The Effect and Mechanism of Regular Exercise on Improving Insulin Impedance: Based on the Perspective of Cellular and Molecular Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Possible Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance
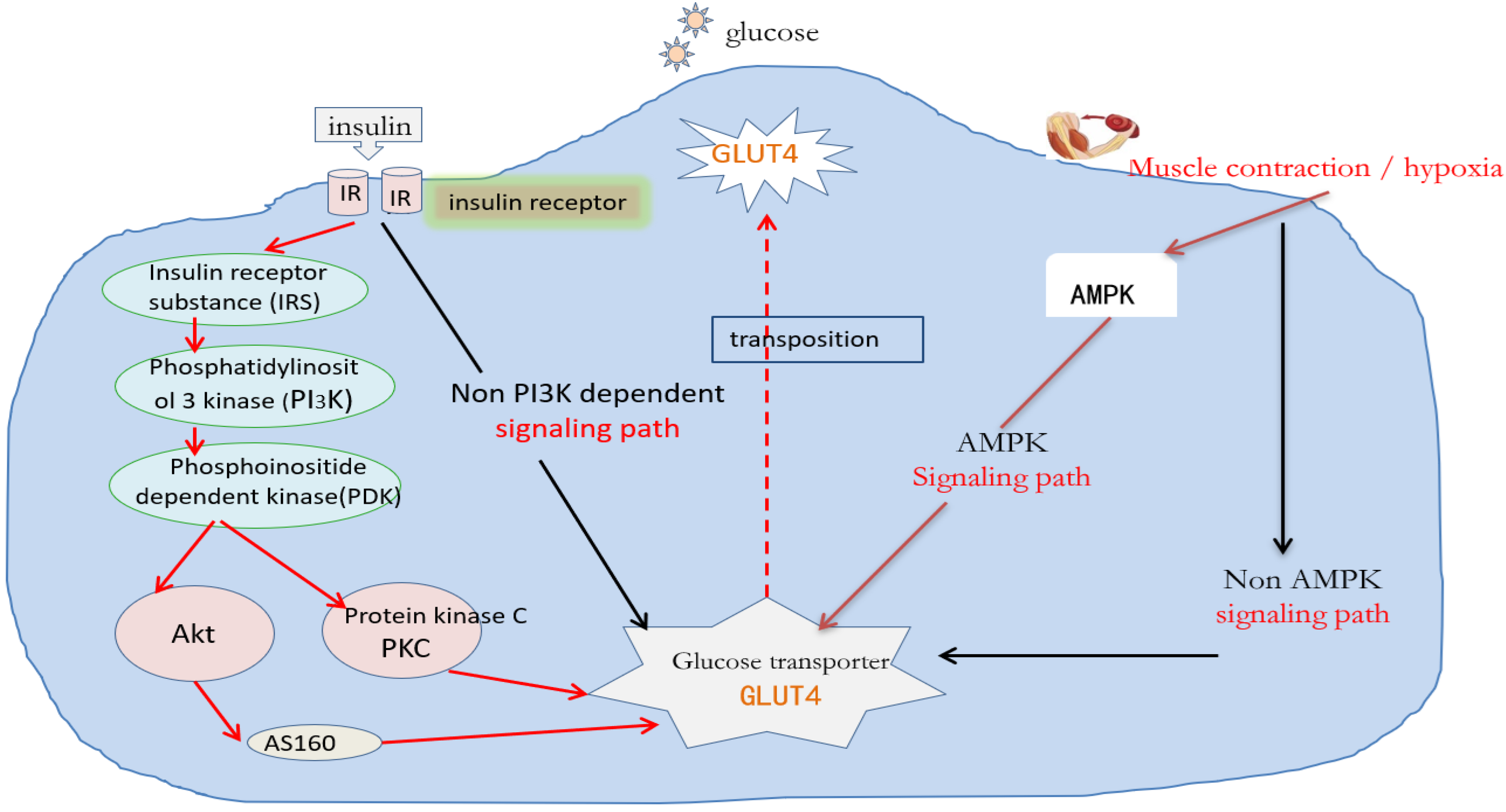
2.1. Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Glucose Absorption
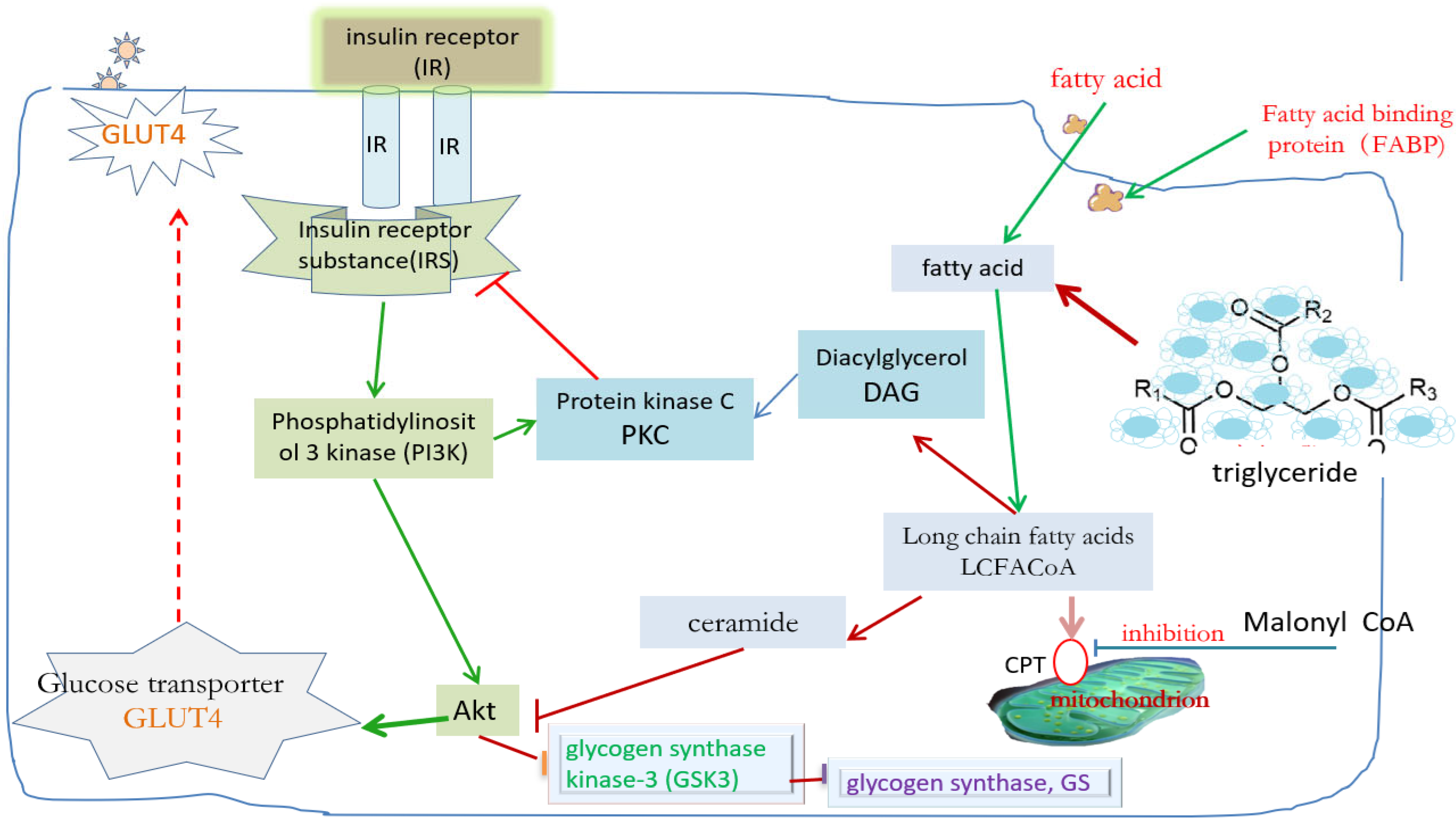
2.2. Molecular Mechanism of Insulin Resistance Induced by Lipid Accumulation in Muscle Tissue
2.3. Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Mechanism Related to Insulin Resistance
3. Possible Mechanism of Exercise Training Improving Muscle Insulin Resistance
3.1. Effect of Exercise on the Insulin Signaling Pathway
3.2. Effect of Exercise on AMPK
3.3. Effect of Exercise on MAPK
3.4. Effect of Exercise on Glucose Transporter
3.5. Effects of Exercise on Hepatic Glucose Synthase and Insulin Sensitivity
3.6. Effect of Exercise on Muscle Fatty Acid Absorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuanxi, L.; Gaoling, W. Analysis of the disease burden of diabetes attributable to different risk categories in China from 1990 to 2021. Mod. Prev. Med. 2024, 51, 4038–4044. [Google Scholar]
- Qing, M.; Wei, C.; Ming, Z. Effect of aerobic combined resistance exercise on patients with type 2 diabetes. Theory Pract. Rehabil. China 2018, 24, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, Z.; Ying, C.; Naya, S. Effect of comprehensive exercise training on asthenia and physical function of elderly patients with diabetes School of nursing. Zhengzhou Univ. 2020, 55, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Benton, C.R.; Holloway, G.P.; Han, X.X.; Yoshida, Y.; Snook, L.A.; Lally, J.; Glatz, J.F.C.; Luiken, J.J.F.P.; Chabowski, A.; Bonen, A. Increased levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1 alpha) improve lipid utilisation, insulin signalling and glucose transport in skeletal muscle of lean and insulin-resistant obese Zucker rats. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2008–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.Y.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Liu, W.Y.; Zheng, M.H. Resmetirom for MASH patients with diabetes: Challenges and opportunities in the real world. Metab.-Clin. Exp. 2024, 156, 155935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binglin, C.; Hongwei, Z.; Jiabao, G. Research status of exercise therapy in early stage of diabetes. Chin. J. Sports Med. 2017, 36, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuemei, Y.; Zhigang, Z.; Yujia, Y.; Mingfen, W. Differences and distribution of medication adherence among chronic disease patients with “three highs” in China. Zhongnan Pharm. 2023, 21, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan Weiming, G.; Huaiju, G.; Qing, Y.; Shihong, D.; Huiyu, J.; Wenjing, C.; Edreira, M.M. Research on the relationship between the increasing incidence of chronic diseases and self-assessment of health and depression in the middle-aged and elderly in China. Mod. Prev. Med. 2024, 51, 4212–4218. [Google Scholar]
- Amati, F.; Dube, J.J.; Alvarez-Carnero, E.; Edreira, M.M.; Chomentowski, P.; Coen, P.M.; Switzer, G.E.; Bickel, P.E.; Stefanovic-Racic, M.; Toledo, F.G.; et al. Skeletal Muscle Triglycerides, Diacylglycerols, and Ceramides in Insulin Resistance Another Paradox in Endurance-Trained Athletes? Diabetes 2013, 60, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.J.; Hou, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Ji, L. Retrospective analysis of the effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes in the real world. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1376850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Bousvarou, M.D.; Kostara, C.E.; Papakonstantinou, E.J.; Salamou, E.; Guzman, E. Insulin resistance and car-diovascular disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Xu, H.C.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.X.; Tian, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, B.; Zhu, B.; et al. Exercise ameliorates muscular excessive mitochondrial fission, insulin resistance and inflammation in diabetic rats via irisin/AMPK activation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Xie, K.L.; Zheng, F.; Liu, S.X. Aerobic Exercise Prevents Insulin Resistance Through the Regulation of miR-492/Resistin Axis in Aortic Endothelium. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2018, 11, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ding, S.Z. ER-Mitochondria Contacts and Insulin Resistance Modulation through Exercise Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Ponce, V.J.; Rodas-Alvarado, L.; Talavera, J.E.; Cruz-Ausejo, L.; Torres-Malca, J.R. Association between insulin resistance and C-reactive protein in a sample of non-obese Peruvians. Rev. Del Curpo Med. Del Hosp. Nac. Almanzor Aguinaga Asenjo 2021, 14, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voldstedlund, C.T.; Sjoberg, K.A.; Schlabs, F.L.; Sigvardsen, C.M.; Andersen, N.R.; Holst, J.J.; Hartmann, B.; Wojtaszewski, J.F.P.; Kiens, B.; McConell, G.K.; et al. Exercise-induced increase in muscle insulin sensitivity in men is amplified when assessed using a meal test. Diabetologia 2024, 67, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Horani, R.A.; Alsays, K.M.; Alrob, O.A. Obesity blunts insulin sensitivity improvements and attenuates strength gains following resistance training in nondiabetic men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2024, 124, 1425–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillen, J.B.; Estafanos, S.; Govette, A. Exercise nutrient interactions for improved postprandial glycemic control and insulin sensitivity. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, G.J.; Swartz, A.M.; Gorgey, A.S.; Berg, A.S.; Gater, D.R. Acute exercise improves glucose effectiveness but not insulin sensitivity in paraplegia. Disabil. Rehabil. 2022, 44, 4656–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, S.; Tamura, Y.; Sugimoto, D.; Kaga, H.; Suzuki, R.; Someya, Y.; Yamasaki, N.; Sato, M.; Kakehi, S.; Kanazawa, A.; et al. A Short-Term High-Fat Diet Worsens Insulin Sensitivity with Changes in Metabolic Parameters in Non-Obese Japanese Men. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.S.; Whytock, K.L.; Strauss, J.A.; Wagenmakers, A.J.M.; Shepherd, S.O. High intramuscular triglyceride turnover rates and the link to insulin sensitivity: Influence of obesity, type 2 diabetes and physical activity. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 47, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, S.; Dandanell, S.; Kristensen, K.B. Influence of exercise amount and intensity on long-term weight loss maintenance and skeletal muscle mitochondrial ROS production in humans. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, J.A.; Houmard, J.A. Introduction-preventing insulin resistance through exercise: A cellular approach. Med. Sci. Exerc. Sport 2004, 36, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Garg, A.; Bhatt, D.L. Empagliflozin improves cardiorespiratory fitness in type 2 diabetes: Translational implications. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 96, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiei, H.; Robinson, E.; Barry, J.; Jung, M.E.; Little, J.P. Short-term exercise training reduces glycaemic variability and lowers circulating endothelial microparticles in overweight and obese women at elevated risk of type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An Ding Kim, M.S.; Rodrigues, B. AMPK Regulation of Cardiac Metabolism in Heart Disease. Adv. Biochem. Health Dis. 2018, 3, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirin, C.; Zeynep, G.; Ozlem, A. Development of type 2 diabetes risk assessment model for Turkish society. J. Diabetes Metab. disorders 2023, 23, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslacher, H.; Fallmann, H.; Waldhausl, C.; Hartmann, E.; Wagner, O.F.; Waldhausl, W. Type 2 diabetes care: Improvement by standardization at a diabetes rehabilitation clinic. An observational report. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siques, P.; Brito, J.; Flores, K. Long-Term Chronic Intermittent Hypobaric Hypoxia Induces Glucose Transporter (GLUT4) Translocation Through AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) in the Soleus Muscle in Lean Rats. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, T.A.; de Lima, E.A.; Teixeira, A.A.; Biondo, L.A.; Rocha, L.A.F.; Valadao, I.C.; Silveira, L.S.; Cabral-Santos, C.; de Souza, C.O.; Neto, J.C.R. Aerobic training improves NAFLD markers and insulin resistance through AMPK-PPAR-alpha signaling in obese mice. Life Sci. 2021, 266, 118868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.K.; Hosaka, T.; Harada, N.; Nakaya, Y.; Funaki, M. Activation of Akt through 5-HT2A receptor ameliorates serotonin-induced degradation of insulin receptor substrate-1 in adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 365, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neff, A.M.; Yu, J.; Taylor, R.N.; Bagchi, I.C.; Bagchi, M.K. Insulin Signaling Via Progesterone-Regulated Insulin Receptor Substrate 2 is Critical for Human Uterine Decidualization. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqz021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki-Suzuki, N.; Arai, K.; Ogata, T.; Kasahara, K.; Sakoda, H.; Chida, K.; Asano, T.; Pessin, J.E.; Hakuno, F.; Takahashi, S.-I. Growth Hormone Inhibition of Glucose Uptake in Adipocytes Occurs without Affecting GLUT4 Translocation through an Insulin Receptor Substrate-2-Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-dependent Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6061–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.Y.; Yu, Q.L.; Chang, B.; Guo, Q.; Xu, S.T.; Yi, X.J.; Cao, S.C. MOTS-c interacts synergistically with exercise intervention to regulate PGC-1 alpha expression, attenuate insulin resistance and enhance glucose metabolism in mice via AMPK signaling pathway. Biochim. ET Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, D.S.; Marchbank, T.; Playford, R.J.; Jones, A.W.; Thatcher, R.; Davison, G. Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein and gut permeability responses to exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.W.; Luo, X.F.; Dai, T.Y.; Peng, L.; Song, S.; Li, L.-F.; Tao, L.; Shi, C.-Y.; et al. Moringa oleifera Leaf Petroleum Ether Extract Inhibits Lipogenesis by Activating the AMPK Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, M.; Jung, B.; Liang, F.; Azuelos, I.; Hussain, S.; Goldberg, P.; Godin, R.; Danialou, G.; Chaturvedi, R.; Rygiel, K.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Lipid Accumulation in the Human Diaphragm during Mechanical Ventilation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.A.J.; Hardie, D.G. Metabolism of inflammation limited by AMPK and pseudo-starvation. Nature 2013, 493, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Zhang, Y.F.; Ga, Q.; Bai, Z.Z.; Ge, R.L. Increased Insulin Sensitivity by High-Altitude Hypoxia in Mice with High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Is Associated with Activated AMPK Signaling and Subsequently Enhanced Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Skeletal Muscles. Obes. Facts 2020, 13, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, S.; Wang, F.B.H.; Zou, J.H.; Zhang, Y.F. Aerobic exercise regulates blood lipid and insulin resistance via the toll-like receptor 4-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinases/AMP-activated protein kinases signaling pathway. Mol. Medcine Rep. 2018, 17, 8339–8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Li, J.J.; Lu, Y.F. Effects of resistance training on insulin sensitivity in the elderly: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2021, 19, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frandsen, J.; Poggi, A.I.; Ritz, C.; Larsen, S.; Dela, F.; Helge, J.W. Peak Fat Oxidation Rate Is Closely Associated With Plasma Free Fatty Acid Concentrations in Women; Similar to Men. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 696261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surapongchai, J.; Rattanavichit, Y.; Buniam, J.; Saengsirisuwan, V. Exercise Protects Against Defective Insulin Signaling and Insulin Resistance of Glucose Transport in Skeletal Muscle of Angiotensin II-Infused Rat. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emamgholipour, S.; Ebrahimi, R.; Bahiraee, A.; Niazpour, F.; Meshkani, R. Acetylation and insulin resistance: A focus on metabolic and mitogenic cascades of insulin signaling. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.L.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y.Z.; Zhao, L.; Huang, R.X.; Luo, L.; Lai, F.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; et al. Bayesian network analysis of factors influencing type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, and their comorbidities. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauger, P.C.; Hordijk, P.L. Shear Stress-Induced AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Modulation in Endothelial Cells: Its Role in Metabolic Adaptions and Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomax, T.; Ashraf, S.; Yilmaz, G.; Harmancey, R. Lack of Uncoupling Protein 3 Protects from High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity, Systemic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Rats. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Dan, P.; Xi, J.H.; Chen, Z.W.; Zhang, P.; Wei, W.; Zhao, Y. Novel soybean polypeptide dglycin alleviates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hoek, A.M.; de Jong, J.C.B.C.; Worms, N.; van Nieuwkoop, A.; Voskuilen, M.; Menke, A.L.; Lek, S.; Caspers, M.P.; Verschuren, L.; Kleemann, R. Diet and exercise reduce pre-existing NASH and fibrosis and have additional beneficial effects on the vasculature, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle via organ-crosstalk. Metab.-Clin. Exp. 2021, 124, 154873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, J.G.; Gudiksen, A.; Bertholdt, L.; Overby, P.; Villesen, I.; Schwartz, C.L. Skeletal muscle IL-6 regulates muscle substrate utilization and adipose tissue metabolism during recovery from an acute bout of exercise. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaane, T.; Motala, A.A.; McKune, A.J. Effects of Short-Term Exercise in Overweight/Obese Adults with Insulin Resistance or Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Diabetes Metab. 2018, 9, 1000816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, G.P.; Schwenk, R.W.; Luiken, J.J.F.P.; Glatz, J.F.C.; Bonen, A. Fatty acid transport in skeletal muscle: Role in energy provision and insulin resistance. Clin. Lipidol. 2010, 5, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, V.; Stickford, J.L.; Bhammar, D.M.; Babb, T.G. Aerobic exercise training without weight loss reduces dyspnea on exertion in obese women. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2016, 221, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaspelkis, B.B. Resistance training improves insulin signaling and action in skeletal muscle. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2006, 34, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ragheb, R.; Shanab, G.M.L.; Medhat, A.M.; Seoudi, D.M.; Adeli, K.; Fantus, I.G. Free fatty acid-induced muscle insulin resistance and glucose uptake dysfunction: Evidence for PKC activation and oxidative stress-activated signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 389, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, T.T.; Zhou, P.Q.; Li, R.J.; Liu, Z.F.; Xie, J.Y.; Hua, T.; Sun, Q. Exercise ameliorates insulin resistance and improves ASK1-mediated insulin signalling in obese rats. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 10930–10938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, N.F.; Chang, T.J. Inflammatory Status and Macrophage Infiltration in Relation to Insulin Resistance and Dyslipidemia among Morbid Obese Subjects. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, J.; Baetiong, A.; Kaufman, H.; Huynh, M.; Leschinsky, A.; Fresquez, A.; White, C.; DiMario, J.X.; Gazmuri, R.J. Improved exercise capacity in cyclophilin-D knockout mice associated with enhanced oxygen utilization efficiency and augmented glucose uptake via AMPK-TBC1D1 signaling nexus. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 11443–11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folchini, F.; Nonato, N.L.; Feofiloff, E.; D’Almeida, V.; Nascimento, O.; Jardim, J.R. Association of oxidative stress markers and C-reactive protein with multidimensional indexes in COPD. Chronic Respir. Dis. 2011, 8, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravona-Springer, R.; Lutski, M.; Beeri, M.S.; Goldbourt, U.; Tanne, D. C-reactive protein in midlife is associated with depressive symptoms two decades later among men with coronary heart disease. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2020, 74, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.W.; Xu, Z.; Wan, J.Y.; Hua, T.M.; Sun, Q.Y. Exercise ameliorates insulin resistance and improves SIRT6-mediated insulin signaling transduction in liver of obese rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antinozzi, C.; Marampon, F.; Sgro, P.; Tombolini, V.; Lenzi, A.; Crescioli, C.; Di Luigi, L. Comparative study of testosterone and vitamin D analogue, elocalcitol, on insulin-controlled signal transduction pathway regulation in human skeletal muscle cells. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungan, C.M.; Gordon, B.S.; Williamson, D.L. Acute treadmill exercise discriminately improves the skeletal muscle insulin-stimulated growth signaling responses in mice lacking REDD1. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, 14104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Yang, N.; Zhao, X.C.; Zhang, W.; Bai, X.W.; Li, A.; Yang, W.; Lu, L. Proteasome activation by insulin-like growth factor-1/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling promotes exercise-induced neurogenesis. Stem Cells 2020, 8, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hao, J.; Tang, D.; Wen, Y.Z.; Zhao, P.; Chen, H.; Lv, Y.; Yang, X. Antidiabetic Activity of a Flavonoid-Rich Extract from Sophora davidii (Franch.) Skeels in KK-Ay Mice via Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, K.; Ato, S.; Yokokawa, T.; Sato, K.; Fujita, S. Resistance training recovers attenuated APPL1 expression and improves insulin-induced Akt signal activation in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 314, E564–E571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtaszewski, J.F.P.; Nielsen, P.; Hansen, B.F.; Richter, E.A.; Kiens, B. Isoform-specific and exercise intensity-dependent activation of 5 ‘-AMP-activated protein kinase in human skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2000, 528, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarbjerg, S.J.; Jorgensen, S.B.; Rose, A.J.; Jeppesen, J.; Jensen, T.E.; Treebak, J.T.; Birk, J.B.; Schjerling, P.; Wojtaszewski, J.F.P.; Richter, E.A. Genetic impairment of AMPK alpha 2 signaling does not reduce muscle glucose uptake during treadmill exercise in mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E924–E934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.S.R.; Fonseca, G.F.A.C.; Ottone, N.C.D.; Silva, P.A.; Antonaccio, R.F.; Silva, G.; Rocha, M.d.S.A.; Coimbra, C.C.; Esteves, E.A.; Mang, Z.A.; et al. Strength training improves insulin resistance and differently affects mitochondria in skeletal muscle and visceral adipose tissue in high-fat fed mice. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croymans, D.M.; Paparisto, E.; Lee, M.M.; Brandt, N.; Le, B.K.; Lohan, D.; Lee, C.C.; Roberts, C.K. Resistance training improves indices of muscle insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in overweight/obese, sedentary young men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, P.; Morandi, C.; Brouwer, G.R.; Xu, L.F.; Montessuit, C.; Brink, M. Neuregulin-1 triggers GLUT4 translocation and enhances glucose uptake independently of insulin receptor substrate and ErbB3 in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Lin, H.Q.; Lin, W.T.; Xu, X.Y. Exercise Ameliorates Insulin Resistance of Type 2 Diabetes through Motivating Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Mediated Skeletal Muscle Cell Autophagy. Biology 2020, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sponder, M.; Lichtenauer, M.; Wernly, B.; Paar, V.; Hoppe, U.; Emich, M.; Fritzer-Szekeres, M.; Litschauer, B.; Strametz-Juranek, J. Serum heart-type fatty acid-binding protein decreases and soluble isoform of suppression of tumorigenicity 2 increases significantly by long-term physical activity. J. Investig. Med. 2019, 67, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhaes, F.C.; Vieira, D.V.; Matos, M.A.; Pinhal, K.C.; Escobar, K.; Dias-Peixoto, M.F.; Rocha-Vieira, E.; Amorim, F.T. High Intensity Interval Training Changes Skeletal Muscle Insulin Signalling Pathway of Obese Individuals. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.C.; da Rocha, A.L.; Pinto, A.P.; Pauli, J.R.; de Moura, L.P.; Mekary, R.A.; de Freitas, E.C.; da Silva, A.S.R. Excessive training impairs the insulin signal transduction in mice skeletal muscles. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 230, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.R.; Park, K.H.; Kim, B.J.; Yoon, C.S.; Kim, U.H. Exercise Ameliorates Insulin Resistance via Ca2+ Signals Distinct From Those of Insulin for GLUT4 Translocation in Skeletal Muscles. Diabetes 2015, 64, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeChick, A.; Hetz, R.; Lee, J.; Speelman, D.L. Increased Skeletal Muscle Fiber Cross-Sectional Area, Muscle Phenotype Shift, and Altered Insulin Signaling in Rat Hindlimb Muscles in a Prenatally Androgenized Rat Model for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, K.; Arias, E.B.; Kanzaki, M.; Cartee, G.D. Effects of Acute Exercise Combined With Calorie Restriction Initiated Late-in-Life on Insulin Signaling, Lipids, and Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle From Old Rats. J. Gerontol. Ser. A-Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammers, G.; Poelkens, F.; van Duijnhoven, N.T.L. Expression of genes involved in fatty acid transport and insulin signaling is altered by physical inactivity and exercise training in human skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E1245–E1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Luo, J.; Hao, C. The Effect and Mechanism of Regular Exercise on Improving Insulin Impedance: Based on the Perspective of Cellular and Molecular Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094199
Zhang T, Liu Y, Yang Y, Luo J, Hao C. The Effect and Mechanism of Regular Exercise on Improving Insulin Impedance: Based on the Perspective of Cellular and Molecular Levels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094199
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tingran, Yongsen Liu, Yi Yang, Jiong Luo, and Chen Hao. 2025. "The Effect and Mechanism of Regular Exercise on Improving Insulin Impedance: Based on the Perspective of Cellular and Molecular Levels" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094199
APA StyleZhang, T., Liu, Y., Yang, Y., Luo, J., & Hao, C. (2025). The Effect and Mechanism of Regular Exercise on Improving Insulin Impedance: Based on the Perspective of Cellular and Molecular Levels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094199




