Space Use and Movements of Southeastern Breeding Double-Crested Cormorants (Nannopterum auritum) in the United States
Abstract
1. Introduction
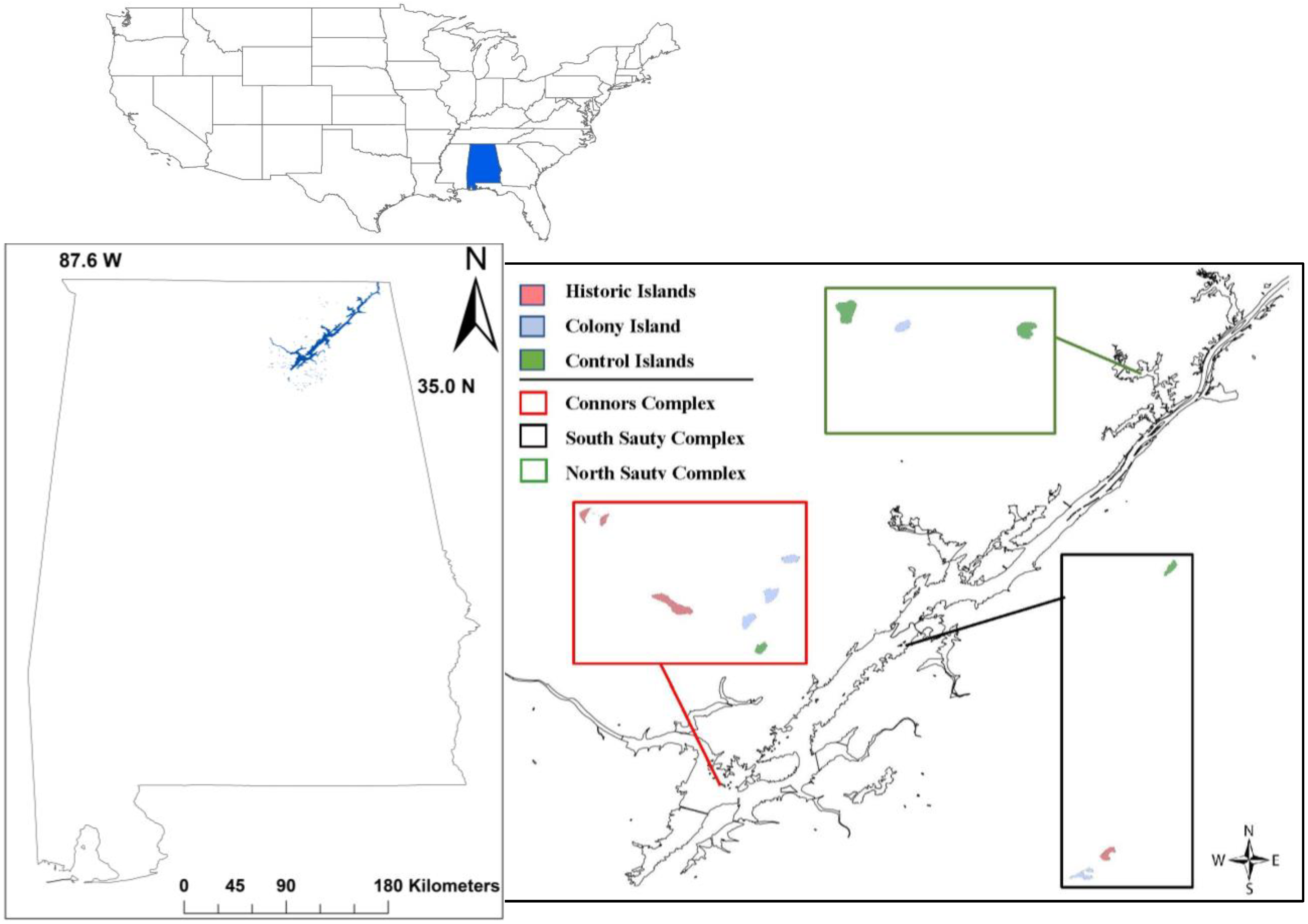
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wires, L.R.; Cuthbert, F.J. Historic Populations of the Double-crested Cormorant (Phalacrocorax auritus): Implications for Conservation and Management in the 21st Century. Waterbirds 2006, 29, 9–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, B.; King, D.T.; Tobin, M.E.; Harrel, J.B.; Smith, P.L. Double-crested Cormorant movements in relation to aquaculture in eastern Mississippi and western Alabama. Waterbirds 2004, 27, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dorr, B.S.; Fielder, D.G. Double-Crested Cormorants: Too Much of a Good Thing? Fisheries 2017, 42, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barras, S.C. Double-Crested Cormorants in Alabama; USDA National Wildlife Research Center-Staff Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; p. 77.
- Lafferty, D.J.; Hanson-Dorr, K.C.; Prisock, A.M.; Dorr, B.S. Biotic and abiotic impacts of Double-crested cormorant breeding colonies on forested islands in the southeastern United States. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 369, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaumet, A.; Dorr, B.; Wang, G.; Taylor, J.D.; Chipman, R.B.; Scherr, H.; Bowman, J.; Abraham, K.F.; Doyle, T.J.; Cranker, E. Determinants of local and migratory movements of Great Lakes double-crested cormorants. Behav. Ecol. 2011, 22, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, B.S.; Hatch, J.J.; Weseloh, D.V. Double-crested Cormorant (Phalacrocorax auritus), version 2.0. In Birds of North America; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, J.T.; Richmond, M.E.; Rudstam, L.G.; Mattison, P.M. Foraging location and site fidelity of the Double-crested Cormorant on Oneida Lake, New York. Waterbirds 2005, 28, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wires, L.R.; Cuthbert, F.J. Characteristics of Double-crested Cormorant colonies in the U.S. Great Lakes island landscape. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapanian, M.A. Interspecific Interactions, Habitat Use, and Management of Double-crested Cormorants (Phalacrocorax auritus) in the Laurentian Great Lakes: An Introduction. J. Great Lakes Res. 2002, 28, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.T.; Richmond, M.E. Daily foraging patterns of adult Double-crested Cormorants during the breeding season. Waterbirds 2007, 30, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glahn, J.F.; Reinhold, D.S.; Sloan, C.A. Recent population trends of Double-crested Cormorants wintering in the delta region of Mississippi: Responses to roost dispersal and removal under a recent depredation order. Waterbirds 2000, 23, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Burr, P.C.; Avery, J.L.; Street, G.M.; Strickland, B.K.; Dorr, B.S. Historic and contemporary use of catfish aquaculture by piscivorous birds in the Mississippi Delta. Condor 2020, 122, duaa036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.T.; Blackwell, B.F.; Dorr, B.S.; Belant, J.L. Effects of aquaculture on migration and movement patterns of Double-crested Cormorants. Hum.-Wildl. Interact. 2010, 4, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Scherr, H.; Bowman, J.; Abraham, K.F. Migration and Winter Movements of Double-Crested Cormorants Breeding in Georgian Bay, Ontario. Waterbirds 2010, 33, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.T.; Strickland, B.K.; Radomski, A. Winter and summer home ranges and core use areas of Double-crested Cormorants captured near aquaculture facilities in the southeastern United States. Waterbirds 2012, 35, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dorr, B.S.; Taylor, J.D.; Werner, S.J.; King, D.T.; Farquhar, J.F.; Mazzocchi, I.M.; McCullough, R.D. Summer and Migrational Movements of Satellite-Marked Double-Crested Cormorants from a Breeding Colony Managed by Egg-Oiling in Lake Ontario, USA. Waterbirds 2012, 35, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, B.S.; Aderman, T.; Butchko, P.H.; Barras, S.C. Management effects on breeding and foraging numbers and movements of double-crested cormorants in the Les Cheneaux Islands, Lake Huron, Michigan. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmole, N.P. The regulation of numbers of tropical oceanic birds. IBIS 1963, 103b, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encyclopedia of Alabama. Guntersville Dam and Lake. 2015. Available online: http://encyclopediaofalabama.org/ARTICLE/h-2621 (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- Sawyer, C.N. Basic concepts of eutrophication. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1966, 38, 737–744. [Google Scholar]
- Olin, M.; Rask, M.; Ruuhljärvi, J.; Kurkilahti, M.; Ala-Opas, P.; Ylönen, O. Fish community structure in mesotrophic and eutrophic lakes of southern Finland: The relative abundances of percids and cyprinids along a trophic gradient. J. Fish Biol. 2002, 60, 593–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Survey Staff, Natural Resources Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Web Soil Survey. Available online: https://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov (accessed on 23 October 2016).
- Tennessee Wildlife Resource Agency. (n.d.); Tennessee State Government—TN.gov. Guntersville Reservoir Fishing. Available online: https://www.tn.gov/twra/fishing/where-to-fish/cumberland-plateau-r3/guntersville-reservoir.html (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- Moran, L.K.; Dorr, B.S.; Hanson-Dorr, K.C.; Moore, R.J.; Rush, S.A. Stable isotope analyses of movement and pre usage of Double-crested Cormorants in a reservoir system of the southeastern United States. Food Webs 2022, 31, e00220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, K.L.; Esswein, S.T.; Dorr, B.S.; Yarrow, G.K.; Johnson, R.J. Using species distribution models to define nesting habitat of the eastern metapopulation of Double-crested Cormorants. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veum, L.M.; Dorr, B.S.; Hanson-Dorr, K.; Moore, R.J.; Rush, S. Double-crested Cormorant colony effects on soil chemistry, vegetation structure and avian diversity. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 453, 117588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migratory Bird Permits; Removal of Depredation Orders for Double-crested Cormorants to Protect Aqua-Culture Facilities and Public Resources; 83 Fed. Reg. 32805 (codified as 50 CFR 21); Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- King, D.T.; Tobin, M.E. Capture and telemetry techniques for Double-crested Cormorants (Phalacrocorax auritus). Proc. Vertebr. Pest Conf. 2000, 19, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, T.C. A harness for radio-tagging raptorial birds. Inland Bird Band. News 1972, 44, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 26 November 2017).
- Calenge, C. The package “adehabitat” for the R software: A tool for the analysis of space and habitat use by animals. Ecol. Model. 2006, 197, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worton, B.J. Kernel methods for estimating the utilization distribution in home-range studies. Ecology 1989, 70, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, D.E.; Powell, R.A. An evaluation of the accuracy of kernel density estimators for home range analysis. Ecology 1996, 77, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glahn, J.F.; May, A.; Bruce, K.; Reinhold, D. Censusing Double-crested Cormorants (Phalacrocorax auritus) at their winter roosts in the Delta Region of Mississippi. Colonial Waterbirds 1996, 19, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.T. Movements of Double-crested Cormorants among winter roosts in the Delta Region of Mississippi. J. Field Ornithol. 1996, 67, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Enstipp, M.R.; Grémillet, D.; Jones, D.R. The effects of depth, temperature and food ingestion on the foraging energetics of a diving endotherm, the Double-crested Cormorant (Phalacrocorax auritus). J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.D.; Roby, D.D.; Collis, K. Foraging patterns of male and female Double-crested Cormorants nesting in the Columbia River estuary. Can. J. Zool. 2004, 82, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sex | Colony Affiliation | Breeding Season | Incubation | Chick-Rearing | Post-Fledge | All Movements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May–July | 9–30 May | 31 May–4 July | 5 July–15 August | |||
| Male | South Sauty | 73.8 | 106.8 | 55.8 | - | 73.8 |
| Male | South Sauty | 17.2 | 40.7 | 6.3 | 16.0 | 6.8 |
| Female | South Sauty | - | - | - | 82.1 | 82.1 |
| Female | South Sauty | 80.8 | 172.3 | 36.6 | 62.0 | 64.6 |
| Female | South Sauty | 68.4 | 216.2 | 2.2 | - | 68.4 |
| Male | Connors | 12.3 | 27.3 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 9.5 |
| Female | Connors | 8.4 | 8.4 | - | - | 8.4 |
| Male | Connors | 20.5 | 29.8 | 1.3 | - | 20.5 |
| = | 40.2 ± 32.3 | 98.9 ± 80.6 | 18.3 ± 22.6 | 42.0 ± 31.0 | 41.8 ± 33.2 |
| Breeding Season | Incubation | Chick-Rearing | Post-Fledge | All Movements | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May–July | 9–30 May | 31 May–4 July | 5 July–15 August | ||
| Female | 52.5 ± 31.6 | 132.3 ± 89.4 | 19.4 ± 17.2 | 72.1 ± 10.1 | 55.9 ± 32.5 |
| Male | 30.95 ± 24.9 | 51.15 ± 32.5 | 17.75 ± 22.1 | 12.05 ± 4.0 | 27.6 ± 31.3 |
| South Sauty | 60.1 ± 25.1 | 134 ± 66.5 | 25.2 ± 22.1 | 53.4 ± 27.7 | 59.1 ± 26.8 |
| Connors | 13.7 ± 5.0 | 21.8 ± 9.6 | 4.5 ± 3.2 | 8.1 ± 0 | 12.8 ± 5.5 |
| Sex | Colony Affiliation | Breeding Season | Incubation | Chick-Rearing | Post-Fledge | All Movements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May–July | 9–30 May | 31 May–4 July | 5 July–15 August | |||
| Male | South Sauty | 11.3 | 16.9 | 10.8 | - | 11.4 |
| Male | South Sauty | 1.6 | 6.3 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 1.0 |
| Female | South Sauty | - | - | - | 13.1 | 13.1 |
| Female | South Sauty | 7.2 | 25.1 | 3.3 | 5.7 | 5.4 |
| Female | South Sauty | 8.2 | 30.1 | 0.3 | - | 8.2 |
| Male | Connors | 1.6 | 3.6 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 1.6 |
| Female | Connors | 1.2 | 1.2 | - | - | 1.2 |
| Male | Connors | 3.7 | 5.6 | 0.2 | - | 3.7 |
| = | 5.0 ± 4.0 | 14.6 ± 11.2 | 2.8 ± 4.1 | 5.5 ± 4.7 | 6.4 ± 5.9 |
| Breeding Season | Incubation | Chick-Rearing | Post-Fledge | All Movements | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May–July | 9–30 May | 31 May–4 July | 5 July–15 August | ||
| Female | 5.5 ± 3.8 | 18.8 ± 12.6 | 3.2 ± 4.4 | 9.4 ± 3.7 | 7.0 ± 5.0 |
| Male | 4.6 ± 4.6 | 8.1 ± 5.2 | 1.8 ± 1.5 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 5.4 ± 4.8 |
| South Sauty | 7.1 ± 3.5 | 19.6 ± 9.0 | 3.7 ± 4.3 | 6.8 ± 4.8 | 7.8 ± 4.3 |
| Connors | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 3.5 ± 1.8 | 0.8 ± 0.6 | 1.7 ± 0 | 2.2 ± 1.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moran, L.L.K.; Dorr, B.S.; Hanson-Dorr, K.C.; Moore, R.J.; Rush, S.A. Space Use and Movements of Southeastern Breeding Double-Crested Cormorants (Nannopterum auritum) in the United States. Diversity 2023, 15, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030453
Moran LLK, Dorr BS, Hanson-Dorr KC, Moore RJ, Rush SA. Space Use and Movements of Southeastern Breeding Double-Crested Cormorants (Nannopterum auritum) in the United States. Diversity. 2023; 15(3):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030453
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoran, Leah L. K., Brian S. Dorr, Katie C. Hanson-Dorr, R. J. Moore, and Scott A. Rush. 2023. "Space Use and Movements of Southeastern Breeding Double-Crested Cormorants (Nannopterum auritum) in the United States" Diversity 15, no. 3: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030453
APA StyleMoran, L. L. K., Dorr, B. S., Hanson-Dorr, K. C., Moore, R. J., & Rush, S. A. (2023). Space Use and Movements of Southeastern Breeding Double-Crested Cormorants (Nannopterum auritum) in the United States. Diversity, 15(3), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030453







