Mammal Species Richness at a Catena and Nearby Waterholes during a Drought, Kruger National Park, South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Data Analyses
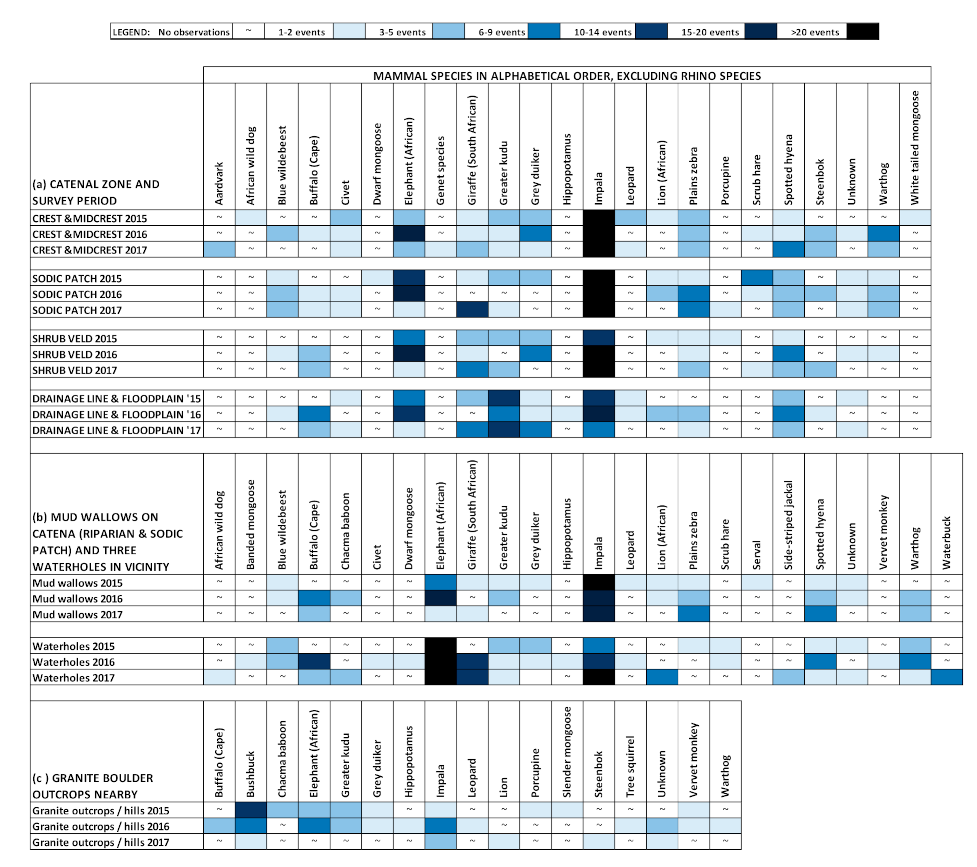
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Species Richness and Habitat Description
4.2. Waterholes and Ephemeral Mud Wallows
4.3. Feeding Guild and Body Size
4.4. General Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maurer, B.A. The relationship between distribution and abundance in a patchy environment. Oikos 1990, 58, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertenbach, W.P.D. Landscapes of the Kruger National Park. Koedoe 1983, 26, 9–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.H. On the relationship between abundance and distribution of species. Am. Nat. 1984, 124, 255–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, K.J. The multiple forms of the interspecific abundance-distribution relationship. Oikos 1996, 76, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, I.P.J.; Grant, C.C. Managing surface-water in a large semi-arid savanna park: Effects on grazer distribution patterns. J. Nat. Cons. 2009, 17, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosh, C.A.; Reyers, B.; Van Jaarsveld, A.S. Estimating the abundances of large herbivores in the Kruger National Park using presence-absence data. Anim. Cons. 2004, 7, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, F.; Scogings, P. Browsing intensity of herbaceous forbs across a semi-arid savanna catenal sequence. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2015, 100, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Toit, J.T. Large herbivores and savanna heterogeneity. In The Kruger Experience: Ecology and Management of Savanna Heterogeneity; Du Toit, J.T., Biggs, H.C., Rogers, K.H., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 292–309. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrom, R.; Skarpe, C. The abundance of large wild herbivores in a semi-arid savanna in relation to seasons, pans and livestock. Afr. J. Ecol. 1999, 37, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, D.W.; Gross, J.E.; Laca, E.A.; Rittenhouse, L.R.; Coughenour, M.B.; Swift, D.M.; Sims, P.I. Mechanisms that result in large herbivore grazing distribution patterns. J. Range Manag. 1996, 49, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, I.P.J.; Riddell, E.S.; Cullum, C.; Petersen, R. Kruger National Park research supersites: Establishing long-term research sites for cross-disciplinary, multiscaled learning. Koedoe 2013, 55, Art. #1107, 7p. Available online: https://koedoe.co.za/index.php/koedoe/article/view/1107/1489 (accessed on 12 February 2021). [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weil, R.R.; Brady, N.C. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 15th ed.; Pearson Education Limited: Harlow, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khomo, L.M.; Rogers, K.H. Proposed mechanism for the origin of sodic patches in Kruger National Park, South Africa. Afr. J. Ecol. 2005, 43, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, D.; Le Roux, P.A.L.; Van Tol, J. Identification of hydropedological flowpaths in Stevenson-Hamilton catena from soil morphological, chemical and hydraulic properties. Koedoe 2020, 62, a1584. Available online: https://koedoe.co.za/index.php/koedoe/article/view/1584 (accessed on 12 February 2021). [CrossRef]
- Janecke, B.B.; Bolton, J.G. Variation in mammal diversity and habitat affect heterogeneity and processes of a granite catena. Koedoe 2020, 62, a1592. Available online: https://koedoe.co.za/index.php/koedoe/article/view/1592 (accessed on 12 February 2021). [CrossRef]
- Janecke, B.B.; Van Tol, J.; Smit, I.P.J.; Van Aardt, A.C.; Riddell, E.S.; Seaman, M.T.; Swart, W.J.; Du Preez, P.J.; Le Roux, P.A.L. Biotic and abiotic connections on a granitic catena: Framework for multidisciplinary research. Koedoe 2020, 62, a1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucina, L.; Rutherford, M.C. (Eds.) The Vegetation of South. Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland; Strelizia 19; South African National Biodiversity Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton-Barber, B.; Berger, L.R. Prime Origins Guide to Exploring Kruger. Your Key to Unlocking Kruger’s Wildlife Treasure; Prime Origins: Cape Town, South Africa, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, C.C.; Scholes, M.C. The importance of nutrient hot-spots in the conservation and management of large wild mammalian herbivores in semi-arid savannas. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 130, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, K.; Ndlovu, M.; Perez-Rodriguez, A. Use of artificial waterholes by animals in the southern region of the Kruger National Park. Afr. J. Wildl. Res. 2018, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, J.E.; Parr, C.L.; Mangena, E.H.; Archibald, S. Droughts decouple African savanna grazers from their preferred forage with consequences for grassland productivity. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, R.D. The Behavior Guide to African Mammals: Including Hoofed Mammals, Carnivores, Primates, 20th ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, South Africa, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package; R Package 2.2-1. 2. 1-2. 2018. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313502495_Vegan_Community_Ecology_Package (accessed on 12 February 2021).
- Colwell, R.K. Biodiversity: Concepts, Patterns and Measurement. In The Princeton Guide to Ecology; Simon, A.L., Ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Janecke, B.B. Vegetation structure and spatial heterogeneity in the Granite Supersite, Kruger National Park. Koedoe 2020, 62, a1591. Available online: https://koedoe.co.za/index.php/koedoe/article/view/1591 (accessed on 12 February 2021). [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.; Benhamou, S.; Yoganand, K.; Owen-Smith, N. Coping with Spatial Heterogeneity and Temporal Variability in Resources and Risks: Adaptive Movement Behaviour by a Large Grazing Herbivore. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smit, I.P.J.; Grant, C.C.; Devereux, B.J. Do artificial waterholes influence the way herbivores use the landscape? Herbivore distribution patterns around rivers and artificial water sources in a large African savanna park. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 136, 85–99. [Google Scholar]
- Redfern, J.V.; Ryan, S.J.; Getz, W.M. Defining herbivore assemblages in the Kruger National Park: A correlative coherence approach. Oecologia 2006, 146, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnaby, T. Beat About the Bush—Mammals, 2nd ed.; Jacana Media: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Smith, N.; Martin, J. Identifying space use at foraging arena scale within the home ranges of large herbivores. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfern, J.V.; Grant, C.C.; Gaylard, A.; Getz, W.M. Surface water availability in the management of herbivore distributions in an African savanna ecosystem. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 63, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, D.; Holden, P.L.; Collinson, R.F.H. Veld management on the game ranch. In Veld management in South Africa; Tainton, N.M., Ed.; University of Natal Press: Pietermaritzburg, South Africa, 1999; pp. 261–279. [Google Scholar]
- Redfern, J.V.; Grant, R.; Biggs, H.; Getz, W.M. Surface-water constraints on herbivore foraging in the Kruger National Park, South Africa. Ecology 2003, 84, 2092–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylard, A.; Owen-Smith, N.; Redfern, J. Surface water availability: Implications for heterogeneity and ecosystem processes. In The Kruger Experience: Ecology and Management of Savanna Heterogeneity; Du Toit, J.T., Biggs, H.C., Rogers, K.H., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 171–188. [Google Scholar]
- Fryxell, J.M.; Sinclair, A.R.E. Causes and consequences of migration by large herbivores. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1988, 3, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrash, I.; Theron, G.; Bothma, J.D.P. Dry season herbivore densities around drinking troughs in the Kruger National Park. J. Arid. Environ. 1995, 29, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothma, J.d.P.; Van Rooyen, N.; Van Rooyen, M.W. Using diet and plant resources to set wildlife stocking densities in African savannas. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2004, 32, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volmer, R.; Hertler, C. The effect of competition on shared food resources in carnivore guilds. Q. Int. 2016, 413, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macandza, V.A.; Owen-Smith, N.; Cain, J.W. Habitat and resource partitioning between abundant and relatively rare grazing ungulates. J. Zool. 2012, 287, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Toit, J.T.; Owen-Smith, N. Body size, population metabolism, and habitat specialization among large African herbivores. Am. Nat. 1989, 113, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malherbe, J.; Smit, I.; Wessels, K.; Beukes, P. Recent droughts in the Kruger National Park as reflected in the extreme climate index. Afr. J. Range For. Sci. 2020, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, S.C.J. Animal behavior. In Game Ranch Management, 6th ed.; Bothma, J.d.P., Du Toit, S.G., Eds.; Van Schaik Publishers: Pretoria, South Africa, 2016; pp. 385–391. [Google Scholar]
| Common Name | Scientific Name | Feeding Guild | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aardvark | Orycteropus afer | Insectivore | Medium |
| African wild dog | Lycaon pictus | Carnivore | Medium |
| Banded mongoose | Mungos mungo | Carnivore | Small |
| Black rhinoceros | Diceros bicornis | Browser | Mega |
| Blue wildebeest | Connochaetes taurinus | Grazer | Large |
| Buffalo (Cape) | Syncerus caffer | Grazer | Mega |
| Bushbuck | Tragelaphus scriptus | Browser | Medium |
| Chacma baboon | Papio ursinus | Omnivore | Medium |
| Civet | Civettictis civetta | Omnivore | Medium |
| Dwarf mongoose | Helogale parvula | Carnivore | Small |
| Elephant (African) | Loxodonta africana | Mixed feeder | Mega |
| Genet species | Genetta species | Carnivore | Small |
| Giraffe (South African) | Giraffa giraffa (G. camelopardalis—old name) | Browser | Mega |
| Greater kudu | Tragelaphus strepsiceros | Browser | Large |
| Grey/Common duiker | Sylvicapra grimmia | Browser | Dwarf |
| Hippopotamus | Hippopotamus amphibius | Grazer | Mega |
| Impala | Aepyceros melampus | Mixed feeder | Medium |
| Leopard | Panthera pardus | Carnivore | Medium |
| Lion (African) | Panthera leo | Carnivore | Large |
| Plains zebra | Equus quagga | Grazer | Large |
| Porcupine | Hystrix africaeaustralis | Vegetarian | Medium |
| Scrub hare | Lepus saxatilis | Vegetarian | Small |
| Serval | Leptailurus serval | Carnivore | Medium |
| Side-striped jackal | Canis adustus | Carnivore | Medium |
| Slender mongoose | Galerella sanguinea | Carnivore | Small |
| Spotted hyena | Crocuta crocuta | Carnivore | Large |
| Steenbok | Raphicerus campestris | Browser | Dwarf |
| Tree squirrel | Paraxerus cepapi | Vegetarian | Small |
| Vervet monkey | Chlorocebus pygerythrus | Omnivore | Small |
| Warthog | Phacochoerus africanus | Grazer | Medium |
| Waterbuck | Kobus ellipsiprymnus | Grazer | Large |
| White rhinoceros | Ceratotherium simum | Grazer | Mega |
| White-tailed mongoose | Ichneumia albicauda | Insectivore | Small |
| Species | Number of Events | Total Events | Max Number of Individuals | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | ||
| De la Porte waterhole | |||||||
| Baboon | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Buffalo | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Elephant | 0 | 10 | 25 | 35 | 0 | 14 | 18 |
| Giraffe | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 11 | 0 |
| Hippopotamus | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Spotted hyena | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Impala | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Scrub hare | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Warthog | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Kwaggaspan waterhole | |||||||
| Baboon | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Buffalo | 0 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 22 | 30 |
| Bushbuck | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Elephant | 14 | 30 | 5 | 49 | 16 | 21 | 6 |
| Giraffe | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 1 |
| Grey duiker | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Impala | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Leopard | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Plains zebra | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Scrub hare | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Warthog | 4 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Waterbuck | 0 | 0 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Renosterkoppies waterhole | |||||||
| Baboon | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Blue wildebeest | 1 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Buffalo | 0 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Elephant | 13 | 16 | 3 | 32 | 30 | 18 | 1 |
| Giraffe | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Greater kudu | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 0 |
| Impala | 3 | 5 | 56 | 64 | 2 | 70 | 90 |
| Lion | 0 | 0 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Spotted hyena | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Vervet monkey | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Warthog | 1 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 3 |
| Wild dog | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| Zone | Survey Period | Total Events | Species Richness | Shannon Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crest and midslope | 2015 | 54 | 12 | 1.91 |
| 2016 | 97 | 14 | 1.74 | |
| 2017 | 58 | 12 | 2.01 | |
| Sodic patch | 2015 | 93 | 12 | 1.61 |
| 2016 | 136 | 11 | 1.34 | |
| 2017 | 86 | 11 | 1.67 | |
| Shrub veld | 2015 | 33 | 9 | 1.85 |
| 2016 | 61 | 9 | 1.69 | |
| 2017 | 52 | 9 | 1.76 | |
| Riparian area | 2015 | 43 | 8 | 1.75 |
| 2016 | 68 | 13 | 2.18 | |
| 2017 | 50 | 9 | 1.97 | |
| Catena total | 2015 | 209 | 17 | 1.89 |
| 2016 | 335 | 17 | 1.67 | |
| 2017 | 248 | 17 | 2.08 | |
| Mud wallows | 2015 | 40 | 11 | 1.65 |
| 2016 | 59 | 9 | 1.84 | |
| 2017 | 45 | 7 | 1.66 | |
| Granite outcrops | 2015 | 28 | 9 | 1.83 |
| 2016 | 36 | 11 | 2.03 | |
| 2017 | 9 | 4 | 1.15 | |
| De la Porte Waterhole | 2015 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 2016 | 17 | 7 | 1.20 | |
| 2017 | 32 | 4 | 0.73 | |
| Kwaggaspan Waterhole | 2015 | 26 | 7 | 1.41 |
| 2016 | 38 | 7 | 0.81 | |
| 2017 | 19 | 4 | 1.23 | |
| Renosterkoppies Waterhole | 2015 | 22 | 6 | 1.28 |
| 2016 | 44 | 9 | 1.89 | |
| 2017 | 80 | 7 | 1.05 | |
| Waterhole total | 2015 | 73 | 10 | 1.38 |
| 2016 | 150 | 17 | 1.98 | |
| 2017 | 191 | 11 | 1.36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janecke, B.B. Mammal Species Richness at a Catena and Nearby Waterholes during a Drought, Kruger National Park, South Africa. Diversity 2021, 13, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080387
Janecke BB. Mammal Species Richness at a Catena and Nearby Waterholes during a Drought, Kruger National Park, South Africa. Diversity. 2021; 13(8):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080387
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanecke, Beanélri B. 2021. "Mammal Species Richness at a Catena and Nearby Waterholes during a Drought, Kruger National Park, South Africa" Diversity 13, no. 8: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080387
APA StyleJanecke, B. B. (2021). Mammal Species Richness at a Catena and Nearby Waterholes during a Drought, Kruger National Park, South Africa. Diversity, 13(8), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080387







