in the lake inlets, and 16 on the lake edges (Figure 1). Zooplankton, phytoplankton, and environmental factors were taken simultaneously from two vertical points at each sampling site, i.e., 0.5 m below the water surface and 0.5 m above the bottom, and integrated into a single one. Rotifer and phytoplankton samples were collected in 1 L plastic bottles and fixed in the field with 1% Lugol iodine solution. Each sample was precipitated in our laboratory for 48 h and condensed to 30 mL. The cladocera and copepod samples were collected with 10 L of mixed water through a 60 µm plankton net, with an opening area of 346 cm2. Subsequently, the samples were transferred to 50 mL plankton bottles and preserved with 4% formaldehyde solution (final concentration), followed by washing the plankton net three times. All biological samples were brought back to the laboratory and observed under a light microscope (Olympus, BX53, Tokyo, Japan). We identified the species according to the method of Zhang and Huang [45]; 1 mL sub-samples of rotifers were counted in a counting chamber twice, while 5 mL sub-samples of crustaceans were counted for all 50 mL samples [45]. One count of 0.1 mL of phytoplankton sub-samples and two repetitions were taken for the average value [46].
During the field measurements, parameters like water temperature, electric conductivity, pH, dissolved oxygen, water depth, and transparency were measured using a Secchi disk. Additionally, two 0.5 L water samples were collected at each point in opaque bottles for laboratory analysis of total phosphorus (TP) and total nitrogen (TN) [47].
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Dominant Species and Environmental Factors
Dominant species of plankton are representative and can clearly explain species assemblages [48,49], so this study primarily analyzes the co-occurrence relationships among these dominant species. Dominant species of plankton refer to the species with the highest number of individuals that play a decisive role in the existence and development of aquatic biological communities [50].
For each species, we calculated the McNaughton dominance index (Y), Y = (Ni/N) × fi, where Ni was the total number of individuals of species i in all samples, N was the total number of all species in all samples, and fi was the occurrence frequency of species i. When Y > 0.02, the species was registered as the dominant species [51]. We also calculated community parameters (richness, Shannon–Weiner index, and Pielou index) of dominant species.
In order to eliminate the covariance effect between environmental factors, we calculated the variance inflation factor (VIF) and excluded environmental factors with VIF > 10.
2.3.2. Model Structure Setup and Fitting
Using the Hierarchical Modeling of Species Communities (HMSC) within the Joint Species Distribution Model (JSDM) [10,52,53], we modeled the pairwise co-occurrence among the dominant zooplankton and phytoplankton in Shengjin Lake. JSDMs allow modeling of multiple species simultaneously and estimate relationships between species through residual correlations after considering the effects of environmental variables [9,10]. Given that the structure of plankton community data is of abundance type, we employed a lognormal Poisson function for the error distribution in the model, accounting for spatial random effects at sampling points. To comprehensively investigate the distinctions and connections between environmental factors and biological interactions, we considered two types of models. The first type is the full model (Full model), incorporating environmental covariates and spatial random effects. The second type is the environmental factor model (Environmental model), containing only environmental covariates without spatial random effects.
Spatial random effects in the Full model are represented using latent variables to simulate the spatial structure of occurrence data and associations between species [9]. Pairwise species co-occurrence matrices generated by each model were used to determine the probabilities of co-occurrence among zooplankton and phytoplankton, indicating positive or negative associations. The Environmental model elucidated the relationships between species due to their responses to included environmental variables, while the Full model captured residual correlations after removing the effects of measured environmental variables. Given the obligatory nature of interactions among zooplankton and phytoplankton, it is anticipated that the residual correlations in the Full model mainly represent non-random co-occurrence patterns arising from biological interactions among zooplankton and phytoplankton. To assess species responses to variables included in the model, we visualized estimates of ecological niche parameters [53]. Variance partitioning analysis was conducted to determine factors contributing to the occurrence of zooplankton and phytoplankton [53]. By comparing the variance partitioning results of fixed effects and latent variables in the Full model with the fixed effects in the Environmental model, we identified the relative importance of environmental variables and latent variables in explaining the compositions of zooplankton and phytoplankton. For the above analysis, if the posterior probability of the correlation not equaling zero exceeds 0.95, it is also considered to be statistically significant [53].
Upon establishing the HMSC model structure, the parameter estimation phase involves fitting the data utilizing the sampleMcmc function. For each model, we executed two parallel Bayesian Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) chains, iterating 10,000 times, discarding the initial 5000 iterations as burn-in, and thinning the remaining 5000 iterations by a factor of 20 to generate 500 samples. Consequently, each model produced a total of 1000 samples. Convergence was assessed by computing the potential scale reduction factors for the beta (species responses to included covariates) and omega (species interactions) parameters of the HMSC model, alongside visually examining MCMC trace plots. When the potential scale reduction factor nears 1, it signifies satisfactory MCMC convergence [52].
2.3.3. Data Analysis Tools
Community parameters and environmental factor analysis were performed using the “vegan” packages in R 3.4.1. All models were fitted using R version 4.3.3 with the “hmsc” package version 3.0 [54]. The correlation plot was constructed using the “corrplot” package version 0.92 [55], and the variance partitioning plot was created using the “ggplot2” package version R 3.3.3 [56].
3. Results
3.1. Biological and Environmental Factors
During the months of April and July, a total of 81 species of zooplankton were identified, comprising 41 species of rotifers, 17 species of cladocerans, and 23 species of copepods. In the same period, 144 species of phytoplankton from seven phyla were recorded, including 50 species of diatoms, 48 species of chlorophytes, 23 species of cyanobacteria, 4 species of cryptophytes, 3 species of euglenoids, 3 species of dinoflagellates, and 3 species of chrysophytes. The dominant species of zooplankton totaled 16, comprising 3 species of rotifers, 5 species of cladocerans, and 8 species of copepods. The dominant species of phytoplankton totaled 10, including 4 species of diatoms, 2 species of cyanobacteria, and 3 species of chlorophytes (Table 1). The richness based on dominant species was 19.45, the Shannon–Weiner index was 2.23, and the Pielou index was 0.75.

Table 1.
The dominant species of zooplankton and phytoplankton in Shengjin Lake.
The following environmental factors were analyzed (Table 2) and screened to exclude dissolved oxygen (VIF > 10).

Table 2.
Environmental factors affecting the co-occurrence pattern of zooplankton and phytoplankton at 44 sampling sites in the Shengjin Lake area.
3.2. Model Evaluation
Both the Full and Environmental models exhibit good explanatory power, as evidenced by the AUC values (Full model: 0.81; Environmental model: 0.78) and TjurR2 values (Full model: 0.15; Environmental model: 0.12).
3.3. The Co-Occurrence Between Zooplankton and Phytoplankton
In the Full model, the random variables account for the co-occurrence phenomena that remain after the influence of environmental variables is removed, and the residual correlations between zooplankton and phytoplankton are typically very strong. The results show that among the 54 combinations of zooplankton and phytoplankton in Shengjin Lake, 16 pairs are statistically remarkable (ρ > 0.95). Residual correlations showed that, due to biotic interactions, both rotifers and copepods exhibited more correlations with phytoplankton than cladocerans, which had no correlation with phytoplankton (Figure 2a). Copepods had more significant correlations with phytoplankton than rotifers (copepods: 14 pairs; rotifers: 2 pairs) (Figure 2a). Among copepods, six species were negatively correlated with phytoplankton, while two species were positively correlated (Figure 2a). Only a single species, Trichocerca stylata, exhibited a positive correlation with the diatoms and the cyanobacteria (Figure 2a). In the Environmental model, their co-occurrence is driven by the shared response of species to environmental conditions, and the results show that only one rotifer species (Trichocerca stylata) is positively correlated with the chlorophyta (Scenedesmus quadricauda) (Figure 2b).
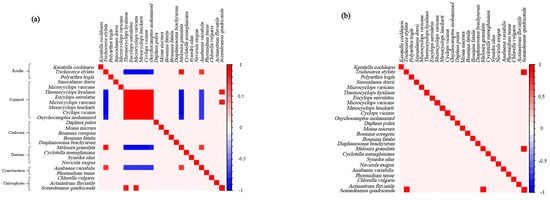
Figure 2.
Correlation between zooplankton and phytoplankton in Shengjin Lake. (a) Residual correlation shows species associations after removing the effects of environmental variables included in the Full model. (b) Species associations influenced exclusively by environmental variables. Red indicates a positive correlation, while blue indicates a negative correlation.
3.4. Drivers of Zooplankton and Phytoplankton Co-Occurrence
The variance decomposition results of fixed and random effects show that in the Full model, random variables account for 12.5% of the explained variance, while seven environmental variables account for 87.5% of the explained variance. Environmental variables play a substantial role in explaining the distribution of zooplankton and phytoplankton, with transparency (19.7%) being the most explanatory environmental variable, followed by electrical conductivity (16%) and total phosphorus (TP) (12.9%), and then pH (12.7%), total nitrogen (TN) (9.9%), water depth (8.4%), and water temperature (8.1%) (Figure 3a). A higher percentage of stochasticity was seen in copepods. In the Environmental model, the variance partitioning results of environmental variables are essentially consistent with the Full model, with transparency (26%) being the most explanatory environmental variable, followed by electrical conductivity (21.3%) and TP (13.1%), and then pH (12.6%), TN (10.6%), water depth (8.4%), and water temperature (7.9%) (Figure 3b). Transparency explained a high proportion of the distribution of most species. Conductivity explained a more average proportion of species. Total phosphorus explained a high proportion of the distribution of dendrobatids; pH explained a relatively high proportion of rotifers and copepods. Other environmental variables had low and insignificant proportions. Although the random variables explain less variance than the environmental variables, the potential variables have a relatively high proportion (12.5%) in each component.
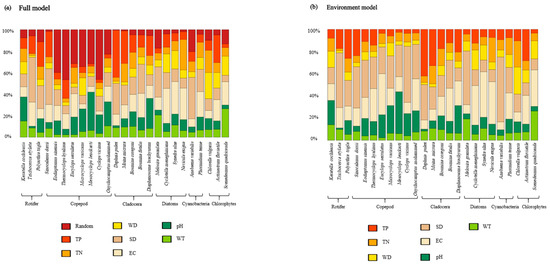
Figure 3.
Variance partitioning among the environmental variables (fixed effects) and the spatial latent variable (random effect) included in the Full model (a), and among the fixed effects of the Environmental model (b) used for modeling zooplankton and phytoplankton in the Shengjin Lake.
The niche response heatmaps of zooplankton and phytoplankton to the variables included in the model show that when the posterior probability is 0.95, some species exhibit correlations with environmental variables (Figure 4). Since environmental variables only had an effect on the co-occurrence of Trichocerca stylata and Scenedesmus quadricauda (Figure 3b), we focused on describing the environmental factors associated with this species pair. The pH, transparency, and TP were all significantly correlated with Trichocerca stylata-Scenedesmus quadricauda. Specifically, pH was positively correlated with them, while transparency and TP were negatively correlated with them.
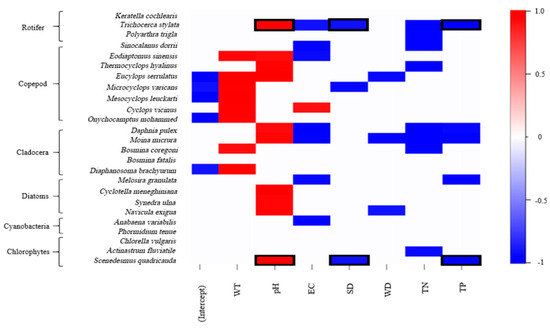
Figure 4.
Niche heat map of zooplankton and phytoplankton in Shengjin Lake, with positive (red) and negative (blue) responses to environmental variables generated by the Full model. Displays only the estimated parameters for which the corresponding posterior probability of being non-zero exceeded 0.95; black boxes indicate the response of species co-occurring due to environmental factors to environmental variables.
4. Discussion
In Shengjin Lake, we discovered a rich diversity of zooplankton and phytoplankton. Although our sampling was confined to spring and summer, we still recorded a relatively high species diversity compared to other seasons [57,58]. On this basis, the dominant species were selected as the main research objects because they are representative and the results can be clearly displayed. These zooplankton and phytoplankton have complex correlations with each other, such as predation, competition, or symbiosis [59]. They are also frequently used as bioindicators of environmental changes due to their rapid responses. Therefore, exploring the co-occurrence of zooplankton and phytoplankton and the factors influencing it should provide new insights into maintaining the stability of freshwater ecosystems and offer significant implications for the conservation and management of biodiversity.
The residual correlation matrix of the Full model reveals the complex co-occurrence patterns of zooplankton and phytoplankton under the influence of biotic interactions. Rotifers and copepods are strongly correlated with phytoplankton, whereas cladocerans show no significant correlation. Studies suggest that cladocerans may reduce their direct correlations with phytoplankton due to competition with other zooplankton and predation pressure. Copepods have more species pairs with correlations to phytoplankton than rotifers (copepods: 14 pairs; rotifers: 2 pairs), indicating a more complex co-occurrence relationship. The dominant zooplankton group we found was copepods, with eight species, but within them, which are divided into calanoids and cyclopoids, there are clear differences. Calanoid copepods are also highly efficient feeders; they select for larger, more nutritious, and motile prey, which typically includes ciliates and flagellated phytoplankton, among others [60]. Therefore, their co-occurrence with phytoplankton was not significant in this study. However, cyclopoids are generally omnivorous, switching from herbivory when they are nauplii and copepodites to carnivorous when they become adults [61]. In the co-occurrence relationship between rotifers and phytoplankton, only one rotifer showed a positive correlation with one diatom and one cyanobacterium. The dominant rotifer species we identified were primarily algivorous and occupied a relatively narrow ecological niche, mainly feeding on small-sized phytoplankton. This indicates that they exhibit higher selectivity and a distinct preference for certain phytoplankton types [35,62]. On the other hand, when phytoplankton are large enough to reduce predation by rotifers, the feeding preference may promote small phytoplankton growth [62,63]. This feeding preference and feeding relationship likely contribute to their positive co-occurrence pattern. Copepods mainly show a negative correlation with phytoplankton, reflecting their negative co-occurrence pattern. Copepods have a broad ecological niche and diverse food choices, preying not only on phytoplankton but also on small zooplankton, which increases their correlation with phytoplankton [64]. In this study, cyclopoids are omnivores with diverse feeding habits, primarily preying on phytoplankton (diatoms and chlorophytes, etc.) and occasionally consuming rotifers [65,66]. Copepods generally prefer larger food particles, which provide a refuge for smaller phytoplankton species [67,68]. An exception is a small number of copepods that show a positive correlation with chlorophytes, which may be a manifestation of ecosystem self-regulation [64]. Chlorophytes (such as Scenedesmus quadricauda) are one of the main phytoplankton causing eutrophication in water bodies. Cladocerans, by preying on chlorophytes, can prevent their over-proliferation from causing negative impacts on the aquatic ecosystem [69].
In the Environmental model, the influence of environmental factors on the co-occurrence of zooplankton and phytoplankton is only reflected in the rotifer–chlorophyta pair (Figure 2b). Rotifers exhibit a positive correlation with chlorophytes, but no correlation is observed between them in the Full model (Figure 2b). Both rotifers and chlorophytes share similar responses to certain environmental variables; for instance, they are negatively correlated with transparency and total phosphorus (TP) and positively correlated with pH. Transparency, TP, and pH are also the environmental variables with higher explanatory power for species co-occurrence (Figure 3b), indicating that they significantly influence the co-occurrence of rotifers and phytoplankton, facilitating their co-occurrence [2,30]. These results collectively suggest that the co-occurrence of one rotifer and chlorophytes is driven by shared environmental preferences. We conducted the following analysis regarding the impact of the three aforementioned environmental factors on the co-occurrence of zooplankton and phytoplankton. In water bodies with higher transparency, sufficient light availability can promote the growth of phytoplankton, thereby providing more food resources for zooplankton [59]. However, zooplankton in such waters are also more susceptible to predation by fish [59], leading to a decrease in their numbers and potentially resulting in algal blooms [70]. In contrast, nutrient availability is the key limiting factor. Moderate concentrations of total phosphorus (TP) in water can facilitate the growth and reproduction of phytoplankton. Nevertheless, excessively high TP concentrations can trigger over-proliferation of phytoplankton, causing algal blooms and disrupting the balance of aquatic ecosystems [71]. We speculate that rotifers and phytoplankton are more likely to coexist in areas with lower transparency and TP levels, which indirectly indicates that the co-occurrence of rotifers and phytoplankton occurs in relatively stable aquatic ecological environments. Moreover, rotifers tend to thrive in slightly alkaline waters, and most phytoplankton also prefer to grow in neutral to slightly alkaline conditions [63].
The variance partitioning analysis of the Full model indicates that environmental variables are the primary factors explaining species co-occurrence, but they are only significant for a subset of rotifers (Figure 3a) and cannot fully account for the distribution patterns of species. While random variables account for only a small portion of the explanation of species distribution, they represent a relatively high proportion among the components (Random: 12.5%; Conductivity: 16%; TP: 12.9%; pH: 12.7%; TN: 9.9%; Depth: 8.4%; Temperature: 8.1%). These random variables, which reflect species interactions such as competition, predation, and mutualism, are ubiquitous in ecosystems and cannot be overlooked [63], as they have a notable impact on the majority of zooplankton (Figure 3a). Therefore, our study concludes that the co-occurrence patterns of zooplankton and phytoplankton are jointly determined by environmental factors and species interactions.
The two fitted models we constructed contain overlapping information, namely the same environmental predictors, but the complete model further includes random variables. According to the diagnostic results of the models, both the Full model and the Environmental model have good explanatory power, with the complete model showing higher explanatory capacity and better model fit. This provides a reliable data basis for further analyzing the impact of environmental factors and biological interactions on the distribution of zooplankton and phytoplankton [2]. The Full model offers information for our attempt to unravel the relative importance of environmental and biological factors in species distribution, and the comparison between residual correlations and environmental correlations allows us to infer the driving forces behind the co-occurrence of zooplankton and phytoplankton.
5. Conclusions
This study used HMSC within JSDMs to examine the co-occurrence patterns of zooplankton and phytoplankton in Shengjin Lake. The models were validated through cross-validation, showing strong predictive capabilities. The results suggest that the co-occurrence patterns are shaped by a combination of environmental factors (transparency, pH, total phosphorus) and biological interactions (predation and competition). Only one rotifer positively co-occurred with one diatom and one cyanobacterium due to their algivores and feeding preferences for small phytoplankton. The predominantly negative co-occurrence of copepods with one diatom and one cyanobacterium may be due to the omnivorous nature of cyclopoids and interspecific competition among cyclopoids, which reduces their encounters with phytoplankton. Environmental factors such as water transparency, total phosphorus (TP), and pH also significantly influenced these patterns, with some rotifer species more likely to co-occur with phytoplankton in areas of lower transparency and TP levels, and in slightly alkaline waters. To maintain plankton community stability and diversity, we recommend regular monitoring of key environmental factors and implementing measures to control nutrient inputs, reduce eutrophication, and regulate pH levels. Special attention should be given to sensitive species like rotifers to ensure habitat stability and prevent species over-proliferation. This research provides insights into the complex dynamics of plankton communities and offers guidance for protecting biodiversity and maintaining the balance of aquatic ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S., P.X. and C.L.; methodology, Y.S. and C.L.; formal analysis, Y.S. and C.L.; investigation, Y.S., Y.L. and Y.W.; data curation, Y.S., Y.L., Y.W. and C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.S. and C.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.S. and C.L.; visualization, Y.S. and C.L.; supervision, P.X. and C.L.; funding acquisition, C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Monitoring Project of Biodiversity in the Shengjin Lake National Nature Reserve (2022BFAFN02495).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Freilich, M.A.; Wieters, E.; Broitman, B.R.; Marquet, P.A.; Navarrete, S.A. Species co-occurrence networks: Can they reveal trophic and non-trophic interactions in ecological communities? Ecology 2018, 99, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, J.P.; Gonçalves, D.V.; Garcia-Raventós, A.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Varandas, S.; Froufe, E.; Teixeira, A.; Hui, F.K.C.; Filipe, A.F.; Sousa, R. Joint species distribution models unveil co-occurrences between freshwater mussels and their fish hosts. J. Biogeogr. 2023, 50, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspin, T.; House, A. Alpha and beta diversity and species co-occurrence patterns in headwaters supporting rare intermittent-stream specialists. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 67, 1188–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiguet, F. Unravelling species co-occurrence in a steppe bird community of inner mongolia: Insights for the conservation of the endangered jankowski’s bunting. Divers. Distrib. 2020, 26, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amen, M.; Mod, H.K.; Gotelli, N.J.; Guisan, A. Disentangling biotic interactions, environmental filters, and dispersal limitation as drivers of species co-occurrence. Ecography 2018, 41, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivellone, V.; Bougeard, S.; Giavi, S.; Krebs, P.; Balseiro, D.; Dray, S.; Moretti, M. Factors shaping community assemblages and species co-occurrence of different trophic levels. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 4745–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutkiewicz, S.; Follett, C.L.; Follows, M.J.; Henderikx-Freitas, F.; Ribalet, F.; Gradoville, M.R.; Coesel, S.N.; Farnelid, H.; Finkel, Z.V.; Irwin, A.J. Multiple biotic interactions establish phytoplankton community structure across environmental gradients. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2024, 69, 1086–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Stoeckl, K.; Geist, J. Joint species models reveal the effects of environment on community assemblage of freshwater mussels and fishes in european rivers. Divers. Distrib. 2017, 23, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovaskainen, O.; Abrego, N. Joint Species Distribution Modelling: With Applications in R; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, L.J.; Tingley, R.; Morris, W.K.; Golding, N.; O’Hara, R.B.; Parris, K.M.; Vesk, P.A.; McCarthy, M.A. Understanding co-occurrence by modelling species simultaneously with a joint species distribution model (jsdm). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Hou, N. Recovery capacity of constructed wetlands in response to multiple disturbances: Microbial interaction perspective. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 408, 131155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinl, K.L.; Harris, T.D.; Elfferich, I.; Coker, A.; Zhan, Q.; Domis, L.N.D.S.; Morales-Williams, A.M.; Bhattacharya, R.; Grossart, H.-P.; North, R.L.; et al. The role of organic nutrients in structuring freshwater phytoplankton communities in a rapidly changing world. Water Res. A J. Int. Water Assoc. 2022, 219, 118573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, D.K.; Elmarsafy, M.; Vucic, J.M.; Teillet, M.; Pretty, T.J.; Cohen, R.S.; Huynh, M. Which physicochemical variables should zooplankton ecologists measure when they conduct field studies? J. Plankton Res. 2021, 43, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimzadeh, G.; Alimohammadi, M.; Kahkah, M.R.R.; Mahvi, A.H. Relationship between algae diversity and water quality–A case study: Chah niemeh reservoir southeast of Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougi, A. Ph adaptation stabilizes bacterial communities. npj Biodiversity 2024, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraón, E.; Fernández-González, C.; Tarran, G.A. Effect of temperature, nutrients and growth rate on picophytoplankton cell size across the atlantic ocean. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28034. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.Z.; Ouyang, L.L.; Shen, A.L.; Wang, Y.L. The cell cycle of phytoplankton: A review. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2022, 53, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declerck, S.A.; de Senerpont Domis, L.N. Contribution of freshwater metazooplankton to aquatic ecosystem services: An overview. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 2795–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.K.; Arnott, S.E.; Shead, J.A.; Derry, A.M. The recovery of acid-damaged zooplankton communities in Canadian lakes: The relative importance of abiotic, biotic and spatial variables. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavan, E.L.; Henson, S.A.; Belcher, A.; Sanders, R. Role of zooplankton in determining the efficiency of the biological carbon pump. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, C.R.; Barry, J.P. Habitat heterogeneity, disturbance, and productivity work in concert to regulate biodiversity in deep submarine canyons. Ecology 2010, 91, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D.; Castillo, M.M.; Capps, K.A.; Allan, J.D.; Castillo, M.M.; Capps, K.A. Energy flow and nutrient cycling in aquatic communities. In Stream Ecology: Structure and Function of Running Waters; Springer: Cham, Switherland, 2021; pp. 357–381. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Dai, B.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z. Initial recovery of fish faunas following the implementation of pen-culture and fishing bans in floodplain lakes along the yangtze river. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wu, P.; Ma, X.; Zhou, L. Spatial-temporal analysis of landscape ecological risk in different seasons during the past 30 years in lake shengjin wetland, lower reaches of the yangtze river. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 813–825. [Google Scholar]
- Rennella, A.M.; Geronazzo, M.D.; Romero, M.; Boveri, M.; Rosso, J.J. Hydrological variability, zooplankton availability and the shift between planktivore-benthivore feeding behaviour in the visual predator fish, odontesthes bonariensis. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2019, 102, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentzky, V.C.; Tittel, J.; Jäger, C.G.; Bruggeman, J.; Rinke, K. Seasonal succession of functional traits in phytoplankton communities and their interaction with trophic state. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakos, V.; Matthews, B.; Hendry, A.P.; Levine, J.; Loeuille, N.; Norberg, J.; Nosil, P.; Scheffer, M.; De Meester, L. Ecosystem tipping points in an evolving world. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wu, X.; Hou, J.; Peng, S.; Lin, X.; Ge, X.; Yan, D.; Lin, G. Monitoring the dynamics of aquatic vegetation in a typical shallow lake using the water bloom index algorithm—A case study in bao’an lake in the middle reaches of the yangtze river. Plants 2024, 13, 3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Jiang, X.; Xie, Z.; Heino, J. Eutrophication is better indicated by functional traits than taxonomic composition of macroinvertebrate assemblages in floodplain lakes. Biodivers. Conserv. 2024, 33, 4257–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranston, A.; Cooper, N.; Bro-Jørgensen, J. Using joint species distribution modelling to identify climatic and non-climatic drivers of afrotropical ungulate distributions. Ecography 2024, 2024, e07209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, J.; Mao, F.; Peng, W.; Chen, Q. Effect of environmental factors on macrobenthic community structure in chishui river basin. Sustainability 2025, 17, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sun, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of plankton community structures and environmental factors in typical water bodies of eastern China. Ecol. Front. 2025, 45, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Xiao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Luo, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, D.; Niu, Y. Structural characteristics of plankton community in dongting lake and its relationship with water environmental factors. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisz, M.S.; Pottier, J.; Kissling, W.D.; Pellissier, L.; Lenoir, J.; Damgaard, C.F.; Dormann, C.F.; Forchhammer, M.C.; Grytnes, J.A.; Guisan, A. The role of biotic interactions in shaping distributions and realised assemblages of species: Implications for species distribution modelling. Biol. Rev. 2013, 88, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandarkar, S.; Paliwal, G. Trophic status in freshwater lentic ecosystem of dhukeshwari temple pond deori with reference to zooplanktonic assemblage. Int. J. Environ. Rehabil. Conserv. 2017, 8, 145–159. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, U.; Sommer, F. Cladocerans versus copepods: The cause of contrasting top–down controls on freshwater and marine phytoplankton. Oecologia 2006, 147, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Deng, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Z. Temporal and spatial variations in phytoplankton: Correlations with environmental factors in Shengjin lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14144–14156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, L.Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J. Dynamic ecosystem service value in the wetland of Shengjin lake national nature reserve. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2018, 45, 909–915. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Xiang, C.; Wu, L.; Xu, Y. High-resolution paleoclimatic changes recorded in lake Shengjin, lower reaches of the Yangtze river over the last millennium. Quat. Sci. 2022, 42, 421–434. [Google Scholar]
- Anhui Provincial Department of Ecology and Environment. Anhui Ecological and Environmental Statistical Bulletin 2023 [EB/OL]. (2024-12-17). Available online: https://sthjt.ah.gov.cn/public/21691/122622271.html (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- Gong, X.-H.; Ding, Q.-Q.; Jin, M.; Xue, B.; Zhang, L.; Yao, S.-C.; Wang, Z.; Lu, S.; Zhao, Z. Screening of priority pollutants and risk assessment for surface water from Shengjin lake. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2021, 42, 4727–4738. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Dong, B.; Wang, P.; Sheng, S.; Sun, L.; Fang, L.; Li, H.; Liu, L. Research on ecological risk assessment in land use model of Shengjin lake in Anhui province, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 2665–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, J. Influence of the sluice on water level and area of Yangtze river-connected lakes: A case study in Shengjin lake. J. Water Resour. Water Eng 2018, 29, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-H.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.-H. Remote sensing monitoring on spatial differentiation of suspended sediment concentration in a river-lake system based on sentinel-2 msi imaging: A case for Shengjin lake and connected Yangtze river section in Anhui province. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2020, 41, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Huang, X.F. Methods for Study on Freshwater Plankton; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Wei, Y. The Freshwater Algae of China: Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology; China Science Publishing & Media: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- State Environmental Protection Bureau (Sepb). Methods of Monitoring and Analysis for Water and Wastewater, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China. (In Chinese)
- Yang, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, C.; Sun, B.; Wang, X.; Shi, X. Seasonal changes in phytoplankton biomass and dominant species in the changjiang river estuary and adjacent seas: General trends based on field survey data 1959–2009. J. Ocean Univ. China 2014, 13, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Chen, K.; Liu, L.; Hu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, D. Niche and interspecific association with respect to the dominant phytoplankton species in different hydrological periods of lake Wuchang, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 985672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.W.; Sun, X.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z. Spatial niches of dominant zooplankton species in the Yantai offshore waters. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5822–5833. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, S.; Li, M.; Zheng, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, M.; Hu, J.; Tang, J.; Hu, S.; Dong, F.; Zhao, X. Macroinvertebrate communities in the big east lake water network in relation to environmental factors. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2017, 418, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovaskainen, O.; Tikhonov, G.; Norberg, A.; Guillaume Blanchet, F.; Duan, L.; Dunson, D.; Roslin, T.; Abrego, N. How to make more out of community data? A conceptual framework and its implementation as models and software. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warton, D.I.; Blanchet, F.G.; O’Hara, R.B.; Ovaskainen, O.; Taskinen, S.; Walker, S.C.; Hui, F.K. So many variables: Joint modeling in community ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, G.; Opedal, Ø.H.; Abrego, N.; Lehikoinen, A.; de Jonge, M.M.; Oksanen, J.; Ovaskainen, O. Joint species distribution modelling with the R-package hmsc. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simko, T.; Wei, T. R Package “Corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix, Version 0.88. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Wickham, M.H. Package ‘ggplot2’. Create elegant data visualisations using the grammar of graphics. Version 2016, 2, 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, A.; Yu, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, K. Seasonal variation characteristics and the factors affecting plankton community structure in the Yitong river, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Liang, Y.; Li, C.; Svenning, J.C. How do rotifer communities respond to floating photovoltaic systems in the subsidence wetlands created by underground coal mining in China? J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 339, 117816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, C.E.; Fischer, J.M.; Bollens, S.M.; Overholt, E.P.; Breckenridge, J.K. Toward a more comprehensive theory of zooplankton diel vertical migration: Integrating ultraviolet radiation and water transparency into the biotic paradigm. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 1603–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiørboe, T. How zooplankton feed: Mechanisms, traits and trade-offs. Biol. Rev. 2011, 86, 311–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hairston, H.N.G. Food limitation in a wild cyclopoid copepod population: Direct and indirect life history responses. Oecologia 1998, 115, 320–330. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, J.J. Food niches of planktonic rotifers: Diversification and implications. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2022, 67, 2218–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tackx, M.; Dauta, A.; Julien, F.; Buffan-Dubau, E. Rotifers stimulate the specific uptake rate in lotic phototrophic biofilms. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.-K.; Wang, Y.-G.; Zhou, L.-T.; Wang, S.-H.; Jiang, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, P.-F. Characterization of the ecological niche and interspecific connectivity of plankton in Baiyangdian lake by combining ecological networks. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2024, 45, 5298–5307. [Google Scholar]
- Lampman, G.G.; Makarewicz, J.C. The phytoplankton zooplankton link in the lake ontario food web. J. Great Lakes Res. 1999, 25, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhar, P. Role of phytoplankton and zooplankton as health indicators of aquatic ecosystem: A review. Int. J. Innov. Res. Study 2013, 2, 489–500. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, U.; Sommer, F.; Santer, B.; Jamieson, C.; Boersma, M.; Becker, C.; Hansen, T. Complementary impact of copepods and cladocerans on phytoplankton. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meester, L.; Declerck, S.A.; Ger, K.A. Beyond daphnia: A plea for a more inclusive and unifying approach to freshwater zooplankton ecology. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 4693–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.A.; do Nascimento Moura, A. Ecological impacts of freshwater algal blooms on water quality, plankton biodiversity, structure, and ecosystem functioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliwicz, Z.M. Relative significance of direct and indirect effects of predation by planktivorous fish on zooplankton. Hydrobiologia 1994, 272, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Jiang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Feng, J. Effects of environmental concentrations of total phosphorus on the plankton community structure and function in a microcosm study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).