Non-Thermal Plasma Attenuates TNF-α-Induced Endothelial Inflammation via ROS Modulation and NF-κB Inhibition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
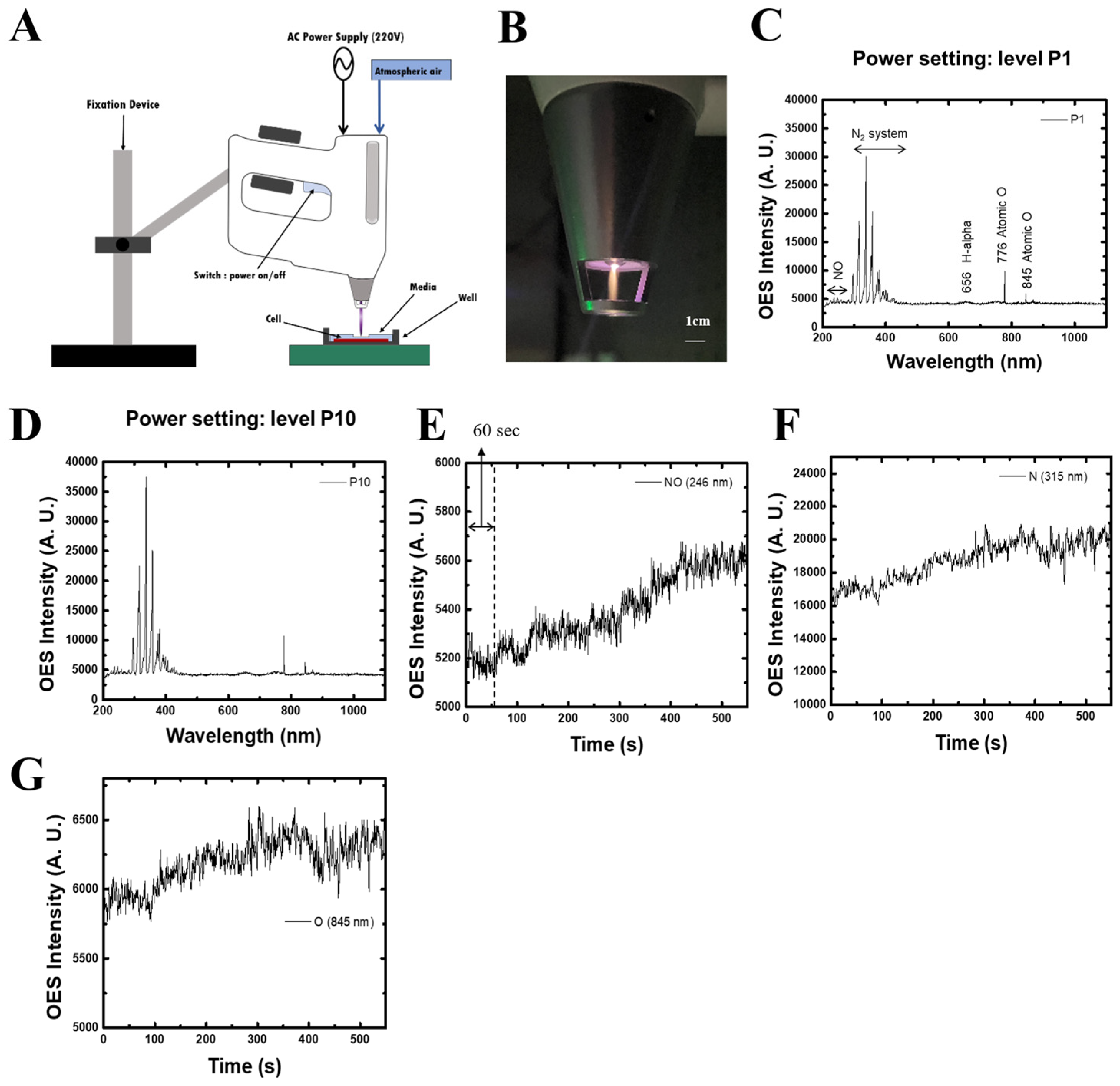
2.1. Characterization of Non-Thermal Plasma (NTP)
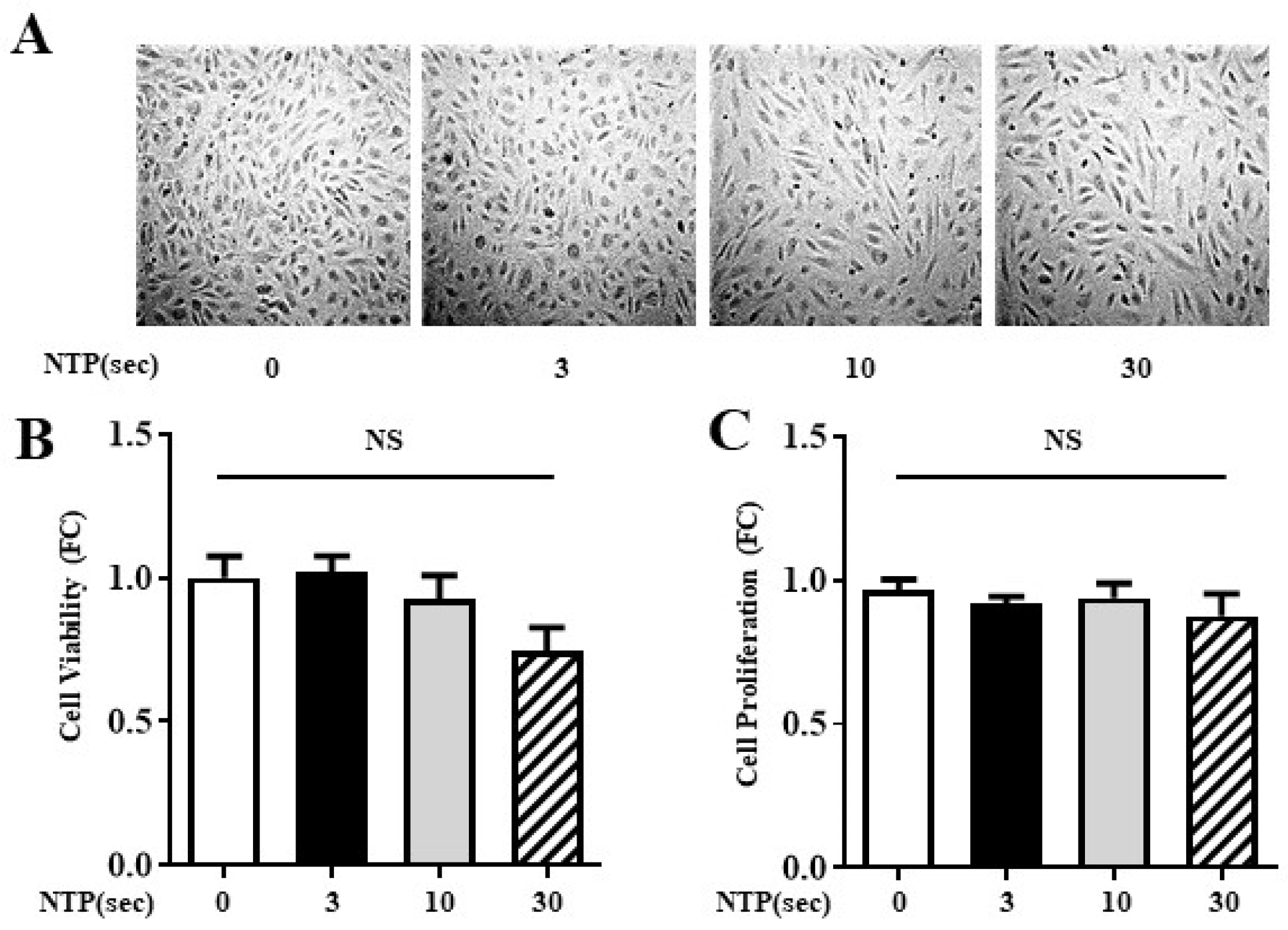
2.2. NTP Treatment Does Not Compromise HUVEC Viability or Proliferation
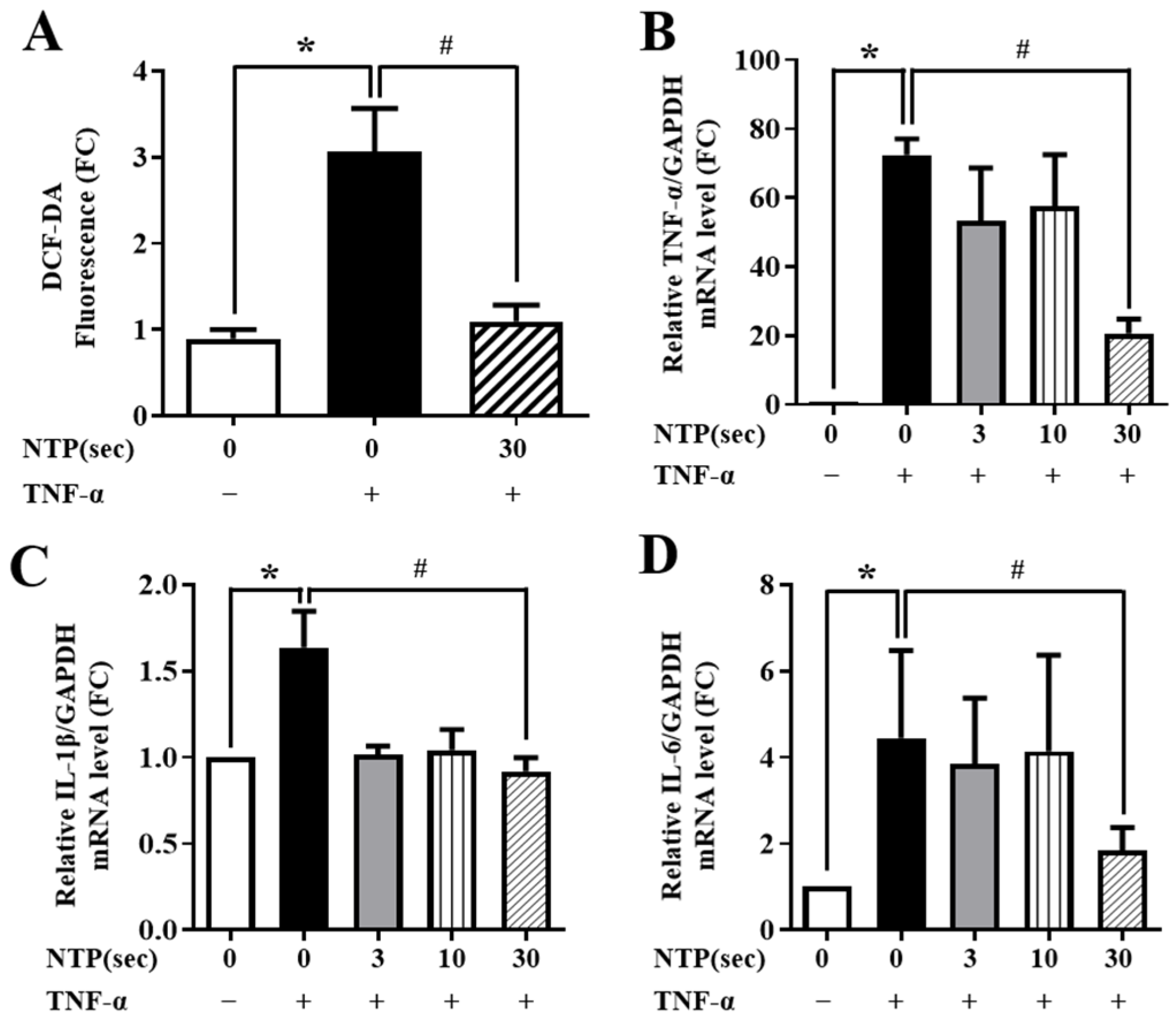
2.3. NTP Treatment Inhibits TNF-α-Induced ROS Generation and Inflammatory Cytokine Expression by HUVECs
2.4. NTP Treatment Inhibits TNF-α-Induced Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines and Monocyte Adhesion by HUVECs
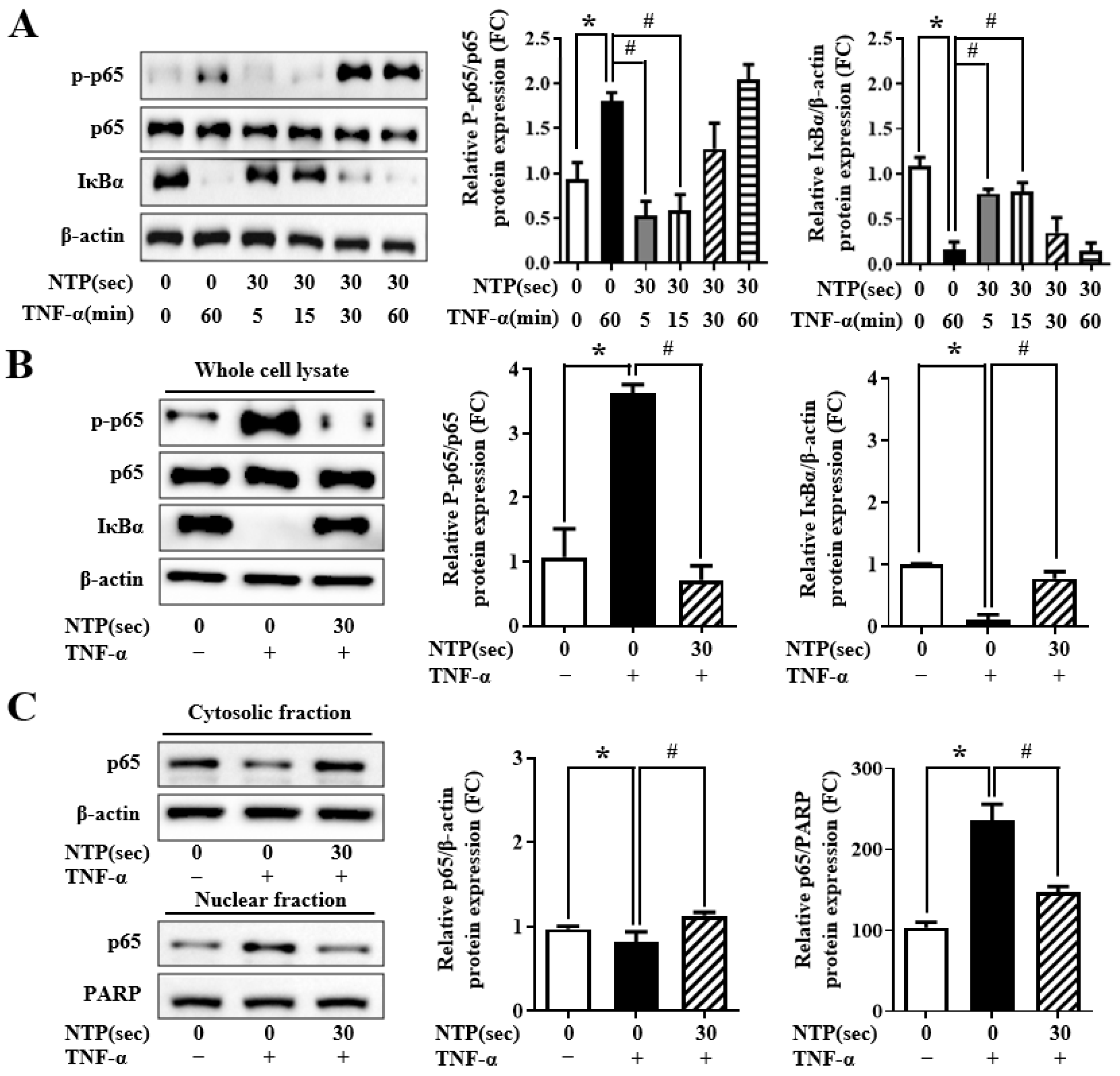
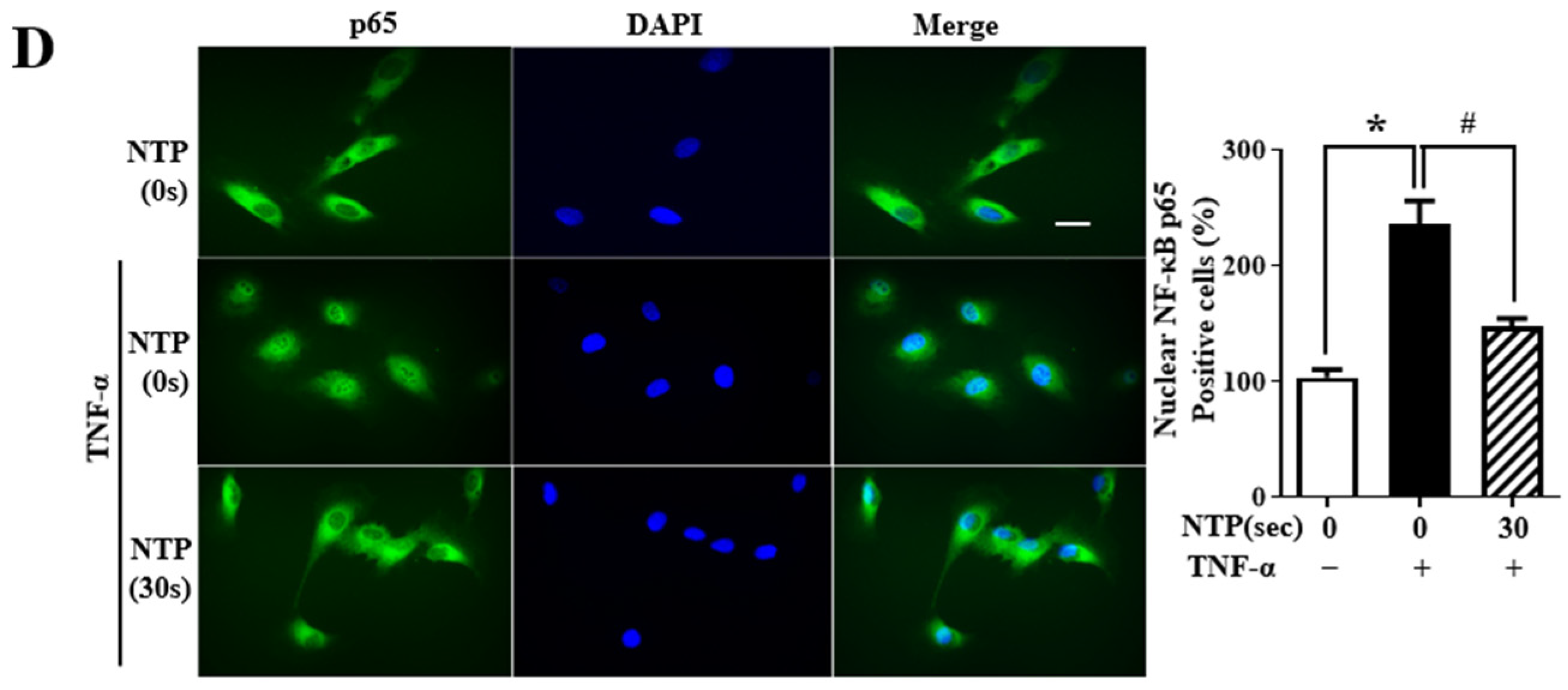
2.5. NTP Treatment Inhibits TNF-α-Induced NF-κB-p65 Signaling by HUVECs
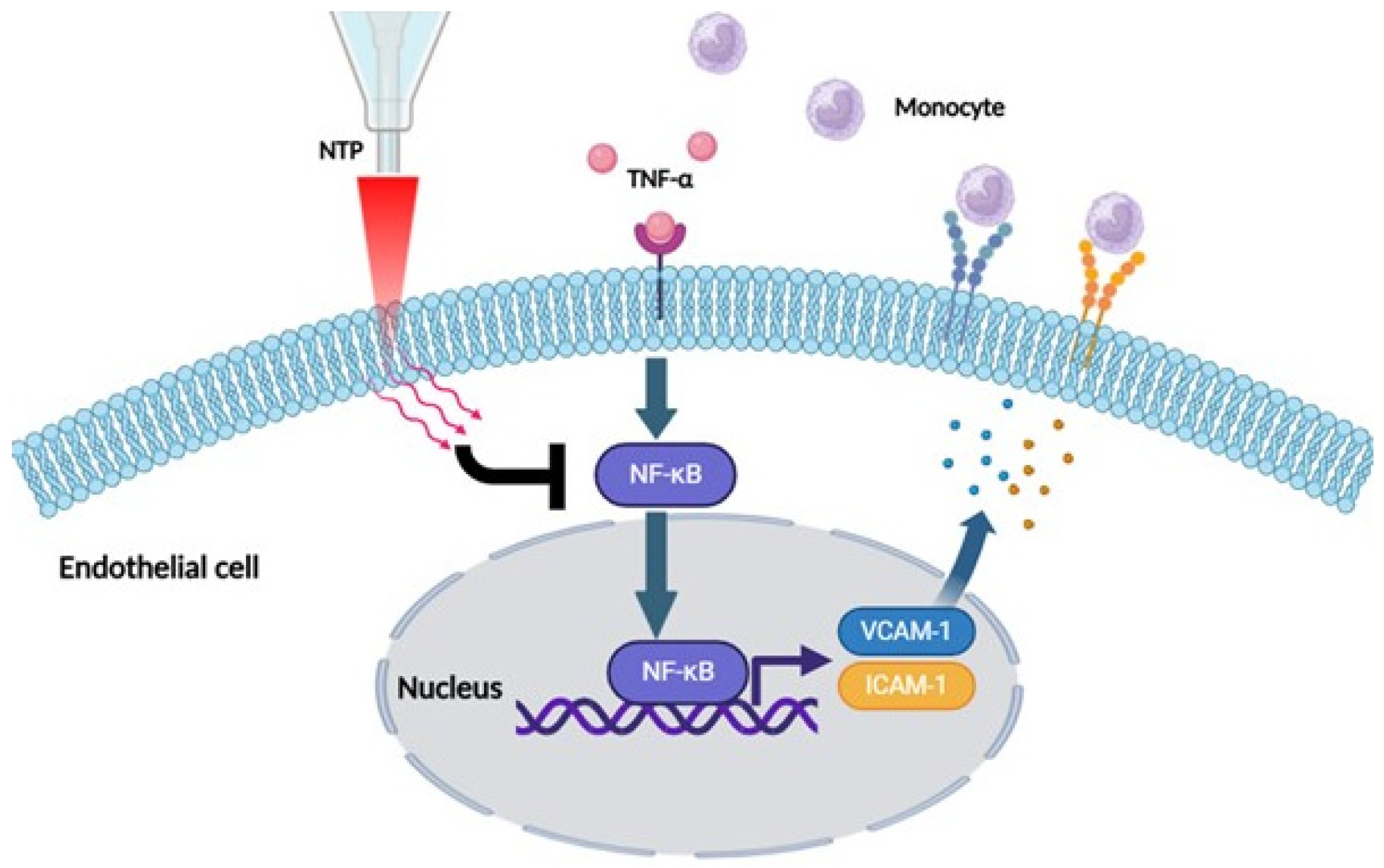
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. NTP Treatment
4.3. Cell Viability and Cell Proliferation Assay
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Immunofluorescence
4.6. Preparation of Nuclear and Cytosolic Fractions
4.7. Monocyte Adhesion Assay
4.8. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.9. Detection of Total ROS
4.10. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NTP | Non-thermal plasma |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cell |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| ICAM | Intracellular adhesion molecule |
| VCAM | Vascular adhesion molecule |
| IL | Interleukin |
| NF-κB | Nuclear transcription factor termed kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cell |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| qPCR | Real-time polymerase chain reaction |
References
- Yan, X.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, C.; Shi, Z.; Wang, B.; Ostrikov, K.K. Plasma medicine for neuroscience-an introduction. Chin. Neurosurg. J. 2019, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, P.; Vanraes, P.; Kumar, N.; Bogaerts, A. Possible Synergies of Nanomaterial-Assisted Tissue Regeneration in Plasma Medicine: Mechanisms and Safety Concerns. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, T.; Semmler, M.L.; Schafer, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Emmert, S.; Boeckmann, L. Plasma Medicine: Applications of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma in Dermatology. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 3873928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suschek, C.V. Plasma Applications in Biomedicine: A Groundbreaking Intersection between Physics and Life Sciences. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunov, O.; Zablotskii, V.; Churpita, O.; Chanova, E.; Sykova, E.; Dejneka, A.; Kubinova, S. Cell death induced by ozone and various non-thermal plasmas: Therapeutic perspectives and limitations. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haertel, B.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.D.; Lindequist, U. Non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma possible application in wound healing. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Toyokuni, S.; Kajiyama, H.; Kikkawa, F.; Hori, M. Molecular mechanisms of non-thermal plasma-induced effects in cancer cells. Biol. Chem. 2018, 400, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moszczynska, J.; Roszek, K.; Wisniewski, M. Non-Thermal Plasma Application in Medicine-Focus on Reactive Species Involvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Hori, M. Medical applications of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2017, 60, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, D.; Sata, M. Frontiers of inflammatory disease research: Inflammation in cardiovascular-cerebral diseases. Inflamm. Regen. 2021, 41, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyane, T.S.; Jere, S.W.; Houreld, N.N. Oxidative Stress in Ageing and Chronic Degenerative Pathologies: Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Counteracting Oxidative Stress and Chronic Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimbrone, M.A., Jr.; Garcia-Cardena, G. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Shu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M. Endothelial Response to Pathophysiological Stress. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, e233–e243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Saredy, J.; Yang, W.Y.; Sun, Y.; Lu, Y.; Saaoud, F.; Drummer, C., IV; Johnson, C.; Xu, K.; Jiang, X.; et al. Vascular Endothelial Cells and Innate Immunity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, e138–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Moon, S.O.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Koh, Y.S.; Koh, G.Y. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), and E-selectin through nuclear factor-kappa B activation in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7614–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHale, J.F.; Harari, O.A.; Marshall, D.; Haskard, D.O. Vascular endothelial cell expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 at the onset of eliciting contact hypersensitivity in mice: Evidence for a dominant role of TNF-alpha. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, C.; Sun, X.; Kazama, K.; Yi, B.; Cheng, F.; Guo, Z.F.; Sun, J. NDRG1 Signaling Is Essential for Endothelial Inflammation and Vascular Remodeling. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martin, R.; Hoeth, M.; Hofer-Warbinek, R.; Schmid, J.A. The transcription factor NF-kappa B and the regulation of vascular cell function. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, E83–E88. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.P.; Bald, A.; Cassatella, M.A. Activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by inflammatory stimuli in human neutrophils. Blood 1997, 89, 3421–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalghatgi, S.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A.; Clyne, A.M. Endothelial cell proliferation is enhanced by low dose non-thermal plasma through fibroblast growth factor-2 release. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.U.; Kim, H.J.; Ma, S.; Oh, D.Y.; Jang, J.Y.; Seo, C.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, C.H. Liquid plasma promotes angiogenesis through upregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase-induced extracellular matrix metabolism: Potential applications of liquid plasma for vascular injuries. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Boiti, A.; Vallone, D.; Foulkes, N.S. Reactive Oxygen Species Signaling and Oxidative Stress: Transcriptional Regulation and Evolution. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, S.J.; Kikuchi, D.S.; Hernandes, M.S.; Xu, Q.; Griendling, K.K. Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic and Inflammatory Signaling. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, A.; de Oliveira, J.; da Silva Pontes, L.V.; de Souza Junior, J.F.; Goncalves, T.A.F.; Dantas, S.H.; de Almeida Feitosa, M.S.; Silva, A.O.; de Medeiros, I.A. ROS: Basic Concepts, Sources, Cellular Signaling, and its Implications in Aging Pathways. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1225578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jin, T.; Fu, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Xu, T. Non-thermal plasma-treated melatonin inhibits the biological activity of HCC cells by increasing intracellular ROS levels and reducing RRM2 expression. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Tu, Y.; Zhou, J. Non-thermal plasma inhibits tumor growth and proliferation and enhances the sensitivity to radiation in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3405–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, K.N.; Ma, J.; Shen, J.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, F.; Cai, Z.; Han, W. Non-thermal plasma induces mitochondria-mediated apoptotic signaling pathway via ROS generation in HeLa cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 633, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Genes | Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| VCAM-1 | Sense | 5′-GTTGAATGCGGGAGTAT-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-TTCATGTTGGCTTTTCTTGC-3′ | |
| ICAM-1 | Sense | 5′-AGAGGTTGAACCCCACAGTC-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-TCTGGCTTCGTCAGAATCAC-3′ | |
| TNF-α | Senses | 5′-CCCAGGGACCTCTCTCTAATCA-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-AGCTGCCCCTCAGCTTGAG-3′ | |
| IL-1β | Sense | 5′-TGGCAATGAGGATGACTTGTTC-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-CTGTAGTGGTCGGAGATT-3′ | |
| IL-6 | Sense | 5′-CCACTCACCTCTTCAGAACG-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-CATCTTTGGAAGGTTCAGGTTG-3′ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.; Piao, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.-W.; Jeon, B.H.; Oh, S.-H.; Kim, C.-S. Non-Thermal Plasma Attenuates TNF-α-Induced Endothelial Inflammation via ROS Modulation and NF-κB Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094449
Kim J-H, Kim S, Piao S, Kim M, Kim D-W, Jeon BH, Oh S-H, Kim C-S. Non-Thermal Plasma Attenuates TNF-α-Induced Endothelial Inflammation via ROS Modulation and NF-κB Inhibition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094449
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Joo-Hak, Seonhee Kim, Shuyu Piao, Minsoo Kim, Dae-Woong Kim, Byeong Hwa Jeon, Sang-Ha Oh, and Cuk-Seong Kim. 2025. "Non-Thermal Plasma Attenuates TNF-α-Induced Endothelial Inflammation via ROS Modulation and NF-κB Inhibition" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094449
APA StyleKim, J.-H., Kim, S., Piao, S., Kim, M., Kim, D.-W., Jeon, B. H., Oh, S.-H., & Kim, C.-S. (2025). Non-Thermal Plasma Attenuates TNF-α-Induced Endothelial Inflammation via ROS Modulation and NF-κB Inhibition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094449








