A New Class of Pathogenic Non-Coding Variants in GLA
Abstract
1. Introduction
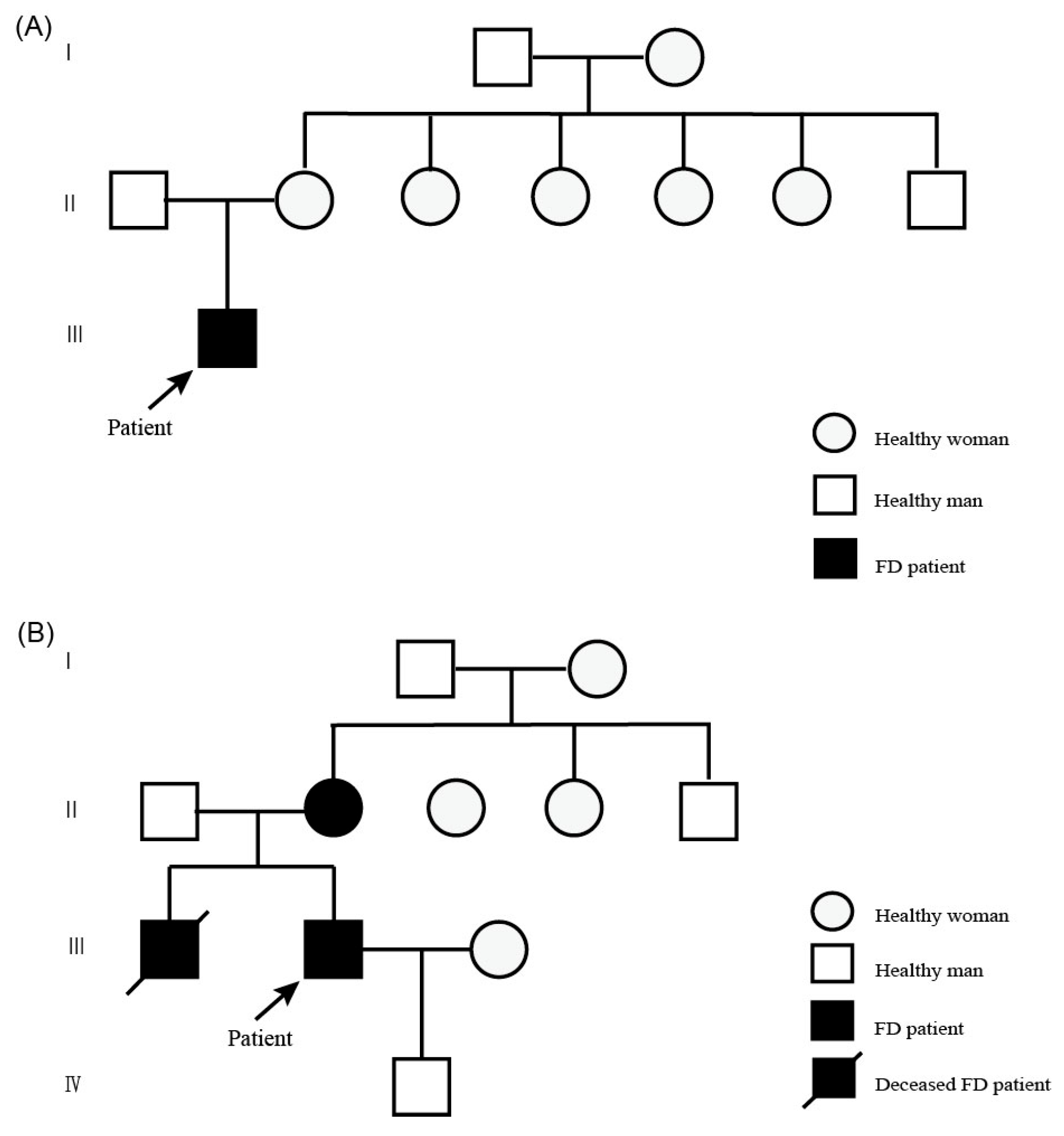
2. Case Description
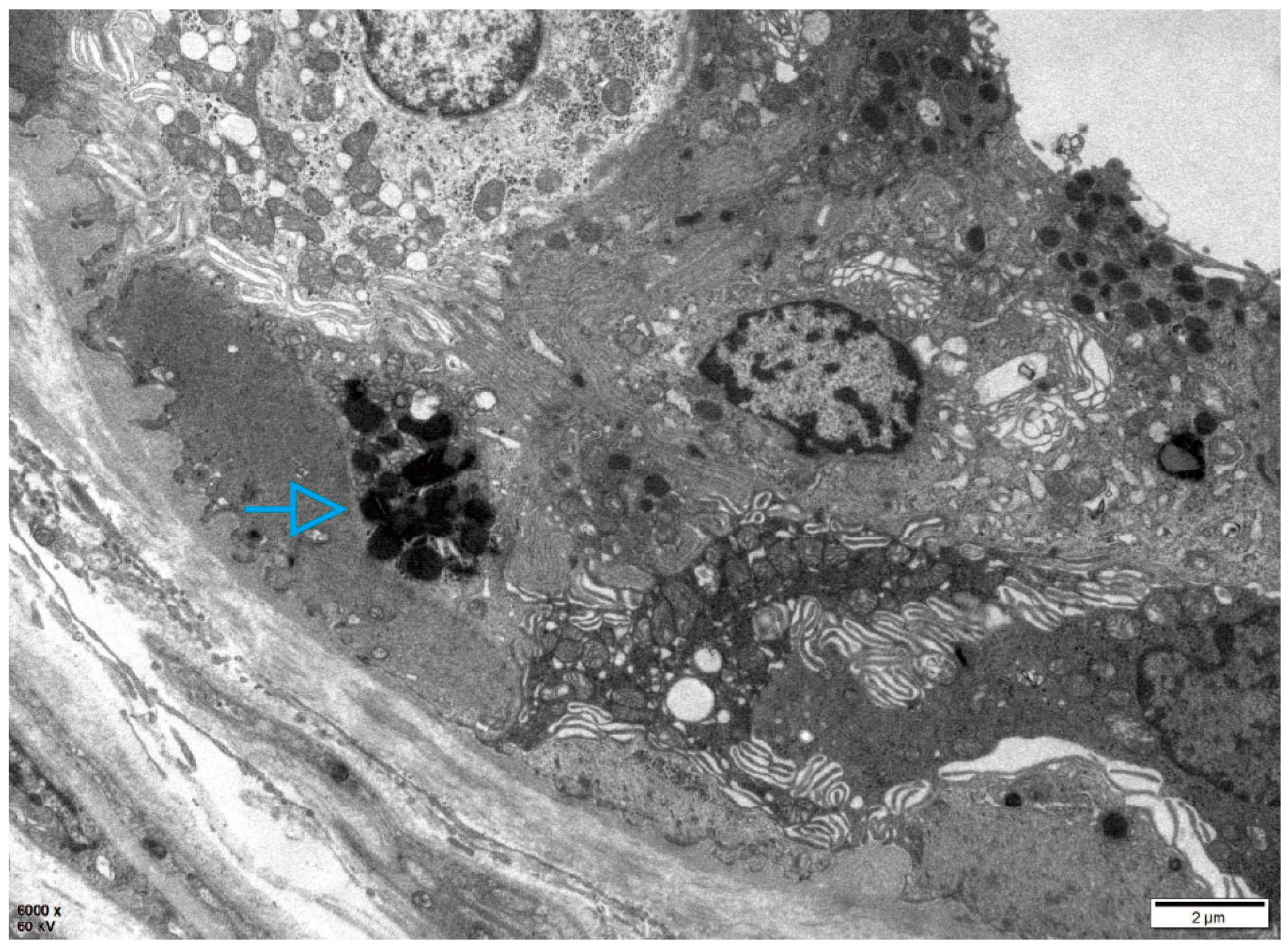
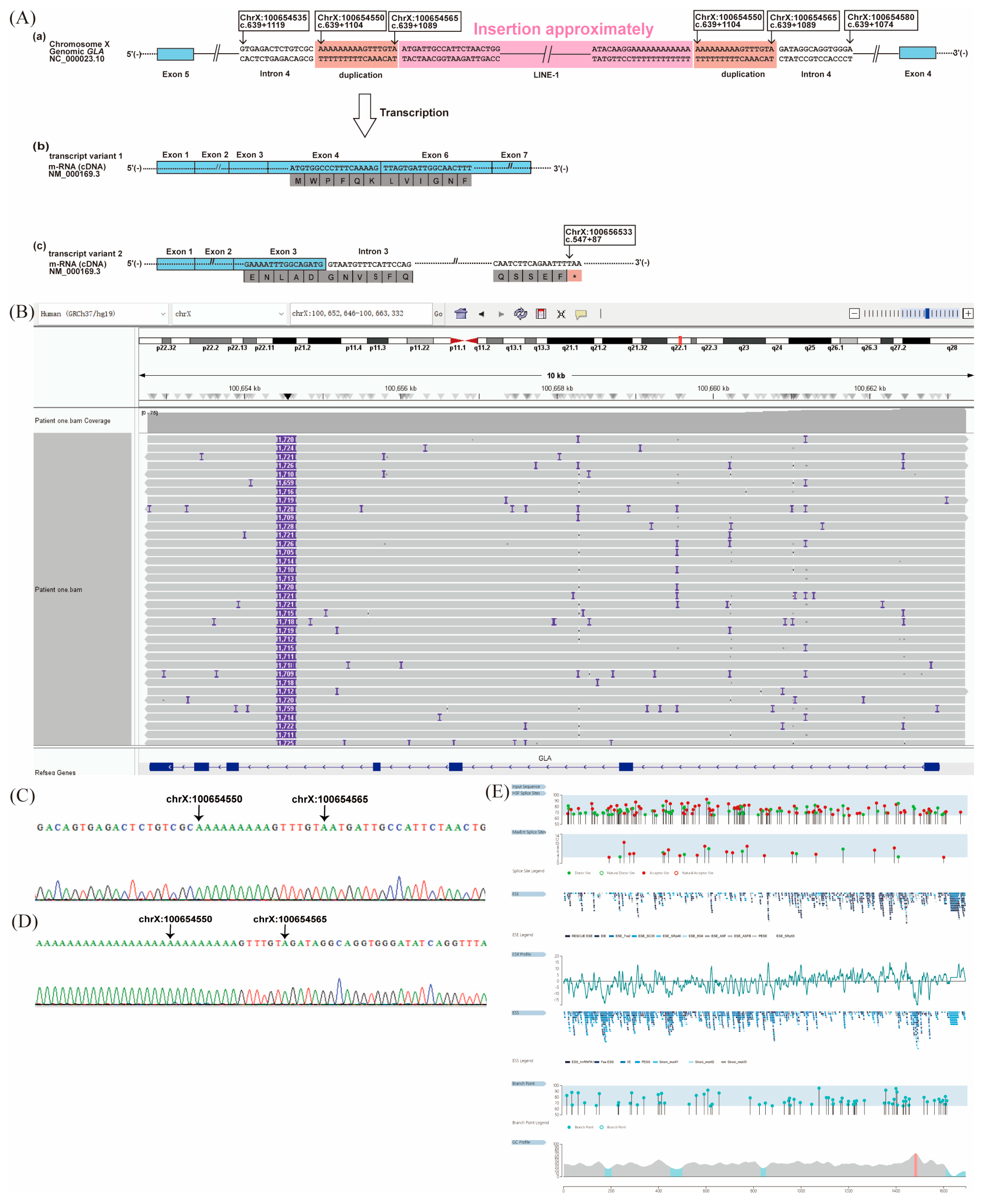
2.1. Patient 1
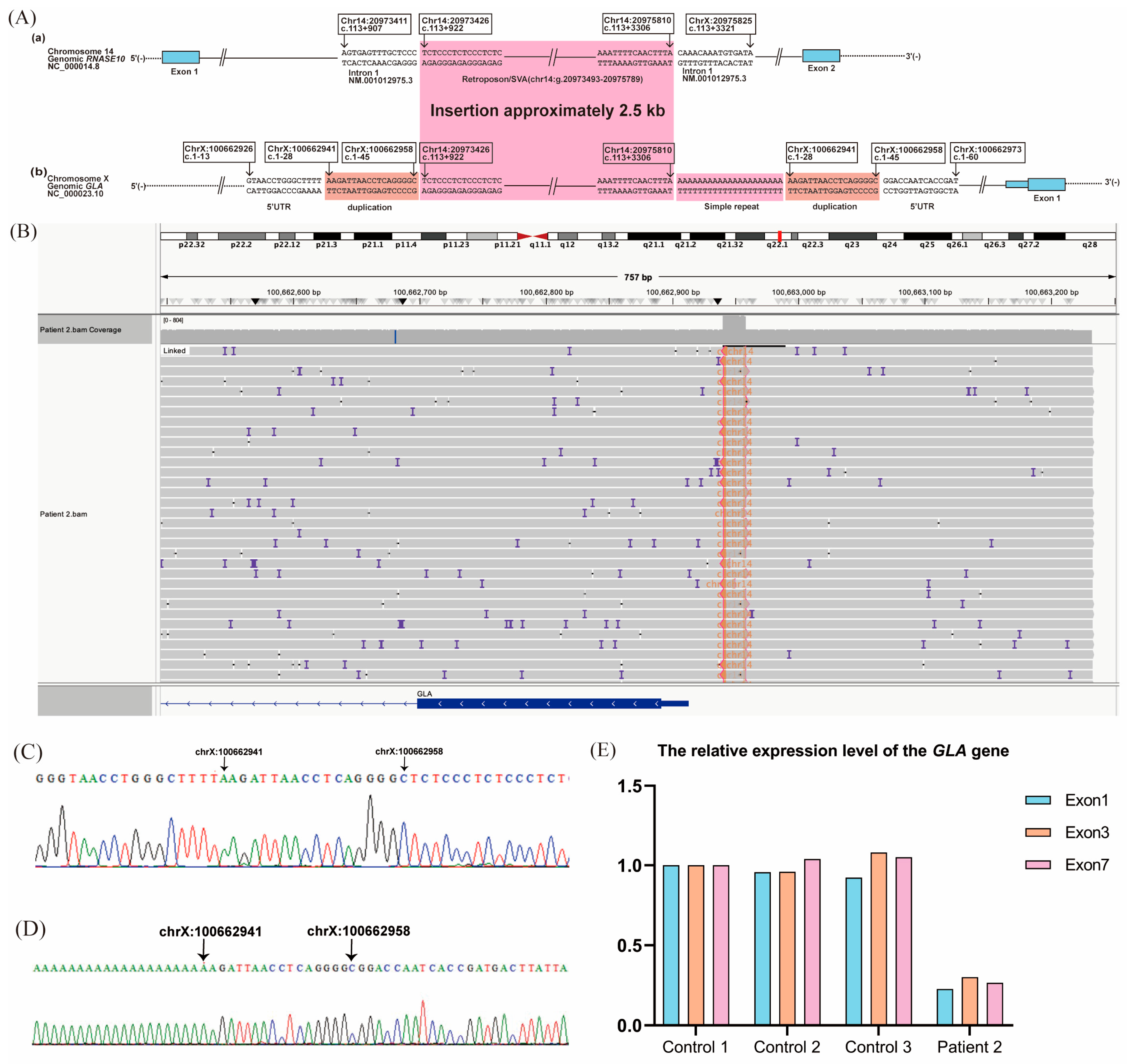
2.2. Patient 2
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ortiz, A.; Germain, D.P.; Desnick, R.J.; Politei, J.; Mauer, M.; Burlina, A.; Eng, C.; Hopkin, R.J.; Laney, D.; Linhart, A.; et al. Fabry disease revisited: Management and treatment recommendations for adult patients. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 123, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieroni, M.; Moon, J.C.; Arbustini, E.; Barriales-Villa, R.; Camporeale, A.; Vujkovac, A.C.; Elliott, P.M.; Hagege, A.; Kuusisto, J.; Linhart, A.; et al. Cardiac Involvement in Fabry Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, M.; Mauhin, W.; Belmatoug, N.; Garnotel, R.; Bedreddine, N.; Catros, F.; Ancellin, S.; Lidove, O.; Gaches, F. When and How to Diagnose Fabry Disease in Clinical Pratice. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 360, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter Huurne, M.; Parker, B.L.; Liu, N.Q.; Qian, E.L.; Vivien, C.; Karavendzas, K.; Mills, R.J.; Saville, J.T.; Abu-Bonsrah, D.; Wise, A.F.; et al. GLA-modified RNA treatment lowers GB3 levels in iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes from Fabry-affected individuals. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 110, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Chimenti, C.; Cianci, V.; Gallieni, M.; Lanzillo, C.; La Russa, A.; Limongelli, G.; Mignani, R.; Olivotto, I.; Pieruzzi, F.; et al. Females with Fabry disease: An expert opinion on diagnosis, clinical management, current challenges and unmet needs. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 12, 1536114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filoni, C.; Caciotti, A.; Carraresi, L.; Donati, M.A.; Mignani, R.; Parini, R.; Filocamo, M.; Soliani, F.; Simi, L.; Guerrini, R.; et al. Unbalanced GLA mRNAs ratio quantified by real-time PCR in Fabry patients’ fibroblasts results in Fabry disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 16, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornreich, R.; Desnick, R.J. Fabry disease: Detection of gene rearrangements in the human alpha-galactosidase A gene by multiplex PCR amplification. Hum. Mutat. 1993, 2, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffmann, R.; Forni, S.; Swift, C.; Brignol, N.; Wu, X.; Lockhart, D.J.; Blankenship, D.; Wang, X.; Grayburn, P.A.; Taylor, M.R.G.; et al. Risk of death in heart disease is associated with elevated urinary globotriaosylceramide. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffmann, R.; Swift, C.; McNeill, N.; Benjamin, E.R.; Castelli, J.P.; Barth, J.; Sweetman, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, X. Low frequency of Fabry disease in patients with common heart disease. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2018, 20, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, M.; Ferreira, S.; Al-Dilaimi, A.; Bögeholz, S.; Goesmann, A.; Kalinowski, J.; Knabbe, C.; Faber, L.; Oliveira, J.P.; Rudolph, V. Fabry disease: Detection of Alu-mediated exon duplication by NGS. Mol. Cell. Probes 2019, 45, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, T.; Mavrikiou, G.; Alexandrou, A.; Spanou-Aristidou, E.; Savva, I.; Christodoulides, T.; Krasia, M.; Christophidou-Anastasiadou, V.; Sismani, C.; Drousiotou, A.; et al. Novel GLA Deletion in a Cypriot Female Presenting with Cornea Verticillata. Case Rep. Genet. 2016, 2016, 5208312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuraba, H.; Tsukimura, T.; Togawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Ohtsuka, T.; Sato, A.; Shiga, T.; Saito SOhno, K. Fabry disease in a Japanese population-molecular and biochemical characteristics. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2018, 17, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domm, J.M.; Wootton, S.K.; Medin, J.A.; West, M.L. Gene therapy for Fabry disease: Progress, challenges, and outlooks on gene-editing. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2021, 134, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, D.P.; Oliveira, J.P.; Bichet, D.G.; Yoo, H.-W.; Hopkin, R.J.; Lemay, R.; Politei, J.; Wanner, C.; Wilcox, W.R.; Warnock, D.G. Use of a rare disease registry for establishing phenotypic classification of previously unassigned GLA variants: A consensus classification system by a multispecialty Fabry disease genotype-phenotype workgroup. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 57, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Hao, N.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, Z.; Mao, A.; Meng, W.; Liu, J. Long-read sequencing enables comprehensive molecular genetic diagnosis of Fabry disease. Hum. Genom. 2024, 18, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, S.; Nakao, S.; Minamikawa-Tachino, R.; Desnick RJFan, J.-Q. Alternative splicing in the alpha-galactosidase A gene: Increased exon inclusion results in the Fabry cardiac phenotype. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Fabry Disease Expert Panel. Expert consensus for diagnosis and treatment of Fabry disease in China (2021). Chin. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 321–330. [CrossRef]
- den Dunnen, J.T.; Dalgleish, R.; Maglott, D.R.; Hart, R.K.; Greenblatt, M.S.; McGowan-Jordan, J.; Roux, A.-F.; Smith, T.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Taschner, P.E.M.; et al. HGVS Recommendations for the Description of Sequence Variants: 2016 Update. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Murik, O.; Mann, T.; Zeevi, D.A.; Altarescu, G. Detection of single nucleotide and copy number variants in the Fabry disease-associated GLA gene using nanopore sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz-Drago, R.; Custódio, N.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. Deep intronic mutations and human disease. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 1093–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbrother, W.G.; Chasin, L.A. Human genomic sequences that inhibit splicing. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 6816–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbrother, W.G.; Yeh, R.-F.; Sharp, P.A.; Burge, C.B. Predictive identification of exonic splicing enhancers in human genes. Science 2002, 297, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Rolish, M.E.; Yeo, G.; Tung, V.; Mawson MBurge, C.B. Systematic identification and analysis of exonic splicing silencers. Cell 2004, 119, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pengelly, R.J.; Bakhtiar, D.; Borovská, I.; Královičová, J.; Vořechovský, I. Exonic splicing code and protein binding sites for calcium. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 5493–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palhais, B.; Dembic, M.; Sabaratnam, R.; Nielsen, K.S.; Doktor, T.K.; Bruun, G.H.; Andresen, B.S. The prevalent deep intronic c. 639+919 G>A GLA mutation causes pseudoexon activation and Fabry disease by abolishing the binding of hnRNPA1 and hnRNP A2/B1 to a splicing silencer. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016, 119, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.; Sun, C.; Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Shu, J.; Meng, L.; Deng, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Exonization of a deep intronic long interspersed nuclear element in Becker muscular dystrophy. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 979732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, K.; Callens, T.; Wernstedt, A.; Messiaen, L. The NF1 gene contains hotspots for L1 endonuclease-dependent de novo insertion. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesi, V.; Genovese, S.; Lepri, F.R.; Catino, G.; Loddo, S.; Orlando, V.; Di Tommaso, S.; Morgia, A.; Martucci, L.; Di Donato, M.; et al. Deep Intronic LINE-1 Insertions in NF1: Expanding the Spectrum of Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Rearrangements. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.L.; Hsieh, A.C. The Untranslated Regions of mRNAs in Cancer. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnebusch, A.G.; Ivanov IPSonenberg, N. Translational control by 5′-untranslated regions of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science 2016, 352, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayeski, P.J.; Weidmann, C.A.; Kumar, J.; Lackey, L.; Mustoe, A.M.; Busan, S.; Laederach, A.; Weeks, K.M. Global 5′-UTR RNA structure regulates translation of a SERPINA1 mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 9689–9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooblall, K.G.; Boon, H.; Cranston, T.; Stevenson, M.; Pagnamenta, A.T.; Rogers, A.; Grozinsky-Glasberg, S.; Richardson, T.; Flanagan, D.E.; Taylor, J.C.; et al. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (MEN1) 5′UTR Deletion, in MEN1 Family, Decreases Menin Expression. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2021, 36, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Bai, M.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; et al. 5′-UTR SNP of FGF13 causes translational defect and intellectual disability. ELife 2021, 10, e63021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Lin, E.W.; Tran, A.; Jin, H.; Ho, N.I.; Veit, A.; Cortes-Ciriano, I.; Burns, K.H.; Ting, D.T.; Park, P.J. The landscape of human SVA retrotransposons. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 11453–11465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletto, G.; Terreri, M.; Maurizio, I.; Ruggiero, E.; Cernilogar, F.M.; Vaine, C.A.; Cottini, M.V.; Shcherbakova, I.; Penney, E.B.; Gallina, I.; et al. G-quadruplexes in an SVA retrotransposon cause aberrant TAF1 gene expression in X-linked dystonia parkinsonism. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 11571–11586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Yu, J.; Li, P.; Luan, X.; Cao, L.; Zhao, J.; Yu, M.; Zhang, W.; Lv, H.; Xie, Z.; et al. Expansion of GGC Repeat in GIPC1 Is Associated with Oculopharyngodistal Myopathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 106, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ling, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, M.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, W. A New Class of Pathogenic Non-Coding Variants in GLA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27020945
Yuan Y, Zhang X, Ling C, Zhao Y, Yu M, Wang Z, Yuan Y, Xie Z, Zhang W. A New Class of Pathogenic Non-Coding Variants in GLA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(2):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27020945
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yujing, Xinyu Zhang, Chen Ling, Yawen Zhao, Meng Yu, Zhaoxia Wang, Yun Yuan, Zhiying Xie, and Wei Zhang. 2026. "A New Class of Pathogenic Non-Coding Variants in GLA" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 2: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27020945
APA StyleYuan, Y., Zhang, X., Ling, C., Zhao, Y., Yu, M., Wang, Z., Yuan, Y., Xie, Z., & Zhang, W. (2026). A New Class of Pathogenic Non-Coding Variants in GLA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(2), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27020945





