Continuing our studies on bioactive constituents of Rubus aleaefolius Poir. (family Rosacae) [1,2], we report here a new pentacyclic triterpene ester, 3b-O-trans-ferulyl-2b,19b-dihydroxy-urs-12-en- 28-oic acid (1) from Rubus aleaefolius Poir., which inhibits mammalian cell cycle at G2/M phase.
The roots (3 kg) of R. aleaefolius were extracted with 60% aqueous alcohol to give an alcoholic extract (435 g) possessing potential inhibitory activity on cell cycle of tsFT210 cells [1]. The alcoholic extract was thus suspended in water and then extracted successively with chloroform and ethyl acetate to obtain an active ethyl acetate extract (78 g). This extract was further separated by repeated solvent-extraction, silica gel column chromatography, preparative HPLC and recrystallization procedure in a bioassay-guided manner to obtain pure 1 (26.4 mg).
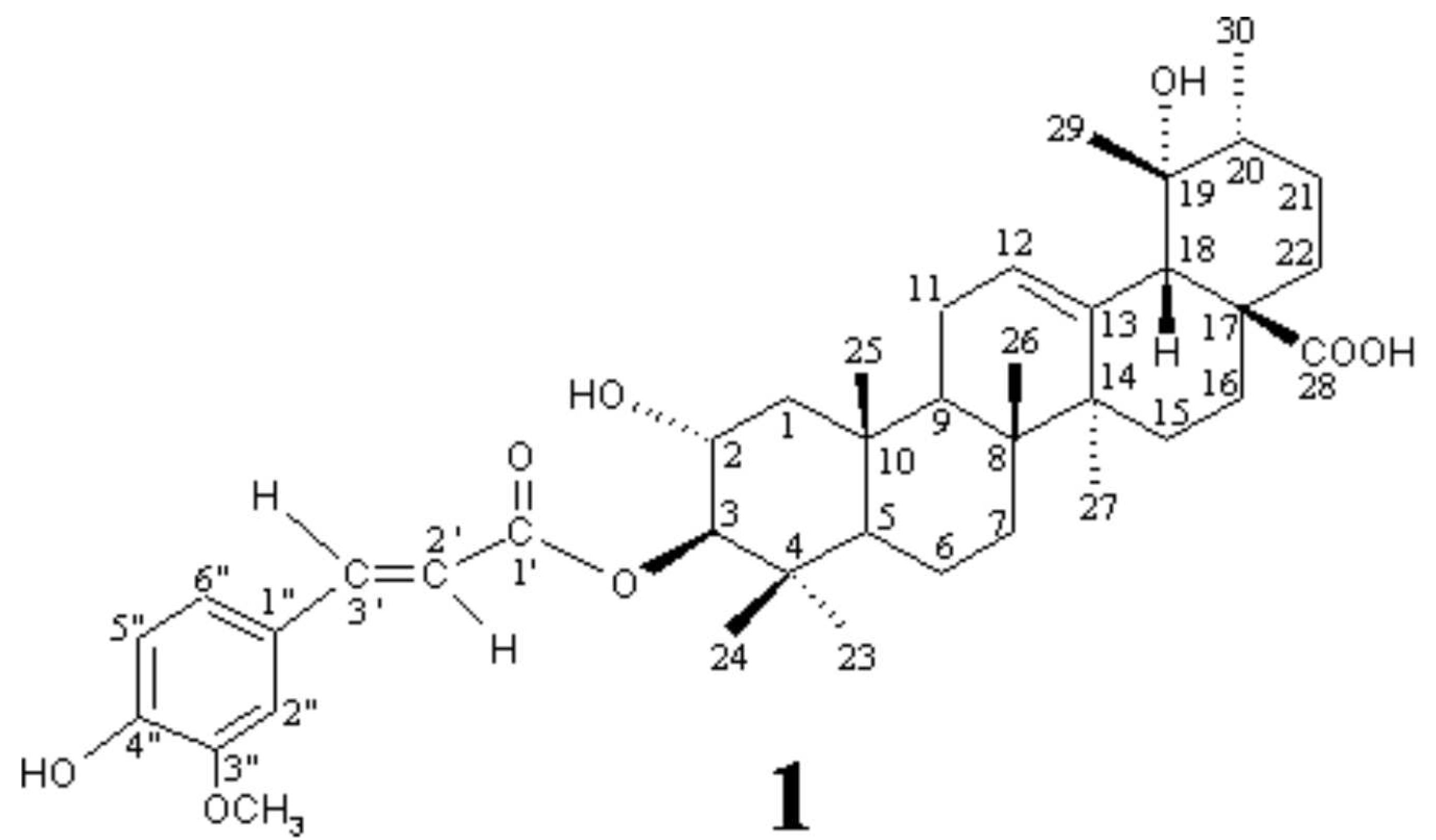
Compound 1, white crystal powder (from MeOH), mp 232-234°C, [a]25D +1.6° (c 0.23, MeOH), gave positive reaction to the Libermann-Burchard and FeCl3 reagents, showing typical colors for triterpenoid and phenol, respectively, and its molecular formula, C40H56O8 (molecular weight 664), was determined by positive HR-ESI-MS measurement. It showed UV absorptions at 233 nm (log e 4.05), 299 sh (4.11) and 325 (4.25) ascribable to an a,b-unsaturated aromatic moiety and the IR spectrum indicated the presence of OH (3448 cm-1), COOH (3400-2400 br and 1697 cm-1), conjugated ester C=O (1715 cm-1), conjugated aromatic ring (1630, 1596, 1515), and C-O (1268, 1175, 1034 cm-1) groups in 1.
The 1H NMR spectrum of 1 showed signals ascribable to a trans-ferulyl (d; 3.90 s, 3H, OCH3; 6.43 d, J=15.9 Hz, 2'-H; 6.81 d, J=7.7 Hz, 5"-H; 7.08 br d, J=7.7 Hz, 6"H; 7.21 br s, 2"-H; 7.63 d, J=15.9 Hz, 3'-H) [3,4], a single olefin (d 5.30 br s, 12-H), six tert-methyl and a sec-methyl (d 0.93 3H, d, J=6.6 Hz, 30-H3) groups. These data and the above structural information from UV and IR spectra revealed that 1 is an ursolic acid derivative with a trans-ferulyl group. The 13C NMR spectrum of 1 resembled those of known 3b-O-trans-ferulyl-2a-hydroxy-urs-12-en-28-oic acid [3] (2) except for the remarkable downfield shift of C-19 signal and slight changes of several carbons around C-19, indicating that 1 is a 19-O-substituted derivative of 2.
Eventually, detailed analyses of the 1H and 13C NMR spectra by means of DEPT and PFG 2D NMR (1H-1H COSY, HMQC, HMBC and NOESY) techniques enabled us to establish the structure of 1 as 3b-O-trans-ferulyl-2a,19a-dihydroxy-urs-12-en-28-oic acid. Briefly, location of the O-ferulyl group at C-3 could be determined by the HMBC correlation between 3-H and C-1', and the trans-2a,3b-O-substitution was evident from the chemical shift and J values of 2-H (d 3.85 ddd, J=11, 9.9, 4.4 Hz) and 3-H (d 4.63 d, J=9.9 Hz) [3,4]. The chemical shift and J values of a-axial 16-H (d 2.59 td, J=13.4, 4.3 Hz) established both the 19a-OH stereochemistry and the cis-stereochemistry of the ring-D/E junction [5].
Compound 1 inhibited the cell cycle progression of synchronously cultured tsFT210 cells [1] at the G2/M phase with the MIC value of 37.6 mmol/L. Although several 3-O-ferulyl derivatives of ursolic acid have hitherto been reported [3,4], the present result provides a new pentacyclic triterpene ester, 1, as a new cell cycle inhibitor, which may possesses potential anticancer effect.
UV lmax nm (log e) in MeOH: 202 (4.32), 213 (4.21), 233 (4.05), 299 sh (4.11), 325 (4.25).
IR nmax cm-1 (KBr): 3448 (OH), 3400-2400 br (COOH), 2970, 2937, 2884 (CH3 & CH2), 1715 (conjugated ester C=O), 1697 (COOH), 1630 (C=C), 1596, 1515 (aromatic ring), 1452, 1379 (CH3 & CH2), 1268, 1175, 1126, 1034 (C-O).
Positive ESI-MS m/z: 665 [M+H]+, 687 [M+Na]+; negative ESI-MS m/z: 663 [M-H]-; positive HR-ESI-MS m/z: 665.4053 (calcd for C40H57O8 [M+H]+ 665.4048), 687.3858 (calcd for C40H56O8Na [M+Na]+ 687.3867).
1H-NMR (600 MHz, CD3OD): d 1.06 (dd, ca. J=12.6, 11 Hz, 1-Hax.), 2.02 (dd, J=12.6, 4.4 Hz, 1-Heq.), 3.85 (ddd, J=11, 9.9, 4.4 Hz, 2-H), 4.64 (d, J=9.9 Hz, 3-H), 1.02 (br d, J=12.1 Hz, 5-H), 1.58 and 1.63 (both m, 6-H2), 1.35 (br d, ca. J=13.2 Hz, 7-Heq.), 1.62 (br t, J=13.2 Hz, 7-Hax.), 1.81 (m, 9-H), 2.00 and 2.04 (both AB type, 11-H2), 5.30 (br s, 12-H), 1.02 (br d, J=12.1 Hz, 15-Heq.), 1.82 (overlapped with 9-H, 15-Hax.), 2.59 (td, J=13.7, 4.3 Hz, 16-Hax.), 1.52 (dm, J=13.7 Hz, 16-Heq.), 2.51 (br s, 18-H), 1.35 (m, 20-H), 1.23 and 1.73 (m and AB type, 21-H2), 1.73 (AB type, 22-Heq.), 1.62 (br t, J=13.2 Hz, 22-Hax.), 0.90 (3H, s, 23-H3), 0.96 (3H, s, 24-H3), 1.062 (3H, s, 25-H3), 0.81 (3H, s, 26-H3), 1.97 (3H, s, 27-H3), 1.20 (3H, s, 29-H3), 0.93 (3H, d, J=6.6 Hz, 30-H3), 6.43 (d, J=16 Hz, 2'-H), 7.63 (d, J=16 Hz, 3'-H), 7.21 (br s, 2"-H), 6.81 (d, J=7.7 Hz, 5"-H), 7.08 (br d, J=7.7 Hz, 6"-H), 3.90 (3H, s, 3"-OCH3). The above signal assignments were based on the results of PFG 2D NMR (1H-1H COSY, HMQC, HMBC and NOESY) experiments.
13C-NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): d 48.55 t (C-1), 67.65 d (C-2), 85.64 d (C-3), 40.65 s (C-4), 56.46 d (C-5), 19.58 t (C-6), 34.03 t (C-7), 42.68 s (C-8), 8.71 d (C-9), 39.00 s (C-10), 24.75 t (C-11), 129.14 d (C-12), 140.16 s (C-13), 41.14 s (C-14), 29.59 t (C-15), 26.60 t (C-16), 48.72 s (C-17), 55.09 d (C-18), 73.57 s (C-19), 43.09 d (C-20), 27.30 t (C-21), 39.22 t (C-22), 29.25 t (C-23), 18.32 q (C-24), 16.60 q (C-25), 17.07 q (C-26), 24.83 q (C-27), 182.29 s (C-28), 27.05 q (C-29), 17.50 q (C-30), 169.61 s (C-1'), 116.16 d (C-2'), 146.50 d (C-3'), 127.90 s (C-1"), 111.58 d (C-2"), 149.40 s (C-3"), 150.53 s (C-4"), 116.49 d (C-5"), 124.04 d (C-6"), 56.51 q (OCH3). The above signal assignments were based on the results of DEPT and PFG 2D NMR (1H-1H COSY, HMQC, HMBC and NOESY) experiments.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Q. Sun, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, for collection and identification of the plant materials. This work was supported by the Found from NNSFC (C.-B. Cui, No.39825126), the Found from Ministry of Science and Technology (C.-B. Cui, No.G1998051113), China, and the Found for Cheung Kong Scholar (C.-B. Cui) from Ministry of Education of China.
References
- Cui, C.-B.; Zhao, Q.-C.; Cai, B.; Yao, X.-S.; Osada, H. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2002, 4, 243–252. [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.-C.; Cui, C.-B.; Cai, B.; Yao, X.-S.; Osada, H. Molbank 2002, M327.
- Häberlein, H.; Tschiersch, K.-P. Phytochem. 1994, 35, 765–768.
- Shimizu, M.; Uemitsu, M.; Shirota, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Tezuka, Y. Chem. Phar. Bull. 1996, 44, 2181–2182.
- Aquino, R.; Simone, F. D.; Vincieri, F. F.; Pizza, C.; Gacs-Baitz, E. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 559–564. [PubMed]
© 2003 MDPI. All rights reserved.