HMGB1 Regulates Adipocyte Lipolysis via Caveolin-1 Signaling: Implications for Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
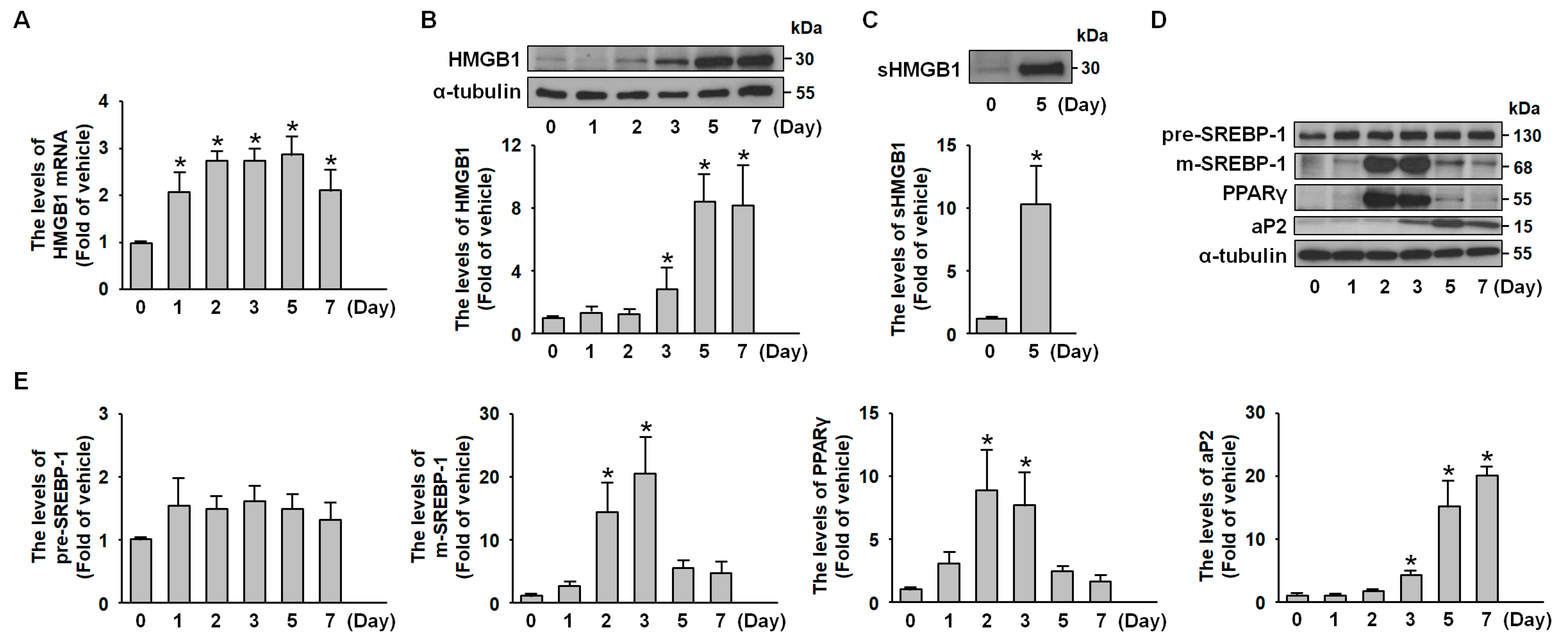
2.1. HMGB1 Expression Is Increased During 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Differentiation
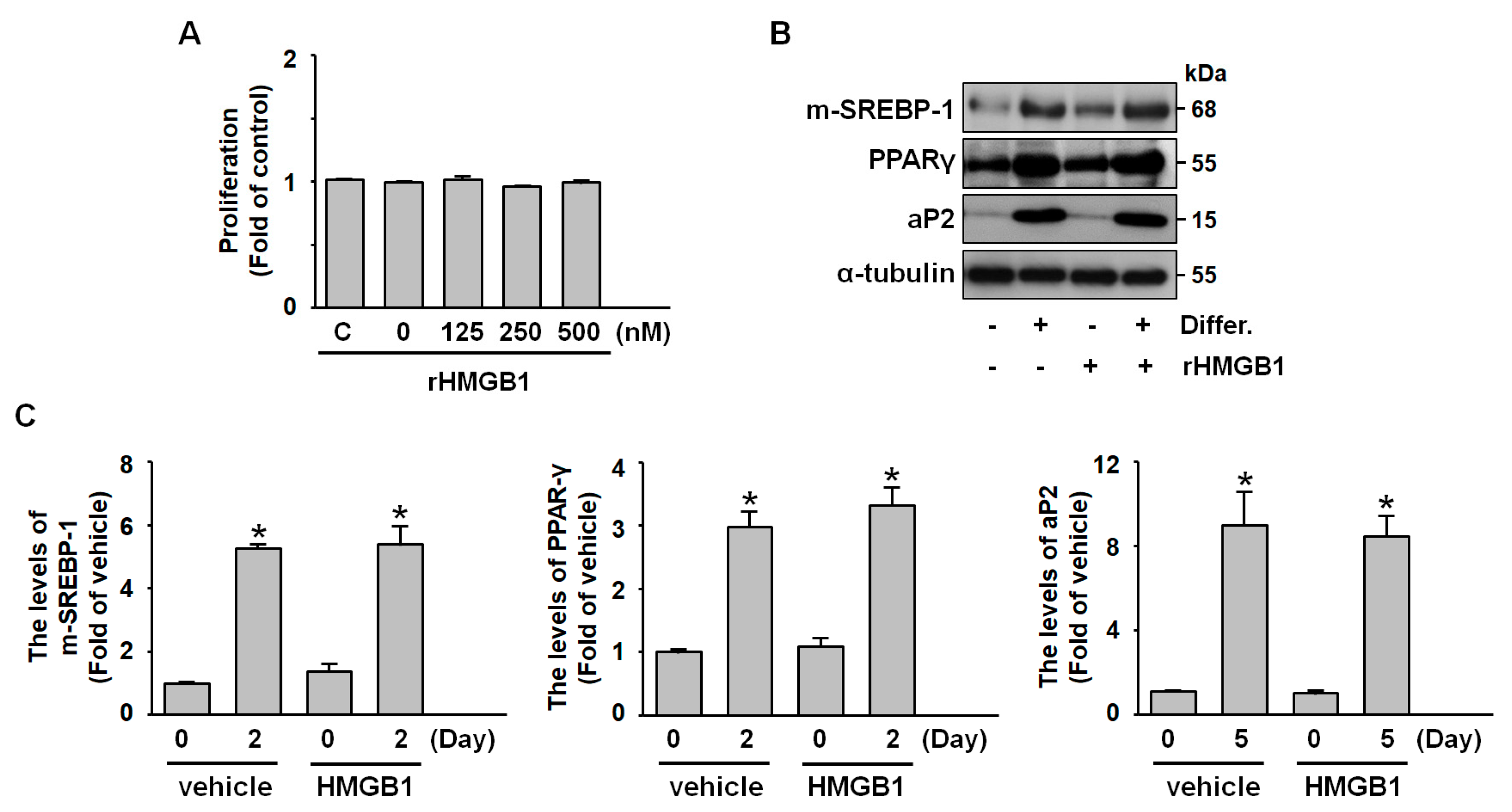
2.2. Exogenous HMGB1 Does Not Affect Adipogenesis, Including Preadipocyte Proliferation and Differentiation
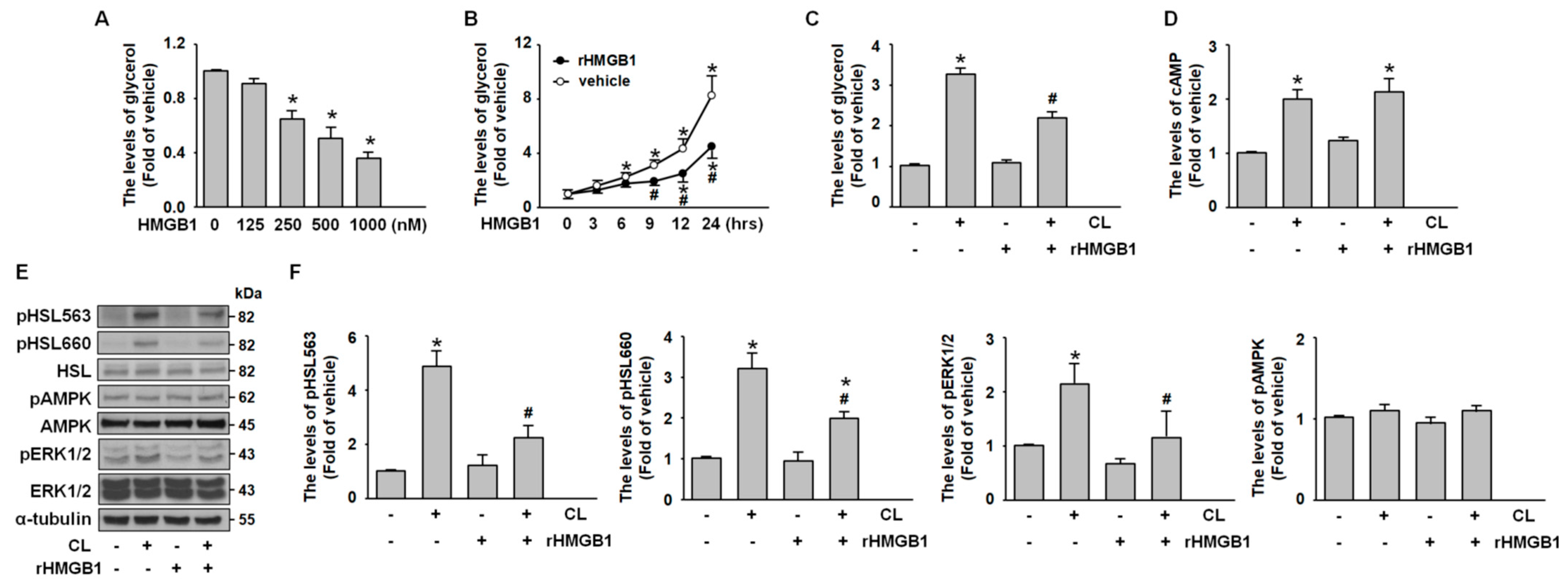
2.3. CL-316,243 Induces Adipocyte Lipolysis via PKA- and ERK-Mediated HSL Activation
2.4. HMGB1 Suppresses Adipocyte Lipolysis by Inhibiting PKA-HSL Phosphorylation and ERK Activation
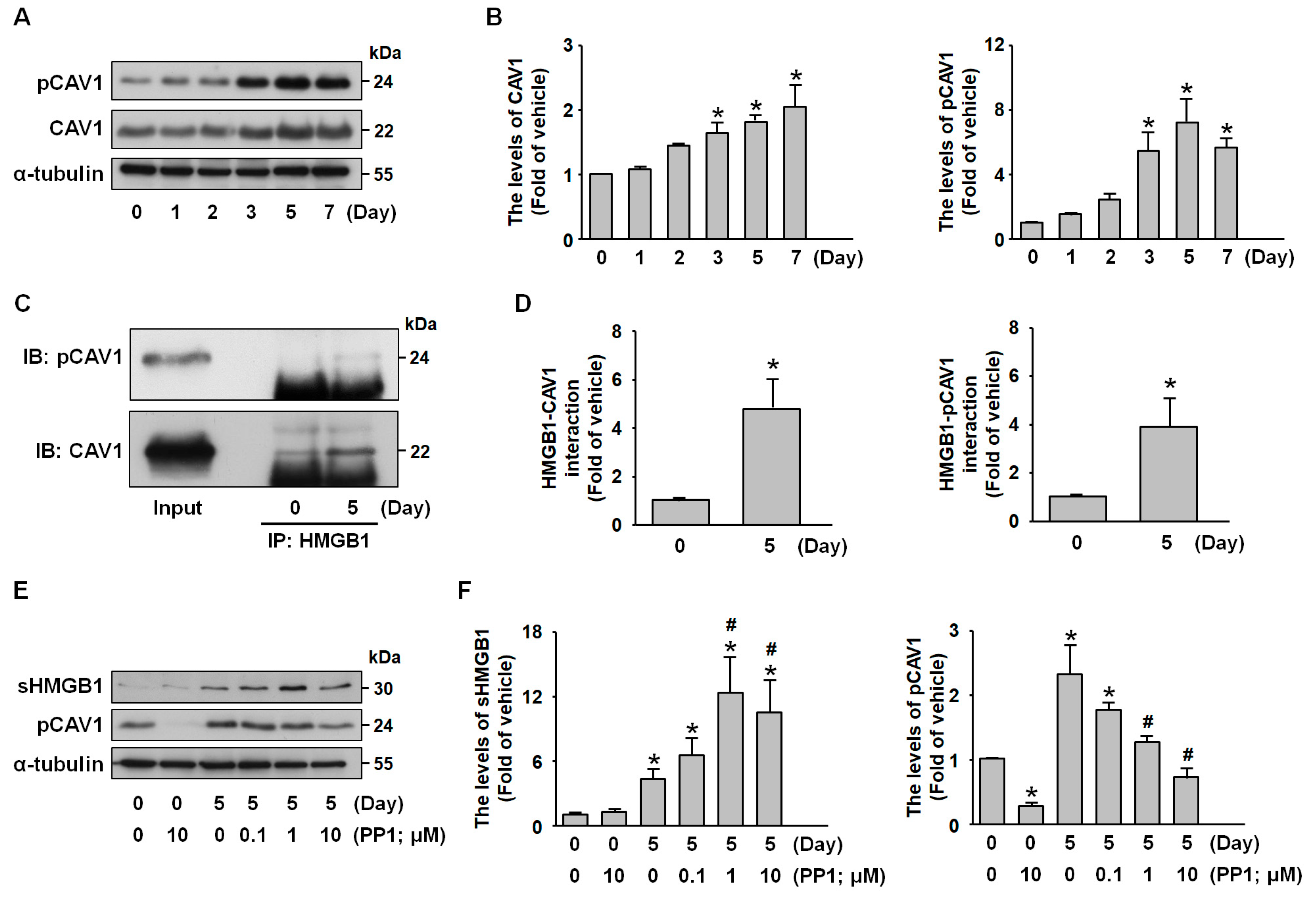
2.5. Src Signaling Mediates CAV1-HMGB1 Binding and Inhibits HMGB1 Release
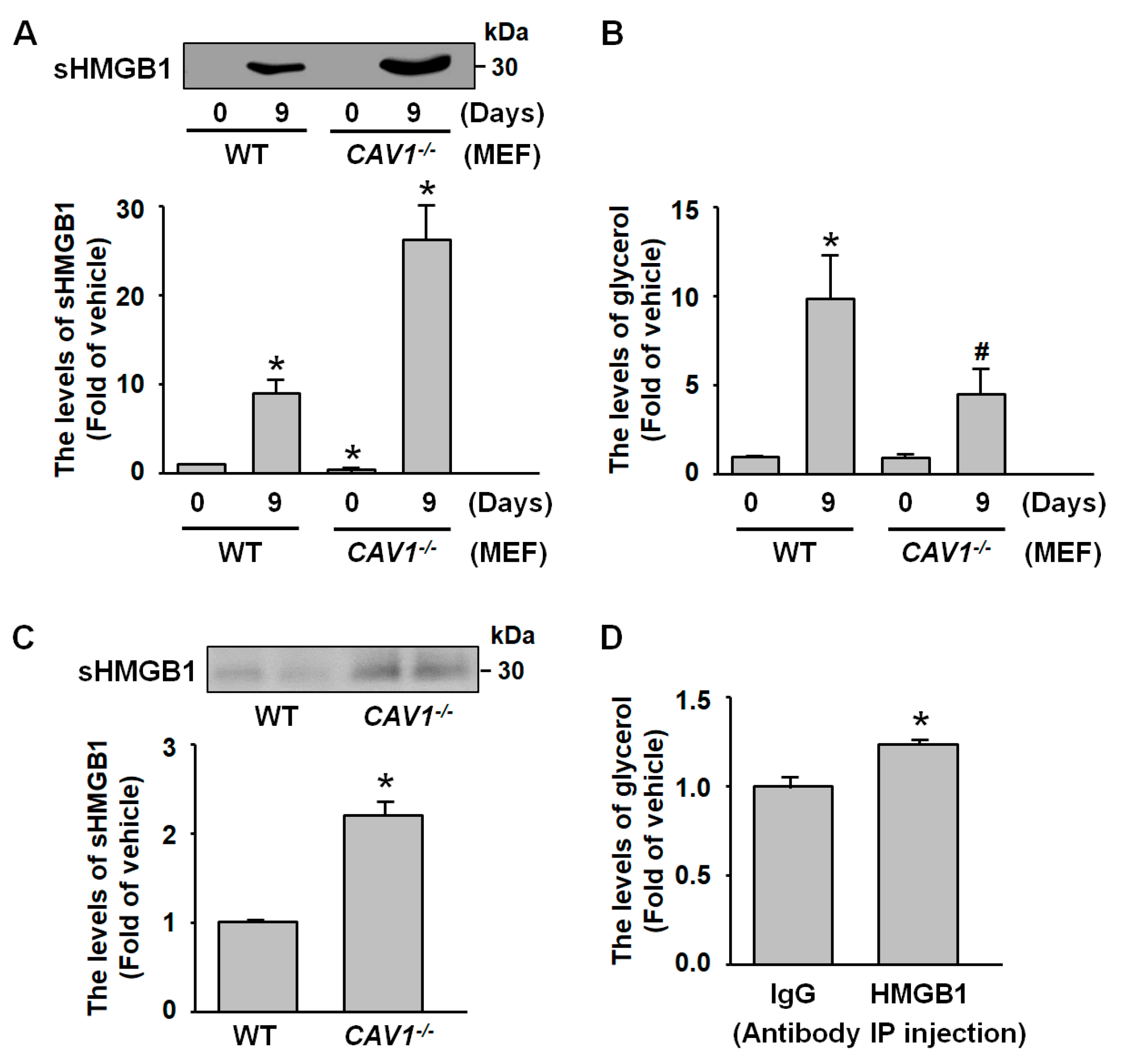
2.6. sHMGB1 Suppresses Fat Breakdown In Vitro and In Vivo
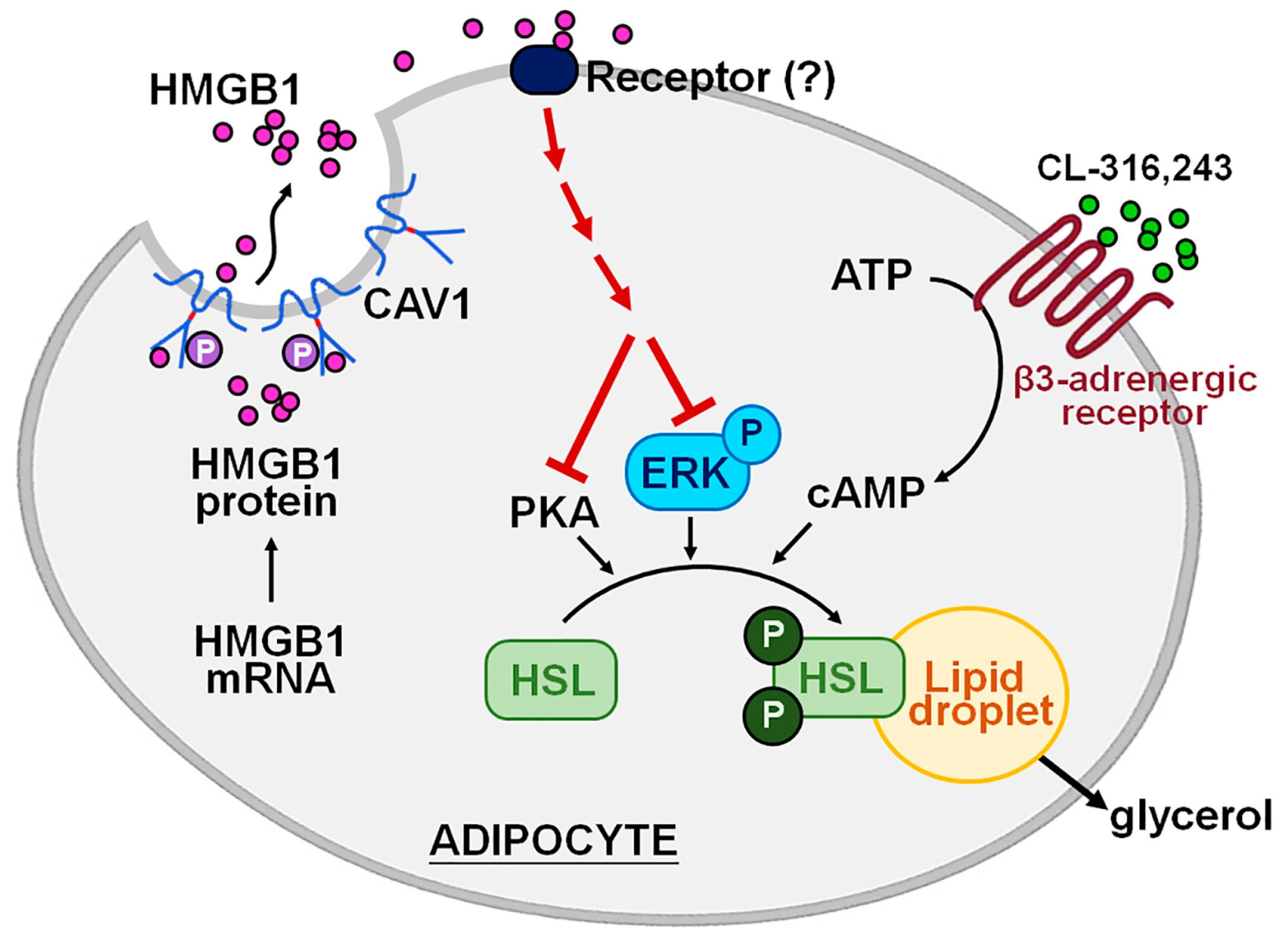
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Mice
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. 3T3-L1 Preadipocyte Differentiation
4.5. MEF Isolation
4.6. RT-PCR
4.7. Preparation of Whole Cell Lysates
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Immunoprecipitation Assay
4.10. Cell Proliferation
4.11. Measurement of Glycerol Secretion and Cellular Triglyceride Levels
4.12. Measurement of Cellular cAMP Concentrations
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pisetsky, D.S.; Erlandsson-Harris, H.; Andersson, U. High-mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1): An alarmin mediating the pathogenesis of rheumatic disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraba, R.; Suica, V.I.; Uyy, E.; Ivan, L.; Antohe, F. Hyperlipidemia stimulates the extracellular release of the nuclear high mobility group box 1 protein. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 346, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T.; Yamakuchi, M.; Biswas, K.K.; Aryal, B.; Yamada, S.; Hashiguchi, T.; Maruyama, I. HMGB1 is secreted by 3T3-L1 adipocytes through JNK signaling and the secretion is partially inhibited by adiponectin. Obesity 2016, 24, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, M.S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, B.; Kim, Y.H.; Son, M.; Shin, J.S. Immunological significance of HMGB1 post-translational modification and redox biology. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Cao, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Jin, Z.; Ye, J.; Ren, Y.; Wei, Y.; Xue, Y.; Chen, D.; et al. HMGB1 prefers to interact with structural RNAs and regulates rRNA methylation modification and translation in HeLa cells. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, P.; Liu, L.; Huang, Q.; Liu, H.; Ren, S.; Wei, P.; Wang, C.; et al. HMGB1: An important regulator of myeloid differentiation and acute myeloid leukemia as well as a promising therapeutic target. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieleniak, A.; Wójcik, M.; Woźniak, L.A. Structure and physiological functions of the human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2008, 56, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadie, J.M.; Bae, H.B.; Deshane, J.S.; Bell, C.P.; Lazarowski, E.R.; Chaplin, D.D.; Thannickal, V.J.; Abraham, E.; Zmijewski, J.W. Toll-like receptor 4 engagement inhibits adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase activation through a high mobility group box 1 protein-dependent mechanism. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKernan, K.; Varghese, M.; Patel, R.; Singer, K. Role of TLR4 in the induction of inflammatory changes in adipocytes and macrophages. Adipocyte 2020, 9, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, M.K.; Viranaicken, W.; Girard, A.C.; Festy, F.; Cesari, M.; Roche, R.; Hoareau, L. Inflammation triggers high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) secretion in adipose tissue, a potential link to obesity. Cytokine 2013, 64, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, H.; Su, S.; Harshfield, G.; Sullivan, J.; Webb, C.; Blumenthal, J.A.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Treiber, F.A.; et al. High-mobility group box-1 is associated with obesity, inflammation, and subclinical cardiovascular risk among young adults: A longitudinal cohort study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2776–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.R.; Milner, J.J.; Makowski, L. The inflammation highway: Metabolism accelerates inflammatory traffic in obesity. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 249, 218–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Wen, H.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Hung, M.S.; Lu, H.C.; Chen, W.L.; Chang, C.H. Caveolin-1 secreted from adipose tissues and adipocytes functions as an adipogenesis enhancer. Obesity 2017, 25, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellakis, P.; Agrotis, A.; Kyaw, T.S.; Koulis, C.; Ahrens, I.; Mori, S.; Takahashi, H.K.; Liu, K.; Peter, K.; Nishibori, M.; et al. High-mobility group box protein 1 neutralization reduces development of diet-induced atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein e-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroor, A.R.; Jia, G.; Sowers, J.R. Cellular mechanisms underlying obesity-induced arterial stiffness. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 314, R387–R398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yue, Y.; Xiong, S. Extracellular HMGB1 augments macrophage inflammation by facilitating the endosomal accumulation of ALD-DNA via TLR2/4-mediated endocytosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.F.; Chen, S.F.; Lee, T.S.; Lee, H.F.; Chen, S.F.; Shyue, S.K. Caveolin-1 deletion reduces early brain injury after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.H.; Chen, S.F.; Huang, T.Y.; Tzeng, C.F.; Chiang, A.S.; Kou, Y.R.; Lee, T.S.; Shyue, S.K. Impaired Cd14 and Cd36 expression, bacterial clearance, and Toll-like receptor 4-Myd88 signaling in caveolin-1-deleted macrophages and mice. Shock 2011, 35, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crewe, C.; Chen, S.; Bu, D.; Gliniak, C.M.; Wernstedt Asterholm, I.; Yu, X.X.; Joffin, N.; de Souza, C.O.; Funcke, J.B.; Oh, D.Y.; et al. Deficient caveolin-1 synthesis in adipocytes stimulates systemic insulin-independent glucose uptake via extracellular vesicles. Diabetes 2022, 71, 2496–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.M.; Cho, S.H.; Yoon, J.C. Adipose Tissue and metabolic health. Diabetes Metab. J. 2023, 47, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, E.E.; Hamm, J.K.; Verhagen, L.A.; Peroni, O.; Katic, M.; Flier, J.S. Adipose triglyceride lipase: Function, regulation by insulin, and comparison with adiponutrin. Diabetes 2006, 55, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; He, J.; Jiang, H.; Zu, L.; Zhai, W.; Pu, S.; Xu, G. Direct effect of glucocorticoids on lipolysis in adipocytes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchivileva, I.E.; Tan, K.S.; Gambarian, M.; Nackley, A.G.; Medvedev, A.V.; Romanov, S.; Flood, P.M.; Maixner, W.; Makarov, S.S.; Diatchenko, L. Signaling pathways mediating beta3-adrenergic receptor-induced production of interleukin-6 in adipocytes. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 2256–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, L.; Campos, A.; Leyton, L.; Quest, A.F.G. Caveolin-1 function at the plasma membrane and in intracellular compartments in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb-Abraham, E.; Shvartsman, D.E.; Donaldson, J.C.; Ehrlich, M.; Gutman, O.; Martin, G.S.; Henis, Y.I. Src-mediated caveolin-1 phosphorylation affects the targeting of active Src to specific membrane sites. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2013, 24, 3881–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogero, S.; Grassi, F.; Aguzzi, A.; Voigtländer, T.; Ferrier, P.; Ferrari, S.; Bianchi, M.E. The lack of chromosomal protein Hmg1 does not disrupt cell growth but causes lethal hypoglycaemia in newborn mice. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinado, J.R.; Quirós, P.M.; Pulido, M.R.; Mariño, G.; Martínez-Chantar, M.L.; Vázquez-Martínez, R.; Freije, J.M.; López-Otín, C.; Malagón, M.M. Proteomic profiling of adipose tissue from Zmpste24-/- mice, a model of lipodystrophy and premature aging, reveals major changes in mitochondrial function and vimentin processing. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2011, 10, M111.008094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Yu, L.; Zhang, G.; Liu, G.; Yang, C.; Wang, H.; Song, X. Regulation of autophagy-related protein and cell differentiation by high mobility group box 1 protein in adipocytes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1936386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Okano, S.; Kistler, C.; Fernandez-Rojo, M.A.; Hill, M.M.; Parton, R.G. Spatiotemporal regulation of early lipolytic signaling in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32097–32107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, M.J.; Stellingwerff, T.; Heigenhauser, G.J.; Spriet, L.L. Effects of plasma adrenaline on hormone-sensitive lipase at rest and during moderate exercise in human skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2003, 550, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, M.J.; Holmes, A.G.; Pinnamaneni, S.K.; Garnham, A.P.; Steinberg, G.R.; Kemp, B.E.; Febbraio, M.A. Regulation of HSL serine phosphorylation in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 290, E500–E508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPherson, R.E.; Castellani, L.; Beaudoin, M.S.; Wright, D.C. Evidence for fatty acids mediating CL 316,243-induced reductions in blood glucose in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 307, E563–E570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Peng, X.; Li, X.; Tu, T.; Yang, H.; Teng, S.; Zhang, W.; Xing, Z.; Tang, J.; Hu, X.; et al. HMGB1 impairs endothelium-dependent relaxation in diabetes through TLR4/eNOS pathway. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 8641–8652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Long, J.; Li, W.; Yang, C.; Loughran, P.; O’Doherty, R.; Billiar, T.R.; Deng, M.; Scott, M.J. Hepatocyte high-mobility group box 1 protects against steatosis and cellular stress during high fat diet feeding. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Personnaz, J.; Piccolo, E.; Dortignac, A.; Iacovoni, J.S.; Mariette, J.; Rocher, V.; Polizzi, A.; Batut, A.; Deleruyelle, S.; Bourdens, L.; et al. Nuclear HMGB1 protects from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through negative regulation of liver X receptor. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabg9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Dong, F.; Zaid, M.; Kumar, A.; Zha, X. ABCA1 protein enhances Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-stimulated interleukin-10 (IL-10) secretion through protein kinase A (PKA) activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40502–40512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curson, J.E.B.; Liu, L.; Luo, L.; Muusse, T.W.; Lucas, R.M.; Gunther, K.S.; Vajjhala, P.R.; Abrol, R.; Jones, A.; Kapetanovic, R.; et al. TLR4 phosphorylation at tyrosine 672 activates the ERK/c-FOS signaling module for LPS-induced cytokine responses in macrophages. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, e2250056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado Del Pozo, C.; Ruiz, H.H.; Arivazhagan, L.; Aranda, J.F.; Shim, C.; Daya, P.; Derk, J.; MacLean, M.; He, M.; Frye, L.; et al. A receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily regulates adaptive thermogenesis. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 773–791.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Ling, Z.; Tan, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, T.; Hou, C.; Chen, Y. High mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1) interacts with receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) to promote airway smooth muscle cell proliferation through ERK and NF-κB pathways. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 3268–3278. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, P.E.; Lewis, R.Y.; Volonte, D.; Engelman, J.A.; Galbiati, F.; Couet, J.; Kohtz, D.S.; van Donselaar, E.; Peters, P.; Lisanti, M.P. Cell-type and tissue-specific expression of caveolin-2. Caveolins 1 and 2 co-localize and form a stable hetero-oligomeric complex in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29337–29346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Cai, B.; Li, Y.; Su, W.; Zhao, X.; Gong, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, C.; et al. HMGB1 and Caveolin-1 related to RPE cell senescence in age-related macular degeneration. Aging 2019, 11, 4323–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, D.; Peng, T.; Gou, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z. High mobility group box protein 1 boosts endothelial albumin transcytosis through the RAGE/Src/Caveolin-1 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razani, B.; Combs, T.P.; Wang, X.B.; Frank, P.G.; Park, D.S.; Russell, R.G.; Li, M.; Tang, B.; Jelicks, L.A.; Scherer, P.E.; et al. Caveolin-1-deficient mice are lean, resistant to diet-induced obesity, and show hypertriglyceridemia with adipocyte abnormalities. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8635–8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.A.; Delépine, M.; Boutet, E.; El Mourabit, H.; Le Lay, S.; Meier, M.; Nemani, M.; Bridel, E.; Leite, C.C.; Bertola, D.R.; et al. Association of a homozygous nonsense caveolin-1 mutation with Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancioppi, V.; Daffara, T.; Romanisio, M.; Ceccarini, G.; Pelosini, C.; Santini, F.; Bellone, S.; Mellone, S.; Baricich, A.; Rabbone, I.; et al. A new mutation in the CAVIN1/PTRF gene in two siblings with congenital generalized lipodystrophy type 4: Case reports and review of the literature. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1212729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Rojo, M.A.; Gongora, M.; Fitzsimmons, R.L.; Martel, N.; Martin, S.D.; Nixon, S.J.; Brooks, A.J.; Ikonomopoulou, M.P.; Martin, S.; Lo, H.P.; et al. Caveolin-1 is necessary for hepatic oxidative lipid metabolism: Evidence for crosstalk between caveolin-1 and bile acid signaling. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sil, R.; Ray, D.; Chakraborti, A.S. Glycyrrhizin ameliorates metabolic syndrome-induced liver damage in experimental rat model. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2015, 409, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.P.; Yu, P.; Jia, J.G.; Chen, R.Z.; Zou, Y.Z.; Ge, J.B. Simvastatin suppresses vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-) mice by downregulating the HMGB1-RAGE axis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, P.G.; Marcel, Y.L.; Connelly, M.A.; Lublin, D.M.; Franklin, V.; Williams, D.L.; Lisanti, M.P. Stabilization of caveolin-1 by cellular cholesterol and scavenger receptor class B type I. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 11931–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Matsuda, A.; An, J.; Koshiba, R.; Nishio, J.; Negishi, H.; Ikushima, H.; Onoe, T.; Ohdan, H.; Yoshida, N.; et al. Conditional ablation of HMGB1 in mice reveals its protective function against endotoxemia and bacterial infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20699–20704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Rouhiainen, A.; Li, Z.; Guo, S.; Rauvala, H. Regulation of Neurogenesis in Mouse Brain by HMGB1. Cells 2020, 9, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, E.W.; Schwartz, J.H.; Freddolino, P.L.; Zhang, Y. PEPPI: Whole-proteome protein-protein interaction prediction through structure and sequence similarity, functional association, and machine learning. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, J.C.-N.; Chiu, K.-T.; Chen, C.-H.; Wang, C.-H.; Shyue, S.-K.; Lee, T.-S. HMGB1 Regulates Adipocyte Lipolysis via Caveolin-1 Signaling: Implications for Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094222
Hsu JC-N, Chiu K-T, Chen C-H, Wang C-H, Shyue S-K, Lee T-S. HMGB1 Regulates Adipocyte Lipolysis via Caveolin-1 Signaling: Implications for Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094222
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Julia Chu-Ning, Kuan-Ting Chiu, Chia-Hui Chen, Chih-Hsien Wang, Song-Kun Shyue, and Tzong-Shyuan Lee. 2025. "HMGB1 Regulates Adipocyte Lipolysis via Caveolin-1 Signaling: Implications for Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094222
APA StyleHsu, J. C.-N., Chiu, K.-T., Chen, C.-H., Wang, C.-H., Shyue, S.-K., & Lee, T.-S. (2025). HMGB1 Regulates Adipocyte Lipolysis via Caveolin-1 Signaling: Implications for Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094222






