Food versus Disturbance: Contradictory Effects of Human Activities on an Opportunistic Seabird Breeding in an Oligotrophic Marine System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
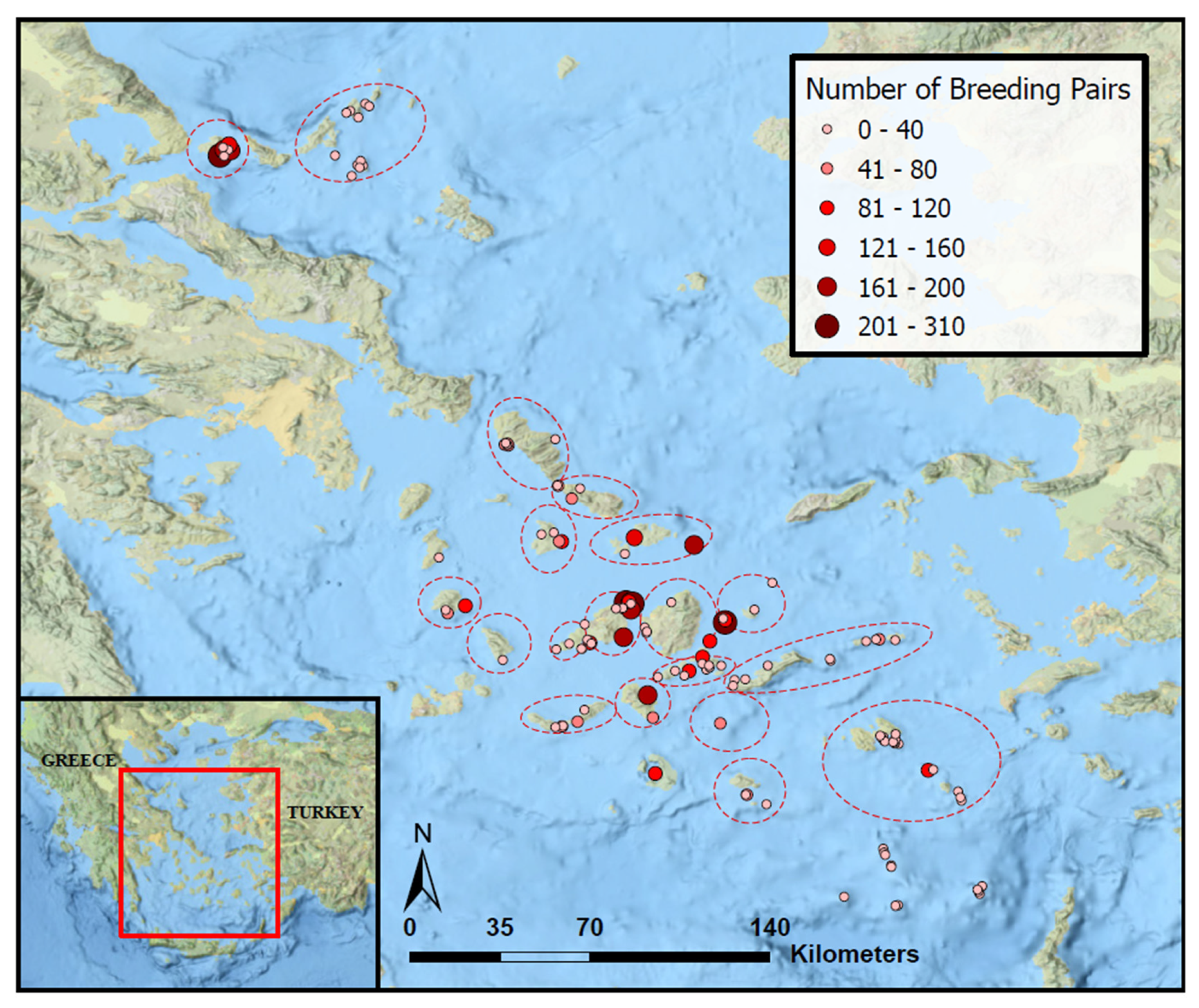
2.1. Study Area
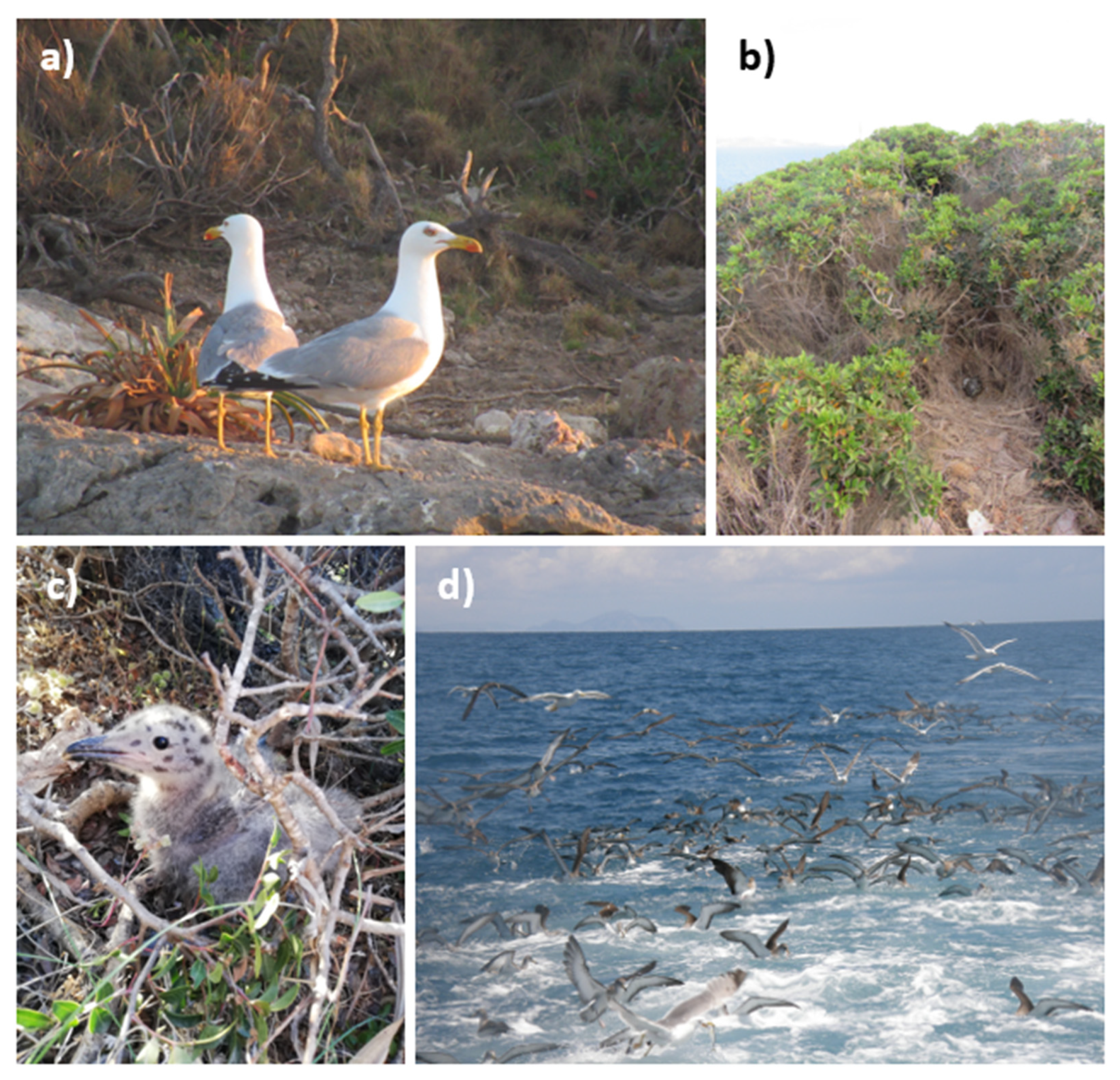
2.2. Wildlife
2.3. Human Land and Resource Use
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Local (Islet-Level) Analysis
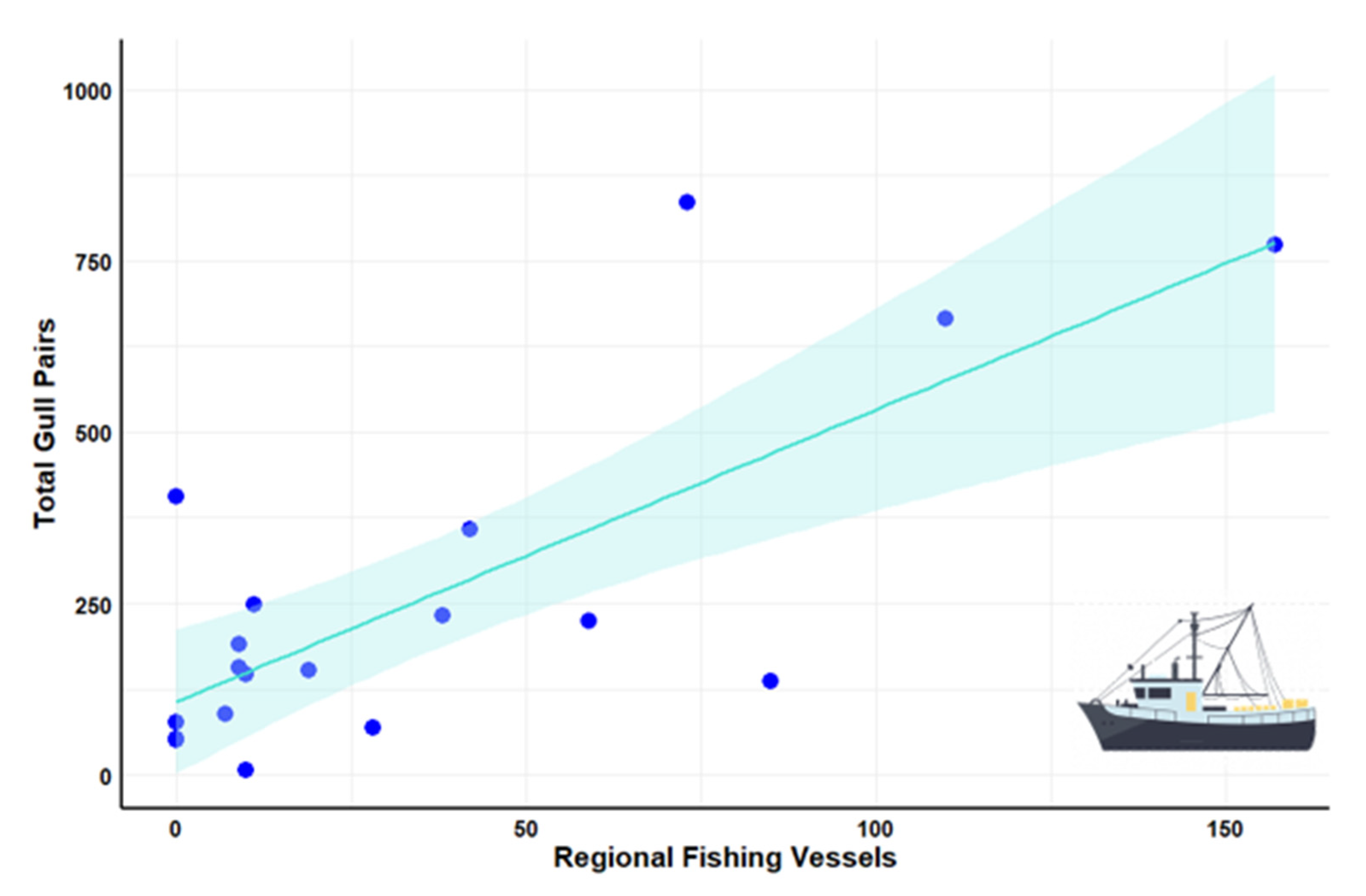
3.2. Regional Analysis
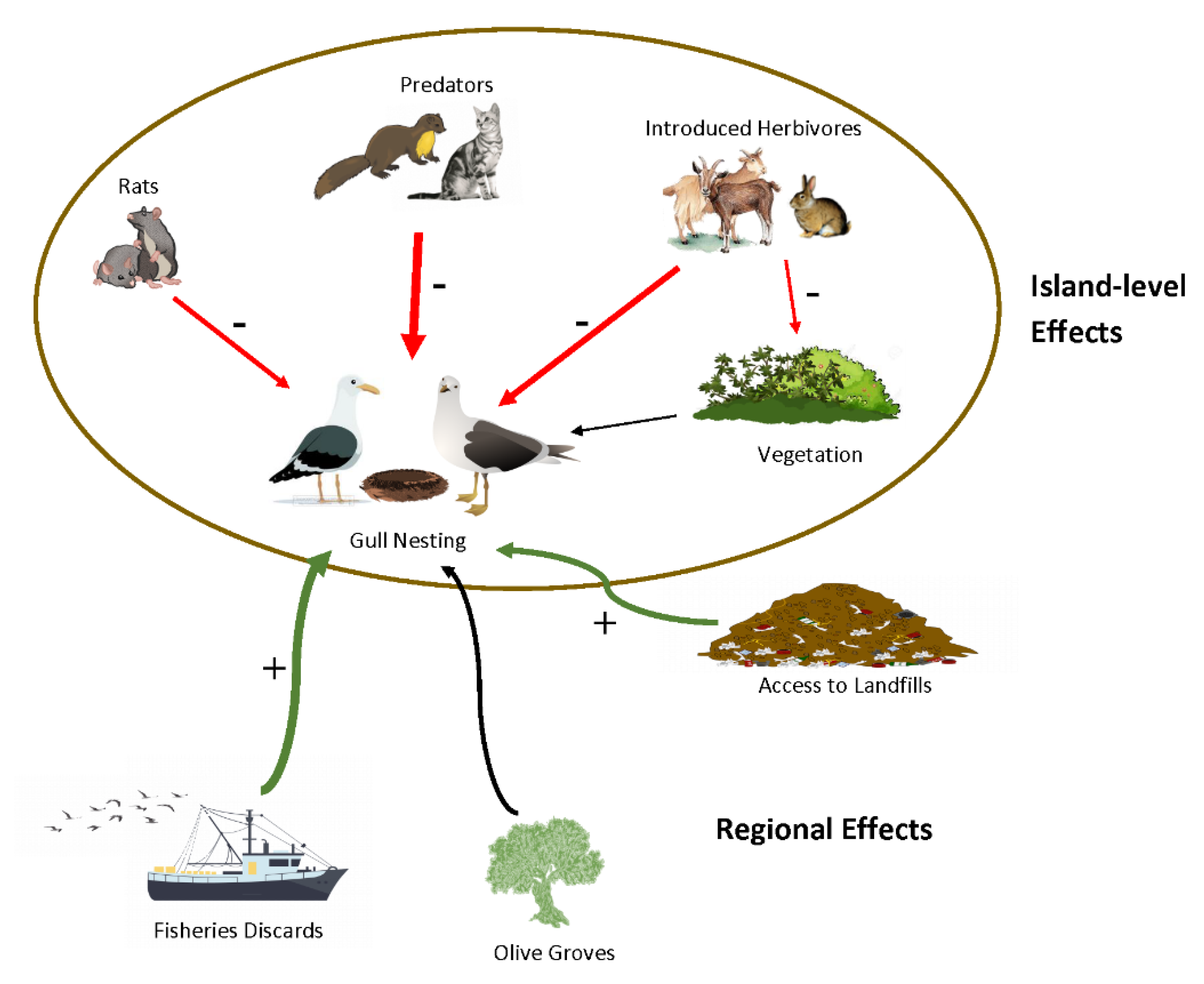
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.C.; Kueffer, C. Island biodiversity in the Anthropocene. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2019, 44, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, C.P.H.; Anderson, W.B.; Towns, D.R.; Bellingham, P.J. Seabird Islands: Ecology, Invasion, and Restoration; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Klöck, C.; Fink, M. Dealing with Climate Change on Small Islands: Towards Effective and Sustainable Adaptation; Göttingen University Press: Göttingen, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.-L.; Thibault, J.-C.; Bretagnolle, V. Black rats, island characteristics, and colonial nesting birds in the Mediterranean: Consequences of an ancient introduction. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 1452–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, W.B.; Polis, G.A. Nutrient fluxes from water to land: Seabirds affect plant nutrient status on Gulf of California islands. Oecologia 1999, 118, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainright, S.C.; Haney, J.C.; Kerr, C.; Golovkin, A.N.; Flint, M.V. Utilization of nitrogen derived from seabird guano by terrestrial and marine plants of St. Paul, Pribilof Islands, Bering Sea, Alaska. Mar. Biol. 1998, 131, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croll, D.A.; Maron, J.L.; Estes, J.A.; Danner, E.M.; Byrd, G.V. Introduced predators transform Subarctic islands from grassland to tundra. Science 2005, 307, 1959–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Piñero, F.; Polis, G.A. Bottom-up dynamics of allochthonous input: Direct and indirect effects of seabirds on islands. Ecology 2000, 81, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medail, F.; Quezel, P. Hot-Spots for Conservation of Plant Biodiversity in the Mediterranean Basin. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1997, 84, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosc, E.; Bricaud, A.; Antoine, D. Seasonal and interannual variability in algal biomass and primary production in the Mediterranean Sea, as derived from 4 years of SeaWiFS observations. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, GB1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Pagou, K.; Moraitou-Apostolopoulou, M.; Ignatiades, L. Seasonal horizontal and vertical variability in primary production and standing stocks in phytoplankton and zooplankton in the Cretan Sea and Straits of the Cretan Arc (March 1994–January 1995). Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 625–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, P.; Tchobanoglous, G. Sustainable use of water in the Aegean Islands. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fric, J.; Portolou, D.; Manolopoulos, A.; Kastritis, T. Important Areas for Seabirds in Greece; Hellenic Ornithological Society (HOS/BirdLife Greece): Athens, Greece, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Triantis, K.A.; Mylonas, M. Greek islands, biology. In Encyclopedia of Islands; Gillespie, R., Glague, D.A., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 388–392. [Google Scholar]
- Blumstein, D.T.; Daniel, J.C. The loss of anti-predator behavior following isolation on islands. Proc. R. Soc. B 2005, 272, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coblentz, B.E. The effects of feral goats (Capra hircus) on island ecosystems. Biol. Conserv. 1978, 13, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizicki, Z.S.; Tamez, V.; Galanopoulou, A.P.; Avramidis, P.; Foufopoulos, J. Long-term effects of feral goats (Capra hircus) on Mediterranean island communities: Results from whole island manipulations. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 1537–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.P.; Tershy, B.R.; Zavaleta, E.S.; Croll, D.A.; Keitt, B.S.; Finkelstein, M.E.; Howald, G.R. Severity of the effects of invasive rats on seabirds: A global review. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffino, L.; Bourgeois, K.; Vidal, E.; Duhem, C.; Paracuellos, M.; Escribano, F.; Sposimo, P.; Baccetti, N.; Pascal, M.; Oro, D. Invasive rats and seabirds after 2000 years of an unwanted coexistence on Mediterranean islands. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 1631–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, P.; Perrow, M.R.; Larsson, H. Seabirds: The New Identifications Guide; Lynx Edicions: Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal, E.; Medail, F.; Tatoni, T. Is the yellow-legged gull a superabundant bird species in the Mediterranean? Impact on fauna and flora, conservation measures and research priorities. Biodivers. Conserv. 1998, 7, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, V.; Herrando, S.; Voříšek, P.; Franch, M.; Kipson, M.; Milanesi, P.; Martí, D.; Anton, M.; Klvaňová, A.; Kalyakin, M.V.; et al. European Breeding Bird Atlas 2: Distribution, Abundance and Change; European Bird Census Council & Lynx Edicions: Barcelona, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Arizaga, J.; Herrero, A.; Galarza, A.; Hidalgo, J.; Aldalur, A.; Cuadrado, J.F.; Ocio, G. First-year movements of Yellow-legged Gull (Larus michahellis) from the Southeastern Bay of Biscay. Waterbirds 2010, 33, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.F.; Ramos, J.A.; Palva, V.H.; Calado, J.G.; Matos, D.M.; Ceia, F.R. Foraging strategies of a generalist seabird species, the yellow-legged gull, from GPS tracking and stable isotope analyses. Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egunez, A.; Zorrozua, N.; Aldalur, A.; Herrero, A.; Arizaga, J. Local use of landfills by a yellow-legged gull population suggests distance-dependent resource exploitation. J. Avian Biol. 2018, 49, e01455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karris, G.; Ketsilis-Rinis, V.; Kalogeropoulou, A.; Xirouchakis, S.; Machias, A.; Maina, I.; Kavadas, S. The use of demersal trawling discards as a food source for two scavenging seabird species: A case study of an eastern Mediterranean oligotrophic marine ecosystem. Avian Res. 2018, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Kaschner, K.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Aguzzi, J.; Ballesteros, E.; Bianchi, C.N.; Corbera, J.; Voultsiadou, E. The Biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, Patterns, and Threats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oro, D.; Genovart, M.; Tavecchia, G.; Fowler, M.S.; Martínez-Abraín, A. Ecological and evolutionary implications of food subsidies from humans. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 1501–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, E.; Hedman, H.; Pafilis, P.; Bergen, K.; Foufopoulos, J. Effects of touristic development on Mediterranean island wildlife. Landscape Ecol. 2019, 34, 2719–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Belasen, A.; Pafilis, P.; Bednekoff, P.; Foufopoulos, J. Effects of feral cats on the evolution of anti-predator behaviours in island reptiles: Insights from an ancient introduction. P. R. Soc. B 2014, 281, 20140339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, F.M.; Bonnaud, E.; Vidal, E.; Tershy, B.R.; Zavaleta, E.S.; Donlan, C.J.; Keitt, B.S.; Le Corre, M.; Horwath, S.V.; Nogales, M. A global review of the impacts of invasive cats on island endangered vertebrates. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 3503–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishery Country Profile: Greece. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/facp/grc?lang=en (accessed on 19 April 2021).
- Arcos, J.M.; Oro, D.; Sol, D. Competition between the yellow-legged gull Larus cachinnans and Andouin’s gull Larus audouinii associated with commercial fishing vessels: The influence of season and fishing fleet. Mar. Biol. 2001, 139, 807–816. [Google Scholar]
- Cama, A.; Abellana, R.; Christel, I.; Ferrer, X.; Vieites, D.R. Living on predictability: Modelling the density distribution of efficient foraging seabirds. Ecography 2012, 35, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, M.; Oro, D.; Ruiz, X. Dependence of Yellow-legged Gulls (Larus cachinnans) on food from human activity in two Western Mediterranean colonies. Avocetta 1994, 18, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Duhem, C.; Vidal, E.; Legrand, J.; Tatoni, T. Opportunistic feeding responses of the Yellow-legged Gull Larus michahellis to accessibility of refuse dumps. Bird Study 2003, 50, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhem, C.; Roche, P.; Vidal, E.; Tatoni, T. Effects of anthropogenic food resources on yellow-legged gull colony size on Mediterranean islands. Popul. Ecol. 2008, 50, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, C. Heterogeneous composition of anthropogenic litter recorded in nests of Yellow-legged gull (Larus michahellis) from a small Mediterranean island. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oro, D. Effects of trawler discard availability on egg laying and breeding success in the lesser black-backed gull Larus fuscus in the western Mediterranean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 132, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, A.E. Estimating numbers of colonial nesting seabirds: A comparison of techniques. Proc. Colon. Waterbird Group 1980, 3, 235–244. [Google Scholar]
- General Population Census 2011. Hellenic Statistical Authority (ELSTAT), 2011. Available online: https://www.statistics.gr/en/2011-census-pop-hous (accessed on 9 August 2020).
- Masseti, M. Atlas of Terrestrial Mammals of the Ionian and Aegean Islands; de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Arizaga, J.; Aldalur, A.; Herrero, A.; Cuadrado, J.F.; Díez, E.; Crespo, A. Foraging distances of a resident yellow-legged gull (Larus michahellis) population in relation to refuse management on a local scale. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2014, 60, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Fisheries Commission for the Mediterranean—Fleet Register. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. Available online: http://www.fao.org/gfcm/data/fleet/register/en/ (accessed on 29 June 2020).
- European Union Corine Land Cover 2018. Copernicus Land Monitoring Service, European Environment Agency (EEA). Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover/clc2018?tab=download (accessed on 7 October 2020).
- Vidal, E.; Roche, P.; Bonnet, V.; Tatoni, T. Nest-density distribution patterns in a yellow-legged gull archipelago colony. Acta Oecol. 2001, 22, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxe, S.; West, S.G.; Aiken, L.S. The Analysis of Count Data: A Gentle Introduction to Poisson Regression and Its Alternatives. J. Pers. Assess 2009, 91, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, O.J. Multiple Comparisons among Means. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1961, 56, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with R, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Symonds, M.R.E.; Moussalli, A. A brief guide to model selection, multimodel inference and model averaging in behavioural ecology using Akaike’s information criterion. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2011, 65, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Multimodel Inference, 2nd ed; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cheke, A.S.; Ashcroft, R.E. Mammals and butterflies new to Amorgos (Kiklades), with notes on reptiles and amphibians. Parnass. Arch. 2017, 5, 11–27. [Google Scholar]
- Latorre, L.; Larrinaga, A.R.; Santamaria, L. Rats and Seabirds: Effects of egg size on predation risk and the potential of conditioned taste aversion as a mitigation method. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Igual, J.M.; Forero, M.G.; Gomez, T.; Orueta, J.F.; Oro, D. Rat control and breeding performance in Cory’s shearwater (Calonectris diomedea): Effects of poisoning effort and habitat features. Anim. Conserv. 2006, 9, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, P.; Santiago Cabello, J.S.; Varnham, K. Long term rodent control in Rdum tal-Madonna Yelkouan shearwater colony. In Island Invasives: Scaling up to Meet the Challenge; Veitch, C.R., Clout, M.N., Martin, A.R., Russel, J.C., West, C.J., Eds.; Occasional Paper of the IUCN Species Survival Comission: Gland, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Hata, K.; Osawa, T.; Hiradate, S.; Kachi, N. Soil erosion alters soil chemical properties and limits grassland plant establishment on an oceanic island even after goat eradiation. Restor. Ecol. 2018, 27, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pafilis, P.; Anastasiou, I.; Sagonas, K.; Valakos, E.D. Grazing by goats on islands affects the populations of an endemic Mediterranean lizard. J. Zool. 2013, 290, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.P. Prognosis for ecosystem recovery following rodent eradication and seabird restoration in an island archipelago. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calado, J.G.; Matos, D.M.; Ramos, J.A.; Moniz, F.; Cela, F.R.; Granadeiro, J.P.; Palva, V.H. Seasonal and annual differences in foraging ecology of two gull species breeding in sympatry and their use of fishery discards. J. Avian Biol. 2017, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.; Ramírez, F.; Sanpera, C.; Jover, L.; Ruiz, X. Diet of Yellow-legged Gull (Larus michahellis) chicks along the Spanish Western Mediterranean coast: The relevance of refuse dumps. J. Ornithol. 2009, 150, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, E.; Oro, D.; Martínez-Abraín, A.; Igual, J.M.; Bertolero, A.; Bosch, M.; Tavecchia, G. Predictable anthropogenic food subsidies, density-dependence and socio-economic factors influence breeding investment in a generalist seabird. J. Avian Biol. 2017, 48, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garthe, S.; Scherp, B. Utilization of discards and offal from commercial fisheries by seabirds in the Baltic Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2003, 60, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracho Estévanez, C.A.; Prats Aparicio, S. Competitive inter- and intraspecific dominance relations in three gull species. Revista Catalana d’Ornitologia 2019, 35, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Abraín, A.; González-Solis, J.; Pedrocchi, V.; Genovart, M.; Abella, J.C.; Ruiz, X.; Jiménez, J.; Oro, D. Kleptoparasitism, disturbance, and predation of yellow-legged gulls on Audouin’s gulls in three colonies of the western Mediterranean. Sci. Mar. 2003, 67, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skórka, P.; Wójcik, J.; Martyka, R. Colonization and population growth of Yellow-legged Gull Larus cachinnans in southeastern Poland: Causes and influence on native species. Ibis 2005, 147, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekian, M.; Shagholian, J.; Hosseinpour, Z. Pathogen presence in wild birds inhabiting landfills in Central Iran. Eco-Health 2021, 18, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, J.; Grémilet, D.; Afán, I.; Miranda, F.; Bouten, W.; Gorero, M.G.; Figuerola, J. Pathogen transmission risk by opportunistic gulls moving across human landscapes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, A.T.; Allan, J.R. Use of Raptors to Reduce Scavenging Bird Numbers at Landfill Sites. Wildl. Soc. B. 2006, 34, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, M.; Oro, D.; Cantos, F.J.; Zabala, M. Short-term effects of culling on the ecology and population dynamics of the yellow-legged gull. J. Appl. Ecol. 2000, 37, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model | AIC | ΔAIC |
|---|---|---|
| Gull Pairs ~ Rats + Grazers + Veg_cover + Dist_landfill + Fishing vessels | 1203 | |
| Gull Pairs ~ Rats + Grazers + Veg_cover + Dist_landfill | 1205 | 2 |
| Gull Pairs ~ Rats + Grazers + Veg_cover | 1215 | 12 |
| Gull Pairs ~ Rats + Grazers | 1308 | 105 |
| Gull Pairs ~ Rats | 1317 | 114 |
| Variable | β | Effect Size (eβ) | SE | t | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 3.57 | 35.5 | 0.43 | 8.30 | <0.001 *** |
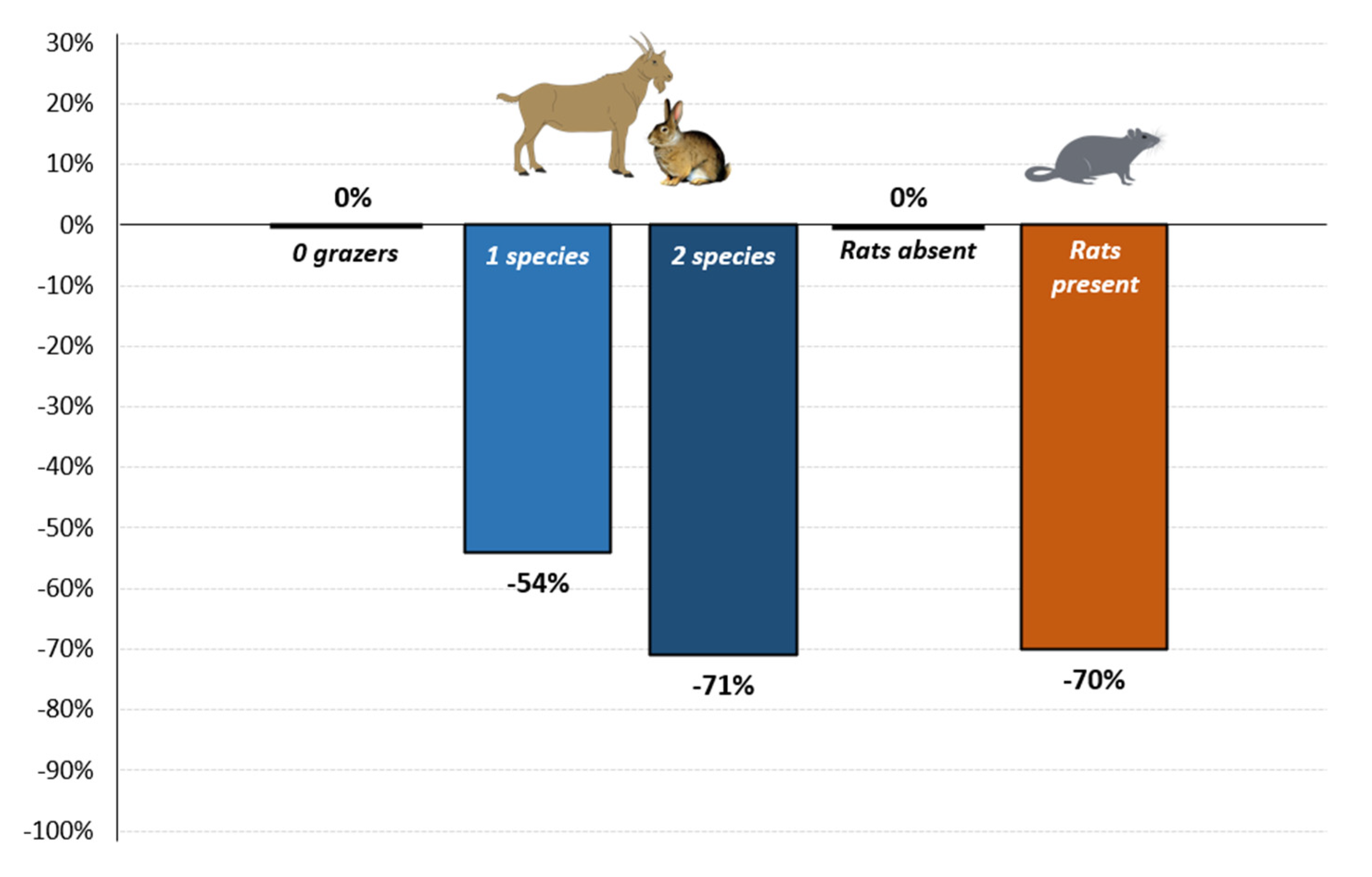
| Islet Rats | −1.21 | 0.30 | 0.33 | −3.63 | <0.001 *** |
| 1 Grazer | −0.78 | 0.46 | 0.35 | −2.21 | 0.027 * |
| 2 Grazers | −1.23 | 0.29 | 0.47 | −2.65 | 0.008 ** |
| Vegetation_Cover | 0.72 | 2.05 | 0.56 | 1.29 | 0.20 |
| Distance_landfill | −0.039 | 0.96 | 0.0091 | −4.27 | <0.001 *** |
| Variable | Correlation Coefficient | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Main (inhabited) island area | 0.34 | 0.16 |
| Human population | 0.42 | 0.07 |
| Total islet area | 0.14 | 0.56 |
| Fishing vessels | 0.75 | <0.001 * |
| Olive grove area | 0.49 | 0.03 |
| Average distance to nearest port | −0.14 | 0.56 |
| Average distance to nearest landfill | −0.13 | 0.35 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carlberg, R.A.; Karris, G.; Verma, M.; Foufopoulos, J. Food versus Disturbance: Contradictory Effects of Human Activities on an Opportunistic Seabird Breeding in an Oligotrophic Marine System. Diversity 2022, 14, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14060421
Carlberg RA, Karris G, Verma M, Foufopoulos J. Food versus Disturbance: Contradictory Effects of Human Activities on an Opportunistic Seabird Breeding in an Oligotrophic Marine System. Diversity. 2022; 14(6):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14060421
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarlberg, Rachael A., Georgios Karris, Manish Verma, and Johannes Foufopoulos. 2022. "Food versus Disturbance: Contradictory Effects of Human Activities on an Opportunistic Seabird Breeding in an Oligotrophic Marine System" Diversity 14, no. 6: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14060421
APA StyleCarlberg, R. A., Karris, G., Verma, M., & Foufopoulos, J. (2022). Food versus Disturbance: Contradictory Effects of Human Activities on an Opportunistic Seabird Breeding in an Oligotrophic Marine System. Diversity, 14(6), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14060421







