Abstract
A new bis cyclometallated Ir(III) phosphor, [Ir(ppy)2L]PF6 (ppy = 2-phenylpyridine, L = 4,4′-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-6,6′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine was prepared and structurally characterized in the solid state (X-ray diffraction) and solution (1 and 2D NMR spectroscopy). The compound exhibited yellow photoluminescence (λem = 562 nm). The quantum yield Φ was solvent-dependent (5% in acetonitrile and 19% in dichloromethane solutions, respectively).
1. Introduction
In recent years, iridium-based phosphors have received much attention because of their potential use in a vast range of applications including bioimaging [1,2,3], photoredox catalysis [4,5], sensing [6,7] and optoelectronic devices [8,9,10,11].
The most studied class of these compounds unambiguously belongs to tris and bis cyclometalled Ir(III) complexes of type Ir(C^N)3 (homoleptic) and Ir(C^N)2(L^X) (heteroleptic), respectively. In this formulation, C^N stands for the cyclometallating anionic chelating ligand, where L^X is the ancillary ligand (anionic or neutral). These are emitted from either 3MLCT or, more frequently, a mixed 3MLCT-3LC state [5,8,9]. An interesting subcategory of heteroleptic bis cyclometallated Ir(III) complexes contains ppy (the anion of 2-phenylpyridine) and a diimine type (N^N) ancilliary ligand. The major advantage [Ir(C^N)2 (N^N)]+ compounds have to offer is that cyclometallating and especially the ancillary ligands, can be independently modified to fine-tune the emission energy [12,13,14,15,16].
Rubén D. Costa et al. [16] synthesized a series of [Ir(ppy)2(N^N)][PF6] complexes, successively adding methyl and phenyl groups to the 6- and 4-positions of 2.2′-bipyridine (bpy) in the archetypal complex [Ir(ppy)2(bpy)][PF6] (used as reference). A blue shift of the emission maximum was observed for all complexes compared to the reference. More importantly, the photoluminescence quantum yield reached its maximum value (Φ = 0.54) when both methyl and phenyl substituents were present (N^N = 6,6′-dimethyl-4,4′-diphenyl-2,2′-bipyridine). The impressive quantum efficiency was ascribed to self-quenching reduction due to the addition of bulky groups at the periphery of the complex.
Prompted by these results, we decided to prepare, characterize and investigate the photophysical properties of a similar complex, Bis(2-phenylpyridinato,-C2′,N)[4,4′-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-6,6′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine] iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate [Ir(ppy)2L]PF6 (1). The only change made on the N^N ligand compared to the studied one 6,6′-dimethyl-4,4′-diphenyl-2,2′-bipyridine was the insertion of strong electron-withdrawing fluorine at the 4-position of the phenyl ring. Our goal was to reveal the effect of this substitution on the emission energy and quantum efficiency.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. NMR Spectroscopy in Solution
The 1H-NMR spectrum of 1 was recorded in acetone-d6 and is depicted in Figure 1. It consists of a set of well-separated sharp signals, indicative of the complex symmetry and integrity in the solution. 1H assignments, as well as complexation-induced changes (Δδ) in chemical shifts, are listed in Table 1. It should be noted that the ppy/L column values correspond to 1H chemical shifts in the complex [Ir(ppy)2(CH3CN)2]PF6 (which was synthesized using the method reported in [17]) and the studied diimine. From the data cited in Table 1, it is evident that both ligands interact strongly with the metal center [18,19]. Interestingly, the presence of the ancillary ligand induces further changes to proton chemical shifts of the already metal bound ppy in Ir(ppy)2 moiety.
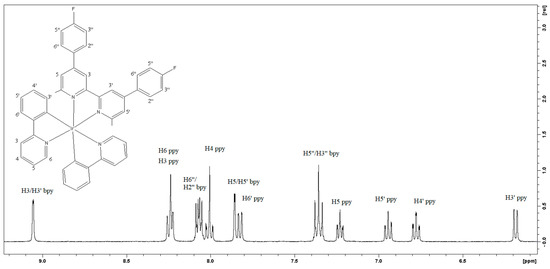
Figure 1.
The 1HNMR spectrum of [Ir(ppy)2L][PF6] in acetone-d6 at 500 MHz at 298K.

Table 1.
The 1H NMR data (δ, ppm) of ppy/L and the complex 1 ([Ir(ppy)2L)][PF6]).
2.2. Photophysical Properties
2.2.1. Electronic Absorption Spectroscopy
The UV-Vis spectrum (Figure 2) of 1 (c = 1.1 × 10−5 M) has been acquired in acetonitrile (298K). According to the absorption studies of similar systems [5,8,9,12,14,15,16,20], the high energy band was assigned the 1LLCT transitions (π→π*) while the shoulders at 330 and near 400 nm were attributed to spin-allowed metal-to-ligand charge-transfer (1MLCT). Finally, the weak absorption tail observed at λ > 450 nm was assigned to spin-forbidden 3MLCT transitions [21,22,23].
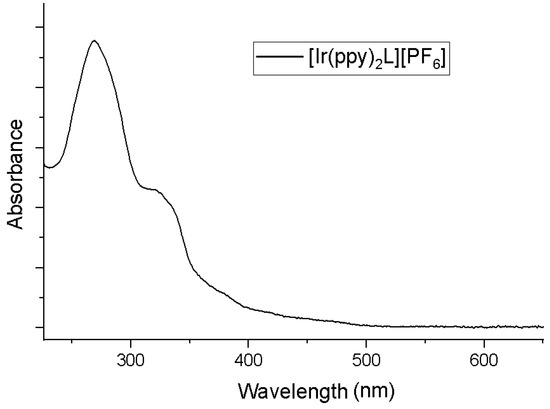
Figure 2.
The UV-Vis spectrum of [Ir(ppy)2L]PF6 (1) in acetonitrile.
2.2.2. Emission Spectrum
The photoluminescence spectrum of compound (1) was registered in deaerated (Ar) CH3CN solution (1.1 × 10−5 M) at room temperature (Figure 3). The observed band, centered at λem = 562 nm (yellow emitter), appeared broad and unstructured, as typically expected for emissions from 3MLCT or mixed 3MLCT/3LLCT excited states [16,20,21,22,23]. The emission wavelength of 562 nm is very close to the value (λem =559 nm) recorded for the reference complex [Ir(ppy)2(N^N)][PF6] (N^N= 6,6′-dimethyl-4,4′-diphenyl-2,2′-bipyridine) [16]. Surprisingly the photoluminescence quantum yield of our compound was found to be very low (Φ = 5%) compared to the reference’s one (Φ = 54%). It seems that fluorine substitution at the 4-position of the phenyl ring had almost no effect on the HOMO-LUMO gap but strongly promoted the loss of the excitation energy via non-radiative pathways. One possible explanation for this differentiation might be the different nature of the mixed 3MLCT/3LLCT emissive state (i.e., more 3LLCT character in complex 1). It is reported that excited 3LLCT states are more photochemically active and prone to distortion, leading to deactivated interactions with polar solvents [24]. Nevertheless, the Φ value of 1 increased considerably in deaerated CH2Cl2 (Φ = 19%).
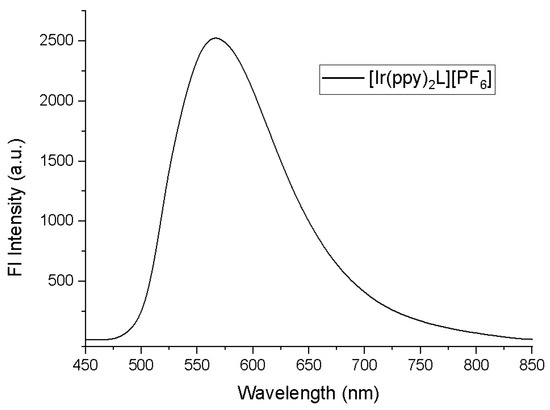
Figure 3.
The photoluminescence spectrum of [Ir(ppy)2L]PF6 in acetonitrile (λexc = 350 nm).
2.3. Description of the Structure (X-ray)
The X-ray crystal structure of complex 1 was obtained from single crystals grown by the slow vapor diffusion of diethyl ether into a concentrated solution of the complex in dichloromethane. We formulated 1 as [Ir(ppy)2L]PF6⋅(solvent), where ppy is the anion of phenylpyridine and L is 4,4′-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-6,6′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine, and crystallized in the monoclinic space group P21/c. Its asymmetric unit consists of a cation [Ir(ppy)2L]+ and the counter anion PF6−. The electron density attributable to the solvated molecules could not be modeled and was removed. Selected bond distances (Å) and angles (o) for the coordination sphere of Ir(III) in the cation are presented in Table 2, while the structure of the cation is depicted in Figure 4.

Table 2.
Selected structural characteristics of compound 1.
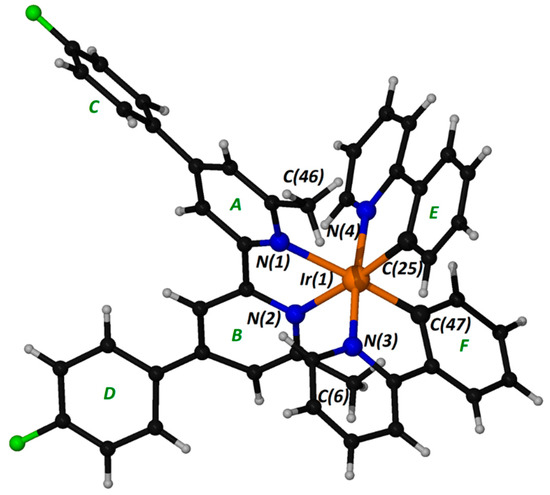
Figure 4.
A “ball and stick” diagram of the cation in compound 1 with a partial labelling scheme. Ring labels are also included for discussion in the text.
Despite the bad quality crystal, the structural determination of 1 confirmed the gross structural features of the complex.
The geometry around Ir(III) is octahedral with distortions expected in tris-chelate metal complexes, while the bond lengths and angles of the cation in 1 match well with those previously reported for similar complexes. The approximately octahedral geometry is confirmed with the two pyridine rings of the cyclometallated ppy ligands-oriented trans to each other and the two phenyl rings in cis orientation. [16,25,26] The Ir-N bond distances to the substituted bipyridyl ligand [mean value 2.23 Å] lie on the upper limit of the literature values, probably due to the strong electron-withdrawing properties of the fluorine atoms. [16,26,27] The bite angles of the chelated ligands are comparable with the literature values of the N(1)-Ir(1)-N(2) angle (≈77°), which are systematically smaller than those of the cyclometallated ppy ligands (≈81°). The stronger interaction of the cyclometallated ligands with iridium(III), compared to that of the substituted bipyridyl, was confirmed by the differences in Ir–N bond lengths (mean values: Ir-Nppy, 2.025; Ir-Nbipyridyl, 2.23 Å).
While the coordination domains of the ppy ligands can be considered planar (the dihedral angles between the pyridine and phenyl rings are correspondingly 6.5 and 5.2° for ppy E and F), the bipyridyl ligand is severely twisted. The dihedral angle between pyridine rings A and B is 28.2°; additionally, the phenyl substituents are also twisted with respect to the pyridine ring to which they are bonded, making least-squares planes angles of 22.1° for rings A, C and 42.6° for rings B, D.
The methyl groups of 4,4′-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-6,6′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine embrace the coordination core and interact with relatively strong intramolecular C-H ⋅⋅⋅ π interactions with the phenyl rings of the ppy ligands (related distances: C(46) ⋅⋅⋅ centroid E, 3.24; H(46B) ⋅⋅⋅ centroid E, 2.66; C(6) ⋅⋅⋅ centroid F, 3.35; H(6B) ⋅⋅⋅ centroid F, 2.35 Å).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
All solvents were of an analytical grade and were used without further purification. N-acetonyl pyridinium chloride, AgPF6 and NH4OAc were purchased from Aldrich. IrCl3xH2O, diacetyl, 2-bromo-1-p-methyl-ethanone, 4-fluorobenzaldehyde and piperidine were purchased from Alfa Aesar. The ligand L = 4,4′-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-6,6′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine and the complex [Ir(ppy)2(CH3CN)2][PF6] were prepared according to reported procedures [17,28].
3.2. Methods
The high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrum (HR-ESI-MS) (Figure S1) of the compound was obtained on a Thermo Scientific, LTQ Orbitrap XL™ system. C, H and N elemental analysis was performed on a Perkin-Elmer 2400 Series II analyzer. 1D (1H) and 2D (TOCSY, NOESY, HSQC, HMBC) spectra (Figures S2–S5) were acquired on Bruker Avance spectrometer operating at 500.13 MHz and processed using Topspin 4.07 (Bruker Biospin GmbH, Ettlingen, Germany). The emission study was carried out using a Jasco FP-8300 fluorometer equipped with a xenon lamp source and an integrated sphere for solid samples. The relative photoluminescence quantum yield was calculated using the equation Qs = Qr(Ar/As)(Es/Er)(ns/nr)2. ‘A’ stands for the absorbance of the solution, ‘E’ for the integrated fluorescence intensity of the emitted light, ‘n’ is the refractive index of the solvent, while the subscripts ‘r’ and ‘s’ correspond to the reference and the sample, respectively. An air equilibrated aqueous solution of [Ru(bpy)3]Cl2 was employed as reference (Qr = 0.04) [29]
3.3. Crystal Structure Determination
A suitable needle-like yellow crystal of compound 1, with approximate dimensions 0.30 × 0.025 × 0.02 mm3, was glued to a thin glass fiber with a cyanoacrylate (super glue) adhesive and placed on the goniometer head. Diffraction data were collected on a Bruker D8 Quest Eco diffractometer, equipped with a Photon II detector and a TRIUMPH (curved graphite) monochromator utilizing Mo Ka radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å) and using the APEX 3 software package [30]. A total of 800 frames were collected with φ and ω scans. The collected frames were integrated with the Bruker SAINT software using a wide-frame algorithm. The integration of the data using a monoclinic unit cell yielded a total of 58631 reflections with a maximum θ angle of 25.00° (0.84 Å resolution), of which 7473 were independent (completeness = 98.5%, Rint = 16.30%, Rsig = 9.30%) and 4739 (63.41%) were greater than 2σ(F2). The final cell constants of a = 16.295(8), b = 12.504(5), c = 21.712(9) Å, β = 103.013(16) °, V = 4310(3) Å3, were based upon the refinement of the XYZ-centroids of 8599 reflections above 20 σ(I) with 4.810 ° < 2θ < 45.616 °. Data were corrected for absorption effects using the Multi-Scan method (SADABS) [31]. The ratio of the minimum to the maximum apparent transmission was 0.609. The P21/c space group was assigned, and the structure was solved using the Bruker SHELXT Software Package and refined by full-matrix least-squares techniques on F2 (SHELXL 2018/3) [32] via the ShelXle interface [33]. Further experimental crystallographic details for 1: Data/restraints/parameters, 7473/6/543; (Δ/σ)max = 0.002; (Δρ)max/(Δρ)min = 1.616/–1.356 eÅ–3; Goodness of Fit, 1.094; R indices [I > 2σ(I)], Robs = 0.0905, wRobs = 0.2514; R indices [all data], Rall = 0.1317, wRall = 0.2727. The non-H atoms were treated anisotropically, while organic H atoms were placed in calculated, ideal positions and refined by riding on their respective carbon atoms. PLATON [34] was used for geometric calculations, and X-Seed [35] for molecular graphics.
Data were collected from a few different crystals, but their quality did not allow the collection of a better data set. The crystals were opaque and appeared to lose their solvency. Some residual electron densities, assigned to solvent molecules, could not be modeled and were treated with the SQUEEZE routine implemented in PLATON. To confirm the assignment of the coordinated C and N atoms of the phenylpyridine molecules, several models were used in the refinement, spanning from simple C/N to N/C swap to different ppy molecules with partial occupancies coordinated in different positions. In all cases, the R values were increased, or several atoms came up with a non-positive definite.
Full details on the structure can be found in the CIF file deposited with CCDC. CCDC 2245354 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif (accessed on 28 February 2023).
3.4. Synthesis
Synthesis of [Ir(ppy)2L]PF6 (1)
In a two-neck 100 mL round-bottom flask, 20 mL of 1,2 dichloroethane (Ar-degassed), 20 mg of [Ir(ppy)2(CH3CN)2][PF6] (0.027 mmol) and 12.3 mg of L (0.033 mmol) were added. The solution was refluxed for 24 h under N2. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the crude product was washed with acetonitrile (2–3 mL, in portions) to extract the desired complex. The washings were combined, followed by the slow addition of diethyl ether. A yellow solid was precipitated, collected and dried under a vacuum. Yield: 75% (m = 18 mg). C46H34N4PF8Ir: calc.% C, 54.27; H, 3.37; N, 5.50. Found C, 54.29; H, 3.40; N, 5.45. 1H NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6) δ (ppm) L: 9.07 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 2H); 8.07 (m, 4H); 7.87 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 2H); 7.35 (m, 4H). ppy: 8.26 (m, 4H); 8.01 (m, 2H); 7.83 (m, 2H); 7.24 (m, 2H); 6.96 (m, 2H); 6.78 (td, J = 7.6, 1.3 Hz, 2H); 6.19 (d, J = 7,7 Hz, 2H). 13C NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6) δ (ppm) L: 26.1 (CH3); 116.2 (C5″/C3″); 120.4 (C3/C3′); 125.6 (C5/C5′); 129.9 (C6″C2″); 132.1 (C4/C4″); 158.9 (C2); 162.1 (C1″); 163.9 (C6). ppy: 119.8 (C3); 122.0 (C5′); 123.3 (C5); 124.8 (C6′); 129.7 (C4′); 131.5 (C3′); 138.6 (C4); 143.6 (C2′); 148 (C1′); 150.3 (C6); 167.5 (C2). HR ESI MS: cal. m/z = 873.2375, found m/z = 873.2361 for C46H34F2N4Ir+. UV-Vis (dichloromethane): λmax (nm), ε (M−1 cm−1) 269 (36363); 327 (17272); 386 (4727); 480 (954).
4. Conclusions
Overall, we synthesized and structurally characterized (NMR, X-ray diffraction) the novel cyclometallated Ir(III) complex Bis(2-phenylpyridinato,-C2′,N)[4,4′-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-6,6′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine] iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate. The compound is a yellow emitter (λ = 562 nm), exhibiting a photoluminescence quantum yield ranging from Φ = 5% (CH3CN) to Φ = 19% (CH2Cl2). The fluorine substituents at the 4-position of the phenyl rings do not affect the emission maximum. On the contrary, the quantum yield was significantly reduced.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded online, Figure S1: HR ESI-MS spectrum of the complex in acetone (top) and theoretical spectrum for the fragment [Ir(ppy)2L]+ (C46H34F2N4Ir+); Figure S2: 1H-1H-TOCSY NMR spectrum of the complex; Figure S3: 1H-1H-NOESY NMR; Figure S4: 1H-13C HMQC NMR; Figure S5: 1H-13C HMBC NMR; File S1: crystal structure of the compound (*.mol); File S2: crystal structure of the compound (*.cif) file; File S3 (checkcif, pdf file).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: G.M.; Supervision: G.M.; Formal analysis: D.G. and J.C.P. Investigation: D.G.; X-ray crystallography: J.C.P., Writing—original draft: D.G. and J.C.P. Writing—review and editing: G.M. and J.C.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
CCDC 2245354 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge via https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/. All other data in this study can be found in Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank The Network of Research Supporting Laboratories at the University of Ioannina for providing access to the use of MS, NMR and X-ray diffraction facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
References
- Zhao, Q.; Huang, C.; Li, F. Phosphorescent Heavy-Metal Complexes for Bioimaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S.; Din, I.; Raheel, A.; Tameez ud Din, A. Cyclometalated Iridium (III) Complexes: Recent Advances in Phosphorescence Bioimaging and Sensing Applications. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporale, C.; Massi, M. Cyclometalated Iridium(III) Complexes for Life Science. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 363, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, J.-H.; Kim, D.; Rathnayake, M.D.; Sittel, S.; Weaver, J.; Teets, T.S. Photoredox Catalysis on Unactivated Substrates with Strongly Reducing Iridium Photosensitizers. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 4069–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, F.; Baschieri, A.; Sambri, L.; Armaroli, N. Excited-State Engineering in Heteroleptic Ionic Iridium(III) Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 1492–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.-L.; Lin, S.; Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Leung, C.-H. Luminescent Chemosensors by Using Cyclometalated Iridium(III) Complexes and Their Applications. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, T.U.; Donnelly, P.S. Labelling Proteins and Peptides with Phosphorescent d6 Transition Metal Complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 375, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.-G.; Zheng, Y.-X.; Zuo, J.-L.; Pan, Y. Rational Design of Phosphorescent Iridium(III) Complexes for Emission Color Tunability and Their Applications in OLEDs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 374, 55–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.L.P.; Bejoymohandas, K.S. Evolution of 2, 3′-Bipyridine Class of Cyclometalating Ligands as Efficient Phosphorescent Iridium(III) Emitters for Applications in Organic Light Emitting Diodes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2016, 29, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; He, L. Blue-Emitting Iridium(III) Complexes for Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells: Advances, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo, A.B.; Garon, S.; Sajoto, T.; Djurovich, P.I.; Tsyba, I.M.; Bau, R.; Thompson, M.E. Cationic Bis-Cyclometalated Iridium(III) Diimine Complexes and Their Use in Efficient Blue, Green, and Red Electroluminescent Devices. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 8723–8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housecroft, C.E.; Constable, E.C. Over the LEC Rainbow: Colour and Stability Tuning of Cyclometallated Iridium(III) Complexes in Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 350, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, C.D.; Cerdá, J.; Junquera-Hernández, J.M.; Pertegás, A.; Bolink, H.J.; Constable, E.C.; Neuburger, M.; Ortí, E.; Housecroft, C.E. Colour Tuning by the Ring Roundabout: [Ir(C^N)2(N^N)] + Emitters with Sulfonyl-Substituted Cyclometallating Ligands. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 42815–42827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.D.; Ortí, E.; Bolink, H.J. Recent Advances in Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells. Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 2115–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranoff, E.; Bolink, H.J.; Constable, E.C.; Delgado, M.; Häussinger, D.; Housecroft, C.E.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Neuburger, M.; Ortí, E.; Schneider, G.E. Tuning the Photophysical Properties of Cationic Iridium(III) Complexes Containing Cyclometallated 1-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)-1H-Pyrazole through Functionalized 2,2′-Bipyridineligands: Blue but Not Blue Enough. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.D.; Ortí, E.; Tordera, D.; Pertegás, A.; Bolink, H.J.; Graber, S.; Housecroft, C.E.; Sachno, L.; Neuburger, M.; Constable, E.C. Stable and Efficient Solid-State Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells Based on a Series of Hydrophobic Iridium Complexes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2011, 1, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, B.; Garces, F.O.; Watts, R.J. Synthesis and Characterizations of Cyclometalated Iridium(III) Solvento Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Neuburger, M.; Poleschak, I.; Zehnder, M. Functionalised 2,2′-Bipyridine Ligands for the Preparation of Metallostars; X-Ray Structures of Free Ligands and Preparation of Copper(I) and Silver(I) Complexes. Polyhedron 2003, 22, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Kopecky, P.; Martin, C.J.; Wright, I.A.; Zampese, J.A.; Bolink, H.J.; Pertegas, A. Solution, Structural and Photophysical Aspects of Substituent Effects in the N^N Ligand in [Ir(C^N)2(N^N)]+ Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 8086–8103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, J.C.; Castellano, F.N. Archetypal Iridium(III) Compounds for Optoelectronic and Photonic Applications: Photophysical Properties and Synthetic Methods. In Iridium (III), in Optoelectronic and Photonics Applications, 1st ed.; Zysman-Colman, E., Ed.; Willey: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781119007135. [Google Scholar]
- Dreyse, P.; González, I.; Cortés-Arriagada, D.; Ramírez, O.; Salas, I.; González, A.; Toro-Labbe, A.; Loeb, B. New Cyclometalated Ir(III) Complexes with Bulky Ligands with Potential Applications in LEC Devices: Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Their Photophysical Properties. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 6253–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.D.; Ortí, E.; Bolink, H.J.; Graber, S.; Housecroft, C.E.; Constable, E.C. Efficient and Long-Living Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skórka, Ł.; Filapek, M.; Zur, L.; Małecki, J.G.; Pisarski, W.; Olejnik, M.; Danikiewicz, W.; Krompiec, S. Highly Phosphorescent Cyclometalated Iridium(III) Complexes for Optoelectronic Applications: Fine Tuning of the Emission Wavelength through Ancillary Ligands. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 7284–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, R.V.; Hogan, C.F.; James, B.D.; Wilson, D.J.D. Photophysical and Electrochemical Properties of Phenanthroline-Based Biscyclometallated Iridium Complexes in Aqueous and Organic Media. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 2011, 4816–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, N.; Karaman, M.; Yakali, G.; Tugsuz, T.; Denizalti, S.; Demic, S.; Dindar, B.; Can, M. Structure−Property Relationship in Amber Color Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cell with TFSI Counteranion: Enhancing Device Performance by Different Substituents on N∧N Ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 4410–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhr, K.J.; Bastatas, L.D.; Shen, Y.; Mitchell, L.A.; Frazier, G.A.; Taylor, D.W.; Slinker, J.D.; Holliday, B.J. Phenyl substitution of cationic bis-cyclometalated iridium(III) complexes for iTMC-LEECs. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 17807–17823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, L.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.-X.; Jiang, W.-L.; Yin, G.-Q.; Tan, H.; Li, X.; Xu, L.; Yang, H.-B. Photoswitchable Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) within a heterometallic Ir–Pt macrocycle. Chem. Comm. 2019, 55, 11119–11122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malzner, F.J.; Brauchli, S.Y.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Neuburger, M. Halos Show the Path to Perfection: Peripheral Iodo-Substituents Improve the Efficiencies of Bis(Diimine)Copper(I) Dyes in DSCs. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 48712–48723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitoshi Ishida, H.; Tobita, S.; Hasegawac, Y.; Katoh, R.; Nozaki, K. Recent advances in instrumentation for absolute emission quantum yield measurements. Coord. Chem. Rev 2010, 254, 2449–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruker. APEX 3. In SAINT, SHELXT; Bruker AXS Inc.: Fitchburg, WI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübschle, C.B.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Dittrich, B. ShelXle: A Qt graphical user interface for SHELXL. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spek, A.L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2009, 65, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, L.J. X-Seed—A Software Tool for Supramolecular Crystallography. J. Supramol. Chem. 2001, 1, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).