Assessment of Sesamia nonagrioides (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) EcR and USP Genes as Targets for Exogenous Non-Persistent RNAi
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing and Staging of Larvae
2.2. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis & Sequencing
2.3. Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
2.4. Hemolymph dsEcR427 Administration
2.4.1. dsRNA Quantity/Control Treatments
2.4.2. Targeting SnEcR427
2.4.3. Bacterial Administration of dsEcR427
2.4.4. Hemolymph dsUSP689 Administration Using Bacterial dsRNA Extracts
3. Results
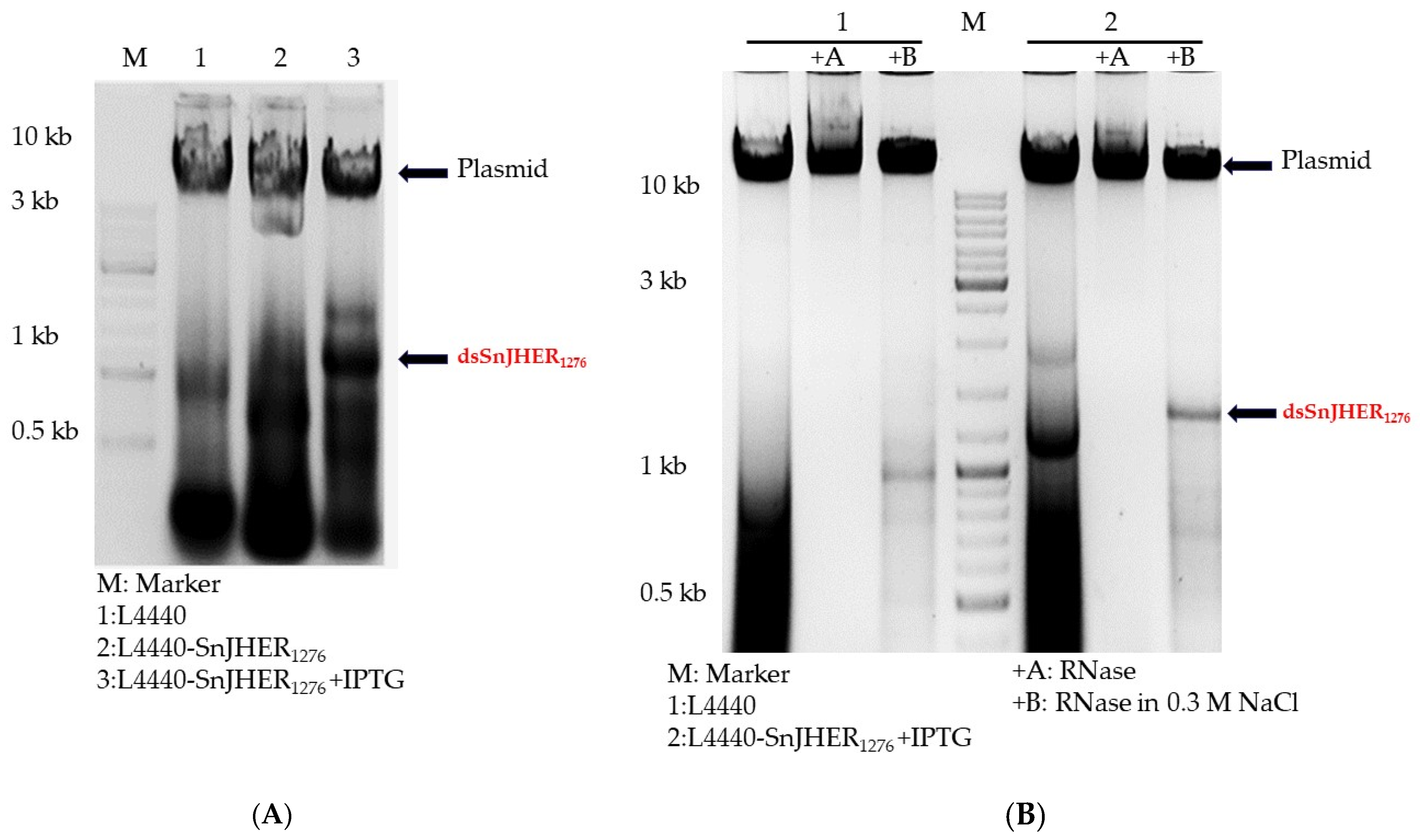
3.1. Optimization of Bacterial dsRNA Synthesis
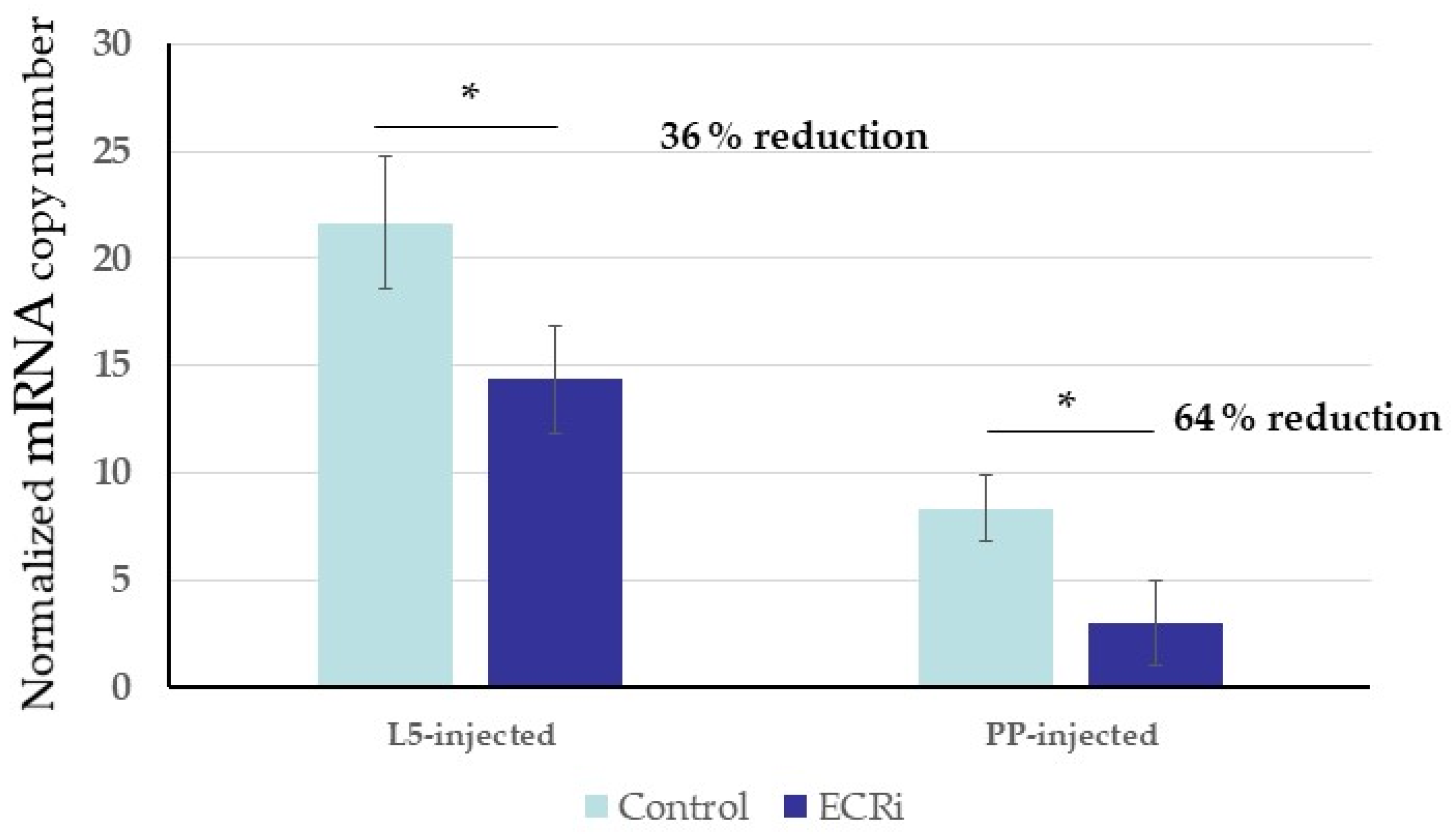
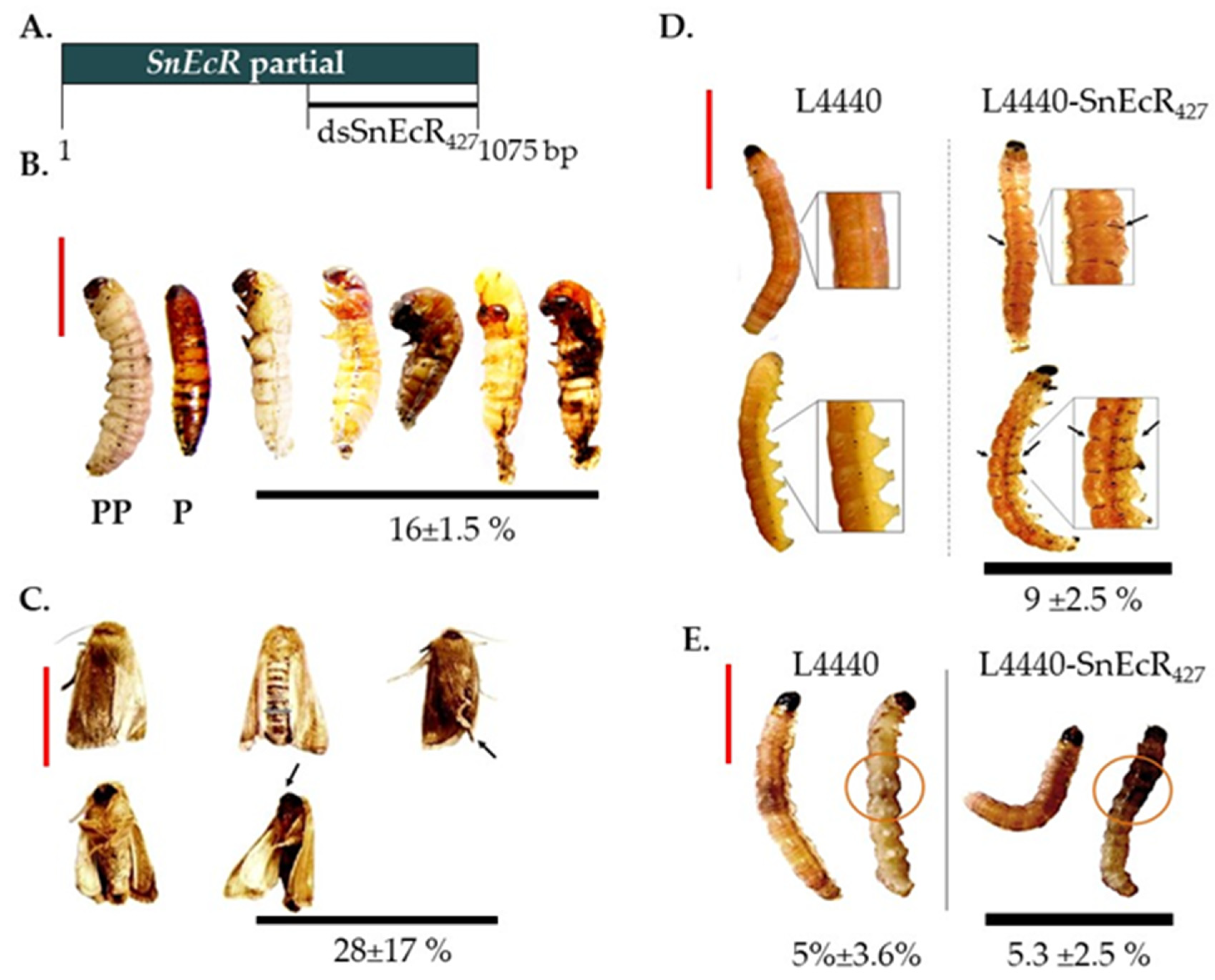
3.2. Functional Analysis of S. nonagrioides Ecdysone Receptor Gene Using Different RNAi Delivery Methods
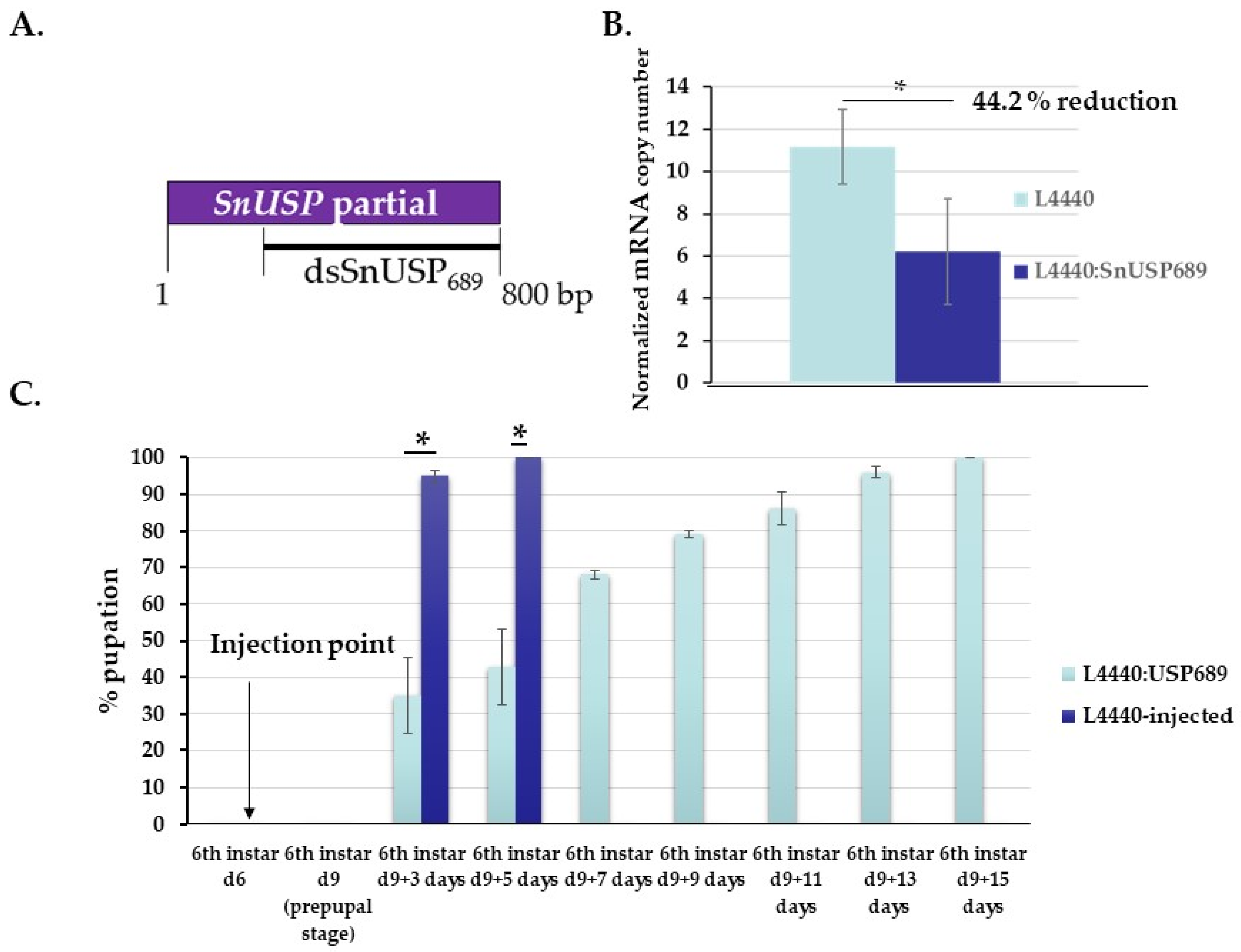
3.3. Functional Analysis of S. nonagrioides USP Gene
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hannon, G.J. RNA Interference. Nature 2002, 418, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynant, N.; Santos, D.; Broeck, J.V. The Evolution of Animal Argonautes: Evidence for the Absence of Antiviral AGO Argonautes in Vertebrates. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmons, L.; Court, D.L.; Fire, A. Ingestion of Bacterially Expressed DsRNAs Can Produce Specific and Potent Genetic Interference in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Gene 2001, 263, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuschl, T.; Zamore, P.D.; Lehmann, R.; Bartel, D.P.; Sharp, P.A. Targeted MRNA Degradation by Double-Stranded RNA in Vitro. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 3191–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennerdell, J.R.; Carthew, R.W. Heritable Gene Silencing in Drosophila Using Double-Stranded RNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzitoyeva, S.; Dimitrijevic, N.; Manev, H. Intra-Abdominal Injection of Double-Stranded RNA into Anesthetized Adult Drosophila Triggers RNA Interference in the Central Nervous System. Mol. Psychiatry 2001, 6, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rajagopal, R.; Sivakumar, S.; Agrawal, N.; Malhotra, P.; Bhatnagar, R.K. Silencing of Midgut Aminopeptidase N of Spodoptera Litura by Double-Stranded RNA Establishes Its Role AsBacillus Thuringiensis Toxin Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 46849–46851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.N.; Santos, A.; Pinto, F.S.; Gontijo, N.F.; Lehane, M.J.; Pereira, M.H. RNA Interference of the Salivary Gland Nitrophorin 2 in the Triatomine Bug Rhodnius Prolixus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) by DsRNA Ingestion or Injection. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 36, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, J.A.; Bogaert, T.; Clinton, W.; Heck, G.R.; Feldmann, P.; Ilagan, O.; Johnson, S.; Plaetinck, G.; Munyikwa, T.; Pleau, M. Control of Coleopteran Insect Pests through RNA Interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.-B.; Cai, W.-J.; Wang, J.-W.; Hong, G.-J.; Tao, X.-Y.; Wang, L.-J.; Huang, Y.-P.; Chen, X.-Y. Silencing a Cotton Bollworm P450 Monooxygenase Gene by Plant-Mediated RNAi Impairs Larval Tolerance of Gossypol. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, J.A.; Roberts, J.K. Progress towards RNAi-Mediated Insect Pest Management. Adv. Insect Physiol. 2014, 47, 249–295. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Peng, H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, H.; Xie, Q.; Tang, B.; Zhang, W. Developmental Control of a Lepidopteran Pest Spodoptera Exigua by Ingestion of Bacteria Expressing DsRNA of a Non-Midgut Gene. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H. RNA Interference of Four Genes in Adult Bactrocera Dorsalis by Feeding Their DsRNAs. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourti, A.; Swevers, L.; Kontogiannatos, D. In Search of New Methodologies for Efficient Insect Pest Control: The RNAi “Movement”. In Biological Control of Pest and Vector Insects; InTech Rijeka: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, K.H.; Waterhouse, P.M. RNAi for Insect-Proof Plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1231–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swevers, L.; Smagghe, G. Use of RNAi for Control of Insect Crop Pests. In Arthropod-Plant Interactions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 177–197. [Google Scholar]
- Terenius, O.; Papanicolaou, A.; Garbutt, J.S.; Eleftherianos, I.; Huvenne, H.; Kanginakudru, S.; Albrechtsen, M.; An, C.; Aymeric, J.-L.; Barthel, A. RNA Interference in Lepidoptera: An Overview of Successful and Unsuccessful Studies and Implications for Experimental Design. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashuta, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wiggins, B.E.; Ramaseshadri, P.; Segers, G.C.; Johnson, S.; Meyer, S.E.; Kerstetter, R.A.; McNulty, B.C.; Bolognesi, R. Environmental RNAi in Herbivorous Insects. RNA 2015, 21, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, J.N.; Kalsi, M.; Sethi, A.; Narva, K.E.; Fishilevich, E.; Singh, S.; Mogilicherla, K.; Palli, S.R. Reduced Stability and Intracellular Transport of DsRNA Contribute to Poor RNAi Response in Lepidopteran Insects. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Saha, T.T.; Pei, G.; Raikhel, A.S.; Zou, Z. Hormone and Receptor Interplay in the Regulation of Mosquito Lipid Metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2709–E2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghbeish, N.; Tsai, C.-C.; Schubiger, M.; Zhou, J.Y.; Evans, R.M.; McKeown, M. The Dual Role of Ultraspiracle, the Drosophila Retinoid X Receptor, in the Ecdysone Response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3867–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhadialla, T.S.; Carlson, G.R.; Le, D.P. New Insecticides with Ecdysteroidal and Juvenile Hormone Activity. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 545–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, S.R.; Hormann, R.E.; Schlattner, U.; Lezzi, M. Ecdysteroid Receptors and Their Applications in Agriculture and Medicine. Vitam. Horm. 2005, 73, 59–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kottaipalayam-Somasundaram, S.R.; Jacob, J.P.; Aiyar, B.; Merzendorfer, H.; Nambiar-Veetil, M. Chitin Metabolism as a Potential Target for RNAi-based Control of the Forestry Pest Hyblaea Puera Cramer (Lepidoptera: Hyblaeidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 78, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ma, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, D.; Song, X.; Ren, X.; Ma, Y. Combined Transcriptomic Analysis and RNA Interference Reveal the Effects of Methoxyfenozide on Ecdysone Signaling Pathway of Spodoptera Exigua. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Chen, H.; Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Xia, L. RNA Interference of the Ecdysone Receptor Genes EcR and USP in Grain Aphid (Sitobion Avenae F.) Affects Its Survival and Fecundity upon Feeding on Wheat Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.-Y.; Deng, P.; Zhang, Q.; Li, A.; Fu, K.-Y.; Guo, W.-C.; Li, G.-Q. Ecdysone Receptor Isoforms Play Distinct Roles in Larval–Pupal–Adult Transition in Leptinotarsa Decemlineata. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.-Y.; Du, J.-L.; Mu, L.-L.; Guo, W.-C.; Li, G.-Q. Importance of Taiman in Larval-Pupal Transition in Leptinotarsa Decemlineata. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ament, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Blatti, C.A.; Hong, F.; Liang, Z.S.; Negre, N.; White, K.P.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L.; Mizzen, C.A. The Transcription Factor Ultraspiracle Influences Honey Bee Social Behavior and Behavior-Related Gene Expression. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hult, E.F.; Huang, J.; Marchal, E.; Lam, J.; Tobe, S.S. RXR/USP and EcR Are Critical for the Regulation of Reproduction and the Control of JH Biosynthesis in Diploptera Punctata. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 80, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiannatos, D.; Swevers, L.; Maenaka, K.; Park, E.Y.; Iatrou, K.; Kourti, A. Functional Characterization of a Juvenile Hormone Esterase Related Gene in the Moth Sesamia Nonagrioides through RNA Interference. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiliotopoulos, A.; Gkouvitsas, T.; Fantinou, A.; Kourti, A. Expression of a CDNA Encoding a Member of the Hexamerin Storage Proteins from the Moth Sesamia Nonagrioides (Lef.) during Diapause. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 148, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkouvitsas, T.; Kontogiannatos, D.; Kourti, A. Differential Expression of Two Small Hsps during Diapause in the Corn Stalk Borer Sesamia Nonagrioides (Lef.). J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontogiannatos, D.; Gkouvitsas, T.; Kourti, A. The Expression Patterns of the Clock Genes Period and Timeless Are Affected by Photoperiod in the Mediterranean Corn Stalk Borer, Sesamia Nonagrioides. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 94, e21366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiannatos, D.; Swevers, L.; Kourti, A. Recent Gene Multiplication and Evolution of a Juvenile Hormone Esterase-Related Gene in a Lepidopteran Pest. Gene Rep. 2016, 4, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkouvitsas, T.; Kontogiannatos, D.; Kourti, A. Expression of the Hsp83 Gene in Response to Diapause and Thermal Stress in the Moth Sesamia Nonagrioides. Insect Mol. Biol. 2009, 18, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkouvitsas, T.; Kontogiannatos, D.; Kourti, A. Cognate Hsp70 Gene Is Induced during Deep Larval Diapause in the Moth Sesamia Nonagrioides. Insect Mol. Biol. 2009, 18, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, E.; He, Q.; Liu, S.; Tian, L.; Sheng, Z.; Peng, Q.; Guan, J.; Shi, M.; Li, K.; Gilbert, L.I. MET Is Required for the Maximal Action of 20-Hydroxyecdysone during Bombyx Metamorphosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e53256. [Google Scholar]
- Molnár, A.; Csorba, T.; Lakatos, L.; Várallyay, É.; Lacomme, C.; Burgyán, J. Plant Virus-Derived Small Interfering RNAs Originate Predominantly from Highly Structured Single-Stranded Viral RNAs. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7812–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.G.; Michel, K.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Siegfried, B.D.; Hunter, W.B.; Smagghe, G.; Zhu, K.Y.; Douglas, A.E. Towards the Elements of Successful Insect RNAi. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joga, M.R.; Zotti, M.J.; Smagghe, G.; Christiaens, O. RNAi Efficiency, Systemic Properties and Novel Delivery Methods for Pest Insect Control: What We Know So Far. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, S.R. RNA Interference in Colorado Potato Beetle: Steps toward Development of DsRNA as a Commercial Insecticide. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2014, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, K.; Christiaens, O.; Pertry, I.; Bailey, A.; Niblett, C.; Ghislain, M.; Gheysen, G.; Smagghe, G. RNAi-based Gene Silencing through DsRNA Injection or Ingestion against the African Sweet Potato Weevil Cylas Puncticollis (Coleoptera: Brentidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Ma, W.; Wang, X.; Gao, M.; Dai, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; Chen, S.; Ding, L. Next-generation Transgenic Cotton: Pyramiding RNAi and Bt Counters Insect Resistance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Carrière, Y. Surge in Insect Resistance to Transgenic Crops and Prospects for Sustainability. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Issa, M.S.; Cooper, A.M.; Zhu, K.Y. RNA Interference: Applications and Advances in Insect Toxicology and Insect Pest Management. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 120, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellichirammal, N.N.; Gupta, P.; Hall, T.A.; Brisson, J.A. Ecdysone Signaling Underlies the Pea Aphid Transgenerational Wing Polyphenism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1419–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Aksoy, E.; Çalışkan, M.E.; Bakhsh, A. Transgenic Potato Lines Expressing Hairpin RNAi Construct of Molting-Associated EcR Gene Exhibit Enhanced Resistance against Colorado Potato Beetle (Leptinotarsa Decemlineata, Say). Transgenic Res. 2019, 28, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.-Q.; Liu, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Qi, H.-S.; Wei, Z.-J.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Li, S. Improvement of Pest Resistance in Transgenic Tobacco Plants Expressing DsRNA of an Insect-Associated Gene EcR. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38572. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, H.J.; Raza, A.; Amin, I.; Scheffler, J.A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Brown, J.K.; Mansoor, S. RNAi-Mediated Mortality of the Whitefly through Transgenic Expression of Double-Stranded RNA Homologous to Acetylcholinesterase and Ecdysone Receptor in Tobacco Plants. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Xu, X.; Liang, Y.; Tian, H.; Pan, Z.; Jin, S.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W. The Insect Ecdysone Receptor Is a Good Potential Target for RNAi-Based Pest Control. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiannatos, D.; Kolliopoulou, A.; Swevers, L. 4 The ‘Trojan Horse’ Approach for Successful RNA Interference in Insects. In RNAi for Plant Improvement and Protection; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2021; pp. 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kolliopoulou, A.; Kontogiannatos, D.; Swevers, L. The Use of Engineered Plant Viruses in a Trans-Kingdom Silencing Strategy against Their Insect Vectors. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swevers, L.; Kontogiannatos, D.; Kolliopoulou, A.; Ren, F.; Feng, M.; Sun, J. Mechanisms of Cell Entry by DsRNA Viruses: Insights for Efficient Delivery of DsRNA and Tools for Improved RNAi-Based Pest Control. Front. Physiol. 2021, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kontogiannatos, D.; Swevers, L.; Kourti, A. Assessment of Sesamia nonagrioides (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) EcR and USP Genes as Targets for Exogenous Non-Persistent RNAi. Diversity 2021, 13, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120677
Kontogiannatos D, Swevers L, Kourti A. Assessment of Sesamia nonagrioides (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) EcR and USP Genes as Targets for Exogenous Non-Persistent RNAi. Diversity. 2021; 13(12):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120677
Chicago/Turabian StyleKontogiannatos, Dimitrios, Luc Swevers, and Anna Kourti. 2021. "Assessment of Sesamia nonagrioides (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) EcR and USP Genes as Targets for Exogenous Non-Persistent RNAi" Diversity 13, no. 12: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120677
APA StyleKontogiannatos, D., Swevers, L., & Kourti, A. (2021). Assessment of Sesamia nonagrioides (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) EcR and USP Genes as Targets for Exogenous Non-Persistent RNAi. Diversity, 13(12), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13120677






