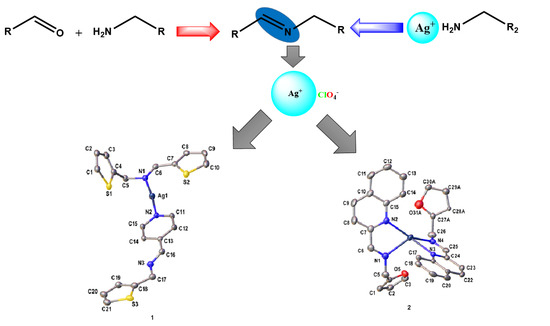
Ag(I) Complexes of Imine Derivatives of Unexpected 2-Thiophenemethylamine Homo-Coupling and Bis-(E)-N-(furan-2-ylmethyl)-1-(quinolin-2-yl)methanimine
Abstract
1. Introduction
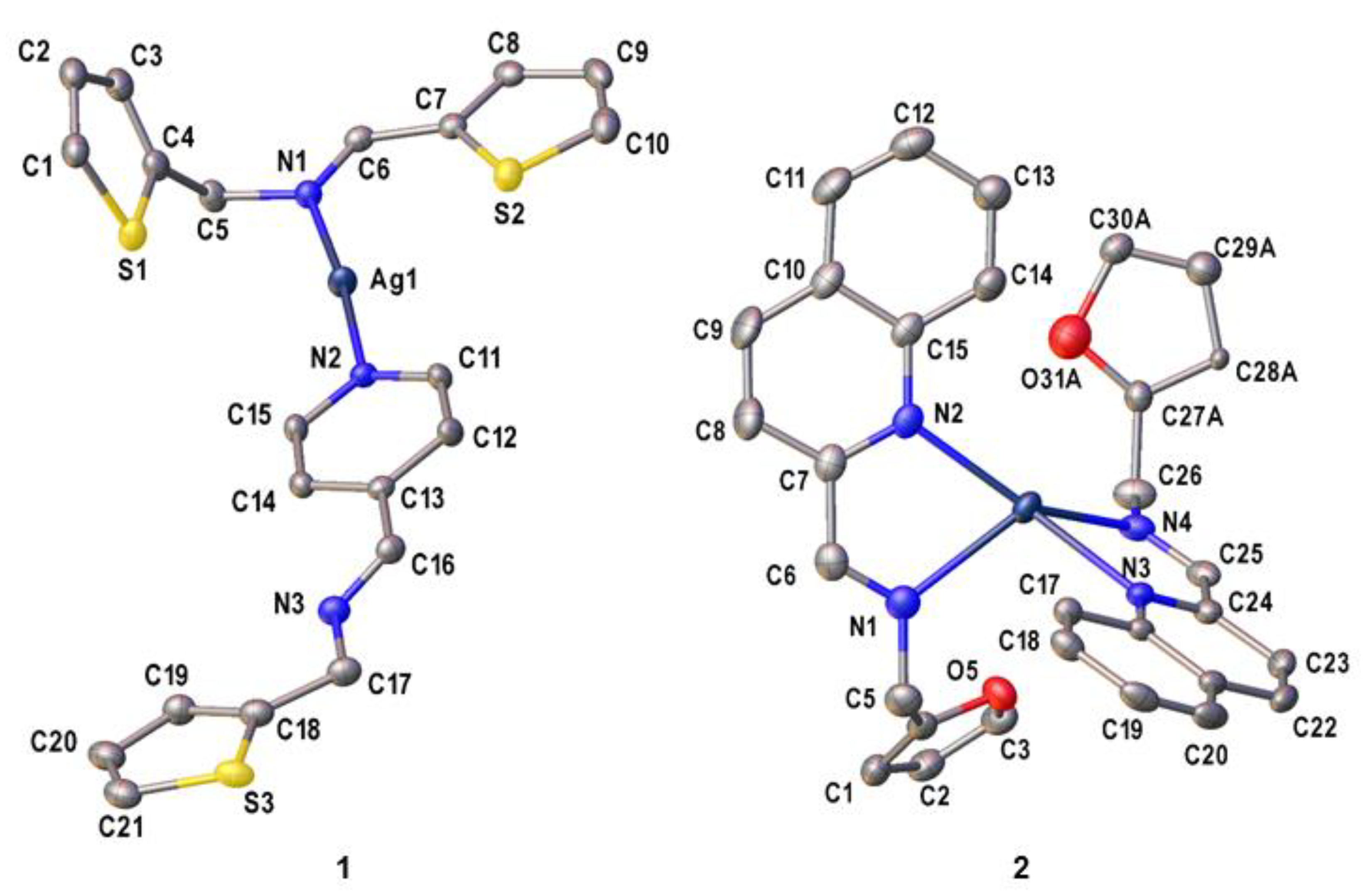
2. Results
Crystal Structures
3. Materials and Methods
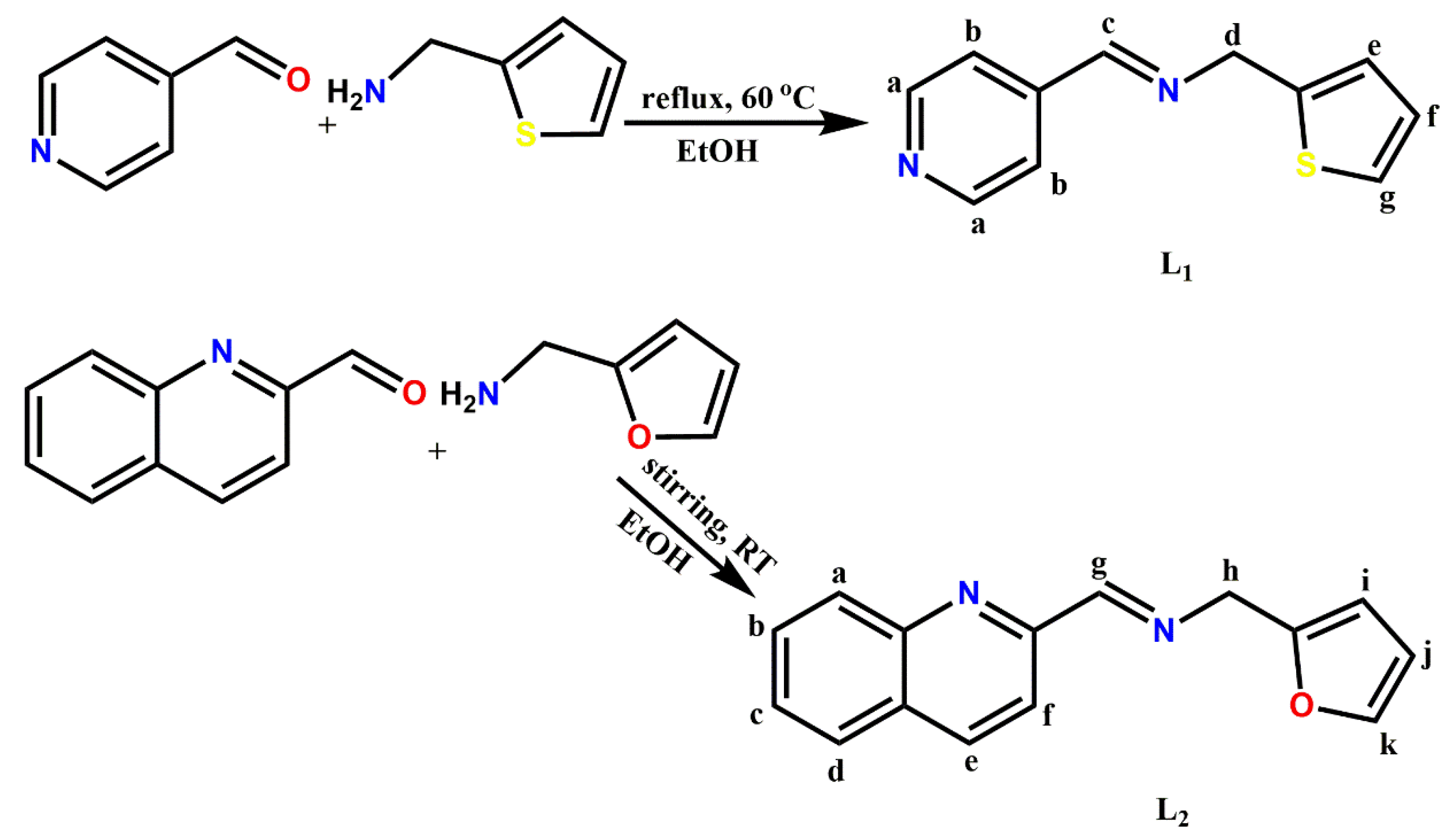
3.1. Synthesis of Pyridinyl (L1) and Quinolinyl (L2) Schiff bases
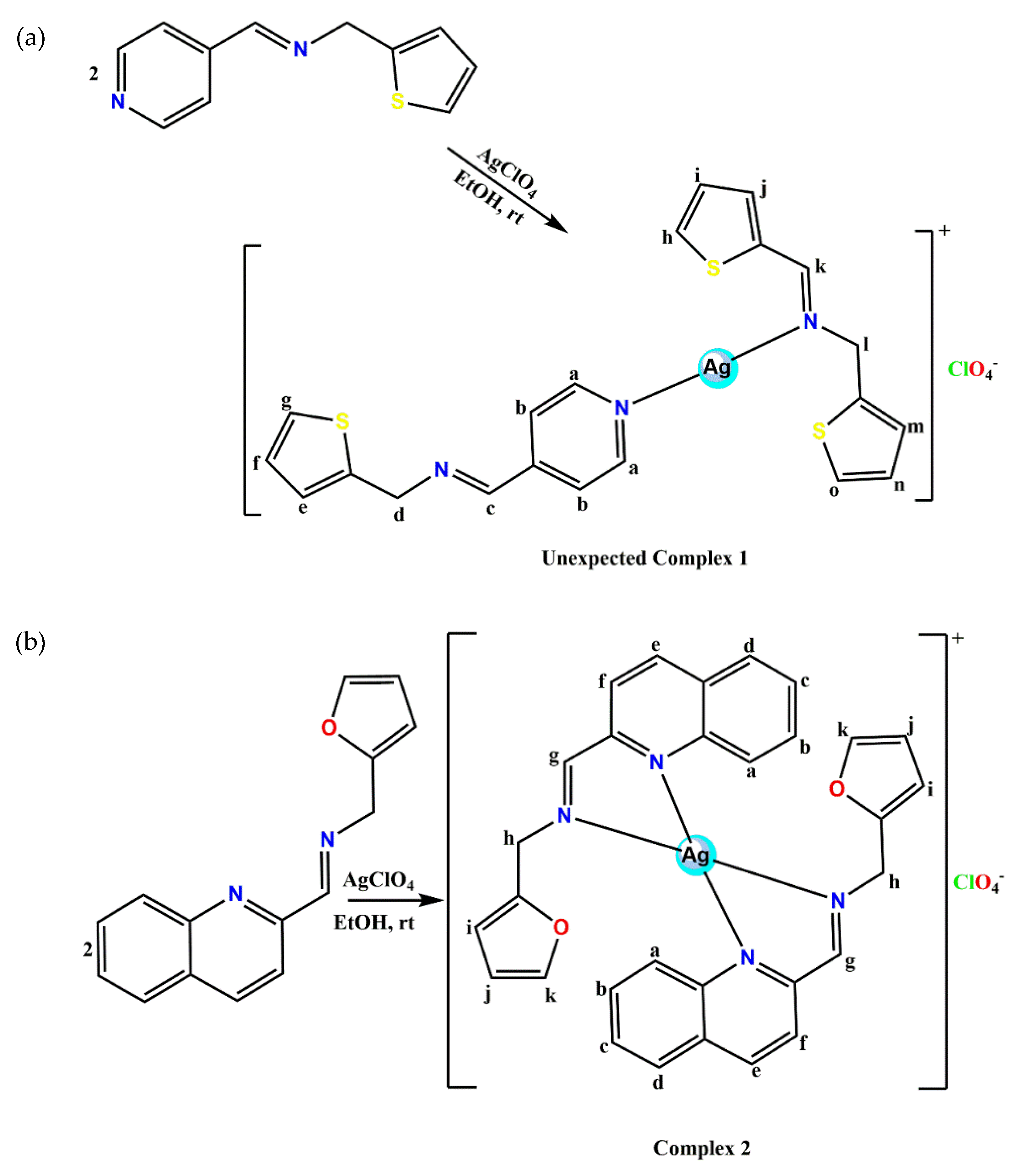
3.2. Synthesis of Pyridinyl and Quinolinyl Ag(I) Complexes
3.3. X-ray Crystallography
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prakash, A.; Adhikari, D. Application of Schiff bases and their metal complexes—A Review. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2011, 3, 1891–1896. [Google Scholar]
- Rudrapal, M. Chemistry and Biological Importance of Heterocyclic Schiff’s Bases. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 3, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yu, L.; He, L.; Liu, Y.-M.; Cao, Y.; Fan, K.-N. Direct one-pot reductive imination of nitroarenes using aldehydes and carbon monoxide by titania supported gold nanoparticles at room temperature. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Shao, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhang, X.; Tang, S.; Sun, J. Rhodium-Catalyzed C horizontal lineN Bond Formation through a Rebound Hydrolysis Mechanism and Application in beta-Lactam Synthesis. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 4124–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casnati, A.; Voronov, A.; Ferrari, D.G.; Mancuso, R.; Gabriele, B.; Motti, E.; Della Ca’, N. PdI2 as a Simple and Efficient Catalyst for the Hydroamination of Arylacetylenes with Anilines. Catalysts 2020, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sun, W.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Cao, Q.; Fang, W.; Zhao, Q. Efficient imine synthesis from oxidative coupling of alcohols and amines under air atmosphere catalysed by Zn-doped Al2O3 supported Au nanoparticles. J. Catal. 2019, 377, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Dutta, B.; Mullick, K.; Kuo, C.-H.; Poyraz, A.S.; Suib, S.L. Aerobic Oxidation of Amines to Imines by Cesium-Promoted Mesoporous Manganese Oxide. ACS Catalysis 2015, 5, 4394–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largeron, M. Protocols for the Catalytic Oxidation of Primary Amines to Imines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2013, 5225–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Sarkar, P.; Husain, A.; Marella, A.; Zaman, M.S.; Akhter, M.; Shaharyar, M.; Alam, O.; Azam, F. Synthesis of quinoline attached-furan-2(3H)-ones having anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties with reduced gastro-intestinal toxicity and lipid peroxidation. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2011, 76, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, M.; Hanif, S.; Sherwani, M.A.; Mohammad, O.; Al-Resayes, S.I. Pharmacologically significant complexes of Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) of novel Schiff base ligand, (E)-N-(furan-2-yl methylene) quinolin-8-amine: Synthesis, spectral, XRD, SEM, antimicrobial, antioxidant and in vitro cytotoxic studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1092, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturiqi, A.S.; Alaghaz, A.-N.M.A.; Ammar, R.A.; Zayed, M.E. Synthesis, Spectral Characterization, and Thermal and Cytotoxicity Studies of Cr(III), Ru(III), Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) Complexes of Schiff Base Derived from 5-Hydroxymethylfuran-2-carbaldehyde. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenger-Smith, J.; Chakraborty, I.; Sameera, W.M.C.; Mascharak, P.K. Antimicrobial silver(I) complexes derived from aryl-benzothiazoles as turn-on sensors: Syntheses, properties and density functional studies. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 471, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.; Chakraborty, I.; Rojas-Andrade, M.; Mascharak, P.K. Silver complexes of ligands derived from adamantylamines: Water-soluble silver-donating compounds with antibacterial properties. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 168, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhai, L.-L.; Fan, J.; Chen, K.; Sun, W.-Y. Silver(I) complexes of 4-(2-oxazolinyl)pyridine: Counteranion dependent structural diversity. Polyhedron 2012, 46, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, A.V. Van der Waals volumes and radii. J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 68, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, W.; Wei, D.; Chen, J.-H.; Ng, S.W.; Yang, G. Adducts of triangular silver (i) 3, 5-bis (trifluoromethyl) pyrazolate with thiophene derivatives: A weak interaction model of desulfurization. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 16162–16166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Powell, D.R.; Houser, R.P. Structural variation in copper(I) complexes with pyridylmethylamide ligands: Structural analysis with a new four-coordinate geometry index, tau4. Dalton Trans. 2007, 9, 955–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.-H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Froehlich, R. Supramolecular helical architecture assembled by double-helical [Ag2L2] units. J. Organomet. Chem. 2004, 689, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatikonda, R.; Bulatov, E.; Kalenius, E.; Haukka, M. Construction of Coordination Polymers from Semirigid Ditopic 2,2′-Biimidazole Derivatives: Synthesis, Crystal Structures, and Characterization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 5918–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, A.A.; Zamisa, S.J.; Omondi, B. Crystal structure of 4-(1-phenylimidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)benzoic acid (C20H14N2O2). Z. Krist. N. Cryst. Struct. 2019, 234, 1157–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Adeleke, A.A.; Zamisa, S.J.; Omondi, B. Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis((E)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)phenol)zinc(II), C24H20Cl2N4O2Zn. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2020, 235, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, A.A.; Zamisa, S.J.; Islam, M.S.; Olofinsan, K.; Salau, V.F.; Mocktar, C.; Omondi, B. Quinoline Functionalized Schiff Base Silver (I) Complexes: Interactions with Biomolecules and In Vitro Cytotoxicity, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities. Molecules 2021, 26, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeleke, A.A.; Islam, M.S.; Sanni, O.; Mocktar, C.; Zamisa, S.J.; Omondi, B. Aryl variation and anion effect on CT-DNA binding and in vitro biological studies of pyridinyl Ag(I) complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 214, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAINT, B. Data Reduction Software; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bruker, A. Saint and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure solution with ShelXT. Acta Cryst. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: An. update. J. Appl. Cryst. 2012, 45, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Ag—Npy | 2.123(2) | |
| Ag—Nqy | 2.272(2) 2.377(2) | |
| Ag—Nim | 2.122(2) | 2.377(3) 2.265(2) |
| Npy—Ag—Nim | 174.31(8) | |
| Nqy—Ag—Nim | 143.77(8) 99.46(7) 72.06(7) 72.01(7) |
| 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C21H19.9AgClN3O4.13S3 | C30H25AgClN4O6.25 |
| Formula Weight | 619.80 | 684.86 |
| Crystal system | Triclinic | monoclinic |
| Space group | P-1 | C2/c |
| a(Å) | 10.8978(5) | 21.4229(10) |
| b(Å) | 11.0223(5) | 15.9905(10) |
| c(Å) | 11.7827(5) | 18.1880(9) |
| α(°) | 97.086(2) | 90 |
| β(°) | 116.347(4) | 116.615(3) |
| γ(°) | 107.320(3) | 90 |
| V(Å3) | 1155.54(10) | 5570.3(5) |
| Z | 2 | 8 |
| ρcalc(gcm−3) | 1.781 | 1.633 |
| µ (mm−1) | 1.295 | 0.873 |
| F(000) | 624.0 | 2776.0 |
| Crystal size (mm3) | 0.2 × 0.18 × 0.14 | 0.26 × 0.12 × 0.08 |
| θ range for data collection (°) | 4.042 to 55.75 | 3.318 to 56.514 |
| Index ranges | −14 ≤ h ≤ 14, −14 ≤ k ≤ 8, −15 ≤ l ≤ 15 | −28 ≤ h ≤ 28, −21 ≤ k ≤ 21, −24 ≤ l ≤ 24 |
| Reflections collected | 20931 | 49838 |
| Independent reflections | 5488 [Rint = 0.0195, Rsigma = 0.0200] | 6881 [Rint = 0.0297, Rsigma = 0.0176] |
| Completeness to theta = 28.96 | 99.5% | 100.0% |
| Data / restraints / parameters | 5488/198/379 | 6881/139/469 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.050 | 1.053 |
| R indices [I > 2sigma(I)] | R1 = 0.0274, wR2 = 0.0668 | R1 = 0.0323, wR2 = 0.0844 |
| R indices (all data) | R1 = 0.0303, wR2 = 0.0685 | R1 = 0.0367, wR2 = 0.0876 |
| Largest diff. peak and hole (e Å−3) | 1.06 and −0.60 | 1.19 and −0.77 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adeleke, A.A.; Zamisa, S.J.; Omondi, B. Ag(I) Complexes of Imine Derivatives of Unexpected 2-Thiophenemethylamine Homo-Coupling and Bis-(E)-N-(furan-2-ylmethyl)-1-(quinolin-2-yl)methanimine. Molbank 2021, 2021, M1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1235
Adeleke AA, Zamisa SJ, Omondi B. Ag(I) Complexes of Imine Derivatives of Unexpected 2-Thiophenemethylamine Homo-Coupling and Bis-(E)-N-(furan-2-ylmethyl)-1-(quinolin-2-yl)methanimine. Molbank. 2021; 2021(2):M1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1235
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdeleke, Adesola A., Sizwe J. Zamisa, and Bernard Omondi. 2021. "Ag(I) Complexes of Imine Derivatives of Unexpected 2-Thiophenemethylamine Homo-Coupling and Bis-(E)-N-(furan-2-ylmethyl)-1-(quinolin-2-yl)methanimine" Molbank 2021, no. 2: M1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1235
APA StyleAdeleke, A. A., Zamisa, S. J., & Omondi, B. (2021). Ag(I) Complexes of Imine Derivatives of Unexpected 2-Thiophenemethylamine Homo-Coupling and Bis-(E)-N-(furan-2-ylmethyl)-1-(quinolin-2-yl)methanimine. Molbank, 2021(2), M1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1235