Identification of Hub Genes and Key Pathways Associated with Sepsis Progression Using Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis and Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result
2.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
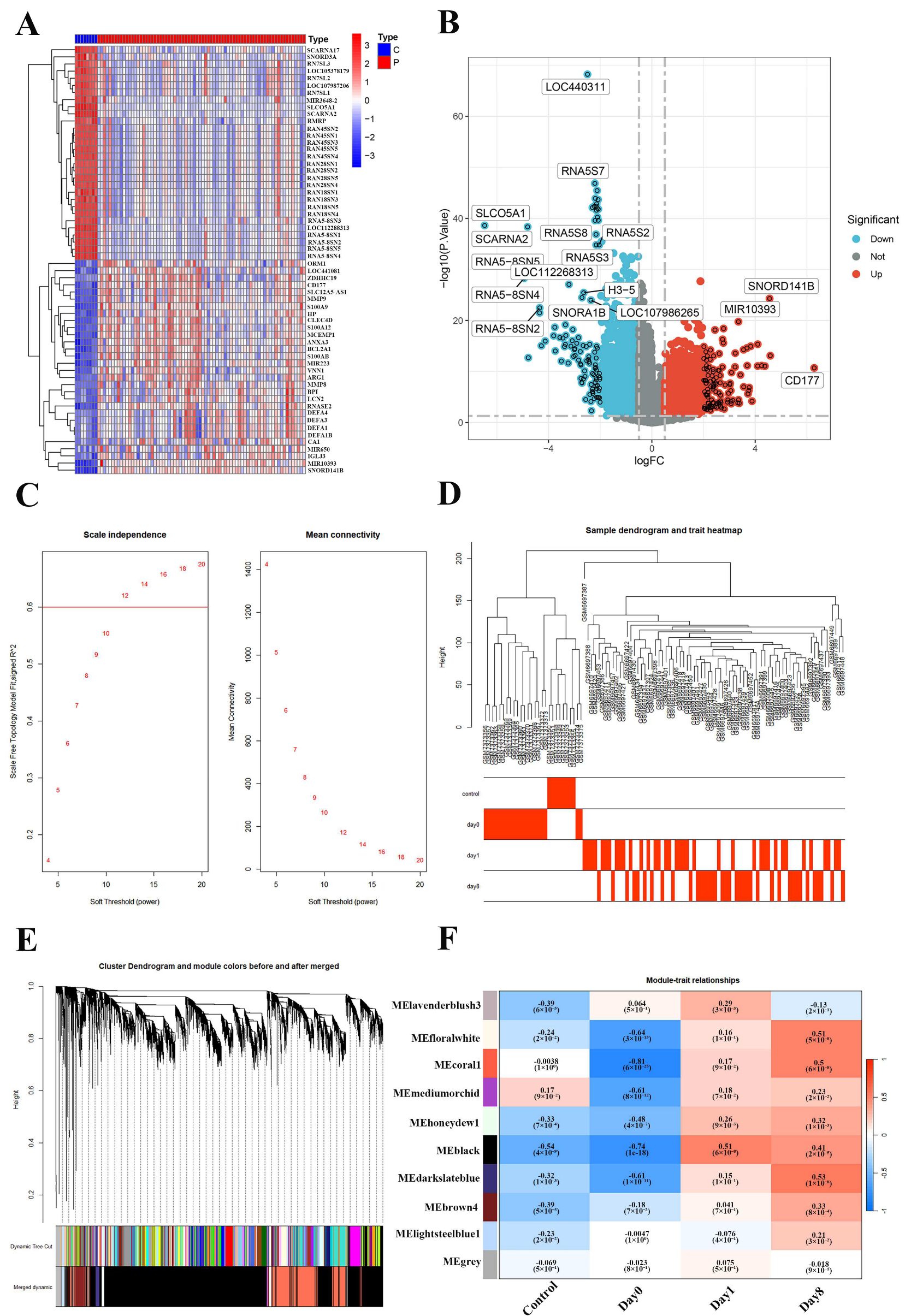
2.2. Construction of Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network of the Sepsis and Normal
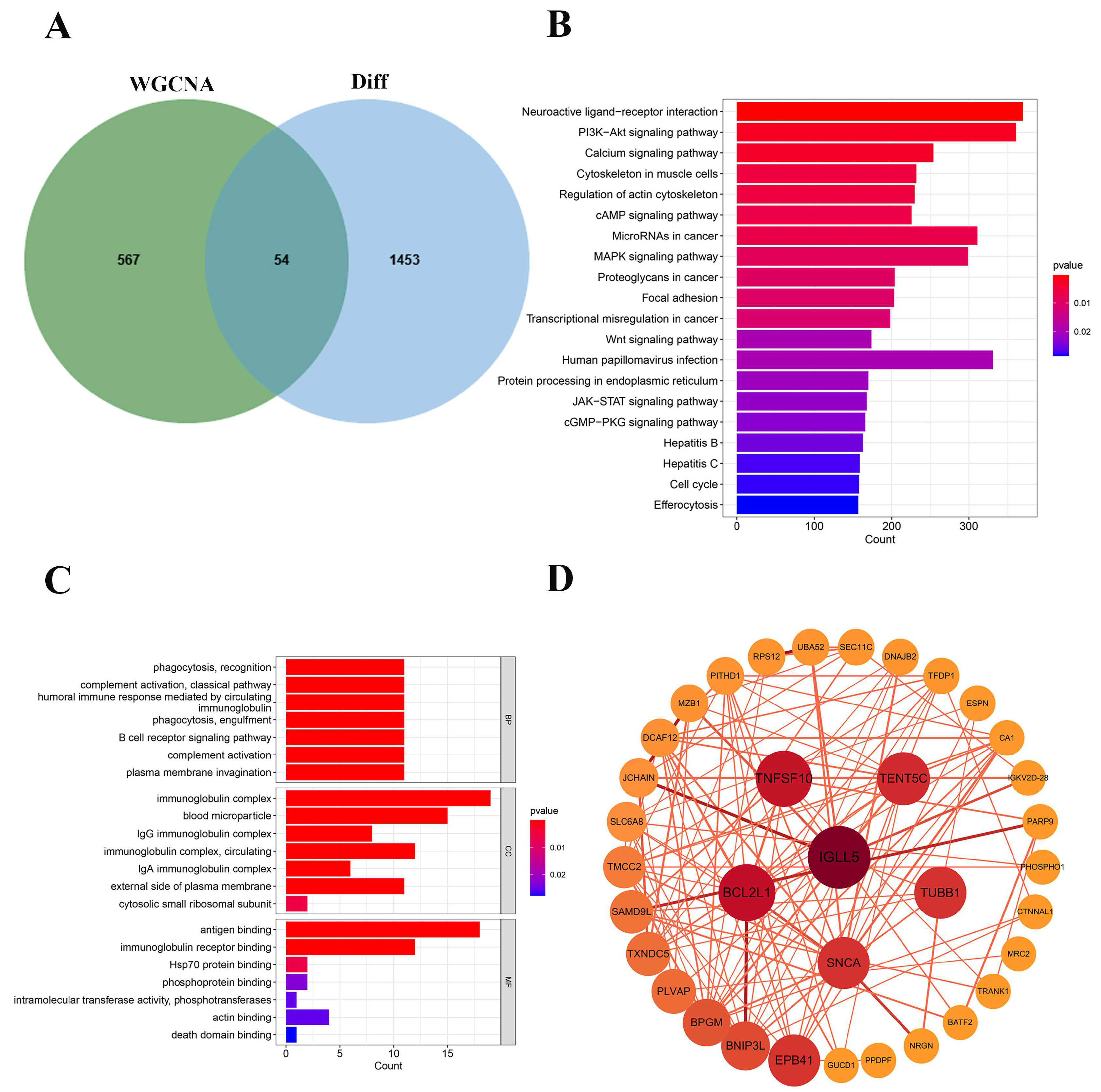
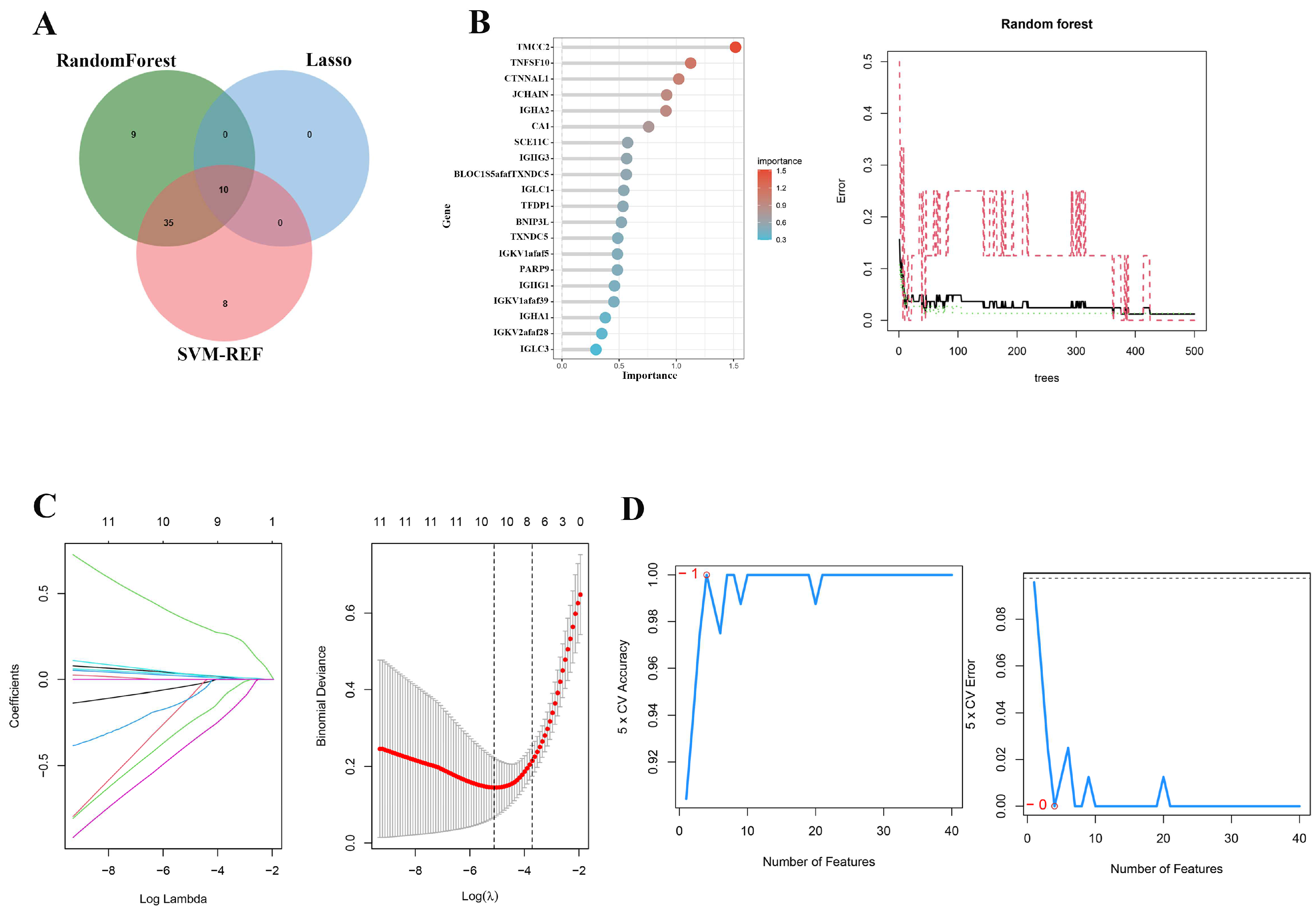
2.3. Multi-Algorithm Feature Selection for Identifying Key Genes in Sepsis Progression
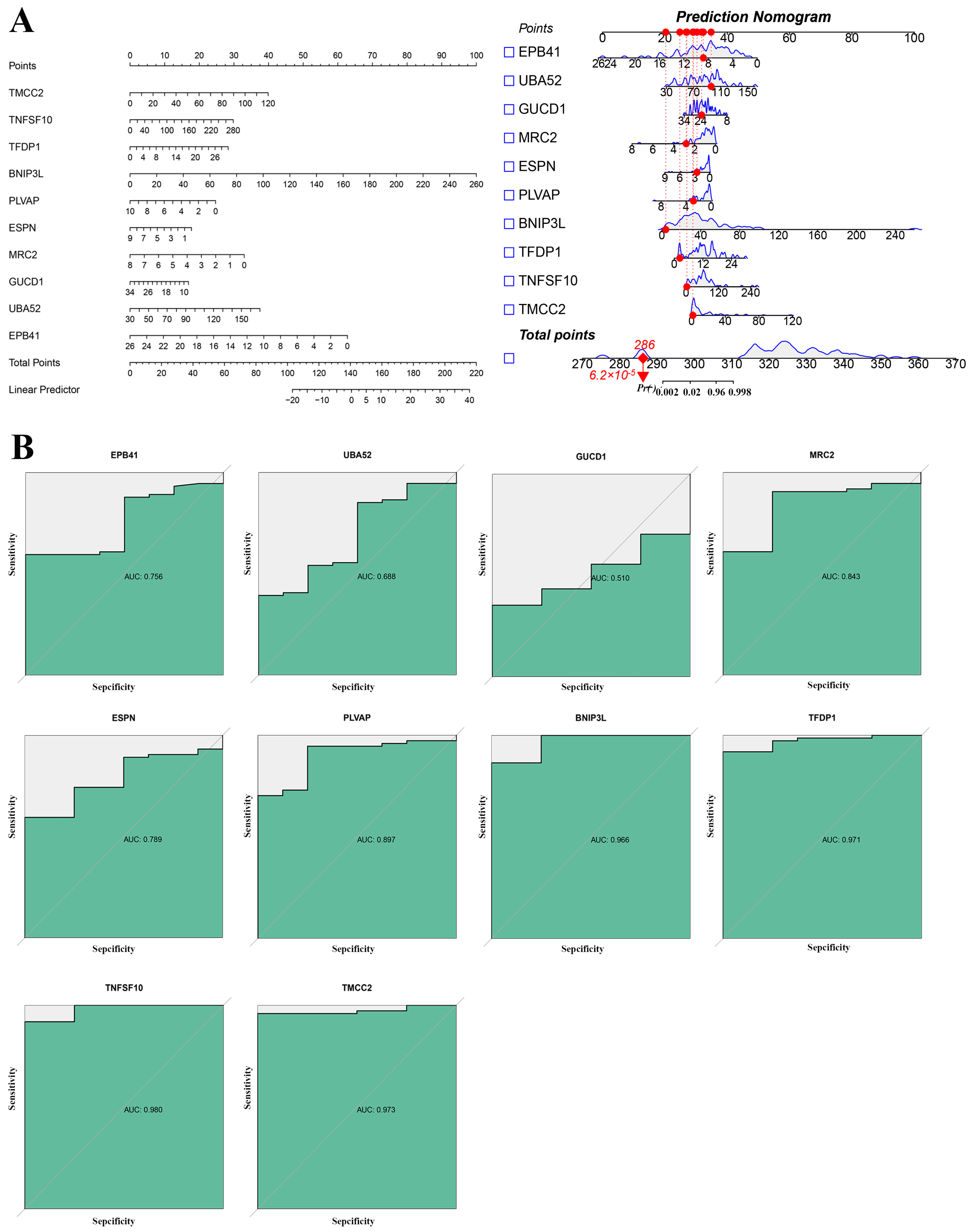
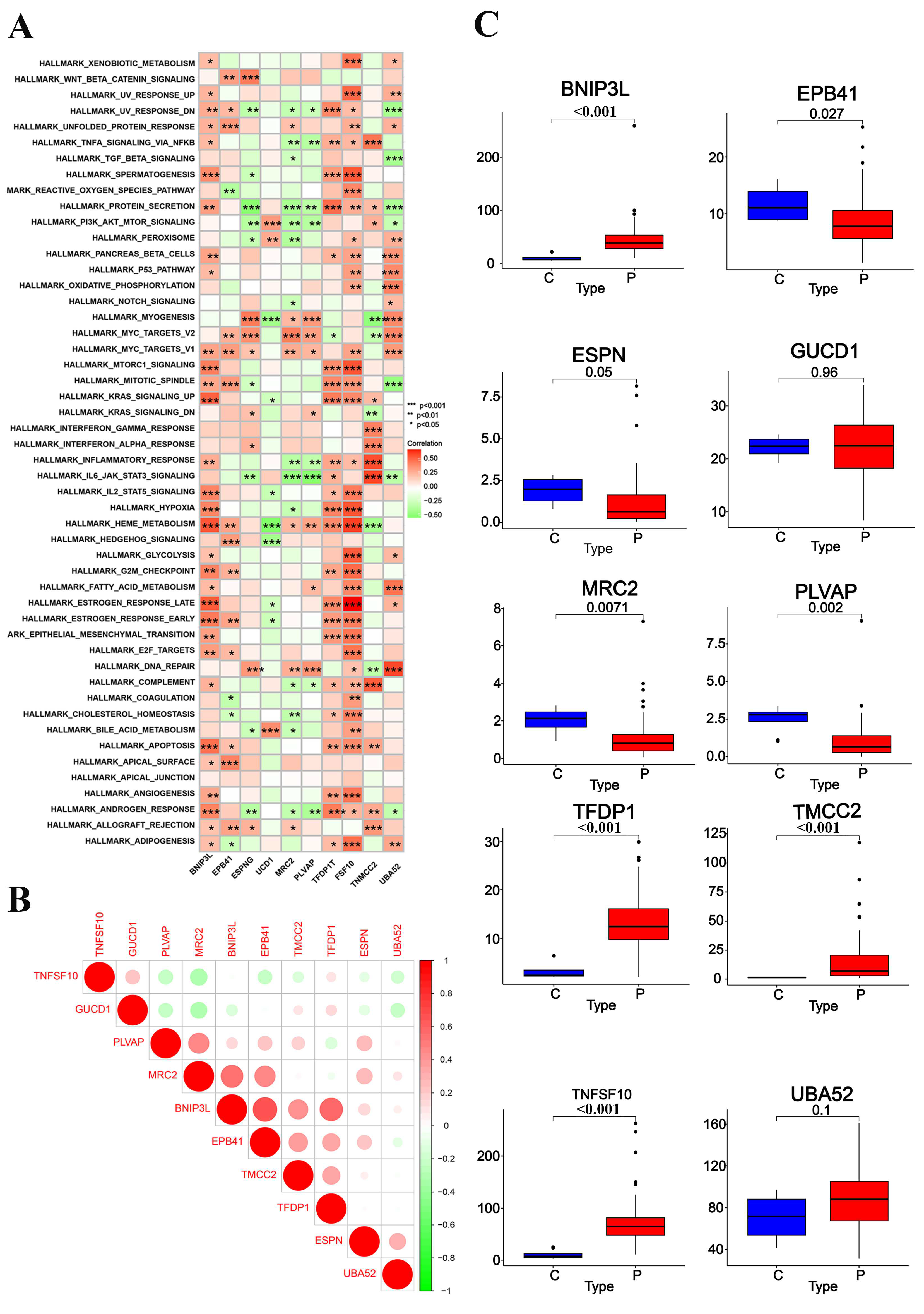
2.4. Key Genes Identified in Sepsis Progression
2.5. Identification of Key Genes in Sepsis Progression Using Transcriptomic Analysis
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Data Processing
3.2. Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
3.3. Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment Analysis
3.4. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)
3.5. Method for Disease Feature Gene Selection Using Three Machine Learning Classification Algorithms
3.6. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Analysis
3.7. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
3.8. Statistical Analysis and Differential Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, I.C.; Chen, H.H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Hsiao, T.H.; Ko, T.M.; Chao, W.C. Whole transcriptome analysis to explore the impaired immunological features in critically ill elderly patients with sepsis. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaszewski, R.A.; Jones, H.E.; Gersuk, V.H.; Russell, P.; Simpson, A.; Brealey, D.; Walker, J.; Thomas, M.; Whitehouse, T.; Ostermann, M.; et al. Presymptomatic diagnosis of postoperative infection and sepsis using gene expression signatures. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.Y.; Luo, F.; Wu, C.Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Q.Z.; He, S.X.; Li, W.M.; Zhang, W.M.; Cheng, Y.M.; Yang, P.M.; et al. Identification of potential biomarkers in the peripheral blood of neonates with bronchopulmonary dysplasia using WGCNA and machine learning algorithms. Medicine 2024, 103, e37083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.L.; He, W.X.; Tang, J.N.; Liao, X.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.M.; Wu, G. Identification of Important Modules and Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Based on WGCNA. Oncotargets Ther. 2020, 13, 6805–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Yoo, H.; Jeon, K. Bioinformatics Analysis of Gene Expression Profiles for Diagnosing Sepsis and Risk Prediction in Patients with Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.P.; Liu, W.; An, J.Q.; Yang, P.; Guo, L.H.; Li, Y.Q.; Lv, J.; Yu, S. Transcriptome analyses and weighted gene coexpression network analysis reveal key pathways and genes involved in the rapid cold resistance of the Chinese white wax scale insect. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 107, e21781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach. Learn. 2002, 46, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M. Caret: Classification and Regression Training, ascl:1505.003; Astrophysics Source Code Library: Houghton, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A. Rstatix: Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Satistical Tests. R Package Version 0.7.2. 2023. Available online: https://rpkgs.datanovia.com/rstatix/ (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Kassambara, A. ggpubr: ‘ggplot2’ Based Publication Ready Plots. R Package Version 0.6.0. 2023. Available online: https://rpkgs.datanovia.com/ggpubr/ (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Li, J.; Shen, L.; Qian, K. Global, regional, and national incidence and mortality of neonatal sepsis and other neonatal infections, 1990–2019. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1139832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Gerlach, H.; Vogelmann, T.; Preissing, F.; Stiefel, J.; Adam, D. Mortality in sepsis and septic shock in Europe, North America and Australia between 2009 and 2019-results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Xu, Y.; Yin, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Peng, J.M.; Dong, R.; Hu, X.Y.; et al. National incidence and mortality of hospitalized sepsis in China. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruserud, Ø.; Mosevoll, K.A.; Bruserud, Ø.; Reikvam, H.; Wendelbo, Ø. The regulation of neutrophil migration in patients with sepsis: The complexity of the molecular mechanisms and their modulation in sepsis and the heterogeneity of sepsis patients. Cells 2023, 12, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Jiang, N.; Ju, X. Artesunate ameliorates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by activating the mTOR/AKT/PI3K axis. Gene 2020, 759, 144969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, L.; Dong, S. Sivelestat ameliorates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 128, 111466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosmann, M.; Ward, P.A. The inflammatory response in sepsis. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in sepsis-induced immune dysfunction. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, J. Comprehensive analysis of sialylation-related genes and construct the prognostic model in sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, P.C.R.; Sáinz-Fuertes, R.; Lovestone, S. The impact of a novel apolipoprotein E and amyloid-β protein precursor-interacting protein on the production of amyloid-β. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 26, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brealey, D.; Karyampudi, S.; Jacques, T.S.; Novelli, M.; Stidwill, R.; Taylor, V.; Singer, M. Mitochondrial dysfunction in a long-term rodent model of sepsis and organ failure. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 286, R491–R497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Q.; Zhang, H.-L.; Wang, Y.; Xiu, H.; Lu, Y.; He, N.; Yin, L. Identification of Hub Genes and Key Pathways Associated with Sepsis Progression Using Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis and Machine Learning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094433
Sun Q, Zhang H-L, Wang Y, Xiu H, Lu Y, He N, Yin L. Identification of Hub Genes and Key Pathways Associated with Sepsis Progression Using Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis and Machine Learning. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094433
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Qinghui, Hai-Li Zhang, Yichao Wang, Hao Xiu, Yufei Lu, Na He, and Li Yin. 2025. "Identification of Hub Genes and Key Pathways Associated with Sepsis Progression Using Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis and Machine Learning" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094433
APA StyleSun, Q., Zhang, H.-L., Wang, Y., Xiu, H., Lu, Y., He, N., & Yin, L. (2025). Identification of Hub Genes and Key Pathways Associated with Sepsis Progression Using Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis and Machine Learning. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094433





