Abstract
The taxonomic history of the Amphiesma sensu lato has long been confused, and this complex was recently divided into three genera, i.e., Amphiesma Duméril, Bibron, and Duméril, 1854 sensu stricto, Hebius Thompson, 1913, and Herpetoreas Günther, 1860. Being the least known genus, Herpetoreas is reviewed herein through an integrative taxonomic approach. Our results indicate that specimens previously referred to Hebius parallelus (Boulenger, 1890) from Mêdog, Tibet, China, represent a new species. We describe here this new species and refer it to the genus Herpetoreas; therefore, we remove Hebius parallelus from the Chinese herpetofauna. A diagnostic key to all the species of Herpetoreas is also provided. Furthermore, we re-evaluate the diagnostic characters of the three genera formerly confused with Amphiesma, namely, Amphiesma, Hebius, and Herpetoreas. We provide a key to these three morphologically similar genera. We also emphasize the importance of the maxillary teeth and hemipenial morphology in the generic diagnosis in the family Natricidae.
1. Introduction
The taxonomic history of the genus Amphiesma Duméril, Bibron, and Duméril, 1854 has long been confused and controversial mainly due to their morphological similarities, wide distribution, and cryptic diversity [1,2,3]. Species of this genus have successively been placed in the genera Tropidonotus Boie, 1826 and Natrix Laurenti, 1768 [1,4,5,6]. A first wide-scale revision of the genus Natrix sensu lato was provided by Malnate [1]. Guo et al. [3] subsequently divided Amphiesma into three genera, i.e., Amphiesma, Hebius Thompson, 1913, and Herpetoreas Günther, 1860 based on phylogenetic analysis. After this generic division, the genus Amphiesma became monotypic, including only the well-known species Amphiesma stolatum (Duméril, Bibron, and Duméril, 1854) while the genus Hebius represents the most specious genus of Natricidae [3]. The third genus, in contrast, Herpetoreas mainly distributed in the southern foothills of the Himalayas, represents a lesser-known group among the three former genera of Amphiesma sensu lato [3,7].
After its revalidation, the genus Herpetoreas (type species: Herpetoreas sieboldii Günther, 1860, by monotypy) included only three species, namely, Her. sieboldii, Her. platyceps (Blyth, 1854), and a newly described species, Her. burbrinki Guo, Zhu, Liu, Zhang, Li, Huang & Pyron, 2014. Guo et al. [3] suggested that Herpetoreas might include additional species temporarily referred to Hebius. Two more Hebius species, i.e., Heb. xenura (Wall, 1907) and Heb. pealii (Sclater, 1891), were successively found to be nested within the genus Herpetoreas instead of Hebius and thus moved to the former genus [7,8]. However, little remains known about Herpetoreas species, mainly because some are known only from a handful of specimens [8]. Previous old records have not been re-evaluated [3,9]. Although Guo et al. [3] recommended that further taxonomic revision may be necessary in the future, previous studies only focused on generic assignments of the Herpetoreas members. No taxonomic review of the genus Herpetoreas had been previously published [7,8].
More importantly, the generic assignments of many species of Amphiesma sensu lato remain elusive. For example, many species were found to be assigned to the wrong genus [7,8]. Most recently, Deepak et al. [10] also indicated the non-monophyly of the genus Hebius, and transferred Heb. monticola (Jerdon, 1854) to the genus Amphiesma (to be Amphiesma monticolum) based on their multilocus phylogeny of natricid snakes. Such a widespread wrong generic affiliations within the genus Amphiesma sensu lato were mainly due to their morphological similarities [3]. Thus, the re-evaluation of the definition of generic boundaries is sorely needed.
In the genus Hebius, David et al. [11] revised the complex of species of Hebius parallelus (Boulenger, 1890). These authors revalidated Hebius clerki (Wall, 1925), long considered a synonym of Heb. parallelus, and confined the distribution area of Heb. parallelus to the Khasi Hills and Naga Hills, in Northeast India. On the contrary, Heb. clerki has a much wider distribution, from Sikkim (Northeast India) to Yunnan Province (southwestern China) across northern Myanmar. As a consequence, records of Heb. parallelus from Yunnan were referred to Heb. clerki [11].
Zhao et al. [12] recorded Heb. parallelus (as Amphiesma parallela) based on two specimens from Mêdog County, Xizang Autonomous Region (Tibet), China. Their identifications have not been re-evaluated and still remain unknown; no comment on the generic assignment of these specimens was provided by David et al. [11]. Che et al. [13] recently found specimens from Tibet, identified as Hebius cf. parallelus, to be clustered within Herpetoreas lineages and sister to Her. burbrinki, and thus transferred Hebius cf. parallelus to Herpetoreas, as Herpetoreas cf. parallelus. However, the taxonomic identity of Herpetoreas cf. parallelus recorded from Mêdog, Tibet, remained unsettled since major morphological differences exist between the Tibetan population and the original description of Heb. parallelus [13,14].
In the present study, we re-evaluate the taxonomic status of the Herpetoreas specimens from China through an integrative taxonomy approach. Results indicate that specimens of Herpetoreas cf. parallelus from Mêdog (Tibet) are clearly different from Hebius parallelus and other members of Herpetoreas. Specimens from Mêdog represent an undescribed species that we describe here. Furthermore, we provide detailed taxonomic accounts of the genus Herpetoreas and a diagnostic key to all members of this genus. To avoid further taxonomic confusions of Amphiesma sensu lato, a preliminary diagnostic key to the genera Amphiesma, Hebius, and Herpetoreas is also provided based on pholidosis, maxillary teeth, and hemipenial morphology.
2. Materials and Methods
Sampling. Two female specimens were newly collected from Mêdog, Tibet, PR China. After collection, snakes were euthanized, and fresh liver tissues were taken and preserved in 95% ethanol prior to the fixation of specimens in 10% buffered formalin. Specimens were transferred to 75% ethanol after three days for permanent storage, and deposited in the Herpetological Museum, Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CIB), PR China. Other Herpetoreas specimens were also examined based on museum collections (Appendix A), additional museum abbreviations see below.
Museum abbreviations. ANU—Anhui Normal University Museum, Wuhu, China. CAS—California Academy of Sciences, San Francisco, USA. BNHS—Bombay Natural History Society, Museum, Mumbai, India. CIB—Herpetological Museum, Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, China. FMNH—The Field Museum, Chicago, USA. IMC—Indian Museum, Calcutta, India (no longer extant, now = ZSI). KIZ—Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, China. KSC—Kohima Science College, Kohima, India. MCZ—Department of Herpetology, Museum of Comparative Zoology, Harvard University, Cambridge, USA. MHNG—Museum d’Histoire Naturelle, Geneva, Switzerland. MNHN—Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris, France. NHMUK (formerly BMNH)—The Natural History Museum, London, United Kingdom. NMW—Naturhistorisches Museum Wien, Vienna, Austria. ROM—Royal Ontario Museum, Toronto, Canada. SICAU—Sichuan Agricultural University, Ya’an, China. SYS—The Museum of Biology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China. UMMZ—Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, USA. USNM—National Museum of Natural History [formerly United States National Museum], Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C., USA. VNMN—Vietnam National Museum of Nature, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, Hanoi, Vietnam. YBU—Yibin University, Yibin, China. ZISP—Zoological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg, Russia. ZMB—Zoologisches Museum für Naturkunde der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany. ZSI/ERS—Zoological Survey of India (Eastern Regional Station), Shillong, India.
Morphological data. Definitions of pholidosis characters and their counting methods mainly followed Zhao [15], as follows: internasals (IN), prefrontals (PrF), frontals (F), parietals (P), loreals (L), preoculars (PrO), postoculars (PtO), supraoculars (SpO), suboculars (SbO), supralabials (SpL), infralabials (IfL), anterior temporals (aTEM), posterior temporals (pTEM), chin shields (CS), dorsal scale rows (DSR), ventrals (VEN), and subcaudals (SC). Dorsal scale rows were taken at one head length behind head, at midbody, and at one head length before cloaca, respectively. The number of ventral plates is counted according to Dowling [16], the counting method of supracaudal scales reduction followed Malnate et al. [17]. Symmetric characters were given as left/right and averages were used in the analyses. In addition, maxillary teeth (MT) of the left sides were also counted under microscope.
External measurements and methods followed Ren et al. [2], all measurements were made with digital calipers to the nearest 0.1 mm. Morphometric characters and measurements were taken as follows: total length (TL): distance from the tip of the snout to the tip of tail; snout-vent length (SVL): distance from the tip of the snout to the posterior margin of cloaca; tail length (TaL): distance from the posterior margin of cloaca to the tail tip; head length (HL): distance from the tip of the snout to the posterior margins of the parietals; head width (HW): maximum head width. The following ratios were also obtained from raw measurements, including TaL/TL: ratio tail length/total length; HL/HW: ratio head length/head width.
Hemipenial morphology. The hemipenial materials were prepared from left side of preserved, adult male specimens, everting methods were adapted from Myers et al. [18], Pesantes [19], Zaher et al. [20], Jiang [21]. The descriptive terminology of hemipenial morphology follows Cope [22], Dowling et al. [23], Zhang et al. [24]. Everted hemipenes were re-inflated with colored petroleum jelly. We photographed the hemipenis using a digital camera attached to a tripod head, and performed the combination and montage of multifocal photographs using the Helicon Focus (7.0.2 Pro) software (Helicon Soft Ltd., Kharkiv, Ukraine).
The following measurements were also used for hemipenial description: hemipenial total length (HTL): distance from the bottom of the truncus to the tip of most distant point in vertical direction; hemipenial truncus length (HCL): distance from the bottom of the truncus to the tip of crotch in vertical direction; hemipenial total width (HTW): the widest distance of the hemipenis in horizontal direction. The following ratios were also obtained from raw measurements, including HTL/HTW, HCL/HTL.
Molecular analyses. Genomic DNA was extracted from macerated liver or muscle tissue samples using an Ezup Column Animal Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Sangon Biotech, China), according to the protocols of the manufacturer. Primer pairs used for amplification and sequencing included L14910/H16064 [25] for cytochrome b (Cyt b), 16Sar-L/16Sar-H [26] for 16S rRNA (16S), and S77/S78 [27] for oocyte maturation factor MOS (CMOS). PCR products were purified and then sequenced in both directions using an ABI 3730xL sequencer by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China).
Initial nucleotide sequences were verified using Geneious Pro 4.8.4 [28] and translated into amino-acid sequences for quality check, and then deposited in GenBank (Table 1). In addition to our newly generated sequences, we included homologous sequences of all available Herpetoreas members from GenBank. Sibynophis subpunctatus was chosen to root the tree based on previous phylogenetic studies [29]. Sequences were aligned using MEGA 10.1.6 [30] with default settings and checked visually for minor manual justifications.

Table 1.
Sequences of Herpetoreas and related taxa used in this study.
Maximum likelihood (ML) analysis was conducted in RAxML v8.2.10 [31] under the best-fit substitution model (GTRGAMMA) based on the AIC criterion, as implemented in PartitionFinder 2 [32]. Bootstrap proportions (BSP) were investigated with 1000 bootstrap replicates using the fast-bootstrapping algorithm, otherwise under default parameters. Bayesian inference (BI) analyses were performed in MrBayes 3.2.6 [33], two Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) initiated from random trees and run for 1 × 107 generations and sampled every 100 generations, the first 25% of trees were discarded as “burn-in”. Convergence of MCMC chains and effective sampling size (ESS) were checked in Tracer 1.6 [34], ensuring a sample size > 200 for all parameters.
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analyses
The final alignment of the three gene dataset consisted of 2149 bp, and includes 1074 bp from Cyt b, 503 bp from 16S, and 572 bp from CMOS. GTR+G was selected as the best-fit model for both ML and BI analysis. For phylogenetic analyses, a majority rule consensus tree inferred from BI was consistent with the ML tree, and the topologies of our results are largely agreeing with previous analysis (Figure 1) [3,8,10,13].
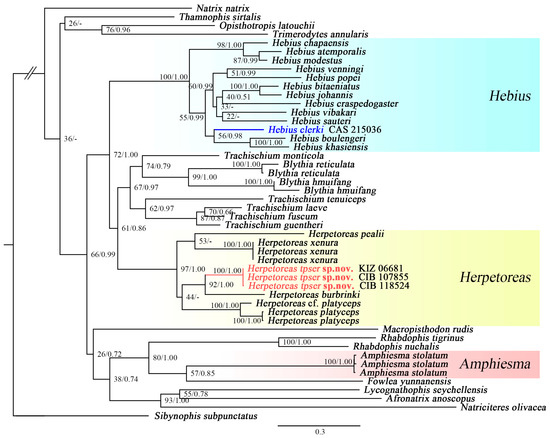
Figure 1.
Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree inferred from mtDNA Cyt b, 16S, and nuDNA gene CMOS, depicting phylogenetic relationships of Herpetoreas and related genera in Natricidae. Numbers above branches are bootstrap proportions and Bayesian posterior probability (BSP/BPP), respectively. “-” indicates different topologies between Bayesian inference phylogenetic tree and ML tree.
Among our sample, three genera of Amphiesma sensu lato were recovered as strongly supported clades within the family Natricidae, that were highly diverged with long basal branch lengths. The genus Herpetoreas was recovered as monophyletic with current samplings (BSP = 97/BPP = 1.00). Although interspecific relationships among congeners within Herpetoreas were not fully resolved, the final consensus tree yielded high supportive values (BSP > 70; BPP > 0.95) for key nodes concerning the relationship between the Tibetan population with recognized congeners. The Tibetan population was recovered as a highly diverged monophyletic clade (BSP = 100/BPP = 1.00) within Herpetoreas, which was sister to Herpetoreas burbrinki (BSP = 92/BPP = 1.00). The sequences considered to be Herpetoreas cf. parallelus (KIZ 06681) by Che et al. [13] showed no genetic divergence to our newly sequenced Tibetan population (marked in red), and we consider them to be conspecific. The sample of Hebius clerki (CAS 215036, marked in blue) from Nujiang County, Yunnan Province, China, previously misidentified as Hebius parallelus, was nested within the genus Hebius (Figure 1; Table 1).
Although the Tibetan population was previously identified as Hebius parallelus, morphological comparisons indicate that the Tibetan population is easily distinguished by a suit of characters against Hebius parallelus (see Comparison below). Furthermore, the Tibetan population is recovered to be a distinct evolutionary lineage of the genus Herpetoreas (Figure 1), and morphologically differs from all known species of this genus (Table 2). Therefore, we describe the Mêdog population of Herpetoreas as a new species herein. On the generic level, we review the taxonomic history of Herpetoreas. Moreover, in despite of the fact that phylogenetic definitions of Amphiesma sensu lato have been clarified [3], the morphological difference of Amphiesma sensu lato still remains unknown. Based on morphological comparisons of specimens from Amphiesma sensu lato, we provide diagnostic characters and a diagnostic key to the genera Amphiesma, Hebius, and Herpetoreas.

Table 2.
Morphological comparisons among congeners of the genus Herpetoreas. “-” indicates missing data.
3.2. Taxonomic Account
Herpetoreas Günther, 1860
Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11A.
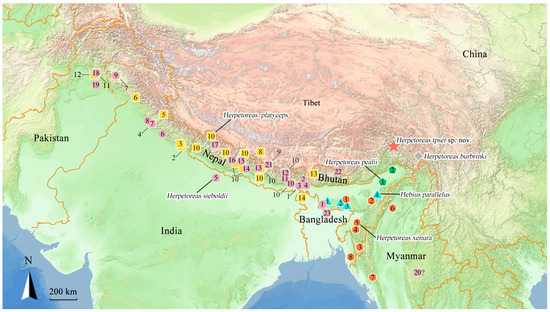
Figure 2.
General distribution map of members of Herpetoreas and Hebius parallelus, star represents the type locality of Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov. from Mêdog County, Xizang Autonomous Region (Tibet), China; rhombus represents the locality of Her. burbrinki; pentagon: Her. pealii; hexagon: Her. xenura; square: Her. platyceps; circle: Her. sieboldii; triangle: Heb. parallelus. Detailed information of numbers of the localities were listed in Appendix B.
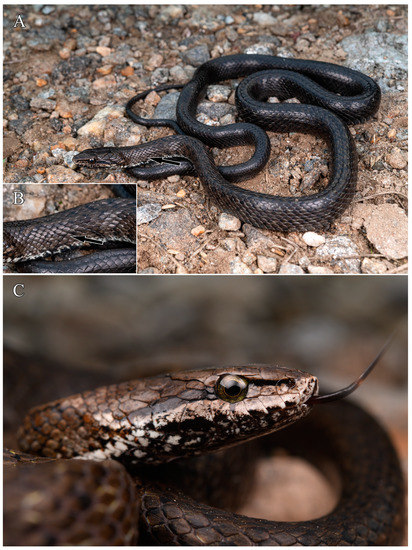

Figure 3.
Herpetoreas platyceps showing color in life, Gyirong County, Xizang Autonomous Region, China. (A) general view; (B) close-up of dorsal scale rows at anterior body, showing moderate keeling on outer rows; (C) lateral head view. Photographs by Shuo Qi.
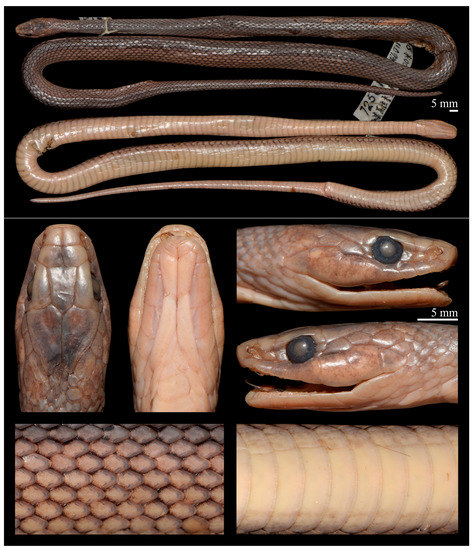

Figure 4.
Preserved specimen of Herpetoreas cf. platyceps, CIB 8420, adult female, Nyalam County, Xizang Autonomous Region, China. Photographs by Jun-Jie Huang.
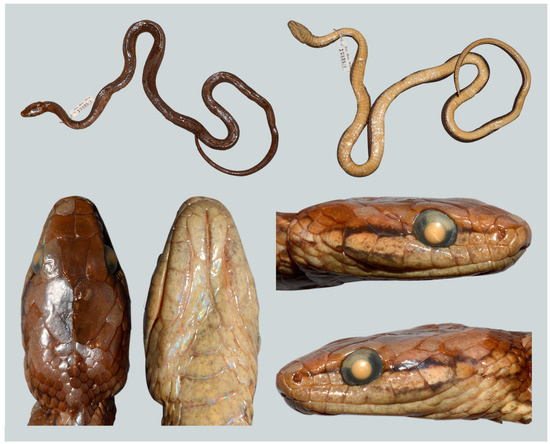

Figure 5.
Preserved specimen of Herpetoreas sieboldii, NMW 22383: 1, adult male, Darjeeling, West Bengal, India. Not to scale. Photographs by Gernot Vogel.
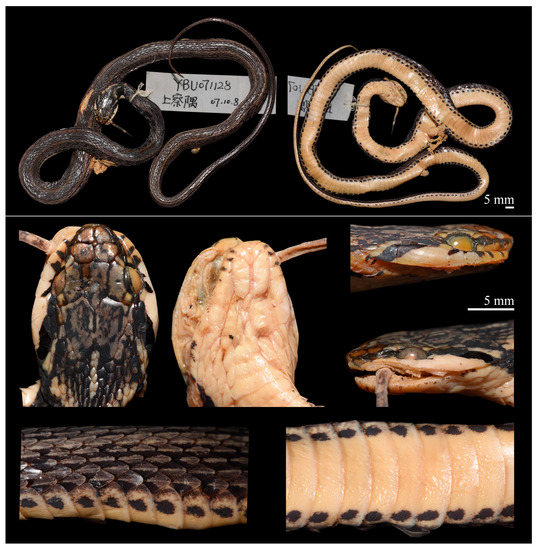

Figure 6.
Preserved holotype of Herpetoreas burbrinki, YBU 071128, adult male, Zayü County, Xizang Autonomous Region, China. Photographs by Jin-Long Ren.

Figure 7.
Herpetoreas tpsersp. nov. showing color in life, KIZ 06681, adult female, from 80K, Mêdog County, Xizang Autonomous Region, China. (A) dorsolateral view; (B) ventral view. Photographs by Mian Hou.

Figure 8.
Herpetoreas tpsersp. nov. showing color in life, KIZ 06681, adult female, from 80K, Mêdog County, Xizang Autonomous Region, China. (A) dorsal head view; (B) ventral head view; (C) right side of head view; (D) left side of head view. Photographs by Mian Hou.
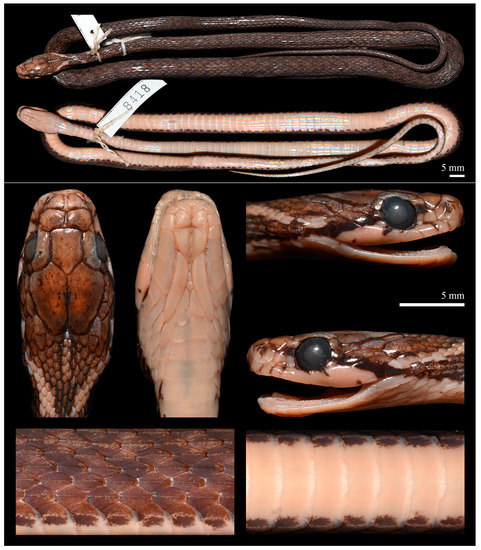
Figure 9.
Preserved holotype of Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov., CIB 8418, adult male, Beibeng, Mêdog County, Xizang Autonomous Region, China. Photographs by Jun-Jie Huang.
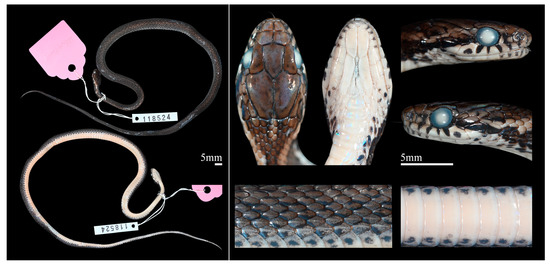
Figure 10.
Preserved paratype of Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov., CIB 118524, subadult, Mêdog County, Xizang Autonomous Region, China. Photographs by Jun-Jie Huang.
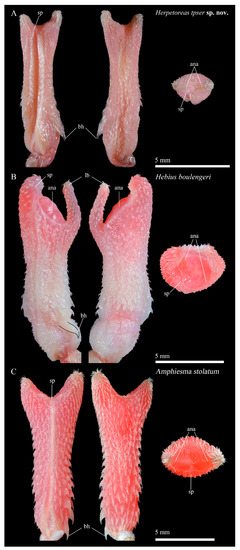
Figure 11.
Sulcate, asulcate, and apical sides of the hemipenis distinguishing different genera of Amphiesma sensu lato. (A) Amphiesma stolatum, SYS r001727; (B) Hebius boulengeri, SYS r001680; (C) Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov., CIB 107855. Photographs by Jun-Jie Huang (A,C) and Jin-Long Ren (B). Legend——sp: sulcus spermaticus; bh: basal hook; ana: apical naked area; lb: left lobe of hemipenis.
Herpetoreas Günther, 1860, Proc. Zool. Soc. London, 1860 (1): 156–157 [38]. Type species: Herpetoreas sieboldii Günther, 1860.
Type species.Herpetoreas sieboldii Günther, 1860 by monotypy.
Contents. The genus Herpetoreas currently includes six species:
Herpetoreas platyceps (Blyth, 1854)
Herpetoreas sieboldii Günther, 1860
Herpetoreas pealii (Sclater, 1891)
Herpetoreas xenura (Wall, 1907)
Herpetoreas burbrinki Guo, Zhu, Liu, Zhang, Li, Huang, and Pyron, 2014
Herpetoreas tpsersp. nov., herein described.
Diagnosis. (1) Head moderately distinct from neck; (2) body cylindrical, maximum TL 660–943 mm; (3) tail relatively long, TaL/TL 0.227–0.317; (4) nostrils and eye directed laterally; (5) supralabials 8–9, usually 3rd–5th or 4th and 5th entering orbit; (6) dorsal scale rows 19-19-17; weakly to distinctly keeled, notched at their apical part; (7) ventrals 136–234; (8) cloacal plate and subcaudals divided or not; (9) maxillary teeth 13–23, slightly enlarged posteriorly, last two to three distinctly enlarged, separated from anterior teeth by a small diastema; (10) hemipenis short and thin, shallowly bilobed, spinous throughout with single basal hook; (11) sulcus spermaticus single, centripetal, extends to the inner right lobe or to the crotch only; (12) apical naked area on the crotch weakly developed, not protruding, not visible from asulcate surface; (13) venter yellowish-beige, each ventral scale decorated with dark spots at lateral edge or not (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11A).
Key to species ofHerpetoreas
1A Subcaudals single..........................................................................................H. xenura
1B Subcaudals divided.....................................................................................................2
2A Cloacal plate single..........................................................................................H. pealii
2B Cloacal plate divided..................................................................................................3
3A Ventrals fewer than 168................................................................... H. tpser sp. nov.
3B Ventrals no less than 168............................................................................................4
4A Tail relatively long, TaL/TL > 0.300........................................................H. burbrinki
4B Tail relatively short, TaL/TL ≤ 0.300..........................................................................5
5A A high proportion of the length of the tail with 4 supracaudal scale rows to that with 6 supracaudal scale rows high, SC4/SC6 = 1.43.....................H. platyceps
5B A low proportion of the length of the tail with 4 supracaudal scale rows to that with 6 supracaudal scale rows high, SC4/SC6 = 0.53..............................H. sieboldii
Etymology. The etymology of the genus nomen of Herpetoreas was not specified by Günther [38]. It consists of the Greek noun “herpeton”, meaning “reptiles”, and of the Greek substantive ορειος, oreios, seemingly latinized in oreas, meaning “living or inhabiting mountains”. Based on this substantive, the grammatical gender of Herpetoreas is masculine.
We suggest “Himalaya Mountain Keelback” as its English common name, and Xǐ Shān Fù Liàn Shé Shǔ (喜山腹链蛇属) as its Chinese common name.
Distribution. The distribution pattern of Herpetoreas species is typical of distinct biogeographic boundaries, members of this genus are mainly known from southern foothills of the Himalaya Mountains as well as Eastern Himalayas, including northeastern Pakistan, northern and northeastern India, southwestern China (Tibet), Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan, and Myanmar (Figure 2).
3.2.1. Herpetoreas platyceps (Blyth, 1854)
Tropidonotus platyceps Blyth, 1854, J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal, 23 (3): 297 [39]. Type locality: “Darjeeling, Bengal” [= Darjeeling, West Bengal, North India, 27°02′ N, 88°16′ E, elevation ca. 2100 m] via lectotype selection.
Tropidonotus platyceps—Blyth, 1854: 297 (in part) [39]; Günther, 1860: 162 [38]; Günther, 1861: 217 [40]; Günther, 1862: 53 [41]; Günther, 1864: 264, plate 22: Figure D [5]; Theobald, 1868: 55 [42]; Stoliczka, 1870: 191 [43]; Anderson, 1871: 176 [44]; Stoliczka, 1872: 130 [45]; Blanford, 1875: 196 [46]; Theobald, 1876: 174 [47]; Blanford, 1878: 23 [48]; Atkinson, 1882: 76 [49]; Hubrecht, 1882: 142 [50]; Boulenger, 1888: 598 [51]; Phipson, 1888: 51 [52]; Boulenger, 1890: 343 [14]; Boulenger, 1893: 248 [53]; Cardew, 1897: 592 [54]; Wall, 1909: 340 [55]; Annandale, 1912: 49 [56]; Cataly, 1914: 30 [57]; Werner, 1929: 28 [58]; Prater, 1933: 393 [59].
Rhabdophis platyceps—Wall, 1923: 604 [60].
Natrix platyceps—Shaw et al. 1939: 118 [61]; Smith, 1943: 305 [6]; Smith, 1951: 728 [62]; Smith and Battersby, 1953: 703 [63]; Swan and Leviton, 1962: 114 [64]; Deoras, 1965: 87 [65]; Waltner, 1975: 18 [66]; Zhao et al. 1977: 64 (in part) [67]; Khan, 1980: 136 [68]; Hu et al. 1980: 76 [69]; Khan, 1982: 4 [70].
Natrix (Rhabdophis) platyceps—Smith, 1951: 728 [62].
Amphiesma platyceps—Malnate, 1960: 50 [1]; Malnate, 1966: 11 [35]; Fleming and Fleming, 1974: 430 [71]; Kramer, 1977: 729 [72]; Nanhoe and Ouboter, 1987: 33 [73]; Zhao and Adler, 1993: 228 [74]; Das, 1994: 31 [75]; Das, 1996: 53 [76]; Das et al. 1998: 152 [77]; Zhao et al. 1998: 76 [78]; Rao, 2000: 112 [79]; Das, 2002: 18 [80]; Khan, 2002: 82 [81]; Schleich et al., 2002: 435 (plate 84, Figure 250), 813 [82]; Das, 2003: 473 [83]; Tillack, 2003: 21 [84]; Khan, 2004: 196 [85]; Whitaker and Captain, 2004: 26, 206 [86]; Zhao, 2006: 170 [15]; Zhao, 2006: 93, Figure 55, 1–2 [87]; Sharma, 2007: 212 [88]; Ahsan et al., 2009: 116 [89]; Li et al., 2010: 167 [9]; Reza, 2010: 64 [90]; Wangyal, 2011: 118 [91]; Wangyal, 2013: 4777 [92]; Wallach et al. 2014: 32 [93]; David et al. 2015: 391–393 [11]; Sahi and Koul, 2020: 893 [94].
Natrix (Amphiesma) platyceps—Mertens, 1969: 64 [95].
Amphiesma cf. platyceps—Ahmed et al. 2009: 155 [96].
Herpetoreas platyceps—Guo et al. 2014: 437 [3]; Aengals et al. 2018: 21 [97]; Che et al. 2020: 677 [13]; Wang et al. 2020: Appendix 16 [98]; Boundy, 2021: 95 [99]; Huang, 2021: 424 [100].
Tropidonotus dipsas Blyth, 1854, J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal, 23 (3): 297 [39]. Type locality: “Vicinity of Darjiling”.
Zamenis himalayanus Steindachner, 1867, Verh. Der Kais.-Königlichen Zool.-Bot. Ges. Wien., 17: 513 [101]. Types: NMW, Nos. 18569, 18570: 1–2. Type locality: “Simla und Kulu (Himalaya)” [=Shimla and Kullu, Himachal Pradesh, India].
Tropidonotus firthi Wall, 1914, J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc., 23 (1), 166–167 [102]. Type locality: “Takdah in the Eastern Himalayas”.
Tropidonotus himalayanus—Anderson, 1871: 178 [44].
Zamenis himalayanus—Steindachner, 1867: 513 [101]; Günther, 1872: 14 [103]; Hubrecht, 1882: 141 [50].
Rhabdophis firthi—Wall, 1923: 606 [60].
Tropidonotus firthi—Werner, 1929: 29 [58].
Type. Lectotype, ZSI 7482 (formerly IMC 7482), a 692+ mm specimen (W.S. Sherwill, 1843–1854), designated by Malnate [35]: 11.
Referred specimens (n = 29).—India (n = 25). West Bengal: NMW 22383: 2, NMW 22383: 5, Darjeeling; BNHS 80-11, Turjun tea estate, Darjeeling. Sikkim: FMNH 15827, “Mangpu, Sikkim”; BMNH 60.3.19.1354, no specific locality. Uttarakhand: BNHS 80-3, Almora; BMNH 1911.9.8.2, Binsar. Himachal Pradesh: NMW 18569, NMW 18570: 1–2, “Simla and Kulu (Himalaya)”, now Shimla and Kullu; BNHS 80-2, Dalhousie, about 1828 m; BNHS 80-5 (b), 80-7, Shimla; BMNH 1911.5.9.1, Upper Sutlej Valley, about 2133 m. Jammu and Kashmir: MNHN 1988.6484, above Doda, between Makambagi and Ularbagi, Udamphur District, about 2,800 m; ZMB 7293, “Kashmir”; BMNH 96.11.20.5–6, Kashmir, Gulmarg. No specific locality: BMNH 70.1 1.30.36A–D, about 3048 m; BMNH 1903.6.22.23; USNM 48469–70).—Pakistan (n = 1). Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. BNHS 580, Thandiani.—China (n = 1). Xizang A.R.: CIB 8420, Zhangmu, Nyalam, about 2400 m.—Nepal (n = 2). Jumla: BMNH 1953. 1. 1. 63, 7600 feet. No specific locality: BMNH 45. 1. 12. 570. Of these, nine specimens were physically examined (see Appendix A), and data of 20 other specimens were obtained from the literature [35].
Diagnosis. (1) body cylindrical, TL 755–927 mm; (2) tail moderate, TaL/TL 0.232–0.286; (3) dorsal scale rows 19-19-17; weekly keeled only on five to seven mid-dorsal scale rows, namely, on the 3rd–9th to 5th–9th dorsal scale rows plus the vertebral row; (4) ventrals 180–234; (5) cloacal plate and subcaudals divided; (6) subcaudals 78–99; (7) supralabials 8, 3rd, 4th and 5th entering orbit; (8) maxillary teeth 18–22, slightly enlarged posteriorly, last two distinctly enlarged, separated from anterior teeth by small diastema; (9) hemipenis short and thin, shallowly bilobed, spinous throughout with single basal hook; (10) sulcus spermaticus single, centripetal, extends to the tip of inner right lobe; (11) the upper edge of the supralabials bordered by dark postocular streak; (12) dorsal color highly variable, dorsum frequently speckled with small dark spots; (13) venter yellowish-beige, each ventral decorated with a pair of dark spots at lateral edges or not.
Distribution. This species is widely distributed across Southern Asia, including northern Pakistan, northern India, southwestern China (Tibet), Nepal, Bangladesh, and western Bhutan (Paro), 1250–3700 m a.s.l. [93] (Figure 2).
Comments. Although Herpetoreas platyceps has been widely recorded across southern Asia, few studies have focused on the cryptic diversity of this highly variable species. For example, previously considered a junior synonym of Her. platyceps, the type species of Herpetoreas, Her. sieboldii is morphologically similar to Her. platyceps [6,35]. Malnate [35] revised and re-described both Her. sieboldii and Her. platyceps, indicating that the dorsal scale rows of Her. platyceps are feebly keeled only on five to seven mid-dorsal scale rows without exception. However, Her. platyceps specimens from Gyirong County, Tibet, China are distinctly differ from descriptions provided by Malnate [35] in having stronger keeled dorsal scales along the anterior body (Figure 3B). Further phylogenetic work is recommended to incorporate the topotype of Her. platyceps to clarify whether this variation is caused by cryptic diversity or intraspecific variation. In addition, see comments under Her. sieboldii.
3.2.2. Herpetoreas sieboldii Günther, 1860
Herpetoreas sieboldii Günther, 1860, Proc. Zool Soc. London, 28 (1): 156–157 [38]. Type locality: “Sikkim, Himalaya (7500 feet above the level of the sea)” [=Sikkim State, Northeast India, elevation 2286 m a.s.l.].
Herpetoreas sieboldii—Günther, 1860: 156 [38]; Günther, 1864: 257 [5]; Theobald, 1868: 54 [42]; Theobald, 1876: 172 [47]; Guo et al. 2014: 437 [3]; Aengals et al. 2018: 21 [97]; Boundy, 2021: 95 [99].
Amphiesma sieboldii—Malnate, 1966: 14 [35]; Dierl and Gruber, 1979: 45 [104]; Welch, 1988: 34 [105]; Das, 1994: 31 [75]; Das, 1996: 53 [76]; Das, 1997: 40 [106]; David et al. 1998: 92 [107]; Kahn, 2002: 83 [81]; Das, 2003: 473 [83]; Khan, 2004: 196 [85]; Whitaker and Captain, 2004: 26 [86]; David et al. 2005: 174 [108]; Ahsan et al. 2009: 116 [89]; Das, 2010: 334, plate 68 [109]; Reza, 2010: 64 [90]; Wangyal, 2011: 120 [91]; Das, 2012: 117 [110]; Wallach et al. 2014: 33 [93]; David et al. 2015: 375 [11].
Natrix platyceps—Smith, 1943: 305 (in part) [6]; Schleich et al. 2002: 813 (in part) [82]; Tillack, 2003: 21 (in part) [84].
Natrix sieboldii—Khan, 1980: 136 [68]; Khan, 1982: 4 [70].
Type. Holotype, NHMUK (formerly BMNH) 1946.1.13.16, a 917 mm male (H.R.A. von Schlagintweit, A. von Schlagintweit, and R. von Schlagintweit, 1854–1858).
Referred specimens (n = 54).—India (n = 22). Assam: BNHS 80-8, Garo Hills, Tura. Sikkim: BNHS 80-10, Gangtok. West Bengal: CAS-SU 15973, NMW 22383: 1, NMW 22383: 3–4, BMNH 70.11.30.37M–N, Darjeeling; BNHS 1835, Lebong; MCZ 58238–40, Takdah; BNHS 80-15, BMNH 53.8.12.30K–L, BMNH 60.3.19.1352, no specific locality. Uttar Pradesh: BNHS 80-9, Gonda. Uttarakhand: BMNH 1905.10.27.1, UMMZ 77237, Mussoorie, 1828–2133 m. Himachal Pradesh: BNHS 582, 80-5a, Shimla; BNHS 80-6, Taradevi hill, near Shimla.—Pakistan (n = 2). Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: BNHS 581, Thandiani. Punjab: BNHS 80-14, Rawalpindi, Ghora Galli.—China (n = 3). Xizang A. R.: CAS 177474, between Chinese check point at Zhangmu (Khasa) (28°07′ N-85°59′ E) and the Nepal border on the Lhasa-Kathmandu Rd., Nyalam county, Xigaze Prefecture, 2000–2100 m; CAS 177672–177673, locality same to CAS 177474, 2300–2500 m.—Nepal (n = 26). BMNH 1913.5.22.1, “Maikola Valley, E. Nepal”, now Mai Kola, 2133–3048 m; CAS 90690, “above Deppur”, about 1676 m; FMNH 109762, Amp Pipal, about 1219 m; FMNH 131966, Chapagaon, Kathmandu Valley; FMNH 131967, Kathmandu Valley; FMNH 190856, Arun Valley, at Num Bridge across Arun River; FMNH 204499, above Num, 6400′ in forest area; MHNG 1355.72–73, Astam, near Hyangcha, 1600 m; MNHN 2003.3614, east of Mounasko Pass, between Surkie Pass and Chheskam, Eastern Region, 2400 m; ZMB 4551, “Himalaya”; ZMB 10231, Sikkim; FMNH 204500–504, no specific locality. BMNH 1953.1.1.64, Balangra Pass, about 3657 m; BMNH 1962.1047, Hatia, Arun River, about 1981 m; BMNH 1955.1.13.71, Lumsum, NW. Beni, 1981 m; BMNH 1962.1048, Maewa khola, Sangwe, 1981 m; BMNH 1955.1.13.69–70, Taglung, S. Tukucha, 2895 m; BMNH 1950.1.5.59–60, Thangjet, 1524 m; BMNH 45.1.12.572, no specific locality.—Myanmar (? See below) (n = 1). Shan State, BNHS 80.4, Taung-gyi. Of these, 24 specimens were physically examined (see Appendix A), and data of 30 other specimens were obtained from the literature [35].
Diagnosis. (1) body cylindrical, TL 729–943 mm; (2) tail relatively long, TaL/TL 0.242–0.300; (3) dorsal scale rows 19-19-17; all keeled but some may not be keeled in outermost rows; (4) ventrals 168–216; (5) cloacal plate and subcaudals divided; (6) subcaudals 81–111; (7) supralabials 8, 3rd, 4th and 5th entering orbit; (8) maxillary teeth 19–23, slightly enlarged posteriorly, last two distinctly enlarged, separated from anterior teeth by small diastema; (9) hemipenis short and thin, shallowly bilobed, spinous throughout with single basal hook; (10) sulcus spermaticus single, centripetal, extends to the tip of lobe; (11) a light, dark-bordered crescent extends from the last supralabial up and back over the nape; (12) dorsum frequently speckled with small light spots; (13) venter often darkened posteriorly or usually with a lateral series of dark streaks.
Comparison. Herpetoreas sieboldii differs from Her. platyceps by having (1) all dorsal scale rows keeled vs. keeled on five to seven mid-dorsal scale rows; (2) 168–216 ventrals vs. 180–234 ventrals; (3) A low proportion of the length of the tail with 4 supracaudal scale rows to that with 6 supracaudal scale rows, SC4/SC6 = 0.53 vs. SC4/SC6 = 1.43; (4) ventral surface of body mostly darkened poteriorly vs. usually immaculate.
Distribution. India, Nepal, China (Tibet), Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar (? See below), and Pakistan, 1219–3657 m a.s.l. (Figure 2).
Comments. The genus Herpetoreas has long been regarded as a junior synonym of Amphiesma [1], of which the species Her. sieboldii has long been synonymized with Her. platyceps [6,84]. Although Malnate [35] revalidated sieboldii as a separate species and provided distinctive characters between Her. sieboldii and Her. platyceps, the number of ventrals in Her. sieboldii listed by Malnate [35] is distinctly lower than its original description (168–207 vs. 216) [38], thus further pholidosis confirmation is needed especially for the holotype. Guo et al. [3] revalidated the genus Herpetoreas to accommodate the following three species: Her. sieboldii, Her. platyceps, and Her. burbrinki. However, no genetic data are available for Her. sieboldii to our knowledge [7,8,13]. Further study is also recommended to clarify the relationships between Her. sieboldii and Her. platyceps. In addition, see comments under Her. platyceps.
David et al. [11] reported three specimens (CAS 177474, 177672–177673,) of Her. sieboldii from Zhangmu, Xizang Autonomous Region (Tibet), China. However, no morphological data was provided and the species is previously not listed from Chinese herpetofauna [98]. The distribution record from Myanmar provided by Malnate [35] was based on a single specimen (BNHS 80.4) from Shan State (Figure 2), which was considered to be highly isolated. We question the Burmese record of Her. sieboldii pending further confimation.
3.2.3. Herpetoreas pealii (Sclater, 1891)
Tropidonotus pealii Sclater, 1891, J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal, 60 (3): 241, pl. 6, figs. 4a–c [111]. Type locality: “Sibsagar district of Assam” [= Sibsagar District, North Assam State, Northeast India, ca. 26°59′ N, 94°38′ E, elevation ca. 100 m].
Tropidonotus pealii—Boulenger, 1893: 214 [53].
Natrix peali [sic]—Wall, 1923: 600 [60]; Smith, 1943: 291 [6].
Amphiesma peali [sic]—Malnate, 1960: 50 [1]; Sharma, 2007: 206 [88].
Paranatrix pealii—Mahendra, 1984.
Amphiesma pealii—Das, 1994: 31 [75]; Das, 1996: 53 [76]; Das et al. 1998: 151 [77]; Das, 2003: 473 [83]; Whitaker and Captain, 2004: 25 [86]; Ahmed et al. 2009: 19 [96]; Wallach et al. 2014: 32 [93].
Hebius pealii—Guo et al. 2014: 438 [3]; Das and Das, 2017: 168 [112]; Aengals et al. 2018: 21 [97]; Purkayastha and David, 2019: 86 [113]; Boundy, 2021: 92 [99].
Herpetoreas pealii—Das et al. 2020: 309 [8].
Type. Syntypes (2), BMNH 1946.1.13.43 and ZSI 4034 (formerly IMC), two males, longer syntype 508 mm (S.E. Peal, 1872–1891).
Referred specimens (n = 2). —India. BMNH 1946.1.13.43, Sibsagar district, Assam; WII-ADR547, Siang district, northeast India. Data were obtained from the literature [8,113].
Diagnosis. (1) Body cylindrical, TL 451–660 mm; (2) tail moderate long, TaL/TL 0.227–0.259; (3) dorsal scale rows 19-19-17; moderately keeled except for outermost row at anterior and midbody; (4) ventrals 136–142; (5) cloacal plate single, subcaudals divided; (6) subcaudals 69–77; (7) supralabials 9, 4th and 5th entering orbit; (8) maxillary teeth 13–21, slightly enlarged posteriorly, last two distinctly enlarged, separated from anterior teeth by small diastema; (9) hemipenis short and thin, shallowly bilobed, spinous throughout with single basal hook; (10) sulcus spermaticus single; (11) dorsum dark brown above with paler and darker spots; (12) venter yellowish-beige, each ventral decorated with a pair of dark spots at lateral edges that are connected to form a continuous ventrolateral line.
Comparison. Herpetoreas pealii differs from both Her. platyceps and Her. sieboldii by having (1) single cloacal plate vs. divided cloacal plate; (2) fewer ventral scales 136–142 vs. 180–234 in Her. platyceps and 168–216 in Her. sieboldii; (3) fewer subcaudals 69–77 vs. 78–99 in Her. platyceps and 81–111 Her. sieboldii; (4) only two supralabials entering orbit, supralabial formula 3-2-4 vs. three supralabial entering orbit, supralabial formula 2-3-3.
Distribution. Northeastern India, 100–120 m a.s.l. (Figure 2).
Comments. This is a poorly known species with only three specimens known up to now [8]. Das et al. [8] redescribed the species based on newly obtained specimen and transferred the species to the current genus Herpetoreas according to their phylogenetic results.
3.2.4. Herpetoreas xenura (Wall, 1907)
Tropidonotus xenura Wall, 1907, J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. (1906–1907), 17 (3): 616–617, pl. 1, Figure 2 [36].
Natrix xenurus—Wall, 1923: 601 [60].
Natrix xenura—Smith, 1943: 292 [6]; Romer, 1945: 431 [114].
Paranatrix xenura—Mahendra, 1984.
Amphiesma xenura—Das, 1994: 31 [75]; Das, 1996: 54 [76]; Pawar and Birand, 2001: 102 [115]; Das, 2003: 474 [83]; Whitaker and Captain, 2004: 152, 190 [86]; David et al. 2007: 54 [116]; Sharma, 2007: 210 [88]; Wogan et al. 2008: 87 [117]; Ahsan et al. 2009: 118 [89]; Das, 2010: 335 plate 68 [109]; Reza, 2010: 64 [90]; Das, 2012: 118 [110]; Wallach et al. 2014: 35 [93].
Hebius xenura—Guo et al. 2014: 438 [3]; Aengals et al. 2018: 21 [97]; Purkayastha and David, 2019: 85 [113].
Herpetoreas xenura—Lalronunga et al. 2020: 196 [7]; Muansanga et al. 2021: 82 [118].
Type. Holotype, IMC, lost fide Smith [6]: 292.
Type locality. Unknown.
Referred specimens (n = 3). Detailed voucher unknown. Data were obtained from the literature [6,8,36].
Diagnosis. (1) Body cylindrical, TL 590–660 mm; (2) tail relatively long, TaL/TL 0.271–0.302; (3) dorsal scale rows 19-19-17; all strongly keeled; (4) ventrals 158–165; (5) cloacal plate usually single, subcaudals single; (6) subcaudals 82–105; (7) supralabials 9 (10), 4th–5th entering orbit; (8) maxillary teeth 22–23, gradually enlarged posteriorly, last two distinctly enlarged, separated from anterior teeth by a small diastema; (9) hemipenis short and thin, shallowly bilobed, extends to 8th subcaudals; (10) sulcus spermaticus single; (11) dorsum dark olive-brown with indistinct narrow blackish cross-bars or series of spots; (12) venter off-whitish, each ventral decorated with a pair of dark brown square spots on their lateral edges.
Comparison.Herpetoreas xenura differs from Her. platyceps, Her. sieboldii and Her. pealii by having single subcaudals vs. divided subcaudals. Particularly, Her. xenura differs from Her. platyceps and Her. sieboldii in having fewer ventrals 158–165 vs. 180–234 in Her. platyceps and 168–216 in Her. sieboldii; only two supralabials entering orbit, supralabial formula 3-2-4 vs. three supralabial entering orbit, supralabial formula 2-3-3; from Her. pealii by having more ventrals 158–165 vs. 136–142, a longer tail, TaL/TL 0.271–0.302 vs. TaL/TL 0.227–0.259, and more subcaudals 82–105 vs. 69–77.
Distribution. Northeast India, Bangladesh and Myanmar, 124–1444 m a.s.l. (Figure 2).
Comments. A morphologically distinct but poorly known species, Wall [36] indicated that both the cloacal and subcaudal scales are in a single row when describing the species. Particularly, the supracaudal scales are arranged in even rows though the subcaudals are entire, which is distinct among many groups of snakes such as Bungarus (Elapidae), Aspidura (Natricidae), Achalinus (Xenodermidae), etc. [36]. Lalronunga et al. [7] transferred the species into Herpetoreas based on their phylogenetic trees, whereas no redescription was provided especially for the maxillary teeth.
3.2.5. Herpetoreas burbrinki Guo, Zhu, Liu, Zhang, Li, Huang, and Pyron, 2014
Herpetoreas burbrinki Guo Zhu, Liu, Zhang, Li, Huang, and Pyron, 2014, Zootaxa, 3873 (4): 438, Figure 3 [3]. Type locality: “Zayu County, Xizang A. R., China, at an elevation of 1889 m above sea level”.
Herpetoreas burbrinki Guo et al. 2014: 438 [3]; Che et al. 2020: 671 [13]; Das et al. 2020: 313 [8]; Wang et al. 2020: Appendix 16 [98]; Boundy, 2021: 94 [99]; Huang, 2021: 426 [100]; Peng et al. 2021: 434 [37].
Type. Holotype. YBU 071128, a 757 mm adult male specimen.
Referred specimens (n = 2).—China. Xizang A. R.: YBU 071128, Zayü County, ANU 20210006 Xiachayu Town, Zayu County. Of these, the holotype was physically examined (see Appendix A), and data of another specimen was obtained from the literature [37].
Diagnosis. (1) Tail relatively long, TaL/TL 0.285–0.304; (2) dorsal scale rows 19-19-17; moderately keeled, notched at apex; (3) supralabials 8 (9), 3rd–5th entering orbit; (4) one (two) preoculars; (5) three postoculars; (6) ventrals 169–172; (7) cloacal plate and subcaudals divided, subcaudals 94–96; (8) reduction of dorsal scales rows from 19 to 17 scale occurring above ventral scale position 105–108; (9) reduction of the supracaudal scales rows from 8 to 6 (SC8TO6) occurring above subcaudal 62–63; (10) venter yellowish-beige in preservative, each ventral decorated with a pair of dark spots at lateral edges (Figure 6).
Comparison. Herpetoreas burbrinki differs from Her. platyceps by having a longer tail, TaL/TL 0.285–0.304 vs. TaL/TL 0.232–0.286, fewer ventrals 169–172 vs. 180–234; from Her. sieboldii by having 1st SC6 22th–23th vs. 25th–28th, SC6 40–41 vs. 27–38, a clear ventral color pattern with a pair of dark spots on each side of ventral scale vs. ventral surface darkened posteriorly with a greyish suffusion of variable intensity; from Her. pealii by having divided cloacal plate and subcaudals vs. cloacal plate single, subcaudals paired in Her. pealii and both cloacal plate and subcaudals paired in Her. xenura.
Distribution. Zayü County, Xizang Autonomous Region, China, this species is still known only from its type locality; 1889–1938 m a.s.l. (Figure 2).
Comments. Herpetoreas burbrinki is still known only from two specimens to our best knowledge [37]. The holotype of Her. burbrinki (YBU 071128) was firstly reported as Amphiesma cf. craspedogaster from Tibet, China by Guo et al. [119], and its measurement provided by Guo et al. [3] is consistent with Guo et al. [119], i.e., SVL 495 mm, TaL 130 mm. However, we re-examined the holotype of Her. burbrinki (YBU 071128) and found our observations are mostly in agreement with previous studies for most of characters except for a longer SVL (527 mm vs. 495 mm) and a distinctly longer tail (TaL 230 mm vs. 130 mm; TaL/TL 0.304 vs 0.208) [3,119]. The measurements of the holotype of Her. burbrinki provided by the current study were based on our data, which were also similar to the newly reported female specimen Tal/TL 0.304 vs. 0.285 (ANU 20210006) [37].
3.2.6. Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov.
http://zoobank.org/CAB44C8A-1C8C-4962-ADAC-5AFF2FE4F6C0 (accessed on 26 November 2021)
Chresonymy.
Amphiesma khasiensis—Zhao and Li, 1985: 106 [120]; Zhao et al. 1986: 201 [121].
Amphiesma parallela—Zhao and Li, 1987: 49 [12].
Amphiesma parallelum—Zhao and Adler, 1993: 227 (in part) [74]; Li et al. 1995: 264 [122]; Zhao et al. 1998. 74 (in part) [78]; Zhao, 2006: 169 (in part) [15]; Zhao, 2006: 92, Figure 54 [87]; Li et al. 2010: 166 [9].
Hebius parallelum—Guo et al. 2014: 438 (in part) [3].
Herpetoreas cf. parallelum—Che et al. 2020: 673 [13].
Holotype. CIB 8418 (field no. 73II5194), adult male, from Beibeng Town to De’ergong Village, Mêdog County, Nyingchi City, Xizang Autonomous Region, China (ca. 1300 m a.s.l.), collected by Er-Mi Zhao and Xue-En Wu, on 28 July 1973.
Paratypes CIB 8419 (field no. T8370131), adult female, from Ani Bridge, Beibeng Town, Mêdog County, Nyingchi City, Xizang Autonomous Region, China (ca. 1200 m a.s.l.), collected by Sheng-Quan Li, on 18 July 1983. CIB 118523 (field no. JK202005293), adult female, from Ani Bridge (29°3289′ N, 95°1780′ E, ca. 1087 m a.s.l.), Beibeng Town, Mêdog County, Nyingchi City, Xizang Autonomous Region, China, collected by Xiao-Yong Ding in May, 2016. CIB 118524 (field no. LAB2019437), adult female, from the forest near Hanmi (29°3809′ N, 95°112′ E, ca. 2280 m a.s.l.), Mêdog County, Nyingchi City, Xizang Autonomous Region, China, collected by Xiao-Yong Ding in September, 2019.
Diagnosis. (1) Body cylindrical, TL 387–679 mm; (2) tail relatively long, TaL/TL 0.262–0.317; (3) dorsal scale rows 19-19-17; all keeled or may not be so on outermost rows; (4) ventrals 153–167; (5) cloacal plate and subcaudals divided; (6) subcaudals 79–97; (7) supralabials 8–9, 3rd–5th or 4th–6th entering orbit; (8) maxillary teeth 20–21, slightly enlarged posteriorly, last two distinctly enlarged, separated from anterior teeth by small diastema; (9) hemipenis short and thin, shallowly bilobed, spinous throughout with a single basal hook; (10) sulcus spermaticus single, centripetal, extends to crotch; (11) a light, dark-bordered crescent extending from the last supralabial up and back over the nape; (12) dorsum reddish-brown in life, speckled with short dark stripes; (13) venter reddish-orange in life, each ventral decorated with dark spots at lateral edge (Figure 7).
Description of the holotype. Body slender, TL 519 mm, cylindrical and elongate; head moderately large, HL/SVL 0.03, HL/HW 1.49, moderately distinct from neck; snout broad, obtuse as seen from above; eye large, EW 2.65 mm, EW/SOL 2.64; pupils round; nostrils crescentic, piercing in the middle of the nasal, directed laterally.
Dorsal scale rows 19-19-17, moderately keeled throughout, scales of the first dorsal scales keeled just after neck; notched at apex.
Dorsal scale row reductions (Formula (1)):
Two preventrals, ventrals 158; tail complete, particularly long, TaL 165 mm, TaL/TL 0.317, tapering posteriorly; subcaudals 96, all paired, with single terminal rod; cloacal plate divided.
Position of the reduction to 6 suprascale rows around the tail at 20th SC. Range, in number of subcaudals spanned, of the portion of the tail with 6 supracaudal scale rows from 20th–44th SC, 25 subcaudals in total; range of the length of tail with 4 supracaudal scale rows: 47th–87th SC, 41 subcaudals in total; ratio: length with 4 supracaudal scale rows/length of the portion of tail with 6 supracaudal scale rows: 1.64.
Dorsal side of head scales complete including 2 internasals, 2 prefrontals, 2 supraoculars, 1 frontal, and 2 parietals. Rostral wider than high, width approximately twice as long as high, visible from above; nasals subpentagonal, slightly elongate, about 1.2 times longer than high, completely divided, anterior part slightly larger than the posterior one; nostrils located on the anterior part of nasals; internasals subtriangular, in broad contact with each other, not in contact with loreal, about equal length to width, distinctly narrowing anteriorly, the width of the posterior margin approximately twice as long as the anterior margin; 2 prefrontals, subhexagonal, slightly broader than long, about 1.3 times longer than internasals; prefrontal sutures about equal length to internasal sutures; frontal pentagonal, elongate, length 1.45 times longer than width, about twice as long as prefrontal; supraocular 1/1, rectangular, elongate, narrowed anteriorly, about 2.1 times longer than width; parietals large, length 1.95 times longer than width, 1.5 times longer than frontal; parietals in broad contact with each other, parietal suture subequal to length of frontal. Loreal 1/1, subquadrangle, small, about equal in length to depth, in contact with 2nd–3rd supralabials, not entering orbit; preoculars 1/1, depth about 1.7 times longer than width, about two times higher than loreal; postoculars 3/3, size decreasing from top to bottom; supralabials 9/8, 2nd–3rd in contact with the loreal, 4th–6th entering orbit on the left side, 3rd–5th entering orbit on the right side, penultimate one largest; temporals in 3 rows, elongate, variable and asymmetric, anterior temporals 2 (left) and (1 + 1/1) (right), broadly in contact with supralabials 7–8 on the left side, supralabials 6–7 on the right side, followed by 2 + 2 (left) and 1 + 2 (right) posterior temporals; mental subtriangular, width 2.5 times longer than high; 10/9 infralabials, first pair in contact with each other after mental, 1st–5th/1st–4th in contact with anterior chin shields; chin shields pairs two; posterior chin shields 1.3 times longer than anterior ones, separated from each other by small scales; mental groove apparent (Figure 8).
Maxillary teeth 19 + 2, slightly enlarged posteriorly, last two distinctly enlarged, separate from anterior maxillary teeth by a small diastema, not grooved.
The left side of hemipenis is missing, the description of hemipenis in retracted condition is based on the right side. The organ is shallowly bilobed, retracted hemipenis extending to SC 7 with its crotch extending to SC 6; the fork point of m. retractor penis magnus extending to SC 8, origin of m. retractor penis magnus at level of SC 21.
Coloration in preservative. Dorsal surface of head overall creamish-beige, yellowish-brown or blackish-brown, usually more distinctly paler on anterior half of head (Figure 9). Upper surfaces of internasals, anterior sides of prefrontals, and central part of frontal yellowish-beige, sparsely decorated with irregular blackish-brown spots. Upper cephalic scales irregularly and incompletely edged with blackish brown; these dark outlines of dorsal head scales usually become more distinct on their posterior margins. Lateral sides of parietals distinctly darker, almost forming two thick lateral stripes along the outer margins. Parietals speckled with dark brown, a pair of elliptic beige spots symmetrically present on inner sides of corresponding scales, just separated by parietal sutures. A six-scales-long, two-scales-wide beige sagittal line extends just behind parietal suture. Coloration of sides of the head distinctly separated by a narrow, oblique, dark streak, which originates from posterior margins of nasals, goes through upper edges of loreal and preocular, extends from middle postocular downwards to last supralabials until corner of mouth. Coloration above this dark streak as upper surface of head, whereas that below uniformly creamish-beige. Posterior edges of supralabials 1–3, upper margins of 4th–6th (left) or 3rd–5th (right) supralabials bordered by darker stripes. Posterior bottom corners of penultimate supralabials with a dark spot. Chin and throat uniformly creamish-yellow; anterior margin of mental and posterior corners of last two infralabials with faint, darker edges.
Dorsal surface of body umber or dark brown. Some dorsal scales are slightly darker, each dorsal scale more or less scattered with paler spots. A conspicuous, pale (cream or pale yellow), V or Y-shaped chevron extends onto neck, starting on each side from behind last supralabial and reaching upper surface of neck, pointing backwards, not in contact with beige sagittal line just behind parietal suture. Venter uniformly creamish-yellow, with outer edges of ventral scales dark brown or blackish-brown, in contact with the short streaks of lower edges of 1st DSR. Ventral surface of subcaudals uniformly colored as venter (Figure 9).
Description of paratypes and variation. Paratypes and other specimens known generally resemble the holotype in morphological characters, except for having a wider range of total length (TL 387–679 mm vs. 519 mm) and a slightly shorter tail (TaL/TL 0.262–0.313 vs. 0.317). They have 153–167 ventrals (vs. 158 in the holotype), 79–97 subcaudals (vs. 96), and the following dorsal scale row reductions (Formula (2)):
Notably, CIB 8419 has a different dorsal scale row formula 18-19-17 (vs. 19-19-17); CIB 107855 has two preoculars and two postoculars on both sides, 8 infralabials on the left side; CIB 107855 and CIB 118524 have divided subcaudals but the 8th and 7th–9th are single, respectively. Both the anterior and posterior temporals are asymmetric and highly variable, aTEM 1–2 or (1 + 1/1) and pTEM in 2, 1–2 + 2 or 1/(1 + 2) (Figure 10; Table 3).

Table 3.
Morphological characters of Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov. specimens.
Coloration in life. In life, dorsal surface of head and neck are bright yellowish brown; the background color of supralabials, loreals, and lower part of preoculars is yellowish off-white; posterior corner of eye streak is bordered with reddish orange (Figure 7 and Figure 8). The sagittal line just behind the parietal suture and the chevrons along each side of neck are bright reddish orange, slightly paler than the background color of neck, barely visible in general view. The dorsal surface of body is yellowish-brown, brownish-red, or reddish-ochre, gradually tending to become darker towards the posterior part of the body, sparsely speckled with small dark blotches and spots, especially on the outer margins of dorsal scales. The background color of the lateral surface is darker than dorsal body surface, giving a dark maroon hue; caudal scales are narrowly edged with dark grey, forming several continuous or not, dark zigzag streaks on the posterior part of the tail.
The ventral surface of head is creamish-white, speckled with dark, grey, and beige, especially on the posterior margin of the infralabials. The first preventral is as throat, whereas the second preventral is decorated with bright reddish-orange. The ventral surface of body is glossy bright jacinth, reddish-orange or even scarlet posteriorly, distinctly separated from ventral head surface from the first ventral scale and throat. Ventral scales are ornated with a pair of more or less conspicuous blackish-brown spots on both sides, these spots progressively become larger and more distinct posteriorly and do not connect with each other. The ventral part of the tail is the same as the venter, whereas the subcaudals are more or less decorated with lateral blackish spots and nearly immaculate towards tail tip.
Hemipenis. The description of hemipenis in everted condition is based on the left side of CIB 107855 (Figure 11A). The organ is thin and short, hemipenial total length (HTL) 10.7 mm, hemipenial total width (HTW) 3.0 mm. HTL/HTW 3.6; Y-shaped, shallowly bilobed, hemipenial truncus length (HCL): 9.8 mm, HCL/HTL 0.92. Both the sulcate and asulcate surfaces are densely ornamented with spines and spinules; a large basal hook is present at the proximal part of truncus, which at least two times higher than the adjacent spines. The sulcus spermaticus is single, extending to the base of inner right lobe where it takes a centripetal position. Sulcus lip highly developed and raised, walls covered with spinules.
In situ, the hemipenis extends up to SC 6–7 with its crotch extending to SC 4–6; the fork point of m. retractor penis magnus extends to SC 7–8, the origin of m. retractor penis magnus invariably at level of SC 21.
Comparisons.Herpetoreas tpsersp. nov. was previously misidentified as Hebius parallelus [13]. The new species differs from Heb. parallelus by having (1) a longer tail (TaL/TL 0.262–0.317 vs. 0.221–0.252), (2) more subcaudals (79–97 vs. 63–77), (3) fewer preoculars (usually a single preocular vs. 2 preoculars); (4) more strongly keeled dorsal scales (1st dorsal scale row moderately keeled throughout vs. smooth or at best feebly keeled); (5) the presence of a chevron on the upper part of the neck (vs. absent); (6) a different ventral color in life (ventral surface of body and tail bright jacinth, reddish-orange to scarlet vs. pale yellow).
Herpetoreas tpsersp. nov. is the sister taxon of Her. burbrinki with current samplings in our molecular phylogeny (Figure 1). It can be separated from the latter species by having (1) a shorter body length (maximum TL 679 mm vs. 757 mm in Her. burbrinki), (2) fewer ventrals (153–167 vs. 169–172), (3) a more restricted range of subcaudals with 6 supracaudal scale rows (25–31 scales vs. 40–41 scales), and (4) a different dorsal color pattern (dorsal scales irregularly speckled with small dark blotches or spots with no definite pattern vs. each side of body with a faint yellowish dorsolateral stripe).
For the other four congeners, Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov. differs from Her. platyceps by having 153–167 ventrals (vs. 180–234 ventrals), the location of the 1st subcaudal at which the tail has 6 supracaudal scale rows (1st SC6) between SC 13th–30th (vs. SC 9th), sulcus spermaticus extending to the crotch (vs. extending to the tip); from Her. sieboldii by having 153–167 ventrals (vs. 168–207 ventrals), the proportion of the length of the tail with 4 supracaudal scale rows to that with 6 supracaudal scale rows (SC4/SC6) 1.06–1.64 (vs. 0.53), sulcus spermaticus extending to the crotch only vs. extending to the tip of the lobes; from Her. pealii and Her. xenura by having divided cloacal plate and subcaudals (vs. cloacal single in Her. pealii and Her. xenura, and subcaudals all single in Her. xenura).
In addition, Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov. may be confused with Hebius clerki; it can be distinguished from the latter species by the presence of a diastema before the enlarged maxillary teeth (vs. absent in Heb. clerki), a different ventral color in life (ventral surface of body and tail bright jacinth, reddish-orange to scarlet vs. bright yellow to white). For the morphological differences with reference to other members of the genera Amphiesma and Hebius, see the discussion below.
Etymology. The specific epithet tpser (pronounced as “/tɪpsər/”) is the acronym of “Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research” of China, which greatly promoted the scientific research of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. All specimens of Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov. were collected during The First/The Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research.
We suggest “Mêdog Himalayas Keelback” as its English common name, and Mò Tuō Fù Liàn Shé (墨脱腹链蛇) as its Chinese common name.
Distribution and Natural history.Herpetoreas tpsersp. nov. is presently only known from Beibeng and adjacent Ani Bridge, Hanmi, and 80K, Mêdog County, southeastern Xizang Autonomous Region (Tibet), southwestern China, at an altitude of 1087–2280 m a.s.l. This species inhabits evergreen broad-leaf forest or the moist fields of forest margins covered with dense vegetation close to the water (Figure 12). All known specimens were collected in daytime, on a cloudy or mildly rainy day; this species is possibly diurnal. The species has a fierce disposition and bites when handled, often holding the mouth open while on the defensive.
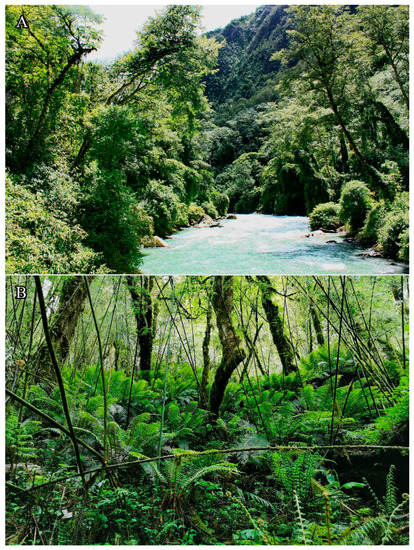

Figure 12.
Habitat of Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov. in Mêdog County, southwestern Xizang Autonomous Region, southwestern China. (A) Ani Bridge; (B) Hanmi. Photographs by Ke Jiang.
Herpetoreas tpsersp. nov. was observed sympatrically with Amolops aniqiaoensis, Trimeresurus medoensis, Protobothrops kaulbacki, and Elaphe taeniura in Ani Bridge (~1100 m a.s.l.), with Polypedates braueri, Zhangixalus burmanus, Nanorana medogensis, Japalura austeniana, Asymblepharus nyingchiensis, and Ovophis zayuensis in 80 K (~2100 m a.s.l.), with Amolops medogensis, Nanorana medogensis, Ovophis zayuensis, Protobothrops jerdonii, and Pseudoxenodon macrops in Hanmi (~2200 m a.s.l.).
Comments.Herpetoreas tpsersp. nov. was previously misidentified as Hebius parallelus. Although the Tibetan record of Heb. parallelus has been clarified in this work, other records outside China still need to be studied. For example, another specimen (KSC 414) reported from Nagaland, northeastern India largely agrees with Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov. but differs from the latter in its strongly colored and patterned dorsal coloration (see Ao et al. [123]: Figure 1 and Figure 2), which should be identified as Heb. clerki [11]. Furthermore, Kramer [72] doubted the occurrence of Heb. parallelus west of 88° E and supposed that the Nepalese records might be questionable. The description of Heb. cf. parallelus from Nepal provided by Schleich et al. [82] is similar to Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov. except for having a slightly higher number of ventrals (163–172 vs. 153–167) and a pair of parietal spots (vs. absent). Thus, the systematics of the genus Herpetoreas still remain poorly known, and its biodiversity probably has been underestimated.
4. Discussion
4.1. Morphological Characters of the Genera Previously Confused with Amphiesma
The genus Herpetoreas has long been considered as a synonym of the genus Amphiesma, mainly due to its morphological similarities [1,3,14]. Guo et al. [3] divided the genus Amphiesma auctorum into three genera—Amphiesma, Hebius, and Herpetoreas based on their phylogenetic results. The morphological diagnoses of these three genera have long remained to be elusive [3], which broadly caused taxonomic confusions [7,8]. Although the diagnostic key provided by Ren et al. [2] includes three genera of the former genus Amphiesma sensu lato, it could be only applied to species known from China and Vietnam. More importantly, it has been a challenging task to elucidate a morphological diagnosis of these three morphologically similar and speciose genera, especially for their conservativeness of pholidosis characters and general appearance. For example, these three genera previously confused with Amphiesma are similar to each other in having the following key generic diagnosis in the family Natricidae [124,125]: (1) head moderately distinct from neck; (2) nostrils situated and directed laterally or dorsolaterally; (3) eyes relatively moderate to large; (4) prefrontals mostly paired; (5) common dorsal scale rows, as 19-19-17; (6) largely overlapped ventral scale counts, as 118–158 in Amphiesma, both min. and max. in A. stolatum [6]; as 101–187 in Hebius, min. in Heb. viperinus [126], max. in Heb. arquus [127]; as 136–234 in Herpetoreas, min. in Her. pealii, max. in Her. platyceps (Table 2). Thus, the general morphological features cannot distinguish Amphiesma sensu lato.
Hemipenial morphology has been widely applied for diagnosis in the family Natricidae, especially at a genus level [1,24,128]. Malnate [1]: 47 also highlighted the effectiveness of hemipenial morphology and maxillary teeth in generic identifications of natricid taxa. We compared pholidosis, hemipenial morphology, and maxillary teeth of Amphiesma sensu lato, and found that different genera could be readily distinguished by a suit of characters including (1) the number of supralabials in contact with the nasals; (2) the diastema before the distinctly enlarged posterior maxillary teeth; (3) the direction of progression of the sulcus spermaticus; (4) the position of the distal end of sulcus spermaticus; (5) the relative size of the basal hook of the hemipenis; (6) the degree of heterogeneity between the left and right lobe of the hemipenis; (7) the conditions of apical naked areas of the hemipenis (protruding or not); and (8) the visibility of apical naked area from asulcate surface (Figure 11; Table 4).

Table 4.
Morphological comparisons among different genera of Amphiesma sensu lato.
Specifically, the genus Amphiesma is the most morphologically distinct genus among the three different genera of Amphiesma sensu lato, which could be also reflected by its distant related phylogenetic relationship with reference to both Hebius and Herpetoreas (Figure 1, also see Deepak et al. [10]). The genus Amphiesma differs from both Hebius and Herpetoreas in having (1) only the 1st supralabial in contact with nasal vs. 1st–2nd supralabials in contact with nasal; (2) sulcus spermaticus extends to the middle of crotch vs. extends to the base or the tip of inner side of right lobe; (3) basal hook slightly higher than the adjacent spines vs. basal hook at least two times higher than the adjacent spines; (4) hemipenis sparsely ornamented with spines vs. densely ornamented with spines (Figure 11; Table 4). Furthermore, the genus Amphiesma differs from Hebius in having a diastema before the distinctly enlarged diastema vs. absent. Although the hemipenial morphology is currently unknow for A. monticolum, a second member of Amphiesma [10], the character that 1st supralabial in contact with nasal is still capable of identification.
Secondly, Herpetoreas is different from Hebius in the morphology of maxillary teeth and hemipenis. Herpetoreas differs from Hebius in having the presence of diastema before the distinctly enlarged posterior maxillary teeth vs. absent in Hebius. The morphology of dentition has been considered as key diagnosis in the taxonomic history of natricid snake since Malnate [1], and this character is proved to be conservative within a given genus, such as Fowlea [130,131], Rhabdophis (only except for some ecological specialists) [132], and Opisthotropis [125]. Thus, the dentition is considered to be of significant value in distinguishing Herpetoreas from Hebius.
Additionally, although it has been broadly demonstrated that hemipenial morphology is a key morphological diagnosis in the taxonomy of Reptilia [23,133,134], very few are known in the genus Hebius and Herpetoreas [8,24,128,129]. Das et al. [8] briefly compared the hemipenial morphology within the genus Herpetoreas, while their differences among Amphiesma sensu lato remained unknown. Nevertheless, based on our current samplings, Hebius and Herpetoreas could also be distinguished from each other by hemipenial morphology. The morphology of hemipenis in Hebius has been depicted as shallowly bilobed, densely spinose, with nude crotch and a single sulcus spermaticus mostly extending to the base (sometimes the tip) of short lobes [24,128,129]. The apical naked area in the genus Hebius is highly developed, which extends proximally onto the asulcate surface (e.g., in Heb. venningi, see Cadle [128]: 9) or protrudes from crotch to different degree (e.g., in Heb. optatus, see Zhang et al. [24]: 41, Figure 52B and Appendix C, Figure A1H). Although this apical naked area has been previously recorded, few attentions have been given to the distinct hemipenial character, which is rare in other Asian natricid taxa and regarded to be significant [128,133,134]. In the current study, two distinct morphs of hemipenis are defined in the genus Hebius, based on the degree of crotch protrusion and the shape of lobes, which includes (1) morph I: apical naked area slightly protruded with relatively long and slender lobes (Figure 13C2); (2) morph II: apical naked area distinctly protruded with relatively short and vestigial lobes (Figure 11B and Figure 13(C3,C4), Appendix C). The genus Herpetoreas, in contrast to Hebius, differs from all the two Hebius morphs in having less developed apical nude area, which is invisible from asulcate surface vs. well-developed apical nude area, which is visible from the asulcate surface in Hebius (Figure 13).
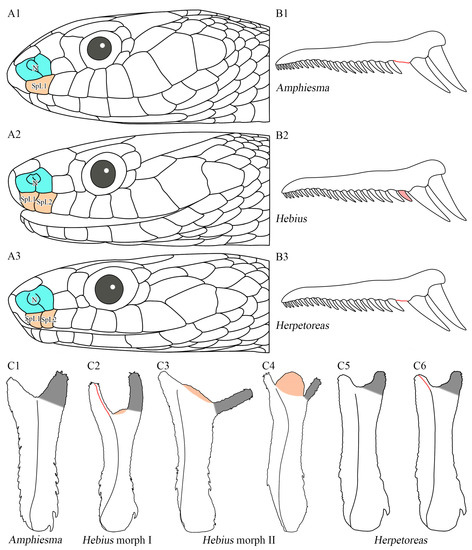
Figure 13.
Comparisons of morphological features of Amphiesma sensu lato, showing diagnostic characters among the genera Amphiesma, Hebius, and Herpetoreas. (A) lateral head view, showing different numbers of supralabials (SpL, in orange) in contact with nasals (N, in blue) in different genera: (A1). Amphiesma stolatum, YBU 12081A; (A2). Hebius boulengeri, SYS r001680; (A3). Herpetoreas tpser sp. nov., CIB 107855. (B) schematic diagrams of maxillary teeth and diastema (in red) in different genera: (B1). Amphiesma, diastema present; (B2). Hebius, diastema absent; (B3). Herpetoreas, small diastema present. (C) schematic diagrams of hemipenial morphology in different genera, showing differences in direction and the position of the distal end of sulcus spermaticus (in red); the area of apical naked areas (in orange); and the condition of the left lobe of hemipenis (in grey). Not to scale. Line drawings by Jin-Long Ren.
Consequently, we emphasize the importance of hemipenial morphology and maxillary teeth in generic identifications of the Family Natricidae, due to the conservative evolution of pholidosis characters in natricid snakes [1]. Nevertheless, Hebius is the most specious genus in Natricidae (~47 species) [99,135], and morphological data of more species are also needed to improve the diagnosis.
Key to the three genera of previously confused with Amphiesma
1A Nasal in contact with 1st supralabial only; sulcus spermaticus extends straight to the center of the crotch.................................................................................Amphiesma
1B Nasal in contact with 1st–2nd supralabials; sulcus spermaticus laterally extends to the side of crotch or inner right side of lobe...........................................................2
2A Diastema before enlarged posterior maxillary teeth present; (hemipenis) apical naked area on the crotch weakly developed, not protruding, not visible from asulcate surface.............................................................................................Herpetoreas
2B Diastema before enlarged posterior maxillary teeth absent; (hemipenis) apical naked area highly developed, protruding to different degree, visible from asulcate surface............................................................................................................Hebius
4.2. Generic Assignment of Some Hebius Snakes
After the taxonomic revision of Amphiesma sensu lato, Hebius parallelus was considered as a member of Hebius based on molecular phylogenetic results [3]. David et al. [11] subsequently confined Heb. parallelus to northeastern India only, and revalidated Amphiesma clerki to the genus Hebius to accommodate populations from the Eastern Himalayas, northern Myanmar, and western Yunnan, China. Therefore, the sample of Heb. parallelus (CAS 215036) from Yunnan, China used in Guo et al. [3] would actually represent Hebius clerki (Figure 1; Table 1). Recently, Che et al. [13] reconstructed the phylogenetic tree of the genus Herpetoreas with inclusion of sample of Hebius cf. parallelus from Mêdog, Tibet, China and transferred the species to Herpetoreas. However, our results indicated that the taxon identified as Hebius cf. parallelus from Mêdog, Tibet, China is a misidentification of the new species Herpetoreas tpser described above.
We cannot here ascertain the generic position of Hebius parallelus (Tropidonotus parallelus Boulenger, 1890: 345. Type locality, by virtue of lectotype designation: “Sikhim”, i.e., now Sikkim, India). The lectotype was designated by Kramer [72]: NHMUK 1946.1.13.53, adult male; collected and deposited by Sir Joseph Dalton Hooker. No genetic sequence of this rare species is available. However, we noticed that Heb. parallelus is similar to species currently referred to Herpetoreas in having (1) a similar number of maxillary teeth, 21–22 vs. 13–23 min. in Her. pealii, max. in Her. xenura, (2) posterior teeth distinctly enlarged, (3) the presence of diastema before the enlarged maxillary teeth. Nevertheless, we here refrain from referring Hebius parallelus to the genus Herpetoreas pending the availability of phylogenetic analyses.
Since the diagnostic characters of species previously referred to Amphiesma sensu lato have long been unclear, the generic assignments of several Hebius taxa to the genus Hebius were recently found to be inappropriate [7,8]. Moreover, Guo et al. [3] also rightly suggested that the genus Herpetoreas may contain additional species then referred to Hebius. Particularly, the generic allocation of a newly described species, namely, Hebius lacrima Purkayastha and David, 2019, needs to be further ascertained. Hebius lacrima agrees with the diagnosis of Herpetoreas in having “24 gradually enlarged maxillary teeth, followed, with a diastema, by 3 distinctly enlarged posterior teeth”, a major difference from the genus Hebius [113] (Table 4; Figure 13B). The morphological differences provided by Purkayastha et al. [113] also cannot distinguish it from Herpetoreas when one takes all present members of the latter genus into account, including (1) ventrals scales counts 147 in Heb. lacrima vs. 136–234 (min. in Her. pealii; max. in Her. platyceps), and tail length ratio TaL/TL, 0.301 in Heb. lacrima vs. 0.227–0.317 (min. in Her. pealii; max. in Her. tpser). The distribution range of Hebius lacrima also falls within the known distribution range of Herpetoreas. Therefore, we question the generic assignment of Hebius lacrima, and recommend further molecular phylogenetic analyses to clarify the taxonomic confusions still present among species of the former genus Amphiesma sensu lato.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-T.L.; methodology, J.-L.R.; software, K.J.; validation, J.-J.H., and P.D.; formal analysis, J.-L.R. and P.D.; investigation, K.J.; resources, J.-T.L.; data curation, J.-L.R.; writing—original draft preparation, J.-L.R., K.J. and J.-T.L.; writing—review and editing, J.-L.R. and P.D.; visualization, J.-J.H.; supervision, J.-T.L.; project administration, J.-T.L. and K.J.; funding acquisition, J.-T.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (STEP) (2019QZKK0501); Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, CAS (QYZDB-SSW-SMC058); the International Partnership Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (151751KYSB20190024); Biological Resources Programme, Chinese Academy of Sciences (KFJ-BRP-017-14, KFJBRP-017-65); the CAS“Light of West China” Program (2018XBZG_JCTD_001) and Talent Program from Organization Department of Sichuan Provincial Committee.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CIBDWLL2021023, 21 December 2021). Research procedures were carried out in accordance with national and institutional regulations.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Names of the new species were formally registered in the database ZooBank (http://zoobank.org (accessed on 26 November 2021)). Specimens were deposited in the Herpetological Museum, Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CIB). The newly generated sequences were deposited in GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank (accessed on 26 November 2021)).
Acknowledgments
We thank Xiao-Yong Ding for his help in the field; Shuo Qi (SYS), Mian Hou (Sichuan Normal University), and Gernot Vogel (Society for Southeast Asian Herpetology) for providing photos; Di-Hao Wu for photograph editing; Anastasio Zographos (Montmorency, France) for his assistant with classical Greek nouns. It is a pleasure to thank Ying-Yong Wang (SYS), Zhi-Tong Lyu (SYS), Jian Wang (SYS), Ke Lv (CIB) for the loan and examination of specimens; Kai Wang for his help in specimen examination. We are also grateful to all curators of museums and institutions cited in the “Materials and Methods” for having allowed us to specimens deposited in their collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Specimens Examined (n = 225). * Indicates Hemipenes Examined
Genus Amphiesma Duméril, Bibron, and Duméril, 1854 (n = 5)
Amphiesma stolatum (n = 5) China. Guangdong Province. SYS r000052, Renhua County, Mt. Danxia; SYS r002147, Xinyi City, Dawuling. Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. SYS r001727*, Chongzuo City, Longzhou County; KIZ 7I0015, Chongzuo City, Nalong, 230 m. Yunnan Province. KIZ 79012, Pingbian County, Qianjin, 960 m.
Genus Hebius Thompson, 1913 (n = 180)
Hebius annamensis (n = 1). Vietnam. Quang Tri Province. ROM 33290, “Bau Cap”.
Hebius atemporalis (n = 5). China. Yunnan Province. KIZ 090312, KIZ 09124, YBU 14259, Mengzi County; KIZ 79013, Pingbian County, Qianjin; KIZ 91II0001, Kunming City, Huahongdong, 2100 m.
Hebiuscf. bitaeniatus (n = 9) China. Yunnan Province. KIZ 90I165, KIZ 90I174, Dayao County, Santai, 2100 m. Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. YBU 11204–05, Tianlin County, Cenwanglaoshan. Guizhou Province. SYS r002171*, Shuicheng County, Yezhong; YBU 11136–37, YBU 14137, Leishan County, Mt. Leigong; YBU 12150, Rongjiang County, Pingyang.
Hebius boulengeri (n = 17). China. Guangdong Province. SYS r001506, SYS r001680*, SYS r001685, SYS r001900, CIB 118637*, Xinyi City, Dawuling; SYS r001749, SYS r001801, SYS r002016, Gaozhou City, Xianrendong; SYS r000223, Fengkai County, Heishiding; SYS r001179, Chaozhou City, Jiaoshuikeng Village; SYS r002210, Shixing County, Chebaling. Fujian Province. YBU 12163, Dehua County, Mt. Daiyun. Jiangxi Province. SYS r001003, Xunwu County, Jilong Village; SYS r001371, Xinfeng County, Mt. Jinpen. Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. SYS r001552, Huanjiang, Mt. Jiuwan. Yunnan Province. KIZ 79I034, Cangyuan County, 1200 m. Vietnam. Vinh Phuc Province. VNMN 06218, Tamdao, 687 m.
Hebius chapaensis (n = 10). Vietnam. Lao Cai Province. VNMN 05791, VNMN 06102–106, Sa Pa; VNMN 3277, Bat Xat, Y Ty, 2030 m. China. Yunnan Province. YBU 14026, Pingbian County, Mt. Dawei, 1993 m; CIB 110718*, Mengla County; SYS r001240, Mengla County, Zhushihe Village, 930 m.
Hebius craspedogaster (n = 11) China. Zhejiang Province. SYS r002253, SYS r002469, Suichang County, Wangcunkou Town, 780–810 m; YBU 17186, Dongyang City, Xujiazhuang. Fujian Province. CIB 8250–52, Nanping City, Mt. Wuyi, 730–1100 m. Jiangxi Province. SYS r000735, SYS r000901, Shangrao City, Mt. Tongbo. Hunan Province. SYS r000878*, SYS r002093, Shuangpai County, Mt. Yangming. Guizhou Province. KIZ 7620755, Leishan County.
Hebius johannis (n = 3) China. Yunnan Province. CIB 103939, Yulong County, Shuhe Ancient Town, 2457 m; KIZ 79001, Ninglang County; SYS r002402, Chengjiang County.
Hebius khasiensis (n = 4) China. Yunnan Province. SYS r002568, Yingjiang County; CIB 118636*, CIB 118641*, Mengla County; KIZ 75I399, Menglian County, Lafu Village, 1620 m.
Hebius metusia (n = 23) China. Sichuan Province. CIB 78163–64, SYS r001604*, Hongya County, Mt. Wawu; CIB 8168, Hongya, Liujiang; CIB 101971–72, Tianquan County, Xingou Town, 1400 m; YBU 16129, Yingjing County, Xinmiao Town; CIB 101973, CIB 106522, YBU 16142, YBU 19076, Shimian County, Liziping, 2030 m; YBU 16143, Shimian County, Dahongshan; YBU 17254, Shimian, Tianwan Town; YBU 17255, Shimian County, Huilong Town; CIB 102742, Lushan County, Dachuanhe, 2017 m; CIB 8176, SYS r000725, Leshan City, Mt. Emei, 1100 m; YBU 18231–233, Ebian County, Heizhugou; YBU 15178–79, Muchuan County; CIB 118638*, Mianning County, Yele Town.
Hebius modestus (n = 10) China. Yunnan Province. CIB 72352–53, Tengchong City, Dakun Village, 1720 m; CIB 8275, Baoshan City, Bawan Village, 1800 m; KIZ 79I098, KIZ 79I300, Yongde County, 1560–1900 m; KIZ 75I324, Menglian County, Lafu Village, 1620 m; SYS r002185*, Xinping County. Guizhou Province. CIB 8276–67, Luodian County, Bamao Town, 920 m. Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. SYS r001557, Tianlin County, Cenwanglaoshan, 1500 m.
Hebius octolineatus (n = 7). China. Yunnan Province. YBU 14425–26, Xundian County, Qixing Town; KIZ II0492, KIZ II0495, Ludian County, 2500 m; KIZ 94602, Kunming City, Xiama Village. Guizhou Province. KIZ 781105, KIZ 781308, Weining County.
Hebius optatus (n = 6) China. Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. KIZ 750001, Daxin County; KIZ 780378, Quanzhou County, Dongshan; SYS r001629, Longshen County, Huaping, 800 m. Guizhou Province. SYSr002081–SYSr002082, Jishou City, Aizhai Town. Sichuan Province. Unlabaled*, Yibin City.
Hebius parallelus (n = 18). India. Sikkim (?). BMNH 1946.1.13.53 (lectotype of Tropidonotus parallelus Boulenger, 1890), “Sikkim”. Meghalaya. BMNH 1946.1.12.83–84, BMNH 1946.1.13.48 (3 former syntypes of Tropidonotus parallelus Boulenger, 1890), “Khasi Hills”; ZSI 3852, “Shillong”; ZSI/ERS 112, ZSI/ERS 205, ZSI/ERS 2785, ZSI/ERS 3076–3077, Shillong, Risa Colony; ZSI/ERS 272, ZSI/ERS 9059, Shillong, Tripura Castle Road; ZSI/ERS 450, ZSI/ERS 970, Shillong, Fruit Garden; ZSI/ERS 3253, East Khasi Hills District, Mawlai; ZSI/ERS 8262, East Khasi Hills, Mawphlang; ZSI/ERS 9060, Garo Hills, Selbelgiri. Nagaland. Unpreserved specimen, near the Tragopan Sanctuary (25.63549N-094.01261E), Khonoma. No locality. ZSI 4397, “Madras Hills”, in error.
Hebius popei (n = 16) China. Hainan Province. CIB 118640*, Lingshui County, Mt. Diaoluo; YBU 17001, Ledong County, Jianfengling. Guangdong Province. SYS r002252*, Yingde City, Shimentai; SYS r000091, SYS r000558, SYS r001065, Renhua County. Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. SYS r001532, Guanyang County, Qianjiadong, 1000 m; SYS r001634, Longsheng County, Huaping, 600 m; SYS r002517, SYS r002519, Guiping City, 73–293 m; YBU 19016, Cangwu County, Mushuang Town. Jiangxi Province. SYS r000073, SYS r000081, Guixi City, Yangjifeng. Hunan Province. SYS r002091, Shuangpai County, Mt. Yangming. Guizhou Province. KIZ 791143, Libo County, Chengguan; SYS r000237, Libo County, Maolan.
Hebius sangzhiensis (n = 3) China. Hunan Province. SYS r001397 (paratype of Hebius sangzhiensis), CIB 118639*, Sangzhi County, Mt. Tianping; YBU 16145, Sangzhi County, Mt. Badagong.
Hebius sauteri sauteri (n = 10) China. Taiwan Province. CAS 18984, Pingtung County; CAS 18988 (paratype of Natrix copei Van Denburgh, 1909), Tainan City, Guanziling. Hainan Province. YBU 17001, Ledong County, Jianfengling. Jiangxi Province. SYS r000323*, Ji’an City, Mt. Jinggang; SYS r000162, SYS r001258, SYS r001266*, Longnan County, Mt. Jiulian, 400 m. Hunan Province. SYS r001766*, Guidong County, Mt. Bamian. Guangdong Province. SYS r001150, Xinyi City, Sihe Town. Guizhou Province. SYS r000275, Libo County, Maolan.
Hebius sauteri maximus (n = 3) China. Sichuan Province. CIB 118635*, Yibin City, Mt. Laojun; YBU 18170, Dujiangyan City, Jiezi Town. Guizhou Province. SYS r002041*, Bijie City, Xiachang Village.
Hebius septemlineatus (n = 10) China. Yunnan Province. KIZ 74II0177, KIZ 74II0183, Tengchong County, Dakuang, 1800 m; SYS r001223, SYS r001225*, Tengchong County, Mt. Gaoligong, 2040 m; YBU 15161–62, Tengchong County, Mazhan Town; KIZ 75II0235, KIZ 75II0236, Yingjiang County, Tongbiguan, 1350 m; KIZ II0511, KIZ II0520, Longchuan County, 800–1300 m.
Hebius venningi (n = 5) Myanmar. Kachin State. CAS 238901, Myitkyina District, Moenyin Township, 358 m. Chin State. CAS 233206, Phalum District, Haka Township, 1634 m; CAS 235175, Mindat District, Mindat Township, 992 m; CAS 234777, Mindat District, Kanpatlat Township, 1238 m. No locality. YBU 18229.
Hebius vibakari (n = 3) China. Jilin Province. SYS r002217, Huinan County, Longwan. Russia. ZISP 15546, ZISP 16073, “Far East”.
Hebius weixiensis (n = 5) China. Yunnan Province. CIB 8257–59, KIZ II0501, Yulong County, Ludian Town, 2500 m; SICAU 2020082701*, Weixi County, Gongnong Village, 2127 m.
Hebius yanbianensis (n = 1) China. YBU 15018 (holotype of Hebius yanbianensis), Yanbian County, Zemulong Town.
GenusHerpetoreasGünther, 1860 (n = 40)
Herpetoreas burbrinki (n = 1) China. Xizang Autonomous Region. YBU 071128 (holotype of Herpetoreas burbrinki), Zayü County.
Herpetoreas platyceps (n = 9). India. Sikkim. FMNH 15827, “Mangpu, Sikkim”. West Bengal. NMW 22383:2, NMW 22383:5, Darjeeling. Himachal Pradesh. NMW 18569, NMW 18570:1–2, Shimla and Kullu (Syntypes of Zamenis himalayanus Steindachner, 1867). Jammu and Kashmir. MNHN 1988.6484, Udamphur District, between Makambagi and Ularbagi, above Doda, about 2800 m; ZMB 7293, “Kashmir”. China. Xizang Autonomous Region. CIB 8420, Nyalam County, Zhangmu, 2400 m.
Herpetoreas sieboldii (n = 24). India. Sikkim. ZMB 10231, no precise locality. West Bengal. CAS-SU 15973, Darjeeling; NMW 22383:1, NMW 22383:3–4, Darjeeling. China. Xizang Autonomous Region. CAS 177474, CAS 177672–177673, Nyalam County, Zhangmu, 2000–2500 m. Nepal. BMNH 1913.5.22.1, Mai Kola; CAS 90690, above Deppur, 1676 m; FMNH 109762, Amp Pipal, 1219 m; FMNH 131966, Chapagaon, Kathmandu Valley; FMNH 131967, Kathmandu Valley; FMNH 190856, Num Bridge across Arun River, Arun Valley; FMNH 204499, above Num, in forest area, 1950 m; MHNG 1355.72–73, near Hyangcha, Astam, 1600 m; MNHN 2003.3614, Eastern Region, between Surkie Pass and Chheskam, east of Mounasko Pass, 2400 m; ZMB 4551, “Himalaya”; FMNH 204500–504, no precise locality.
Herpetoreastpser (n = 6) China. Xizang Autonomous Region. CIB 8418 (holotype of Herpetoreas tpser), Mêdog County, Beibeng, 1300 m; CIB 8419, CIB 118523 (paratypes of Herpetoreas tpser), Mêdog County, Ani Bridge, 1087–1200 m; CIB 118524 (paratype of Herpetoreas tpser), Mêdog County, Hanmi, 2280 m; CIB 107855*, Mêdog County, Hanmi, 2127 m; KIZ 06681, Mêdog County, 80K.
Appendix B

Table A1.
Detailed information of the distribution sites showed in Figure 2.
Table A1.
Detailed information of the distribution sites showed in Figure 2.
| Taxon Name | Authority | Symbol | No. | Locality | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herpetoreas platyceps | (Blyth, 1854) | square | 1 | India: West Bengal, Darjeeling | Malnate [35] |
| 2 | India: Uttarakhand, Almora | Malnate [35] | |||
| 3 | India: Uttarakhand, Binsar | Malnate [35] | |||
| 4 | India: Himachal Pradesh, Shimla | Malnate [35] | |||
| 5 | India: Himachal, Upper Sutlej | Malnate [35] | |||
| 6 | India: Himachal Pradesh, Dalhousie | Malnate [35] | |||
| 7 | India: Jammu and Kashmir, Gulmarg | Malnate [35] | |||
| 8 | China: Xizang (Tibet), Gyirong | Che et al. [13] | |||
| 9 | China: Xizang (Tibet), Nyalam | Che et al. [13] | |||
| 10 | Nepal: widely distributed | Nanhoe et al. [73], Schleich et al. [82] | |||
| 11 | Pakistan: Punjab, Rawalpindi | Malnate [35] | |||
| 12 | Pakistan: Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Changla Gali | Khan [81] | |||
| 13 | Bhutan: Paro District, Pachu Bank | Wangyal [92] | |||
| 14 | Bangladesh: “northwest and northern part” | Ahsan et al. [89] | |||
| Herpetoreas sieboldii | Günther, 1860 | circle | 1 | India: Assam, Garo Hills, Tura | Malnate [35] |
| 2 | India: Sikkim, Gvangtok | Malnate [35] | |||
| 3 | India: West Bengal, Darjeeling | Malnate [35] | |||
| 4 | India: West Bengal, Takdah | Malnate [35] | |||
| 5 | India: Uttar Pradesh, Gonda | Malnate [35] | |||
| 6 | India: Uttarakhand, Mussoorie | Malnate [35] | |||
| 7 | India: Himachal Pradesh, Shimla | Malnate [35] | |||
| 8 | India: Himachal Pradesh, Tara devi hill | Malnate [35] | |||
| 9 | India: Jammu and Kashmir, Gulmarg | Malnate [35] | |||
| 10 | Nepal: Province No. 1, Mai Kola | Malnate [35] | |||
| 11 | Nepal: Province No. 1, Maiwa Khola | Malnate [35] | |||
| 12 | Nepal: Province No. 1, Hatia | Malnate [35] | |||
| 13 | Nepal: Bagmati Province, Thangjet | Malnate [35] | |||
| 14 | Nepal: Gandaki Province, Amppipal | Malnate [35] | |||
| 15 | Nepal: Gandaki Province, Taglung | Malnate [35] | |||
| 16 | Nepal: Gandaki Province, Lumsum | Malnate [35] | |||
| 17 | Nepal: Karnali Province, Balangra Pass | Malnate [35] | |||
| 18 | Pakistan: Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Thandiani | Malnate [35] | |||
| 19 | Pakistan: Punjab, Rawalpindi | Malnate [35] | |||
| 20 | Myanmar (?): Shan State, Taunggyi | Malnate [35] | |||
| 21 | China: Xizang (Tibet), Nyalam | David et al. [11] | |||
| 22 | Bhutan: Trashiyangtse, Bumdeling | Wangyal [91] | |||
| 23 | Bangladesh: no specific locality | Ahsan et al. [89] | |||
| Herpetoreas pealii | (Sclater, 1891) | pentagon | 1 | India: Assam, Sibsagar district | Sclater [111] |
| 2 | India: Northeast India, Siang district | Das et al. [8] | |||
| Herpetoreas xenura | (Wall, 1907) | hexagon | 1 | India: Meghalaya, Khasi Hills | Smith [6] |
| 2 | India: Nagaland, Kohima | Romer [114] | |||
| 3 | India: Mizoram, Pala Lake Area | Pawar et al. [115] | |||
| 4 | India: Mizoram, Aizawl | Pawar et al. [115] | |||
| 5 | India: Mizoram, North Hlimen | Muansanga et al. [118] | |||
| 6 | Myanmar: northwest Sagaing | Wogan et al. [117] | |||
| 7 | Myanmar: Rakhine, Rakhine Hills | Wogan et al. [117] | |||
| 8 | Bangladesh: Bandarban District, Keokradong | Ahsan et al. [89] | |||
| Herpetoreas burbrinki | Guo, Zhu, Liu, Zhang, Li, Huang, and Pyron, 2014 | rhombus | - | China: Xizang (Tibet), Zayü | Guo et al. [3] |
| Herpetoreas tpser | This study | star | - | China: Xizang (Tibet), Mêdog | This study |
| Hebius parallelus | (Boulenger, 1890) | triangle | 1 | India: Meghalaya, Selbalgiri | David et al. [11] |
| 2 | India: Meghalaya, Shillong and its vicinity | David et al. [11] | |||
| 3 | India: Meghalaya, Mawphlang | David et al. [11] | |||
| 4 | India: Nagaland, Khonoma | David et al. [11] |
Appendix C. Sulcate Surfaces of Hemipenis in the Genus Hebius
Figure A1.
(A). Hebius bitaeniatus, SYS r002171; (B). Hebius septemlineatus, SYS r001225, basal hook broken; (C). Hebius weixiensis, SICAU 2020082701; (D). Hebius metusia, CIB 118638; (E). Hebius sauteri, SYS r002041; (F). Hebius popei, SYS r002252; (G). Hebius boulengeri, CIB 118637; (H). Hebius optatus, unlabeled. Information see Appendix A. Scale bar = 5 mm. Photographs by Jun-Jie Huang and Jin-Long Ren.
References
- Malnate, E.V. Systematic division and evolution of the colubrid snake genus Natrix, with comments on the subfamily Natricinae. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 1960, 112, 41–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.-L.; Wang, K.; Nguyen, T.T.; Hoang, C.V.; Zhong, G.-H.; Jiang, K.; Guo, P.; Li, J.-T. Taxonomic re-evaluation of the monotypic genus Pararhabdophis Bourret, 1934 (Squamata: Colubridae: Natricinae) with discovery of its type species, P. chapaensis, from China. Zootaxha 2018, 4486, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zhu, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.X.; Huang, Y.Y.; Pyron, R.A. A taxonomic revision of the Asian keelback snakes, genus Amphiesma (Serpentes: Colubridae: Natricinae), with description of a new species. Zootaxa 2014, 3873, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stejneger, L. Herpetology of Japan and adjacent territory. Bull. United States Natl. Mus. 1907, 58, 1–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, A.C.L.G. The Reptiles of British India; Hardwicke: London, UK, 1864; p. 452. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.A. The Fauna of British India, Ceylon and Burma, including the Whole of the Indo-Chinese Subregion. Reptilia and Amphibia. Vol. III. Serpentes; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1943; p. 583. [Google Scholar]
- Lalronunga, S.; Lalrinchhana, C.; Vanramliana, V.; Das, A.; Gower, D.J.; Deepak, V. A multilocus molecular perspective on the systematics of the poorly known Northeast Indian colubrid snakes Blythia reticulata (Blyth, 1854), B. hmuifang Vogel, Lalremsanga & Vanlalhrima, 2017, and Hebius xenura (Wall, 1907). Zootaxa 2020, 4768, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Gower, D.J.; Deepak, V. Lost and found: Rediscovery and systematics of the Northeast Indian snake Hebius pealii (Sclater, 1891). Vertebr. Zool. 2020, 70, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, E.; Dong, B. Amphibians and Reptiles of Tibet; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010; p. 251. [Google Scholar]
- Deepak, V.; Cooper, N.; Poyarkov, N.A.; Kraus, F.; Burin, G.; Das, A.; Narayanan, S.; Streicher, J.W.; Smith, S.-J.; Gower, D.J. Multilocus phylogeny, natural history traits and classification of natricine snakes (Serpentes: Natricinae). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2021, zlab099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, P.; Agarwal, I.; Athreya, R.; Mathew, R.; Vogel, G.; Mistry, V.K. Revalidation of Natrix clerki Wall, 1925, an overlooked species in the genus Amphiesma Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854 (Squamata: Natricidae). Zootaxa 2015, 3919, 375–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, E.M.; Li, S.Q. A new lizard of Tenuidactylus and a new Tibetan snake record of Amphiesma. Acta Herpetol. Sin. 1987, 6, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Che, J.; Jiang, K.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Y.-P. Amphibians and Reptiles in Tibet, Diversity and Evolution; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 803. [Google Scholar]
- Boulenger, G.A. The Fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Reptilia and Batrachia; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1890; p. 541. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, E.M. Snakes of China. Vol. I.; Anhui Science and Technology Publishing House: Hefei, China, 2006; p. 372. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, H.G. A proposed standard system of counting ventrals in snakes. Br. J. Herpetol. 1951, 1, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Malnate, E.V.; Underwood, G. Australasian natricine snakes of the genus Tropidonophis. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 1988, 140, 59–201. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, C.W.; Cadle, J.E. On the snake hemipenis, with notes on Psomophis and techniques of eversion: A response to Dowling. Herpetol. Rev. 2003, 34, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Pesantes, O.S. A method for preparing the hemipenis of preserved snakes. J. Herpetol. 1994, 28, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaher, H.; Prudente, A.L.C. Hemipenes of Siphlophis (Serpentes, Xenodontinae) and techniques of hemipenial preparation in snakes: A response to Dowling. Herpetol. Rev. 2003, 34, 302–307. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K. A method for evaginating the hemipenis of preserved snakes. Sichuan J. Zool. 2010, 29, 122–123. [Google Scholar]
- Cope, E.D. On the hemipenes of the Sauria. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 1896, 48, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, H.G.; Savage, J.M. A guide to the snake hemipenis: A survey of basic structure and systematic characteristics. Zoologica 1960, 45, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.J.; Hu, S.Q.; Zhao, E.M. Comparative studies and phylogenetic discussions on hemipenial morphology of the Chinese Colubrinae (Colubridae). Acta Herpetol. Sin. 1984, 3, 23–44. [Google Scholar]
- Burbrink, F.T.; Lawson, R.; Slowinski, J.B. Mitochondrial DNA phylogeography of the polytypic North American rat snake (Elaphe obsoleta): A critique of the subspecies concept. Evolution 2000, 54, 2107–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, S.P.; Dinesh, K.P.; Prabhu, M.V.; Shanker, K. Lineage delimitation and description of nine new species of bush frogs (Anura: Raorchestes, Rhacophoridae) from the Western Ghats Escarpment. Zootaxa 2014, 3893, 451–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawson, R.; Slowinski, J.B.; Crother, B.I.; Burbrink, F.T. Phylogeny of the Colubroidea (Serpentes): New evidence from mitochondrial and nuclear genes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 37, 581–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, A.; McKelvy, A.D.; Grismer, L.L.; Bell, C.D.; Lailvaux, S.P. A species-level phylogeny of extant snakes with description of a new colubrid subfamily and genus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A.; Suchard, M.; Xie, D.; Drummond, A. Tracer, Version 1.6, MCMC Trace Analysis Package. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/tracer/ (accessed on 7 March 2018).
- Malnate, E.V. Amphiesma platyceps (Blyth), and Amphiesma sieboldii (Guenther): Sibling species (Reptilia: Serpentes). J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1966, 63, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, F. Some new Asian snakes. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1907, 17, 612–619. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.F.; Huang, S.; Burbrink, F.T.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, P.; Wu, H.L. Morphological description of a new specimen of Herpetoreas burbrinki Guo et al. 2014 (Serpentes: Colubridae). Zootaxa 2021, 5039, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, A. Contributions to a knowledge of the reptiles of the Himalaya mountains. -I. Descriptions of the new species. II. List of Himalayan reptiles, with remarks on their horizontal distribution. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1860, 28, 148–175. [Google Scholar]
- Blyth, E. Notices and descriptions of various reptiles, new or little known. J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal 1854, 23, 287–302. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, A. List of the cold-blooded vertebrata collected by B.H. Hodgson, Esq., in Nepal. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1861, 1861, 213–227. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, A. On new species of snakes in the collection of the British Museum. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1862, 9, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theobald, W.J. Catalogue of reptiles in the Museum of the Asiatic Society of Bengal. J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal 1868, 37, 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Stoliczka, F. Observations on some Indian and Malayan amphibia and reptilia. J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal. 1870, 39, 159–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J. On some Indian reptiles. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1871, 39, 149–211. [Google Scholar]
- Stoliczka, F. Notes on some new species of Reptilia and Amphibia, collected by Dr. W. Waagen in North-Western Panjab. Proc. Asiat. Soc. Bengal 1872, 1872, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Blanford, W.T. List of Reptilia and Amphibia collected by the late Dr. Stoliczka in Kashmir, Ladák, eastern Turkestán, and Wakhán, with descriptions of new species. J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal 1875, 44, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Theobald, W. Descriptive Catalogue of the Reptiles of British India; Thacker, Spink and Company: Calcutta, India, 1876; p. 238. [Google Scholar]
- Blanford, W.T. Scientific Results of the Second Yarkand Mission: Based Upon the Collections and Notes of the Late Ferdinand Stoliczka, Ph. D. Geology; Government of India: Calcutta, India, 1878; p. 26.
- Atkinson, E.T. The Himalayan Districts of the North.-Western Provinces of India; North Western Province and Oudh Government Press: New Delhi, India, 1882; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Hubrecht, A.A.W. List of reptiles and amphibians brought from British India by Mr. Francis Day. Notes Leyden Mus. 1882, 4, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Boulenger, G.A. An account of the Reptilia obtained in Burma, north of Tenasserim, by M.L. Fea, of the Genova Civic Museum. Ann. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Genova 1888, 6, 593–604. [Google Scholar]
- Phipson, H. Catalogue of snakes in the society’s collection. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1888, 3, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Boulenger, G.A. Catalogue of the Snakes in the British Museum (Natural History). Vol. I. Containing the Families Typhlopidae, Glauconiidae, Boidae, Ilysiidae, Uropeltidae, Xenopeltidae, and Colubridae Aglyphae, part; British Museum of Natural History: London, UK, 1893; p. 448. [Google Scholar]
- Cardew, A. A rough key to the identification of Indian Ophidia. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1897, 10, 585–596. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, F. Notes on snakes from the neighbourhood of Darjeeling. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1909, 19, 337–357. [Google Scholar]
- Annandale, N. Zoological results of the Abor Expedition, 1911–1912. II. Reptilia. Rec. Indian Mus. 1912, 8, 37–55. [Google Scholar]
- Cazaly, W.H. The Common Snakes of India and Burma and How to Recognise Them; International Book Distributors: Dehradun, India, 1914; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, F. Übersicht der Gattungen und Arten der Schlangen aus der Familie Colubridae: III. Teil (Colubrinae). Mit einem Nachtrag zu den übrigen Familien. Zool. Jahrbücher. Abt. Für Syst. Geogr. Biol. Tiere 1929, 57, 1–196. [Google Scholar]
- Prater, S. Non-poisonous snakes. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1933, 36, 391–394. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, F. A hand-list of snakes of the Indian empire. Part II. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1923, 29, 598–632. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, G.; Shebbeare, E.; Barker, P. The snakes of northern Bengal and Sikkim. J. Darjeeling Nat. Hist. Soc. 1939, 13, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M. On a collection of amphibians and reptiles from Nepal. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1951, 4, 726–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Battersby, J.C. On a collection of amphibians and reptiles from Nepal. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1953, 6, 702–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, L.W.; Leviton, A.E. The herpetology of Nepal: A history, check list, and zoogeographical analysis of the herpetofauna. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 1962, 32, 103–147. [Google Scholar]
- Deoras, P.J. Snakes of India; National Book Trust: New Delhi, India, 1965; p. 148. [Google Scholar]
- Waltner, R.C. Geographical and altitudinal distribution of amphibians and reptiles in the Himalayas (Part III). Cheetal 1975, 16, 14–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, E.-M.; Jiang, Y.-M.; Shen, Y. Systematic Key to the Reptiles of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1977; p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S. Affinities and zoogeography of herpetiles of Pakistan. Biologia 1980, 26, 113–171. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.-Q.; Huang, M.-H.; Xie, Z.-T.; Zhao, E.-M.; Jiang, Y.-M.; Huang, Q.-Y.; Zong, Y.; Ma, J.-F. Atlas of Chinese Snakes; Shanghai Science & Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1980; p. 166. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M. Some notes on snakes in Pakistan. Hamadryad 1982, 7, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, R.L., Jr.; Fleming, R.L., Sr. Some snakes from Nepal. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1974, 70, 426–437. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, E. Zur Schlangenfauna Nepals. Suisse De Zool. 1977, 84, 721–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanhoe, L.M.; Ouboter, P.E. The distribution of reptiles and amphibians in the Annapurna-Dhaulagiri region (Nepal). Zool. Verh. 1987, 240, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, E.M.; Adler, K. Herpetology of China; Contribution to Herpetology, No. 10; Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles: Oxford, UK, 1993; p. 522. [Google Scholar]
- Das, I. The reptiles of South Asia: Checklist and distributional summary. Hamadryad 1994, 19, 15–40. [Google Scholar]
- Das, I. Biogeography of the Reptiles of South Asia; Krieger Publishing Company: Malabar, FL, USA, 1996; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Das, I.; Dattagupta, B.; Gayen, N.C. History and catalogue of reptile types in the collection of the Zoological Survey of India. J. South Asian Nat. Hist. 1998, 3, 121–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, E.M.; Huang, M.H.; Zong, Y. Fauna Sinica Reptilia, Vol. 3: Squamata, Serpentes; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; p. 522. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, D. A complementary survey of the herpetofauna of Xizang Autonomous Region (Tibet) with discussion of their distribution and current status. Sichuan J. Zool. 2000, 19, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Das, I. A Photographic Guide to Snakes and Other Reptiles of India; Ralph Curtis Publishing: Iona, FL, USA, 2002; p. 144. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S. Die Schlangen Pakistans; Chimaira: Frankfurt, Germany, 2002; p. 209. [Google Scholar]
- Schleich, H.H.; Kästle, W. Amphibians and Reptiles of Nepal; A. R. G. Gantner Verlag Kommanditgesellschaft: Koenigstein, Germany, 2002; p. 1201. [Google Scholar]
- Das, I. Growth of knowledge on the reptiles of India, with an introduction to systematics, taxonomy and nomenclature. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 2003, 100, 446–501. [Google Scholar]
- Tillack, F. On the distribution and biology of the Himalayan mountain keelback, Amphiesma platyceps (Blyth, 1854) and a case of Amphigonia retardata (Serpentes: Colubridae: Natricinae). Sauria 2003, 25, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S. Annotated checklist of amphibians and reptiles of Pakistan. Asiat. Herpetol. Res. 2004, 10, 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker, R.; Captain, A. Snakes of India. The Field Guide; Draco books: Chennai, India, 2004; p. 387. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, E.M. Snakes of China. Vol. II.; Anhui Science and Technology Publishing House: Hefei, China, 2006; p. 279. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R. The Fauna of India and the Adjacent Countries, Vol. 3, Reptilia (Serpentes); Zoological Survey of India: Kolkata, India, 2007; p. 410.
- Ahsan, M.F.; Asmat, G.S.M.; Islam, M.A.; Khan, M.M.H.; Muzaffar, S.B.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Chakma, S. Amphibians and reptiles. In Encyclopedia of Flora and Fauna of Bangladesh. Volume 25; Kabir, S.M.H., Ahmed, M., Ahmed, A.T.A., Rahman, A.K.A., Ahmed, Z.U., Begum, Z.N.T., Hassan, M.A., Khondker, M., Eds.; Asiatic Society of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2009; p. 204. [Google Scholar]
- Reza, A. First record of Amphiesma venningi (Wall, 1910) (Serpentes, Colubridae, Natricinae) from Bangladesh, with notes on its taxonomy, natural history, biogeography and other sympatric species. Hamadryad 2010, 35, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wangyal, J.T. Snakes and lizards from the Bumdeling Wildlife Sanctuary Region of Bhutan: Review of herpetofaunal information and new country records. Herpetol. Rev. 2011, 42, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wangyal, J.T. New records of reptiles and amphibians from Bhutan. J. Threat. Taxa 2013, 5, 4774–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallach, V.; Williams, K.L.; Boundy, J. Snakes of the World. A Catalogue of Living and Extinct Species; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; p. 1209. [Google Scholar]
- Sahi, D.N.; Koul, S. Annotated list of amphibians and reptiles of Jammu and Kashmir State. In Biodiversity of the Himalaya: Jammu and Kashmir State; Dar, G.H., Khuroo, A.A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 889–896. [Google Scholar]
- Mertens, R. Die Amphibien und Reptilien West-Pakistans. Stuttg. Beiträge Zur Nat. 1969, 197, 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.F.; Das, A.; Dutta, S.K. Amphibians and Reptiles of Northeast. India: A Photographic Guide; Aaranyak: Guwahati, India, 2009; p. 169. [Google Scholar]
- Aengals, R.; Sathish Kumar, V.M.; Palot, M.J.; Ganesh, S.R. A Checklist of Reptiles of India. 35 pp. Version 3.0. Available online: www.zsi.gov.in (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- Wang, K.; Ren, J.-L.; Chen, H.M.; Lyu, Z.T.; Guo, X.G.; Jiang, K.; Chen, J.M.; Li, J.-T.; Guo, P.; Wang, Y.Y.; et al. The updated checklists of amphibians and reptiles of China. Biodivers. Sci. 2020, 28, 189–218. [Google Scholar]
- Boundy, J. Snakes of the World: A Supplement; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; p. 273. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S. Sinoophis; The Straits Publishing: Fuzhou, China, 2021; p. 645. [Google Scholar]
- Steindachner, F. Ueber drei neue Schlangenarten. Verh. Kais -Königlichen Zool.-Bot. Ges. Wien. 1867, 17, 513–516. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, F. A new snake of the genus Tropidonotus from the Eastern Himalayas. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1914, 23, 166–167. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, A. Seventh account of new species of snakes in the collection of the British Museum. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1872, 9, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierl, W.; Gruber, U. Habitat conditions in the transitional faunal zone in central Nepal (A report on the German Zoological Expedition to Central Nepal 1973). Spixiana 1979, 2, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, K.R. Snakes of the Orient: A Checklist; Robert, E. Krieger Publ. Co.: Malabar, FL, USA, 1988; p. 183. [Google Scholar]
- Das, I. Checklist of the reptiles of India, with English common names. Hamadryad 1997, 22, 32–45. [Google Scholar]
- David, P.; Vogel, G.; Pauwels, O. Amphiesms optstum (Hu & Djao, 1966) (Serpentes, Colubridae): An addition to the snake fauna of Vietnam, with a list of the species of the genus Amphiesma and note on its type species. J. Taiwan Mus. 1998, 51, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- David, P.; Vogel, G.; Pauwels, O.S. On the occurrence of Amphiesma bitaeniatum (Wall, 1925) in Vietnam, with preliminary remarks on the group of Amphiesma parallelum (Boulenger, 1890) (Serpentes, Colubridae, Natricinae). Salamandra 2005, 41, 167–178. [Google Scholar]
- Das, I. A Field Guide to the Reptiles of South-East. Asia; New Holland Publishers: London, UK, 2010; p. 376. [Google Scholar]
- Das, I. A Naturalist’s Guide to the Snakes of South-East Asia: Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, Myanmar, Borneo, Sumatra, Java and Bali; John Beaufoy Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2012; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Sclater, W.L. Notes on the collection of snakes in the Indian Museum with descriptions of several new species. J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal 1891, 60, 230–250. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Das, I. A Naturalist’s Guide to the Reptiles of India, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka; John Beaufoy Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2017; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Purkayastha, J.; David, P. A new species of the snake genus Hebius Thompson from Northeast India (Squamata: Natricidae). Zootaxa 2019, 4555, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, J. A new record of a rare snake (Natrix xenura) from Assam. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1945, 45, 430–431. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, S.; Birand, A. A Survey of Amphibians, Reptiles, and Birds in Northeast India; Centre for Ecological Research and Conservation: Pune, India, 2001; p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- David, P.; Bain, R.H.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Orlov, N.L.; Vogel, G.; Vu, N.T.; Ziegler, T. A new species of the natricine snake genus Amphiesma from the Indochinese Region (Squamata: Colubridae: Natricinae). Zootaxa 2007, 1462, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wogan, G.O.U.; Vindum, J.V.; Wilkinson, J.A.; Koo, M.S.; Slowinski, J.B.; Win, H.; Thin, T.; Kyi, S.W.; Oo, S.L.; Lwin, K.S.; et al. New country records and range extensions for Myanmar amphibians and reptiles. Hamadryad 2008, 33, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Muansanga, L.; Laltlanhlui, L.; Biakzuala, L.; Rathee, Y.S.; Lalremsanga, H.T. Observations of feeding behavior and a note on clutch size in Wall’s Keelback, Herpetoreas xenura (Wall 1907) (Squamata: Natricidae). Reptiles Amphib. 2021, 28, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Huang, S.; Fu, J.-R.; Liu, S.-Y. Two snakes new to Xizang Autonomous Region. Sichuan J. Zool. 2008, 27, 658–659. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, E.M.; Li, S.Q. Herpetological survey of Mount Namjagbarwa, Tibet. Acta Herpetol. Sin. 1985, 4, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, E.M.; Jiang, Y.M.; Li, S.Q. Reptilian faunal analysis and zoogeographical division of Xizang Autonomous Region. Acta Herpetol. Sin. 1986, 5, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.S.; Mao, X.L.; Wang, Z.W. Biota of the Mt. Namjagbarwa Region; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1995; p. 315. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, J.; David, P.; Bordoloi, S.; Ohler, A. Notes on a collection of snakes from Nagaland, northeast India, with 19 new records for this state. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2004, 11, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- David, P.; Pauwels, O.S.G.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Vogel, G. On the taxonomic status of the Thai endemic freshwater snake Parahelicops boonsongi, with the erection of a new genus (Squamata: Natricidae). Zootaxa 2015, 3948, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.-L.; Wang, K.; Guo, P.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Nguyen, T.T.; Li, J.-T. On the generic taxonomy of Opisthotropis balteata (Cope, 1895)(Squamata: Colubridae: Natricinae): Taxonomic revision of two natricine genera. Asian Herpetol. Res. 2019, 10, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rooij, N. The Reptiles of the Indo-Australian Archipelago. II. Ophidia; EJ Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1917; p. 334. [Google Scholar]
- David, P.; Vogel, G. A new species of the natricine snake genus Amphiesma from Borneo (Squamata: Natricidae). Russ. J. Herpetol. 2010, 17, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Cadle, J.E. Hemipenial morphology in the North American snake genus Phyllorhynchus (Serpentes: Colubridae), with a review of and comparisons with natricid hemipenes. Zootaxa 2011, 3092, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, H.; Iwanaga, S. A systematic review of the snakes allied to Amphiesma pryeri (Boulenger) (Squamata: Colubridae) in the Ryukyu Archipelago, Japan. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1997, 121, 339–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-Q.; Ren, J.-L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, G.X.; Li, J.-T. On the taxonomy of Atretium yunnanensis Anderson, 1879 (Squamata: Natricidae), with redescriptions and natural history data of the poorly known species. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2021, 28, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkayastha, J.; Kalita, J.; Brahma, R.K.; Doley, R.; Das, M. A review of the relationships of Xenochrophis cerasogaster Cantor, 1839 (Serpentes: Colubridae) to its congeners. Zootaxa 2018, 4514, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Shi, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Jono, T.; Fukuda, M.; Mori, A.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Q. A New Species of the Genus Rhabdophis Fitzinger, 1843 (Squamata: Colubridae) in Southwestern Sichuan, China. Asian Herpetol. Res. 2020, 11, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaher, H. Hemipenial morphology of the South American xenodontine snakes: With a proposal for a monophyletic Xenodontinae and a reappraisal of colubroid hemipenes. Bull. Ameican Mus. Nat. Hist. 1999, 20, 1–168. [Google Scholar]
- Cope, E.D. The classification of the Ophidia. Trans. Am. Philos. Soc. 1895, 18, 186–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, P.; Vogel, G.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Orlov, N.L.; Pauwels, O.S.G.; Teynie, A.; Ziegler, T. A revision of the dark-bellied, stream-dwelling snakes of the genus Hebius (Reptilia: Squamata: Natricidae) with the description of a new species from China, Vietnam and Thailand. Zootaxa 2021, 4911, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).