Retrotransposon Protein L1 ORF1p Expression in Aging Central Nervous System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
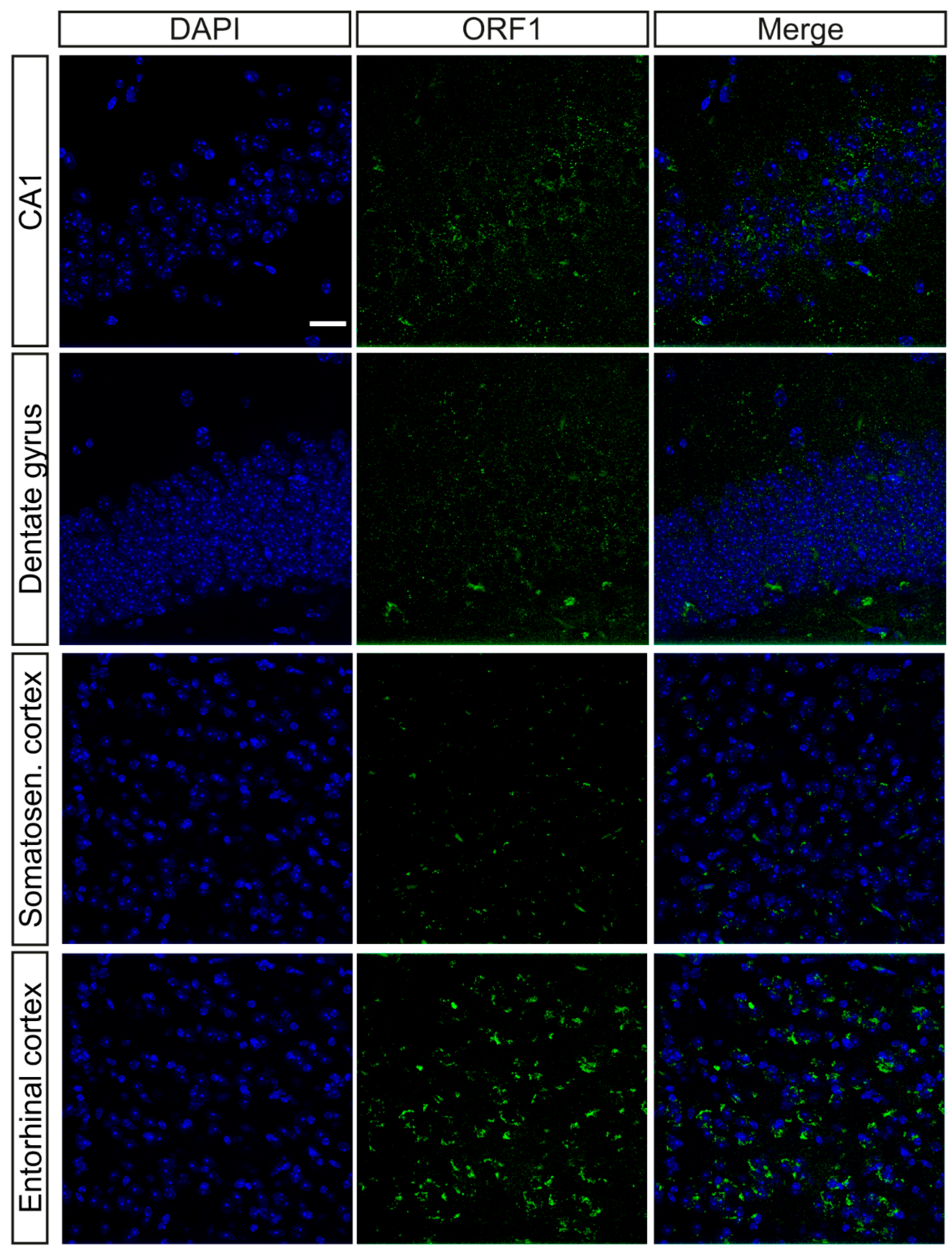
2.1. Characterization of the Presence of ORF1p in the Brain
2.2. ORF1p Distribution Through Brain Cell Types
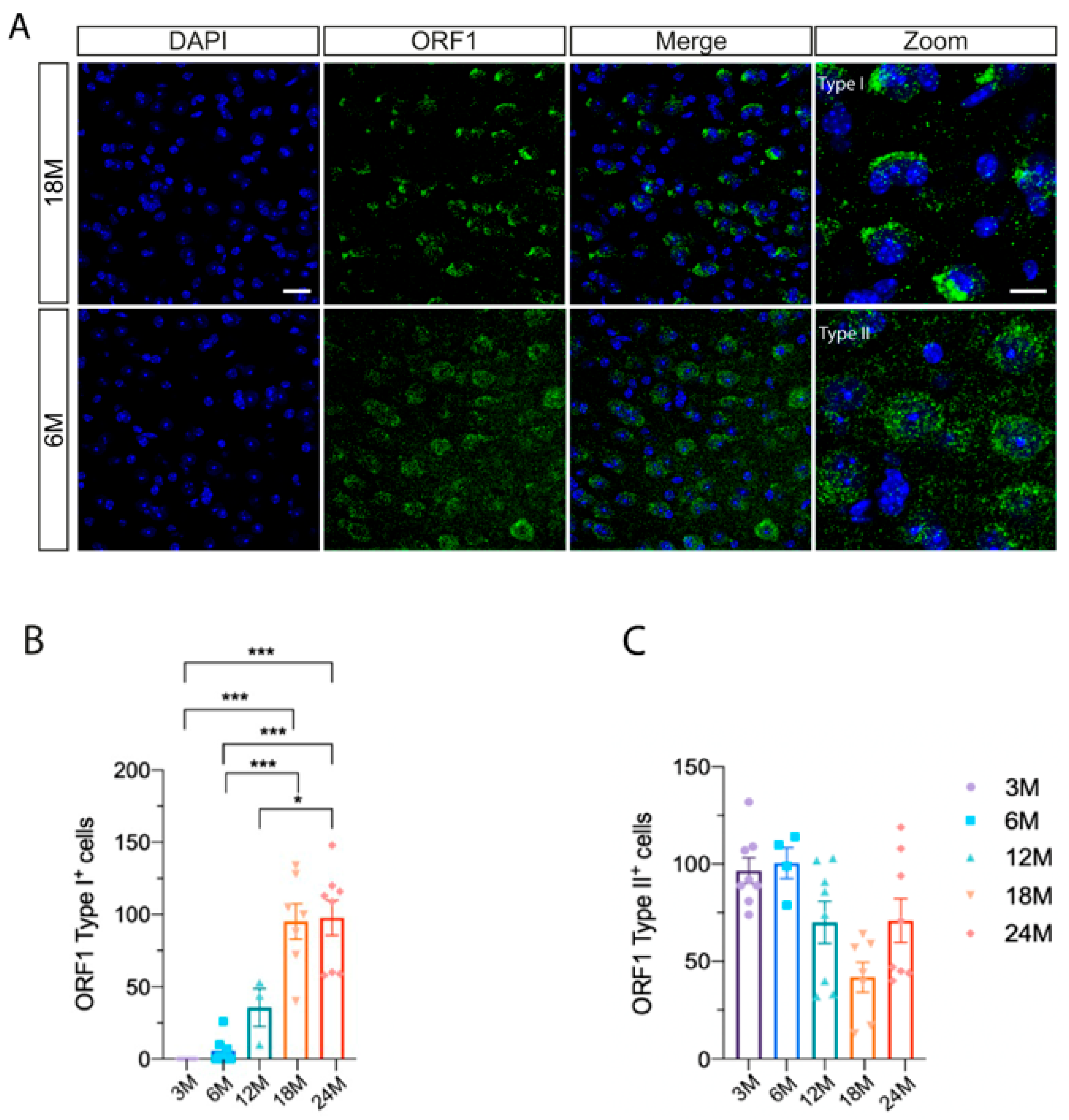
2.3. ORF1p in Microglial Activation During Aging
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Tissue Processing
4.2. Immunofluorescence
4.3. Image Acquisition and Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Gillette, M.; de Santiago, P.R.; Kuhn, E.; Burgess, M.; Doucette, K.; Feng, Y.; Mendez-Dorantes, C.; Ippoliti, P.J.; Hobday, S.; et al. LINE-1 ORF1p as a candidate biomarker in high grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Moran, J.V.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr.; Boeke, J.D. Human L1 retrotransposon encodes a conserved endonuclease required for retrotransposition. Cell 1996, 87, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, K.H. Transposable elements in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancks, D.C.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr. Roles for retrotransposon insertions in human disease. Mob. DNA 2016, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.L. The ORF1 protein encoded by LINE-1: Structure and function during L1 retrotransposition. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2006, 2006, 45621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Bojang, P., Jr.; Hassanin, A.A.I.; Bowers, E.C.; Reyes-Reyes, E.M.; Ramos, I.N.; Ramos, K.S. Line-1: Implications in the etiology of cancer, clinical applications, and pharmacologic targets. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2018, 778, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodier, J.L. Restricting retrotransposons: A review. Mob. DNA 2016, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belancio, V.P.; Roy-Engel, A.M.; Pochampally, R.R.; Deininger, P. Somatic expression of LINE-1 elements in human tissues. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2010, 38, 3909–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Otin, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. Hallmarks of aging: An expanding universe. Cell 2023, 186, 243–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Tyler, J.K. Epigenetics and aging. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravel-Godreuil, C.; Znaidi, R.; Bonnifet, T.; Joshi, R.L.; Fuchs, J. Transposable elements as new players in neurodegenerative diseases. FEBS Lett. 2021, 595, 2733–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.G.; Helfand, S.L. Chromatin structure and transposable elements in organismal aging. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, Y.; Nishisho, I.; Horii, A.; Miyoshi, Y.; Utsunomiya, J.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Nakamura, Y. Disruption of the APC gene by a retrotransposal insertion of L1 sequence in a colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 643–645. [Google Scholar]
- Piskareva, O.; Lackington, W.; Lemass, D.; Hendrick, C.; Doolan, P.; Barron, N. The human L1 element: A potential biomarker in cancer prognosis, current status and future directions. Curr. Mol. Med. 2011, 11, 286–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillie, J.K.; Barnett, M.W.; Upton, K.R.; Gerhardt, D.J.; Richmond, T.A.; De Sapio, F.; Brennan, P.M.; Rizzu, P.; Smith, S.; Fell, M.; et al. Somatic retrotransposition alters the genetic landscape of the human brain. Nature 2011, 479, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrony, G.D.; Cai, X.; Lee, E.; Hills, L.B.; Elhosary, P.C.; Lehmann, H.S.; Parker, J.J.; Atabay, K.D.; Gilmore, E.C.; Poduri, A.; et al. Single-neuron sequencing analysis of L1 retrotransposition and somatic mutation in the human brain. Cell 2012, 151, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cecco, M.; Criscione, S.W.; Peckham, E.J.; Hillenmeyer, S.; Hamm, E.A.; Manivannan, J.; Peterson, A.L.; Kreiling, J.A.; Neretti, N.; Sedivy, J.M. Genomes of replicatively senescent cells undergo global epigenetic changes leading to gene silencing and activation of transposable elements. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B.; Stevens, A.A.; Rajendran, N.; Yeo, B.T.; Greve, D.N.; Van Leemput, K.; Polimeni, J.R.; Kakunoori, S.; Buckner, R.L.; Pacheco, J.; et al. Predicting the location of entorhinal cortex from MRI. Neuroimage 2009, 47, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, H.K.; Buslei, R.; Schmidt-Kastner, R.; Schmidt-Kastner, P.K.; Pietsch, T.; Wiestler, O.D.; Blumcke, I. NeuN: A useful neuronal marker for diagnostic histopathology. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1996, 44, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, D.; Imai, Y.; Ohsawa, K.; Nakajima, K.; Fukuuchi, Y.; Kohsaka, S. Microglia-specific localisation of a novel calcium binding protein, Iba1. Mol. Brain Res. 1998, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa Gonzalez, M.; Valles-Saiz, L.; Hernandez, I.H.; Avila, J.; Hernandez, F.; Perez-Alvarez, M.J. Focal cerebral ischemia induces changes in oligodendrocytic tau isoforms in the damaged area. Glia 2020, 68, 2471–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niraula, A.; Sheridan, J.F.; Godbout, J.P. Microglia Priming with Aging and Stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antignano, I.; Liu, Y.; Offermann, N.; Capasso, M. Aging microglia. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, M.E.; Garza, R.; Sharma, Y.; Petri, R.; Sodersten, E.; Johansson, J.G.; Johansson, P.A.; Atacho, D.A.; Pircs, K.; Madsen, S.; et al. Activation of endogenous retroviruses during brain development causes an inflammatory response. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e106423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betjes, M.G.; Haks, M.C.; Tuk, C.W.; Beelen, R.H. Monoclonal antibody EBM11 (anti-CD68) discriminates between dendritic cells and macrophages after short-term culture. Immunobiology 1991, 183, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeponteau, B. The heterochromatin loss model of aging. Exp. Gerontol. 1997, 32, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Valle, F.; Reddy, P.; Aguirre Vazquez, A.; Izpisua Belmonte, J.C. Reactivation of retrotransposable elements is associated with environmental stress and ageing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, V.; Seluanov, A.; Mita, P.; McKerrow, W.; Fenyo, D.; Boeke, J.D.; Linker, S.B.; Gage, F.H.; Kreiling, J.A.; Petrashen, A.P.; et al. The role of retrotransposable elements in ageing and age-associated diseases. Nature 2021, 596, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, R.; Atacho, D.A.M.; Adami, A.; Gerdes, P.; Vinod, M.; Hsieh, P.; Karlsson, O.; Horvath, V.; Johansson, P.A.; Pandiloski, N.; et al. LINE-1 retrotransposons drive human neuronal transcriptome complexity and functional diversification. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh9543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubersax, J.A.; Ferrell, J.E., Jr. Mechanisms of specificity in protein phosphorylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, P.R.; Jones, C.E.; Furano, A.V. Phosphorylation of ORF1p is required for L1 retrotransposition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4298–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, C.; Gupta, A.; Bortvin, A. Retrotransposon LINE-1 bodies in the cytoplasm of piRNA-deficient mouse spermatocytes: Ribonucleoproteins overcoming the integrated stress response. PLoS Genet. 2023, 19, e1010797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewannieux, M.; Esnault, C.; Heidmann, T. LINE-mediated retrotransposition of marked Alu sequences. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, R.N., 2nd; Vandewege, M.W.; Ray, D.A. Mammalian transposable elements and their impacts on genome evolution. Chromosome Res. 2018, 26, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreani, L.; Ansaloni, F.; Mangoni, D.; Agostoni, E.; Sanges, R.; Persichetti, F.; Gustincich, S. Analysis of LINE1 Retrotransposons in Huntington’s Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 743797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coufal, N.G.; Garcia-Perez, J.L.; Peng, G.E.; Yeo, G.W.; Mu, Y.; Lovci, M.T.; Morell, M.; O’Shea, K.S.; Moran, J.V.; Gage, F.H. L1 retrotransposition in human neural progenitor cells. Nature 2009, 460, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cecco, M.; Ito, T.; Petrashen, A.P.; Elias, A.E.; Skvir, N.J.; Criscione, S.W.; Caligiana, A.; Brocculi, G.; Adney, E.M.; Boeke, J.D.; et al. L1 drives IFN in senescent cells and promotes age-associated inflammation. Nature 2019, 566, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Haq, I.; Ngo, J.C.; Bennett, D.A.; Teich, A.F.; De Jager, P.L.; Olah, M.; Sher, F. Elevated expression of the retrotransposon LINE-1 drives Alzheimer’s disease-associated microglial dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol. 2024, 148, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolicelli, R.C.; Bolasco, G.; Pagani, F.; Maggi, L.; Scianni, M.; Panzanelli, P.; Giustetto, M.; Ferreira, T.A.; Guiducci, E.; Dumas, L.; et al. Synaptic pruning by microglia is necessary for normal brain development. Science 2011, 333, 1456–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles-Saiz, L.; Avila, J.; Hernandez, F. Lamivudine (3TC), a Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor, Prevents the Neuropathological Alterations Present in Mutant Tau Transgenic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vallés-Saiz, L.; Abdelkader-Guillén, A.; Ávila, J.; Hernández, F. Retrotransposon Protein L1 ORF1p Expression in Aging Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094368
Vallés-Saiz L, Abdelkader-Guillén A, Ávila J, Hernández F. Retrotransposon Protein L1 ORF1p Expression in Aging Central Nervous System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094368
Chicago/Turabian StyleVallés-Saiz, Laura, Aaron Abdelkader-Guillén, Jesús Ávila, and Félix Hernández. 2025. "Retrotransposon Protein L1 ORF1p Expression in Aging Central Nervous System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094368
APA StyleVallés-Saiz, L., Abdelkader-Guillén, A., Ávila, J., & Hernández, F. (2025). Retrotransposon Protein L1 ORF1p Expression in Aging Central Nervous System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094368






