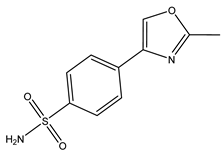
Synthesis and Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Properties of 4-(2-Methyloxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide
Abstract
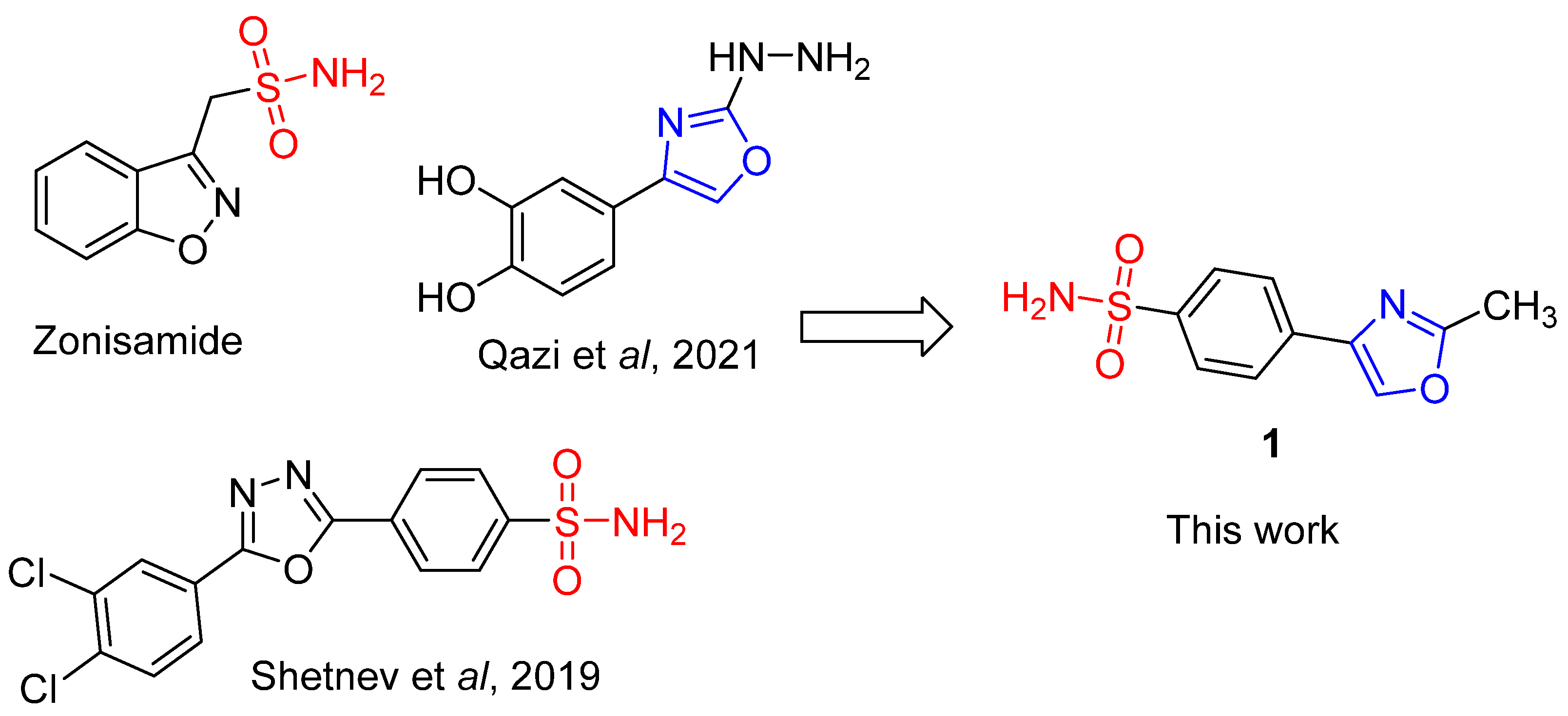
1. Introduction
2. Results
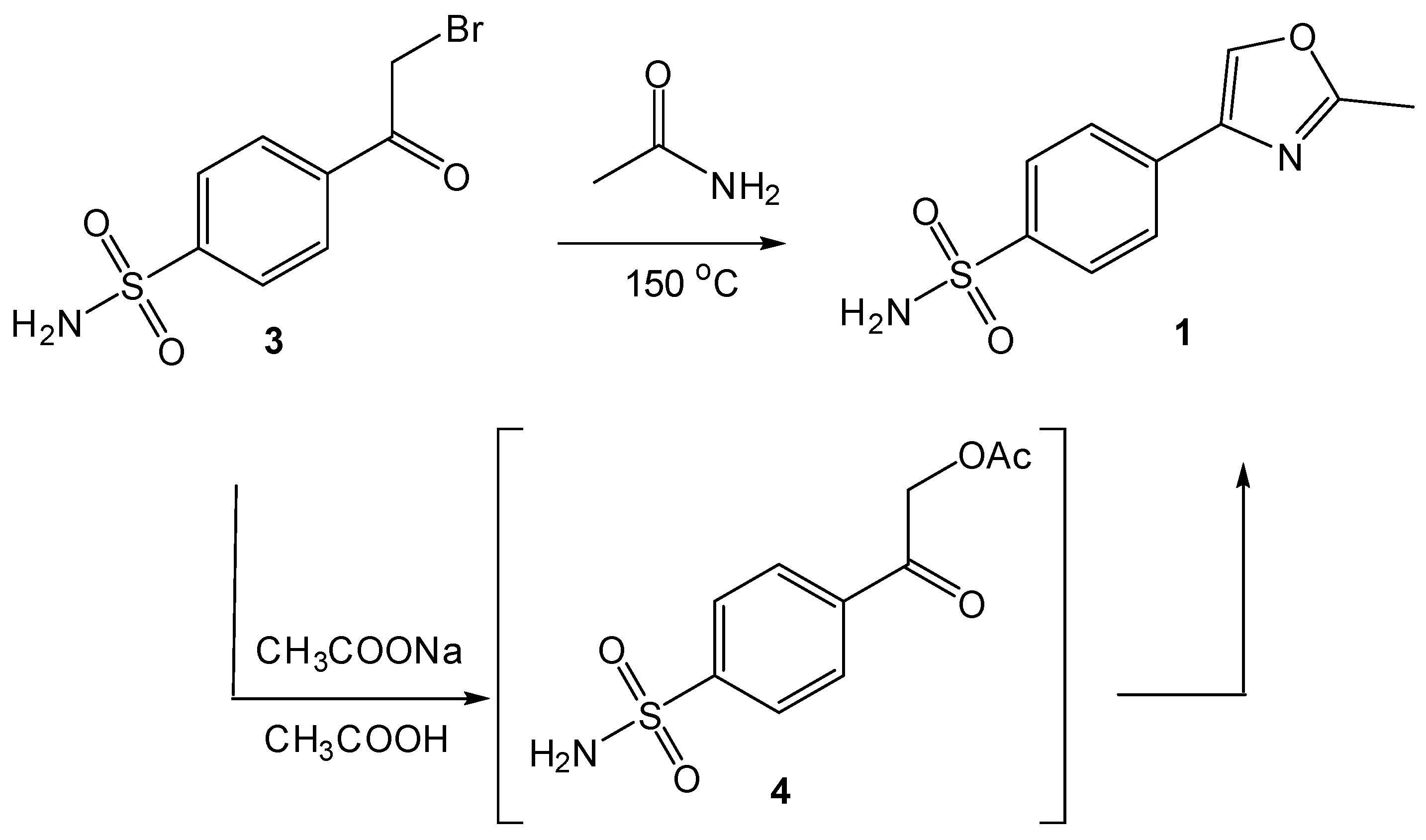
2.1. Chemistry
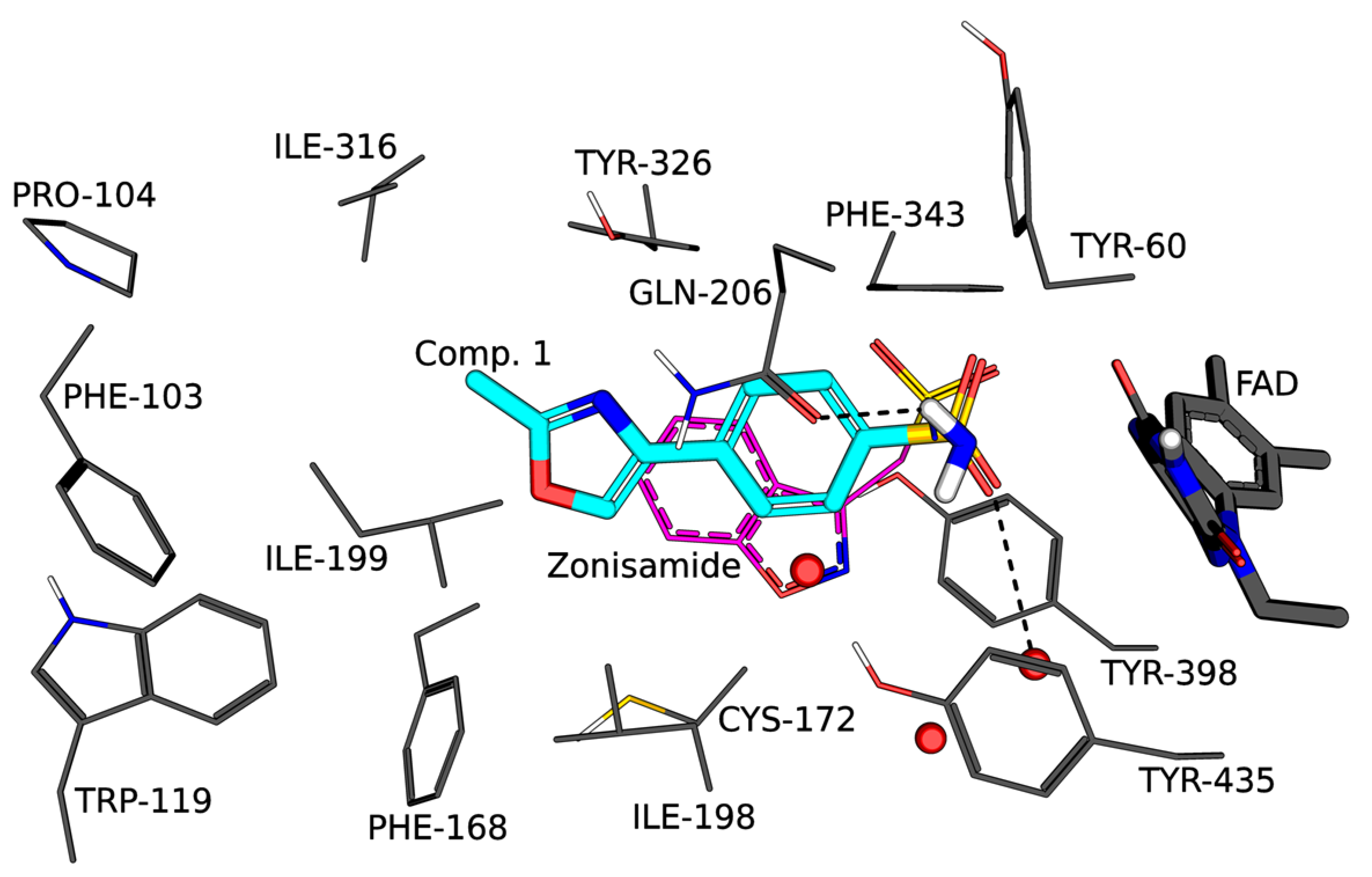
2.2. MAO Inhibition
| Structure | IC50 (μM ± SD) 1 | |
|---|---|---|
| MAO-A | MAO-B | |
 | 43.3 ± 7.12 | 3.47 ± 0.31 |
| Curcumin [24] 2 | 5.02 ± 0.45 | 2.56 ± 0.21 |
| Toloxatone [25] 2 | 3.92 | - |
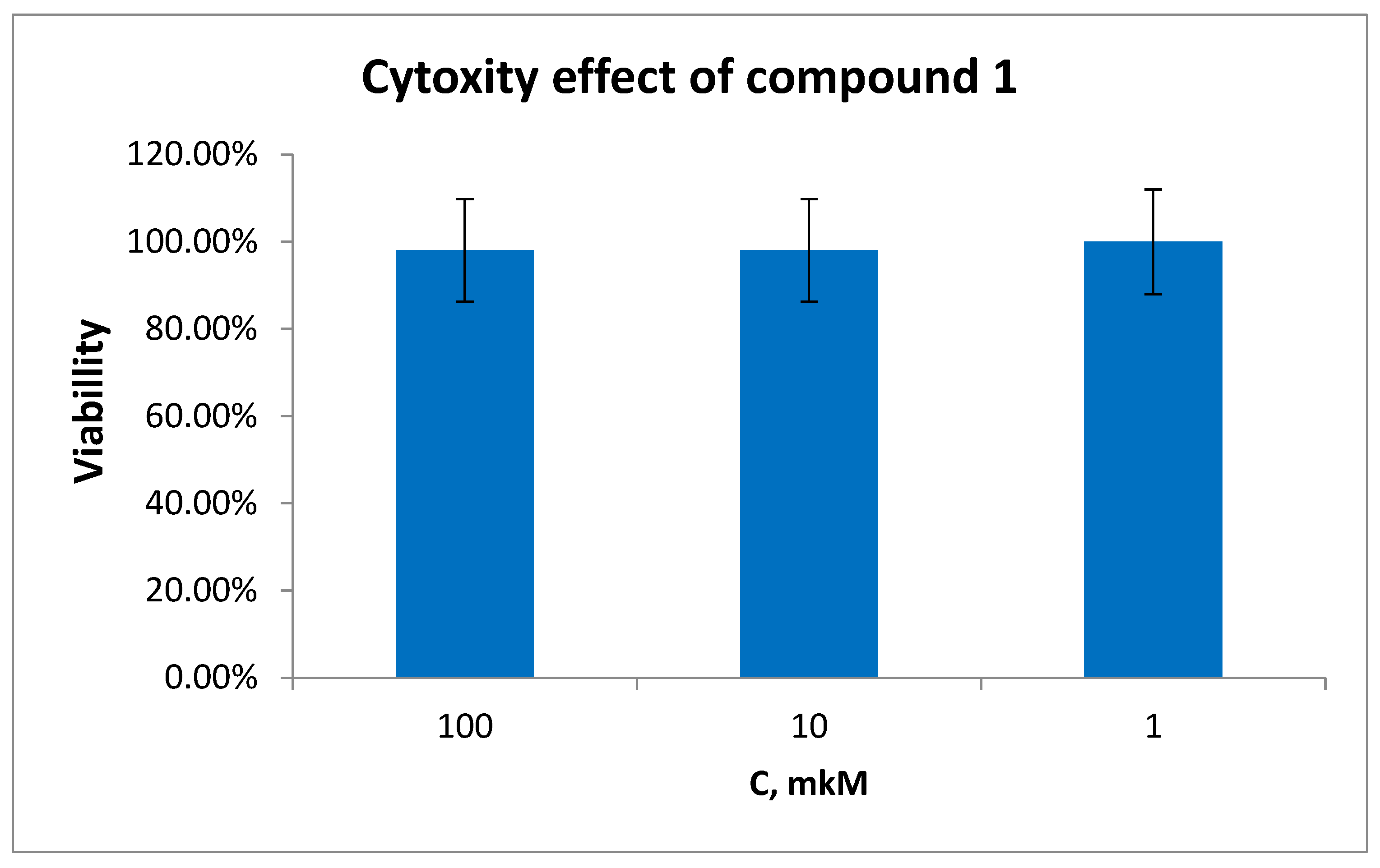
2.3. Cytotoxicity In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
4.2. Procedure for the Preparation of 4-(2-Bromoacetyl)benzenesulfonamide (3)
4.3. Synthesis and Characterization of 4-(2-Methyloxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide (1)
4.4. MAO Inhibition Studies
4.5. Molecular Docking Studies
4.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, Y.Y.; Jenner, P.; Chen, S.D. Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease: Past, Present, and Future. J. Park. Dis. 2022, 12, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szökő, É.; Tábi, T.; Riederer, P.; Vécsei, L.; Magyar, K. Pharmacological aspects of the neuroprotective effects of irreversible MAO-B inhibitors, selegiline and rasagiline, in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1735–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostadkarampour, M.; Putnins, E.E. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: A Review of Their Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Potential and Mechanisms of Action. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 676239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.A.; Chand, K.; Chaves, S. Recent progress in multifunctional metal chelators as potential drugs for Alzheimer’s disease. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 327, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, G.E.; Totterdell, S.; Beales, M.; Meshul, C.K. Impaired glutamate homeostasis and programmed cell death in a chronic MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 219, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaidi, A.A.; Bush, A.I. Iron neurochemistry in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: Targets for therapeutics. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarmouh, N.O.; Messeha, S.S.; Mateeva, N.; Gangapuram, M.; Flowers, K.; Eyunni, S.V.K.; Zhang, W.; Redda, K.K.; Soliman, K.F.A. The Antiproliferative Effects of Flavonoid MAO Inhibitors on Prostate Cancer Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, D.T.; Hoshaw, B.A.; Malberg, J.E.; Rosenzweig-Lipson, S.; Schechter, L.E.; Lucki, I. Differential regulation of central BDNF protein levels by antidepressant and non-antidepressant drug treatments. Brain Res. 2008, 1211, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Sahu, S.; Schachner, M. Phenelzine, a cell adhesion molecule L1 mimetic small organic compound, promotes functional recovery and axonal regrowth in spinal cord-injured zebrafish. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2018, 171, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, N.D.; Limaye, R.P.; Gokhale, D.V.; Patil, T.R. Zonisamide: A review of the clinical and experimental evidence for its use in Parkinson’s disease”. Ind. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 45, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetnev, A.; Shlenev, R.; Efimova, J.; Ivanovskii, S.; Tarasov, A.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. 1,3,4-Oxadiazol-2-ylbenzenesulfonamides as privileged structures for the inhibition of monoamine oxidase B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 126677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qazi, S.U.; Naz, A.; Hameed, A.; Osra, F.A.; Jalil, S.; Iqbal, J.; Shah, S.A.; Mirza, A.Z. Semicarbazones, thiosemicarbazone, thiazole and oxazole analogues as monoamine oxidase inhibitors: Synthesis, characterization, biological evaluation, molecular docking, and kinetic studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 115, 105209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetnev, A.; Kotov, A.; Kunichkina, A.; Proskurina, I.; Baykov, S.; Korsakov, M.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Monoamine oxidase inhibition properties of 2,1-benzisoxazole derivatives. Mol. Divers. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, N.; Mishra, P. Synthesis, monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity and computational study of novel isoxazole derivatives as potential antiparkinson agents. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 79, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzvetkov, N.T.; Antonov, L. Subnanomolar indazole-5-carboxamide inhibitors of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) continued: Indications of iron binding, experimental evidence for optimised solubility and brain penetration. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efimova, J.A.; Shetnev, A.A.; Baykov, S.V.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. 3-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-5-(1H-indol-5-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazole. Molbank 2023, 2023, M1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panova, V.A.; Filimonov, S.I.; Chirkova, Z.V.; Kabanova, M.V.; Shetnev, A.A.; Korsakov, M.K.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Suponitsky, K.Y. Investigation of pyrazolo[1,5-a]quinoxalin-4-ones as novel monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, S.N.; Hassan, S.Y.; Bekhit, A.A.; El Massry, A.M.; Langer, V.; Amer, A. Synthesis of new series of quinoxaline-based MAO-inhibitors and docking studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 4479–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.W.; Leadbetter, M.R.; Bell, N.; Koo-McCoy, S.; Carreras, C.W.; He, L.; Kohler, J.; Kozuka, K.; Labonté, E.D.; Navre, M.; et al. Discovery of tenapanor: A first-in-class minimally systemic inhibitor of intestinal Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scobie, M.; Wallner, O.; Koolmeister, T.; Vallin, K.S.A.; Henriksson, C.M.; Homan, E.; Helleday, T.; Jacques, S.; Desroses, M.; Jacques-Cordonnier, M.-C.; et al. MTH1 Inhibitors for Treatment of Inflammatory and Autoimmune Conditions. U.S. Patent 16,102,170, 31 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Denney, D.B.; Pastor, S.D. Structures in solution of adducts of hexamethylphosphorus triamide and substituded benzils. Phosphorus Sulfur. Silicon Relat. Elem. 1983, 16, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, C.; Aldeco, M.; Mattevi, A.; Edmondson, D.E. Interactions of monoamine oxidases with the antiepileptic drug zo-nisamide: Specificity of inhibition and structure of the human monoamine oxidase B complex. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubalek, F.; Binda, C.; Khalil, A.; Li, M.; Mattevi, A.; Castagnoli, N.; Edmondson, D.E. Demonstration of isoleucine 199 as a structural determinant for the selective inhibition of human monoamine oxidase B by specific reversible inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15761–15766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, D.K.; Juvekar, A.R. Kinetics of Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase Using Curcumin and Ellagic Acid. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, I.; Zimmer, R.; Thiede, H.; Payan, C.; Hergueta, T.; Robin, L.; Puech, A. Comparison of the monoamine oxidase inhibiting properties of two reversible and selective monoamine oxidase-A inhibitors moclobemide and toloxatone, and assessment of their effect on psychometric performance in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1990, 30, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, M.; Turnbull, T.; Sebastian, S.; Kempson, I. The MTT Assay: Utility, Limitations, Pitfalls, and Interpretation in Bulk and Single-Cell Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, C.; Wang, J.; Pisani, L.; Caccia, C.; Carotti, A.; Salvati, P.; Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, A. Structures of human monoamine oxidase B complexes with selective noncovalent inhibitors: Safinamide and coumarin analogs. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5848–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; DeLano Scientific: San Carlos, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shetnev, A.A.; Efimova, J.A.; Korsakov, M.K.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P. Synthesis and Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Properties of 4-(2-Methyloxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide. Molbank 2024, 2024, M1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1787
Shetnev AA, Efimova JA, Korsakov MK, Petzer A, Petzer JP. Synthesis and Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Properties of 4-(2-Methyloxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide. Molbank. 2024; 2024(1):M1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1787
Chicago/Turabian StyleShetnev, Anton A., Julia A. Efimova, Mikhail K. Korsakov, Anél Petzer, and Jacobus P. Petzer. 2024. "Synthesis and Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Properties of 4-(2-Methyloxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide" Molbank 2024, no. 1: M1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1787
APA StyleShetnev, A. A., Efimova, J. A., Korsakov, M. K., Petzer, A., & Petzer, J. P. (2024). Synthesis and Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Properties of 4-(2-Methyloxazol-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide. Molbank, 2024(1), M1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1787