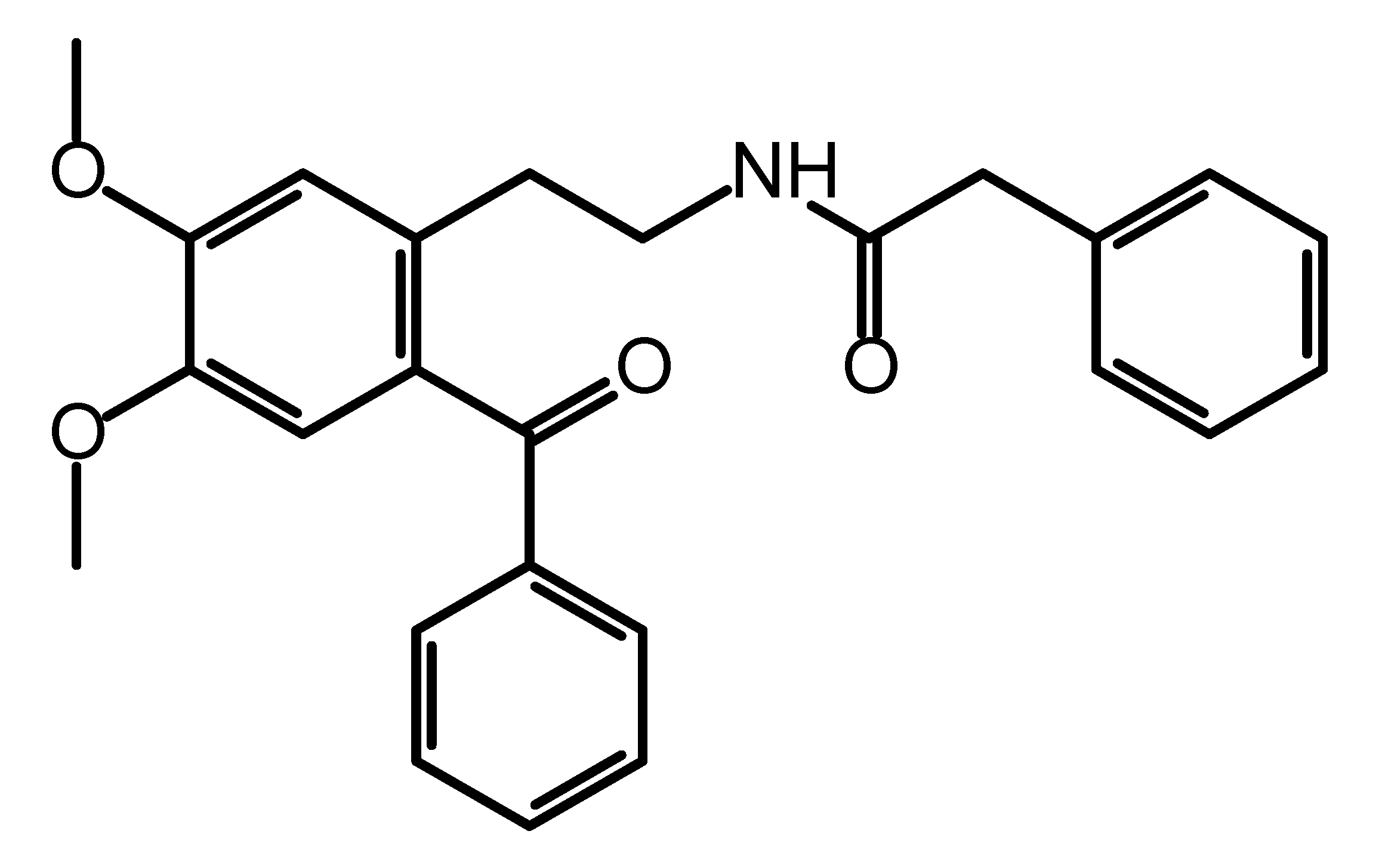
N-(2-Benzoyl-4,5-dimethoxyphenethyl)-2-phenylacetamide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
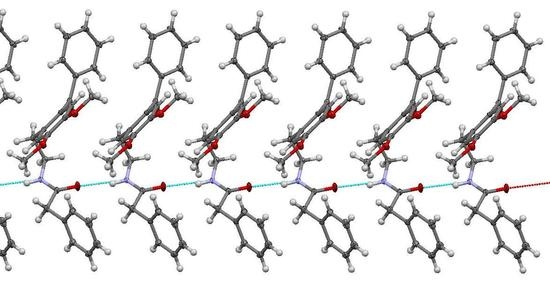
2. Results
3. Experimental Section
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ivanov, I.; Nikolova, S.; Aladjov, D.; Stefanova, I.; Zagorchev, P. Synthesis and Contractile Activity of Substituted 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolines. Molecules 2011, 16, 7019–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindikar, A.V.; Viswanathan, C.L. Substituted 2-[2-(pyridin-3-yl) phenyl] acetamides and ureas: Design, synthesis, and anticonvulsant screening in mice. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelke, S.M.; Bhosale, S.H. Synthesis, antidepressant evaluation and QSAR studies of novel 2-(5H-[1, 2, 4] triazino [5, 6-b] indol-3-ylthio)-N-(substituted phenyl) acetamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4661–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.L.; Chen, J.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Peng, C.T.; Juang, S.H.; Wang, T.C. Synthesis and antiproliferative activities of N-(naphthalen-2-yl)acetamide and N-(substituted phenyl)acetamide bearing quinolin-2(1H)- one and 3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 59, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinova, P.E.; Tsoneva, S.H.; Nikolova, S.A.; Ivanov, I.I. Novel complexes of N-substituted-4,5-dimethoxy-phenylethyl-2-arylketoamides with metal ions. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 51, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, L.J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: An update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
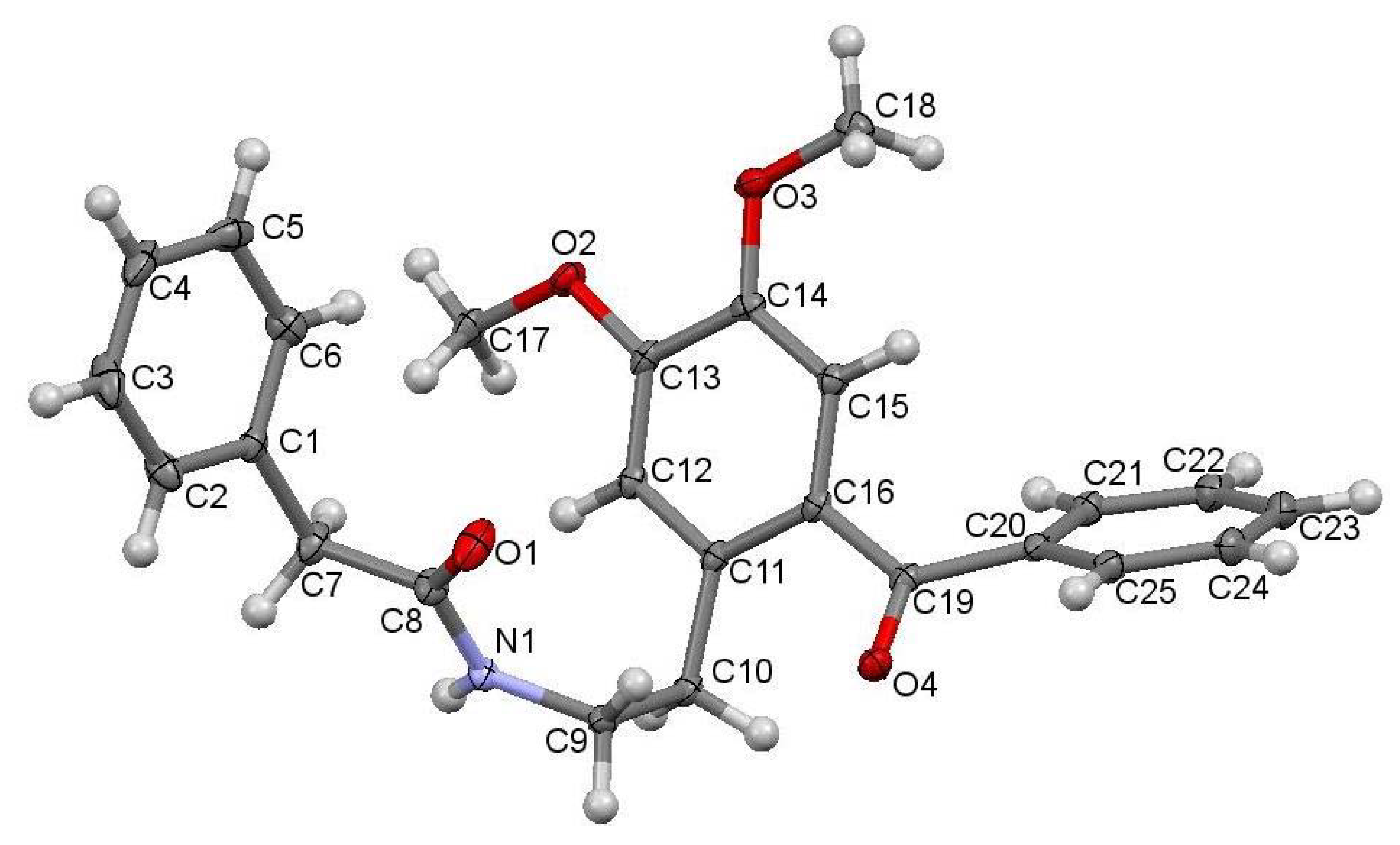


| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1···O1 i | 0.844 (19) | 2.055 (19) | 2.8894 (19) | 169.8 (16) |
| C10—H10A···O4 | 0.97 | 2.39 | 2.8885 (18) | 111 |
| C17—H17A···O2 ii | 0.96 | 2.58 | 3.438 (2) | 149 |
| C17—H17C···O3 i | 0.96 | 2.64 | 3.444 (2) | 142 |
| Crystal Data | |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C25H25NO4 |
| Mr | 403.46 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, C2/c |
| Temperature (K) | 120 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 23.724 (9), 4.9750 (15), 35.816 (15) |
| b (°) | 103.99 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 4102 (3) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Ka |
| m (mm−1) | 0.09 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.54 × 0.26 × 0.11 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | STOE IPDS 2T |
| Absorption correction | Integration ; STOE X-RED32, absorption correction by Gaussian integration |
| Tmin, Tmax | 0.970, 0.993 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2s(I)] reflections | 13109, 4005, 3221 |
| Rint | 0.042 |
| (sin q/l)max (Å−1) | 0.617 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F2 > 2s(F2)], wR(F2), S | 0.041, 0.113, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 4005 |
| No. of parameters | 276 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Dρmax, Dρmin (e Å−3) | 0.26, −0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marinova, P.; Nikolova, S.; Dołęga, A.; Ahmedova, A. N-(2-Benzoyl-4,5-dimethoxyphenethyl)-2-phenylacetamide. Molbank 2022, 2022, M1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1376
Marinova P, Nikolova S, Dołęga A, Ahmedova A. N-(2-Benzoyl-4,5-dimethoxyphenethyl)-2-phenylacetamide. Molbank. 2022; 2022(2):M1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1376
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarinova, Petja, Stoyanka Nikolova, Anna Dołęga, and Anife Ahmedova. 2022. "N-(2-Benzoyl-4,5-dimethoxyphenethyl)-2-phenylacetamide" Molbank 2022, no. 2: M1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1376
APA StyleMarinova, P., Nikolova, S., Dołęga, A., & Ahmedova, A. (2022). N-(2-Benzoyl-4,5-dimethoxyphenethyl)-2-phenylacetamide. Molbank, 2022(2), M1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1376