Characteristic Evaluation and Finite Element Analysis of a New Glass Fiber Post Based on Bio-Derived Polybenzoxazine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
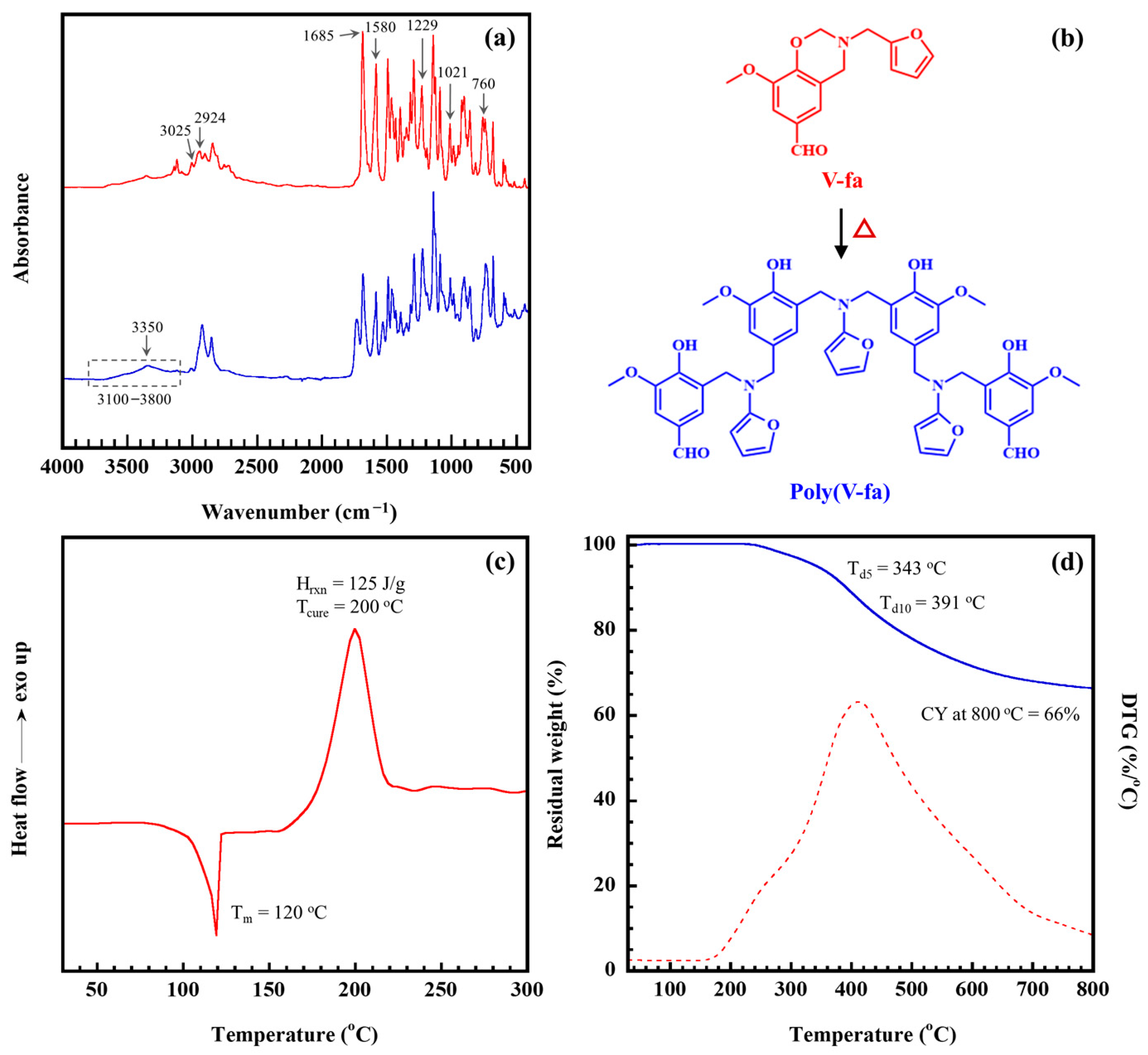
2.1. Characteristics of V-Fa and Poly(V-Fa)
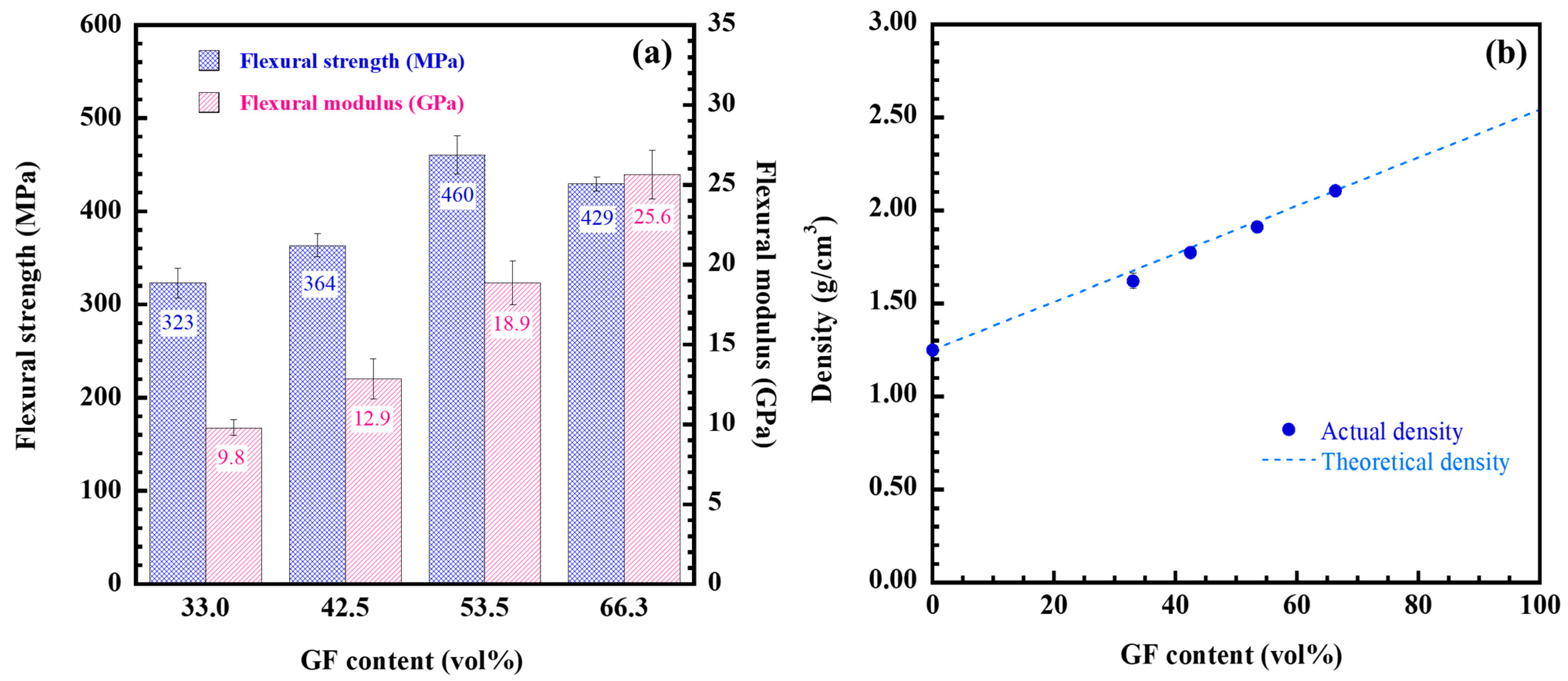
2.2. Flexural Properties of GF/Poly (V-Fa) Composites
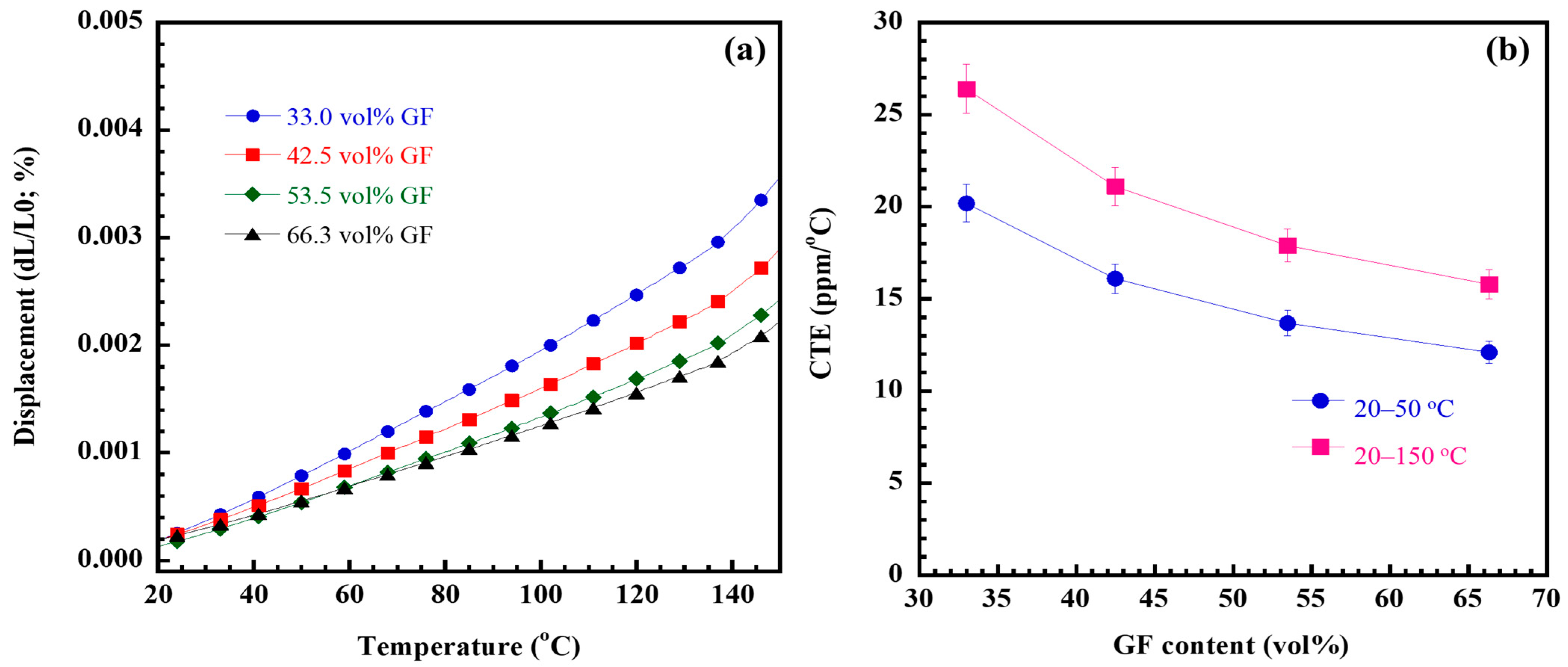
2.3. Thermal Expansion of GF/Poly(V-Fa) Composites
2.4. Thermomechanical Properties of GF/Poly(V-Fa) Composites
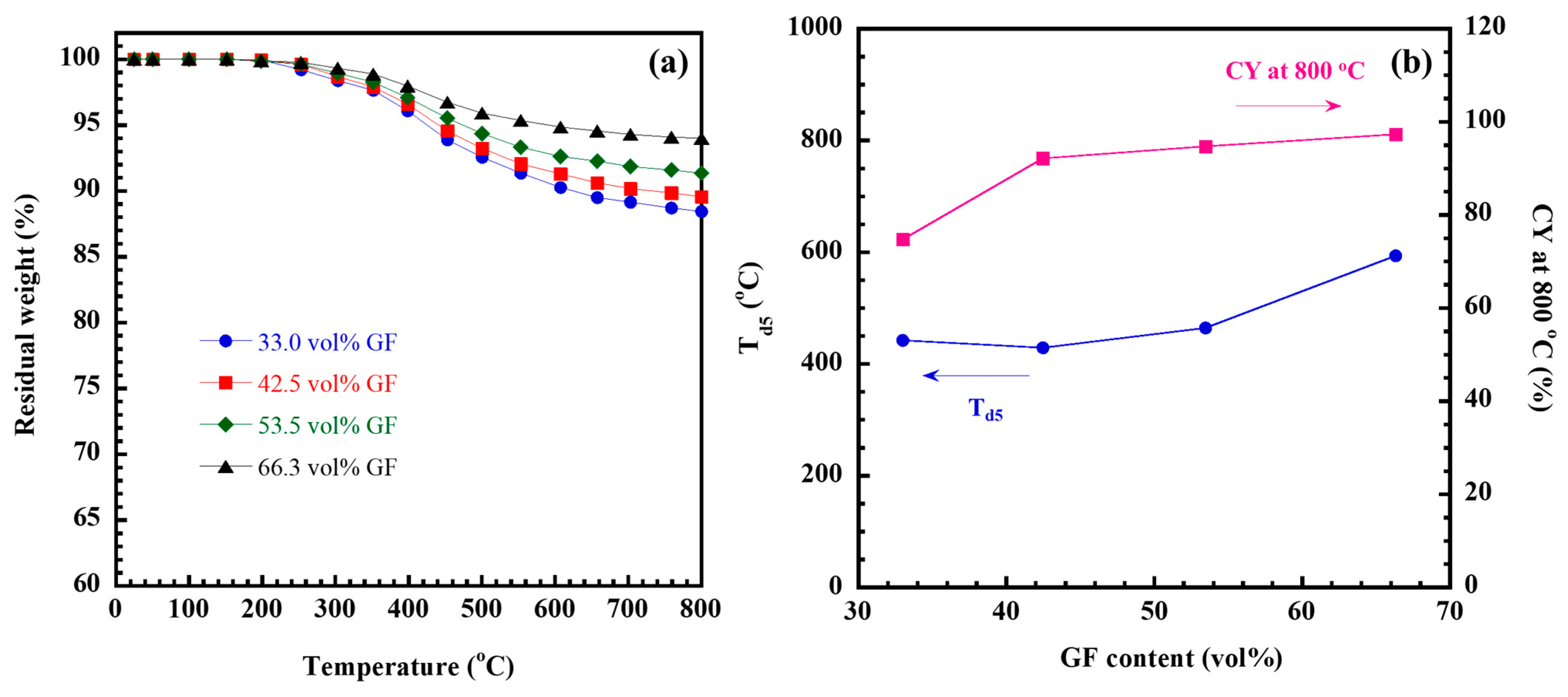
2.5. Thermal Stability of GF/Poly(V-Fa) Composites
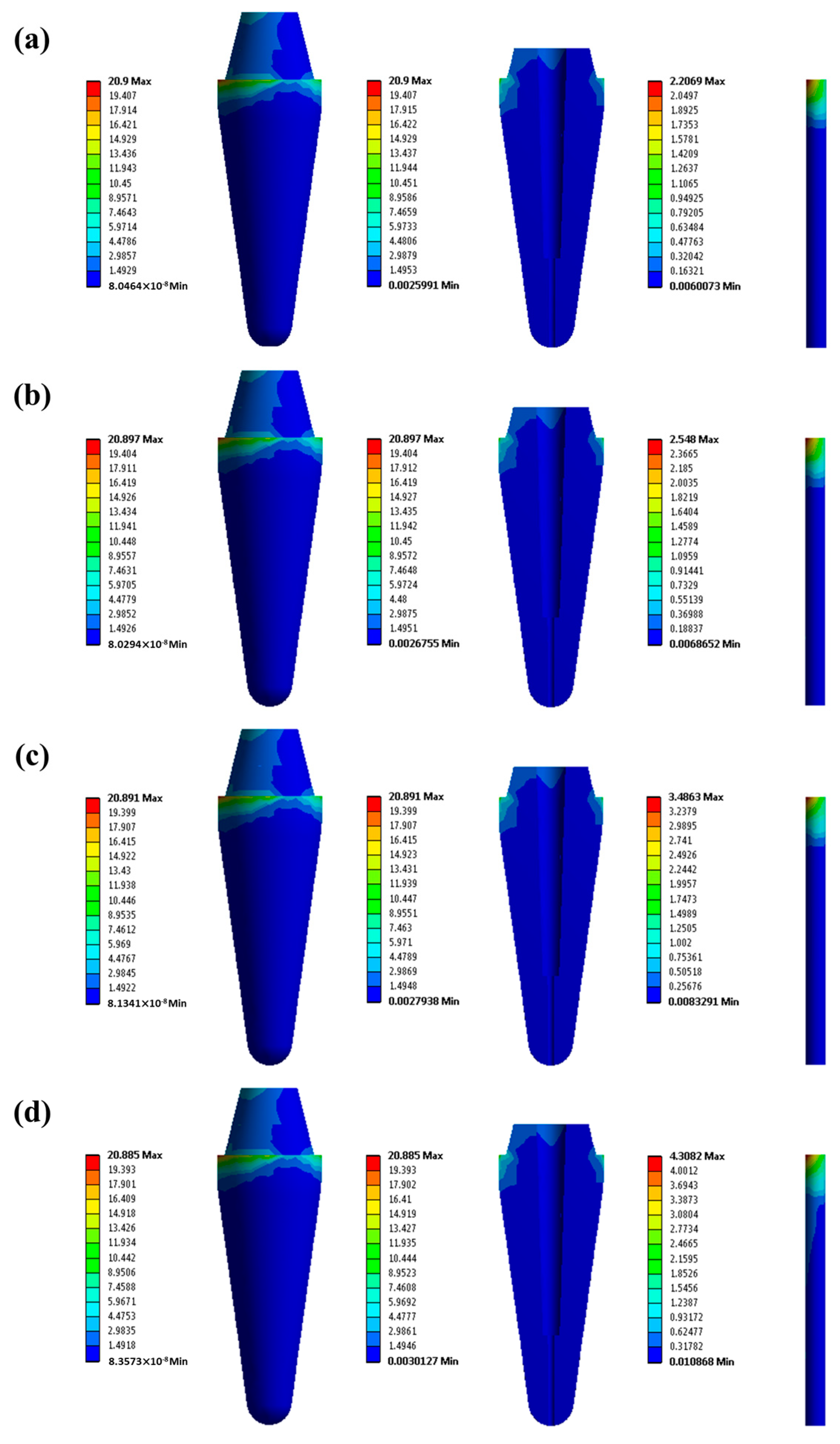
2.6. Feasibility of GF/Poly(V-Fa) Composites for Dental Fiber Post by FEA
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Benzoxazine Resin, Prepreg, and Composite Preparation
3.3. Samples Characterization
3.4. Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magalhães, N.; Maia, B.A.; Braga, M.H.; Santos, R.M.; Correia, N.; Cunha, E. Glass fiber reinforced epoxy-amine thermosets and solvate IL: Towards new composite polymer electrolytes for lithium battery applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolter, N.; Beber, V.C.; Sandinge, A.; Blomqvist, P.; Goethals, F.; Hove, M.V.; Jubete, E.; Mayer, B.; Koschek, K. Carbon, glass and basalt fiber reinforced polybenzoxazine: The effects of fiber reinforcement on mechanical, fire, smoke and toxicity properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, P.; Rimdusit, S.; Jubsilp, C. Near-infrared light-induced sustainable self-healing polymer composites from glass fabric reinforced benzoxazine/epoxy copolymers. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 7808–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Sonwal, S.; Sharma, R.P.; Saini, S.; Huh, Y.S.; Brambilla, E.; Ionescu, A.C. Ranking analysis of tribological, mechanical, and thermal properties of nano hydroxyapatite filled dental restorative composite materials using the R-method. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e70010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Saini, S.; Sonwal, S.; Meena, A.; Huh, Y.S.; Brambilla, E.; Ionescu, A.C. Optimization and ranking of dental restorative composites by entropy-vikor and vikor-matlab. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marovic, D.; Bota, M.; Tarle, F.; Par, M.; Haugen, H.J.; Zheng, K.; Pavić, D.; Miloš, M.; Čižmek, L.; Babić, S.; et al. The influence of copper-doped mesoporous bioactive nanospheres on the temperature rise during polymerization, polymer cross-linking density, monomer release and embryotoxicity of dental composites. Dent. Mater. 2024, 40, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marovic, D.; Par, M.; Tauböck, T.T.; Haugen, H.J.; Negovetic Mandic, V.; Wüthrich, D.; Burrer, P.; Zheng, K.; Attin, T.; Tarle, Z.; et al. Impact of copper-doped mesoporous bioactive glass nanospheres on the polymerisation kinetics and shrinkage stress of dental resin composites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, H.J.; Ma, Q.; Linskens, S.; Par, M.; Mandic, V.N.; Mensikova, E.; Nogueira, L.P.; Taubock, T.T.; Attin, T.; Gubler, A.; et al. 3D micro-CT and O-PTIR spectroscopy bring new understanding of the influence of filler content in dental resin composites. Dent. Mater. 2024, 40, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Agag, T. Handbook of Benzoxazine Resins, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, H.; Froimowicz, P. Advanced and Emerging Polybenzoxazine Science and Technology, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Ran, Q.-C. Polybenzoxazine/fiber composites. In Handbook of Benzoxazine Resins, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 481–494. [Google Scholar]
- Ares-Elejoste, P.; Seoane-Rivero, R.; Gandarias, I.; Iturmendi, A.; Gondra, K. Sustainable alternatives for the development of thermoset composites with low environmental impact. Polymers 2023, 15, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Wang, M.; Jiang, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z. High-performance and degradable polybenzoxazine/VU vitrimer and its application for carbon fiber recycling. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 9113–9122. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, H.; Vaudemont, R.; Frari, D.D.; Verge, P.; Puchot, L.; Bodaghi, M. On the cyclic delamination-healing capacity of vitrimer-based composite laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 177, 107899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhawilai, M.; Hiziroglu, S.; Rimdusit, S. Measurement of ballistic impact performance of fiber reinforced polybenzoxazine/ polyurethane composites. Measurement 2018, 130, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubsilp, C.; Panyawanitchakun, C.; Rimdusit, S. Flammability and thermomechanical properties of dianhydride-modified polybenzoxazine composites reinforced with carbon fiber. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 2067–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, P.; Rimdusit, S.; Karagiannidis, P.; Srisorrchart, U.; Jubsilp, C. Biocompatibility, thermal and mechanical properties of glass fiber-reinforced polybenzoxazine composites as a potential new endodontic post. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 16205–16217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, P.; Nunwong, C.; Sriromreun, P.; Kaewsriprom, P.; Srisorrachatr, U.; Rimdusit, S.; Jubsilp, C. High performance composites based on highly filled glass fiber-reinforced polybenzoxazine for post application. Polymers 2022, 14, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, D.A.; Naiker, V.E.; Phalak, G.A.; More, A.P.; Mhaske, S.T. Synthesis of benzoxazine from eugenol and its co-polymerization with a gallic acid-based epoxy resin for flame retardant application. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 7441–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Lu, X.; Xin, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, C.; Cao, Y. Two novel eugenol-based difunctional benzoxazines: Synthesis and properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 616, 126209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, Y.E.; Uyar, T. Eugenol-derived bio-benzoxazine resins: Synthesis, characterization, and exceptional thermal stability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengrojanakul, P.; Mora, P.; Bunyanuwat, K.; Jubsilp, C.; Rimdusit, S. Improvements in mechanical and shape-memory properties of bio-based composite: Effects of adding carbon fiber and graphene nanoparticles. Polymers 2023, 15, 4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyuz, S.; Kiskan, B. Combination of polyethylenimine and vanillin-based benzoxazine as a straightforward self-healable system with excellent film-forming ability. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, T.; Asrafali, S.P.; Muthusamy, S. New benzoxazines containing polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane from eugenol, guaiacol and vanillin. New. J. Chem. 2025, 39, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appasamy, S.M.G.; Krishnasamy, B.; Ramachandran, S.; Muthukaruppan, A. Vanillin derived partially bio-based benzoxazine resins for hydrophobic coating and anticorrosion applications: Studies on syntheses and thermal behavior. Polym. Plast. Tech. Mat. 2023, 63, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sini, N.K.; Bijwe, J.; Varma, I.K. Thermal behaviour of bisbenzoxazines derived from renewable feed stock vanillin. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 109, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Lu, X.; Xin, Z. Cardanol-based polybenzoxazine coatings: Crosslinking structures, hydrophobicity and corrosion protection properties. J. Polym. Sci. 2024, 62, 2936–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Bai, W.; Zheng, X.; Lin, Q.; Lin, F.; Xu, Y. Two-dimensional lamellar polyimide/cardanol-based benzoxazine copper polymer composite coatings with excellent anti-corrosion performance. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 10766–10777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Li, B.; Ren, D.; Xu, M. Recent progress of low dielectric and high-performance polybenzoxazine-based composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagwu, F.I.; Dossi, E.; Skordos, A.A. High glass transition catalyst-free polybenzoxazine vitrimer through one-pot solventless method. React. Funct. Polym. 2025, 209, 106186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.M.; Qiu, J.J.; Liu, C.M. Bio-based, main-chain type polybenzoxazine precursor derived from sustainable furfurylamine and salicylaldehyde: Synthesis, characterization and properties. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 149, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Sun, Z.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Xiang, D.; Wu, Y.; Que, Y. A phosphorous-containing bio-based furfurylamine type benzoxazine and its application in bisphenol-A type benzoxazine resins: Preparation, thermal properties and flammability. Polymers 2022, 14, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, T.; Asrafali, S.P.; Kim, S.C. Bio-based polybenzoxazine-cellulose grafted films: Material fabrication and properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derradji, M.; Khiari, K.; Mehelli, O.; Abdous, S.; Amri, B.; Belgacemi, R.; Ramdani, N.; Zegaoui, A.; Liu, W. Green composites from vanillin-based benzoxazine and silane surface modified chopped carbon fibers. Polym. Renew. Resour. 2023, 14, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, W.; Trache, D.; Ghalmi, C.; Aidi, S.; Tarchoun, A.F.; Gahfif, F.; Abdelaziz, A.; Thakur, S.; Hussin, M.H. Curing kinetics of composites based on benzoxazine resin and microcrystalline cellulose modified by phosphorus salt. Thermochim. Acta 2024, 735, 179718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudjrari, S.; Derradji, M.; Amri, B.; Djaber, K.; Mehelli, O.; Tazibet, S.; Abdous, S.; Ramdani, N.; Liu, W.; Khadraoui, A. Novel vanillin-based benzoxazine containing phthalonitrile thermosetting system: Simple synthesis, autocatalytic polymerization and high thermomechanical properties. High Perform. Polym. 2022, 34, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, P.; Rimdusit, S.; Karagiannidis, P.; Srisorrachatr, U. Mechanical properties and curing kinetics of bio-based benzoxazine–epoxy copolymer for dental fiber post. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2023, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathumrat, P.; Tiptipakorn, S.; Rimdusit, S. Multiple-shape memory polymers from benzoxazine-urethane copolymers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 065025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Jiang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Yin, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X. Mechanical properties, biosafety, and shearing bonding strength of glass fiber–reinforced PEEK composites used as post-core materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 145, 106047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, J.; Hardan, L.; Kassis, C.; Bourgi, R.; Devoto, W.; Amm, E.; Moussa, C.; Sawicki, J.; Lukomska-Szymanska, M. Influence of resin cement thickness and elastic modulus on the stress distribution of zirconium dioxide inlay-bridge: 3D finite element analysis. Polymers 2021, 13, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, M.; Dang, P.; Xie, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X. PEEK in fixed dental prostheses: Application and adhesion improvement. Polymers 2022, 14, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaldo, M.C.; Luzmila, V.R.; Flor, S.R.; Carlos, L.G.; Ana, A.M.; Rosa, A.A.; César, C.R. Adhesive strength of glass fiber-reinforced posts with silane conditioning versus universal adhesive system conditioning: An in vitro study. J. Int. Oral Health 2024, 16, 290–296. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, F.; Mayer, L.A.; Unterschütz, L.; Ziebolz, D.; Oberueck, N.; Schulz-Kornas, E.; Hahnel, S.; Koenig, A. Effect of powder air polishing and ultrasonic scaling on the marginal and internal interface (tooth-veneer) of ceramic veneers: An in vitro study. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2024, 28, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, P.; Rimdusit, S.; Jubsilp, C. Development, characteristics, and potential applications of green composites from bio-derived polybenzoxazine and glass fiber. Polym. Compos. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Meng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Bai, Y.; Yuan, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; et al. Pyro-catalysis for tooth whitening via oral temperature fluctuation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huidan Wei, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Chen, K.; Sun, J.; Cui, Z.; Wang, C. Preparation and characterization of luminescent polyimide/glass composite fiber. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 4329–4339. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D 792-20; American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM D 792-20) Standard Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Plastics by Displacement. International ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM D 790M-93; American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM D 790M-93) Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. International ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1993.
- Pegoretti, A.; Fambri, L.; Zappini, G.; Bianchetti, M. Finite element analysis of a glass fibre reinforced composite endodontic post. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2667–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Composite Samples | E′ (GPa) | Tg from E″ |
|---|---|---|
| 33.0 vol% GF/poly(V-fa) | 12.5 | 164 |
| 42.5 vol% GF/poly(V-fa) | 15.4 | 167 |
| 53.5 vol% GF/poly(V-fa) | 18.0 | 170 |
| 66.3 vol% GF/poly(V-fa) | 19.8 | 170 |
| Material | Elastic Modulus | Poisson’s Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| Gutta-percha | 6.9 × 10−4 | 0.45 |
| Composite resin | 16.6 | 0.24 |
| Dentin | 18.6 | 0.31 |
| Porcelain (crown) | 120 | 0.28 |
| Periodontal ligament | 6.89 × 10−2 | 0.45 |
| Cortical bone | 13.7 | 0.30 |
| Cancellous bone | 1.37 | 0.30 |
| Gingiva | 19.6 × 10−3 | 0.30 |
| Gold alloy | 93.0 | 0.33 |
| Elastic Constant | GF/Poly(V-Fa) Composite Post at Various GF Contents (vol% (wt%)) | Commercial GF Post [49] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33.0 (50) | 42.5 (60) | 53.5 (70) | 66.3 (80) | ||
| EL, GPa | 9.80 | 12.90 | 18.90 | 25.60 | 37.0 |
| ET = ET′, GPa | 6.39 | 7.92 | 10.31 | 14.59 | 9.50 |
| GLT = GLT′, GPa | 3.58 | 4.32 | 5.47 | 7.50 | 3.10 |
| GTT′, GPa | 2.44 | 3.05 | 4.03 | 5.82 | 3.50 |
| νLT = νLT′ | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.27 |
| νTL = νT′L | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.27 |
| νTT′ | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mora, P.; Rimdusit, S.; Jubsilp, C. Characteristic Evaluation and Finite Element Analysis of a New Glass Fiber Post Based on Bio-Derived Polybenzoxazine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062444
Mora P, Rimdusit S, Jubsilp C. Characteristic Evaluation and Finite Element Analysis of a New Glass Fiber Post Based on Bio-Derived Polybenzoxazine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062444
Chicago/Turabian StyleMora, Phattarin, Sarawut Rimdusit, and Chanchira Jubsilp. 2025. "Characteristic Evaluation and Finite Element Analysis of a New Glass Fiber Post Based on Bio-Derived Polybenzoxazine" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062444
APA StyleMora, P., Rimdusit, S., & Jubsilp, C. (2025). Characteristic Evaluation and Finite Element Analysis of a New Glass Fiber Post Based on Bio-Derived Polybenzoxazine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062444







