SUMO-G5C23-D208G@ZIF-F: A Novel Immobilized Enzyme with Enhanced Stability and Reusability for Organophosphorus Hydrolysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. SUMO-G5C23-D208G Expression and Purification
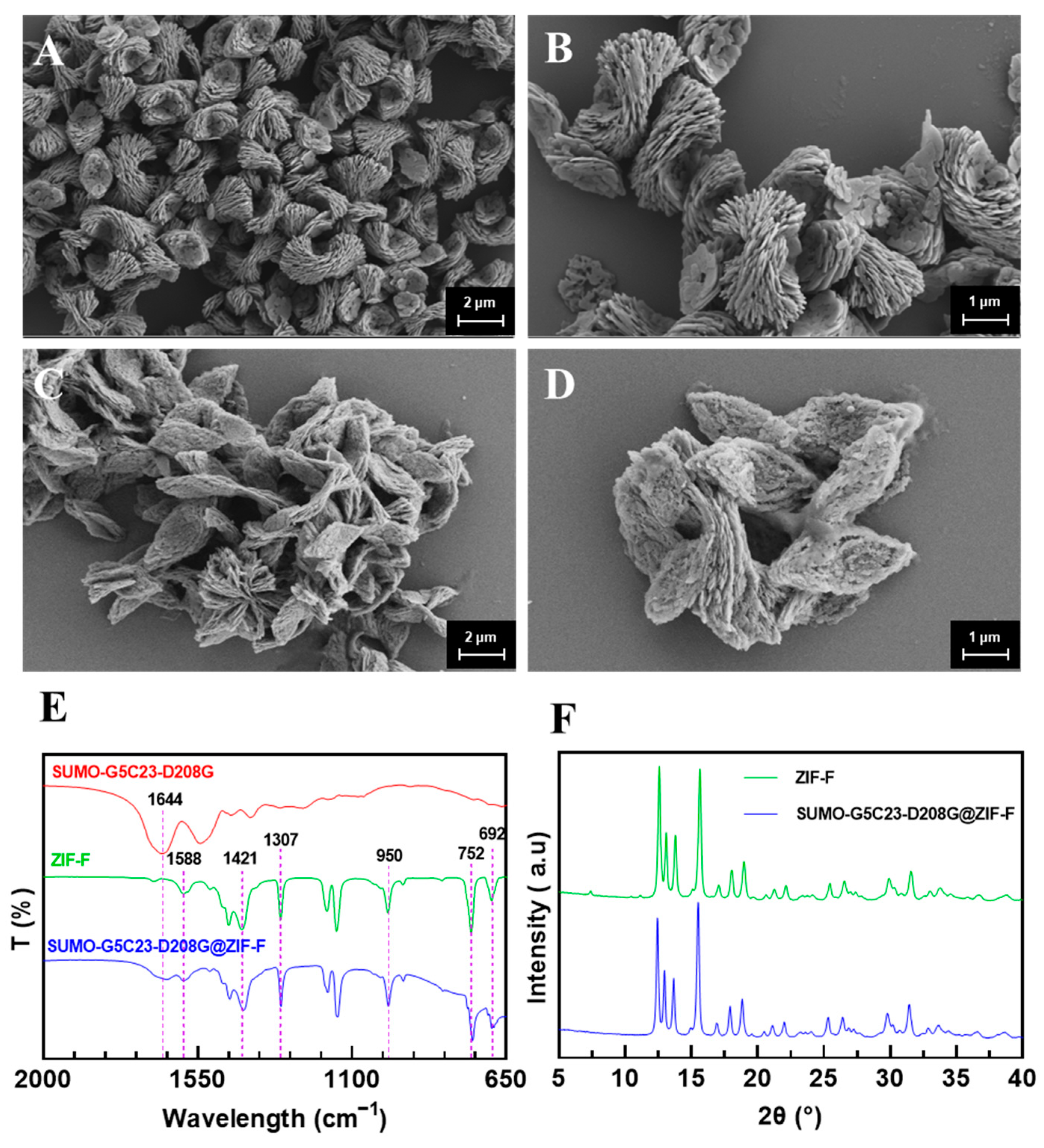
2.2. Characterization of Immobilized Enzymes
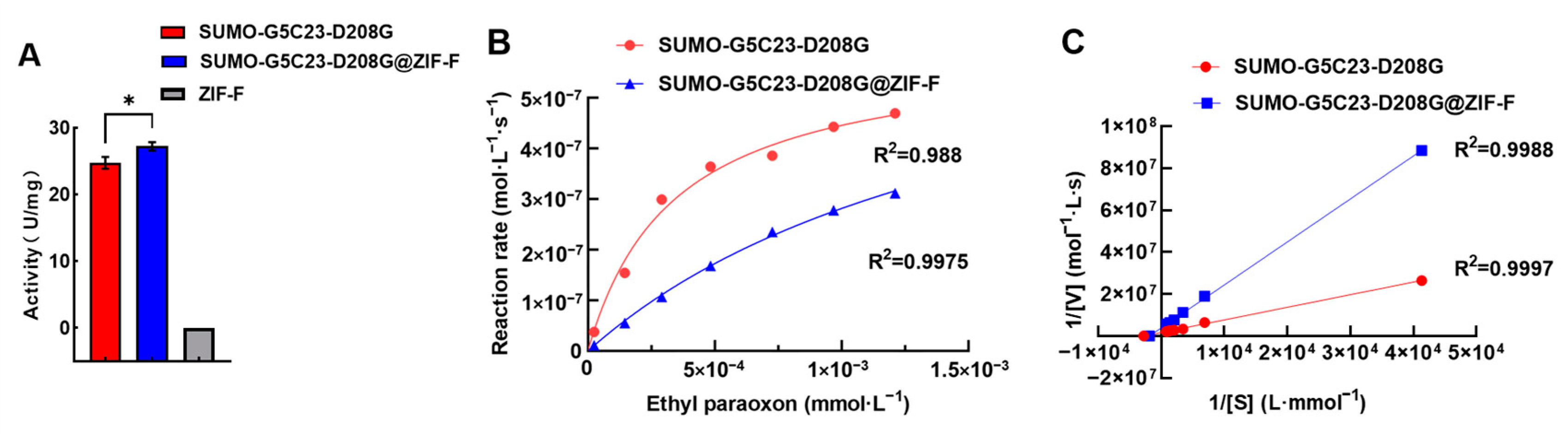
2.3. Determination of Enzyme Activity and Enzyme Kinetic Parameters
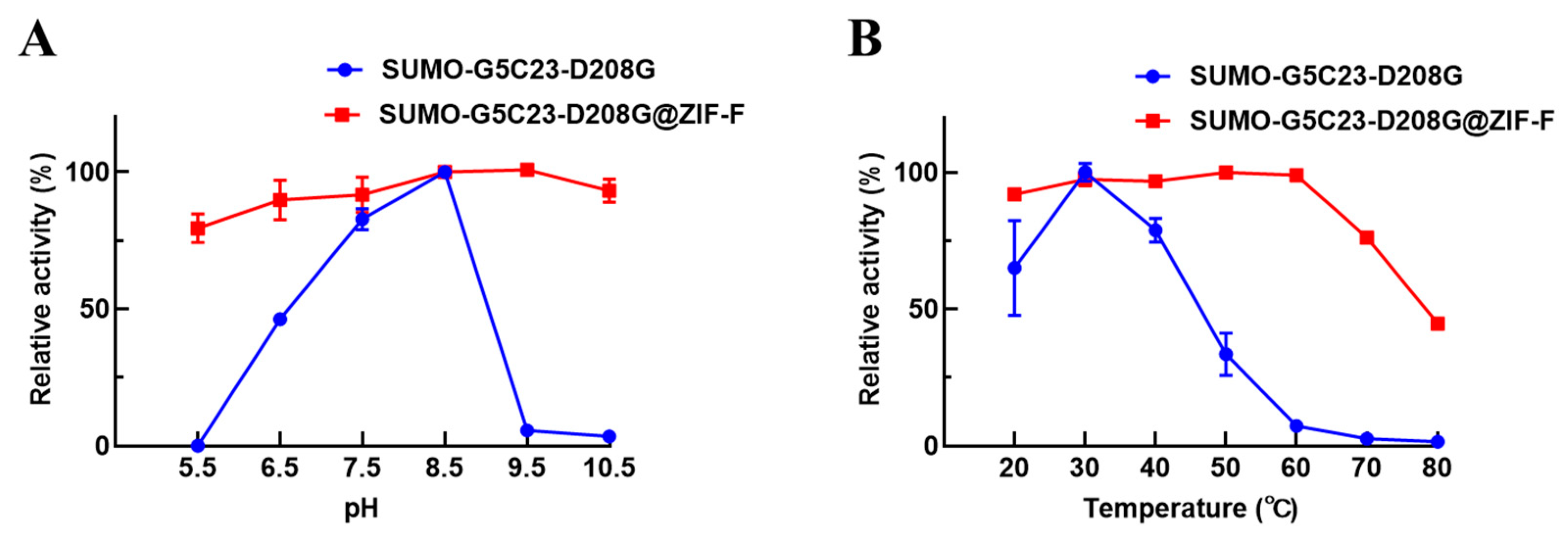
2.4. Examination of the Enzymatic Properties
2.4.1. Catalytic Performance of Biocatalysts
2.4.2. Analysis of Stability Performance
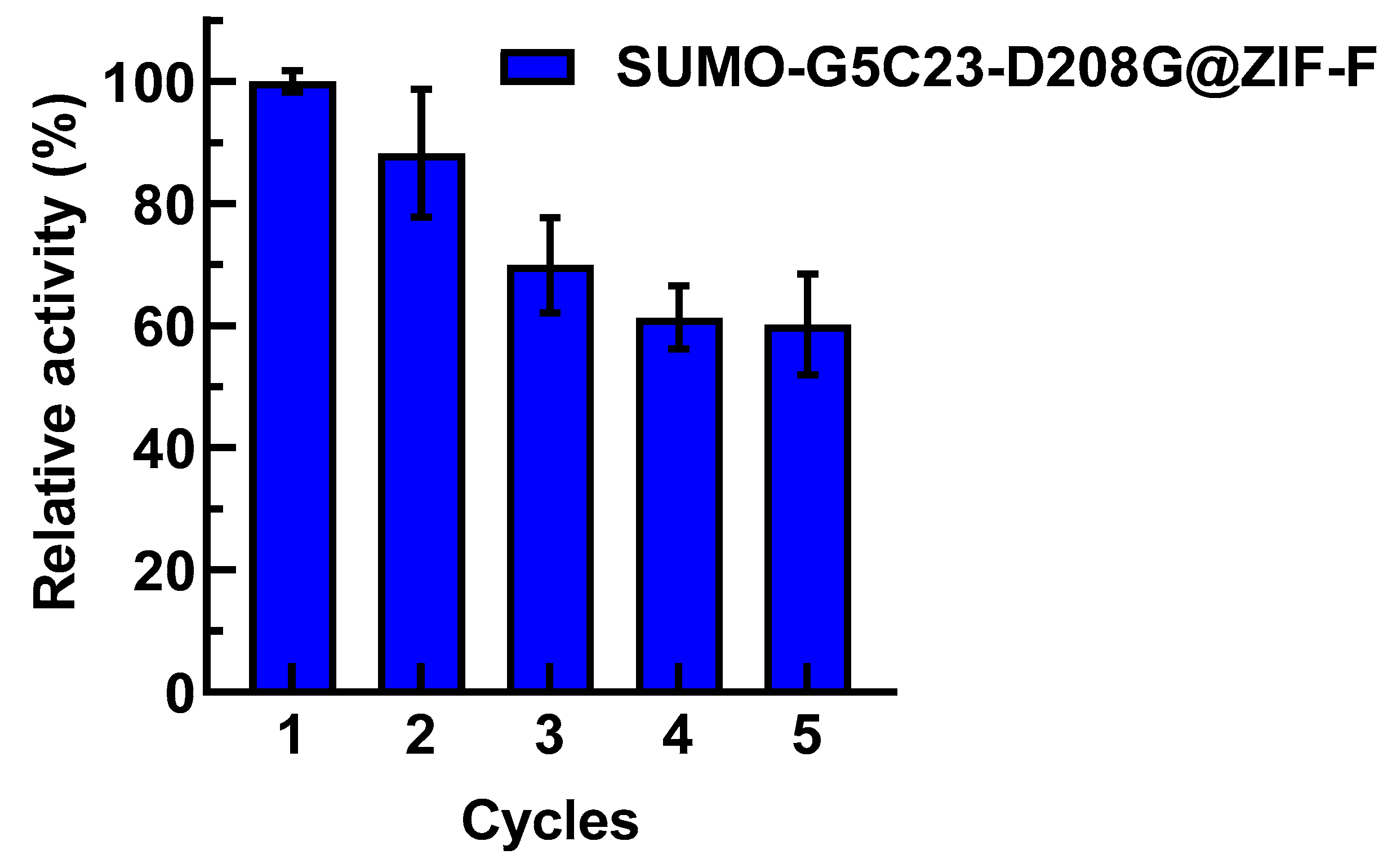
2.5. Reusability Examination of Immobilized Enzyme
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Construction of Expression Vector for the Organophosphorus Hydrolase Mutant SUMO-G5C23-D208G
3.3. Construction of Expression Strain for the Organophosphorus Hydrolase Mutant SUMO-G5C23-D208G
3.4. Fermentation of Bacterial Cells
3.5. Purification and Characterization of Organophosphorus Hydrolase
3.5.1. Preparation of Crude Organophosphorus Hydrolase and Ni-Column Purification
3.5.2. SDS-PAGE Verification of Fractions After Ni-Column Purification
3.6. Preparation of Immobilized Enzymes
3.6.1. Synthesis of ZIF-F
3.6.2. Synthesis of SUMO-G5C23-D208G@ZIF-F
3.7. Analysis of Immobilized Enzyme Features
3.7.1. SEM Characterization of Immobilized Enzyme Morphology
3.7.2. FT-IR
3.7.3. XRD
3.8. Evaluation of Enzyme Activity and Kinetic Properties
3.8.1. Enzyme Activity Assay
3.8.2. Investigation of Enzyme Kinetic Parameters
3.9. Examination of Enzymatic Properties of SUMO-G5C23-D208G and SUMO-G5C23-D208G@ZIF-F
3.9.1. Optimal pH Examination
3.9.2. Optimal Temperature Examination
3.9.3. Organic Solvent Tolerance Examination
3.9.4. Thermal Stability Examination
3.9.5. Storage Stability Examination
3.9.6. Examination of the Reusability of Immobilized Enzyme
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OPH | organophosphorus hydrolase |
| SUMO | Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier |
| ZIF-F | zeolitic imidazolate framework-F |
| MOFs | metal–organic frameworks |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| FT-IR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
References
- Jain, M.; Yadav, P.; Joshi, A.; Kodgire, P. Recombinant Organophosphorus Hydrolase (OPH) Expression in E. coli for the Effective Detection of Organophosphate Pesticides. Protein Expr. Purif. 2021, 186, 105929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, L.; Brun, L.; Jacquet, P.; Lepolard, C.; Armstrong, N.; Torre, C.; Daudé, D.; Ghigo, E.; Chabrière, E. Enzymatic Degradation of Organophosphorus Insecticides Decreases Toxicity in Planarians and Enhances Survival. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherny, I.; Greisen, P.; Ashani, Y.; Khare, S.D.; Oberdorfer, G.; Leader, H.; Baker, D.; Tawfik, D.S. Engineering V-Type Nerve Agents Detoxifying Enzymes Using Computationally Focused Libraries. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2394–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodveldt, C.; Tawfik, D.S. Directed Evolution of Phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas Diminuta for Heterologous Expression in Escherichia Coli Results in Stabilization of the Metal-Free State. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2005, 18, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, X.; Qin, Y.; Huang, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, X. High-Level Expression and Purification of Soluble Recombinant FGF21 Protein by SUMO Fusion in Escherichia Coli. BMC Biotechnol. 2010, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, M.A.A.; Khalifa, H.O.; Yoon, H.J.; Ki, M.-R.; Pack, S.P. Microbial Immobilized Enzyme Biocatalysts for Multipollutant Mitigation: Harnessing Nature’s Toolkit for Environmental Sustainability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, H.; Ali, H.; Rashid, M.H.; Iftikhar, F.; Saif-Ur-Rehman; Nawaz, M.S.; Khan, W.S. Enzyme Immobilization on Metal-Organic Framework (MOF): Effects on Thermostability and Function. Protein Pept. Lett. 2019, 26, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Li, H.-Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. Tetrahedral Imidazolate Frameworks with Auxiliary Ligands (TIF-Ax): Synthetic Strategies and Applications. Molecules 2023, 28, 6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.-X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Q.-S.; Yao, D.-Y.; Wang, S.-H.; Li, D.; Shang, H.-B. The Solvent and Zinc Source Dual-Induced Synthesis of a Two Dimensional Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework with a Farfalle-Shape and Its Crystal Transformation to Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 2437–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C. Immobilization of papain by in situ synthesis of ZIF-F. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 47, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Ning, W.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, K. Improving Protein Solubility and Activity by Introducing Small Peptide Tags Designed with Machine Learning Models. Metab. Eng. Commun. 2020, 11, e00138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archontis, G.; Simonson, T. Proton Binding to Proteins: A Free-Energy Component Analysis Using a Dielectric Continuum Model. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 3888–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Job, L.; Köhler, A.; Escher, B.; Worek, F.; Skerra, A. A Catalytic Bioscavenger with Improved Stability and Reduced Susceptibility to Oxidation for Treatment of Acute Poisoning with Neurotoxic Organophosphorus Compounds. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 321, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Du, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Li, A.; Chou, L.-Y. Enzyme Surface Residues Direct Encapsulation into Metal–Organic Frameworks for Performance Regulation. Angew. Chem. 2025, e202423741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, Z.; Ye, X.; Cui, J.; Wang, Z.; Jia, S. Molecular Simulations Guide Immobilization of Lipase on Nest-like ZIFs with Regulatable Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Surface. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2024, 667, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Carballares, D.; Morellon-Sterling, R.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Stabilization of Enzymes via Immobilization: Multipoint Covalent Attachment and Other Stabilization Strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 52, 107821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcus, V.L.; Mulholland, A.J. Temperature, Dynamics, and Enzyme-Catalyzed Reaction Rates. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2020, 49, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wu, C.; Qin, X.; Liu, G.; Wei, X.; Zhang, H. Covalent Immobilization of α-Amylase on Hollow Metal Organic Framework Coated Magnetic Phase-Change Microcapsules for the Improvement of Its Thermostability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Wu, H.; Guang, C.; Mu, W. Overview of a Bioremediation Tool: Organophosphorus Hydrolase and Its Significant Application in the Food, Environmental, and Therapy Fields. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 8241–8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-H.; Lin, M.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Yu, S.-M.; Wang, A.H.-J.; Ho, T.-H.D. Enhancement of Laccase Activity by Pre-Incubation with Organic Solvents. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.; Baroroh, U.; Madhani, I.N.; Muscifa, Z.S.; Novianti, M.T.; Abidin, M.; Yusuf, M.; Subroto, T. Enzymatic Performance of Aspergillus oryzae α-Amylase in the Presence of Organic Solvents: Activity, Stability, and Bioinformatic Studies. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2024, 18, 11779322241234767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, K. Biotransformations in Organic Chemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-61589-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, M.; Robatjazi, S.-M.; Sadri, M.; Mosaabadi, J.M. Covalent Immobilization of Organophosphorus Hydrolase Enzyme on Chemically Modified Cellulose Microfibers: Statistical Optimization and Characterization. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 124, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, H.; Wei, B.; Liang, H. Enhanced Catalytic Activity and Reusability of Sucrose Phosphorylase@magnetic Nanoparticles by Surface-Coating Amorphous ZIF-67. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 212, 109533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, D.; Nie, M.; Courey, A.J. SUMO as a Solubility Tag and in Vivo Cleavage of SUMO Fusion Proteins with Ulp1. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1177, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Gao, J. Heterologous expression and purification of organophosphorus hydrolase and preliminary evaluation of its antidotal capacity against ethyl parathion. Chin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. J. 2024, 38, 672–680. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Pelt, S. van Enzyme Immobilisation in Biocatalysis: Why, What and How. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6223–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, H.; Körber, C.; Sätzler, K.; Aydin, D.; Kuner, T. Serial Section Scanning Electron Microscopy (S3EM) on Silicon Wafers for Ultra-Structural Volume Imaging of Cells and Tissues. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerdy, N.; Margata, L.; Sembiring, B.M.; Ginting, S.; Putra, E.D.L.; Bakri, T.K. Validation of the Developed Zero-Order Infrared Spectrophotometry Method for Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Tranexamic Acid in Marketed Tablets. Molecules 2021, 26, 6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Ma, M.; Wang, Z.; Cui, F.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhai, Y.; Gao, J. SUMO-G5C23-D208G@ZIF-F: A Novel Immobilized Enzyme with Enhanced Stability and Reusability for Organophosphorus Hydrolysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062469
Wang S, Ma M, Wang Z, Cui F, Li Q, Liu Z, Wang D, Zhai Y, Gao J. SUMO-G5C23-D208G@ZIF-F: A Novel Immobilized Enzyme with Enhanced Stability and Reusability for Organophosphorus Hydrolysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062469
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shunye, Ming Ma, Ziyang Wang, Fengqian Cui, Qiqi Li, Zhuang Liu, Dan Wang, Yanan Zhai, and Jing Gao. 2025. "SUMO-G5C23-D208G@ZIF-F: A Novel Immobilized Enzyme with Enhanced Stability and Reusability for Organophosphorus Hydrolysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062469
APA StyleWang, S., Ma, M., Wang, Z., Cui, F., Li, Q., Liu, Z., Wang, D., Zhai, Y., & Gao, J. (2025). SUMO-G5C23-D208G@ZIF-F: A Novel Immobilized Enzyme with Enhanced Stability and Reusability for Organophosphorus Hydrolysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062469



