Hsa-miR-21-5p and Hsa-miR-145-5p Expression: From Normal Tissue to Malignant Changes—Context-Dependent Correlation with Estrogen- and Hypoxia–Vascularization-Related Pathways Genes: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Data
2.2. MiRNA Expression Changes in Analyzed Groups
2.3. MiRNA and mRNA Expression Correlation
2.3.1. Hsa-miR-21-5p Correlations
2.3.2. Hsa-miR-145-5p Correlations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. High-Molecular-Weight RNA and MiRNA Isolation and Validation
4.2.2. MiRNA Reverse Transcription and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.2.3. Reverse Transcription and qPCR for Analyzed Genes
4.3. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today (Version 1.1); International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France; Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovarian Cancer Statistics|World Cancer Research Fund International. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/cancer-trends/ovarian-cancer-statistics/ (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Englert-Golon, M.; Andrusiewicz, M.; Żbikowska, A.; Chmielewska, M.; Sajdak, S.; Kotwicka, M. Altered Expression of ESR1, ESR2, PELP1 and c-SRC Genes Is Associated with Ovarian Cancer Manifestation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dochez, V.; Caillon, H.; Vaucel, E.; Dimet, J.; Winer, N.; Ducarme, G. Biomarkers and Diagnosis Algorithms for of Ovarian Cancer: CA125, HE4, RMI and ROMA, a Review. J. Ovarian Res. 2019, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovarian Cancer Stages, Survival Rate and Prognosis|OCRA. Available online: https://ocrahope.org/patients/about-ovarian-cancer/staging/ (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Terada, K.Y.; Ahn, H.J.; Kessel, B. Differences in Risk for Type 1 and Type 2 Ovarian Cancer in a Large Cancer Screening Trial. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 27, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.N.; Xie, L.Z.; Shen, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Han, F.J. Insights into the Role of Oxidative Stress in Ovarian Cancer. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8388258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiana, I.N.G.; Angelina, M.; Pemayun, T.G.A. Ovarian Cancer: Pathogenesis and Current Recommendations for Prophylactic Surgery. J. Turk. Ger. Gynecol. Assoc. 2019, 20, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stages and Grades|Target Ovarian Cancer. Available online: https://targetovariancancer.org.uk/about-ovarian-cancer/what-ovarian-cancer/stages-and-grades (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Vang, R.; Shih, I.M.; Kurman, R.J. Ovarian Low-Grade and High-Grade Serous Carcinoma: Pathogenesis, Clinicopathologic and Molecular Biologic Features, and Diagnostic Problems. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2009, 16, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Tew, K.D. Oxidative Stress in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Yokoi, A.; Kato, T.; Ochiya, T.; Yamamoto, Y. The Clinical Impact of Intra- and Extracellular miRNAs in Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cremades, D.; Mompeón, A.; Gómez, X.V.; Hermenegildo, C.; Novella, S. miRNA as a New Regulatory Mechanism of Estrogen Vascular Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahreini, F.; Rayzan, E.; Rezaei, N. microRNA-Related Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Breast Cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.Q.; Ahmed, E.I.; Elareer, N.R.; Junejo, K.; Steinhoff, M.; Uddin, S. Role of miRNA-Regulated Cancer Stem Cells in the Pathogenesis of Human Malignancies. Cells 2019, 8, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Z.; Xi, Q.H.; Ge, W.L.; Zhang, X.Q. Identification of Serum microRNA-21 as a Biomarker for Early Detection and Prognosis in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Cui, Z.; Huang, Y. MicroRNA-21 Promotes the Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Migration Abilities in Ovarian Epithelial Carcinomas through Inhibiting the Expression of PTEN Protein. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 26, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basati, G.; Emami Razavi, A.; Abdi, S.; Mirzaei, A. Elevated Level of microRNA-21 in the Serum of Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, K.; Lin, T.; Pang, Q.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Tai, M.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Y.; Mao, P.; et al. Extracellular miRNA-21 as a Novel Biomarker in Glioma: Evidence from Meta-Analysis, Clinical Validation and Experimental Investigations. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agaoglu, F.Y.; Kovancilar, M.; Dizdar, Y.; Darendeliler, E.; Holdenrieder, S.; Dalay, N.; Gezer, U. Investigation of miR-21, miR-141, and miR-221 in Blood Circulation of Patients with Prostate Cancer. Tumour Biol. 2011, 32, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q.F.; Zhao, Y.M.; Shi, X.Y.; Xu, A.G. Serum miR-21 Level: A Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 14759. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Xie, G.; Lu, Y. Serum microRNA-145 as a Novel Biomarker in Human Ovarian Cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 5305–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qian, Z.; Ma, X.; Lin, X.; You, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Jiang, H. MiR-628-5p Decreases the Tumorigenicity of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells by Targeting at FGFR2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignotti, E.; Calza, S.; Tassi, R.A.; Zanotti, L.; Bandiera, E.; Sartori, E.; Odicino, F.E.; Ravaggi, A.; Todeschini, P.; Romani, C. Identification of Stably Expressed Reference Small Non-coding RNAs for microRNA Quantification in High-grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma Tissues. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonugunta, V.K.; Sareddy, G.R.; Krishnan, S.R.; Cortez, V.; Roy, S.S.; Tekmal, R.R.; Vadlamudi, R.K. Inhibition of mTOR Signaling Reduces PELP1-Mediated Tumor Growth and Therapy Resistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1578–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Shen, L.; Ren, Q.; Zeng, Q.; He, X. Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α in Endometrial Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 587420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, P.; Klacz, J.; Kotulak-Chrzaszcz, A.; Wronska, A.; Stanislawowski, M.; Rybarczyk, A.; Ludziejewska, A.; Kmiec, Z.; Matuszewski, M. Prognostic Significance of VHL, HIF1A, HIF2A, VEGFA and P53 Expression in Patients with Clear-cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Sunitinib as First-line Treatment. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert-Golon, M.; Tokłowicz, M.; Żbikowska, A.; Sajdak, S.; Kotwicka, M.; Jagodziński, P.; Pławski, A.; Andrusiewicz, M. HIF1A, EPAS1, and VEGFA: Angiogenesis and Hypoxia-Related Gene Expression in Endometrium and Endometrial Epithelial Tumors. J. Appl. Genet. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; AlTahan, A.; Jones, D.T.; Buffa, F.M.; Bridges, E.; Interiano, R.B.; Qu, C.; Vogt, N.; Li, J.-L.; Baban, D.; et al. Estrogen Receptor-α Directly Regulates the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Pathway Associated with Antiestrogen Response in Breast Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15172–15177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozieł, M.J.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Estrogens, Estrogen Receptors and Tumor Microenvironment in Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggio, F.; Del Mastro, L.; Bruzzone, M.; Ceppi, M.; Razeti, M.G.; Fregatti, P.; Ruelle, T.; Pronzato, P.; Massarotti, C.; Franzoi, M.A.; et al. Safety of Systemic Hormone Replacement Therapy in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 191, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranathan, P.; Lange, C.A.; Raj, G.V. Minireview: Deciphering the Cellular Functions of PELP1. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, D.; Roy, S.S.; Babu, C.R.; Dandamudi, R.; Curiel, T.J.; Vivas-Mejia, P.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Vadlamudi, R.K. Therapeutic Targeting of PELP1 Prevents Ovarian Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2250–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Liu, K.; He, Q.; Gu, X.; Jiang, C.; Wu, J. Hypoxia Signaling in Cancer: Implications for Therapeutic Interventions. MedComm 2023, 4, e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheeruddin, M.; Qausain, S. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-Alpha (HIF-1α) and Cancer: Mechanisms of Tumor Hypoxia and Therapeutic Targeting. Cureus 2024, 16, e70700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, D.; Watts, D.; Gaete, D.; Sormendi, S.; Wielockx, B. Hypoxia Pathway Proteins and Their Impact on the Blood Vasculature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-L.; Chen, H.-H.; Zheng, L.-L.; Sun, L.-P.; Shi, L. Angiogenic Signaling Pathways and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy for Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziello, J.E.; Jovin, I.S.; Huang, Y. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1 Regulatory Pathway and Its Potential for Therapeutic Intervention in Malignancy and Ischemia. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2007, 80, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Déry, M.-A.C.; Michaud, M.D.; Richard, D.E. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1: Regulation by Hypoxic and Non-Hypoxic Activators. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cao, P.; Li, Z.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Liang, G. EPAS-1 Mediates SP-1-Dependent FBI-1 Expression and Regulates Tumor Cell Survival and Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15689–15699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Lei, L.; Liao, J.; Huang, X.; Shao, Y. Circ_0060731 Mediated miR-21–5p-PDCD4/ESR1 Pathway to Induce Apoptosis of Placental Trophoblasts in Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy. Tissue Cell 2022, 76, 101771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Deng, Y.; Chen, G.; Yang, H. Investigation of the Clinical Significance and Molecular Mechanism of miR-21-5p in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review Based on 24 Studies and Bioinformatics Investigation. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 17, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, A.A.; Heier, C.R.; Huang, Y.-F.; Tully, C.B.; Punga, T.; Punga, A.R. Estrogen Receptor, Inflammatory, and FOXO Transcription Factors Regulate Expression of Myasthenia Gravis-Associated Circulating microRNAs. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Shi, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, W.; Li, X. MicroRNA and Transcription Factor Mediated Regulatory Network Analysis Reveals Critical Regulators and Regulatory Modules in Myocardial Infarction. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Yuan, P. Role of miR-21-5p/ FilGAP Axis in Estradiol Alleviating the Progression of Monocrotaline-induced Pulmonary Hypertension. Anim. Models Exp. Med. 2022, 5, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Litchfield, L.M.; Ivanova, M.M.; Prough, R.A.; Clark, B.J.; Klinge, C.M. Dehydroepiandrosterone-Induces miR-21 Transcription in HepG2 Cells through Estrogen Receptor β and Androgen Receptor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 392, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat-Nakshatri, P.; Wang, G.; Collins, N.R.; Thomson, M.J.; Geistlinger, T.R.; Carroll, J.S.; Brown, M.; Hammond, S.; Srour, E.F.; Liu, Y.; et al. Estradiol-Regulated microRNAs Control Estradiol Response in Breast Cancer Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 4850–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhari, A.; Zarghami, N.; Farzadi, L.; Nouri, M.; Shahnazi, V. Altered of microRNA Expression Level in Oligospermic Patients. Iran. J. Reprod. Med. 2014, 12, 681–686. [Google Scholar]
- Spizzo, R.; Nicoloso, M.S.; Lupini, L.; Lu, Y.; Fogarty, J.; Rossi, S.; Zagatti, B.; Fabbri, M.; Veronese, A.; Liu, X.; et al. miR-145 Participates with TP53 in a Death-Promoting Regulatory Loop and Targets Estrogen Receptor-α in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperigkou, Z.; Franchi, M.; Götte, M.; Karamanos, N.K. Estrogen Receptor Beta as Epigenetic Mediator of miR-10b and miR-145 in Mammary Cancer. Matrix Biol. 2017, 64, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintavalle, M.; Elia, L.; Condorelli, G.; Courtneidge, S.A. MicroRNA Control of Podosome Formation in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Vivo and in Vitro. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.S.; Gonugunta, V.K.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Rao, M.K.; Goodall, G.J.; Sun, L.-Z.; Tekmal, R.R.; Vadlamudi, R.K. Significance of PELP1/HDAC2/miR-200 Regulatory Network in EMT and Metastasis of Breast Cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3707–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, T.; Ge, Q.; Xu, H.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Chen, K. Circular RNA Signature in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 3361–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, F.; Mohajerani, F.; Sadeghizadeh, M. CCAT2 Knockdown Inhibits Cell Growth, and Migration and Promotes Apoptosis through Regulating the Hsa-Mir-145-5p/AKT3/mTOR Axis in Tamoxifen-Resistant MCF7 Cells. Life Sci. 2022, 311, 121183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert-Golon, M.; Tokłowicz, M.; Zbikowska, A.; Sajdak, S.; Kotwicka, M.; Andrusiewicz, M. Differential Expression of HIF1A, EPAS1, and VEGF Genes in Benign and Malignant Ovarian Neoplasia. Cancers 2022, 14, 4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, X.; Gao, H.; Liu, N.; Gao, Y.; Hao, L.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Z. miR-21-3p Inhibits Autophagy of Bovine Granulosa Cells by Targeting VEGFA via PI3K/AKT Signaling. Reproduction 2019, 158, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadeu, F.X.; Mohammed, B.T.; Ioannidis, J. A miRNA Target Network Putatively Involved in Follicular Atresia. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2017, 58, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Ye, A.; Ye, W.; Liao, X.; Qin, G.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Luo, H.; Yi, M.; Xian, L.; et al. Cancer-Secreted Exosomal miR-21-5p Induces Angiogenesis and Vascular Permeability by Targeting KRIT1. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.; Li, L.; Wu, B.; Wang, D. METTL3 m6A-Dependently Promotes miR-21-5p Maturation to Accelerate Choriocarcinoma Progression via the HIF1AN-Induced Inactivation of the HIF1A/VEGF Pathway. Genes Genom. 2022, 44, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linna-Kuosmanen, S.; Tomas Bosch, V.; Moreau, P.R.; Bouvy-Liivrand, M.; Niskanen, H.; Kansanen, E.; Kivelä, A.; Hartikainen, J.; Hippeläinen, M.; Kokki, H.; et al. NRF2 Is a Key Regulator of Endothelial microRNA Expression under Proatherogenic Stimuli. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1339–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-M.; Wu, K.-L.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Chang, W.-A.; Huang, Y.-C.; Jian, S.-F.; Tsai, P.-H.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chong, I.-W.; Hung, J.-Y.; et al. Loss of miR-145-5p Causes Ceruloplasmin Interference with PHD-Iron Axis and HIF-2α Stabilization in Lung Adenocarcinoma-Mediated Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Yan, Z.-P.; Lu, N.-N.; Xu, Q.; He, J.; Qian, X.; Yu, J.; Guan, X.; Jiang, B.-H.; Liu, L.-Z. Downregulation of miR-145 Associated with Cancer Progression and VEGF Transcriptional Activation by Targeting N-RAS and IRS1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gene Regul. Mech. 2013, 1829, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Meng, F.; Xue, N.; Pang, G.; Wang, Q.; Ma, H. Inducible miR-145 Expression by HIF-1α Protects Cardiomyocytes against Apoptosis via Regulating SGK1 in Simulated Myocardial Infarction Hypoxic Microenvironment. Cardiol. J. 2013, 25, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, M.K.; Jaiswar, S.P.; Dwivedi, V.N.; Tripathi, A.K.; Dwivedi, A.; Sankhwar, P. MicroRNA: A New and Promising Potential Biomarker for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2015, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.K.; Blansit, K.; Kiet, T.; Sherman, A.; Wong, G.; Earle, C.; Bourguignon, L.Y.W. The Inhibition of miR-21 Promotes Apoptosis and Chemosensitivity in Ovarian Cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 132, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cantó, E.; Monteiro, M.; Aghababyan, C.; Ferrero-Micó, A.; Navarro-Serna, S.; Mellado-López, M.; Tomás-Pérez, S.; Sandoval, J.; Llueca, A.; Herreros-Pomares, A.; et al. Reduced Levels of miR-145-3p Drive Cell Cycle Progression in Advanced High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. Cells 2024, 13, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohozinski, J.; Edwards, C.L.; Anderson, M.L. Does Expression of the Retrogene UTP14c in the Ovary Pre-Dispose Women to Ovarian Cancer? Med. Hypothes. 2012, 78, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Qin, Y.; Sheng, M.; Cui, X.; Chen, W.; Zhong, J.; Yan, J.; Chen, Y. miR-145 Suppresses Ovarian Cancer Progression via Modulation of Cell Growth and Invasion by Targeting CCND2 and E2F3. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Chen, Y. MicroRNA-145-5p Regulates the Proliferation of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells via Targeting SMAD4. J. Ovarian Res. 2020, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, M.P.; Torres, I.; Avila, A.; Chnaiderman, J.; Valenzuela-Valderrama, M.; Aramburo, J.; Oróstica, L.; Durán-Jara, E.; Lobos-Gonzalez, L.; Romero, C. NGF/TRKA Decrease miR-145-5p Levels in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xiao, Z.H.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; Hao, Q. MiR-145 Is Downregulated in Human Ovarian Cancer and Modulates Cell Growth and Invasion by Targeting p70S6K1 and MUC1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.S.N.; Ip, C.K.M.; Mak, A.S.C.; Wong, A.S.T. A Novel P70 S6 Kinase-microRNA Biogenesis Axis Mediates Multicellular Spheroid Formation in Ovarian Cancer Progression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38064–38077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, L.-Z.; Qian, X.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Li, D.; Lai, L.; Jiang, B.-H. MiR-145 Directly Targets p70S6K1 in Cancer Cells to Inhibit Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muppala, S.; Mudduluru, G.; Leupold, J.H.; Buergy, D.; Sleeman, J.P.; Allgayer, H. CD24 Induces Expression of the Oncomir miR-21 via Src, and CD24 and Src Are Both Post-Transcriptionally Downregulated by the Tumor Suppressor miR-34a. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Jaeger, S.A.; Hirsch, H.A.; Bulyk, M.L.; Struhl, K. STAT3 Activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN and CYLD Are Part of the Epigenetic Switch Linking Inflammation to Cancer. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestris, N.; Danza, K.; Longo, V.; Brunetti, O.; Fucci, L.; Argentiero, A.; Calabrese, A.; Cataldo, I.; Tamma, R.; Ribatti, D.; et al. Angiogenesis in Adenosquamous Cancer of Pancreas. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 95773–95779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, Y. Integrative Analysis Identifies Potential Ferroptosis-Related Genes of Hypoxia Adaptation in Yak. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1022972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Huo, S.; Du, Z.; Yang, Q.; Ren, M.; Liu, S.; Liu, T.; Zhang, G. MicroRNA-Related Transcription Factor Regulatory Networks in Human Colorectal Cancer. Medicine 2019, 98, e15158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasiak, J.; Watala, C.; Tuuminen, R.; Kivinen, N.; Koskela, A.; Uusitalo-Järvinen, H.; Tuulonen, A.; Winiarczyk, M.; Mackiewicz, J.; Zmorzyński, S.; et al. Expression of VEGFA-regulating miRNAs and Mortality in Wet AMD. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 8464–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, A.D.; Andrijono; Winarto, H.; Prijanti, A.R.; Rachmadi, L.; Pakasi, T.A.; Gandamihardja, S.; Wirasugianto, J. Amelia miR-21 and miR-145 as Prognostic Biomarkers for Radiotherapy Responses in Cervical Cancer Patients: A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.; Baek, W.; Seo, Y.; Kim, J.H. From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutics: Understanding MicroRNA-21 in Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-X.; Liu, Z.; Deng, F.; Wang, D.-D.; Li, X.-W.; Tian, T.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.-H. MiR-145: A Potential Biomarker of Cancer Migration and Invasion. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 6739. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, C.K.; Cho, Y.S. Pathogenesis and Biomarkers of Colorectal Cancer by Epigenetic Alteration. Intest. Res. 2024, 22, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otmani, K.; Lewalle, P. Tumor Suppressor miRNA in Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment: Mechanism of Deregulation and Clinical Implications. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 708765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Sanchez, M.; Burraco, P.; Gomez-Mestre, I.; Leonard, J.A. Preservation of RNA and DNA from Mammal Samples under Field Conditions. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokłowicz, M.; Żbikowska, A.; Janusz, P.; Kotwicki, T.; Andrusiewicz, M.; Kotwicka, M. MicroRNA Expression Profile Analysis in Human Skeletal Muscle Tissue: Selection of Critical Reference. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrusiewicz, M.; Słowikowski, B.; Skibińska, I.; Wołuń-Cholewa, M.; Dera-Szymanowska, A. Selection of Reliable Reference Genes in Eutopic and Ectopic Endometrium for Quantitative Expression Studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 78, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, P.H.D.; Lopacinska-Jørgensen, J.; Høgdall, C.K.; Høgdall, E.V. Identification of Stably Expressed microRNAs in Plasma from High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma and Benign Tumor Patients. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 10235–10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
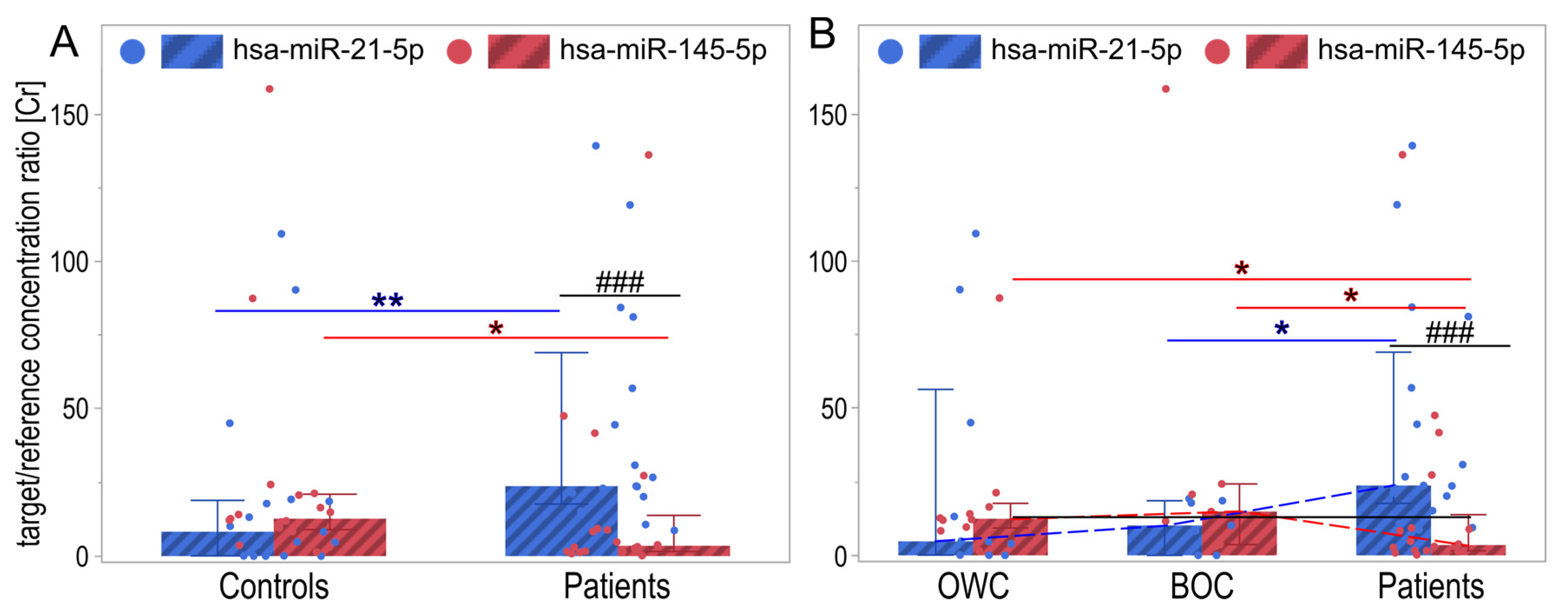
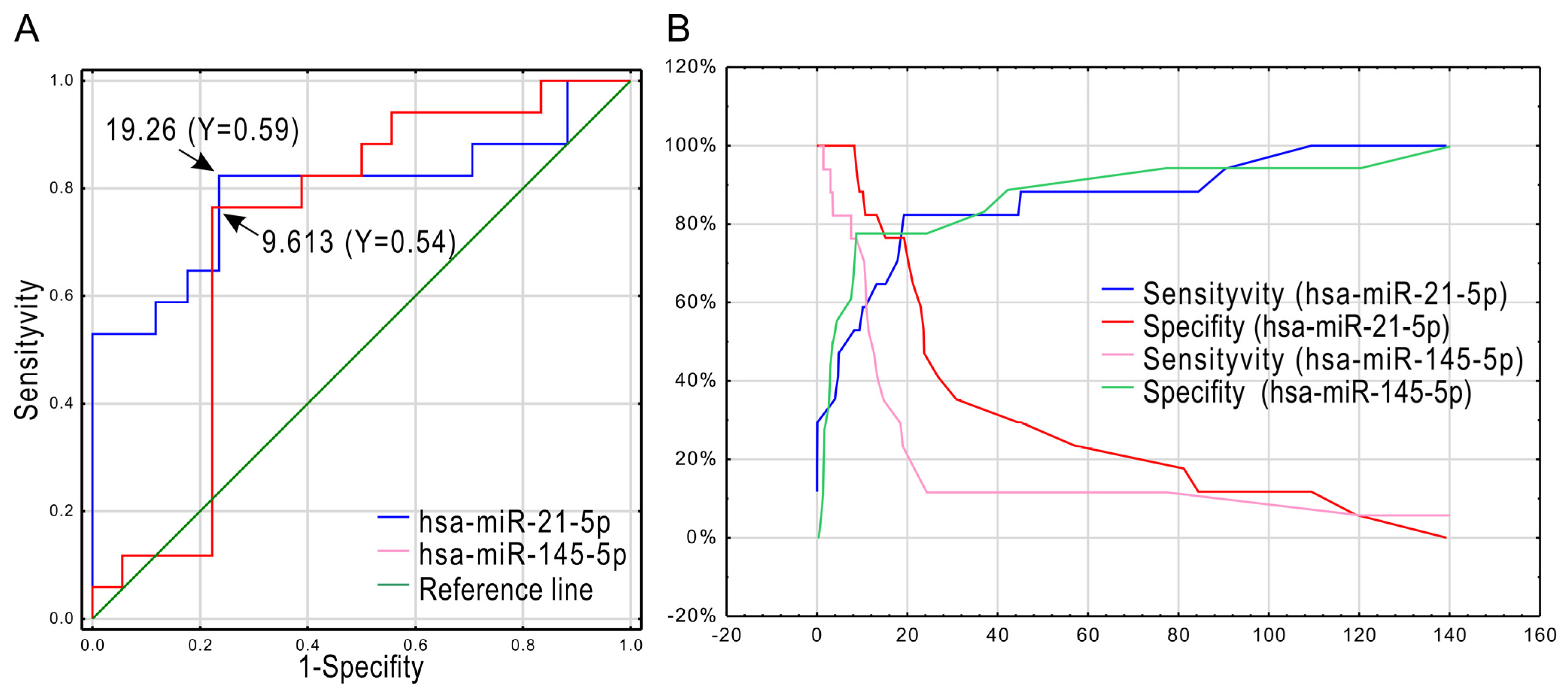
| Parameter | 1st Division | 2nd Division | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls (n = 20) | Patients (n = 20) | p-Value | OWC (n = 10) | BOC (n = 10) | Patients (n = 20) | p-Value | ||
| Age [years] (M ± SD) | 57 ± 11.5 | 61 ± 9.6 | 0.3296 # | 61 ± 10.8 | 54 ± 11.4 | 61 ± 9.6 | 0.1885 $ | |
| Body mass [kg] (M ± SD) | 72 ± 14.5 | 66 ± 16.0 | 0.2367 # | 69 ± 8.6 | 76 ± 18.9 | 66 ± 16.0 | 0.3163 $ | |
| BMI [kg/m2] (M ± SD) | 27.1 ± 6.16 | 25.9 ± 6.38 | 0.5484 # | 26 ± 3.52 | 28.4 ± 8.24 | 25.9 ± 6.38 | 0.5831 $ | |
| Menopause [N] | Yes | 13 | 17 | 0.2733 % | 7 | 6 | 17 | 0.3011 ^ |
| No | 7 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | |||
| Co-morbidities @ [N] | Yes | 11 | 12 | >0.999 % | 7 | 4 | 12 | 0.3771 ^ |
| No | 9 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 8 | |||
| Coexisting tumors [N] | Yes | 6 | 16 | 0.0012 %,RR | 1 | 5 | 16 | 0.0001 ^,BH |
| No | 14 | 4 | 9 | 5 | 4 | |||
| Group/miRNA | M ± SD | Me [Q1–Q3] | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls/hsa-miR-21-5p | 20.3 ± 32.2 | 8.3 [0.1–18.6] | 0.0 | 109.4 |
| Patients/hsa-miR-21-5p | 43.5 ± 39.6 | 23.8 [20.2–57] | 8.7 | 139.3 |
| OWC/hsa-miR-21-5p | 27.2 ± 40.9 | 4.7 [0.1–45.1] | 0.0 | 109.4 |
| BOC/hsa-miR-21-5p | 10.6 ± 8.4 | 10.2 [0–18.6] | 0.0 | 19.3 |
| Controls/hsa-miR-145-5p | 25.4 ± 39.3 | 12.7 [9.6–20.7] | 1.4 | 158.6 |
| Patients/hsa-miR-145-5p | 16.9 ± 33.0 | 3.5 [1.6–9.3] | 0.2 | 136.2 |
| OWC/hsa-miR-145-5p | 19.6 ± 24.4 | 12.4 [9.6–16.5] | 1.4 | 87.5 |
| BOC/hsa-miR-145-5p | 33.8 ± 55.6 | 14.9 [3.7–24.3] | 3.2 | 158.6 |
| Gene | All Cases (n = 40) | Controls (n = 20) | Patients (n = 20) | OWC (n = 10) | BOC (n = 10) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-Value | |
| ESR1 a | 0.18 | 0.3100 | 0.01 | 0.9739 | −0.19 | 0.4709 | 0.43 | 0.2129 | −0.63 | 0.1289 |
| ESR2 a | 0.08 | 0.6547 | 0.44 | 0.0737 | 0.15 | 0.5649 | 0.78 | 0.0084 | −0.27 | 0.5641 |
| PELP1 a | −0.24 | 0.1748 | −0.38 | 0.1379 | 0.34 | 0.1801 | −0.12 | 0.7364 | −0.59 | 0.1590 |
| SRC a | −0.23 | 0.1975 | −0.14 | 0.5795 | −0.13 | 0.6126 | 0.15 | 0.6761 | −0.68 | 0.0897 |
| HIF1A b | 0.03 | 0.8530 | 0.44 | 0.0752 | 0.10 | 0.7045 | 0.45 | 0.1869 | 0.77 | 0.0408 |
| HIF2A b | 0.06 | 0.7541 | 0.21 | 0.4165 | 0.20 | 0.4450 | 0.59 | 0.0739 | −0.16 | 0.7283 |
| VEGFA b | 0.46 | 0.0069 | 0.15 | 0.5698 | 0.19 | 0.4565 | 0.67 | 0.0033 | −0.45 | 0.3104 |
| Gene | All Cases (n = 40) | Controls (n = 20) | Patients (n = 20) | OWC (n = 10) | BOC (n = 10) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-Value | R | p-Value | |
| ESR1 a | −0.10 | 0.5654 | −0.13 | 0.6291 | 0.13 | 0.6155 | −0.07 | 0.8544 | −0.14 | 0.7599 |
| ESR2 a | 0.38 | 0.0258 | 0.22 | 0.3879 | 0.57 | 0.0130 | 0.53 | 0.1157 | −0.33 | 0.4736 |
| PELP1 a | 0.09 | 0.6125 | −0.62 | 0.0085 | 0.64 | 0.0039 | −0.60 | 0.0670 | −0.67 | 0.0971 |
| SRC a | 0.04 | 0.8081 | −0.41 | 0.1005 | 0.25 | 0.3073 | −0.48 | 0.1615 | −0.36 | 0.4316 |
| HIF1A b | 0.30 | 0.0852 | 0.39 | 0.1195 | 0.39 | 0.1093 | 0.22 | 0.5334 | 0.71 | 0.0713 |
| HIF2A b | 0.22 | 0.2014 | −0.12 | 0.6598 | 0.53 | 0.0252 | 0.08 | 0.8287 | −0.25 | 0.5887 |
| VEGFA b | 0.21 | 0.2361 | 0.05 | 0.8372 | 0.10 | 0.6987 | 0.28 | 0.4250 | 0.04 | 0.9394 |
| miRNA Symbol | Assay Reference Number | Mature miRNA Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-21-5p | (477952_mir) | CAACGGAAUCCCAAAAGCAGCUG |
| hsa-miR-145-5p | (477916_mir) | GUCCAGUUUUCCCAGGAAUCCCU |
| hsa-miR-191-5p | (000397_mir) | UAGCUUAUCAGACUGAUGUUGA |
| Gene of Interest | Manufacturers Designation | Cat. No. | Primer Sequence 5′→3′ | Amplicon Length [bp] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESR1 | #69 RD | 04688686001 | F | ccttcttcaagagaagtattcaagg | 160 |
| R | attcccacttcgtagcatttg | ||||
| ESR2 | dHsaCPE5037392 BR | 10041596 | * | 87 | |
| PELP1 | #24 RD | 04686985001 | F | caaggaggagactcacaggag | 131 |
| R | gcagcaggcagtagagttca | ||||
| SRC | #21 RD | 04686942001 | F | gccatgttcactccggttt | 100 |
| R | cagcgtcctcatctggtttc | ||||
| HIF1A | #71 RD | 04688945001 | F | tttttcaagcagtaggaattgga | 76 |
| R | ttccaagaaagtgatgtagtagctg | ||||
| EPAS1 | #39 RD | 04687973001 | F | gaaaacatcagcaagttcatgg | 77 |
| R | cagggatgagtgaagtcaaagata | ||||
| VEGFA | #69 RD | 04688686001 | F | cgaacgtacttgcagatgtga | 88 |
| R | gagagatctggttcccgaaa | ||||
| HPRT | 102,079 RD | 05532957001 | * | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Górecki, M.; Żbikowska, A.; Tokłowicz, M.; Sajdak, S.; Englert-Golon, M.; Andrusiewicz, M. Hsa-miR-21-5p and Hsa-miR-145-5p Expression: From Normal Tissue to Malignant Changes—Context-Dependent Correlation with Estrogen- and Hypoxia–Vascularization-Related Pathways Genes: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094461
Górecki M, Żbikowska A, Tokłowicz M, Sajdak S, Englert-Golon M, Andrusiewicz M. Hsa-miR-21-5p and Hsa-miR-145-5p Expression: From Normal Tissue to Malignant Changes—Context-Dependent Correlation with Estrogen- and Hypoxia–Vascularization-Related Pathways Genes: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094461
Chicago/Turabian StyleGórecki, Mateusz, Aleksandra Żbikowska, Małgorzata Tokłowicz, Stefan Sajdak, Monika Englert-Golon, and Mirosław Andrusiewicz. 2025. "Hsa-miR-21-5p and Hsa-miR-145-5p Expression: From Normal Tissue to Malignant Changes—Context-Dependent Correlation with Estrogen- and Hypoxia–Vascularization-Related Pathways Genes: A Pilot Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094461
APA StyleGórecki, M., Żbikowska, A., Tokłowicz, M., Sajdak, S., Englert-Golon, M., & Andrusiewicz, M. (2025). Hsa-miR-21-5p and Hsa-miR-145-5p Expression: From Normal Tissue to Malignant Changes—Context-Dependent Correlation with Estrogen- and Hypoxia–Vascularization-Related Pathways Genes: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094461








