Abstract
Family Phyllanthaceae belongs to the eudicot order Malpighiales, and its species are herbs, shrubs, and trees that are mostly distributed in tropical regions. Here, we elucidate the molecular evolution of the chloroplast genome in Phyllanthaceae and identify the polymorphic loci for phylogenetic inference. We de novo assembled the chloroplast genomes of three Phyllanthaceae species, i.e., Phyllanthus emblica, Flueggea virosa, and Leptopus cordifolius, and compared them with six other previously reported genomes. All species comprised two inverted repeat regions (size range 23,921–27,128 bp) that separated large single-copy (83,627–89,932 bp) and small single-copy (17,424–19,441 bp) regions. Chloroplast genomes contained 111–112 unique genes, including 77–78 protein-coding, 30 tRNAs, and 4 rRNAs. The deletion/pseudogenization of rps16 genes was found in only two species. High variability was seen in the number of oligonucleotide repeats, while guanine-cytosine contents, codon usage, amino acid frequency, simple sequence repeats, synonymous and non-synonymous substitutions, and transition and transversion substitutions were similar. The transition substitutions were higher in coding sequences than in non-coding sequences. Phylogenetic analysis revealed the polyphyletic nature of the genus Phyllanthus. The polymorphic protein-coding genes, including rpl22, ycf1, matK, ndhF, and rps15, were also determined, which may be helpful for reconstructing the high-resolution phylogenetic tree of the family Phyllanthaceae. Overall, the study provides insight into the chloroplast genome evolution in Phyllanthaceae.
1. Introduction
The family Phyllanthaceae and its closely related sister family Picorodendraceae comprise a separate clade of phyllantoid taxa within the order Malpighiales [1,2]. The species of the family Phyllanthaceae are predominantly tropical in distribution and include herbs, shrubs, and trees [3,4]. This family consists of two subfamilies (Phyllanthoideae and Antidesmatoideae), 10 tribes, 57 genera, and 2050 species [5]. Certain taxonomic discrepancies exist within Phyllanthaceae, i.e., Phyllanthus is polyphyletic since species of genera Breynia, Glochidion, Sauropus, and Synostemon were found embedded in its phylogeny [3,6,7]. Moreover, taxonomic discrepancies exist at intra-genus level since several subgenera and sections of Phyllanthus were paraphyletic [6,8]. Hence, researchers have suggested either merging all embedded genera into Phyllanthus L. to create a giant genus or dividing Phyllanthaceae into several monophyletic genera for grouping morphological similar species [3,6,8]. Phyllanthus L. is considered to be the largest genera of the family Phyllanthaceae having 900 species [8,9], distributed both tropically and sub-tropically [10]. Phyllanthus emblica L. is commonly used as medicine in Asia [11] for its antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-pyretic, diuretic, laxative, stomachic, cardioprotective, and hepatoprotective properties [9,10,12,13,14,15]. The other genus, Leptopus Decne., is made up of nine species consisting of herbs and shrubs, which are distributed in Asia, America, and Europe and grow in open fields and in forests [16]. One of the species of this genus, Leptopus cordifolius, grows in the hilly areas of Pakistan and is also distributed from North India and Nepal to West Himalaya [16].
The chloroplast is an important organelle that plays a vital role in photosynthesis, also possessing a chloroplast genome. The chloroplast genome inherits maternally [17] in most angiosperms and paternally in some gymnosperms [18]. The chloroplast genome has a quadripartite structure and consists of a large single-copy (LSC) region, a small single-copy (SSC) region, and inverted repeat regions (IRa and IRb) [19,20,21]. The chloroplast genome normally ranges from 107 to 218 kb and contains 120 to 130 genes [22]. Many mutational events are reported in the chloroplast genome, including substitutions, insertion-deletions (InDels), repeats, and inversions [23,24,25]. The deletion of certain genes from the chloroplast genome or their transfer to nuclear genomes has also been reported in several plant lineages, including the species of the order Malpighiales to which the family Phyllanthaceae belongs [20,26,27]. The chloroplast genome evolves slowly and lacks the meiotic recombination of the nuclear genome, where homologous chromosomes exchange segments [28]. These properties make the chloroplast genome a suitable molecule for studies ranging from population genetics [29,30] to deep divergence at the genus and family levels [31,32,33,34], including plant evolution and phylogeny, providing deep insight into the evolution of plants [35,36].
In this study, the chloroplast genome of three species was de novo assembled and compared with previously reported chloroplast genomes of six other species of the family Phyllanthaceae. This provided us with deep insight into features of chloroplast genomes of selected species and similarities and differences among the species, elucidating the molecular evolution of the chloroplast genome in the family Phyllanthaceae. Moreover, suitable polymorphic loci were identified, which may be helpful for future phylogenetic inference to resolve taxonomic discrepancies of the family Phyllanthaceae.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Collection and DNA Extraction
The leaves of Phyllanthus emblica and Leptopus cordifolius without apparent disease symptoms were collected during September 2018 from the district Mansehra, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Coordinates of collection points were also recorded with the Global Positioning System (GPS) for Phyllanthus emblica (34°31′50″ N, 72°88′10″ E) and Leptopus cordifolius (34°40′84″ N, 73°31′62″ E). The leaves were washed with distilled water and ethanol before drying with silica. Whole genomic DNA was extracted from the silica dried leaves using the DNeasy Plant Mini Kit manufactured by Qiagen. After confirmation of the quality and quantity on 1% agarose gel and by Thermo Scientific Nanodrop spectrophotometer, DNA was sent for sequencing to Novogene, Hong Kong.
2.2. Sequencing, De Novo Assembly, and Annotation of Chloroplast Genome
The DNA of Phyllanthus emblica L. and Leptopus cordifolius Decne. was sequenced with HiSeq 2500 using paired-end run with 150 bp short read size and 350 bp insert size. We also retrieved the 1.2 Gb raw reads of Flueggea virosa (Roxb. Ex Willd.) Royle (SRR7121487) [37] from the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) of the National Center for Biotechnology, which were sequenced by BGI-seq with 100 bp short reads. The whole genome shotgun was used for the de novo assembly of chloroplast genomes of selected three species using NOVOPlasty. The analysis provided the complete chloroplast genomes of all three species, including LSC regions, IR regions, and SSC region. The accuracy of assembled genomes and their coverage depth were confirmed by mapping short reads to their de novo assembled chloroplast genome using Burrows–Wheeler Aligner (BWA) [38] and visualized in Tablet [39].
De novo assembled chloroplast genomes were annotated using GeSeq [40], whereas the tRNA genes were confirmed by tRNAscan-SE v.2 [41] and ARAGORN v.1.2.3.8 [42] with default parameters. The annotations of protein-coding genes were further confirmed against homologous genes by blast search of NCBI. The five column delimited table of annotations was generated using GB2sequin [43] to submit de novo assembled genomes to GenBank of NCBI along with genomic features.
2.3. Analysis of Chloroplast Genome Features and Inverted Repeat Contraction and Expansion
The de novo assembled chloroplast genomes of Phyllanthus emblica (Pakistan), Leptopus cordifolius, and Flueggea virosa were compared with six previously reported chloroplast genomes of Baccaurea ramiflora Lour., Phyllanthus amarus Schumach. & Thonn., Phyllanthus emblica L. (China), Glochidion chodoense C.S. Lee & H.T.Im., Breynia fruticosa (L.) Müll.Arg, and Sauropus spatulifolius Beille. The lengths of complete chloroplast genome, LSC, SSC, and IRs were compared among the nine species of Phyllanthaceae. Moreover, gene contents, intron contents, and GC contents of all species were compared using Geneious R8.1 [44]. The gene arrangement among the selected species of Phyllanthaceae was determined using Mauve alignment [45] integrated in Geneious R8.1. The contraction and expansion of inverted repeat regions were visualized using IRscope [46].
2.4. Analysis of Codon Usage, Amino Acid Frequency, and Repeats
The relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) and amino acid frequency of each species were determined using Geneious R8.1 [44]. The RSCU value of each species was shown with the help of a heatmap using TBtool [47]. MIcroSAtellite (MISA) [48] was used for the determination of simple sequence repeats (SSRs), with a maximum threshold of 10 for mononucleotide SSRs, 5 for dinucleotide SSRs, 4 for trinucleotide SSRS, and 3 for tetra-, penta-, and hexanucleotide SSRs. REPuter [49] was used for the determination of four types of oligonucleotide repeats, including forward (F), complementary (C), reverse (R), and palindromic (P). Parameters such as repeats size ≥ 30 with at least 90% similarities were adjusted.
2.5. Synonymous, Non-Synonymous, Transition, and Transversion Substitution Analyses
The synonymous (Ks) and non-synonymous (Ka) substitutions were analyzed in TBtool [47] for 77 protein-coding genes using Baccaurea ramiflora Lour. as a reference for all other species, as this species lies basal to the current species following Abdullah et al. [19]. Each gene selection was predicted by considering the ratios of Ka/Ks < 1 purifying selection, Ka/Ks = 1 neutral selection, and Ka/Ks > 1 positive selection [50]. The positive selection on protein coding genes or their codons was further analyzed using the Mixed Effects Model of Evolution (MEME) [51] and Fast Unconstrained Bayesian Approximation (FUBAR) [52] as implemented in the DATAMONKEY web server [53], according to previous parameters [54]. The transition and transversion substitutions of complete genome and protein-coding genes were determined by comparison with closely as well as with distantly related species. The whole genome was aligned using MAFFT, whereas the protein-coding sequences of each species were concatenated, except for ycf1, and also aligned using MAFFT alignment [55]. For closely related species, the genome of P. emblica (Pakistan) was used as a reference for Breynia fruticosa, Phyllanthus amarus, Phyllanthus emblica (China), Glochidion chodoense, and Sauropus spatulifolius. Similarly, for distantly related species, Baccaurea ramiflora was used as a reference for the selected species of Leptopus cordifolius, Flueggea virosa, and Phyllanthus emblica (Pakistan).
2.6. Polymorphism of Protein-Coding Genes
To determine the extent of polymorphism of protein-coding genes for further phylogenetic studies, all protein-coding genes of each species were extracted. The sequence of each gene was multiple aligned using Geneious R8.1 and analyzed in DnaSP v.6 [56].
2.7. Reconstruction of Phylogenetic Tree
For inferring phylogeny, the sequences of 76 protein-coding genes, except ycf1, of each species were extracted and concatenated in Geneious R8.1 [44]. The ycf1 was excluded from the analysis as this gene exists at the junction of IR/SSC, with one part of ycf1 located in the IR region and the other part in the SSC region. The part situated in the IR region showed a different rate of evolution than the part in the SSC region due to rate heterotachy [57,58,59]. These concatenated sequences of all 10 species, including Linum usitatissimum L. as outgroup from the family Linaceae, were multiple aligned using MAFFT [60] extension in Geneious R8.1. The maximum likelihood tree was reconstructed with best fit model GTR + F + G4 and determined by jModelTest 2 [61] using IQ-tree [62] with the same parameters as described previously [54]. The phylogenetic tree was also reconstructed with the identified polymorphic loci following the same approach. However, the best fit model TVM + F + G4 was predicted by jModelTest 2 and applied. The Interactive Tree of Life [63] was used to improve the presentation of the tree.
3. Results
3.1. Chloroplast Genome Features and Organization
HiSeq 2500 produced about 10.52 GB data with 31.4 million reads for Phyllanthus emblica and 7.58 GB data with 22.6 million reads for Leptopus cordifolius. Chloroplast genomes assembled from the data exhibited a high average coverage depth of 855X for Phyllanthus emblica and 375X for Leptopus cordifolius. The Flueggea virosa which was assembled from the SRA data of NCBI showed an average coverage depth of 138X. These three de novo assembled genomes along with the previously reported genome provided an opportunity to perform in-depth comparative chloroplast genomics of members of the family Phyllanthaceae.
The gene contents and organization of the chloroplast genomes of the family Phyllanthaceae are provided in Table 1 and Table 2 and Figure 1. The genomes showed high similarity in gene contents, except rps16, which was missing in Baccaurea ramiflora and Leptopus cordifolius. The chloroplast genomes of all selected species displayed quadripartite structure, comprising IRs (IRa and IRb) that separate the LSC and SSC regions. The length of the complete chloroplast genome ranged from 154,707 (Sauropus spatulifolius) to 161,093 bp (Baccaurea ramiflora), IRs from 23,921 (Sauropus spatulifolius) to 27,128 bp (Phyllanthus amarus), LSC from 83,627 (Leptopus cordifolius) to 89,932 bp (Phyllanthus emblica from Pakistan), and SSC from 17,424 (Leptopus cordifolius) to 19,441 bp (Breynia fruticosa).

Table 1.
Gene content and functional classification of the chloroplast genomes of the family Phyllanthaceae.

Table 2.
Comparison of chloroplast genomes of all nine species of the family Phyllanthaceae.
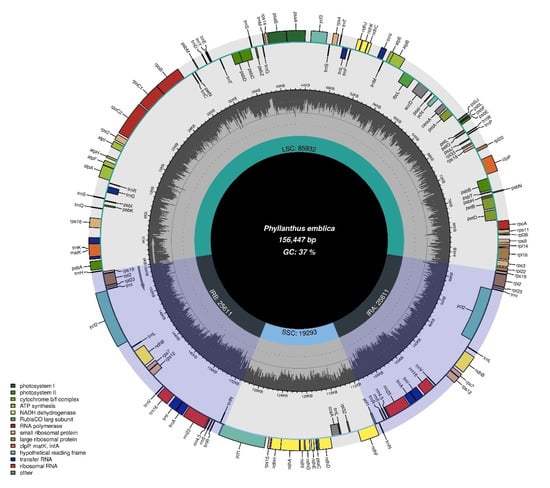
Figure 1.
Circular representation of Phyllanthus emblica chloroplast genome (a representative of all other species). The genes transcribed clockwise are shown inside the circle, whereas genes transcribed anti-clockwise are shown outside the circle.
Chloroplast genomes possessed 111–112 unique genes that showed high similarities in the arrangement within the genomes and no inversion events related to gene rearrangement were found, as predicted by Mauve alignment (Figure 2). Among these 111–112 genes, 77 –78 were protein-coding genes, 30 transfer RNA (tRNA) genes, and 4 ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes (Table 1). Moreover, 16–17 genes were also duplicated in IR regions, including 5–6 protein-coding genes, 7 tRNA genes, and 4 rRNA genes. Here, two pseudogenes of ycf1Ψ and rps19Ψ were excluded, which exist at the junctions of LSC/IRa and SSC/IRa (Table 1). The rps12 gene was a trans-splicing gene; the 5′ end was present in LSC in the form of a single copy, whereas the 3′ end was duplicated in IRa and IRb. The average GC content of the complete chloroplast genome was 36.6–36.8%. LSC was 34.3–34.6%, SSC 30.1–30.8%, and IR 42.3–43.3%. Maximum GC contents were found in IR regions (42.3–43.3%), followed by the LSC region (34.3–34.6%) and the SSC region (30.1–30.8%). The highest GC content of IRs belongs to rRNAs (55.5%) and tRNAs (53%); the genomic features are given in a detailed summary in Table 2.
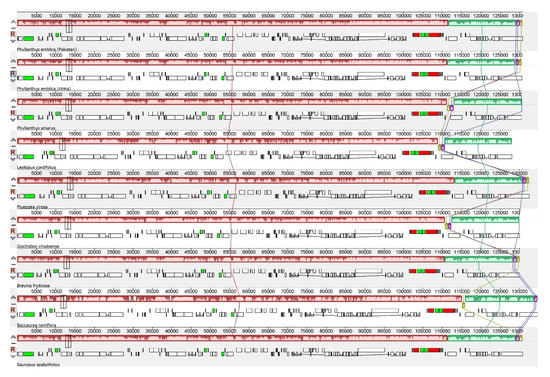
Figure 2.
Mauve alignment of nine species of the family Phyllanthaceae shows high similarities in gene arrangement and gene contents. The small blocks represent genes: red = rRNA; green = tRNA with intron; black = tRNA without intron; white = protein-coding genes. The large reddish color represents LSC and IR regions, while the greenish part represents SSC regions. The small purple and green blocks represent part of the ycf1Ψ gene, e.g., in Leptopus cordifolius the size of ycf1Ψ was 1032 bp and both blocks are present at the start of the large greenish block, while in Flueggea virosa the size of ycf1Ψ was 220 bp and both blocks are present at the end of the large greenish block.
There were 17–18 intron-containing genes of which 11–12 were protein-coding genes and 6 were tRNA genes. Moreover, an intron was found in atpF gene in only Baccaurea ramiflora, which was missing in all other species examined. All protein-coding genes contained one intron, except clpP and ycf3, which had two introns as shown in Table 1. Of these intron-containing genes, three were protein-coding genes and two tRNA genes were also duplicated in IR regions.
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
Phylogenetic analysis of the selected species of the family Phyllanthaceae was performed based on 76 protein-coding genes and suitable polymorphic loci. Both methods provided similar results and resolved the phylogenetic relationship within the family Phyllanthaceae with high bootstrapping support of 100. The genus Phyllanthus was found to be polyphyletic, with P. amarus closely related to G. chodoense instead of P. emblica (Figure 3). The nodes “P. amarus and G. chodoense” and “B. fruticosa and S. spatulifolius” were sisters to one another and were rooted by P. emblica. This whole clade was rooted by F. virosa, followed by L. cordifolius and then by B. ramiflora, which lies basal to the selected species in the tree.
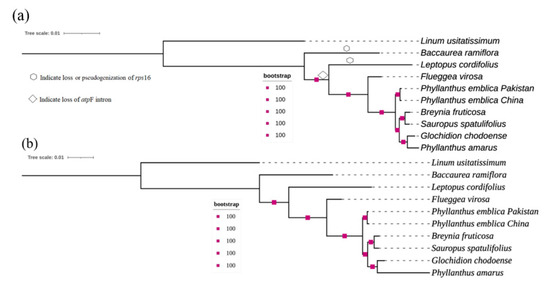
Figure 3.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree reconstructed with a dataset of 76 protein-coding genes (a) and identified polymorphic loci (b). The 100 bootstrapping support was observed for all nodes. The deletion/pseudogenization of rps16 and loss of atpF intron are indicated by the symbols only in the tree constructed with coding sequences to avoid duplication of the same data.
3.3. Inverted Repeat Contraction and Expansion
Comparative analysis of the junctions of LSC/IR and SSC/IR showed similarities among species of the family Phyllanthaceae, except for a few differences that mostly occurred at the junction of LSC/IRb (JLB) (Figure 4). At JLB, the rps19 started from the IRb and entered the LSC regions in six species. Hence, truncated rps19 pseudogene remained at JLA (IRa/LSC) in these species (Figure 4). In the remaining three species, the rps19 completely existed in the LSC regions at the JLB junction and did not lead to the generation of a pseudogene at the JLA junction. The rpl2 gene was completely found in the IR regions away from the JLB and JLA junctions, except in Sauropus spatulifolius, where the rpl2 started from IRb and entered the LSC regions, retaining a pseudogene at the junction of JLA instead of a functional copy due to contraction of IRs. Moreover, at JLA the rpl23 was present in IRb and IRa instead of rpl2. At the SSC/IRb junction (JSB), ndhF was situated entirely in the SSC region in the six species of Baccaurea ramiflora, Flueggea virosa, Phyllanthus emblica (China), Phyllanthus emblica (Pak), Breynia fruticosa, and Sauropus spatulifolius, while it was integrated into the IRb regions within the remaining three species of Phyllanthus amarus, Glochidion chodoense, and Leptopus cordifolius, where it overlapped with the pseudogene of ycf1. The ycf1 started in IRa and ended in SSC, as seen at the JSA (SSC/IRa) junction. Consequently, pseudogene of ycf1 remained at JSB (IRb/SSC), which ranges in size from 195 to 1921 bp. At the junction of JLA (IRa/LSC), the trnH gene was found in all species (Figure 4). Thus, IR contraction and expansion were not responsible for complete duplication of a functional copy of a gene, but they led to the generation of truncated rps19, rpl2, and ycf1 pseudogenes.
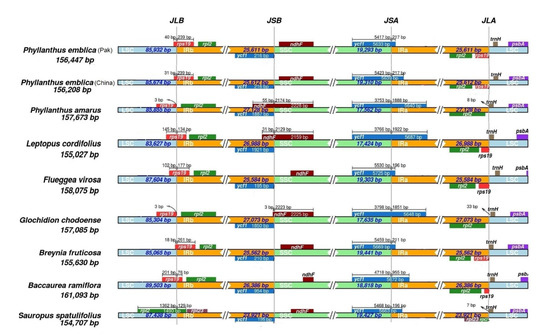
Figure 4.
Contraction and expansion of inverted repeats at the junction of chloroplast genome. JLB: LSC/IRb; JSB: IRb/SSC; JSA: SSC/IRa; JLA: IRa/LSC. Arrows illustrate the distance of genes from the junction site as shown for rps19 at JLB and for trnH at JLA. The scale bar above some genes illustrates the number of base pairs that each gene occupies in specific regions of the chloroplast, e.g., the scale bar above ycf1 represents the part of the gene located in the IR region and the SSC region.
3.4. Codon Usage and Amino Acid Frequency, and Repeats
Codon usage analysis was interpreted in terms of RSCU values. The analysis showed that most of the amino acids were encoded from codons ended with A/T at 3′ (having RSCU > 1) instead of C/G (having RSCU < 1) (Figure S1). The amino acid frequency analysis revealed that leucine was the most encoded amino acid while cysteine was the rarest (Figure S2). Codon usage analysis and amino acid frequency showed high similarities in all species of the family Phyllanthaceae. The simple sequence repeats (SSRs) and oligonucleotide repeats were analyzed in the Cp genome of selected species. The analysis of MISA revealed 630 SSRs mostly consist of A/T motifs in all species (Table S1). All six types of SSRs were based on motif types, including mononucleotide, dinucleotide, trinucleotide, tetranucleotide, pentanucleotide, and hexanucleotide. However, SSRs were predominantly mononucleotide, followed by dinucleotide (Figure S3a). The highest number of SSRs was found in the LSC region, followed by the SSC region and the IR (Figure S3b). The highest number of SSRs (84) was observed in Phyllanthus emblica (China), and the lowest number of SSRs (51) was seen in Glochidion chodoense. The REPuter program detected 311 oligonucleotide repeats with sizes of 30–96 bp. The number of repeats varied from 24 (Glochidion chodoense) to 49 (Baccaurea ramiflora). Most of the oligonucleotide repeats were forward and palindromic, but reverse and complementary repeats were also found (Figure S3c). Most of the repeats ranged in size from 30 to 34 bp (Figure S3d). The number of repeats was higher in LSC than in SSC and IR, whereas some repeats were also shared between LSC/IR, LSC/SSC, and SSC/IR regions of the chloroplast genome (Figure S3e).
3.5. Synonymous and Non-Synonymous Substitutions
The synonymous (Ks) and non-synonymous (Ka) substitutions and their ratio (Ka/Ks) revealed high similarities among the species of Phyllanthaceae (Table S2). The lowest average values of Ka = 0.0298, Ks = 0.1866, and Ka/Ks = 0.1597 were recorded, which showed that high purifying selection pressure acted on the protein-coding genes of species of the family Phyllanthaceae. Two genes—psbL and petL—showed a signature of positive selection in Sauropus spatulifolius and Flueggea virosa, respectively, based on the values of Ka/Ks. However, the results of FUBAR and MEME did not support signature of positive selection.
3.6. Transition and Transversion Substitutions
The transition and transversion substitutions within the complete chloroplast genome and in the protein-coding regions were analyzed. The comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes among the distantly related species of Phyllanthaceae revealed the existence of 10,950–12,603 substitutions (Figure 5a), whereas comparison of closely related species revealed the presence of 257–2077 substitutions (Figure 6a). Furthermore, 3237–3747 substitutions were observed in protein-coding sequences of distantly related species (Figure 5b) and 65–685 substitutions in closely related species (Figure 6b). The ratio of transition and transversion substitutions (Ts/Tv) also revealed variations in both distantly related and closely related species. The Ts/Tv ratio for distantly related species varied from 1.34 to 1.40 (Figure 5c), whereas for closely related species it varied from 0.77 to 1.0 (Figure 6c). The analysis revealed that the Ts/Tv ratio was higher in protein-coding sequences than in the complete chloroplast genome. The Ts/Tv ratio for distantly related species was 2.09–2.34 (Figure 5c) and for closely related species 1.42–1.71 (Figure 6c). The higher Ts/Tv ratio in protein-coding regions showed the occurrence of higher transition substitutions than transversion substitutions. The lower Ts/Tv ratio in the complete genome than in coding regions was due to inclusion of an intergenic spacer region in which higher transversion substitutions take place than transition substitutions.
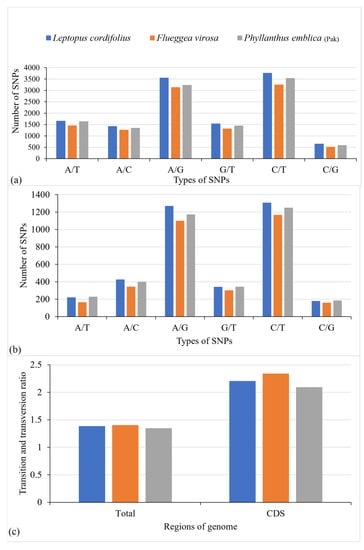
Figure 5.
Comparison of transition and transversion substitutions in distantly related species. (a) The comparison of transition and transversion substitutions within the complete chloroplast genome. (b) Comparison of transition and transversion substitutions within protein-coding sequences. (c) Comparison of the ratio of transition and transversion substitutions in the complete chloroplast genome and in protein-coding sequences. Baccaurea ramiflora was used as a reference for all species.
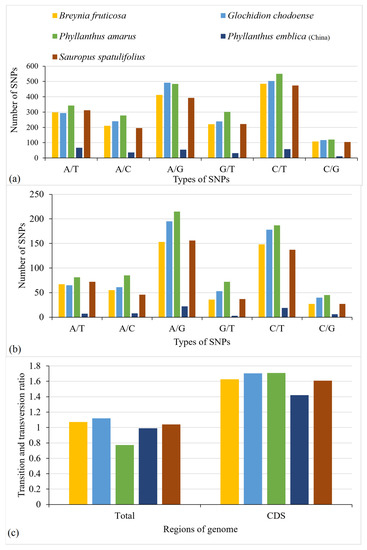
Figure 6.
Comparison of transition and transversion substitutions in closely related species. (a) The comparison of transition and transversion substitutions within the complete chloroplast genome. (b) Comparison of transition and transversion substitutions within protein-coding sequences. (c) Comparison of the ratio of transition and transversion substitutions in the complete chloroplast genome and in protein-coding sequences. Phyllanthus emblica (Pakistan) was used as a reference for all species.
3.7. Intraspecies Variations in Chloroplast Genomes of Phyllanthus Emblica
The intraspecies variations in the chloroplast genomes of Phyllanthus emblica belonging to two different countries—Pakistan and China—with totally different climatic changes were determined. Slight differences emerged in genome size, LSC, and SSC, as shown in Table 2. The numbers of protein-coding genes, unique genes, and IR regions were the same in both species. The comparative analysis of both P. emblica chloroplast genomes revealed 257 SNPs in the whole chloroplast genome, 79 of which belong to coding regions. In total, 108 insertion-deletion (InDel) events with an average length of 5.32 in which 3 InDels belong to coding regions were observed. No InDels or SNPs in genes of transfer RNAs and ribosomal RNAs were seen.
3.8. Polymorphism of Protein-Coding Genes
The polymorphism of all protein-coding genes was assessed to facilitate identification of suitable polymorphic loci for future phylogenetic inference of the family Phyllanthaceae (Table S3). The 15 genes of ≥200 bp were selected. The missing data produced by the highly polymorphic regions due to InDels to provide information about the suitability of these loci were also assessed and are presented in Table 3. These loci included in the analysis were rpl22, ycf1, matK, ndhF, and rps15, as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Polymorphic protein-coding sequences.
4. Discussion
4.1. Chloroplast Genome Assembly from Whole Genome Sequencing and Comparative Chloroplast Genomics
Although the angiosperm’s chloroplast genome is believed to be conserved in both gene content and gene order, with conserved intronic regions in protein-coding genes and tRNA genes. However, the loss of some genes or introns were also reported [20,22,35,64]. Several studies have reported de novo assembled chloroplast genomes from whole genome shotgun reads [65,66]. In the present study, whole genome shotgun sequencing was employed to assemble the complete chloroplast genomes of Phyllanthus emblica (Pak), Leptopus cordifolius, and Flueggea virosa with high coverage depth.
We observed that the chloroplast genome features of the species belonging to the family Phyllanthaceae were highly similar to each other. The intron of atpF gene was deleted in all of the species, except Baccaurea ramiflora, which was present at a basal point in the current species. The rps16 gene was found to be non-functional in the two species of Baccaurea ramiflora (deletion of exon 1) and Leptopus cordifolius (gene loss with only few base pairs remaining). The deletion of the rps16 gene has previously been reported [27] in the species of the order Malpighiales and a functional copy was found for some species in nuclear genome but was not reported in the family Phyllanthaceae due to inclusion of Glochidion chodoense in the comparison containing a functional rps16 gene. Here, comparison of several species helped us to determine the deletion/pseudogenization of rps16 for the first time in the family Phyllanthaceae. The GC content of species of the family Phyllanthaceae is similar to other angiosperms and to other species of the order Malpighiales [20,67,68]. Another gene, infA, was completely absent in the chloroplast genome of the species of the family Phyllanthaceae. The deletion and pseudogenization of the infA gene were also reported in other families of angiosperms, including Araceae [57,66,69], Malvaceae [19], and Malpighiaceae [20]. Since the product of the infA gene has a vital function as a translation initiation factor, it can be inferred that the functional copy of infA has probably been transferred to the nuclear genome [35,70].
Previously, it was documented that IR’s contraction and expansion can generate a pseudo-copy as well as a functional gene copy or may change duplicated genes to a single-copy gene due to transfer of IRs to single-copy regions (LSC or SSC) or may convert a single-copy gene to a duplicated gene when transferred from LSC or SSC to IRs [19,34,57,65]. In our study, the analyzed species were found to be conserved in terms of contraction and expansion of IRs. Likewise, the generation of a pseudo-copy of ycf1, rpl2, and rps19 remained similar to other angiosperms [71,72]. However, the duplication of complete functional genes, such as ycf1, rps15, and rps19, observed in other angiosperms was not detected here [19,57,65].
4.2. Simple Sequence Repeats and Oligonucleotide Repeat Analyses
The highest number of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) was observed in the LSC region as compared with lower numbers in SSC and IR regions. Mononucleotide SSRs (A/T) and dinucleotide SSRs (AT/TA) were more abundant than trinucleotide SSRs, consistent with previous studies [54,73,74,75,76,77]. However, a few studies have reported higher numbers of trinucleotides than of dinucleotides [19,68,78,79]. The SSR marker identified in the current study can serve as a resource for population genetics studies of species of the family Phyllanthaceae. REPuter detected different oligonucleotide repeats, including forward, reverse, complementary, and palindromic repeats in the chloroplast genomes. These repeats originate InDels and substitutions [80,81,82] and can be used as proxies for identification of mutational hotspot regions [69,81,83]. High variations were detected in the number of oligonucleotide repeats, but further analysis involving more species is needed to gain insight into the evolutionary events leading to loss/gain of repeats. Previously, correlations between the identified number of repeats and genome size and phylogenetic position of species have not been established [65].
4.3. Phylogenetics Analysis and Suitable Polymorphic Loci for Further Phylogenetic Inference
The phylogenetic analysis showed that the polyphyletic nature of the genus Phyllanthus was similar to the recently obtained results using nuclear (ITS, PHYC) and chloroplast (matK, accD-psaI, trnS-trnG) markers along with morphological data [6]. Hence, the author suggested the division of the genus Phyllanthus into nine small genera instead of combining the embedded genera to Phyllanthus. Our study was based on 76 protein-coding sequences, which supports the polyphyletic nature of the genus Phyllanthus with a limited number of species. Further sequencing will thus be required to gain broad insight into the phylogenetics of Phyllanthus and the tribe Phyllantheae. A similar phylogenetic position has been reported in other species earlier [4,7]. Certain discrepancies still exist in the phylogeny of the family Phyllanthaceae, which warrant further elaboration [3,4,7]. Here, we have identified 15 suitable highly polymorphic regions from protein-coding sequences based on the comparative analysis of chloroplast genomes. The phylogenetic analysis based on these loci provided similar results to the dataset of 76 genes, which suggests a high efficacy of these loci for phylogenetic inference. These will serve as suitable markers for quality phylogenetic inference of the family Phyllanthaceae, as lineage-specific molecular markers are more authentic, robust, and cost-effective [22,36,83,84,85].
In conclusion, our study provides insight into the molecular evolution of the chloroplast genome and sheds light on the deletion/pseudogenization of rps16 in the family Phyllanthaceae for the first time. However, sequencing and analysis of a broad number of species may elucidate the evolution and biological factors that have led to deletion of this gene. The phylogenetic analysis of our limited species showed the polyphyletic nature of the genus Phyllanthus but sequencing multiple species of this genus may be helpful to reconstruct a high-resolution phylogenetic tree and obtain insight into its systematics. The suitable polymorphic markers determined in this study may also be validated and applied in the future to a large number of species for broad phylogenetic inference of the family Phyllanthaceae.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d13090403/s1, Figure S1. Heatmap representing the relative synonymous codon usage. The y-axis represents 61 amino acid coding codons, and the x-axis represents species names. Phyllanthus emblica (Pak) was included in the comparison. Figure S2. Comparison of amino acid frequency within the species of Phyllanthaceae. The x-axis represents the amino acid with standard symbol, and the y-axis represents the frequency of amino acids. Phyllanthus emblica (Pak) was included in the comparison. Figure S3. Comparison of simple sequence repeats and oligonucleotide repeats among species of the family Phyllanthaceae. (a) Comparison of six types of SSRs. (b) Distributions of SSRs in the LSC, SSC, and IR regions. (c) Comparison of four types of oligonucleotide repeats. (d) Oligonucleotide repeat comparison based on size. (e) Distribution of oligonucleotide repeats in three main regions of the plastome. LSC = large single copy; SSC = small single copy; IR = inverted repeat; F = forward; R = reverse; C = complementary; P = palindromic. Table S1. Simple sequence repeats analysis among species of the family Phyllanthaceae. Table S2. Comparison of synonymous and non-synonymous substitutions among species of the family Phyllanthaceae. Table S3. Polymorphic analysis of protein-coding genes.
Author Contributions
Manuscript drafting, A. and U.R.; data analyses, U.R., A., M.M. and A.J.; data curation, U.R. and A.; data interpretation, U.R., A., P.P. and N.S.; conceptualization, U.R., N.S. and P.P.; review and editing of first draft, N.S. and P.P.; supervision, N.S.; project administration and resources, N.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Open access funding provided by University of Helsinki.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The newly assembled chloroplast genomes have been submitted to the National Center for Biotechnology under accession numbers BK059210 (Flueggea virosa), MZ424188 (Leptopus cordifolius), and MN122078 (Phyllanthus emblica). All of the analyzed data are available in the main manuscript or as Supplementary Material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Chase, M.W.; Christenhusz, M.J.M.; Fay, M.F.; Byng, J.W.; Judd, W.S.; Soltis, D.E.; Mabberley, D.J.; Sennikov, A.N.; Soltis, P.S.; Stevens, P.F.; et al. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 181, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, Z.; Ruhfel, B.R.; Schaefer, H.; Amorim, A.M.; Sugumaran, M.; Wurdack, K.J.; Endress, P.K.; Matthews, M.L.; Stevens, P.F.; Mathews, S.; et al. Phylogenomics and a posteriori data partitioning resolve the Cretaceous angiosperm radiation Malpighiales. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17519–17524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, P.; Kathriarachchi, H.; Wurdack, K. A phylogenetic classification of Phyllanthaceae (Malpighiales; Euphorbiaceae sensu lato). Kew Bull. 2006, 61, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kathriarachchi, H.; Samuel, R.; Hoffmann, P.; Mlinarec, J.; Wurdack, K.J.; Ralimanana, H.; Stuessy, T.F.; Chase, M.W. Phylogenetics of tribe Phyllantheae (Phyllanthaceae; Euphorbiaceae sensu lato) based on nrITS and plastid matK DNA sequence data. Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenhusz, M.J.M.; Byng, J.W. The number of known plants species in the world and its annual increase. Phytotaxa 2016, 261, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouman, R.W.; Keßler, P.J.A.; Telford, I.R.H.; Bruhl, J.J.; Strijk, J.S.; Saunders, R.M.K.; van Welzen, P.C. Molecular phylogenetics of Phyllanthus sensu lato (Phyllanthaceae): Towards coherent monophyletic taxa. Taxon 2021, 70, 72–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathriarachchi, H.; Hoffmann, P.; Samuel, R.; Wurdack, K.J.; Chase, M.W. Molecular phylogenetics of Phyllanthaceae inferred from five genes (plastid atpB, matK, 3′ndhF, rbcL, and nuclear PHYC). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 36, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, R.W.; Keßler, P.J.A.; Telford, I.R.H.; Bruhl, J.J.; Van Welzen, P.C. Subgeneric delimitation of the plant genus Phyllanthus (Phyllanthaceae). Blumea J. Plant. Taxon. Plant. Geogr. 2018, 63, 167–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Wu, L.; Guo, H.; Chen, W.; Cui, Y.; Qi, Q.; Li, S.; Liang, W.; Yang, G.; Shao, Y.; et al. The genus Phyllanthus: An ethnopharmacological, phytochemical, and pharmacological review. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 7584952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaire, B.P.; Subedi, L. Phytochemistry, pharmacology and medicinal properties of Phyllanthus emblica Linn. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.K. Edible Medicinal and Non-Medicinal Plants; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 978-94-007-1763-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, A. A Review on Phytochemical, Pharmacological and Potential Therapeutic Uses of Phyllanthus Emblica. World J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 6, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-C.; Yang, S.-H.; Hsia, S.-M.; Wu, C.-H.; Yen, G.-C. Inhibitory effects of Phyllanthus emblica L. on hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis in vitro. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zhao, M.; Yang, B.; Ren, J.; Shen, G.; Rao, G. Antioxidant and antiproliferative capacities of phenolics purified from Phyllanthus emblica L. fruit. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Sun, Q.; Marques, M.; Witcher, M. Anticancer Properties of Phyllanthus emblica (Indian Gooseberry). Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 950890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vorontsova, M.S.; Hoffmann, P. Revision of the genus leptopus (Phyllanthaceae, Euphorbiaceae sensu lato). Kew Bull. 2009, 64, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H. Transgene containment by maternal inheritance: Effective or elusive? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6879–6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neale, D.B.; Sederoff, R.R. Paternal inheritance of chloroplast DNA and maternal inheritance of mitochondrial DNA in Loblolly pine. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1989, 77, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah; Mehmood, F.; Shahzadi, I.; Waseem, S.; Mirza, B.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T. Chloroplast genome of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis (Malvaceae): Comparative analyses and identification of mutational hotspots. Genomics 2020, 112, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, A.P.A.; Resende-Moreira, L.C.; Buzatti, R.S.O.; Nazareno, A.G.; Carlsen, M.; Lobo, F.P.; Kalapothakis, E.; Lovato, M.B. Chloroplast genomes of Byrsonima species (Malpighiaceae): Comparative analysis and screening of high divergence sequences. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.-M.; Zhao, C.-Y.; Liu, X.-F. Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequences of Kaempferia Galanga and Kaempferia Elegans: Molecular Structures and Comparative Analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.-S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.-J. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Cantino, P.D.; Olmstead, R.G.; Bramley, G.L.C.; Xiang, C.L.; Ma, Z.H.; Tan, Y.H.; Zhang, D.X. A large-scale chloroplast phylogeny of the Lamiaceae sheds new light on its subfamilial classification. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.-H.; Liu, Q.; Hu, W.; Wang, T.; Xue, Q.; Messing, J. Dynamics of chloroplast genomes in green plants. Genomics 2015, 106, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saina, J.K.; Li, Z.Z.; Gichira, A.W.; Liao, Y.Y. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of tree of heaven (Ailanthus altissima (mill.) (sapindales: Simaroubaceae), an important pantropical tree. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah; Mehmood, F.; Heidari, P.; Ahmed, I.; Poczai, P. Pseudogenization of trnT-GGU in chloroplast genomes of the plant family Asteraceae. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, A.A.; Jansen, R.K. The evolutionary fate of rpl32 and rps16 losses in the Euphorbia schimperi (Euphorbiaceae) plastome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.D. Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1985, 19, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I. Evolutionary Dynamics in Taro; Massey University: Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.-F.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.-F.; Shi, F.-X.; Chen, W.-N.; Ge, X.-J. Origins and Domestication of Cultivated Banana Inferred from Chloroplast and Nuclear Genes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henriquez, C.L.; Arias, T.; Pires, J.C.; Croat, T.B.; Schaal, B.A. Phylogenomics of the plant family Araceae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 75, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Duan, X.; Zhang, R.; Guo, C.; Li, L.; Xu, G.; Shan, H.; Kong, H.; Ren, Y. Chloroplast genomic data provide new and robust insights into the phylogeny and evolution of the Ranunculaceae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 135, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Lv, G. Complete chloroplast genome of seven Fritillaria species, variable DNA markers identification and phylogenetic relationships within the genus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdullah; Henriquez, C.L.; Mehmood, F.; Hayat, A.; Sammad, A.; Waseem, S.; Waheed, M.T.; Matthews, P.J.; Croat, T.B.; Poczai, P.; et al. Chloroplast genome evolution in the Dracunculus clade (Aroideae, Araceae). Genomics 2021, 113, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.K.; Cai, Z.; Raubeson, L.A.; Daniell, H.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Muller, K.F.; Guisinger-Bellian, M.; Haberle, R.C.; Hansen, A.K.; et al. Analysis of 81 genes from 64 plastid genomes resolves relationships in angiosperms and identifies genome-scale evolutionary patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19369–19374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, I.; Matthews, P.J.; Biggs, P.J.; Naeem, M.; Mclenachan, P.A.; Lockhart, P.J. Identification of chloroplast genome loci suitable for high-resolution phylogeographic studies of Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott (Araceae) and closely related taxa. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wei, J.; Yang, T.; Mu, W.; Song, B.; Yang, T.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, G.; Li, W.; et al. Molecular digitization of a botanical garden: High-depth whole-genome sequencing of 689 vascular plant species from the Ruili Botanical Garden. Gigascience 2019, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milne, I.; Bayer, M.; Cardle, L.; Shaw, P.; Stephen, G.; Wright, F.; Marshall, D. Tablet-next generation sequence assembly visualization. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq—Versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laslett, D.; Canback, B. ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehwark, P.; Greiner, S. GB2sequin—A file converter preparing custom GenBank files for database submission. Genomics 2019, 111, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.C.E.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple Alignment of Conserved Genomic Sequence With Rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant. 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrie, D.S.; Messer, P.W.; Hershberg, R.; Petrov, D.A. Strong purifying selection at synonymous sites in D. melanogaster. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murrell, B.; Wertheim, J.O.; Moola, S.; Weighill, T.; Scheffler, K.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Detecting individual sites subject to episodic diversifying selection. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murrell, B.; Moola, S.; Mabona, A.; Weighill, T.; Sheward, D.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Scheffler, K. FUBAR: A fast, unconstrained bayesian AppRoximation for inferring selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delport, W.; Poon, A.F.Y.; Frost, S.D.W.; Pond, S.L. Datamonkey 2010: A suite of phylogenetic analysis tools for evolutionary biology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2455–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehmood, F.; Abdullah; Ubaid, Z.; Shahzadi, I.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T.; Poczai, P.; Mirza, B. Plastid genomics of Nicotiana (Solanaceae): Insights into molecular evolution, positive selection and the origin of the maternal genome of Aztec tobacco (Nicotiana rustica). PeerJ 2020, 8, e9552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah; Henriquez, C.L.; Mehmood, F.; Carlsen, M.M.; Islam, M.; Waheed, M.T.; Poczai, P.; Croat, T.B.; Ahmed, I. Complete chloroplast genomes of Anthurium huixtlense and Pothos scandens (Pothoideae, Araceae): Unique inverted repeat expansion and contraction affect rate of evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 2020, 88, 562–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, P.; Novis, P.; Milligan, B.G.; Riden, J.; Rambaut, A.; Larkum, T. Heterotachy and Tree Building: A Case Study with Plastids and Eubacteria. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, A.; Guo, W.; Gupta, S.; Fan, W.; Mower, J.P. Evolutionary dynamics of the plastid inverted repeat: The effects of expansion, contraction, and loss on substitution rates. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Kuma, K.I.; Toh, H.; Miyata, T. MAFFT version 5: Improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v4: Recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W256–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, K.S.; Kwak, M.; Lee, B.; Park, S.J. Complete chloroplast genome of tetragonia tetragonioides: Molecular phylogenetic relationships and evolution in caryophyllales. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, C.L.; Abdullah; Ahmed, I.; Carlsen, M.M.; Zuluaga, A.; Croat, T.B.; Mckain, M.R. Evolutionary dynamics of chloroplast genomes in subfamily Aroideae (Araceae). Genomics 2020, 112, 2349–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah; Henriquez, C.L.; Mehmood, F.; Shahzadi, I.; Ali, Z.; Waheed, M.T.; Croat, T.B.; Poczai, P.; Ahmed, I. Comparison of chloroplast genomes among Species of Unisexual and Bisexual clades of the monocot family Araceae. Plants 2020, 9, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriquez, C.L.; Abdullah; Ahmed, I.; Carlsen, M.M.; Zuluaga, A.; Croat, T.B.; Mckain, M.R. Molecular evolution of chloroplast genomes in Monsteroideae (Araceae). Planta 2020, 251, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzadi, I.; Abdullah; Mehmood, F.; Ali, Z.; Ahmed, I.; Mirza, B. Chloroplast genome sequences of Artemisia maritima and Artemisia absinthium: Comparative analyses, mutational hotspots in genus Artemisia and phylogeny in family Asteraceae. Genomics 2020, 112, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Biggs, P.J.; Matthews, P.J.; Collins, L.J.; Hendy, M.D.; Lockhart, P.J. Mutational dynamics of aroid chloroplast genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Millen, R.S.; Olmstead, R.G.; Adams, K.L.; Palmer, J.D.; Lao, N.T.; Heggie, L.; Kavanagh, T.A.; Hibberd, J.M.; Gray, J.C.; Morden, C.W.; et al. Many parallel losses of infA from chloroplast DNA during angiosperm evolution with multiple independent transfers to the nucleus. Plant. Cell 2001, 13, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah; Waseem, S.; Mirza, B.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T. Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes of Theobroma cacao and Theobroma grandiflorum. Biologia 2020, 75, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poczai, P.; Hyvönen, J. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of the CAM epiphyte Spanish moss (Tillandsia usneoides, Bromeliaceae) and its comparative analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.; Qi, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, L.; Zhong, Y.; Fang, J.; Hu, C. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Actinidia arguta using the PacBio RS II platform. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Woeste, K.E.; Zhao, P. Completion of the Chloroplast Genomes of Five Chinese Juglans and Their Contribution to Chloroplast Phylogeny. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 7, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.-L.; Ding, M.-Q.; Zou, C.-Y.; Zhu, X.-M.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, M.-L.; Shao, J.-R. Comparative analysis of four Buckwheat species based on morphology and complete chloroplast genome sequences. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, F.; Abdullah; Ubaid, Z.; Bao, Y.; Poczai, P. Comparative Plastomics of Ashwagandha (Withania, Solanaceae) and Identification of Mutational Hotspots for Barcoding Medicinal Plants. Plants 2020, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, F.; Abdullah; Shahzadi, I.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T.; Mirza, B. Characterization of Withania somnifera chloroplast genome and its comparison with other selected species of Solanaceae. Genomics 2020, 112, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. The chloroplast genome sequence of bittersweet (Solanum dulcamara): Plastid genome structure evolution in Solanaceae. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iram, S.; Hayat, M.Q.; Tahir, M.; Gul, A.; Abdullah; Ahmed, I. Chloroplast genome sequence of Artemisia scoparia: Comparative analyses and screening of mutational hotspots. Plants 2019, 8, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonald, M.J.; Wang, W.C.; Da Huang, H.; Leu, J.Y. Clusters of nucleotide substitutions and insertion/deletion mutations are associated with repeat sequences. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1000622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah; Mehmood, F.; Shahzadi, I.; Ali, Z.; Islam, M.; Naeem, M.; Mirza, B.; Lockhart, P.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T. Correlations among oligonucleotide repeats, nucleotide substitutions and insertion-deletion mutations in chloroplast genomes of plant family Malvaceae. J. Syst. Evol. 2021, 59, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah; Henriquez, C.L.; Croat, T.B.; Poczai, P.; Ahmed, I. Mutational dynamics of aroid chloroplast genomes II. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 610838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah; Mehmood, F.; Rahim, A.; Heidari, P.; Ahmed, I.; Poczai, P. Comparative plastome analysis of Blumea, with implications for genome evolution and phylogeny of Asteroideae. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 7810–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Henry, R.J.; Rossetto, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Plant DNA barcoding: From gene to genome. Biol. Rev. 2014, 90, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Park, H.-S.; Lee, S.-C.; Lee, J.; Park, J.Y.; Yang, T.-J. Authentication markers for five major Panax species developed via comparative analysis of complete chloroplast genome sequences. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6298–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).