Combination of Berberine and Evodiamine Alleviates Obesity by Promoting Browning in 3T3-L1 Cells and High-Fat Diet-Induced Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
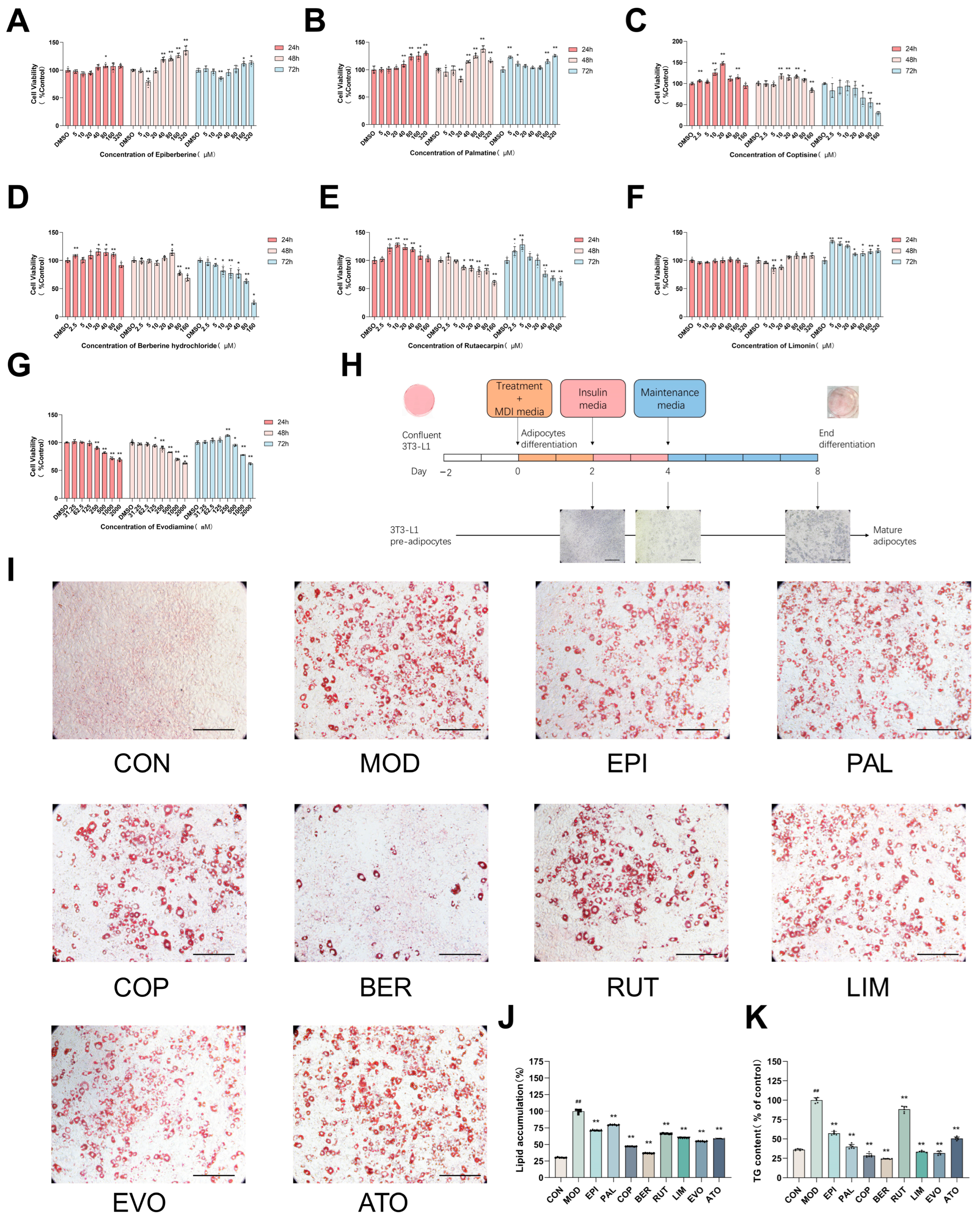
2.1. The Major Components from Coptis Chinensis and Tetradium ruticarpum Inhibit Lipid Accumulation
2.2. Molecular Docking Analysis of BBE and Key Proteins Involved in FGF21/PGC-1α Pathway
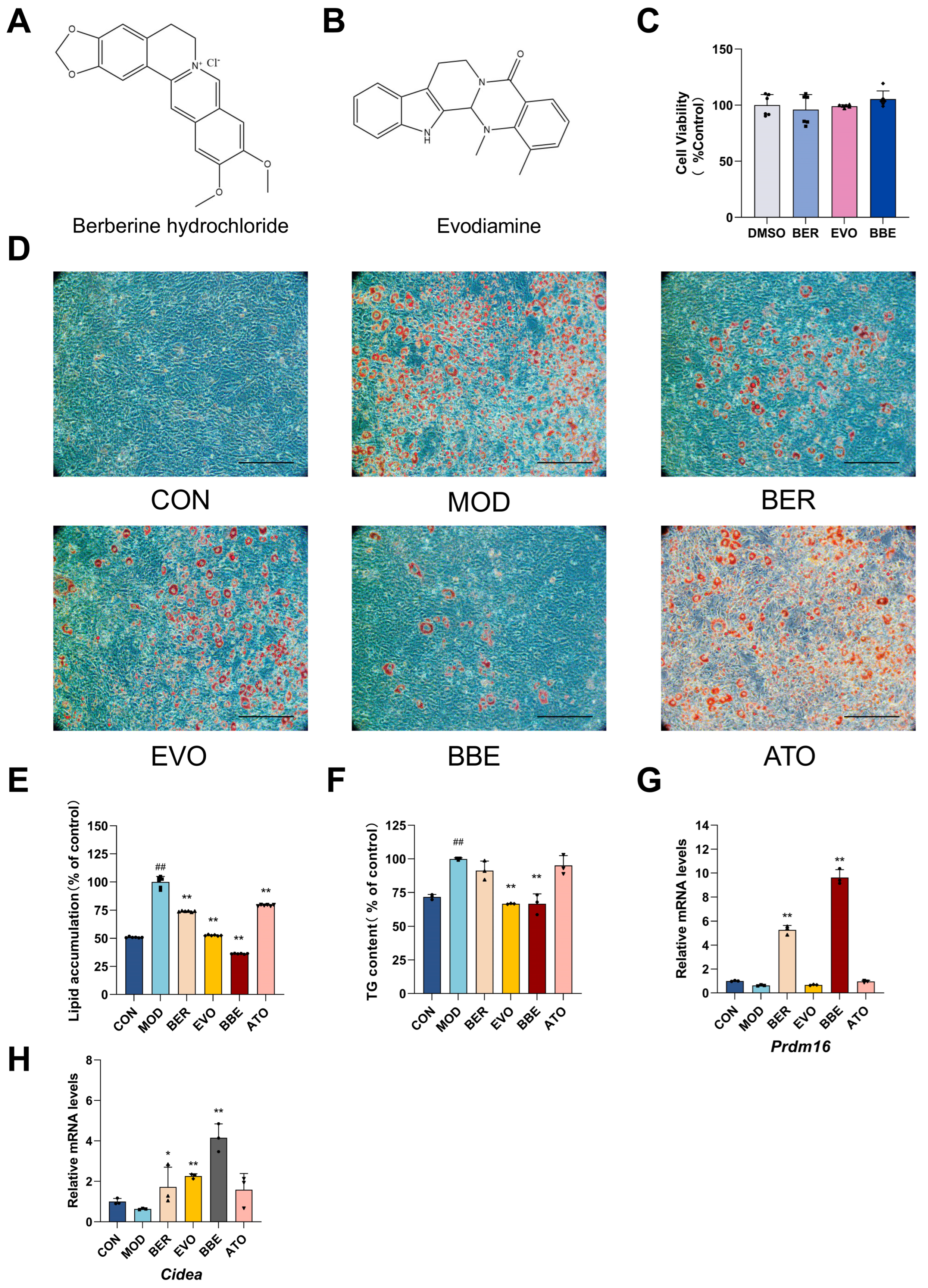
2.3. BBE Promotes Browning and Improves Intracellular Lipid Profiles in 3T3-L1 Cells
2.4. BBE Enhances Thermogenesis in Differentiated 3T3-L1 Cells
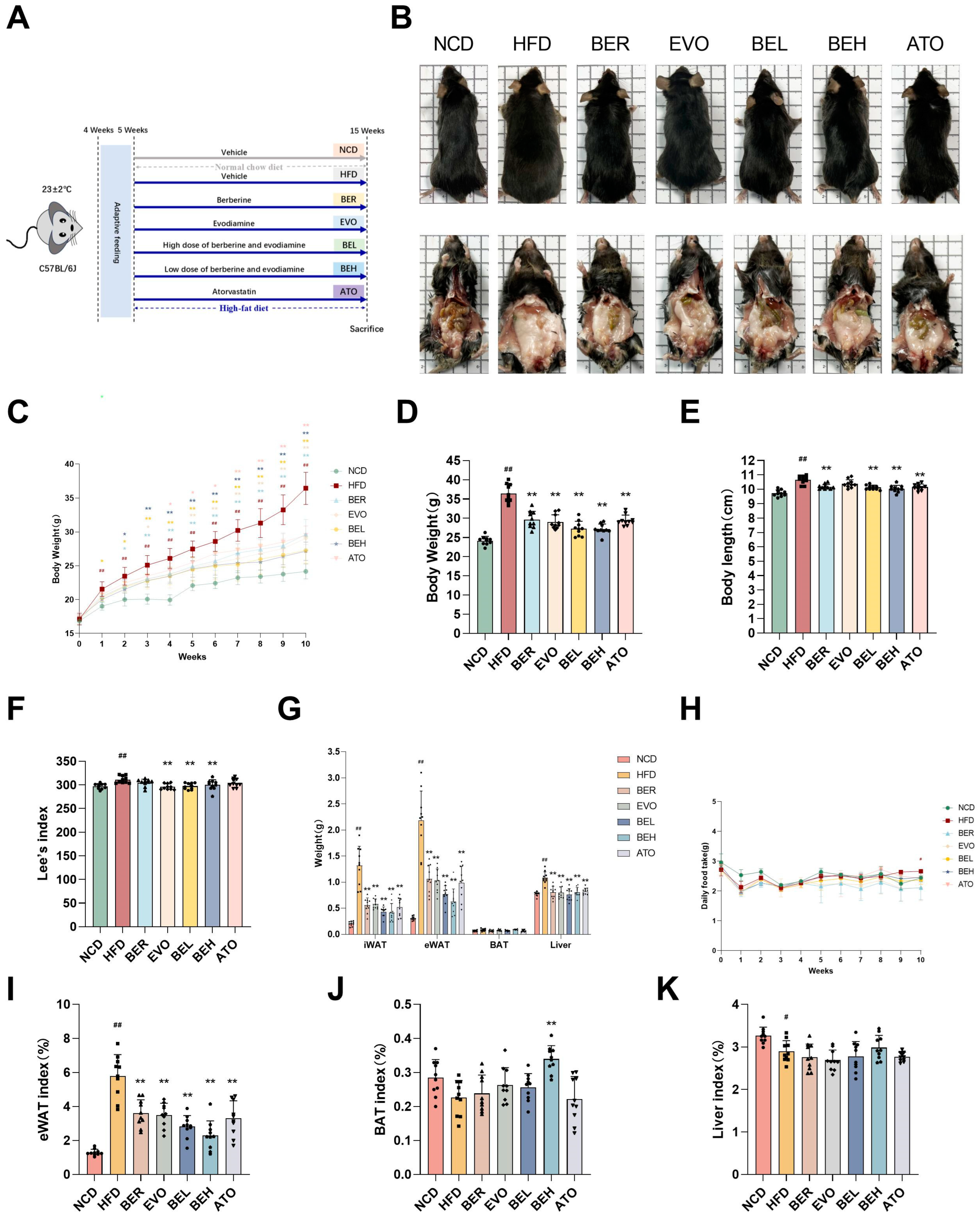
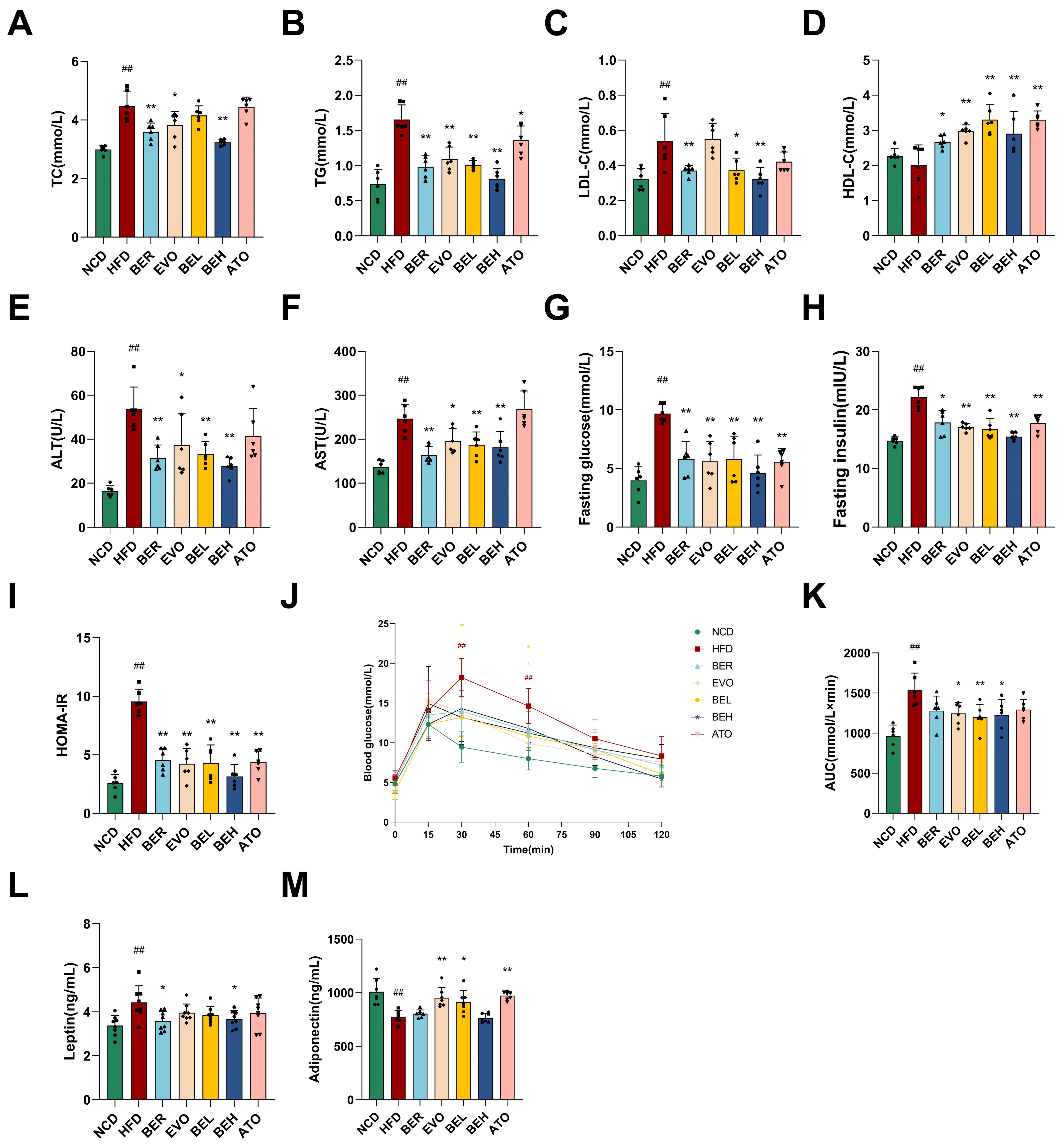
2.5. BBE Reduces Body Weight and Enhances Metabolic Health in Mice Maintained on a High-Fat Diet Regimen
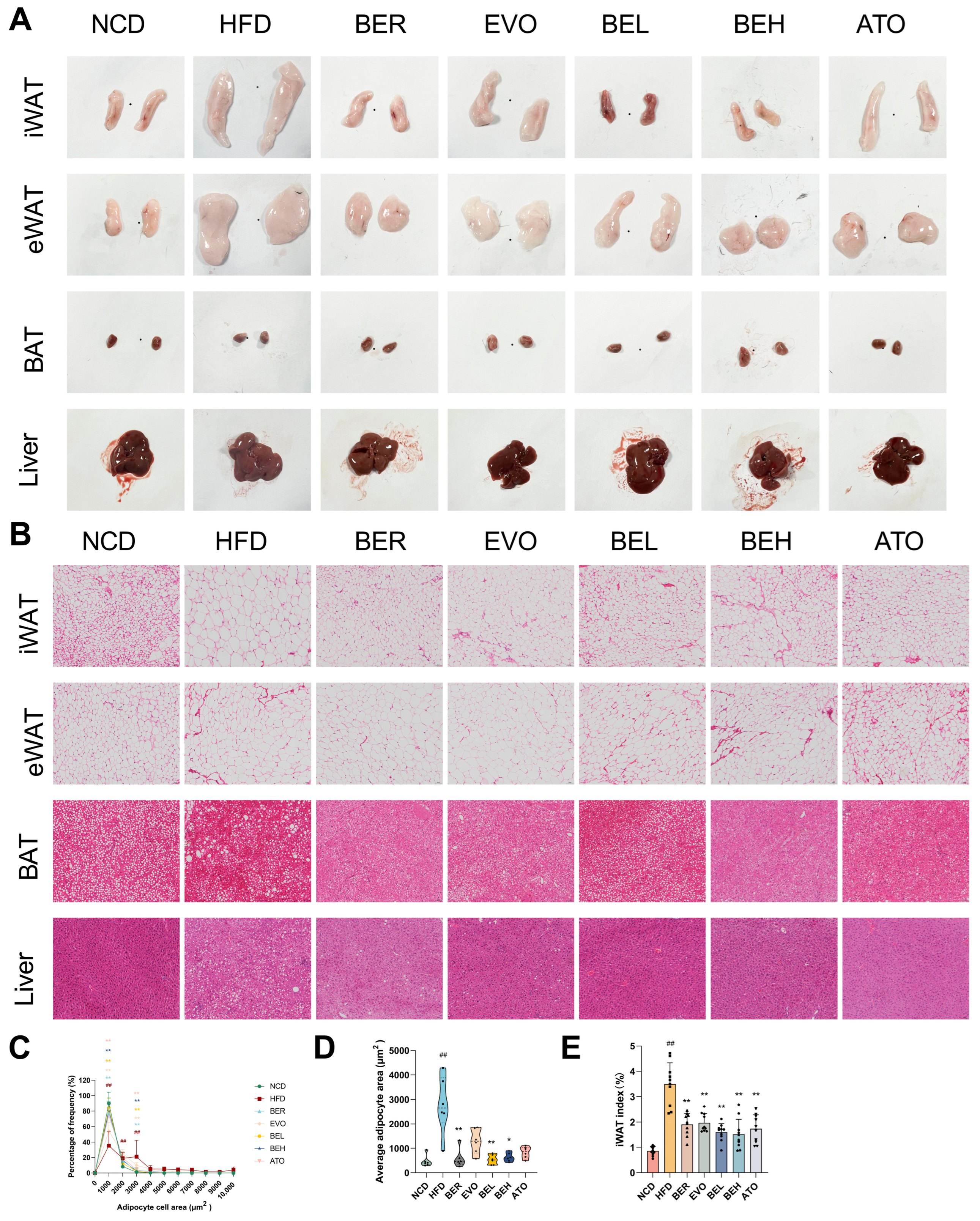
2.6. BBE Reduces Adipocyte Size in Subcutaneous Fat and Lipid Accumulation in Liver
2.7. BBE Promotes iWAT Browning in Obese Mice
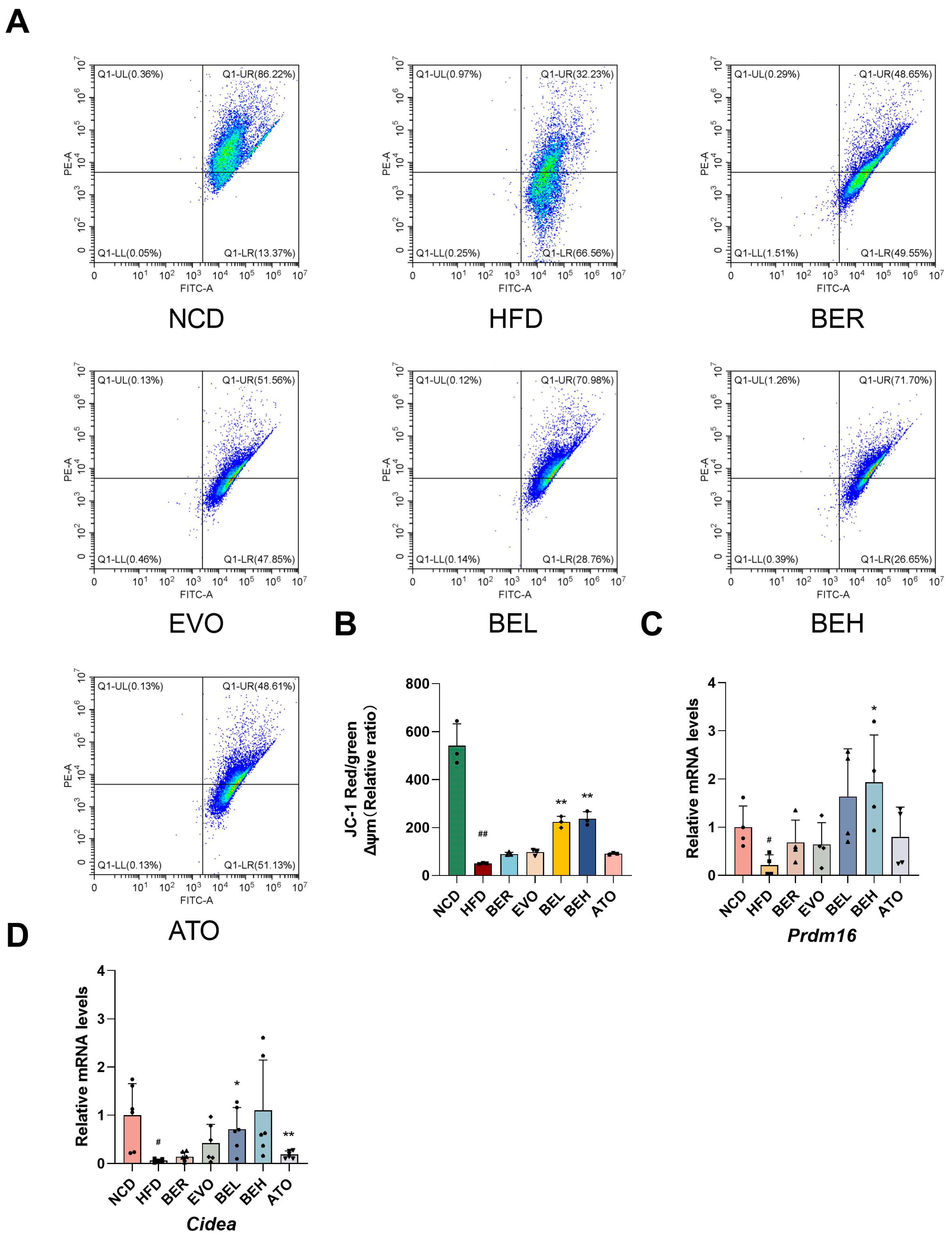
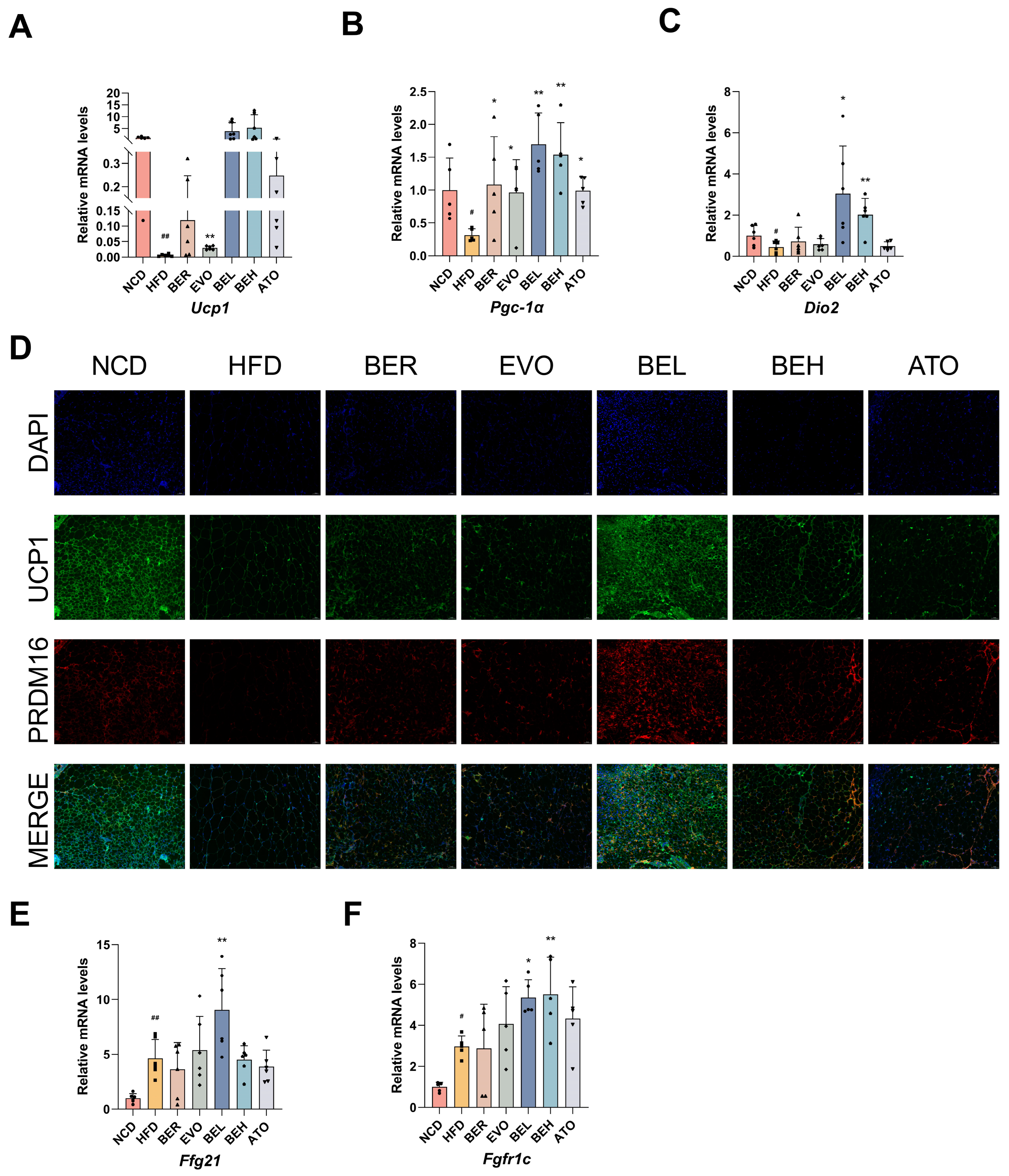
2.8. BBE Promotes iWAT Thermogenesis In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Chemical Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Cell Viability
4.3. Adipocyte Differentiation and Oil Red O Staining
4.4. Animals and Experimental Design
4.5. Analysis of Lipid Profile and Glycemic Indicators
4.6. Detection of BBE by ELISA
4.7. JC-1 Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.8. Histological and Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.9. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Examination
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. In-Silico Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | area under the curve | HOMA | homeostasis model assessment |
| AT | adipose tissue | IBMX | 3-Isobutyl-1-methylxanthine |
| CCK8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 | OGTT | oral glucose tolerance test |
| DAPI | 4ʹ,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride | qRT-PCR | quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium | RIPA | radio immunoprecipitation assay |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum | RT | room temperature |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin | iWAT | inguinal white adipose tissue |
| HDL-C | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol | eWAT | epididymal white adipose tissue |
| LDL-C | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol | BAT | interscapular brown adipose tissue |
| TC | total cholesterol | UCP1 | uncoupling protein 1 |
| TG | triglyceride | DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| SDS-PAGE | SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis | PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene difluoride | WHO | World Health Organization |
| OD | optical density | WAT | white adipose tissue |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | TCM | traditional Chinese medicine |
| BER | berberine hydrochloride | ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| EVO | evodiamine | AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| BBE | a combined berberine and evodiamine treatment | GLU | glucose |
| PAL | palmatine hydrochloride | FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| EPI | epiberberine | P/S | penicillin-streptomycin liquid |
| RUT | rutaecarpine | DEX | dexamethasone |
| HFD | high-fat diet | NCD | normal chow diet |
| COP | coptisine chloride | LIM | limonin |
| PGC-1α | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha | ATO | atorvastatin Calcium |
| PRDM16 | PRdomain-containing16 | CIDEA | Cell Death-Inducing DFF45-Like Effector A |
References
- Campbell, L.A.; Kombathula, R.; Jackson, C.D. Obesity in adults. Lancet 2024, 404, 972–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Okunogbe, A.; Nugent, R.; Spencer, G.; Powis, J.; Ralston, J.; Wilding, J. Economic impacts of overweight and obesity: Current and future estimates for 161 countries. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 79, e009773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qi, J.; Li, L. Phytochemicals as potential candidates to combat obesity via adipose non-shivering thermogenesis. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 147, 104393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funcke, J.-B.; Scherer, P.E. Beyond adiponectin and leptin: Adipose tissue-derived mediators of inter-organ communi-cation. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 1648–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P.; Kajimura, S. The cellular and functional complexity of thermogenic fat. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelt, A.; Heeren, J. Adipose tissue browning and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.-M.; Cho, S.-H.; Yoon, J.C. Adipose Tissue and Metabolic Health. Diabetes Metab. J. 2023, 47, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Fu, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Liao, Q.; Zhuang, T.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; et al. Shengmai San formula alleviates high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice through gut microbiota-derived bile acid promotion of M2 macrophage polarization and thermogenesis. Phytomedicine 2024, 133, 155938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.J.; Xie, Z.S.; Yang, H.; Li, P.; Xu, X.J. Moutan Cortex and Paeoniae Radix Rubra reverse high-fat-diet-induced metabolic disorder and restore gut microbiota homeostasis. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 15, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Qi, M.; Tong, R.; Wang, D.; Ding, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L. Plantago asiatica L. Seed Extract Improves Lipid Accumulation and Hyperglycemia in High-Fat Di-et-Induced Obese Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Tian, M.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zou, W.; Zhao, Y. Zuojin Pill ameliorates chronic atrophic gastritis induced by MNNG through TGF-beta1/PI3K/Akt axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 271, 113893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, R.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, J.; Tang, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Shen, T. Uncovering the mechanism of Huanglian-Wuzhuyu herb pair in treating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 296, 115405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Han, J.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Y.; Shen, T. Efficacy of Zhuyu Pill Intervention in a Cholestasis Rat Model: Mutual Effects on Fecal Metabolism and Microbial Diversity. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 695035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Xu, F.; Liang, B.; Zou, X. The Anti-Obesity Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Lipid Metabolism. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 696603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, C. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicology of the fruit of Tetradium ruticarpum: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 113231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Feng, X.; Song, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, G.; Shen, T.; Zhang, X. Effects and Potential Mechanism of Zhuyu Pill Against Atherosclerosis: Network Pharmacology and Ex-perimental Validation. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wu, P.; Wen, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Tao, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Q.; Shen, T.; et al. The zhuyu pill relieves rat cholestasis by regulating the mRNA expression of lipid and bile metabolism associated genes. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1280864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, K.; Xiong, P.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, X.; Gao, R.; Zhou, X.; Shen, T. Zhuyu Pill Alleviates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Bile Acid Metabolism through the Gut-Liver Axis. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 29033–29045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xia, M.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Hu, X.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Shi, H.; et al. Berberine promotes the recruitment and activation of brown adipose tissue in mice and humans. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Bian, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Xu, X.; Yan, H.; Xia, M.; Chang, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Berberine attenuates nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis through the AMPK-SREBP-1c-SCD1 pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 141, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Yamashita, H. Evodiamine inhibits adipogenesis via the EGFR-PKCalpha-ERK signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3655–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, E.J.; Park, H.G.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, J.M.; Yoo, Y.J.; Cha, J.H. Inhibitory effect of evodiamine alone and in combination with rosiglitazone on in vitro adipocyte differ-entiation and in vivo obesity related to diabetes. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ren, F.; Wei, H.; Liu, L.; Shen, T.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Ren, J.; Ni, H. Combination of berberine and evodiamine inhibits intestinal cholesterol absorption in high fat diet in-duced hyperlipidemic rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Ying, J.; Tang, C.; Wang, Q. Traditional Chinese medicine for anti-Alzheimer’s disease: Berberine and evodiamine from Evodia rutaecarpa. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Qiu, C.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, T.; Cui, Y.L. Intranasal co-delivery of berberine and evodiamine by self-assembled thermosensitive in-situ hydrogels for improving depressive disorder. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 603, 120667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.N.; Han, X.; Xu, L.N.; Yin, L.H.; Xu, Y.W.; Qi, Y.; Peng, J.Y. Enhancement of apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells through synergy of berberine and evodiamine. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Ni, J.; Zhang, C.; Jia, J.; Wu, G.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Berberine Relieves Metabolic Syndrome in Mice by Inhibiting Liver Inflammation Caused by a High-Fat Diet and Potential Association With Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 752512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yende, A.S.; Sharma, D. Obesity, dysbiosis and inflammation: Interactions that modulate the efficacy of immuno-therapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1444589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. The Challenge of Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/the-challenge-of-obesity (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Recalde, M.; Pistillo, A.; Davila-Batista, V.; Leitzmann, M.; Romieu, I.; Viallon, V.; Freisling, H.; Duarte-Salles, T. Longitudinal body mass index and cancer risk: A cohort study of 2.6 million Catalan adults. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, P.A.; Elbein, S.C.; Hirsch, I.B.; Kelley, D.; McGill, J.; Taylor, T.; Weiss, S.R.; Crockett, S.E.; Kaplan, R.A.; Comstock, J.; et al. Role of orlistat in the treatment of obese patients with type 2 diabetes. A 1-year randomized double-blind study. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwal, R.S.; Rucker, D.; Li, S.K.; Curioni, C.; Lau, D.C. Long-term pharmacotherapy for obesity and overweight. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004, 2003, CD004094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi-Sunyer, X.; Astrup, A.; Fujioka, K.; Greenway, F.; Halpern, A.; Krempf, M.; Lau, D.C.; le Roux, C.W.; Violante Ortiz, R.; Jensen, C.B.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of 3.0 mg of Liraglutide in Weight Management. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, B.; Dhingra, A.K. Natural products: A lead for drug discovery and development. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 4660–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.; Han, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, T.; He, K.; Han, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ye, X.; Li, X. Synergetic cholesterol-lowering effects of main alkaloids from Rhizoma Coptidis in HepG2 cells and hypercholesterolemia hamsters. Life Sci. 2016, 151, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, P.C.; Chen, W.Y.; Wang, T.M.; Chu, Y.L. Coptis chinensis, and extracts of guava and mulberry leaves present good inhibiting potential on obesity and associated metabolic disorders in high-fat diet obesity mice model. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2023, 13, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Bai, D.; Wu, X.X. Mechanism of the components compatibility of Scutellariae Radix and Coptidis Rhizoma on mice with hyperlipidemia by regulating the Cyp4a family. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 331, 118263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Lou, G.H.; Zeng, H.R.; Hu, J.; Huang, Q.W.; Peng, W.; Yang, X.B. Coptidis Rhizoma: A comprehensive review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Pharm. Biol. 2019, 57, 193–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakonieczna, S.; Grabarska, A.; Gawel, K.; Wróblewska-Łuczka, P.; Czerwonka, A.; Stepulak, A.; Kukula-Koch, W. Isoquinoline Alkaloids from Coptis chinensis Franch: Focus on Coptisine as a Potential Therapeutic Candidate against Gastric Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.-J.; Noh, J.-W.; Lee, B.-C. Mechanisms and Effect of Coptidis Rhizoma on Obesity-Induced Inflammation: In Silico and In Vivo Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Wang, D.; Ren, S.; Hua, H.; Morikawa, T.; Pan, Y.; Liu, X. Effect of CYP3A inducer/inhibitor on pharmacokinetics of five alkaloids in Evodiae Fructus. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 327, 109146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.B.; Huang, Y.M.; Lau, C.N.; Wat, C.K.; Kong, Y.C. Hypotensive effect of dehydroevodiamine from Evodiae Fructus. Am. J. Chin. Med. 1982, 10, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.F.; Wang, B.X.; Li, T.J.; Tashiro, S.; Minami, M.; Xing, D.J.; Ikejima, T. Evodiamine, a constituent of Evodiae Fructus, induces anti-proliferating effects in tumor cells. Cancer Sci. 2003, 94, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.J.; Liu, J.; Wang, A.T.; Meng, X.T.; Yang, Z.R.; Peng, C.; Guan, H.S.; Wang, C.Y.; Yan, D. Berberine alleviates insulin resistance by reducing peripheral branched-chain amino acids. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 316, E73–E85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Xu, J.; Kang, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Structural changes of gut microbiota during berberine-mediated prevention of obesity and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, S.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, C.; Wu, X. The Protective Effect of Evodiamine in Osteoarthritis: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study in Mice Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 899108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zou, D.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Zhu, N.; Huo, L.; Wang, M.; Hong, J.; Wu, P.; et al. Treatment of type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia with the natural plant alkaloid berberine. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Liu, B.; Zhuang, X.J.; Shen, Y.D.; Tian, H.R.; Ji, Y.; Li, L.X.; Liu, F. Effects of berberine on the serum cystatin C levels and urine albumin/creatine ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018, 98, 3756–3761. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.Q.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.M.; Liu, S. Effects of berberine on diabetes induced by alloxan and a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 108, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Feng, K.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Yuan, T.; Sun, X.; Sun, Q.; Xiang, H.; Wang, H. Berberine Moderates Glucose and Lipid Metabolism through Multipathway Mechanism. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 924851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, X.; Ghanam, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, T.; Zhu, X. Berberine decreases cholesterol levels in rats through multiple mechanisms, including inhibition of cholesterol absorption. Metabolism 2014, 63, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Malainer, C.; Atanasov, A.G.; Heiß, E.H.; Dirsch, V.M.; Wang, L.; Wang, K. Evodiamine Lowers Blood Lipids by Up-Regulating the PPARgamma/ABCG1 Pathway in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 3110–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnke, G.D.; Price, C.J.; Marr, M.C.; Myers, C.B.; George, J.D. Developmental toxicity evaluation of berberine in rats and mice. Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2006, 77, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yin, J.; Gao, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, M. Berberine improves insulin sensitivity by inhibiting fat store and adjusting adipokines profile in human preadipocytes and metabolic syndrome patients. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 363845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, R.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, J.; Yin, D. Coptis chinensis polysaccharides dynamically influence the paracellular absorption pathway in the small intestine by modulating the intestinal mucosal immunity microenvironment. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Liang, R.; Chen, M.; Li, Z.; Tao, X.; Ren, H.; Sheng, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, R.; Zhao, C.; et al. Metabolic characteristics of evodiamine were associated with its hepatotoxicity via PPAR/PI3K/AKT/NF-small ka, CyrillicB/tight junction pathway-mediated apoptosis in zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 279, 116448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.J.; Vernieri, C.; Foiani, M.; Jiang, J.D. Berberine in the treatment of metabolism-related chronic diseases: A drug cloud (dCloud) effect to target multifactorial disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 209, 107496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Chen, F.; Wang, S.; Niu, C.; Liao, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, F. Serum untargeted metabolomics analysis of the mechanisms of evodiamine on type 2 diabetes mellitus model rats. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 6623–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verboven, K.; Wouters, K.; Gaens, K.; Hansen, D.; Bijnen, M.; Wetzels, S.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Goossens, G.H.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Blaak, E.E.; et al. Abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adipocyte size, lipolysis and inflammation relate to insulin resistance in male obese humans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopelman, P.G. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 2000, 404, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Choubey, M.; Patel, S.; Singer, H.A.; Ozcan, L. Adipocyte CAMK2 deficiency improves obesity-associated glucose intolerance. Mol. Metab. 2021, 53, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouchani, E.T.; Kazak, L.; Spiegelman, B.M. Spiegelman, New Advances in Adaptive Thermogenesis: UCP1 and Beyond. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, L.W.; Feng, H.; Tang, Y.; Fu, S.Q.; Liu, X.M.; Zhu, X.Y. The Chinese herbal medicine Dai-Zong-Fang promotes browning of white adipocytes in vivo and in vitro by activating PKA pathway to ameliorate obesity. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1176443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorova, L.D.; Popkov, V.A.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; Silachev, D.N.; Pevzner, I.B.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Babenko, V.A.; Zorov, S.D.; Balakireva, A.V.; Juhaszova, M. Mitochondrial membrane potential. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 552, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.W.; Norman, J.P.; Barbieri, J.; Brown, E.B.; Gelbard, H.A. Mitochondrial membrane potential probes and the proton gradient: A practical usage guide. Biotechniques 2011, 50, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivandzade, F.; Bhalerao, A.; Cucullo, L. Analysis of the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Using the Cationic JC-1 Dye as a Sensitive Fluorescent Probe. Bio-Protoc. 2019, 9, e3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colangeli, L.; Escobar Marcillo, D.I.; Simonelli, V.; Iorio, E.; Rinaldi, T.; Sbraccia, P.; Fortini, P.; Guglielmi, V. The Crosstalk between Gut Microbiota and White Adipose Tissue Mitochondria in Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, M.; Seale, P. Brown and beige fat: Development, function and therapeutic potential. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargut, T.C.L.; Souza-Mello, V.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A. Browning of white adipose tissue: Lessons from experimental models. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2017, 31, 20160051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiger, H.; Keuper, M.; Berti, L.; Hrabe de Angelis, M.; Häring, H.U. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21-Metabolic Role in Mice and Men. Endocr. Rev. 2017, 38, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, T.; Bina, H.A.; Schneider, M.A.; Dunbar, J.D.; Hu, C.C.; Chen, Y.; Moller, D.E.; Kharitonenkov, A. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Corrects Obesity in Mice. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 6018–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondares, E.; Rosell, M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Giralt, M.; Iglesias, R.; Villarroya, F. Hepatic FGF21 Expression Is Induced at Birth via PPARα in Response to Milk Intake and Contributes to Thermogenic Activation of Neonatal Brown Fat. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, F.M.; Kleiner, S.; Douris, N.; Fox, E.C.; Mepani, R.J.; Verdeguer, F.; Wu, J.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E.; et al. FGF21 regulates PGC-1α and browning of white adipose tissues in adaptive thermogenesis. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada-López, T.; Cereijo, R.; Turatsinze, J.V.; Planavila, A.; Cairó, M.; Gavaldà-Navarro, A.; Peyrou, M.; Moure, R.; Iglesias, R.; Giralt, M.; et al. The lipid sensor GPR120 promotes brown fat activation and FGF21 release from adipocytes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondares, E.; Iglesias, R.; Giralt, A.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Giralt, M.; Mampel, T.; Villarroya, F. Thermogenic Activation Induces FGF21 Expression and Release in Brown Adipose Tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 12983–12990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharitonenkov, A.; Shiyanova, T.L.; Koester, A.; Ford, A.M.; Micanovic, R.; Galbreath, E.J.; Sandusky, G.E.; Hammond, L.J.; Moyers, J.S.; Owens, R.A.; et al. FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, R.; Seino, Y.; Ogata, H.; Murase, M.; Iida, A.; Hosokawa, K.; Joo, E.; Harada, N.; Tsunekawa, S.; Hamada, Y.; et al. Chronic high-sucrose diet increases fibroblast growth factor 21 production and energy expenditure in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 49, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkington, A.-C.; Paz, H.A.; Wankhade, U.D. Wankhade, Beige Adipose Tissue Identification and Marker Specificity—Overview. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 599134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpulla, R.C.; Vega, R.B.; Kelly, D.P. Transcriptional integration of mitochondrial biogenesis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, S.; Mepani, R.J.; Laznik, D.; Ye, L.; Jurczak, M.J.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Estall, J.L.; Chatterjee Bhowmick, D.; Shulman, G.I.; Spiegelman, B.M. Development of insulin resistance in mice lacking PGC-1α in adipose tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9635–9640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, D.H.; Moon, S.; Gu, B.; Mantik, K.E.K.; Kwak, H.B.; Ryu, J.K.; Kang, J.H. Ketogenic diet with aerobic exercise can induce fat browning: Potential roles of β-hydroxybutyrate. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1443483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Liang, X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, N.; Zhou, L.J.; Liu, W.W.; Ma, Q.; Hu, B.; Gao, H.; et al. Atractylenolide III from Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz promotes the activation of brown and white adipose tissue through SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddish, K.; Yun, J.W. Dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) negatively regulates UCP1- and ATP-dependent thermogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and C2C12 muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 2023, 475, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ma, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Xia, J.; Liu, D.; Mu, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, D. The Role of β3-Adrenergic Receptors in Cold-Induced Beige Adipocyte Production in Pigs. Cells 2024, 13, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Guo, X.; Fan, B.; Wang, F. Potato protease inhibitor II prevents obesity by inducing browning of white adipose tissue in mice via β3 adrenergic receptor signaling pathway. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 3885–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, P.; Xie, C.; Nichols, R.G.; Ferrell, J.M.; Boehme, S.; Krausz, K.W.; Patterson, A.D.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Chiang, J.Y.L. Intestine farnesoid X receptor agonist and the gut microbiota activate G-protein bile acid receptor-1 signaling to improve metabolism. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Rose, A.J.; Sijmonsma, T.P.; Bröer, A.; Pfenninger, A.; Herzig, S.; Schmoll, D.; Bröer, S. Mice lacking neutral amino acid transporter B0AT1 (Slc6a19) have elevated levels of FGF21 and GLP-1 and improved glycaemic control. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primers | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| PGC-1α-F | ATGTGTCGCCTTCTTGCTCTT |
| PGC-1α-R | GGACCTTGATCTTGACCTGGAA |
| UCP1-F | AGGCTTCCAGTACCATTAGGT |
| UCP1-R | CTGAGTGAGGCAAAGCTGATTT |
| PRDM16-F | GCCGTTCAAGTGCCATCTGT |
| PRDM16-R | CCTCGTGTTCGTGCTTCTTCA |
| CIDEA-F | TCCTCGGCTGTCTCAATGTCA |
| CIDEA-R | GGATGGCTGCTCTTCTGTATCG |
| DIO2-F | GTGGCTGACTTCCTGTTGGTAT |
| DIO2-R | GCACATCGGTCCTCTTGGTT |
| FGF21-F | AGCACACCGCAGTCCAGAA |
| FGF21-R | GTCCTCCAGCAGCAGTTCTCT |
| FGFR1c-F | GATGACCTCACCGCTCTACCT |
| FGFR1c-R | TCTGGCTATGGAAGTCGCTCTT |
| GAPDH-F | CAGTGGCAAAGTGGAGATTGTTG |
| GAPDH-R | TCGCTCCTGGAAGATGGTGAT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Xiong, P.; Zheng, T.; Hu, Y.; Guo, P.; Shen, T.; Zhou, X. Combination of Berberine and Evodiamine Alleviates Obesity by Promoting Browning in 3T3-L1 Cells and High-Fat Diet-Induced Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094170
Zhang H, Xiong P, Zheng T, Hu Y, Guo P, Shen T, Zhou X. Combination of Berberine and Evodiamine Alleviates Obesity by Promoting Browning in 3T3-L1 Cells and High-Fat Diet-Induced Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094170
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huiying, Peiyu Xiong, Tianyan Zheng, Youfan Hu, Pengmei Guo, Tao Shen, and Xin Zhou. 2025. "Combination of Berberine and Evodiamine Alleviates Obesity by Promoting Browning in 3T3-L1 Cells and High-Fat Diet-Induced Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094170
APA StyleZhang, H., Xiong, P., Zheng, T., Hu, Y., Guo, P., Shen, T., & Zhou, X. (2025). Combination of Berberine and Evodiamine Alleviates Obesity by Promoting Browning in 3T3-L1 Cells and High-Fat Diet-Induced Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094170






