USO1 Coordinates Centriolar Satellites to Regulate Male Germ Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
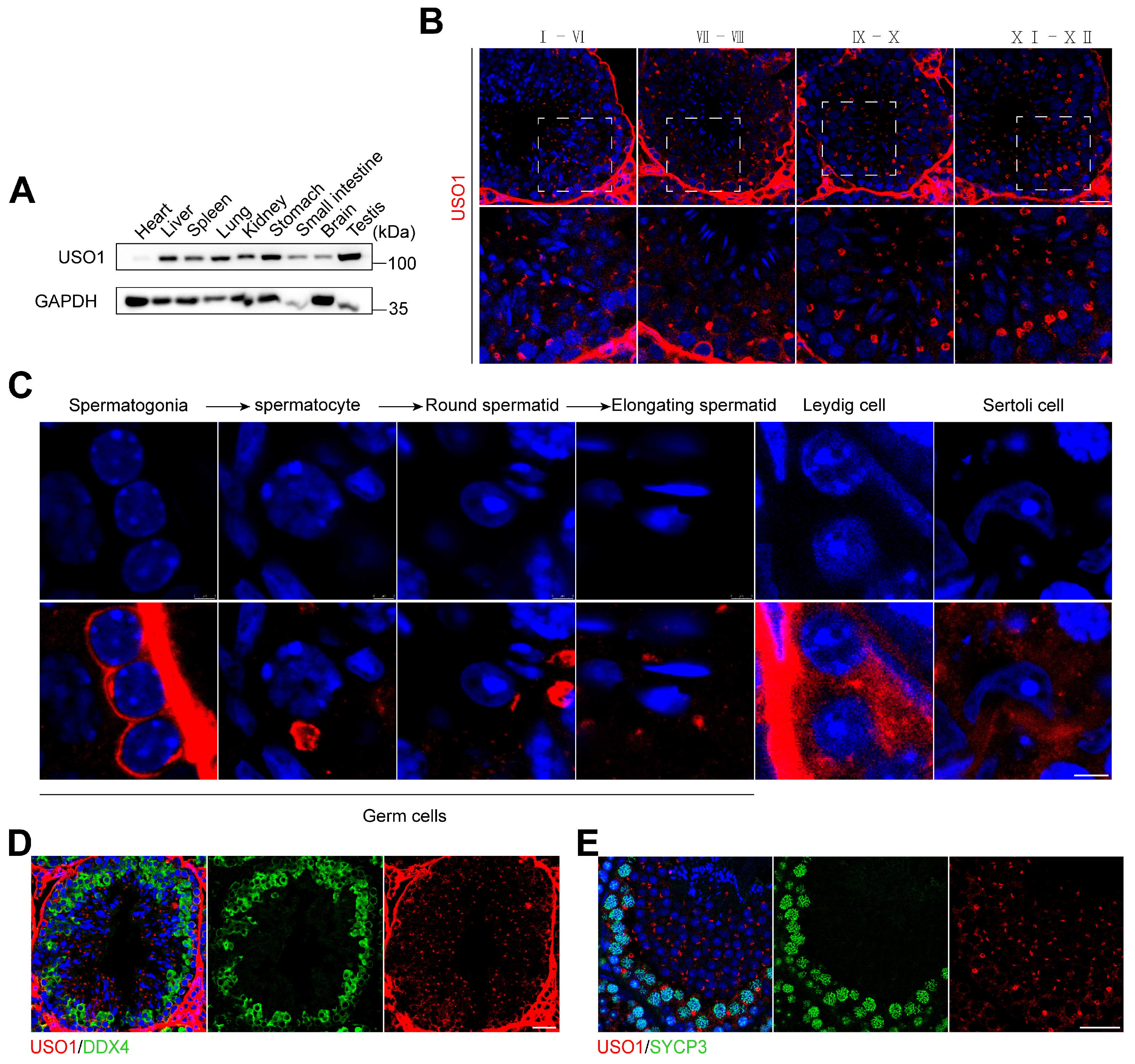
2.1. USO1 Expression in Mouse Germ Cells During Spermatogenesis
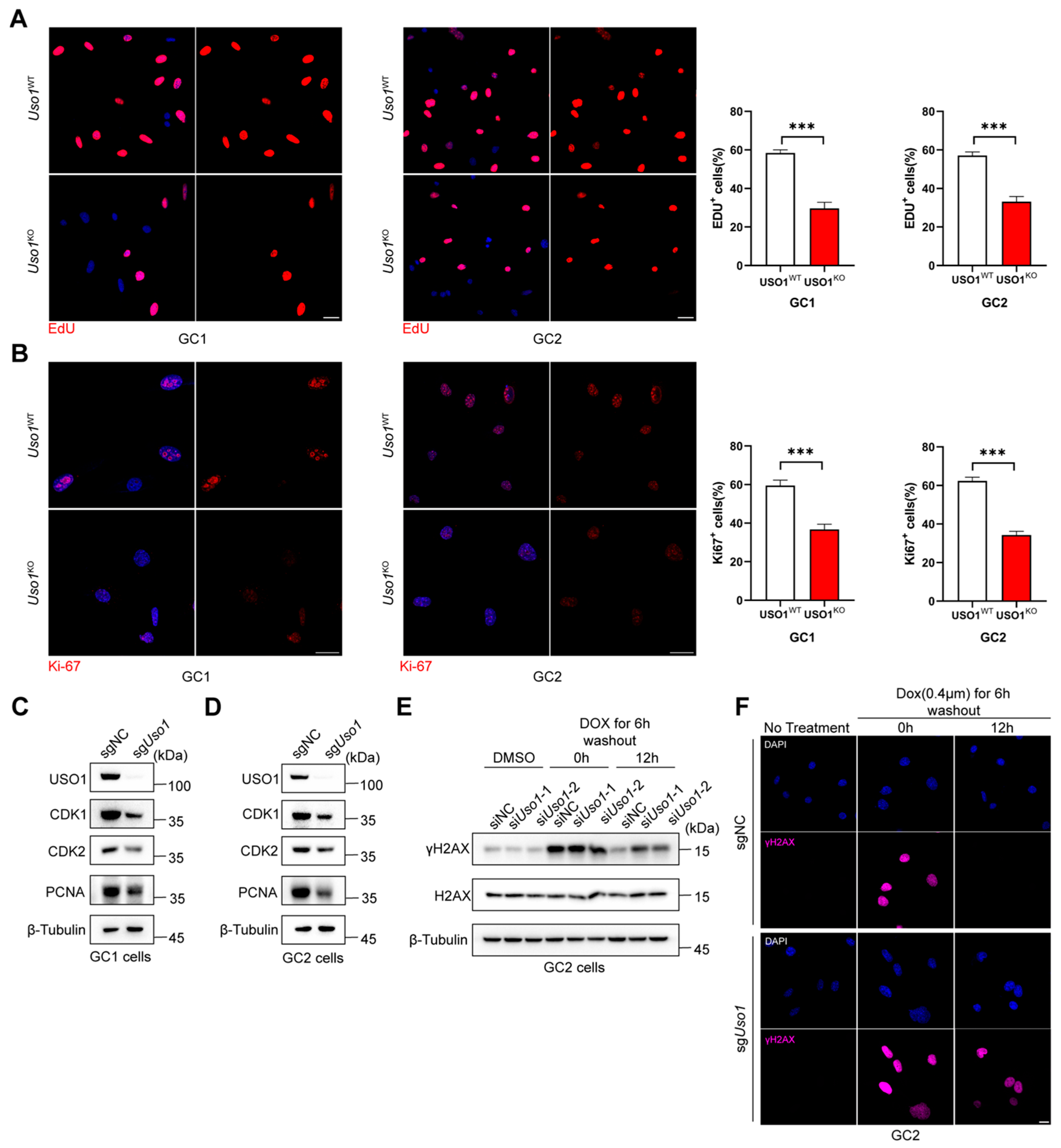
2.2. Uso1 Depletion Inhibits Germ Cell Proliferation and Impairs DNA Damage Repair
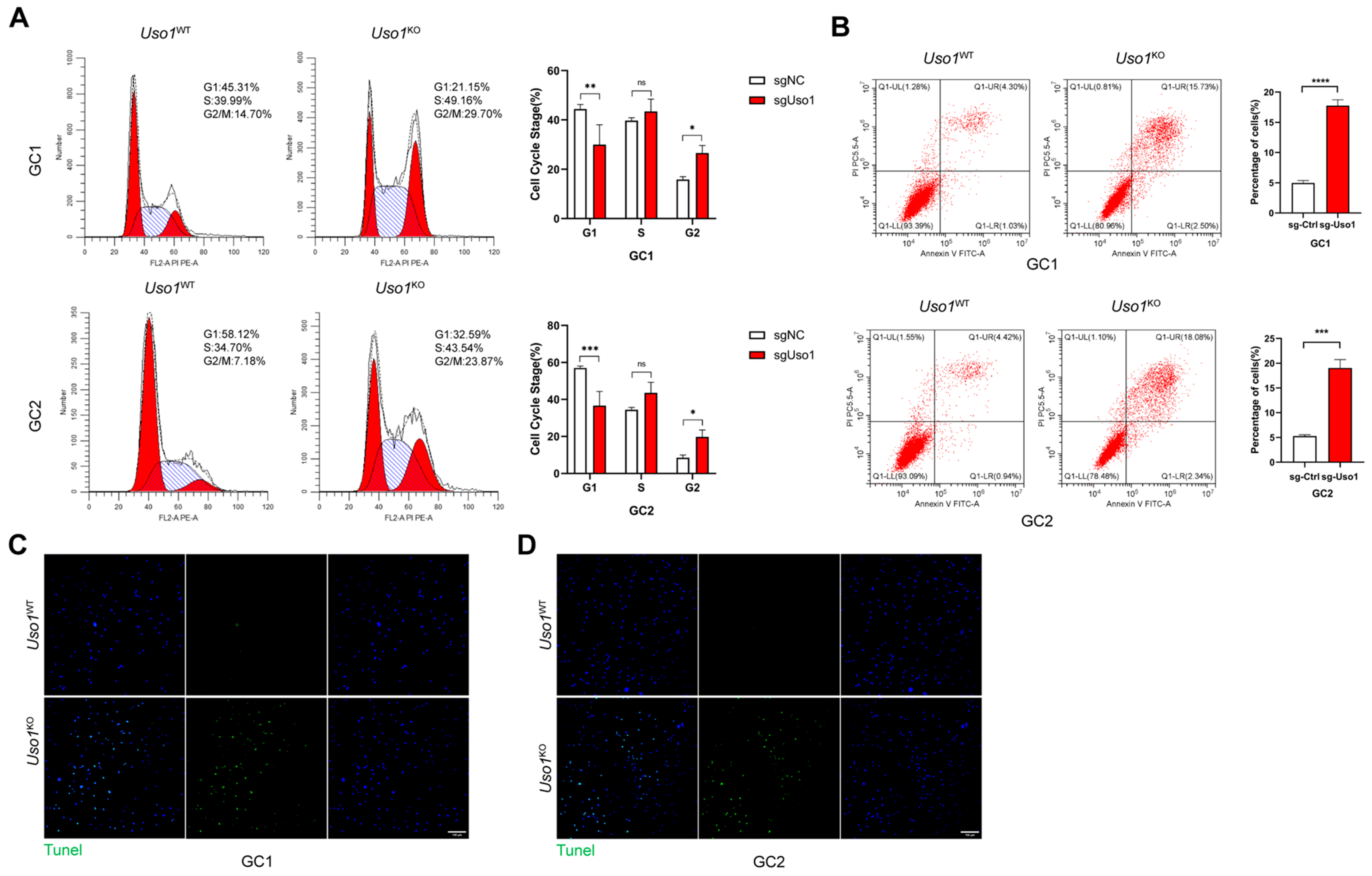
2.3. Uso1 Knockout Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in GC1 and GC2 Cells
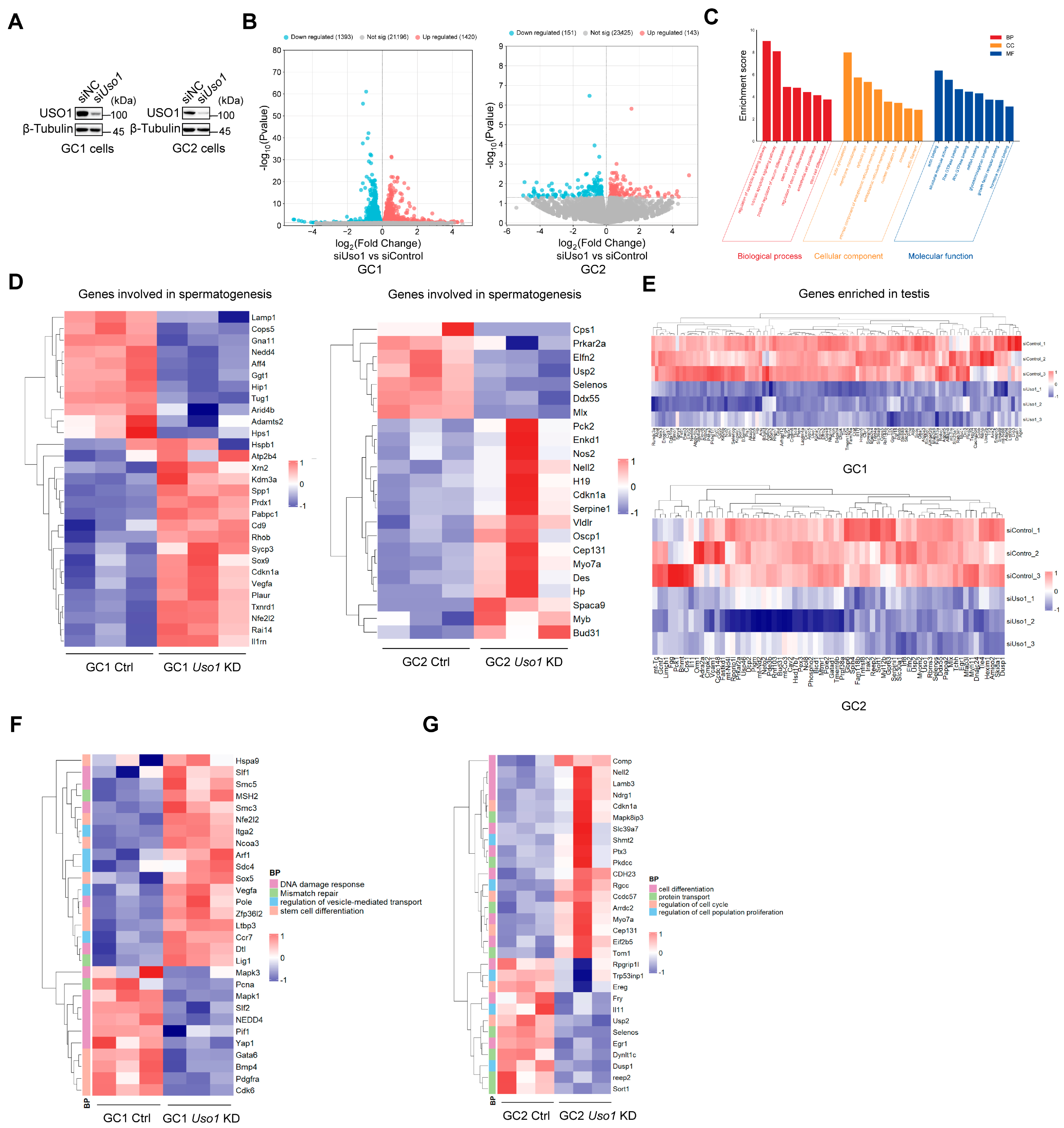
2.4. Knockdown of Uso1 Causes Transcriptional Dysregulation in GC1 and GC2 Cells
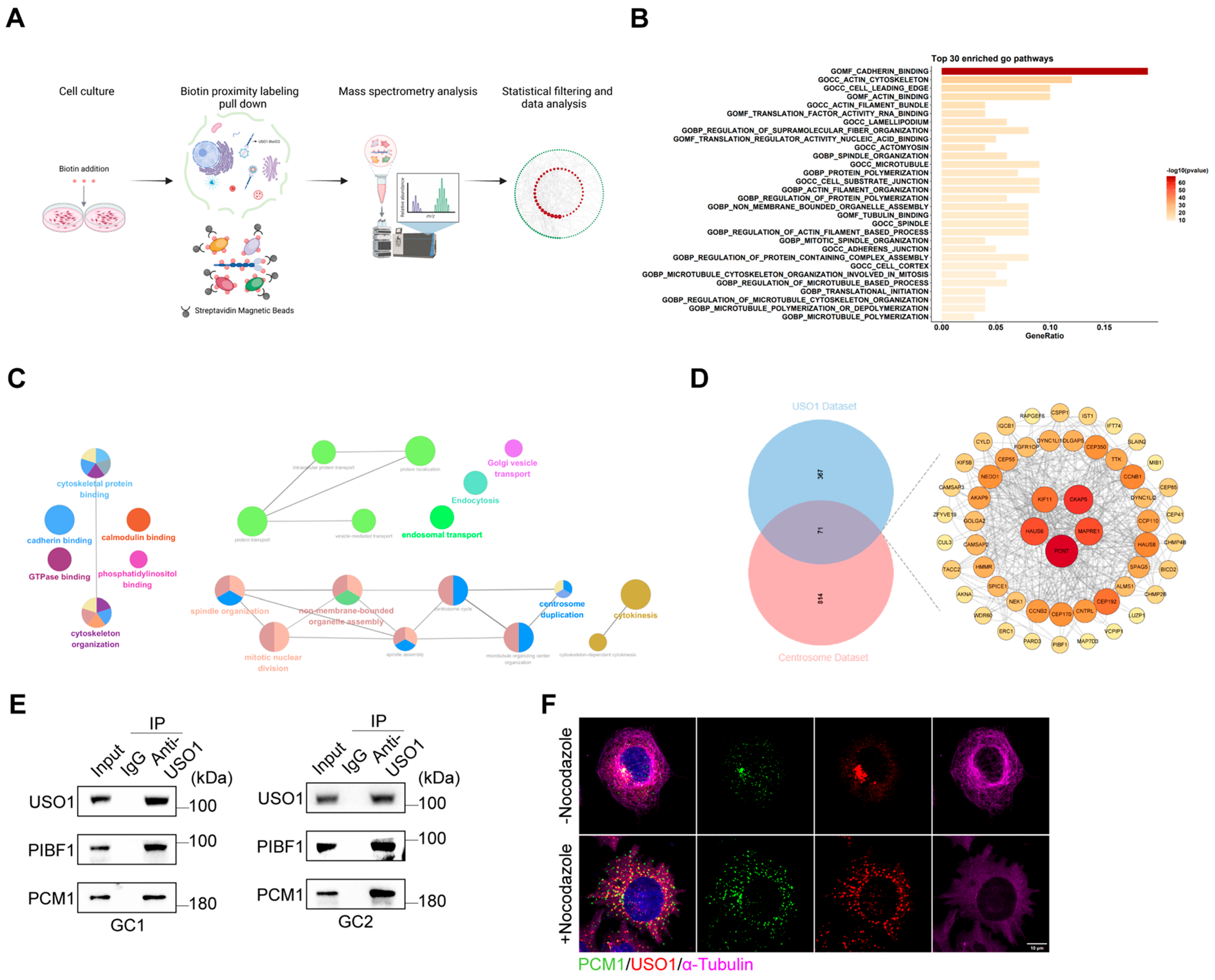
2.5. USO1 Associates with Centriolar Satellite Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Histological Analyses and Immunostaining
4.2. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.3. Western Blotting
4.4. Establishment of Stable Uso1-Knockout Cells
4.5. Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)-Mediated Knockdown
4.6. Cell Cycle Analysis and Cell Apoptosis Assay
4.7. RNA Sequencing Analysis
4.8. Proximity-Dependent Biotin Identification (BioID) Coupled to Affinity Capture and Mass Spectrometry (MS)
4.8.1. Cloning and Constructs
4.8.2. Biotin Proximity Labeling Pulldown and Mass Spectrometry
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griswold, M.D. Spermatogenesis: The Commitment to Meiosis. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, W.J.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Y.K.; Wu, Y.W.; Jiang, Y.; Liao, X.Q.; Huang, F.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; et al. NAT10-mediated N4-acetylcytidine modification is required for meiosis entry and progression in male germ cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 10896–10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Cheng, K.; Kubota, H.; Lan, Y.; Riedel, S.S.; Kakiuchi, K.; Sasaki, K.; Bernt, K.M.; Bartolomei, M.S.; Luo, M.; et al. Histone methyltransferase DOT1L is essential for self-renewal of germline stem cells. Genes Dev. 2022, 36, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.F.; Tan-Tai, W.J.; Li, X.H.; Liu, M.F.; Shi, H.J.; Martin-DeLeon, P.A.; O, W.S.; Chen, H. PHB regulates meiotic recombination via JAK2-mediated histone modifications in spermatogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 4780–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zheng, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Jin, P.; Wang, F. The m6A reader PRRC2A is essential for meiosis I completion during spermatogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, M.G.; Clary, D.O.; Rothman, J.E. A novel 115-kD peripheral membrane protein is required for intercisternal transport in the Golgi stack. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 118, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, C.; Garcia-Mata, R.; Hauri, H.P.; Sztul, E. The p115-interactive proteins GM130 and giantin participate in endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi traffic. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.; Warren, G. In situ cleavage of the acidic domain from the p115 tether inhibits exocytic transport. Traffic 2008, 9, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Davis, S.; Ferro-Novick, S.; Novick, P. Rewiring a Rab regulatory network reveals a possible inhibitory role for the vesicle tether, Uso1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8637–E8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, B.B.; Moyer, B.D.; Balch, W.E. Rab1 recruitment of p115 into a cis-SNARE complex: Programming budding COPII vesicles for fusion. Science 2000, 289, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.S.; Alvarez, C.; Gao, Y.S.; García-Mata, R.; Fialkowski, E.; Sztul, E. The membrane transport factor TAP/p115 cycles between the Golgi and earlier secretory compartments and contains distinct domains required for its localization and function. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthenveedu, M.A.; Linstedt, A.D. Evidence that Golgi structure depends on a p115 activity that is independent of the vesicle tether components giantin and GM130. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthenveedu, M.A.; Linstedt, A.D. Gene replacement reveals that p115/SNARE interactions are essential for Golgi biogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radulescu, A.E.; Mukherjee, S.; Shields, D. The Golgi protein p115 associates with gamma-tubulin and plays a role in Golgi structure and mitosis progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21915–21926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, R.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, H.; Ma, M.; Li, Z. A feedforward loop between JAK/STAT downstream target p115 and STAT in germline stem cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2023, 18, 1940–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duo, S.; Cui, X.; Bao, S.; et al. Globozoospermia and lack of acrosome formation in GM130-deficient mice. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audouard, C.; Christians, E. Hsp90β1 knockout targeted to male germline: A mouse model for globozoospermia. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 95, 1475–1477.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Ito, C.; Natsume, Y.; Sugitani, Y.; Yamanaka, H.; Kuretake, S.; Yanagida, K.; Sato, A.; Toshimori, K.; Noda, T. Lack of acrosome formation in mice lacking a Golgi protein, GOPC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11211–11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentson, L.F.; Agbor, V.A.; Agbor, L.N.; Lopez, A.C.; Nfonsam, L.E.; Bornstein, S.S.; Handel, M.A.; Linder, C.C. New point mutation in Golga3 causes multiple defects in spermatogenesis. Andrology 2013, 1, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funaki, T.; Kon, S.; Tanabe, K.; Natsume, W.; Sato, S.; Shimizu, T.; Yoshida, N.; Wong, W.F.; Ogura, A.; Ogawa, T.; et al. The Arf GAP SMAP2 is necessary for organized vesicle budding from the trans-Golgi network and subsequent acrosome formation in spermiogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 2633–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Kawabe, H.; Suzuki, A.; Shinmyozu, K.; Saga, Y. NEDD4 controls spermatogonial stem cell homeostasis and stress response by regulating messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, D.S.; Chang, J.C.; Kumar, P.D.; Mizukami, I.; Smithson, G.M.; Bradley, S.V.; Parlow, A.F.; Ross, T.S. Huntingtin interacting protein 1 Is a clathrin coat binding protein required for differentiation of late spermatogenic progenitors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 7796–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowski, J.P.; Dumbović, G.; Watson, A.R.; Hwang, T.; Jacobs-Palmer, E.; Chang, N.; Much, C.; Turner, K.M.; Kirby, C.; Rubinstein, N.D.; et al. The Tug1 lncRNA locus is essential for male fertility. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, R.; Zhang, H.; Kong, Y.; Li, K.; Dong, X.; Yan, J.; Han, J.; Feng, L. Different functions of biogenesis of lysosomal organelles complex 3 subunit 1 (Hps1) and adaptor-related protein complex 3, beta 1 subunit (Ap3b1) genes on spermatogenesis and male fertility. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2019, 31, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.D.; Coyaud, É.; Gonçalves, J.; Mojarad, B.A.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Gheiratmand, L.; Comartin, D.; Tkach, J.M.; Cheung, S.W.; et al. A Dynamic Protein Interaction Landscape of the Human Centrosome-Cilium Interface. Cell 2015, 163, 1484–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheiratmand, L.; Coyaud, E.; Gupta, G.D.; Laurent, E.M.; Hasegan, M.; Prosser, S.L.; Gonçalves, J.; Raught, B.; Pelletier, L. Spatial and proteomic profiling reveals centrosome-independent features of centriolar satellites. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkikas, I.; Daskalaki, I.; Kounakis, K.; Tavernarakis, N.; Lionaki, E. MitoSNARE Assembly and Disassembly Factors Regulate Basal Autophagy and Aging in C. Elegans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, P.C.; Shields, D. Tethering function of the caspase cleavage fragment of Golgi protein p115 promotes apoptosis via a p53-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8565–8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Shields, D. Nuclear import is required for the pro-apoptotic function of the Golgi protein p115. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, R.; Novikov, L.; Mukherjee, S.; Shields, D. A caspase cleavage fragment of p115 induces fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus and apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Li, X.; Xing, J.; Cao, F.; Wang, H.; Gong, H.; Zhang, W. Lentivirus-mediated silencing of USO1 inhibits cell proliferation and migration of human colon cancer cells. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millarte, V.; Boncompain, G.; Tillmann, K.; Perez, F.; Sztul, E.; Farhan, H. Phospholipase C γ1 regulates early secretory trafficking and cell migration via interaction with p115. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 2263–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, P.; Kan, C.F.K.; Singh, A.B.; Rius, M.; Kraemer, F.B.; Sztul, E.; Liu, J. Identification of p115 as a novel ACSL4 interacting protein and its role in regulating ACSL4 degradation. J. Proteom. 2020, 229, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.T.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Song, L.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z.Q.; Han, A. Atypical Legionella GTPase effector hijacks host vesicular transport factor p115 to regulate host lipid droplet. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eadd7945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Dai, Z. USO1 promotes tumor progression via activating Erk pathway in multiple myeloma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 78, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.K.; Truong, H.; Tran, T.M.; Lin, T.L.; Casero, D.; Alberti, M.O.; Rao, D.S. Focused CRISPR-Cas9 genetic screening reveals USO1 as a vulnerability in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, M.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Song, H.; Weng, X.; Mi, J.; et al. A novel KMT2A-USO1 fusion gene-induced de novo secondary acute myeloid leukaemia in a patient initially diagnosed with acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 192, e32–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Deng, G.; Su, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Song, S.; Peng, X.; Chen, F. A novel all-trans retinoic acid derivative regulates cell cycle and differentiation of myelodysplastic syndrome cells by USO1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 906, 174199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Luo, Y.; Yi, Y.F. P115 promotes growth of gastric cancer through interaction with macrophage migration inhibitory factor. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 8619–8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, A.; Ryan, L.; Nur, M.M.; Baird, A.M.; Nicholson, S.; Cuffe, S.; Fitzmaurice, G.J.; Ryan, R.; Young, V.K.; Finn, S.P.; et al. USO1 expression is dysregulated in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 1877–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Choi, J.H.; Shah, M.; Kwon, S.M.; Yang, J.; Park, Y.N.; Wang, H.J.; Woo, H.G. USO1 isoforms differentially promote liver cancer progression by dysregulating the ER-Golgi network. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarantotti, V.; Chen, J.; Tischer, J.; Tejedo, C.G.; Papachristou, E.K.; D’Santos, C.S.; Kilmartin, J.V.; Miller, M.L.; Gergely, F. Centriolar satellites are acentriolar assemblies of centrosomal proteins. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e101082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.A.M.; Prosser, S.L.; Romio, L.; Hirst, R.A.; O’Callaghan, C.; Woolf, A.S.; Fry, A.M. Centriolar satellites are assembly points for proteins implicated in human ciliopathies, including oral-facial-digital syndrome 1. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124 Pt 4, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staples, C.J.; Myers, K.N.; Ryan, D.D.B.; Patil, A.A.; Lee, A.J.X.; Swanton, C.; Howell, M.; Boulton, S.J.; Collis, S.J. The centriolar satellite protein Cep131 is important for genome stability. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125 Pt 20, 4770–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staples, C.J.; Myers, K.N.; Beveridge, R.D.D.; Patil, A.A.; Howard, A.E.; Barone, G.; Lee, A.J.X.; Swanton, C.; Howell, M.; Maslen, S.; et al. Ccdc13 is a novel human centriolar satellite protein required for ciliogenesis and genome stability. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127 Pt 13, 2910–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, K.J.; Kim, D.I.; Raida, M.; Burke, B. A promiscuous biotin ligase fusion protein identifies proximal and interacting proteins in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Lin, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, R.; Cai, J.; Feng, X.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, S.; Xie, Y. USO1 Coordinates Centriolar Satellites to Regulate Male Germ Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094274
Li X, Lin P, Zhang Z, Wang R, Cai J, Feng X, Jiang Z, Xu S, Xie Y. USO1 Coordinates Centriolar Satellites to Regulate Male Germ Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094274
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinyi, Peiyi Lin, Zaikuan Zhang, Runzhi Wang, Jing Cai, Xiaosong Feng, Zhihong Jiang, Shengming Xu, and Yajun Xie. 2025. "USO1 Coordinates Centriolar Satellites to Regulate Male Germ Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094274
APA StyleLi, X., Lin, P., Zhang, Z., Wang, R., Cai, J., Feng, X., Jiang, Z., Xu, S., & Xie, Y. (2025). USO1 Coordinates Centriolar Satellites to Regulate Male Germ Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094274




