Abstract
The structure of four hydroxamic acids (HA) that show antifungal activities in complexes with several metals is revealed by single crystal diffraction. The structures of HA with C2, C6, C10, and C12 hydrocarbon chains are reported. The smallest member of the series, N-hydroxyacetamide (HA2), crystallizes in the centrosymmetric space group P21/c while those with longer chain lengths N-hydroxyhexanamide (HA6), N-hydroxydecanamide (HA10), and N-hydroxydodecanamide (HA12) crystallize in the space group P21, and display remarkable packing.
1. Introduction
The first hydroxamic acid (HA) was discovered by Lossen in 1869 (namely, oxalohydroxamic acid: HONH-CO-CO-NHOH). Since then, intensive work has focused on their reactions, structures [1], and biological activities [2,3]. The actual or predominant structures of HA are generally difficult to determine due to phenomena, such as polymorphism, stereoisomerism and tautomerism. In solution, HA are subject to a keto-enolic equilibrium that is highly dependent on the solvent and pH resulting in different tautomers available for the coordination of metal ions. The ketone forms (1 or 3) predominate in acidic solutions, while the enolic forms (2 or 4) are the major ones in alkaline media (Scheme 1) [4,5]. In addition, each of these tautomeric forms may exist as two isomers (Z or E) [1]. This situation can be even more complicated because of the exchanges with other protons present in solution and the quantity of water present in the medium [6]. Despite all these tautomeric forms, it has been reported that the Z-form of HA is predominant [4,6].
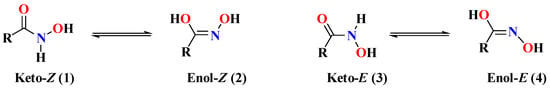
Scheme 1.
Keto-enolic tautomeric forms and Z/E isomers of HA.
The importance of the role of solvent in the change from one stereoisomer to another has been outlined. Indeed, protic solvents stabilize the Z-form by forming intermolecular H-bonds (Figure 1A). The Z-form can also be stabilized by intramolecular H-bonds (Figure 1B) [7]. Additionally, the Z/E ratio decreases with increasing concentration, and decreasing temperature favors the E-form. Previously published data corroborated this, suggesting an increasing stabilization of the E-isomer by intermolecular H-bonding (1C). The degree of molecular association increases with increasing concentrations of HA [8].
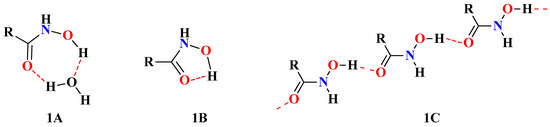
Figure 1.
The chemical structures of HA in Z/E configuration with possible inter- and intra-molecular H-bonds. Z-form stabilization by intermolecular H-bonds (1A) or intramolecular H-bonds (1B) and stabilization of the E-form by intermolecular H-bonding (1C).
HA constitute one of the most important families of organic bioligands, and one of the first physiological roles of these compounds was associated with their use as siderophores, a class of compound iron-sequestering agents [2]. Desferrioxamine B is effectively used to deal with iron overload in transfusion-dependent patients, such as those suffering from thalassemia. In addition to being used as siderophores, HA perform a number of other biological and pharmacological roles. They act as potent and selective inhibitors of a large number of enzymes, such as matrix metalloproteinases, peroxidases, hydrolases, ureases, lipoxygenases, cyclooxygenases, histone deacetylases, and peptide deformylases [2]. HA are reported to possess anti-inflammatory, anti-tubercular, anti-leukemic, anti-microbial, and tumor-inhibiting properties [3]. They perform important roles in the manufacturing of various biologically active drugs, such as anti-depressants, anti-tumor agents, anti-HIV agents, and anti-malarial agents, and are also used in industries as insecticides, antioxidants, as inhibitors of corrosion, and for the extraction of toxic elements [3].
The aim of the present study is the synthesis and analysis of the crystal structures of HA with various chain lengths (C2, C6, C10, and C12). The chemical structures of these HA are shown in Figure 2.
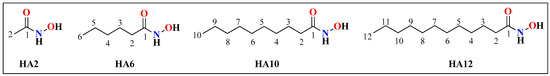
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of N-hydroxyacetamide (HA2), N-hydroxyhexanamide (HA6), N-hydroxydecanamide (HA10), and N-hydroxydodecanamide (HA12).
2. Results and Discussion
The crystal structures of HA2, HA6, HA10, and HA12 are shown in Figure 3. 1H and 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 and 100 MHz, respectively) with δ chemical shifts and assignments, IR and Raman spectroscopy, and melting point and elemental analysis were reported in previous work on antifungal activities and structures of metal complexes of the HA [9].
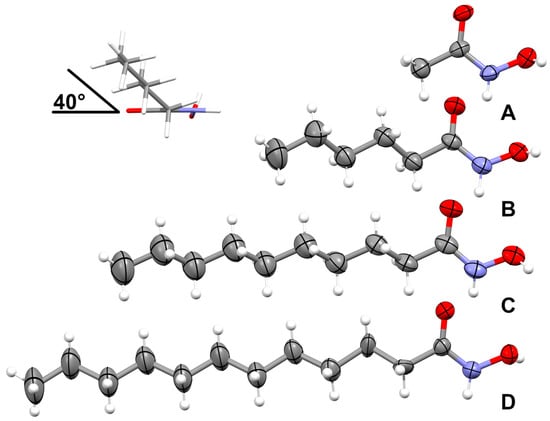
Figure 3.
Crystal structures were obtained with HA2 (A), HA6 (B), HA10 (C), and HA12 (D) with thermal displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. The inset shows the observed tilt of the alkyl chain with respect to the N-hydroxyacetamide plane.
The crystallographic data and refinement details of the four HA are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Crystal data and structure refinement of HA2, HA6, HA10, and HA12.
In all structures, the planar N-hydroxyacamide moieties are isostructural, with both oxygen atoms on the same side of the C-N bond to minimize steric repulsion. The N-hydroxyacetamide (HA2) is already reported as a hemihydrate [10] and in the P 41 space group [1]; the current structure is a polymorph (P21/c space group) showing two molecules in the asymmetric unit (Z’ = 2). The alkyl chains for HA6, HA10, and HA12 are planar with all eclipsed angles. The alkyl chains themselves are set off about 40° from the N-hydroxyacetamide plane. Similar values are observed for N-hydroxyoctanamide [11], but larger values are reported for N-hydroxypropanamide (46–66°) [12]. For HA12, the alkyl chain was found disordered and is refined in two discrete parts with a refined ratio of 53/47. The offset angle of 40° is still preserved, but the first torsion angle is not fully eclipsed (167°).
The structures with the longer alkyl chains are packed in a near orthorhombic cell (monoclinic unit cell with β extremely close to 90°) in such a way that the hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts are arranged in layers. This results in an elaborate network of hydrogen bonds for the N-hydroxyamide moiety where every molecule interacts with four neighbors (Figure 4). The crystal packing of HA6, HA10, and HA12 displays substantial packing similarities (Figure 4). The relative positions and orientation of the HA molecules in the a- and b-direction are identical, with similar hydrogen bond interactions involving the N-hydroxyacetamide. This is also visible by the gradual linear expansion of the c parameter of the unit cell, while a and b remain unchanged (Figure 5). The structure of hydroxyoctanamide [11] with a c- axis of 23.19(4)Å follows the same trend.
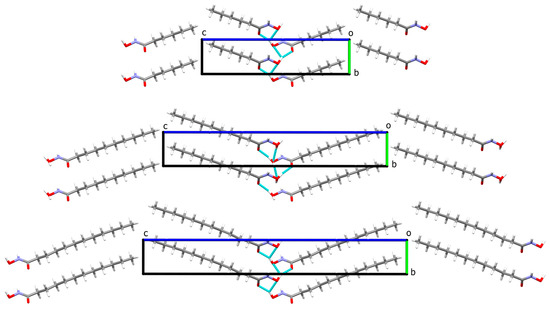
Figure 4.
Crystal packing of HA6, HA10, and HA12 view down the a-axis, illustrating the crystal packing similarities and the conservation of the H-bond interactions (cyan dashed lines), disordered atoms of the HA12 alkyl chain are omitted for clarity.
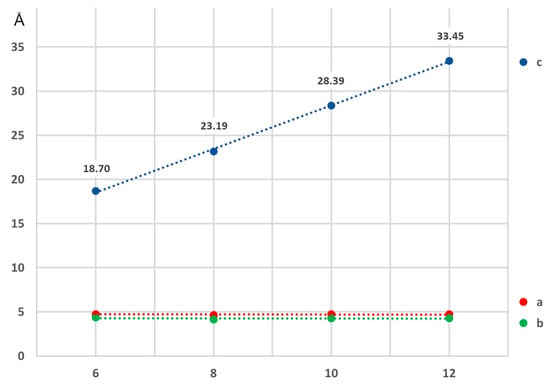
Figure 5.
Variation of the unit cell parameters in function of the number of carbon atoms in the aliphatic chain showing a linear expansion of the c-axis. HA6, HA10, and HA12 (current work), HA8 from [11].
3. Materials and Methods
Ethyl acetate was purchased from Chem-Lab NV. The synthetic method for HA2, HA6, HA10, and HA12 was reported in previous work [9]. In this study, ethyl acetate (EtOAc) was used as a solvent for recrystallizing the HA. To further purify, the crude product was dissolved in hot EtOAc and filtered. The filtrate was cooled to room temperature to afford pure HA as crystals within 72 h. The residual solvent was removed by filtration, and crystals were washed with water and dried under vacuum at 40 °C.
Data collection on the crystal structures was performed at room temperature on a MAR345 image plate using monochromated Mo Kα radiation (Montel mirrors) generated by an Incoatec IµS generator. Data integration and reduction were done in CrysAlisPro version 1.171.37.35, and the implemented absorption correction was applied. The crystal structures were solved by SHELXT [13] and refined by full-matrix least squares against F2 using SHELXL 2018/3 [1,10]. For the OH hydrogen atom in HA10, two possible sites were identified; the occupancy of both sites was fixed at 50%, with the N-O-H angle restrained as tetragonal. Rigid bond restraints were applied to the disordered alkyl chains in HA12. CCDC 2250790–2250793 contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures (accessed on).
4. Conclusions
The geometry of the HA2 corresponds to the structure described by Bracher and Small [10] but in a different space group (P21/c versus P41). Compounds HA6, HA10, and HA12 have structures similar to that of N-hydroxyoctanamide [11], in which a remarkable linear correlation is noticeable between the variation of the c-axis and the number of carbon atoms in the alkyl chain.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded online, cif files for the structures of HA2, HA6, HA10, and HA12. CCDC 2250790–2250793 contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures or found as Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, crystal assay, and all chemical analysis, I.S.S.; visualization, supervision, review, and validation chemical analysis, M.G. and F.D.; crystallization assay, supervision, and review, K.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported through the Fonds De La Recherche Scientifique—FNRS (CDR J.0168.22).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available in a publicly accessible repository. The data presented in this study are openly available in Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, reference number [2250790–2250793].
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Centre d’Instrumentation en Resonance Magnétique (CIREM) for the NMR experiments (M. Luhmer and G. De Leener); the PC2 platform for elemental analyses (UNamur). I.-S. Sow thanks Abdoulaye Yéro Baldé, the former minister of higher education and scientific research of Guinea for his financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors reported no potential conflict of interest.
References
- Dziuk, B.; Zarychta, B.; Ejsmont, K.; Daszkiewicz, Z. Acetylhydroxamic acid. IUCrData 2017, 2, 171390–171395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.P.; Sharma, A. Hydroxamic Acids: A Unique Family of Chemicals with Multiple Biological Activities; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Z.; Sonu, K.; Dongre, A.; Sharma, G.; Sogani, M. A review on Hydroxamic Acids: Widespectrum Chemotherapeutic Agents. Int. J. Biol. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citarella, A.; Moi, D.; Pinzi, L.; Bonanni, D.; Rastelli, G. Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives: From Synthetic Strategies to Medicinal Chemistry Applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 21843–21849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.E.; Manning, D.L. Spectrophotometric Methods of Establishing Empirical Formulas of Colored Complexes in Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 4488–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraml, J.; Tkadlecová, M.; Pataridis, S.; Soukupová, L.; Blechta, V.; Roithová, J.; Exner, O. Ring-substituted benzohydroxamic acids:1H,13C and15N NMR spectra and NH-OH proton exchange. Org. Magn. Reson. 2005, 43, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.A.; Coogan, R.A.; Fitzpatrick, N.J.; Glass, W.K.; Abukshima, D.E.; Shiels, L.; Ahlgrén, M.; Smolander, K.; Pakkanen, T.T.; Pakkanen, T.A.; et al. Conformational behaviour of hydroxamic acids: ab initio and structural studies. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1996, 2673–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.A.; Glass, W.K.; Mageswaran, R.; Mohammed, S.A. 1H and13C NMR studies of isomerism in hydroxamic acids. Org. Magn. Reson. 1991, 29, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, I.S.; Gelbcke, M.; Meyer, F.; Vandeput, M.; Marloye, M.; Basov, S.; Van Bael, M.J.; Berger, G.; Robeyns, K.; Hermans, S.; et al. Synthesis and biological activity of iron(II), iron(III), nickel(II), copper(II) and zinc(II) complexes of aliphatic hydroxamic acids. J. Coord. Chem. 2023, 76, 76–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracher, B.H.; Small, R.W.H. The crystal structure of acetohydroxamic acid hemihydrate. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem. 1970, 26, 1705–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, G.A.; Woods, R.; Buckley, A.N.; White, J.M.; McLean, J. Spectroscopic characterisation of n-octanohydroxamic acid and potassium hydrogen n-octanohydroxamate. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2010, 363, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, G.; Glidewell, C. N-Propionylhydroxylamine forms a three-dimensional hydrogen-bonded framework structure. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Cryst. Struct. Commun. 2001, 57, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).