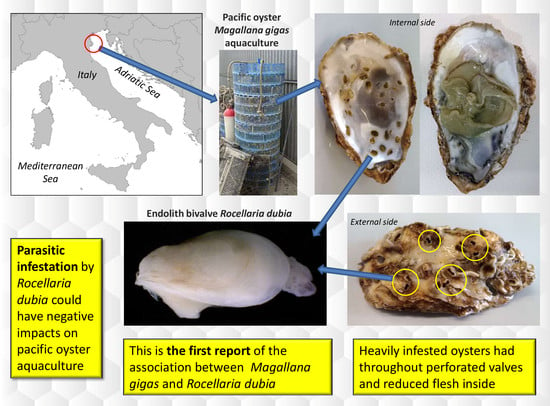
Shell Infestation of the Farmed Pacific Oyster Magallana gigas by the Endolith Bivalve Rocellaria dubia
Abstract
1. Introduction
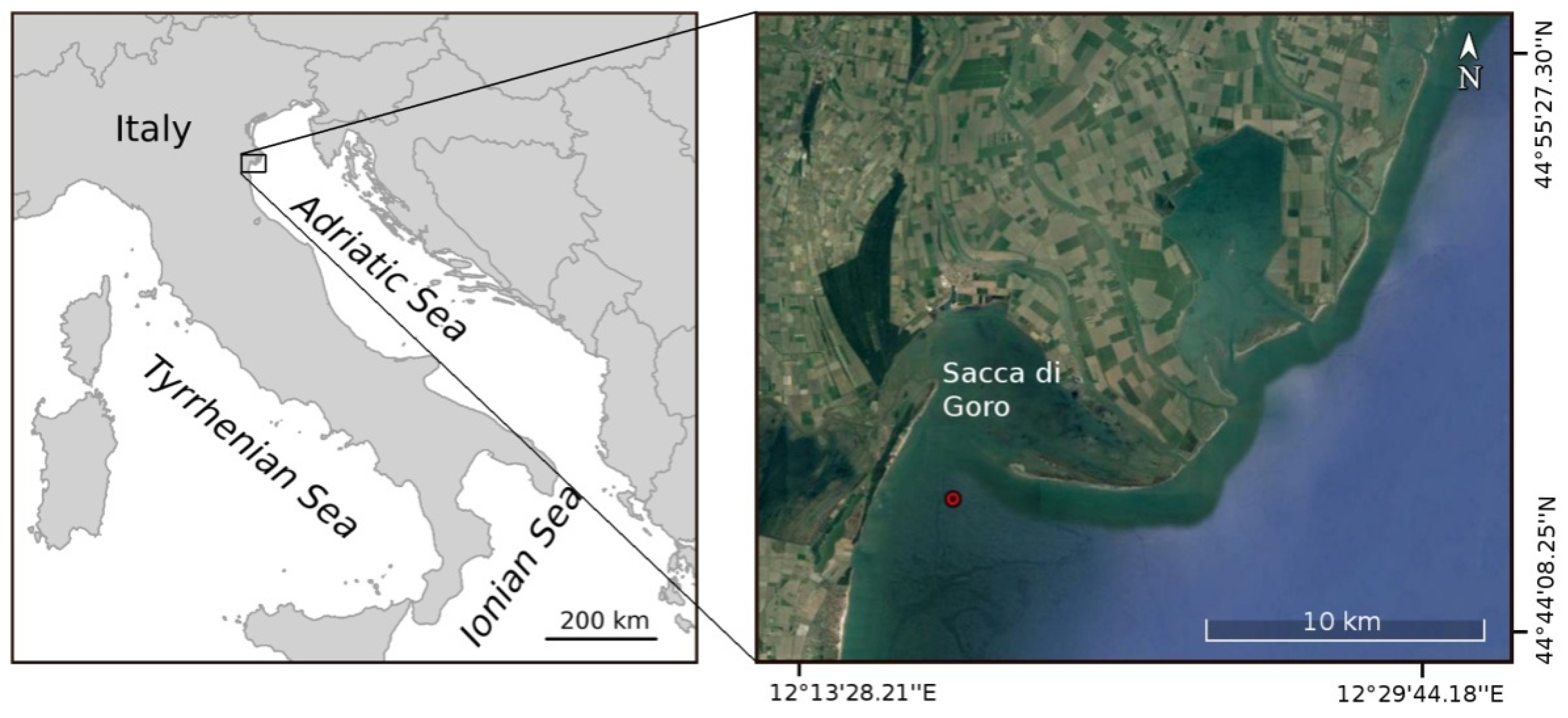
2. Materials and Methods
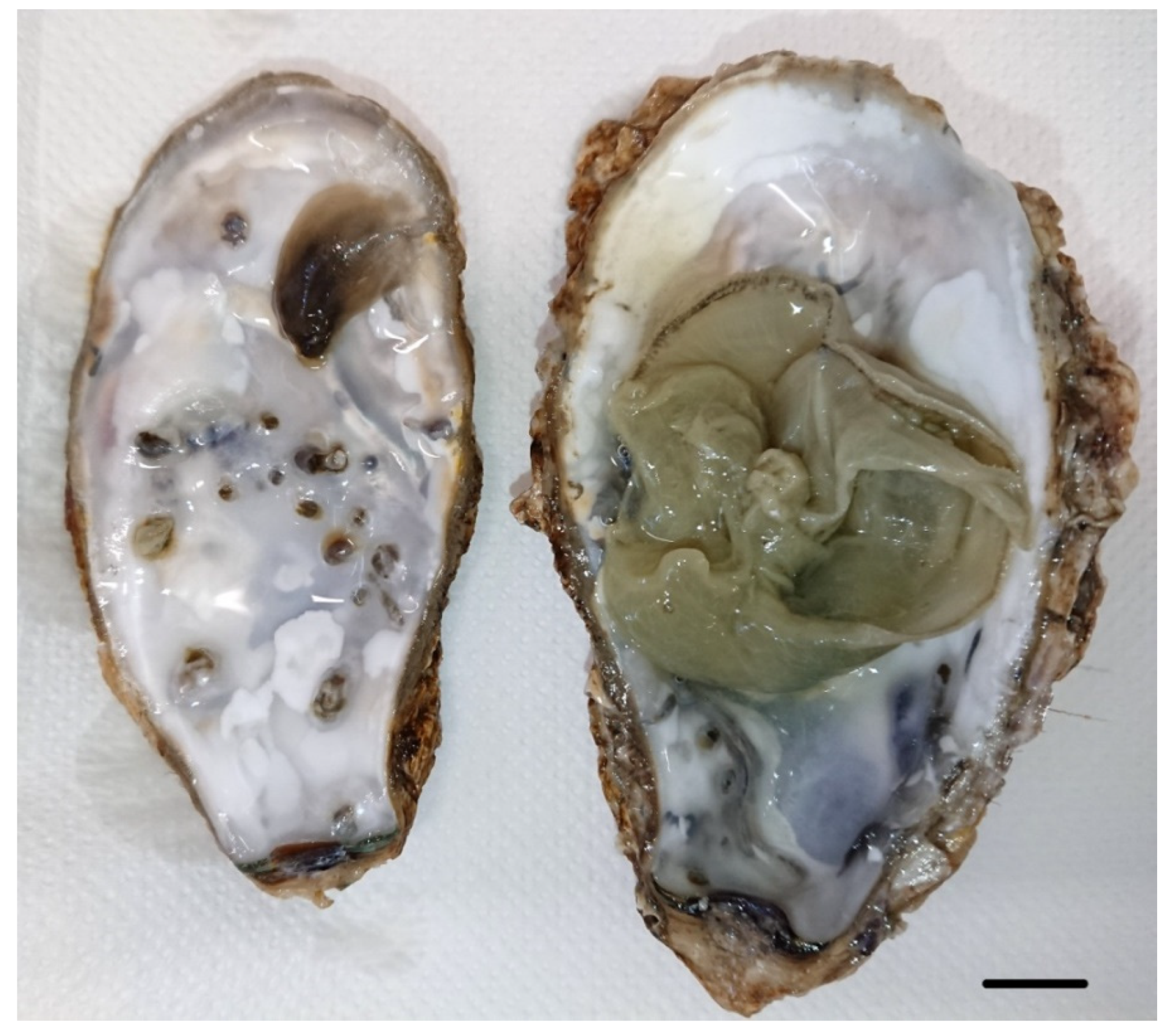
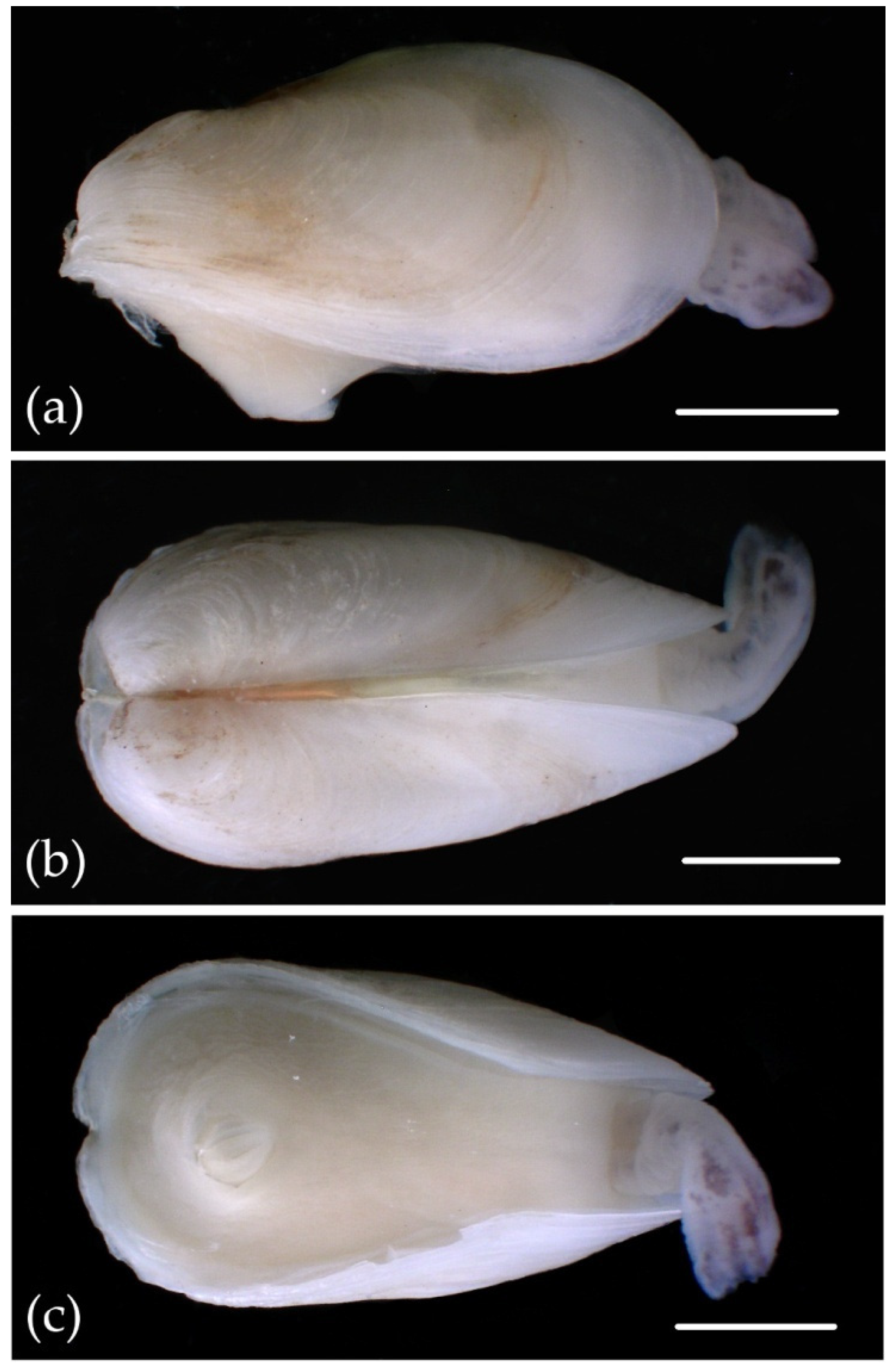
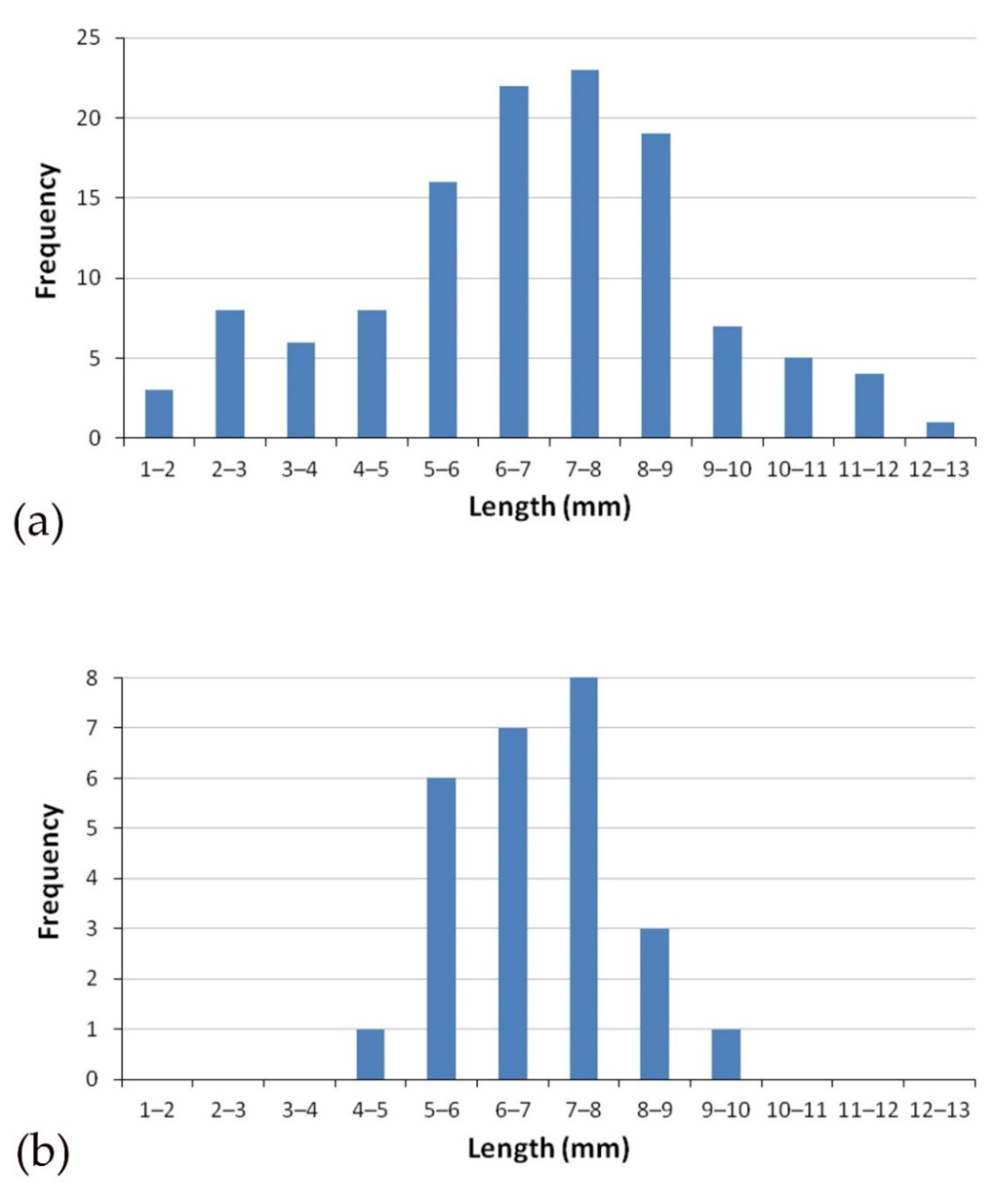
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casoli, E.; Ricci, S.; Antonelli, F.; Perasso, C.S.; Belluscio, A.; Ardizzone, G. Impact and colonization dynamics of the bivalve Rocellaria dubia on limestone experimental panels in the submerged Roman city of Baiae (Naples, Italy). Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 108, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, B.; Peharda, M.; Petrić, M. Functional morphology of Rocellaria dubia (Bivalvia: Gastrochaenidae) with new interpretations of crypt formation and adventitious tube construction, and a discussion of evolution within the family. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2011, 104, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.G.; Sánchez, J.M.P. Moluscos Bivalvos de Canarias; Ediciones del Cabildo Insular de Gran Canaria: Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, 1997; 480p. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, S.; Sacco, C.P.; Antonelli, F.; Petriaggi, B.D. Marine bivalves colonizing Roman artefacts recovered in the Gulf of Pozzuoli and in the Blue Grotto in Capri (Naples, Italy): Boring and nestling species. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 98, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaparelli, S.; Franci, G.; Albertelli, G.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R. Autoecologia del bivalve perforatore Gastrochaena dubia lungo la falesia del promontorio di Portofino. Atti Ass. It. Ocean. Limn. 2003, 16, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Belaústegui, Z.; De Gibert, J.M.; Nebelsick, J.H.; Domènech, R.; Martinell, J. Clyperasteroid echinoid tests as a benthic island for gastrochaenid bivalve colonization: Evidence from the middle Miocene of Terragona, North-East Spain. Palaeontology 2013, 56, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, S.K.; Fearnhead, F.E.; Underwood, C.J. Recent borings in limestone cobbles from Marloes Bay, southwest Wales. Lethaia 2007, 40, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Perna, R. Tube-dwelling in Gastrochaena dubia (Bivalvia): Ecological requirements, functional morphology and structure of the crypt. Boll. Soc. Paleontol. It. 2005, 44, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Albano, P.H. Mediterranean Gastrochaenidae (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Boll. Malacol. 2003, 38, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys, G.J. British Conchology, or an Account of the Mollusca which Now Inhabit the British Isles and the Surrounding Seas. Volume 3. Marine Shells, Comprising the Remaining Conchifera, the Solenoconchia, and Gasteropoda as far as Littorina; John Van Voorst, Paternoster Row: London, UK, 1865; 420p. [Google Scholar]
- Pallary, P. Exploration scientifique du Maroc. Malacologie. Arch. Sci. Du Prot. Français 1912, 2, 1–108. [Google Scholar]
- Poppe, T.; Goto, Y. European Seashells Volume II. (Scaphopoda, Bivalvia, Cephalopoda); Verlag Christa Hemmen: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1993; 221p. [Google Scholar]
- Tebble, N. British Bivalve Seashells; Natural History Museum Publications: London, UK, 1966; 217p. [Google Scholar]
- Ćurin, M.; Peharda, M.; Calcinai, B.; Golubić, S. Incidence of damaging endolith infestation of the edible mytilid bivalve Modiolusbarbatus. Mar. Biol. Res. 2014, 10, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, M.; Fava, F.; Abbiati, M. Spatial–temporal variability of epibenthic assemblages on subtidal biogenic reefs in the northern Adriatic Sea. Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, A.; Cuicchi, C.; Punzo, E.; Santelli, A.; Scarcella, G.; Fabi, G. Patterns of colonization and succession of benthic assemblages in two artificial substrates. J. Sea Res. 2014, 88, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šiletić, T. Marine fauna of Mljet national park (Adriatic Sea, Croatia). 5. Mollusca: Bivalvia. Nat. Croat. 2006, 15, 109–169. [Google Scholar]
- El Ayari, T.; Lahbib, Y.; Trigui El Menif, N. Associated fauna and effects of epibiotic barnacles on the relative growth and reproductive indices of Stramonita haemastoma (Gastropoda: Muricidae). Sci. Mar. 2015, 79, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigui El-Menif, N.; Guezzi, Y.; Le Pennec, M.; Boumaiza, M.; Le Pennec, G. Infestation of the clam Venus verrucosa by Sipunculoidea and the lithophagus bivalve, Gastochaena dubia. Acta Adriat. 2005, 46, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa, K.Y. Competitors and fouling organisms in the hanging culture of the pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg). Mar. Behav. Physiol. 1990, 17, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, T.M.; Griffiths, C.L.; Robinson, T.B. Intra-regional translocations of epifaunal and infaunal species associated with cultured Pacific oysters Crassostrea gigas. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 34, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igić, L. Biotic action in fouling communities on edible shellfish–oysters (Ostrea edulis Linnaeus) and mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck) in the northern Adriatic. Acta Adriat. 1984, 25, 11–27. [Google Scholar]
- Rosell, D.; Uriz, M.J.; Martin, D. Infestation by excavating sponges on the oyster (Ostrea edulis) populations of the Blanes littoral zone (north-western Mediterranean Sea). J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. UK 2001, 79, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato-Okoshi, W.; Okoshi, K.; Koh, B.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Hong, J.S. Polydorid species (Polychaeta: Spionidae) associated with commercially important mollusk shells in Korean waters. Aquaculture 2012, 350–353, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, S.J.; Bergquist, P.R. Spionid polychaete infestations of intertidal pacific oysters Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg), Mahurangi Harbour, northern New Zealand. Aquaculture 1997, 153, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.A.; Sato-Okoshi, W. Polydorid polychaetes on farmed molluscs: Distribution, spread and factors contributing to their success. Aquac. Environ. Interacts. 2015, 7, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezgeta-Balić, D.; Šegvić-Bubić, T.; Stagličić, N.; Lin, Y.; Bojanić, D.V.; Grubisić, L.; Briski, E. Distribution of non-native Pacific oyster Magallana gigas (Thunberg, 1793) along the eastern Adriatic coast. Acta Adriat. 2019, 60, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizel, H.; Héral, M. Introduction into France of the Japanese oyster (Crassostrea gigas). J. Cons. int. Explor. Mer. 1991, 47, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagličić, N.; Šegvić-Bubić, T.; Ezgeta-Balić, D.; Bojanić, D.V.; Grubišić, L.; Žuvić, L.; Lin, Y.; Briski, E. Distribution patterns of two co-existing oyster species in the northern Adriatic Sea: The native European flat oyster Ostrea edulis and the non-native Pacific oyster Magallana gigas. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruesink, J.L.; Lenihan, H.S.; Trimble, A.C.; Heiman, K.W.; Micheli, F.; Byers, J.E.; Kay, M.C. Introduction of non-native oysters: Ecosystem effects and restoration implications. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2005, 36, 643–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordignon, F.; Zomeño, C.; Xiccato, G.; Birolo, M.; Pascual, A.; Trocino, A. Effect of emersion time on growth, mortality and quality of Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas, Thunberg 1973) reared in a suspended system in a lagoon in Northern Italy. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finotti, F. Tecniche di Allevamento Innovative e Qualità di Ostriche Concave (Crassostrea gigas) in Sacca degli Scardovari. Tesi di Laurea Magistrale in Biologia Marina; Università degli Studi di Padova: Padova, Italy, 2017; pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, P.; Brundu, G.; Scolamacchia, M.; Giglioli, A.; Addis, P.; Artioli, Y.; Telfer, T.; Carboni, S. Improving pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas, Thunberg, 1793) production in Mediterranean coastal lagoons: Validation of the growth model “ShellSIM”on traditional and novel farming methods. Aquaculture 2019, 516, 734612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzi, P.; Rambaldi, E.; Cardillo, A.; Dell’Aquila, M.; Di Dato, P.; Cataudella, S. Aquaculture. The state of Italian Aquaculture. In The State of Italian Marine Fisheries and Aquaculture; Cataudella, S., Spagnolo, M., Eds.; Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Forrestry Policies: Rome, Italy, 2011; pp. 239–270. [Google Scholar]
- Harding, J.M.; Mann, R. Age and Growth of Wild Suminoe (Crassostrea ariakensis, Fugita 1913) and Pacific (C. gigas, Thunberg 1793) Oysters from Laizhou Bay, China. J. Shellfish Res. 2006, 25, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaparelli, S.; Franci, G.; Albertelli, G.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R. A non-destructive method to evaluate population structure and bioerosion activity of the Boring bivalve Gastrochaena dubia. J. Coast. Res. 2005, 21, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.G.; McDowell, T.; Namboodiri, N. The Identity of Gastrochaena cuneiformis Spengler, 1783, and the Evolution of Gastrochaena, Rocellaria, and Lamychaena (Mollusca, Bivalvia, Gastrochaenoidea). J. Paleontol. 2008, 82, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenzan, P. Malacologia Jonica. Introduzione allo studio dei Molluschi dello Jonio. Thalassia Jonica 1961, IV, 1–184. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, J. Zoology. Marine. In The Victoria history of the county of Cornwall; Page, W., Ed.; James Street Haymarket: London, UK, 1906; Volume 1, pp. 113–159. [Google Scholar]
- Cerrano, C.; Pica, D.; Di Camillo, C.; Bastari, A.; Torsani, F. Caratterizzazione Biocenotica e Restituzione Cartografica per l’Individuazione di Eventuali Habitat e Specie di Interesse Comunitario nelle Aree Prospicienti le Aree Protette delle Marche. Relazione Tecnica; Università Politecnica delle Marche, Dipartimento Scienze della Vita e dell’Ambiente: Ancona, Italy, 2015; pp. 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Curini Galletti, M.; Galleni, L. Le mitilaie del litorale livornese 1—catalogo faunistico. Atti Soc. Tosc. Sci. Nat. Mem. Serie B 1981, 88, 127–141. [Google Scholar]
- Borja, A.; Franco, J.; Pérez, V. A Marine Biotic Index to Establish the Ecological Quality of Soft-Bottom Benthos Within European Estuarine and Coastal Environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 1100–1114, updated in. Available online: http://ambi.azti.es (accessed on 10 September 2021). [CrossRef]
- Cilenti, L.; Scirocco, T.; Specchiulli, A.; Vitelli, M.L.; Manzo, C.; Fabbrocini, A.; Santucci, A.; Franchi, M.; D’Adamo, R. Quality aspects of Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg, 1793) reared in the Varano Lagoon (southern Italy) in relation to marketability. J. Mar. Biolog. Assoc. UK 2017, 98, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feis, M.E.; Goedknegt, M.A.; Arzul, I.; Chenuil, A.; den Boon, O.; Gottschalck, L.; Kondo, Y.; Ohtsuka, S.; Shama, L.N.S.; Thieltges, D.W.; et al. Global invasion genetics of two parasitic copepods infecting marine bivalves. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, A.; Lucchetti, A. Low-cost tool to reduce biofouling in oyster longline culture. Aquac. Eng. 2008, 39, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, M.W.; Davids, J.K.; Dolmer, P.; Vismann, B.; Hansen, B.W. Moderate establishment success of Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas, on a sheltered intertidal mussel bed. J. Sea Res. 2015, 104, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, R.S.; Morrissey, M.T.; Cheney, D.A.N. Effect of Age and Tissue Weight on the Cadmium Concentration in Pacific Oysters (Crassostrea gigas). J. Shellfish Res. 2007, 26, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, K. Raumkonkurrenz bei Ätzmuscheln. Mar. Biol. 1974, 26, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikac, B.; Tarullo, A.; Colangelo, M.A.; Abbiati, M.; Costantini, F. Shell Infestation of the Farmed Pacific Oyster Magallana gigas by the Endolith Bivalve Rocellaria dubia. Diversity 2021, 13, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13110526
Mikac B, Tarullo A, Colangelo MA, Abbiati M, Costantini F. Shell Infestation of the Farmed Pacific Oyster Magallana gigas by the Endolith Bivalve Rocellaria dubia. Diversity. 2021; 13(11):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13110526
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikac, Barbara, Alessandro Tarullo, Marina Antonia Colangelo, Marco Abbiati, and Federica Costantini. 2021. "Shell Infestation of the Farmed Pacific Oyster Magallana gigas by the Endolith Bivalve Rocellaria dubia" Diversity 13, no. 11: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13110526
APA StyleMikac, B., Tarullo, A., Colangelo, M. A., Abbiati, M., & Costantini, F. (2021). Shell Infestation of the Farmed Pacific Oyster Magallana gigas by the Endolith Bivalve Rocellaria dubia. Diversity, 13(11), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13110526