CELL-SELEX: Novel Perspectives of Aptamer-Based Therapeutics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. SELEX methodology and clinical applications of aptamers
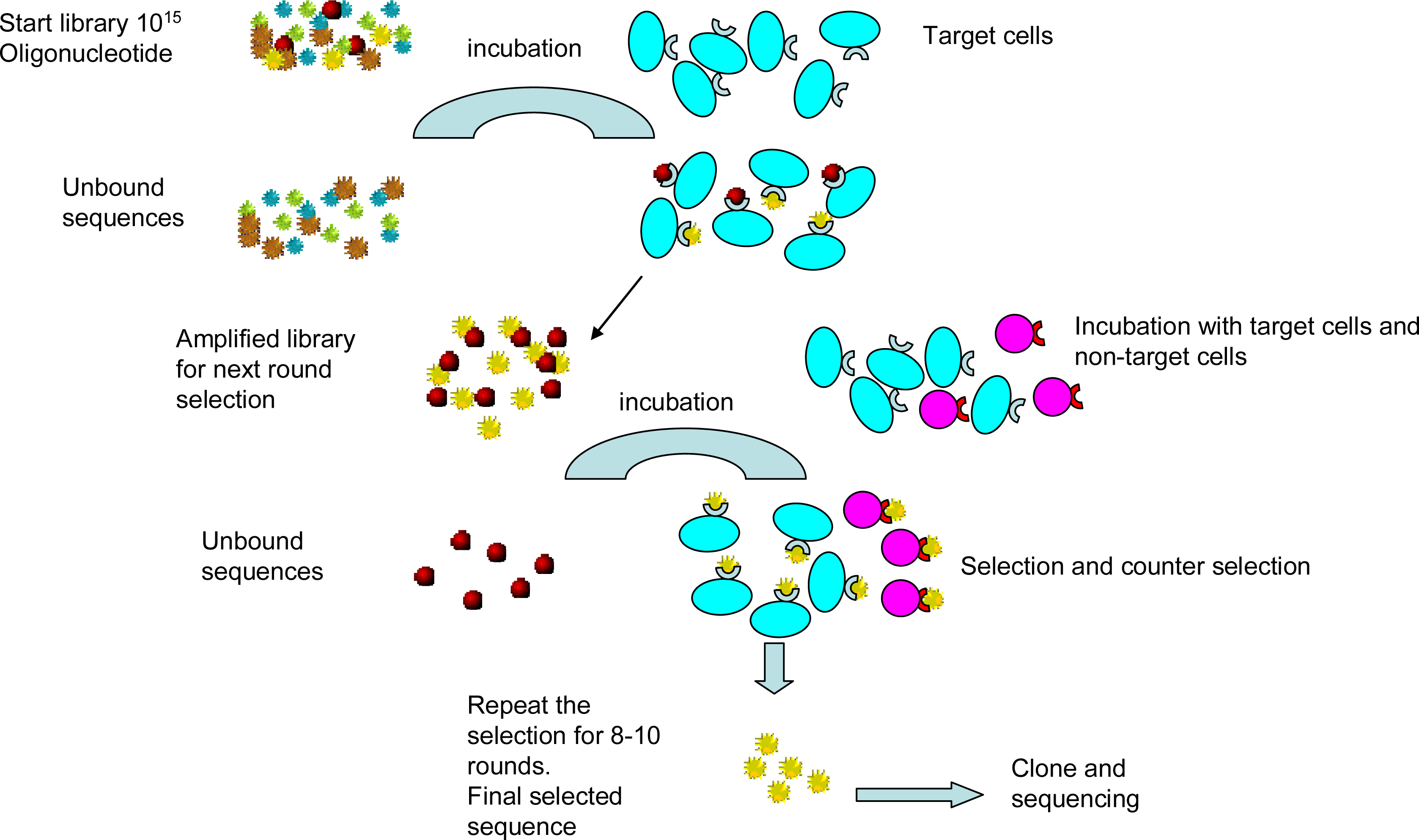
2.1. Cell-SELEX
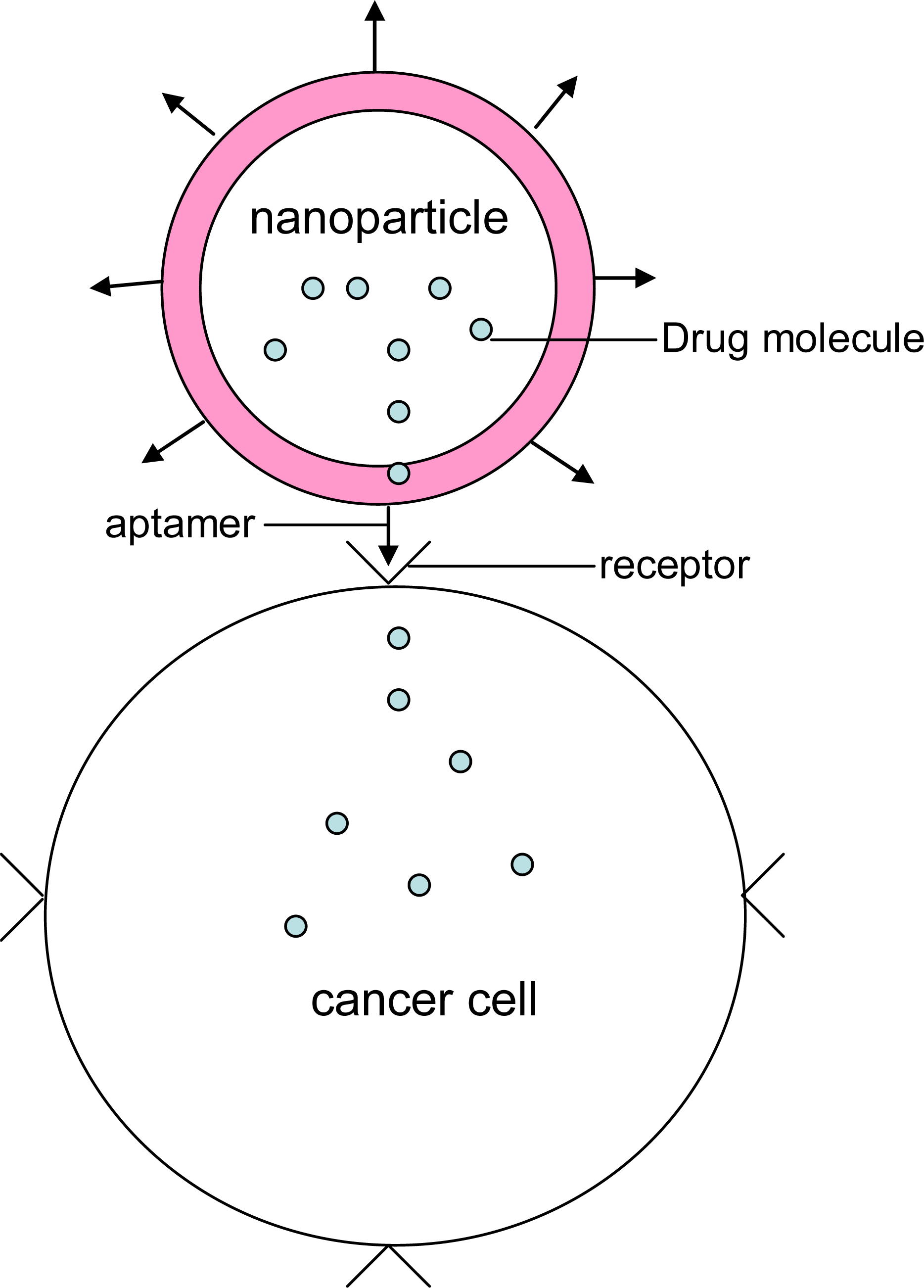
3. Aptamers and nanobiotechnology
4. Aptamers and gene silencing
5. Conclusion
References and Notes
- Tuerk, C; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar]
- Farokhzad, OC; Jon, S; Khademhosseini, A; Tran, TN; Lavan, DA; Langer, R. Nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates: a new approach for targeting prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 7668–7672. [Google Scholar]
- Nimjee, SM; Rusconi, CP; Sullenger, BA. Aptamers: an emerging class of therapeutics. Annu Rev Med 2005, 5, 555–583. [Google Scholar]
- Farokhzad, OC; Karp, JM; Langer, R. Nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for cancer targeting. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2006, 3, 311–324. [Google Scholar]
- Romig, TS; Bell, C; Drolet, DW. Aptamer affinity chromatography: combinatorial chemistry applied to protein purification. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 1999, 731, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Burgstaller, P; Girod, A; Blind, M. Aptamers as tools for target prioritization and lead identification. Drug Discov Today 2002, 7, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Green, LS; Bell, C; Janjic, N. Aptamers as reagents for high-throughput screening. Biotechniques 2001, 30, 1094–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Brody, EN; Willis, MC; Smith, JD; Jayasena, S; Zichi, D; Gold, L. The use of aptamers in large arrays for molecular diagnostics. Mol Diagn 1999, 4, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Schafer, R; Wiskirchen, J; Guo, K; Neumann, B; Kehlbach, R; Pintaske, J; Voth, V; Walker, T; Scheule, AM; Greiner, TO; Hermanutz-Klein, U; Claussen, CD; Northoff, H; Ziemer, G; Wendel, HP. Aptamer-based isolation and subsequent imaging of mesenchymal stem cells in ischemic myocard by magnetic resonance imaging. Rofo 2007, 179, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Ellington, AD; Szostak, JW. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar]
- Ellington, AD; Szostak, JW. Selection in vitro of single-stranded DNA molecules that fold into specific ligand-binding structures. Nature 1992, 355, 850–852. [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic, M. SELEX experiments: new prospects, applications and data analysis in inferring regulatory pathways. Biomol Eng 2007, 24, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasena, SD. Aptamers: an emerging class of molecules that rival antibodies in diagnostics. Clin Chem 1999, 45, 1628–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Tombelli, S; Minunni, M; Mascini, M. Analytical applications of aptamers. Biosens Bioelectron 2005, 15(20), 2424–2434. [Google Scholar]
- Fichou, Y; Férec, C. The potential of oligonucleotides for therapeutic applications. Trends Biotechnol 2006, 24, 563–570. [Google Scholar]
- Nimjee, SM; Rusconi, CP; Harrington, RA; Sullenger, BA. The potential of aptamers as anticoagulants. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2005, 15, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi, CP; Roberts, JD; Pitoc, GA; Nimjee, SM; White, RR; Quick, G, Jr; Scardino, E; Fay, WP; Sullenger, BA. Antidote-mediated control of an anticoagulant aptamer in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 2004, 22, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Quiram, PA; Hassan, TS; Williams, GA. Treatment of naïve lesions in neovascular age-related macular degeneration with pegaptanib. Retina 2007, 27, 851–856. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers, JP; Fintak, DR; Gupta, OP; Regillo, CD; Fineman, MS; Ho, AC. Pegaptanib for choroidal neovascularization in treatment-naïve exudative age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging 2007, 38, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Hicke, BJ; Stephens, AW; Gould, T; Chang, YF; Lynott, CK; Heil, J; Borkowski, S; Hilger, CS; Cook, G; Warren, S; Schmidt, PG. Tumor targeting by an aptamer. J Nucl Med 2006, 47, 668–678. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, DA; Chen, H; Hicke, BJ; Swiderek, KM; Gold, L. A tenascin-C aptamer identified by tumor cell SELEX: systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003, 100, 15416–15421. [Google Scholar]
- Boomer, RM; Lewis, SD; Healy, JM; Kurz, M; Wilson, C; McCauley, TG. Conjugation to polyethylene glycol polymer promotes aptamer biodistribution to healthy and inflamed tissues. Oligonucleotides 2005, 15, 183–195. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, EW; Shima, DT; Calias, P; Cunningham, ET, Jr; Guyer, DR; Adamis, AP. Pegaptanib, a targeted anti-VEGF aptamer for ocular vascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006, 5, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Rakic, JM; Blaise, P; Foidart, JM. Pegaptanib and age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med 2005, 352, 1720–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Y; Girvan, AC; Casson, LK; Pierce, WM, Jr; Qian, M; Thomas, SD; Bates, PJ. AS1411 alters the localization of a complex containing protein arginine methyltransferase 5 and nucleolin. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 10491–10500. [Google Scholar]
- Ireson, CR; Kelland, LR. Discovery and development of anticancer aptamers. Mol Cancer Ther 2006, 5, 2957–2962. [Google Scholar]
- Laber, DA; Taft, BS; Kloecker, GH; Bates, PJ; Trent, JO; Miller, DM. A phase II pilot trial with RP101 in advanced pancreatic carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2006, ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings Part I. 24, 18S. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L; Yoo, S; Dritschilo, A; Belyaev, I; Soldatenkov, V. Targeting Ku protein for sensitizing of breast cancer cells to DNA-damage. Int J Mol Med 2004, 14, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C; Yan, N; Parish, J; Wang, X; Shi, Y; Xue, D. RNA aptamers targeting the cell death inhibitor CED-9 induce cell killing in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 9137–9144. [Google Scholar]
- Horvitz, HR. Nobel lecture. Worms, life and death. Biosci Rep 2003, 23, 239–303. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 1995, 267, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar]
- Buerger, C; Nagel-Wolfrum, K; Kunz, C; Wittig, I; Butz, K; Hoppe-Seyler, F; Groner, B. Sequence-specific peptide aptamers, interacting with the intracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor, interfere with Stat3 activation and inhibit the growth of tumor cells. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 37610–37621. [Google Scholar]
- Nagel-Wolfrum, K; Buerger, C; Wittig, I; Butz, K; Hoppe-Seyler, F; Groner, B. The interaction of specific peptide aptamers with the DNA binding domain and the dimerization domain of the transcription factor Stat3 inhibits transactivation and induces apoptosis in tumor cells. Mol Cancer Res 2004, 2, 170–182. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, KN; Jensen, KB; Julin, CM; Weil, M; Gold, L. High affinity ligands from in vitro selection: complex targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998, 95, 2902–2907. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, D; Li, Y; Tang, Z; Cao, ZC; Chen, HW; Mallikaratchy, P; Sefah, K; Yang, CJ; Tan, W. Aptamers evolved from live cells as effective molecular probes for cancer study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006, 103, 11838–11843. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, D; Cao, ZC; Li, Y; Tan, W. Aptamers evolved from cultured cancer cells reveal molecular differences of cancer cells in patient samples. Clin Chem 2007, 53, 1153–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, D; Tang, Z; Mallikaratchy, P; Xiao, Z; Tan, W. Optimization and modifications of aptamers selected from live cancer cell lines. Chembiochem 2007, 8, 603–606. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z; Shanggunan, D; Wang, K; Shi, H; Sefah, K; Mallikratchy, P; Chen, HW; Li, Y; Tan, W. Selection of aptamers for molecular recognition and characterization of cancer cells. Anal Chem 2007, 79, 4900–4907. [Google Scholar]
- Mukaratirwa, S; de Witte, E; van Ederen, AM; Nederbragt, H. Tenascin expression in relation to stromal tumour cells in canine gastrointestinal epithelial tumours. J Comp Pathol 2003, 129, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Cerchia, L; Ducongé, F; Pestourie, C; Boulay, J; Aissouni, Y; Gombert, K; Tavitian, B; de Franciscis, V; Libri, D. Neutralizing aptamers from whole-cell SELEX inhibit the RET receptor tyrosine kinase. PLoS Biol 2005, 3, e123. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, KT; SchAfer, R; Paul, A; Gerber, A; Ziemer, G; Wendel, HP. A new technique for the isolation and surface immobilization of mesenchymal stem cells from whole bone marrow using high-specific DNA aptamers. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 2220–2231. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, KT; Scharnweber, D; Schwenzer, B; Ziemer, G; Wendel, HP. The effect of electrochemical functionalization of Ti-alloy surfaces by aptamer-based capture molecules on cell adhesion. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 468–474. [Google Scholar]
- Khademhosseini, A; Langer, R. Nanobiotechnology-Drug delivery and tissue engineering. Chemical Engineering Progress 2006, 102, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, JE; Medley, CD; Tang, Z; Shangguan, D; Lofton, C; Tan, W. Aptamer-conjugated nanoparticles for the collection and detection of multiple cancer cells. Anal Chem 2007, 79, 3075–3082. [Google Scholar]
- Herr, JK; Smith, JE; Medley, CD; Shangguan, D; Tan, W. Aptamer-conjugated nanoparticles for selective collection and detection of cancer cells. Anal Chem 2006, 78, 2918–2924. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, JO; So, HM; Jeon, EK. Aptamers as molecular recognition elements for electrical nanobiosensors. Anal Bioanal Chem 2008, 390(4), 1023–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W; Chen, C; Qian, M; Zhao, XS. Aptamer biosensor for protein detection using gold nanoparticles. Anal Biochem 2008, 373(2), 213–219. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, CC; Chiu, SH; Huang, YF; Chang, HT. Aptamer-functionalized gold nanoparticles for turn-on light switch detection of platelet-derived growth factor. Anal Chem 2007, 79, 4798–4804. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, JH; Chen, KH; Strano, MS. Aptamer-capped nanocrystal quantum dots: a new method for label-free protein detection. J Am Chem Soc 2006, 128, 15584–15585. [Google Scholar]
- Natt, F. siRNAs in drug discovery: target validation and beyond. Curr Opin Mol Ther 2007, 9, 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- de Fougerolles, A; Vornlocher, HP; Maraganore, J; Lieberman. Interfering with disease: a progress report on siRNA-based therapeutics. J Nat Rev Drug Discov 2007, 6, 443–453. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, JO, 2nd; Andrechek, ER; Wang, Y; Viles, KD; Rempel, RE; Gilboa, E; Sullenger, BA; Giangrande, PH. Cell type-specific delivery of siRNAs with aptamer-siRNA chimeras. Nat Biotechnol 2006, 24, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, TC; Twu, KY; Ellington, AD; Levy, M. Aptamer mediated siRNA delivery. Nucleic Acids Res 2006, 34, e73. [Google Scholar]
Share and Cite
Guo, K.-T.; Ziemer, G.; Paul, A.; Wendel, H.P. CELL-SELEX: Novel Perspectives of Aptamer-Based Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 668-678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms9040668
Guo K-T, Ziemer G, Paul A, Wendel HP. CELL-SELEX: Novel Perspectives of Aptamer-Based Therapeutics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2008; 9(4):668-678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms9040668
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Ke-Tai, Gerhard Ziemer, Angela Paul, and Hans P. Wendel. 2008. "CELL-SELEX: Novel Perspectives of Aptamer-Based Therapeutics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 9, no. 4: 668-678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms9040668
APA StyleGuo, K.-T., Ziemer, G., Paul, A., & Wendel, H. P. (2008). CELL-SELEX: Novel Perspectives of Aptamer-Based Therapeutics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 9(4), 668-678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms9040668



