Abstract
Epi- and endozoochory are well explored phenomena that contribute to the distribution patterns of plant seeds, spores or fruits by vertebrates. It is less known how soil algae may be redistributed due to analogous interactions. We describe the participation of saprophage Rossiulus kessleri (Julidae, Diplopoda) in soil algae redistribution. The research was carried out in a park area of a large industrial megacity in the Dnipro steppe region (Ukrainian North Steppe subzone), Dnipro city. Research material was collected according to zoological and algological methods. The leaf litter of tree species (ash maple Acer negundo, Italian poplar Populus deltoides, locust Robinia pseudoacacia, European white elm Ulmus laevis, Norway maple Acer platanoides) and living diplopods were collected within 1 m2 quadrats along transects. Millipedes were maintained without feeding for five days, after which they were fed with the litter collected previously. Identification of algoflora was conducted in washes from the surface of diplopods’ bodies, its gut washes, in diplopods’ excretions and leaf litter washes. In the leaf litter, as R. kessleri’s feeding base, 14 soil algae species were identified—Nostoc punctiforme, Bracteacoccus minor, Mychonastes homosphaera, Neospongiococcum sp., Chlamydomonas sp., Chlorella vulgaris, Stichococcus bacillaris, Pseudococcomyxa simplex, Desmococcus olivaceus, Trebouxia spp., Klebsormidium flaccidum, Nephrodiella phaseolus, Navicula pelliculosa and Vischeria magna. In body surface washes, five soil algae species were identified, in gut washes seven algae species were found, while in excretions, just four were observed. It was established that not all algae species from the gut washes of R. kessleri were present in excretions. The presence of some representatives of soil algae, for example, Chlorella vulgaris and Vischeria magna, in natural park litter, body surface washes, gut washes and in excretions of R. kessleri, suggests that the given species pass through the diplopod’s gut and stay undamaged. This indicates that soil saprophage R. kessleri contributes to the dispersal of some soil algae representatives through epi- and endozoochory. Our results represent novel contributions to the knowledge of zoochory. It was shown that animals can be involved in dispersal of not only plant parts but also entire organisms, although it is unknown at what scale diplopods contribute to the diversity and dispersal of algae.
1. Introduction
The relationship between animals and plants is complex and varied. Vertebrates and invertebrates take part in dispersal of plant seeds or spores (diaspores). This phenomenon is called zoochory. Land ecosystem animals (mammals, birds, reptiles and insects) play a prominent role in diaspores dispersal because of animals’ high abundance, taxonomic diversity and high mobility. As it is known, animals can disperse plant diaspores in several ways: 1—eating diaspores (endozoochory); 2—storage of diaspores (synzoochory); 3—attachment of diaspores to the animal body (epizoochory) [1,2,3,4].
The dispersal of diaspores is an important condition for the formation of plant communities. To obtain forecasts for the development of forest assemblages, it is important to know the number and the distance of diaspore dispersal. This feature depends on the animal’s foraging behavior, the characteristics of its habitat and the length of migration routes. Long-distance movements from diaspores contribute to the expansion of plant populations [5,6,7]. The dispersal of diaspores is affected by the animal’s size—the larger the animal is, the more significant its participation in the diaspore transportation. For example, red deer take out of the plant assemblage up to 90% of the diaspores and contribute to the maintenance of plant populations. Meanwhile, some animals live in small areas forming diaspore flows, which are necessary to maintain plant populations [3,8]. Methods of diaspore dispersal are most fully studied in vertebrates, as their participation can be assessed visually. Inversely, it is difficult to assess invertebrate dispersal methods due to their small size, an example being saprophytic invertebrates, which live in and among leaf litter and soil. Co-activity of algae and invertebrates increases the biological activity of the soil and improves its structure [9,10] and, therefore, the specific nature of soil algae assemblage formation is of interest, both within natural ecosystems and forest plantation. Soil algae are distributed mainly in the leaf litter and upper soil layers while going into deeper soil layers, their taxonomic composition and number declines. Algae can be both unicellular and multicellular, be in an active state and in the state of a cyst. Soil algae are resistant to extreme habitat conditions and form independent assemblages, which are part of plant communities and are formed under the influence of terrestrial vegetation [11,12,13,14,15]. Algae play an important role in the functioning of soil microbiota. Living in certain soil layers and on the soil surface, algae representatives have a high species richness [16,17,18]. The leaf litter composition and its presence affect the diversity of the algae present. In most cases, the distribution of algae representatives occurs in a passive way. They get into the soil through cracks, animal passages and cavities. On the soil surface, their distribution can proceed due to hydrochory [19].
Soil as a special ecosystem that has inputs, outputs, storages and flows, creating conditions for biota existence [20]. At the present stage, interest in soil invertebrates has increased even more [21,22,23]. The trophic organization of the soil macrofauna is of particular interest [24,25,26]. Representatives of soil macrofauna are characterized by selectivity in feeding [27,28]. Diplopoda inhabit leaf litter, but in the case of unfavorable conditions, they go deep into the soil. Being active leaf litter decomposers, Diplopoda is of particular interest among saprophagous invertebrates. Leaf litter is the habitat both for diplopods and soil algae. Through the diet, diplopods as well as oribatids, collembola and earthworms, find it possible to swallow passively soil algae along with leaf litter [29,30]. Soil saprophages affect the dynamics of algae number and the redistribution of algae assemblages [31].
The diplopod’s gut is a straight tube differentiated into the anterior middle and posterior sections. The ducts of the salivary glands open into the anterior section, the midgut is lined with a single-layer secreting epithelium and the hindgut has a closing valve. Digestion products are absorbed in the midgut. The composition of digestive enzymes (carbohydrase, lipase and cellulase) allows diplopods to digest not only plant remains, but also vital plant tissues [32,33]. Diplopods are characterized by feeding preferences, which manifest not only in relation to the degree of decomposition of food objects, but also in relation to the source of feeding material. Diplopods’ digestion lasts about 24 h, and their feces are conglomerates consisting of undigested plant residues of amorphous organic matter and mineral parts [34,35].
Both diplopods and soil algae can be found in forest plantations as well as in natural forest ecosystems. Natural forests are not typical for the steppe zone of Ukraine, they are located near the rivers [36]. Park areas of megacities, in most cases, are located in the center of cities. There are tree-planted species and lawn covering the park, where regular park maintenance is taken [37]. Forest stand composition (leaf litter which serves as a food for diplopods and as habitat both for diplopods and soil algae) is different from natural forests. Within the urbanized areas, anthropogenic factors have a negative impact not only on litter invertebrates, but also on the algae population [38,39].
Zoochory and its units (epi-, syn-, endozoochory) consider the participation of animals in the dispersal of diaspores. The participation of diplopods, as soil invertebrate representatives, in the distribution (epi-, endozoochory) of entire organisms (for example, soil algae) has not been studied enough. Ecological peculiarities of diplopods and soil algae, as well as diplopods’ foraging behaviour, allow us to suggest that Diplopoda is a biotic disperser agent in the redistribution of soil algae by endozoochory and epizoochory.
The objective of our study was to establish the possibility of Rossiulus kessleri (Lohmander, 1928) in the distribution of soil algae (endo-, epizoochory) in park areas of an urbanized territory.
2. Material and Methods
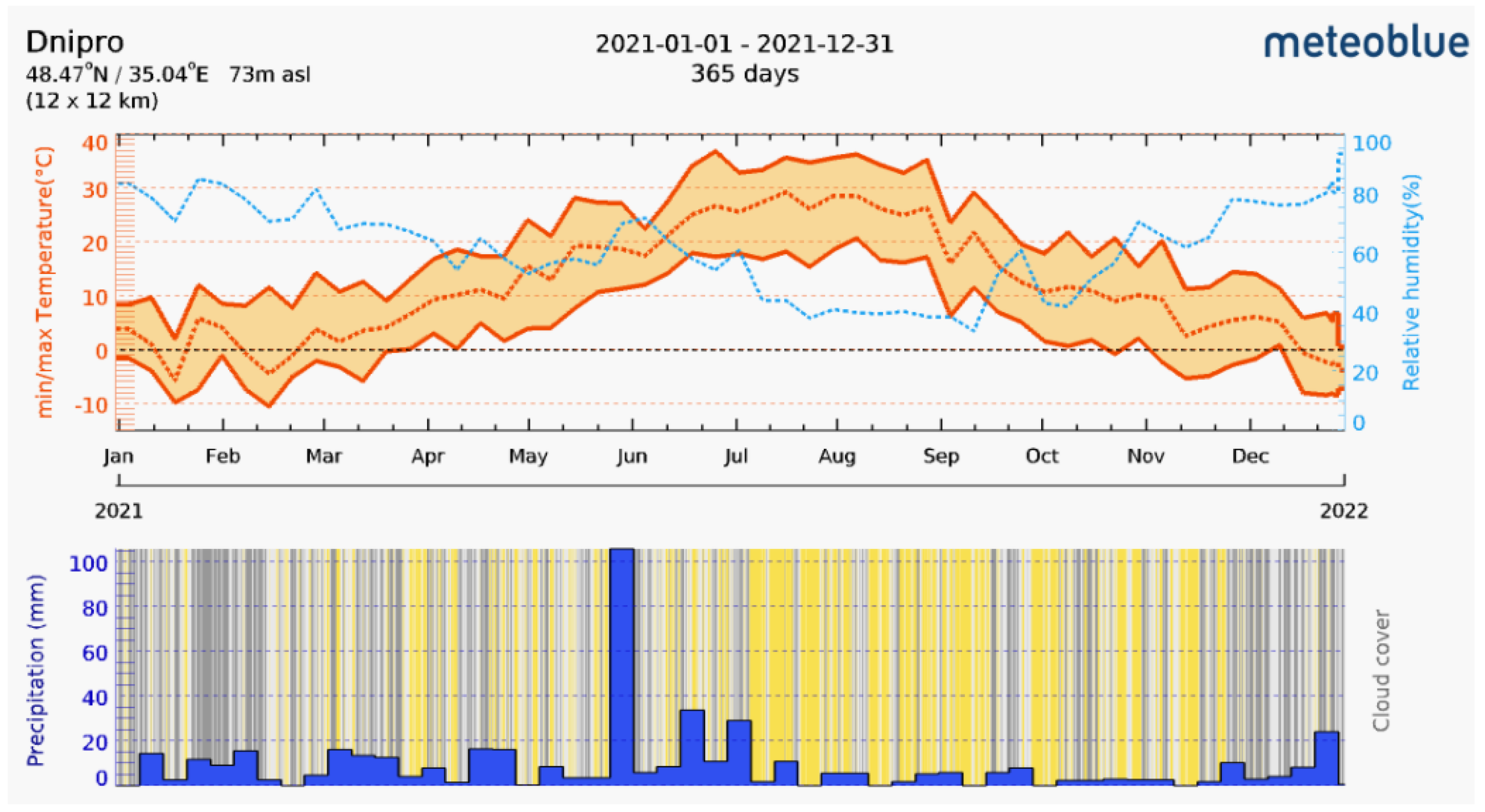
The research was carried out in September of 2021 in the park area of a large industrial megacity in the Dnipro steppe region (Ukrainian North Steppe subzone), Dnipro city (48°28′ N 35°01′ E). The city is situated in the zone of temperate latitudes. Definitive features of the territory are significant fluctuations in weather conditions from year to year. Global climate change in recent years, associated with an increase in maximum and minimum temperatures, as well as their average values, is especially noticeable in the autumn–winter period. These changes affect not only the formation and development of tree plantations in park areas [40] but also the biota representatives of that habitat [25,26]. Temperature and humidity are the main abiotic factors affecting litter and soil macrofauna invertebrates [21,25]. During the period of study, the temperature (°C) ranged from +3 °C to +29 °C (Figure 1). An increase in values of these factors determines the increased vital activity of litter invertebrates and soil algae [16,31].
Figure 1.
Seasonal changes of climate parameters (www.meteoblue.com; accessed on 28 April 2022) in the territory of Dnipro city.
Within Dnipro city territory, we selected one park ecosystem named after Yurii Haharin (48°43′ N 35.04′ E). It is a part of the Botanical Garden of Oles Honchar Dnipro National University and its area is 0.13 km2. The tree plantation of the park was dominated by locust Robinia pseudoacacia L., while inclusions of Norway maple Acer platanoides L., ash maple A. negundo L., European white elm Ulmus laevis Pall., buckeye Aesculus hippocastanum L., Italian poplar Populus deltoides W.Bartram ex Marshall and honey locust Gleditsia triacanthos L. were observed. Stand height was 10–15 m and crown density was 60–80%. The shrub layer was represented by European privet Ligustrum vulgare L., black elder Sambucus nigra L. The grass stand included Poa angustifolia L., greater celandine Chelidonium majus L., common avens Geum urbanum L., Elytrigia Desv. and lawn cover as well. The soil in the park partially retains its natural structure and belongs to the category of surface-transformed soils, so called “urbanozem type”, i.e., the urbic layer (anthropogenically transformed) is less than 50 cm [41]. The litter was two layered, 2.5–3.0 cm thick.
Litter invertebrates in the park area were gathered based on the methods of invertebrate collection [42,43]. Our research was conducted in immediate proximity to trees and study park area had four study plots (1st plot—A. platanoides, 2nd plot—A. negundo + R. pseudoacacia + P. deltoides, 3rd plot—A. negundo, 4th plot—U. laevis). Each plot had five transects and the distance between transects was 3 m. Each transect had five quadrates and the distance between quadrates was 3 m. The size of each quadrate was 1 × 1 m squares. From each set the researcher sampled leaf litter until 10 L volume of litter was collected. For monitoring the diplopods, the method of manual sifting of the litter was used. Living diplopods were separately collected in a container for further laboratory study. Diplopods’ identification was based on morphology according to Chernyy and Golovach [44].
Rossiulus kessleri (Lohmander, 1928) was selected for algo-zoological studies as saprophage representative in our research. It is a photophilous, ecologically plastic species, widely distributed in the steppe and forest steppe zones in the Eastern European Plain. R. kessleri is a common but not abundant species in Central and Southern Ukraine; it cannot migrate fast and its number reaches 50–100 specimens*m−2 in various forest ecosystems [44,45,46]. In the experiment, the mature individuals X–XII ages (3–4 years) were used. Leaf litter from A. negundo, P. deltoides, R. pseudoacacia, U. laevis and A. platanoides, selected in the park area, was proposed as a feeding base. To study the taxonomic algae composition of the excrement, each Diplopoda specimen was placed in a Petri dish, and 10 individuals of R. kessleri were used to consume each litter species. To maintain the purity of the experiment, each individual of R. kessleri was kept without food for five days before the start of the experiment and washed with distilled water in five repetitions. In seven days after the diplopods started feeding, the selected excretions and withdrawn intestines were subjected to algological studies.
The species composition of algae was determined based on the methods of working with cultures using a modified Bold medium [47]. Under laboratory conditions, in order to identify algae on the julid’s body surface, each julid specimen was washed with distilled water (1.5 mL) three times. Then 0.5 mL of the total wash was taken and distributed into Petri dish on the modified Bold medium. To identify the algae of the leaf litter, the litter remains, soaked in a few drops of distilled water, were placed on the medium in Petri dishes. The cultivation was carried out at a temperature of 20 °C and a light intensity of 35 µmol m−2 s−1. The photoperiod 12:12 h was used. A few days after, along the water line on the agar surface, one could observe the growth of individual algae colonies. These growths served as the basis for the isolation of algae into monocultures. When forming mixed growths to obtain monocultures, the technology of seeding with a stroke or using a glass micropipette was used. In the first case, a small amount of algae biomass was taken from a mixed culture with a microbiological loop and transferred to a new Petri dish on Bold agar nutrient medium in a stroke form that was thinning out at the end. In the second case, individual algae cells were sampled with a micropipette capillary and placed into a new Petri dish in a distilled water drop on the Bold agar nutrient medium surface. Microscopic studies were carried out using an XSP-128V light microscope equipped with an oil immersion objective and a microphotographic attachment. Cells, if necessary, were stained with 0.1% methylene blue solution and 1.0% ink solution to determine the structure and general outlines of mucus; acetic azocarmine G and Lugol solution were used to determine the presence of a pyrenoid and its structure and chlorine–zinc–iodine was used to determine the chemical nature of the cell membrane [47]. In some cases, the formation of zoospores was induced to establish their taxonomically significant characters using the techniques described by J. Neustupa et al. [48]. The study of cultures began at the age of seven days and continued up to four months. The referential system of Cyanobacteria was used in accordance with the reports of I. Komarek and A. Anagnostidis [49,50], and the rest of the groups—according to “Syllabus of Plant Families“ [51]. Literature used for identification included Ettl and Gärtner [52,53], and others [49,50,54,55,56,57,58,59]. The experiments were repeated five times during the research period (autumn, 2021).
Mathematical processing of the received data was carried out with the calculation of the mean and standard deviation.
3. Results
In the park named after Y. Haharin, one R. kessleri Diplopoda species was recorded. The average number of the given saprophagous within the park area was 4.1 ± 0.2 specimen*m−2.
The total number of identified algae species within the studied plots is 14, which belonged to four lifeforms. The term “lifeform” reflects the adaptations of soil algae to the habitation in the soil and on its surface [33]. The taxonomic composition of tree litter algae from the park area is formed from representatives of four phyla—Cyanobacteria, Chlorophyta, Heterokontophyta and Streptophyta. Their full number is observed in Norway maple litter (A. platanoides). The percentage of representatives from Cyanobacteria, Heterokontophyta and Streptophyta phyla in the case of Norway maple litter is 35.7% of the total diversity of algae in the studied plot. Chlorophyta phylum is represented by nine species, which constitutes 64.3%. In the case of ash maple (A. negundo), litter Heterokontophyta, Streptophyta phyla are represented by one species each and its percentage is 14.3% (for every species), while Chlorophyta phylum is represented by five species (71.4%). The lowest species richness of algae was found in the smooth elm litter (U. laevis) and algae are represented here by only three species of Chlorophyta phylum. Representatives of the green algae phylum dominate in the algae composition of the park zone (Table 1).

Table 1.
Taxonomic composition of algae and their ecological lifeforms from the litter extracts from the Y. Haharin park of Dnipro city (n = 5).
The taxonomic composition of R. kessleri’s body surface washes contained five species of both Chlorophyta and Heterokontophyta phyla, which belong to two lifeform types (Table 2). According to the received data, green algae Klebsormidium flaccidum (Streptophyta) was not found in R. kessleri’s body surface washes but was discovered in the gut.

Table 2.
Taxonomic composition of algae from R. kessleri’s body surface washes in the Y. Haharin park of Dnipro city (n = 5).
Diplopods are predominantly soil detrivores feeding mainly on decomposing plant materials, but some algae species are common in gut washes of R. kessleri (Table 3).

Table 3.
Taxonomic composition of algae from the gut washes and excretions of R. kessleri (n = 5) in the Y. Haharin park of Dnipro city.
In gut washes of R. kessleri in the megacity park territory, seven species were revealed but it was established that not all algae species from the gut washes are present in excretion ones. Representatives of Chlorophyta phylum (Chlorella vulgaris, Desmococcus olivaceus, Mychonastes homosphaera, Stichococcus bacillaris, Bracteacoccus minor), Heterokontophyta (Vischeria magna) and Streptophyta (K. flaccidum) were found in gut washes of julids from the park named after Y. Haharin in Dnipro city. These algae species can be considered as potential food objects for R. kessleri (Figure 2) within the study territory.
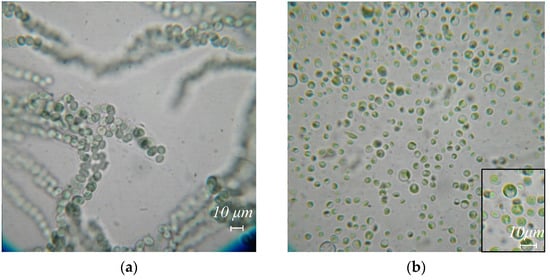
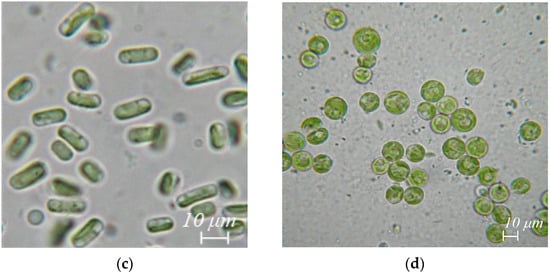
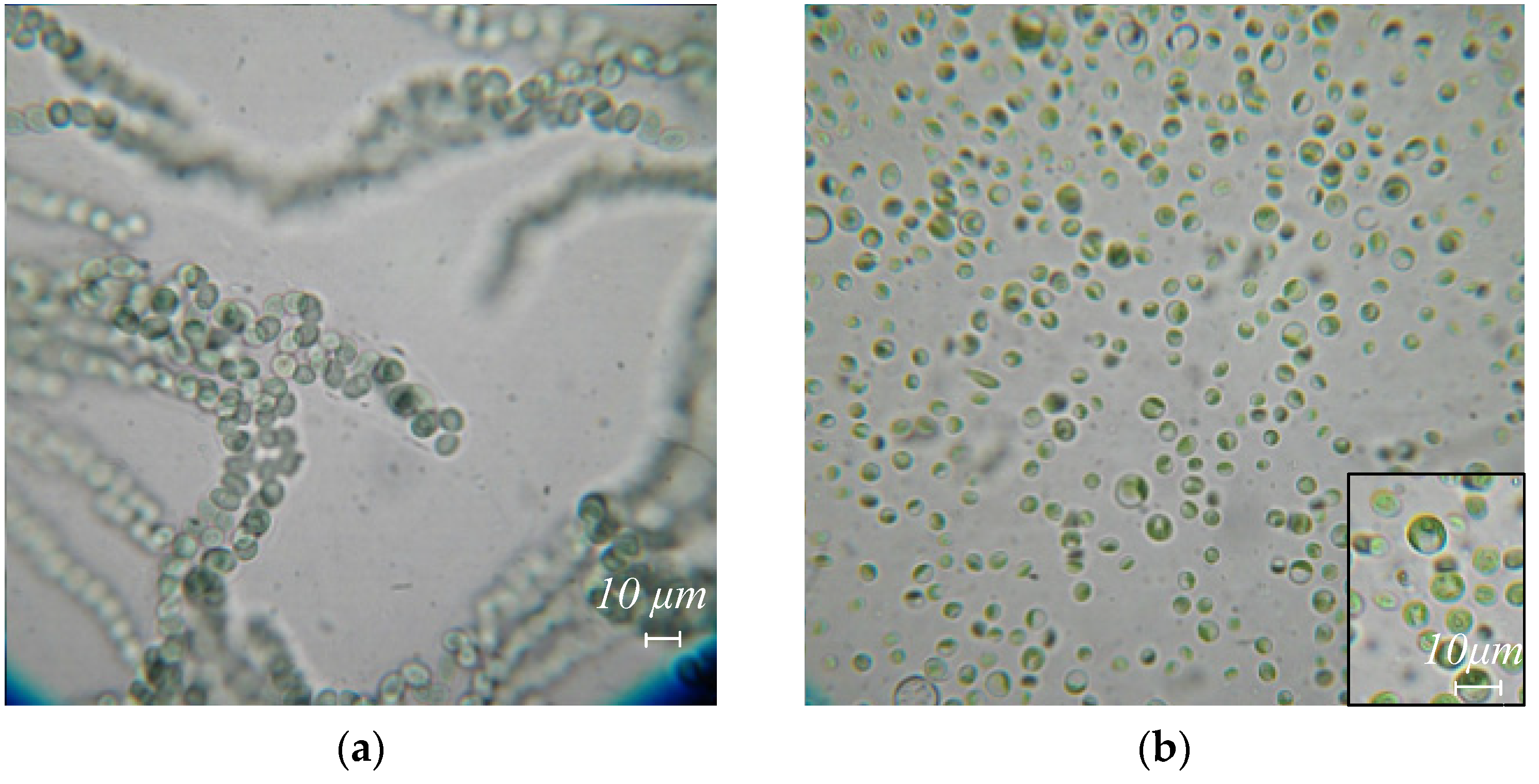
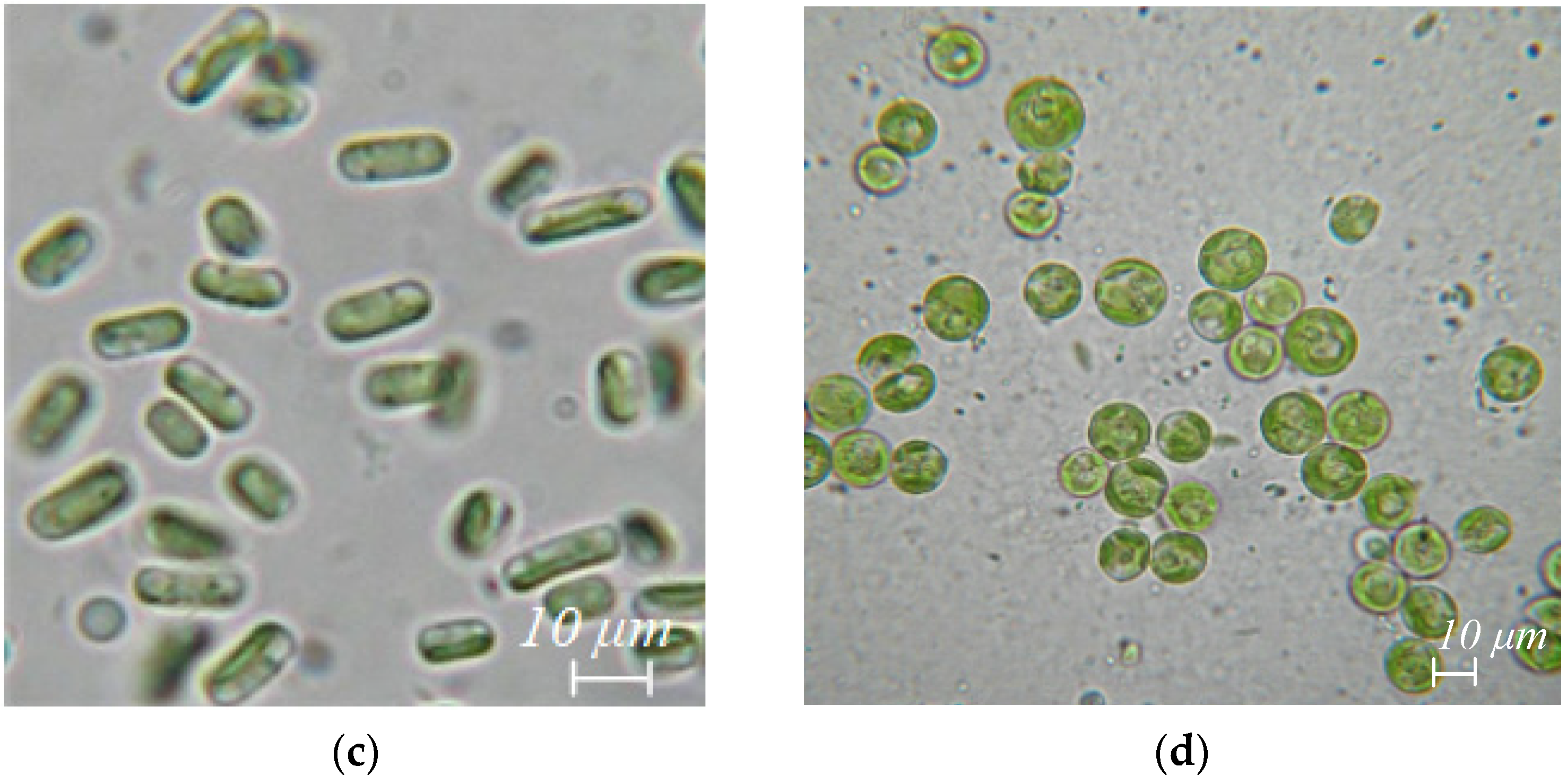
Figure 2.
Algae species extracted from body surface and gut washes, and excretions of R. kessleri: (a) Nostoc sp., (b) Chlorella vulgaris, (c) Stichococcus bacillaris, (d) Vischeria magna.
The trophic activity of R. kessleri represents itself two interrelated processes: the feeding activity includes eating algae representatives, which ultimately leads to the depletion of algae assemblages, and the removing of undigested residues in the form of excretions in the environment. Both types of activity influence the formation of algae assemblages.
4. Discussion
Regular park maintenance, which includes dead wood and leaf litter removal, leads to disturbance in the leaf litter as a habitat for litter invertebrates. In the part of the Y. Haharin Park where the research was carried out, leaf litter is not removed and remains undisturbed. This created favorable conditions for the existence of diplopods, algae species and other invertebrates typically present in litter and soil.
To understand the role of diplopods in algae assemblage formation, it is necessary to know the taxonomic composition of algae species and the ratio of their lifeforms in the leaf litter of A. platanoides, A. negundo + R. pseudoacacia + P. deltoides, A. negundo and U. laevis in the park area of an industrial megacity.
The term “lifeform” includes unicellular and colonial algae representatives with similar adaptations to environmental conditions. Algae lifeforms characterize ecological peculiarities of algae, regardless of systematic affiliation. The nine lifeforms of soil algae were selected conventionally [33]:
Ch-lifeform—includes unicellular and colonial green, partially yellow-green algae that exist in the soil layers but grow on the soil surface with a favorable level of moisture;
Cf-lifeform—includes microscopic thallus of nitrogen-fixing blue-green algae, capable of producing mucous growths on the surface of the soil;
B-lifeform—includes diatoms mobile cells that inhabit the surface of moist soil or the mucus of other algae. Representatives of this lifeform are cold-resistant, light-loving, and many of them are salt-tolerant, but not resistant to drying out;
H-lifeform—includes filiform green and yellow-green algae, susceptible to drought and excessive light. Mottles created by H-representatives often cover stem base of plants and become a basis for complicated communities of soil bloom.
The lifeform scale allows establishing the biological spectrum, which reflects ecological conditions of soil and plant communities in the research area.
Among the 14 algae species found in litter washes, six species (Bracteacoccus minor, Chlorella vulgaris, Pseudococcomyxa simplex, Desmococcus olivaceus, Nephrodiella phaseolus, Vischeria magna) belong to Ch lifeform, three species (Nostoc punctiforme, Mychonastes homosphaera, Stichococcus bacillaris) belong to Cf lifeform, while H lifeform (Klebsormidium flaccidum) and B lifeform (Navicula pelliculosa) are presented by one species each. All four registered lifeforms of soil algae are presented in plantation of A. platanoides. In this plantation, optimal conditions are created for the existence of representatives of all obtained soil algae lifeforms.
The assessment basis of diplopoda’s participation in the epizoochory is the morphological features of its body. A millipede’s body is elongated, consisting of well-defined diplosegments, legs end with claws and are in constant contact with the litter. Only five species (Ch. vulgaris, M. homosphaera, D. olivaceus, V. magna, S. bacillaris) of algae from Chlorophyta and Heterokontophyta phyla are present in body surface washes. Obtained algae species belong to Ch and Cf lifeforms. In R. kessleri, algae from body washes are represented by small cells, the size of which does not exceed 8–10 µm. Apart from size, algae species are capable of producing mucilage that promotes algae cells to stick on diplopods’ body surface. These characteristics allow algae to stay on the surface of the diplopods’ body and, when they move, to settle on the surface of the litter. Diplopoda may be considered as disperser agents of soil algae through epizoochory.
The evaluation of diplopods’ participation in endozoochory was based on the features of their trophic activity: algae may enter the diplopods’ gut in a passive way while diplopods are feeding on litter. Some of the algae cells are digested and some, after passing through the digestive system, remain undamaged (Ch. vulgaris, M. homosphaera, D. olivaceus, V. magna), and then settle into new territories. The soil algae obtained from gut washes and in the excretions of R. kessleri belong to the phyla Chlorophyta and Heterokontophyta. Algae from these phyla can be considered as potential food objects for R. kessleri.
The presence of Ch. vulgaris as well as V. magna in all types of feeding bases is common. These species from park litter are widely distributed and characterized by high tolerance to adverse environmental conditions. The species V. magna (Ch life-form) has high resistance to surfactants, radioactive contamination and is sensitive to soil contamination by heavy metals and petroleum products. It is known that V. magna can be used to assess the toxicity of soil cover and zoning of various areas that are under the anthropogenic influence [15]. The species B. minor (Ch life-form) is a widespread soil algae, found in forests, steppe, desert ecosystems, granite surfaces and others [60,61,62]. According to experiments, it is a thermoresistant species (52 °C) [63]. The noted species (Ch. vulgaris, V. magna, B. minor) is characterized by a wide ecological amplitude; it is well known from soils and the tree litter of natural forest ecosystems and forest plantations, including those within urban areas [14,15,38].
It is known that algae are rich in proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, physiologically valuable fatty acids and protein content in the biomass of some algae, with some reaching up to 71.0% [64,65] and 75.0% of lipids [66]. These characteristics ensure algae’s high nutritional value and importance in the functioning of soil food chains. The gut washes of R. kessleri algae were represented by certain species, which belong to Ch- (B. minor, Ch. vulgaris, D. olivaceus, V. magna), H- (K. flaccidum), and Cf- (M. homosphaera, S. bacillaris) lifeforms. Species belonging to the Ch lifeform were dominated. These species are shade-tolerant, drought-resistant and highly resistant to anthropogenic factors and are widely distributed. Representatives of the Ch lifeform are the first to colonize the surface of the soil and are brought in with dust [31]. There are four algae species identified in R. kessleri excretions. In this case, as well as in gut washes, the Ch lifeform representatives are dominated. The species Ch. vulgaris was present in litter washes from all study plots and remained undamaged after going through digestive system. Trophic activity of R. kessleri contributes to soil algae settlement through endozoochory. Only soil saprophagous invertebrates, R. kessleri in particular, contribute to litter destruction and provide distribution of some representatives of soil algae through zoochory.
The distribution range of algoflora representatives depends on the distance that R. kessleri will reach in this case. If R. kessleri participates in algal dispersion within a limited area, then diplopod contributes to the maintenance of algal populations within assemblages and the preservation of their species richness. If algoflora representatives’ dispersion by R. kessleri is carried out outside the algal assemblages, then endo- and epizoochory ensure their introduction into other assemblages. In the research park, there are no conditions for long-distance migrations of Diplopoda. The park is situated in the center of the city and surrounded by busy roads and residential areas of the city. The location of the park limits diplopods’ migration. Limited mobility of R. kessleri in the park area of the city does not promote algoflora representatives’ dispersion across long distances and its introduction into other soil algae assemblages. In the research park area, R. kessleri contributes to the maintenance the algae species richness at a population level.
5. Conclusions
The concept of Diplopoda participation, as saprophages, in zoochory, has been enriched. It has been established that diplopods participate in epizoochory and endozoochory of soil algae. Their activity contributes to the maintenance of populations within algal assemblages and the preservation of soil algae species richness. Due to ecological features, representatives of Ch lifeforms—those that are resistant to environmental stressors—are most actively distributed by diplopods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.K., I.M. and O.P.; methodology, A.P. and I.M.; analysis, Y.K., A.P. and I.M.; investigation, A.P. and I.M.; data curation, A.P. and I.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.P., Y.K. and I.M.; writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, Y.K., A.P. and I.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by grants 0121U111707, the concept on non-timber forest resources assessment and management in the steppe zone of Ukraine under climate change (Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kajimoto, T. Factors affecting seedling recruitment and survivorship of the Japanese subalpine stone pine, Pinus pumila, after seed dispersal by nutcrackers. Ecol. Res. 2002, 17, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boch, S.; Berlinger, M.; Fischer, M.; Knop, E.; Nentwig, W.; Turke, M.; Prati, D. Fern and bryophyte endozoochory by slugs. Oecologia 2013, 172, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liehrmann, O.; Jegoux, F.; Guilbert, M.A.; Isselin-Nondedeu, F.; Said, S.; Locatelli, Y.; Baltzinger, C. Epizoochorous dispersal by ungulates depends on fur, grooming and social interactions. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 1582–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.G.; Green, A.J.; Hoffman, P.; Weber, V.; Stenert, C.; Lovas-Kiss, A.; Maltchik, L. Seed dispersal by neotropical waterfowl depends on bird species and seasonality. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiade-Bourobou, D.; Hardy, O.J.; Favreau, B.; Moussavou, H.; Nzengue, E.; Mignot, A.; Bouvet, J.-M. Long-distance seed and pollen dispersal inferred from spatial genetic structure in the very low-density rainforest tree, Baillonella toxisperma Pierre, in Central Africa. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 4949–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjos, D.V.; Leal, L.C.; Jordano, P.; Del-Claro, K. Ants as diaspore removers of non-myrmecochorous plants: A meta-analysis. Oikos 2020, 129, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnoli, M.L.; Christianini, A.V. Temporal consistency in interactions among birds, ants, and plants in a neotropical savanna. Oikos 2021, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Robles, A.; Castro, J. Efficiency of endozoochorous seed dispersal in six dry-fruited species (Cistaceae): From seed ingestion to early seedling establishment. Plant Ecol. 2006, 185, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul’bachko, Y.L.; Didur, O.O.; Loza, I.M.; Pakhomov, O.E.; Bezrodnova, O.V. Environmental aspects of the effect of earthworm (Lumbricidae, Oligochaeta) tropho-metabolic activity on the pH buffering capacity of remediated soil (steppe zone, Ukraine). Biol. Bull. 2015, 42, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambarish, C.N.; Sridhar, K.R. Chemical and Microbial Characterization of Feed and Faeces of Two Giant Pill-Millipedes from Forests in the Western Ghats of India. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, R.S.; Barbosa, J.E.L.; Lima, G.Q.; Barbosa, L.G. Periphytic algae dynamics in lentic ecosystems in the Brazilian semiarid. Braz. J. Biol. 2017, 77, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Duan, P.F.; Zhang, P.; Li, M. Variations in cyanobacterial and algal communities and soil characteristics under biocrust development under similar environmental conditions. Plant Soil 2018, 429, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.X.; Liu, Y.D. Primary succession of algal community structure in desert soil. Acta Bot. Sin. 2003, 45, 917–924. [Google Scholar]
- Maltsev, Y.; Maltseva, I. The influence of forest-forming tree species on diversity and spatial distribution of algae in forest litter. Folia Oecol. 2018, 45, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltseva, I.A.; Maltsev, Y.I. Diversity of cyanobacteria and algae in dependence to forest-forming tree species and properties rocks of dump. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltsev, Y.I.; Didovich, S.V.; Maltseva, I.A. Seasonal changes in the communities of microorganisms and algae in the litters of tree plantations in the Steppe zone. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2017, 50, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltsev, Y.I.; Pakhomov, A.Y.; Maltseva, I.A. Specific features of algal communities in forest litter of forest biogeocenoses of the Steppe zone. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2017, 10, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didur, O.A.; Kulbachko, Y.L.; Maltsev, Y.I.; Konovalenko, T.V. Ecology of soil algae cenoses in Norway maple plantation in the recultivated territory of the Western Donbas (Ukraine). Ukr. J. Ecol. 2018, 8, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, K.A.M.; Ritchie, M.E. Effects of macrophyte species richness on wetland ecosystem functioning and services. Nature 2001, 411, 6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Mallet, C.; Portelli, C.; Donnadieu, F.; Bonnemoy, F.; Artigas, J. Stimulation or inhibition: Leaf microbial decomposition in streams subjected to complex chemical contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.F.; Handa, I.T. The ecology of saprophagous macroarthropods (millipedes, woodlice) in the context of global change. Biol. Rev. 2010, 85, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaldi, M.; Jiménez, J.J.; McKey, D.; Mathieu, J.; Velasquez, E.; Zangerlé, A. Ecosystem engineers in a self-organized soil: A review of concepts and future research questions. Soil Sci. 2016, 181, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagner, M.; Romantschuk, M.; Penttinen, O.P.; Egfors, A.; Marchand, C.; Augustsson, A. Assessing toxicity of metal contaminated soil from glassworks sites with a battery of biotests. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Butenschoen, O.; Barantal, S.; Handa, I.T.; Makkonen, M.; Vos, V.; Aerts, R.; Berg, M.P.; McKie, B.; Van Ruijven, J.; et al. Decomposition of leaf litter mixtures across biomes: The role of litter identity, diversity and soil fauna. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brygadyrenko, V.V. Influence of moisture conditions and mineralization of soil solution on structure of litter macrofauna of the deciduous forests of Ukraine steppe zone. Visnyk Dnipropetr. Univ. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 23, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brygadyrenko, V.V. Influence of tree crown density and density of the herbaceous layer on the structure of litter macrofauna of deciduous forests of Ukraine’s steppe zone. Visnyk Dnipropetr. Univ. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 23, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svyrydchenko, A.O.; Brygadyrenko, V.V. Trophic preferences of Rossiulus kessleri (Diplopoda, Julidae) for the litter of various tree species. Folia Oecol. 2014, 41, 202–212. [Google Scholar]
- Šustra, V.; Šimek, M.; Faktorová, L.; Macková, J.; Tajovský, K. Release of greenhouse gases from millipedes as related to food, body size, and other factors. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 44, 107765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didur, O.; Kulbachko, Y.; Ovchynnykova, Y.; Pokhylenko, A.; Lykholat, T. Zoogenic mechanisms of ecological rehabilitation of urban soils of the park zone of megapolis. Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2019, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, A.M.; Beaulieu, F.; Birkhofer, K.; Bluhm, S.L.; Degtyarev, M.I.; Devetter, M.; Goncharov, A.A.; Gongalsky, K.B.; Klarner, B.; Korobushkin, D.I.; et al. Feeding habits and multifunctional classification of soil-associated consumers from protists to vertebrates. Biol. Rev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtina, E.A.; Gollerbah, M.M. Ekologiya Pochvennyih Vodorosley; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1976; 143p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Urbasek, F.; Tajovsky, K. The influence of food and temperature on enzymatic-activities of the millipede Glomeris-hexasticha (Diplopoda). Rev. D Ecol. Et De Biol. Du Sol 1991, 28, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Sustr, V.; Semanova, S.; Rost-Roszkowska, M.M.; Tajovsky, K.; Sosinka, A.; Kaszuba, F. Enzymatic activities in the digestive tract of spirostreptid and spirobolid millipedes (Diplopoda: Spirostreptida and Spirobolida). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. 2020, 241, 110388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loranger-Merciris, G.; Imbert, D.; Bernhard-Reversat, F.; Lavelle, P.; Ponge, J.F. Litter N-content influences soil millipede abundance, species richness and feeding preferences in a semi-evergreen dry forest of Guadeloupe (Lesser Antilles). Biol. Fertil. Soils 2008, 45, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeber, J.; Langel, R.; Meyer, E.; Traugott, M. Dwarf shrub litter as a food source for macro-decomposers in alpine pastureland. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 41, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritsan, Y.I. Ekolohichni Osnovy Peretvoryuyuchoho Vplyvu Lisovoyi Roslynnosti na Stepove Seredovyshche; DNU: Dnipro, Ukraine, 2000; 300p. (In Ukranian) [Google Scholar]
- Hryhoriuk, I.P.; Yavorovskyi, P.P.; Lykholat, Y.V. Tekhnolohii Vyroshchuvannia i Biorehuliatsiia Stiikosti Hazonnykh Roslyn u Miskomu Urbanizovanomu Seredovyshchi: Monohrafiia; NULESU: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2014; 223p. (In Ukranian) [Google Scholar]
- Maltsev, Y.I.; Maltseva, I.A.; Solonenko, A.N.; Bren, A.G. Use of soil biota in the assessment of the ecological potential of urban soils. Biosyst. Divers. 2017, 25, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhylenko, A.P.; Didur, O.O.; Kulbachko, Y.L.; Bandura, L.P.; Chernykh, S.A. Influence of saprophages (Isopoda, Diplopoda) on leaf litter decomposition under different levels of humidification and chemical loading. Biosyst. Divers. 2020, 28, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykholat, Y.V.; Khromykh, N.A.; Ivan’ko, I.A.; Matyukha, V.L.; Kravets, S.S.; Didur, O.O.; Alexeyeva, A.A.; Shupranova, L.V. Otsinka i prohnoz invaziinosti deiakykh adventyvnykh roslyn za vplyvu klimatychnykh zmin u Stepovomu Prydniprov’i. Biosyst. Divers. 2017, 25, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stroganova, M.; Prokofieva, T. Urban soils classification for Russian cities of the taiga zone. Eur. Soil Bur.—Res. Rep. No 2001, 153–156. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237430707_Urban_soils_classification_for_Russian_cities_of_the_taiga_zone (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Oliveira, M.P.A.; Bastos-Pereira, R.; Torres, S.H.S.; Pereira, T.S.; Batista, F.M.; Alves, J.P.; Iniesta, L.F.M.; Bouzan, R.S.; Chagas-Jr, A.; Prous, X.; et al. Choosing sampling methods for Chilopoda, Diplopoda and Isopoda (Oniscidea): A case study for ferruginous landscapes in Brazilian Amazonia. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 143, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.M.; Tarazona, R.; Lohr, B.L.; Narvaez, C.A. Measuring the effect of long-term pitfall trapping on the prevalence of epigeal arthropods: A case study in the Pacific Coast of Colombia. Sociobiology 2021, 68, e5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyy, N.G.; Golovach, S.I. Dvuparnonogiye Mnogonozhki Ravninnykh Territoriy Ukrainy; Naukova dumka: Kiev, Russia, 1993; 55p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Wytwer, J.; Golovatch, S.I.; Penev, L. Variation in millipede (Diplopoda) assemblages in oak woodlands of the Eastern European Plain. Soil Org. 2009, 81, 791–813. [Google Scholar]
- Reip, H.S.; Voigtländer, K. Diplopoda and Chilopoda of Thuringia, Germany. Soil Org. 2009, 81, 635–645. [Google Scholar]
- Gaysina, L.A.; Fazlutdinova, A.I.; Kabirov, R.R. Sovremennyye Metody Vydeleniya i Kultivirovaniya Vodorosley: Uchebnoye Posobiye; BNPU: Ufa, Russia, 2008; 152p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Neustupa, J.; Eliás, M.; Skaloud, P.; Němcová, Y.; Šejnohová, L. Xylochloris irregularis gen. et sp. nov. (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta), a novel subaerial coccoid green alga. Phycologia 2011, 50, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Komárek, J. Cyanoprokaryota. 3rd Part, Heterocytous Genera; Springer Spectrum: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; 1130p. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Cyanoprokaryota. 2. Teil: Oscillatoriales. In Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Büdel, B., Gärtner, G., Krienitz, L., Schagerl, M., Eds.; Elsevier GmbH: München, Germany, 2005; 759p. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, W. Syllabus of Plant Families—A. Engler’s Syllabus der Pflanzenfamilien Part 2/1: Photoautotrophic Eukaryotic Algae; Schweizerbart Science Publishers: Stuttgart, Germany, 2015; 324p. [Google Scholar]
- Ettl, H.; Gärtner, G. Syllabus der Boden-, Luft und Flechtenalgen; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1995; 699p. [Google Scholar]
- Ettl, H.; Gärtner, G. Syllabus der Boden-, Luft und Flechtenalgen; Springer Spektrum: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; 733p. [Google Scholar]
- Ettl, H. Xanthophyceae. In Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Eds.; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1978; 530p. [Google Scholar]
- Ettl, H. Chlorophyta I (Phytomonadina). In Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1983; 807p. [Google Scholar]
- Ettl, H.; Gärtner, G. Chlorophyta II, Tetrasporales, Chlorococcales, Gloeodendrales. In Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Eds.; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1988; 436p. [Google Scholar]
- Ettl, H.; Gärtner, G. Tetrasporales, Chlorococcales, Gloeodendrales, Chlorophyta II. In Süswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Eds.; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1988; 453p. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae. 2/1, Naviculaceae. In Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1986; 576p. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae. 2. Teil: Bacillariaceae, Epithemiaceae. In Subwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heynig, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany; Stuttgart, Germany, 1988; 654p. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, L.A.; Flechtner, V.R. Green algae (Chlorophyta) of desert Microbiotic Crusts: Diversity of North American Taxa. Taxon 2002, 51, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwik-Marcinkowska, J.; Mrozińska, T. Algae and Cyanobacteria in caves of the polish. Pol. Bot. J. 2011, 56, 203–243. [Google Scholar]
- Sanmartín, P.; Méndez, A.; Carballeira, R.; López, E. New insights into the growth and diversity of subaerial biofilms colonizing granite-built heritage exposed to UV-A or UV-B radiation plus red LED light. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 161, 105225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiullin, S.Y.; Mansurova, A.R. Ustoychivost Bracteacoccus minor var. desertorum (Friedmann & Ocampo-Paus) k vozdeystviyu vysokikh temperature. Izv. Samar. Nauchnogo Tsentra Ross. Akad. Nauk. 2011, 13, 5. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Becker, E.W. Micro-algae as a source of protein. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, I.; Misan, A.; Saric, B.; Kos, J.; Mandic, A.; Simeunovic, J.; Kovac, D. Evaluation of protein and lipid content and determination of fatty acid profile in selected species of cyanobacteria. In Proceedings of the 6th Central Europen Congress on Food (CEFood), Novi Sad, Serbia, 23–26 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mata, T.M.; Martinsa, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2010, 14, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).