Differential H3K4me3 Domains in Normal and Colorectal Cancer Cells Reveal Novel Epigenetic Targets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
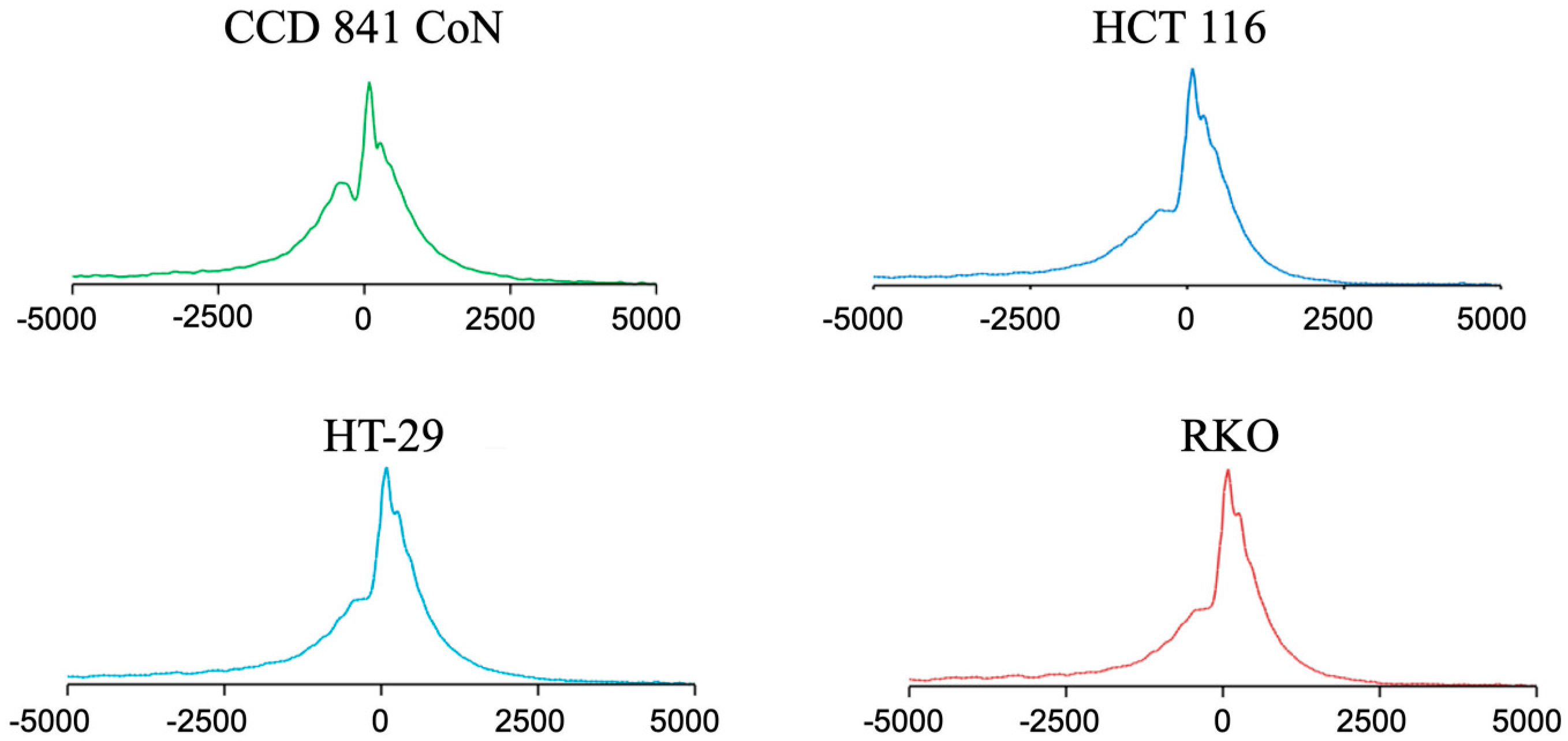
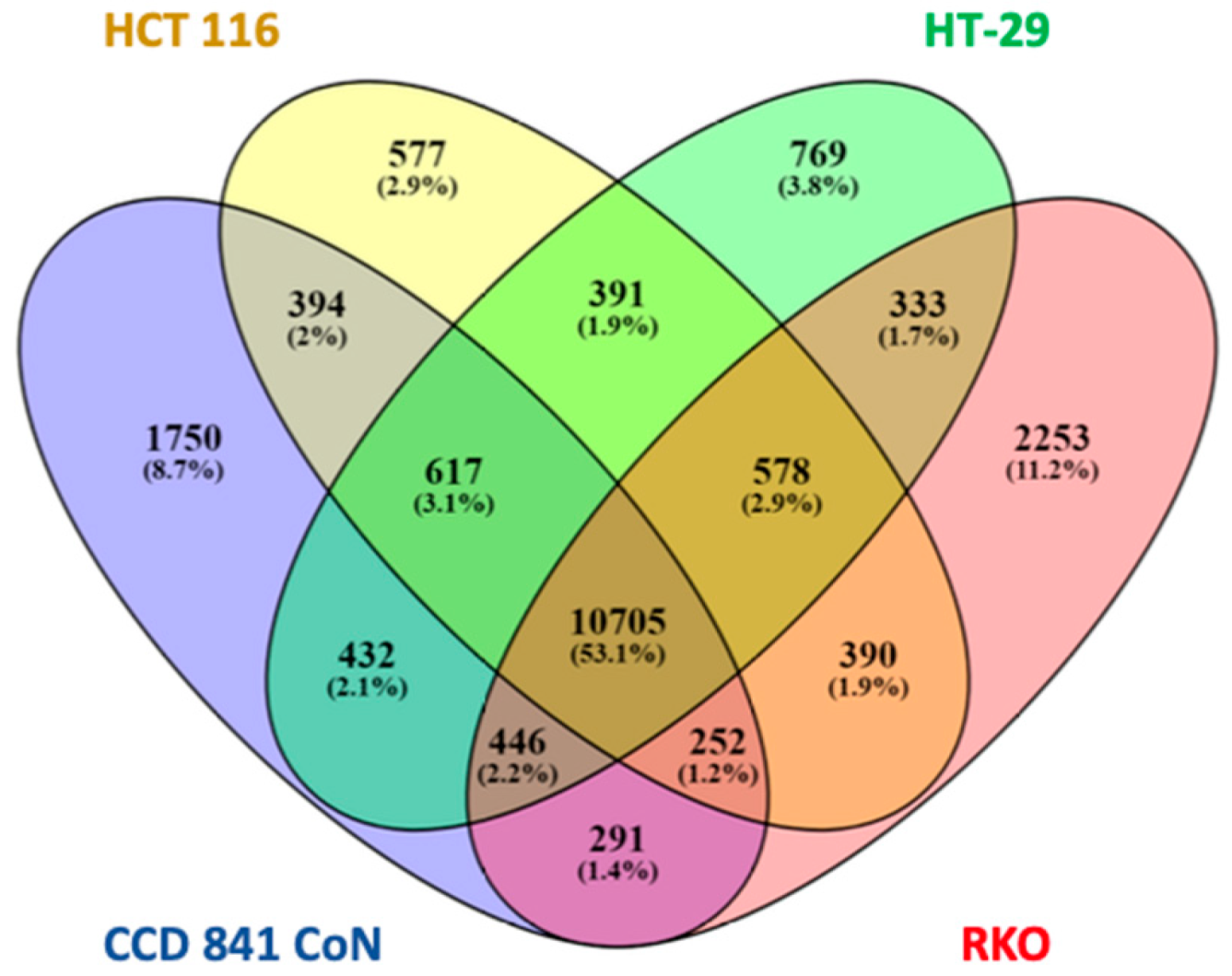
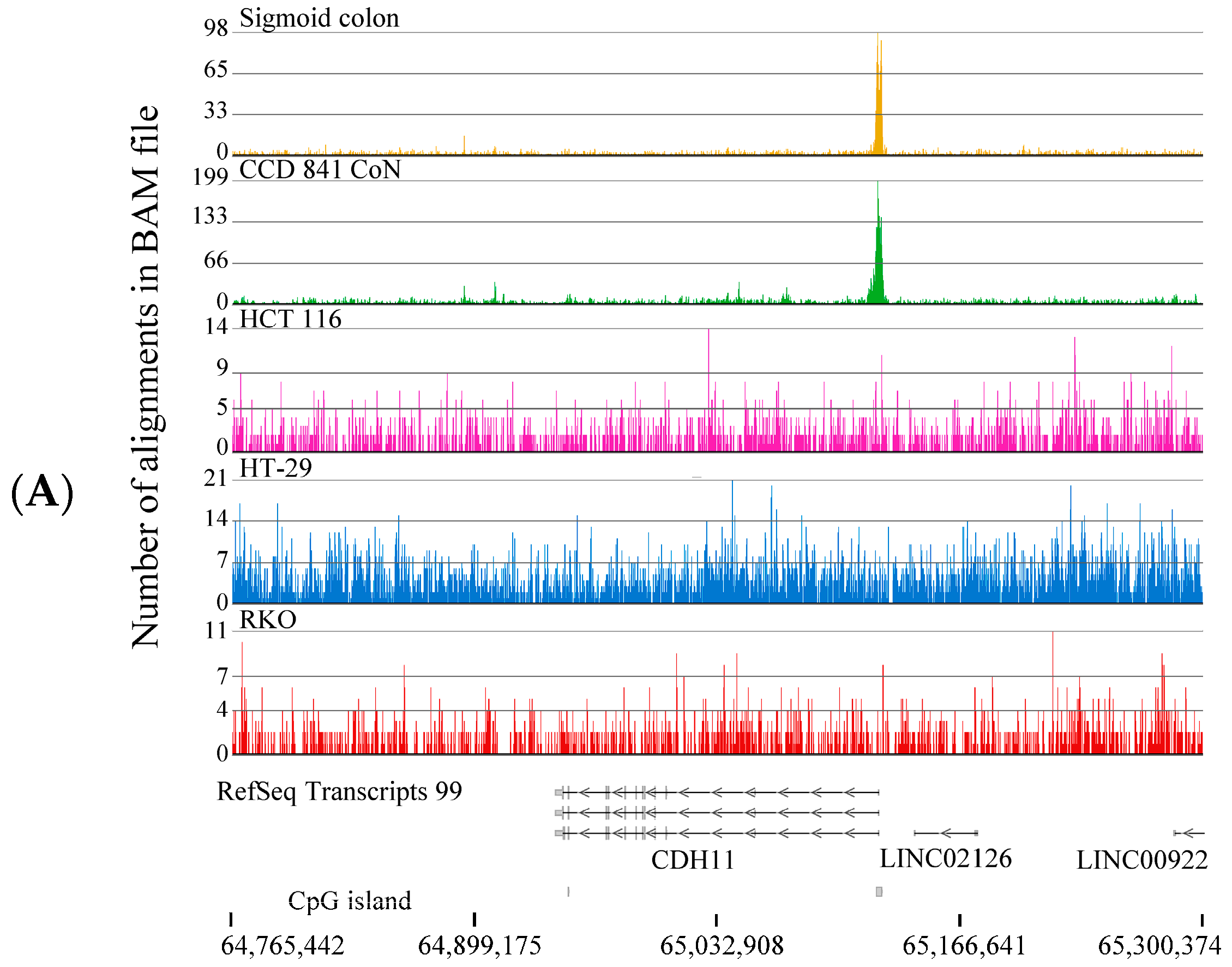
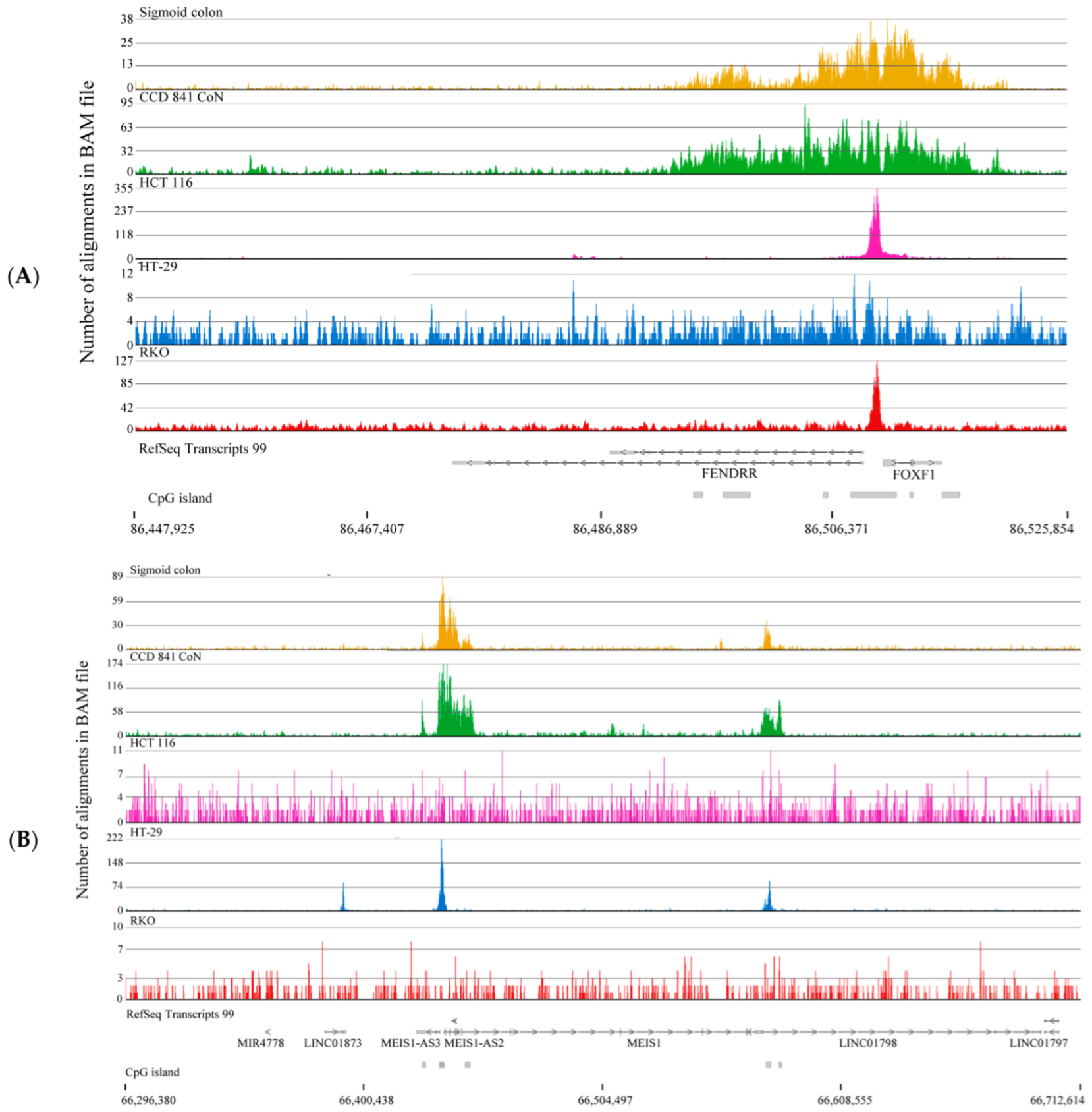
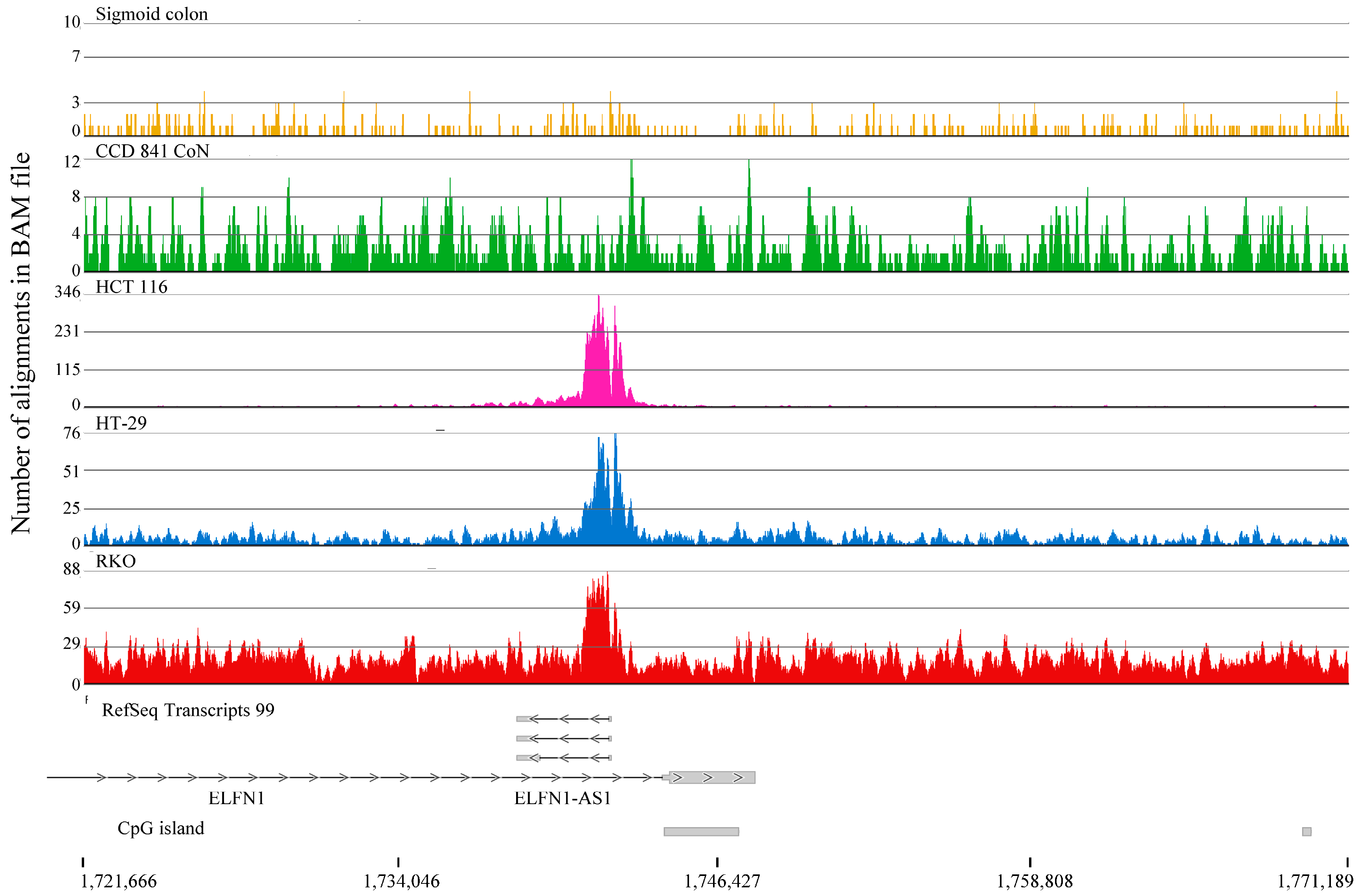
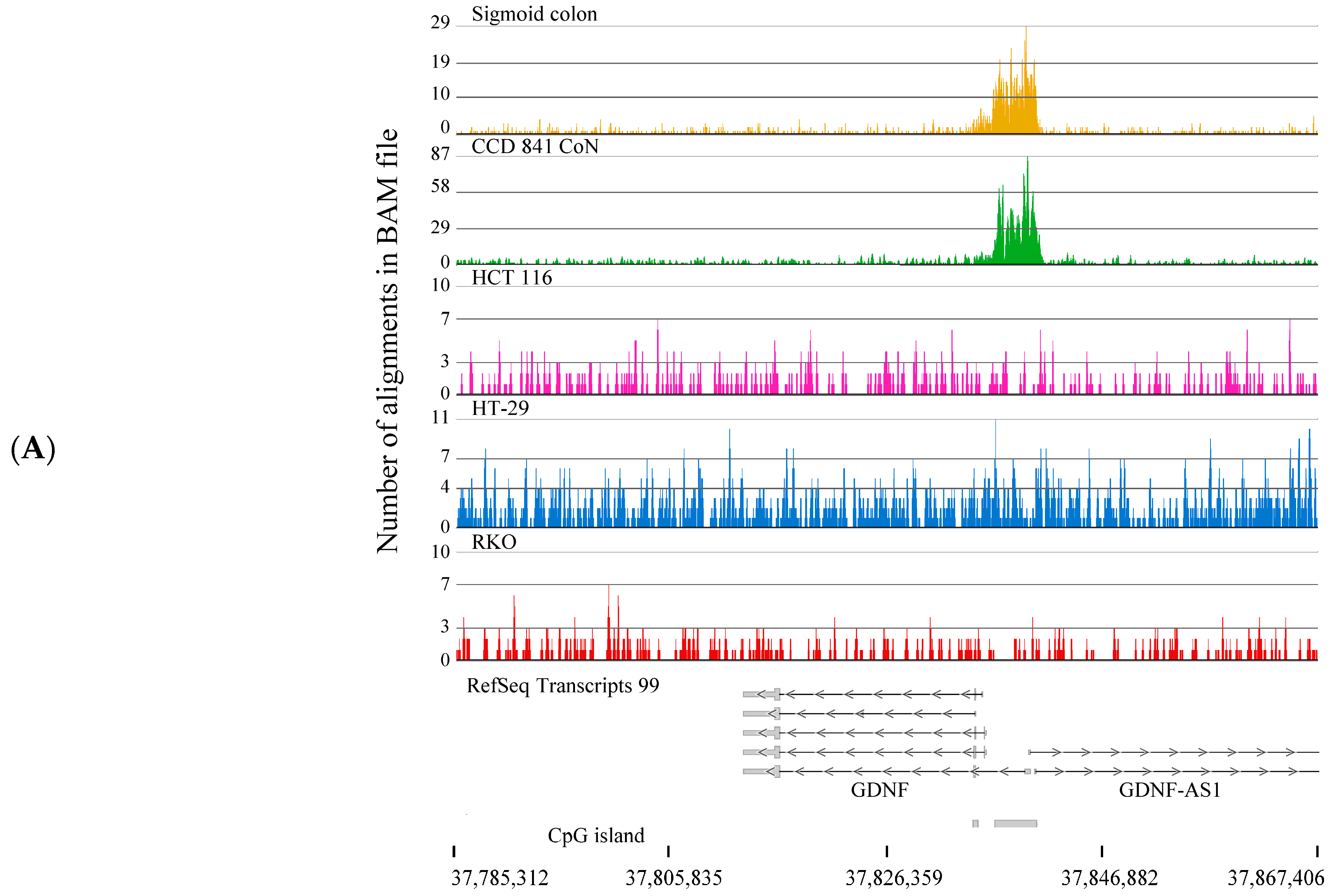
2.1. H3K4me3 Distribution in Normal Colon Versus Colorectal Cancer Cells
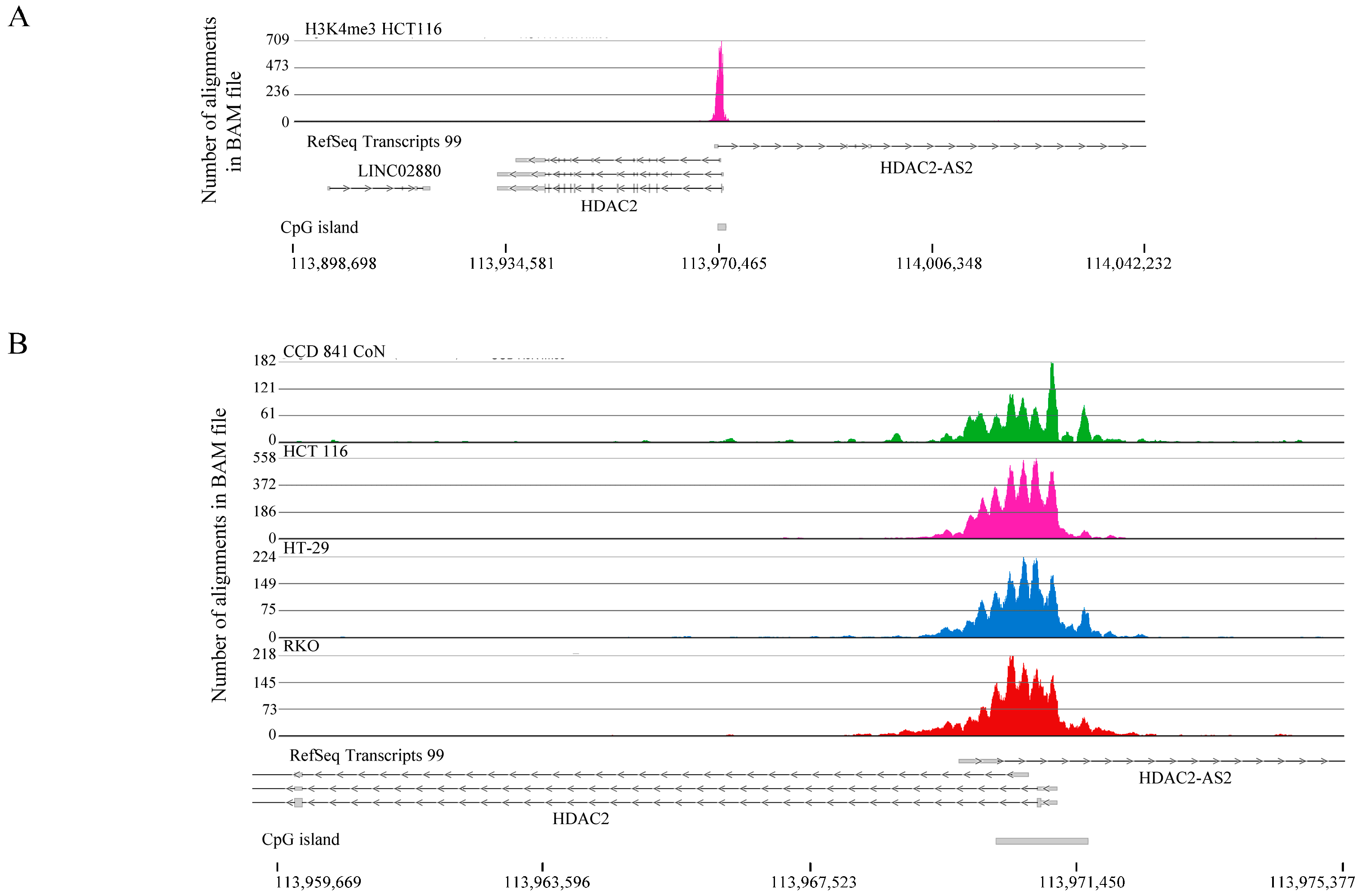
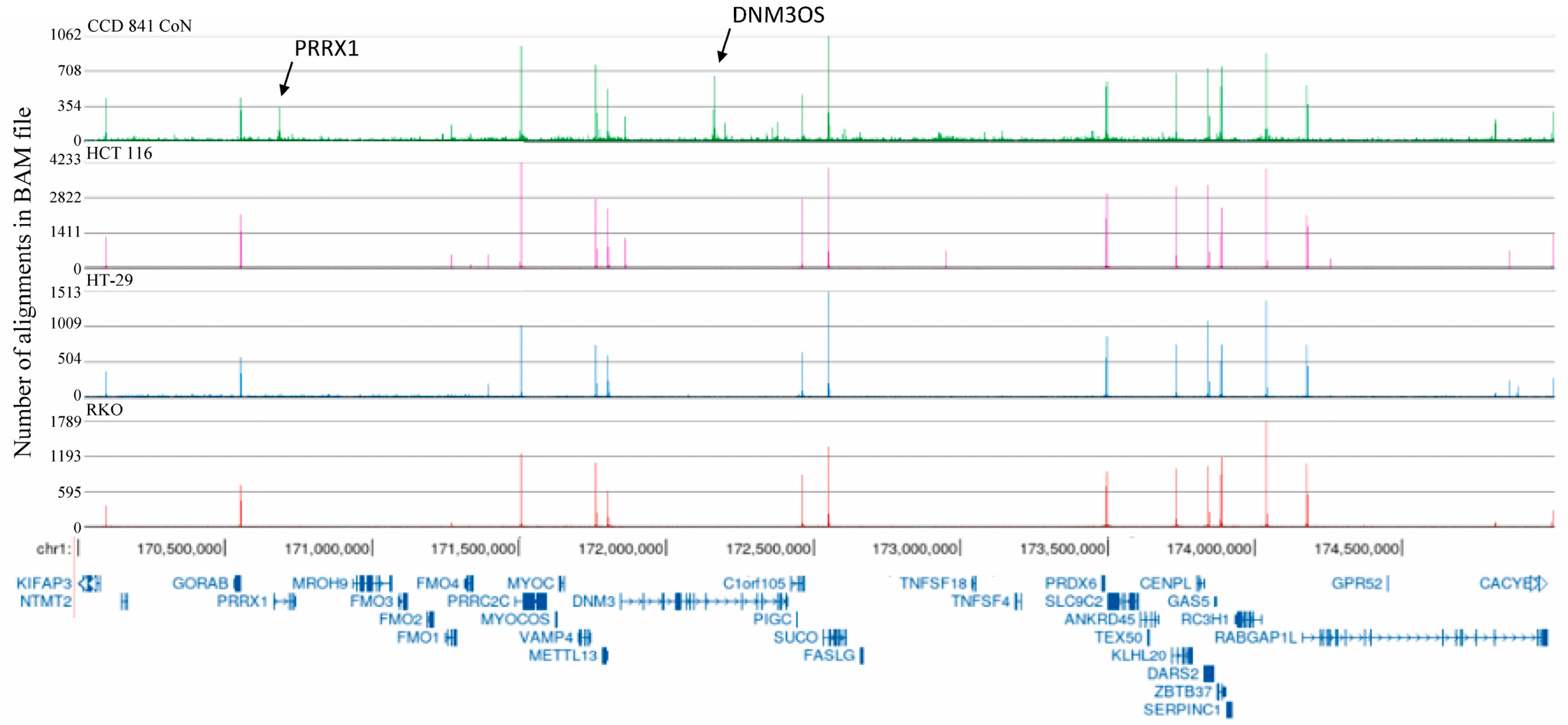
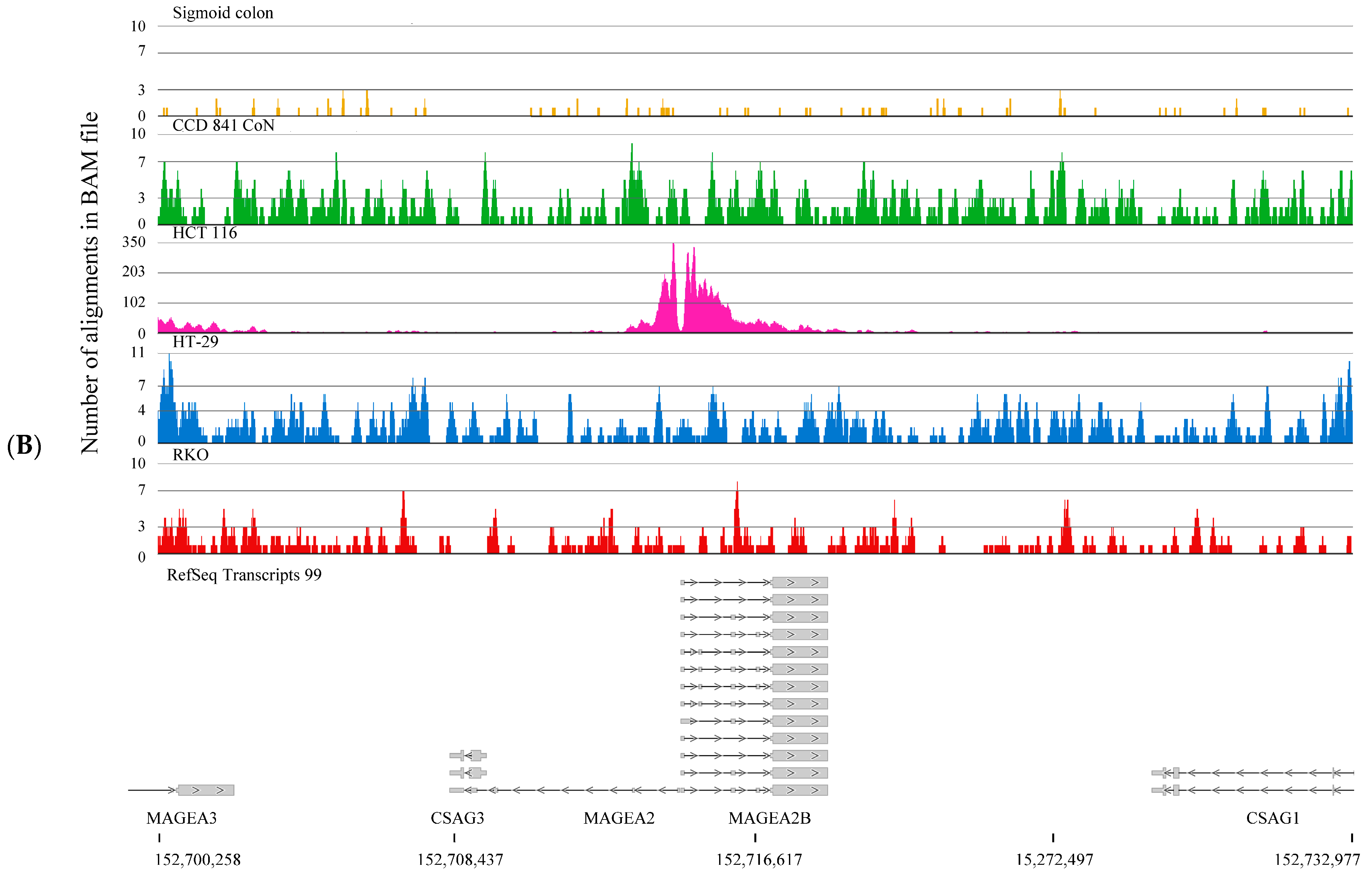
2.2. H3K4me3-Marked Genes Associated with Cell Adhesion and Nervous System Development Were Unique in Normal Colon Cells
2.3. Broad H3K4me3 Domains in Normal Colon Versus Colorectal Cancer Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Histone Isolation and Immunoblot Analysis
4.3. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assays and Sequencing
4.4. Partek Flow Analyses
4.5. Data Collection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, K.; Chen, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X.; Su, J.; Rodriguez, B.; Xi, Y.; Xia, Z.; Chen, X.; et al. Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor-suppressor genes. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, T.K.; Imhof, A. Fast signals and slow marks: The dynamics of histone modifications. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zee, B.M.; Levin, R.S.; A DiMaggio, P.; A Garcia, B. Global turnover of histone post-translational modifications and variants in human cells. Epigenet. Chromatin. 2010, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Helin, K. Roles of H3K4 methylation in biology and disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, 35, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.H.; Gonzalez, C.; Tailor, N.; Hamedani, M.K.; Leygue, E.; Davie, J.R. Dynamic Histone Acetylation of H3K4me3 Nucleosome Regulates MCL1 Pre-mRNA Splicing. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 2196–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukauskas, S.; Tvardovskiy, A.; Nguyen, N.V.; Stadler, M.; Faull, P.; Ravnsborg, T.; Aygenli, B.Ö.; Dornauer, S.; Flynn, H.; Lindeboom, R.G.H.; et al. Decoding chromatin states by proteomic profiling of nucleosome readers. Nature 2024, 627, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, J.W.; Mahadevan, L.C.; Clayton, A.L. Dynamic histone H3 methylation during gene induction: HYPB/Setd2 mediates all H3K36 trimethylation. EMBO J. 2007, 27, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, D.; Marchetti, L.; Mikulasova, A.; Russell, L.J.; Rico, D. Broad H3K4me3 domains: Maintaining cellular identity and their implication in super-enhancer hijacking. BioEssays 2023, 45, e2200239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulasova, A.; Kent, D.; Trevisan-Herraz, M.; Karataraki, N.; Fung, K.T.M.; Ashby, C.; Cieslak, A.; Yaccoby, S.; van Rhee, F.; Zangari, M.; et al. Epigenomic translocation of H3K4me3 broad domains over oncogenes following hijacking of super-enhancers. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, L.K.; Kidder, B.L. Integrative pan cancer analysis reveals epigenomic variation in cancer type and cell specific chromatin domains. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Danielsen, S.A.; Eknaes, M.; Hektoen, M.; Lind, G.E.; Lothe, R.A. Epigenetic and genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Li, W.; Chen, M.; Jiang, M.; Fan, X. LncRNA FIRRE functions as a tumor promoter by interaction with PTBP1 to stabilize BECN1 mRNA and facilitate autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Gao, B.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, G. SLCO1B3 promotes colorectal cancer tumorigenesis and metastasis through STAT3. Aging 2021, 13, 22164–22175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; He, J.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, M.; Zeng, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; He, M.; Zhou, Q.; Feng, D.; et al. ELFN1-AS1 promotes GDF15-mediated immune escape of colorectal cancer from NK cells by facilitating GCN5 and SND1 association. Discov. Oncol. 2023, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, N.S.; El-Khoueiry, A.; Yin, J.; Oberg, A.L.; Flynn, P.; Adkins, D.; Sharma, A.; Weisenberger, D.J.; Brown, T.; Medvari, P.; et al. Combination epigenetic therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) with subcutaneous 5-azacitidine and entinostat: A phase 2 consortium/stand Up 2 cancer study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 35326–35338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, A.; Kozer, N.; Cohen, G.; Carvalho, S.; Duberstein, S.; Almog, O.; Solmesky, L.J.; Shurrush, K.A.; Babaev, I.; Benjamin, S.; et al. PRMT1 inhibition induces differentiation of colon cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Liao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Ye, H.; Chen, F.; Xu, L.; Ye, M.; Duan, S. Hypermethylation of EDNRB promoter contributes to the risk of colorectal cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdi, M.R.; Georges, R.B.; Ali, D.M.; Bedeer, R.F.; Eltahry, H.M.; Gabr, A.-E.H.Z.; Berger, M.R. Modulation of the Endothelin System in Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis: Influence of Epigenetic Mechanisms? Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Neurotrophic factors in enteric physiology and pathophysiology. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Han, T.; Gao, L.; Zhang, D. The Involvement of Glial Cell-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2022, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafranski, P.; Stankiewicz, P. Long Non-Coding RNA FENDRR: Gene Structure, Expression, and Biological Relevance. Genes 2021, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazaeli, H.; Sheikholeslami, A.; Ghasemian, F.; Amini, E.; Sheykhhasan, M. The Emerging Role of LncRNA FENDRR in Multiple Cancers: A Review. Curr. Mol. Med. 2023, 23, 606–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gan, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, R.; Sun, R.; Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Downregulation of MEIS1 mediated by ELFN1-AS1/EZH2/DNMT3a axis promotes tumorigenesis and oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-H.; Ng, H.-I.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, G.-Q. Application of plasma cell-free DNA in screening of advanced colorectal adenoma. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedyuk, V.; Erez, N.; Furth, N.; Beresh, O.; Andreishcheva, E.; Shinde, A.; Jones, D.; Bar Zakai, B.; Mavor, Y.; Peretz, T.; et al. Multiplexed, single-molecule, epigenetic analysis of plasma-isolated nucleosomes for cancer diagnostics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 41, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeh, R.; Sharkia, I.; Fialkoff, G.; Rahat, A.; Gutin, J.; Chappleboim, A.; Nitzan, M.; Fox-Fisher, I.; Neiman, D.; Meler, G.; et al. ChIP-seq of plasma cell-free nucleosomes identifies gene expression programs of the cells of origin. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.H.; Healy, S.; He, S.; Lichtensztejn, D.; Klewes, L.; Sharma, K.L.; Lau, V.; Mai, S.; Delcuve, G.P.; Davie, J.R. Mitogen-induced distinct epialleles are phosphorylated at either H3S10 or H3S28, depending on H3K27 acetylation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.H.; Gonzalez, C.; Cooper, C.; Sun, J.-M.; Chen, H.Y.; Healy, S.; Xu, W.; Smith, K.T.; Workman, J.L.; Leygue, E.; et al. RNA-dependent dynamic histone acetylation regulates MCL1 alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, 1656–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Biological Process (Ensembl) | Benjamini Score |
|---|---|
| Homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules | 5.6 × 10−11 |
| Cell adhesion | 5.5 × 10−9 |
| Nervous system development | 5.3 × 10−8 |
| Axon guidance | 3.9 × 10−6 |
| Potassium ion transmembrane transport | 1.7 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahia, R.K.; Lopez, C.; Nardocci, G.; Davie, J.R. Differential H3K4me3 Domains in Normal and Colorectal Cancer Cells Reveal Novel Epigenetic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062546
Bahia RK, Lopez C, Nardocci G, Davie JR. Differential H3K4me3 Domains in Normal and Colorectal Cancer Cells Reveal Novel Epigenetic Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062546
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahia, Ravinder Kaur, Camila Lopez, Gino Nardocci, and James R. Davie. 2025. "Differential H3K4me3 Domains in Normal and Colorectal Cancer Cells Reveal Novel Epigenetic Targets" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062546
APA StyleBahia, R. K., Lopez, C., Nardocci, G., & Davie, J. R. (2025). Differential H3K4me3 Domains in Normal and Colorectal Cancer Cells Reveal Novel Epigenetic Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062546







