A Novel Homozygous 9385 bp Deletion in the FERMT1 (KIND1) Gene in a Malaysian Family with Kindler Epidermolysis bullosa and a Review of Large Deletions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
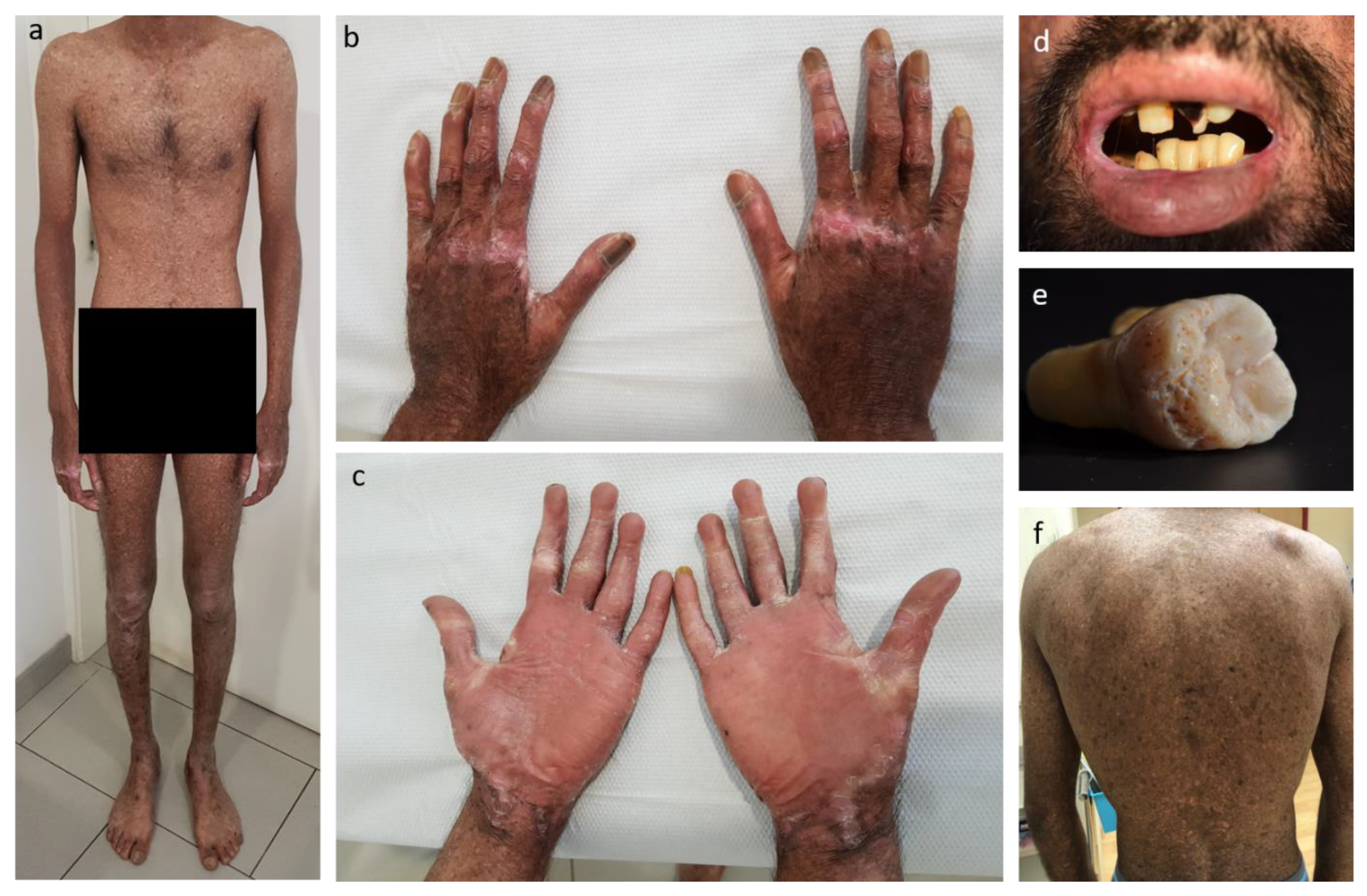
2.1. The Patient
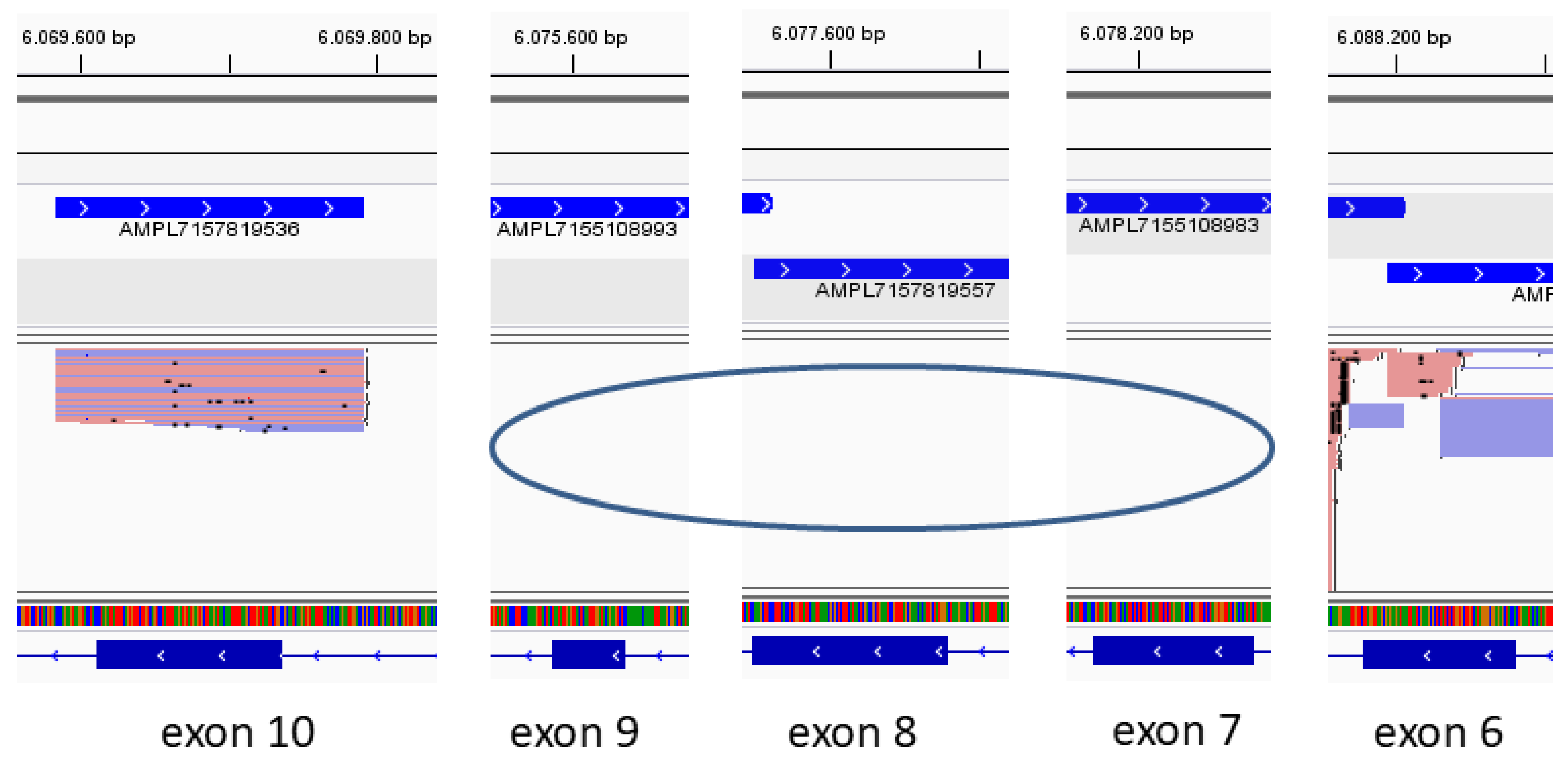
2.2. NGS-Based Variant Analysis
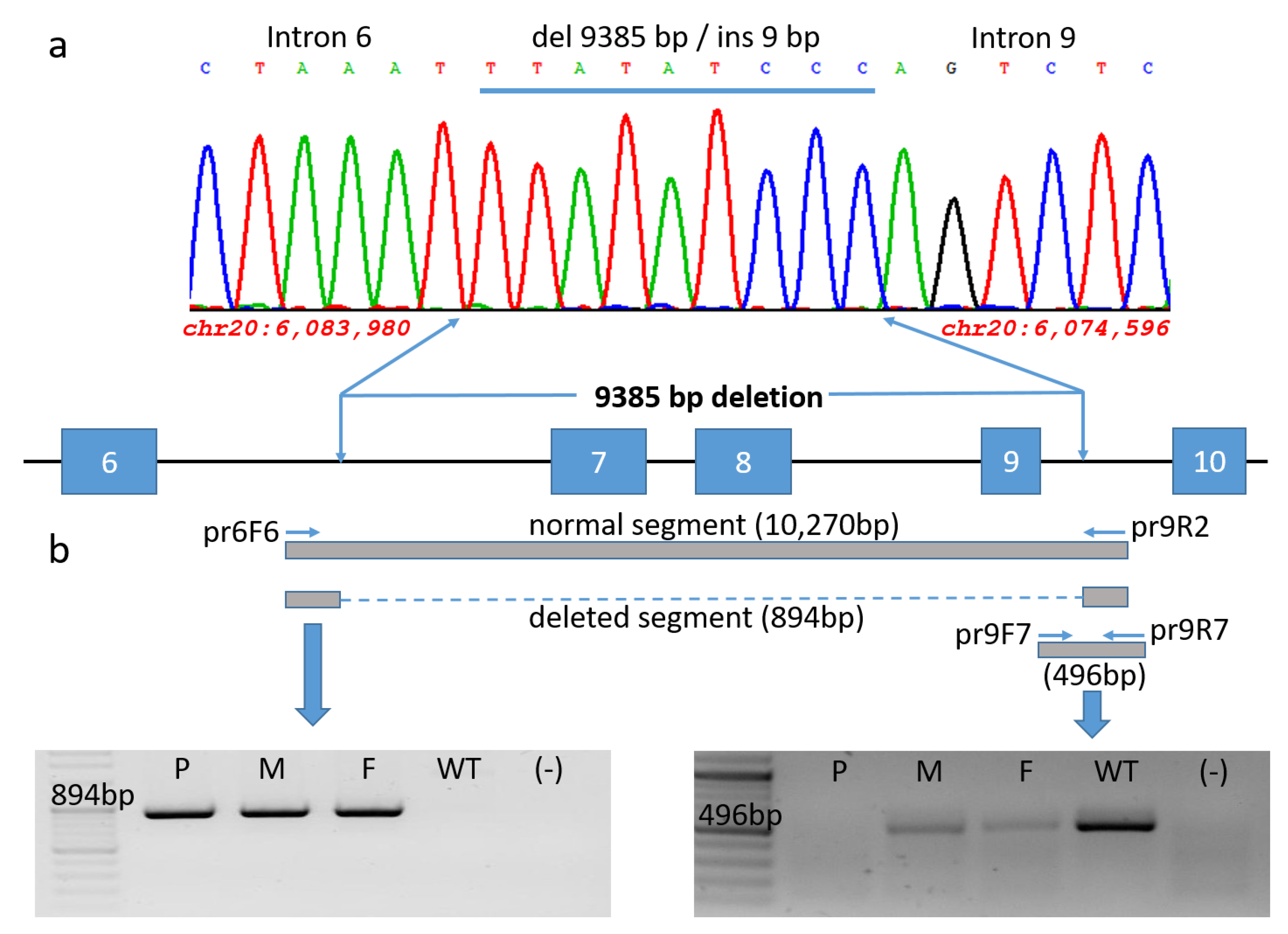
2.3. Variant Identification and Sequence Analysis
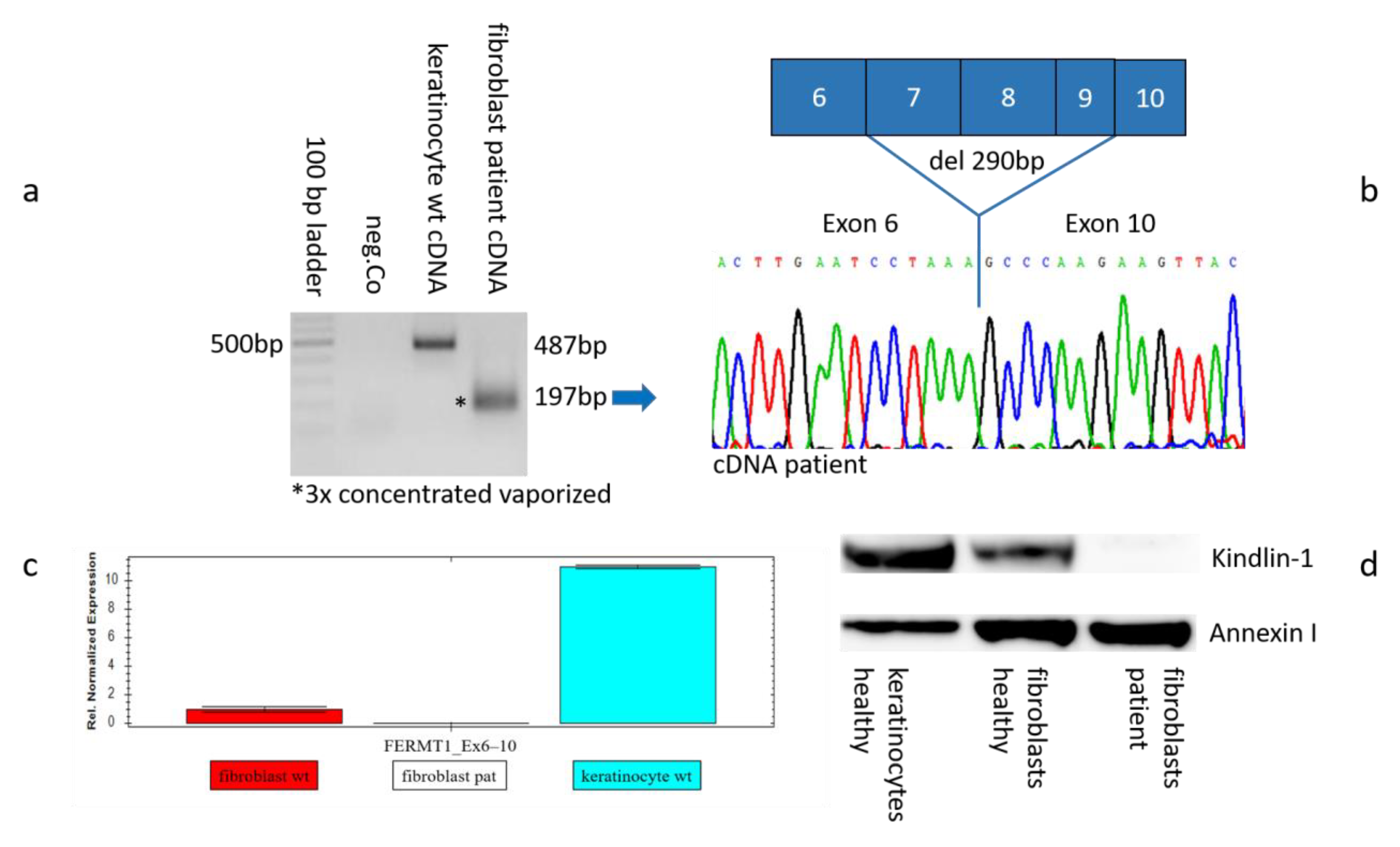
2.4. Genetic Analysis on mRNA Level
2.5. Gene Expression on RNA and Protein Levels
3. Discussion
- Most of them are out-of-frame deletions and affect one or more exons.
- Only one deletion, affecting exons 2–6, is reported to be in-frame with the annotation that the deletion range also contains the translation initiation site (TIS) ATG located in exon 2 [17].
- A deletion eliminating exons 14 and 15 extended beyond the FERMT1 coding region and 3′UTR, leading to partial mRNA decay [16].
- A large deletion (g.-711-1241del), that spanned the putative FERMT1 promoter sequence and the first noncoding exon of the gene including the predicted transcription start site, was associated with a complete blockade and prevention of FERMT1 transcription [18].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Approval
4.2. NGS-Based Variant Analysis
4.3. Primary Cell Isolation
4.4. PCR and Sanger Sequencing
4.5. Real-Time PCR
4.6. Protein Isolation and Western Blot
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FERMT1 | Fermitin Family Member 1 |
| bp | Base Pair |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| Co | Control |
| Del | Deletion |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| EB | Epidermolysis Bullosa |
| F | Father |
| GAPDH | Glycerinaldehyd-3-phosphat-Dehydrogenase |
| GRCh37 | Genome Reference Consortium Human Build 37 |
| HGMD | Human Genome Mutation Database |
| IGV | Integrative Genome Viewer |
| Ins | Insertion |
| JEB | Junctional Epidermolysis bullosa |
| kb | Kilo base |
| KEB | Kindler Epidermolysis bullosa |
| KIND1 | Kindlin 1 |
| LAMB3 | Laminin, beta 3 |
| M | Mother |
| mRNA | Messenger Ribonucleic Acid |
| NGS | Next Generation Sequencing |
| OMIM | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |
| P | Patient |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RT | Revere Transcription |
| UV-B | Ultraviolet-B |
References
- Kindler, T. Congenital Poikiloderma with Traumatic Bulla Formation and Progressive Cutaneous Atrophy. Br. J. Dermatol. 1954, 66, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Has, C.; Bauer, J.W.; Bodemer, C.; Bolling, M.C.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Diem, A.; Fine, J.-D.; Heagerty, A.; Hovnanian, A.; Marinkovich, M.P.; et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, I.A.; Kazandjieva, J.; Vassileva, S.; Dourmishev, A. Kindler syndrome: A case report and proposal for clinical diagnostic criteria. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 2005, 14, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G. A novel frameshift mutation in the FERMT1 gene in a Chinese patient with Kindler syndrome. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, E.; Klausegger, A.; Muss, W.; Deinsberger, U.; Pohla-Gubo, G.; Laimer, M.; Lanschuetzer, C.; Bauer, J.W.; Hintner, H. Novel KIND1 gene mutation in Kindler syndrome with severe gastrointestinal tract involvement. Arch. Dermatol. 2006, 142, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopkar, A.; Malpani, S.S.; Supekar, B.B.; Mukhi, J.I. Kindler syndrome: A rare case report. J. Clin. Images Med. Case Rep. 2021, 2, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.H.; Ashton, G.H.S.; Penagos, H.G.; Lee, J.V.; Feiler, H.S.; Wilhelmsen, K.C.; South, A.P.; Smith, F.J.D.; Prescott, A.R.; Wessagowit, V.; et al. Loss of kindlin-1, a human homolog of the Caenorhabditis elegans actin-extracellular-matrix linker protein UNC-112, causes Kindler syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 73, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Has, C.; Castiglia, D.; del Rio, M.; Diez, M.G.; Piccinni, E.; Kiritsi, D.; Kohlhase, J.; Itin, P.; Martin, L.; Fischer, J.; et al. Kindler syndrome: Extension of FERMT1 mutational spectrum and natural history. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, K.; He, Y.; Wölfle, U.; Esser, P.R.; Brummer, T.; Schempp, C.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Has, C. UV-B-induced cutaneous inflammation and prospects for antioxidant treatment in Kindler syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 5339–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martignago, B.; Lai-Cheong, J.; Liu, L.; Mc Grath, J.; Cestari, T. Recurrent KIND1 (C20orf42) gene mutation, c.676insC, in a Brazilian pedigree with Kindler syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Song, S.; Zhang, J. A novel 3017-bp deletion mutation in the FERMT1 (KIND1) gene in a Chinese family with Kindler syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 160, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Has, C.; Wessagowit, V.; Pascucci, M.; Baer, C.; Didona, B.; Wilhelm, C.; Pedicelli, C.; Locatelli, A.; Kohlhase, J.; Ashton, G.H.; et al. Molecular basis of Kindler syndrome in Italy: Novel and recurrent Alu/Alu recombination, splice site, nonsense, and frameshift mutations in the KIND1 gene. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1776–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaçar, N.; Semerci, N.; Ergin, Ş.; Pascucci, M.; Zambruno, G.; Castiglia, D. A novel frameshift mutation in the KIND1 gene in Turkish siblings with Kindler syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 158, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Has, C.; Ludwig, R.; Herz, C.; Kern, J.; Ussar, S.; Ochsendorf, F.; Kaufmann, R.; Schumann, H.; Kohlhase, J.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L. C-terminally truncated kindlin-1 leads to abnormal adhesion and migration of keratinocytes. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 1192–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Has, C.; Yordanova, I.; Balabanova, M.; Kazandjieva, J.; Herz, C.; Kohlhase, J.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L. A novel large FERMT1 (KIND1) gene deletion in Kindler syndrome. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2008, 52, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bai, J.-L.; Liu, X.-Y.; Qu, Y.-J.; Cao, Y.-Y.; Wang, J.-C.; Jin, Y.-W.; Wang, H.; Song, F. A novel large deletion mutation of FERMT1 gene in a Chinese patient with Kindler syndrome. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2015, 16, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs-Telem, D.; Nousbeck, J.; Singer, A.; McGrath, J.A.; Sarig, O.; Sprecher, E. New intragenic and promoter region deletion mutations in FERMT1 underscore genetic homogeneity in Kindler syndrome. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 39, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Has, C.; Chmel, N.; Levati, L.; Neri, I.; Sonnenwald, T.; Pigors, M.; Godbole, K.; Dudhbhate, A.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Zambruno, G.; et al. FERMT1 promoter mutations in patients with Kindler syndrome. Clin. Genet. 2015, 88, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssefian, L.; Vahidnezhad, H.; Barzegar, M.; Li, Q.; Sotoudeh, S.; Yazdanfar, A.; Ehsani, A.H.; Kajbafzadeh, A.-M.; Mozafari, N.; Daryani, N.E.; et al. The Kindler syndrome: A spectrum of FERMT1 mutations in Iranian families. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1447–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidnezhad, H.; Youssefian, L.; Saeidian, A.H.; Touati, A.; Sotoudeh, S.; Abiri, M.; Barzegar, M.; Aghazadeh, N.; Mahmoudi, H.; Norouz-Zadeh, S.; et al. Multigene Next-Generation Sequencing Panel Identifies Pathogenic Variants in Patients with Unknown Subtype of Epidermolysis Bullosa: Subclassification with Prognostic Implications. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2649–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushi, R.; Tsuboi, R.; Maeda, T.; Kanda, Y.; Sakai, N.; Suzuki, S.; Harada, K. A case of Kindler syndrome in a young Indian female with exon deletion. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 58, e19–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugmans, L.; Kanaar, R.; Essers, J. Analysis of DNA double-strand break repair pathways in mice. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2007, 614, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffolatti, L.; Cardazzo, B.; Nobile, C.; Danieli, G.; Gualandi, F.; Muntoni, F.; Abbs, S.; Zanetti, P.; Angelini, C.; Ferlini, A. Investigating the mechanism of chromosomal deletion: Characterization of 39 deletion breakpoints in introns 47 and 48 of the human dystrophin gene. Genomics 2002, 80, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüdiger, N.S.; Gregersen, N.; Kielland-Brandt, M.C. One short well conserved region of Alu-sequences is involved in human gene rearrangements and has homology with prokaryotic chi. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobard, F.; Bouadjar, B.; Caux, F.; Hadj-Rabia, S.; Has, C.; Matsuda, F.; Weissenbach, J.; Lathrop, M.; Prud’Homme, J.-F.; Fischer, J. Identification of mutations in a new gene encoding a FERM family protein with a pleckstrin homology domain in Kindler syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Has, C.; Kiritsi, D.; Mellerio, J.E.; Franzke, C.-W.; Wedgeworth, E.; Tantcheva-Poor, I.; Kernland-Lang, K.; Itin, P.; Simpson, M.A.; Dopping-Hepenstal, P.J.; et al. The missense mutation p.R1303Q in type XVII collagen underlies junctional epidermolysis bullosa resembling Kindler syndrome. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai-Cheong, J.; Ussar, S.; Arita, K.; Hart, I.; McGrath, J. Colocalization of kindlin-1, kindlin-2, and migfilin at keratinocyte focal adhesion and relevance to the pathophysiology of Kindler syndrome. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidnezhad, H.; Youssefian, L.; Saeidian, A.H.; Boyden, L.M.; Touati, A.; Harvey, N.; Naji, M.; Zabihi, M.; Barzegar, M.; Sotoudeh, S.; et al. Kindler epidermolysis bullosa-like skin phenotype and downregulated basement membrane zone gene expression in poikiloderma with neutropenia and a homozygous USB1 mutation. Matrix Biol. 2021, 99, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, S.M.; Cowin, A.J.; Copeland, B.; Baleato, R.M.; Miyazaki, K.; Ashman, L.K. The role of the tetraspanin CD151 in primary keratinocyte and fibroblast functions: Implications for wound healing. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowin, A.J.; Adams, D.; Geary, S.M.; Wright, M.D.; Jones, J.C.; Ashman, L.K. Wound healing is defective in mice lacking tetraspanin CD151. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahidnezhad, H.; Youssefian, L.; Saeidian, A.H.; Mahmoudi, H.; Touati, A.; Abiri, M.; Kajbafzadeh, A.-M.; Aristodemou, S.; Liu, L.; McGrath, J.A.; et al. Recessive mutation in tetraspanin CD151 causes Kindler syndrome-like epidermolysis bullosa with mul-ti-systemic manifestations including nephropathy. Matrix Biol. 2018, 66, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, U.; Hainzl, S.; Kocher, T.; Hüttner, C.; Klausegger, A.; Gruber, C.; Mayr, E.; Wally, V.; Bauer, J.W.; Murauer, E.M. Trans-splicing improvement by the combined application of antisense strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Size | Primer Reverse | Primer Forward | Diagnostic PCR | Reference | Exon | Deletion | Variant | Geographic Origin | Consanguinity | Sex | Age | Patient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 362 bp | GTGCATGTGTTGCTACGTGC | TGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACC | intron 9/11 | [13] | 10–11 | 3919 bp | g.70250_74168del | Southern Italy (Calabria) | No | F | 41 | 1 |
| 362 bp | GTGCATGTGTTGCTACGTGC | TGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACC | intron 9/11 | [13] | 10–11 | 3919 bp | g.70250_74168del | Southern Italy (Calabria) | Yes | F | 16 | 2 |
| 362 bp | GTGCATGTGTTGCTACGTGC | TGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACC | intron 9/11 | [13] | 10–11 | 3919 bp | g.70250_74168del | Southern Italy (Calabria) | Yes | F | 25 | 3 |
| 2 kb | GGCTGCCAATAATGTTGGTT | CTTGCACCAGCTACCCTCTC | intron 13/15 | [16] | 14–15 | 8241 bp | g.80929_89169del * | Southern Bulgaria | No | M | 32 | 4 |
| 2 kb | GGCTGCCAATAATGTTGGTT | CTTGCACCAGCTACCCTCTC | intron 13/15 | [16] | 14–15 | 8241 bp | g.80929_89169del * | Southern Bulgaria | No | F | 28 | 5 |
| 2 kb | GGCTGCCAATAATGTTGGTT | CTTGCACCAGCTACCCTCTC | intron 13/15 | [16] | 14–15 | 8241 bp | g.80929_89169del * | Southern Bulgaria | No | F | 56 | 6 |
| 763 bp | ATGACAGAGCCCATTTCCTG | AGGCAAGCAGTTAGGCCTAAT | intron 1/6 | [17] | 2–6 | 17,251 bp | g.6121241_6103991del | China | Yes | F | 7 | 7 |
| 425 bp | CTTGGCATTGAACTGTTCGA | GGGGACAGAACAAGACTCCA | promoter/intron 1 | [18] | 1_TSS 2 | 1952 bp | g.-711-1241del | Middle Eastern | Yes | F | n.a. | 8 |
| 425 bp | CTTGGCATTGAACTGTTCGA | GGGGACAGAACAAGACTCCA | promoter/intron 1 | [18] | 1_TSS 2 | 1952 bp | g.-711-1241del | Middle Eastern | Yes | F | n.a. | 9 |
| 425 bp | CTTGGCATTGAACTGTTCGA | GGGGACAGAACAAGACTCCA | promoter/intron 1 | [18] | 1_TSS 2 | 1952 bp | g.-711-1241del | Middle Eastern | Yes | M | n.a. | 10 |
| 425 bp | CTTGGCATTGAACTGTTCGA | GGGGACAGAACAAGACTCCA | promoter/intron 1 | [18] | 1_TSS 2 | 1952 bp | g.-711-1241del | Middle Eastern | Yes | M | n.a. | 11 |
| 2693 bp | GCTCTCCAGGGCATTACAAG | CAATGCCACAGAAAGCTGAA | promo1/intron 1 | [19] | 1_TSS 2 | 38,222 bp | g.6140393_6102171 delinsCAAACTGA | India | Yes | M | 4 | 12 |
| 425 bp | CTTGGCATTGAACTGTTCGA | GGGGACAGAACAAGACTCCA | promoter/intron 1 | [19] | 1_TSS 2 | 1952 bp | g.-711-1241del | Southern Italia (West Sicily) | No | M | 22 | 13 |
| 362 bp | GTGCATGTGTTGCTACGTGC | TGCCTGTAATCCCAGCTACC | intron 9/11 | [19] | 10–11 | 3919 bp | g.70250_74168del * | Southern Italia (West Sicily) | No | M | 15 | 14 |
| 400 bp | AGCCCAAGGGGAGGTATATT 3 | TGGCTCACGCCTGTAATTC 3 | intron 6/9 | [12] | 7–8–9 | 3017 bp | g.63601_66617del | China | Yes | M | 23 | 15 |
| 894 bp | GCCAAATATGAGGGCAATTTT | ACAATGCTTTACAGTGGCAAA | intron 6/9 | this study | 7–8–9 | 9385 bp | g.6083980_6074596 delinsTTATATCCC | Malaysia | Yes | M | 33 | 16 |
| n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | [20] | 5 | 2664 bp 1 | g.6109607_6112272del | Iran | Yes | n.a. | n.a. | 17 |
| n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | [21] | 10 | 7055 bp | c.(1139+1_1265-1)del | Turkey | Yes | F | 13 | 18 |
| n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | [22] | 10–11 | not defined | not defined | India | Yes | F | 21 | 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klausegger, A.; Leditzky, F.; Krämer, S.; Palisson, F.; Yubero, M.J.; Véliz, S.; Koh, M.J.A.; Tan, E.-C.; Laimer, M.; Bauer, J.W.; et al. A Novel Homozygous 9385 bp Deletion in the FERMT1 (KIND1) Gene in a Malaysian Family with Kindler Epidermolysis bullosa and a Review of Large Deletions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094237
Klausegger A, Leditzky F, Krämer S, Palisson F, Yubero MJ, Véliz S, Koh MJA, Tan E-C, Laimer M, Bauer JW, et al. A Novel Homozygous 9385 bp Deletion in the FERMT1 (KIND1) Gene in a Malaysian Family with Kindler Epidermolysis bullosa and a Review of Large Deletions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094237
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlausegger, Alfred, Fabian Leditzky, Susanne Krämer, Francis Palisson, María Joao Yubero, Sebastián Véliz, Mark Jean Aan Koh, Ene-Choo Tan, Martin Laimer, Johann Wolfgang Bauer, and et al. 2025. "A Novel Homozygous 9385 bp Deletion in the FERMT1 (KIND1) Gene in a Malaysian Family with Kindler Epidermolysis bullosa and a Review of Large Deletions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094237
APA StyleKlausegger, A., Leditzky, F., Krämer, S., Palisson, F., Yubero, M. J., Véliz, S., Koh, M. J. A., Tan, E.-C., Laimer, M., Bauer, J. W., & Fuentes, I. (2025). A Novel Homozygous 9385 bp Deletion in the FERMT1 (KIND1) Gene in a Malaysian Family with Kindler Epidermolysis bullosa and a Review of Large Deletions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094237






