Age- and ApoE Genotype-Dependent Transcriptomic Responses to O3 in the Hippocampus of Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
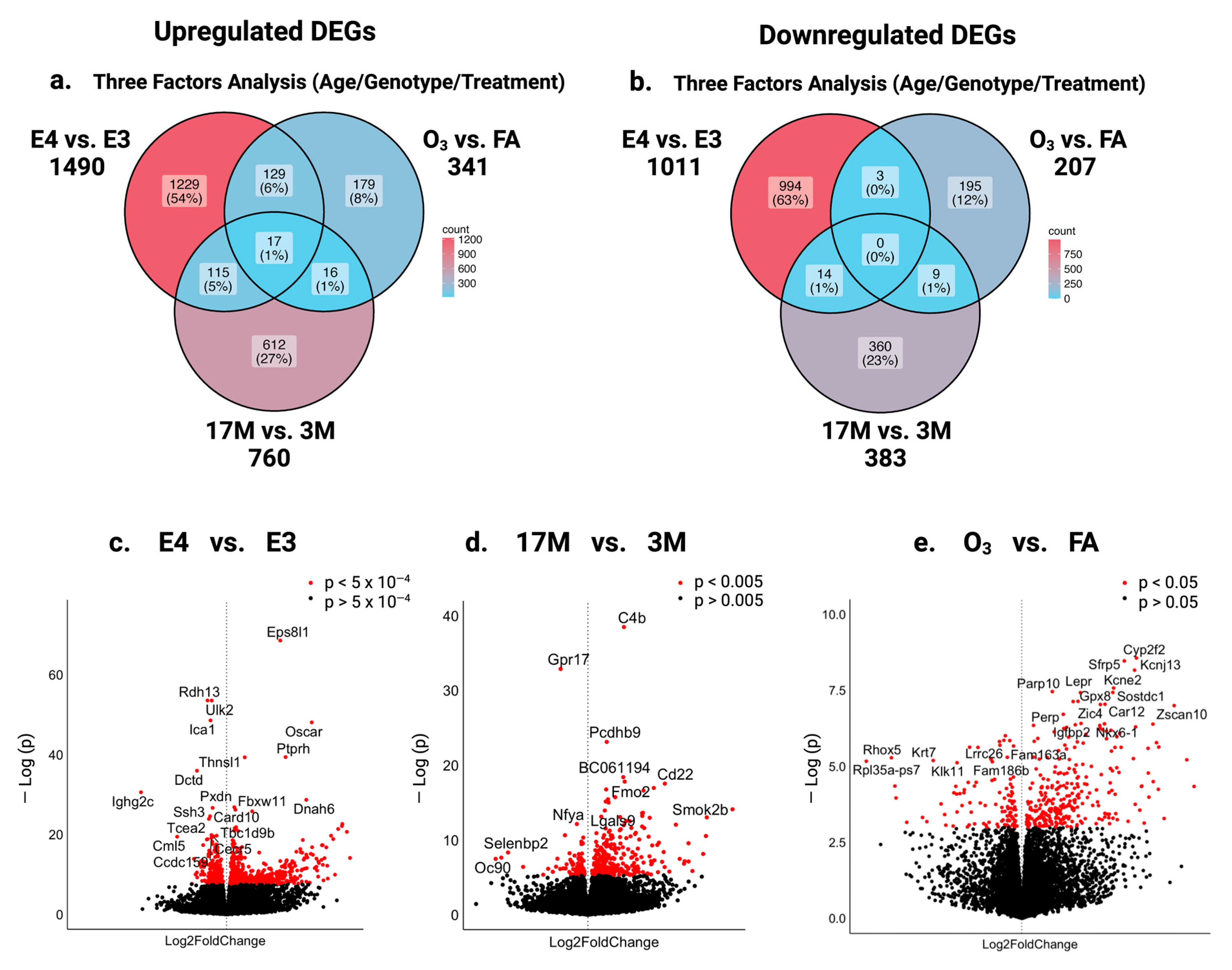
2.1. Impact of ApoE Genotype, Aging, and Ozone Exposure on Gene Expression in the Hippocampus of Male Mice
2.2. Specific Effect of ApoE Genotype, Age, or O3 Exposure on the Gene Expression in the Hippocampus of Mice
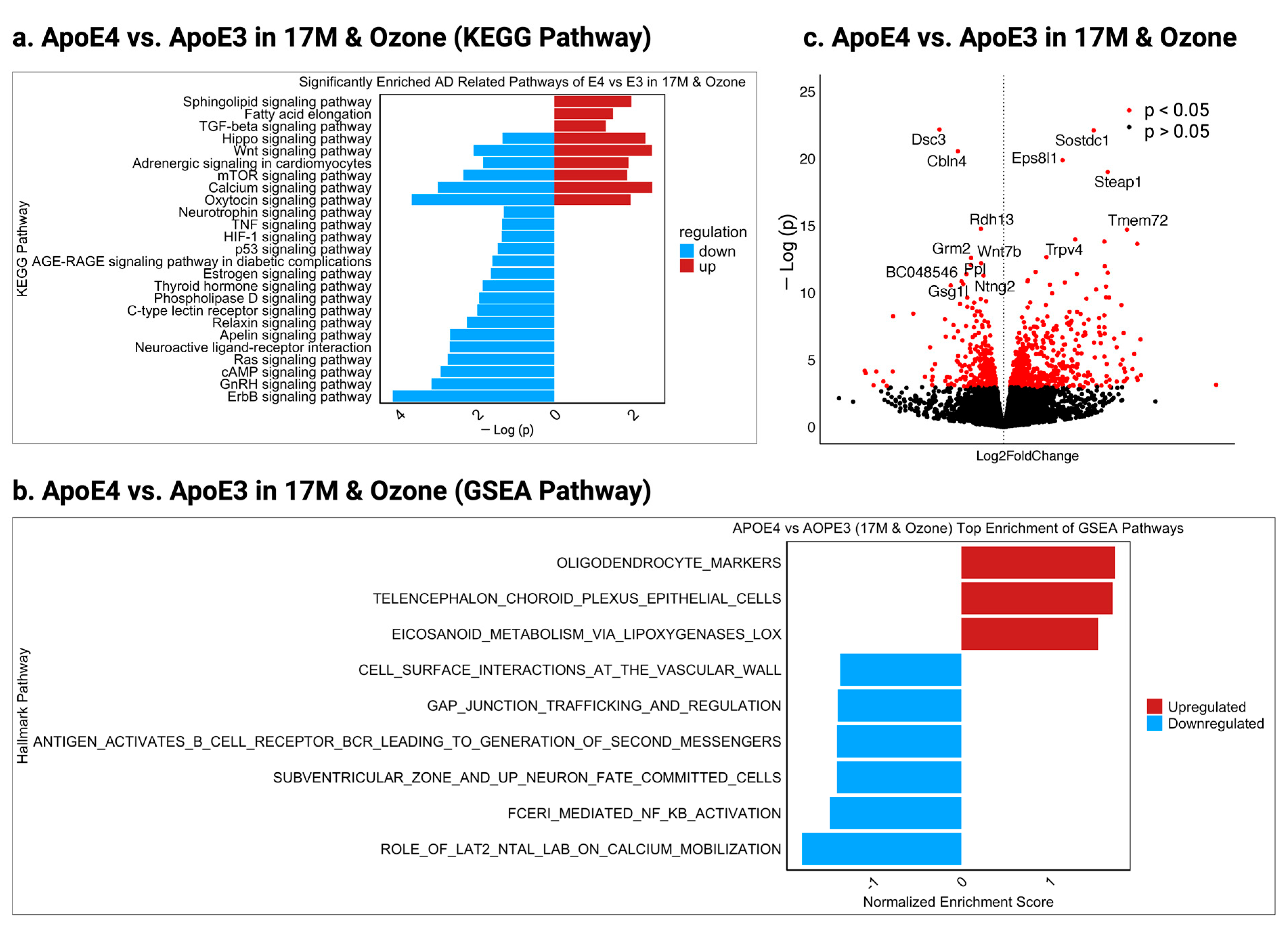
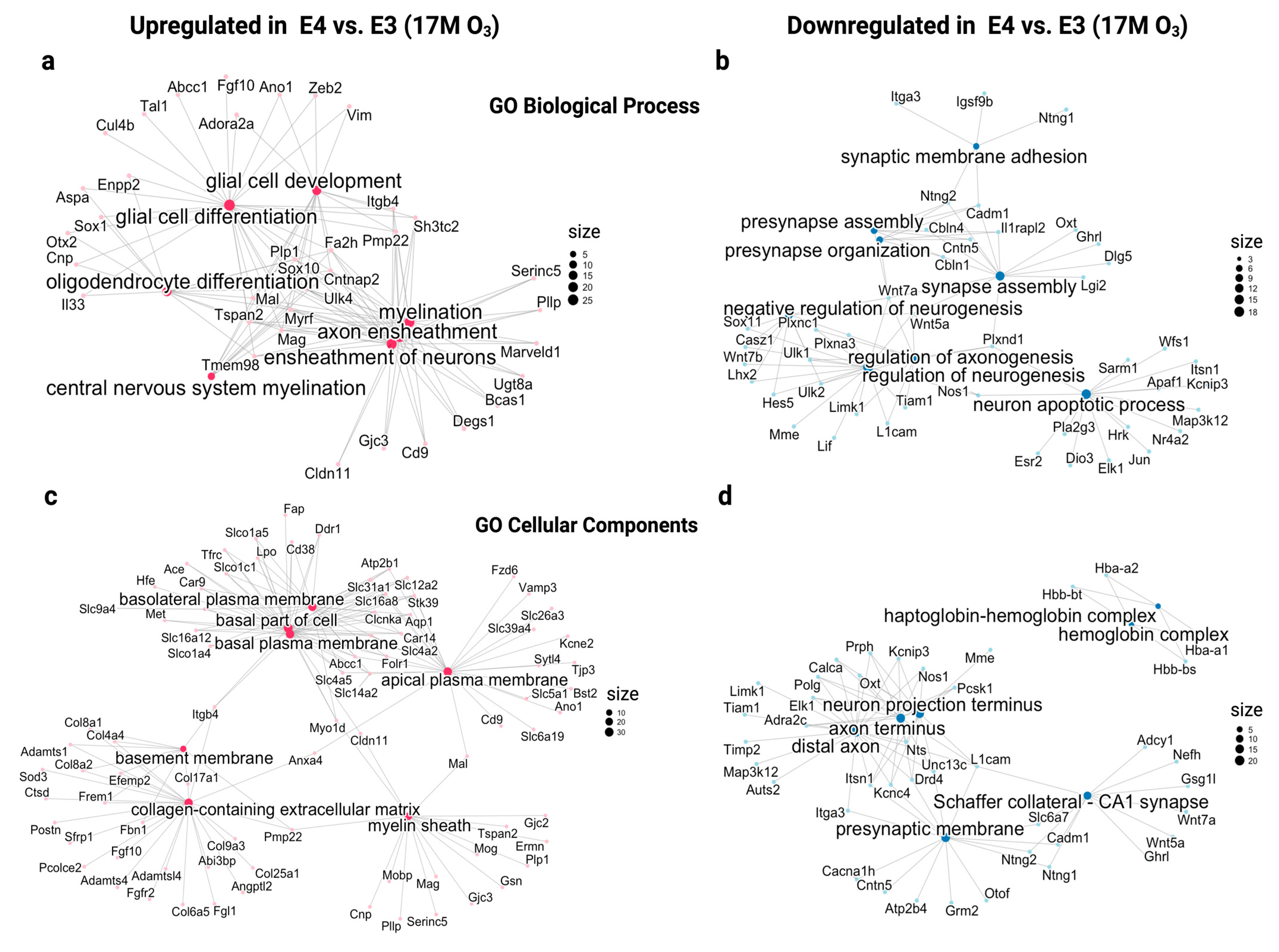
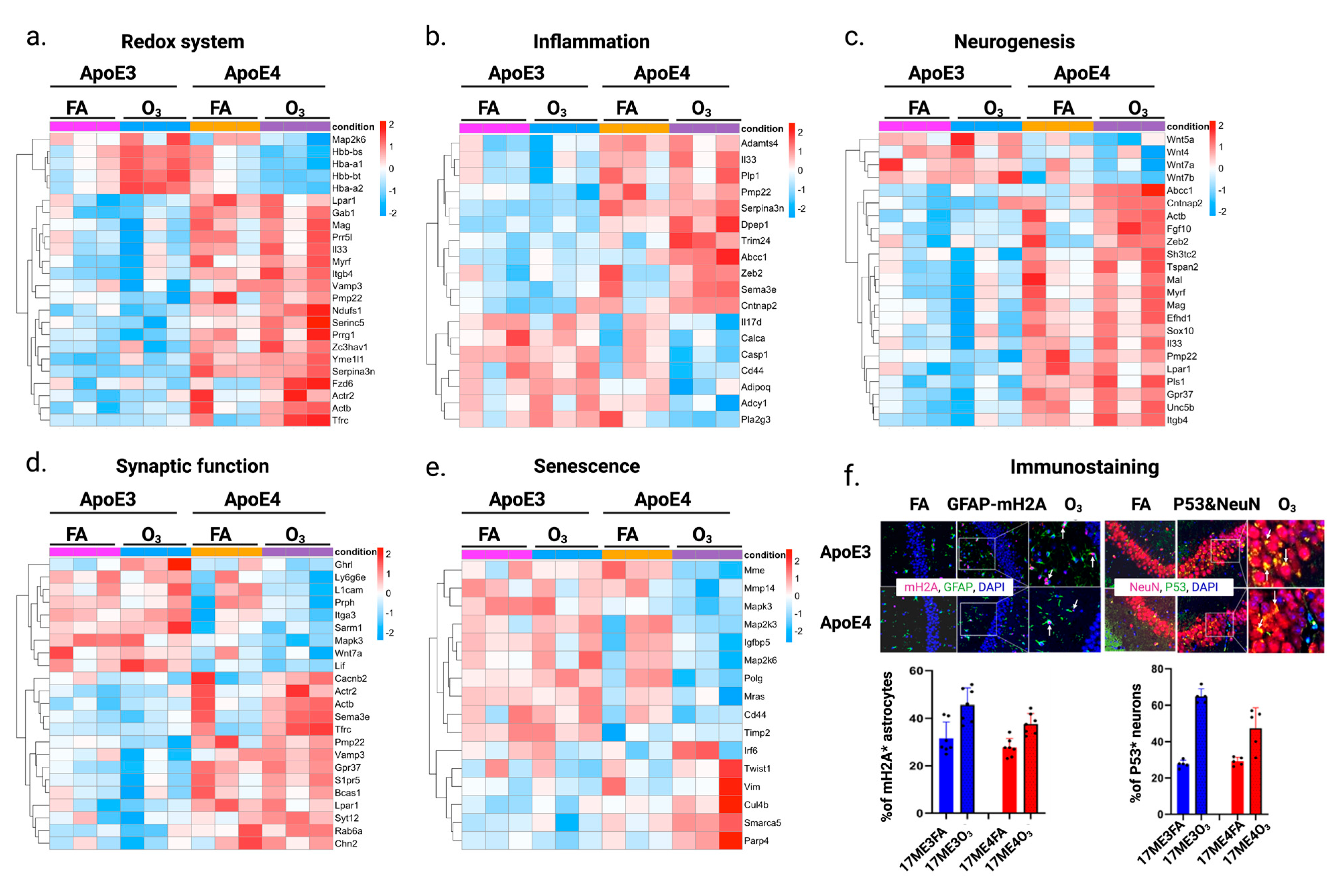
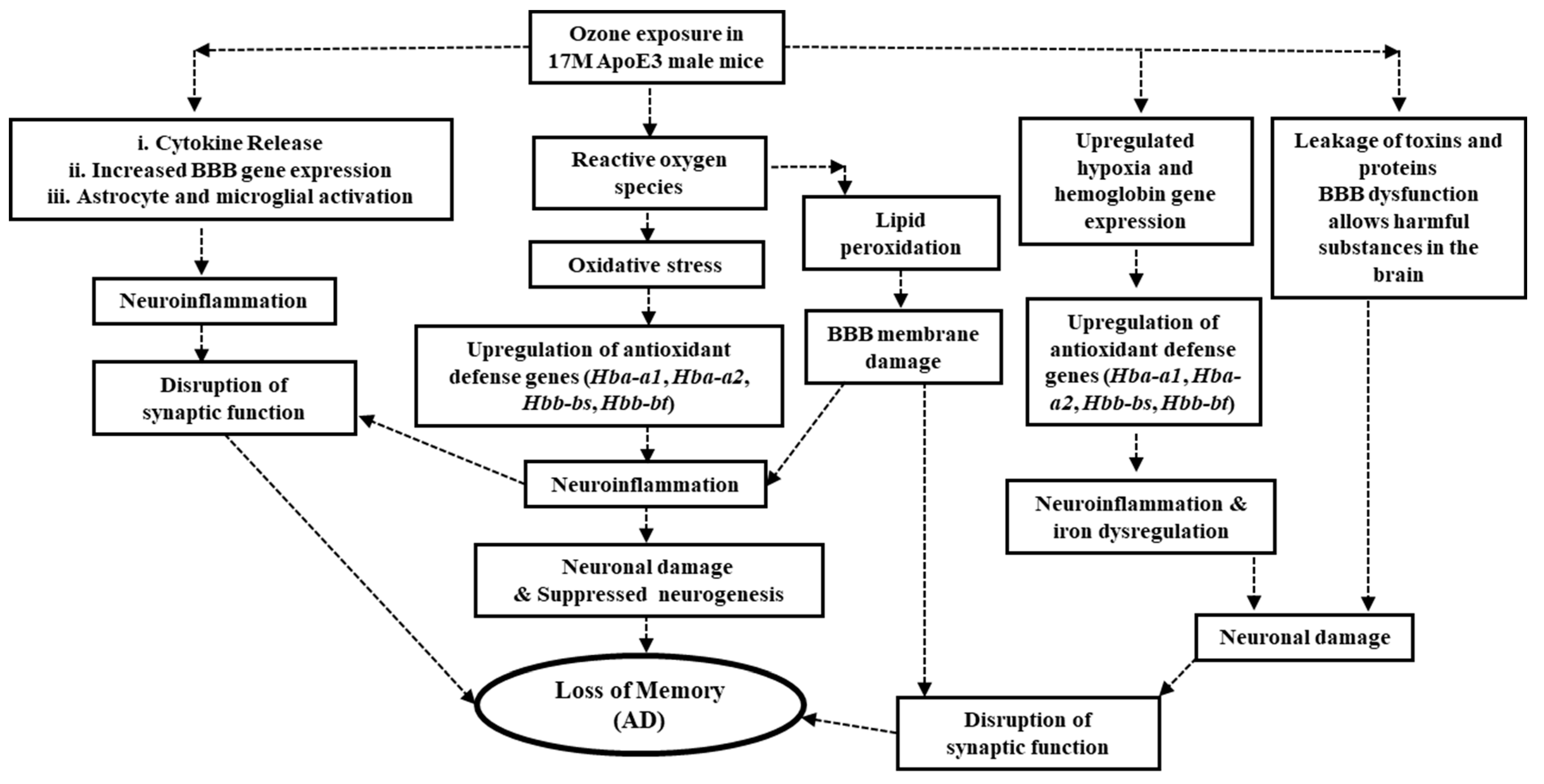
2.3. Dissect the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Increased Susceptibility of Old E3 Mice Exposed to O3
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Exposure
4.2. Tissue Collection and RNA Isolation
4.3. Library Preparation, Sequencing, and Data Processing
4.4. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
4.5. RT-qPCR Validation
4.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chetelat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 1598–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karch, C.M.; Goate, A.M. Alzheimer’s disease risk genes and mechanisms of disease pathogenesis. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corder, E.H.; Saunders, A.M.; Strittmatter, W.J.; Schmechel, D.E.; Gaskell, P.C.; Small, G.W.; Roses, A.D.; Haines, J.L.; Pericak-Vance, M.A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 1993, 261, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Basak, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. The role of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2009, 63, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strittmatter, W.J.; Saunders, A.M.; Schmechel, D.; Pericak-Vance, M.; Enghild, J.; Salvesen, G.S.; Roses, A.D. Apolipoprotein E: High-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Liu, C.C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausubel, F.M.; Brent, R.; Kingston, R.E.; Moore, D.D.; Seidman, J.G.; Smith, J.A.; Struhl, K. (Eds.) Preparation and analysis of RNA. In Current Protocols in Molecular Biology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 4.10.11–14.10.19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.F.; Chen, W.W.; Tong, G.Z. Ozone emitted during copying process—A potential cause of pathological oxidative stress and potential oxidative damage in the bodies of operators. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2003, 16, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Stewart, L.T.; Kuo, H.C.; McGilberry, W.; Wall, S.B.; Liang, B.; van Groen, T.; Bailey, S.M.; Kim, Y.I.; Tipple, T.E.; et al. Cyclic O3 exposure synergizes with aging leading to memory impairment in male APOE epsilon3, but not APOE epsilon4, targeted replacement mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 81, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.L.; McDermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M.; Dominici, F. Ozone and short-term mortality in 95 US urban communities, 1987–2000. JAMA 2004, 292, 2372–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Yu, H.L.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, T.F.; Sun, Y.; Wen, L.L.; Yip, P.K.; Chu, Y.M.; Chen, Y.C. Association between air pollutants and dementia risk in the elderly. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2015, 1, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, H.; Ballinger, C.; Liu, N.; van Groen, T.; Postlethwait, E.M.; Liu, R.M. Cyclic Ozone Exposure Induces Gender-Dependent Neuropathology and Memory Decline in an Animal Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 147, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hernandez-Zimbron, L.F.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Oxidative stress caused by ozone exposure induces beta-amyloid 1-42 overproduction and mitochondrial accumulation by activating the amyloidogenic pathway. Neuroscience 2015, 304, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumaw, C.L.; Levesque, S.; McGraw, C.; Robertson, S.; Lucas, S.; Stafflinger, J.E.; Campen, M.J.; Hall, P.; Norenberg, J.P.; Anderson, T.; et al. Microglial priming through the lung-brain axis: The role of air pollution-induced circulating factors. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, N.M.; Henderson, V.W.; Hodis, H.N.; St John, J.A.; Lurmann, F.; Chen, J.C.; Mack, W.J. Components of air pollution and cognitive function in middle-aged and older adults in Los Angeles. Neurotoxicology 2014, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, E.G.; Cifuentes, M.; Grinstein, G.; Brugge, D.; Shea, T.B. Association of Low-Level Ozone with Cognitive Decline in Older Adults. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 61, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, Y.M.; Wu, W.D.; Jiang, Y.; Zhuo, L.B. Combined exposure of heat stress and ozone enhanced cognitive impairment via neuroinflammation and blood brain barrier disruption in male rats. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857 Pt 3, 159599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, H.J.; Dunbar, A.L.; Lombo, C.G.; Ahmed, C.; Thang, M.; Messenger, E.J.; Mumaw, C.L.; Johnson, J.A.; Kodavanti, U.P.; Oblak, A.L.; et al. The bidirectional lung brain-axis of amyloid-beta pathology: Ozone dysregulates the peri-plaque microenvironment. Brain 2023, 146, 991–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrer, L.A.; Cupples, L.A.; Haines, J.L.; Hyman, B.; Kukull, W.A.; Mayeux, R.; Myers, R.H.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Risch, N.; van Duijn, C.M. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA 1997, 278, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raber, J.; Wong, D.; Yu, G.Q.; Buttini, M.; Mahley, R.W.; Pitas, R.E.; Mucke, L. Apolipoprotein E and cognitive performance. Nature 2000, 404, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Gao, J.; Chen, P.; Yin, M.; Zhao, W. Decreased immunoglobulin G in brain regions of elder female APOE4-TR mice accompany with Abeta accumulation. Immun. Ageing 2019, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello-Medina, P.C.; Prado-Alcala, R.A.; Rivas-Arancibia, S. Effect of Ozone Exposure on Dendritic Spines of CA1 Pyramidal Neurons of the Dorsal Hippocampus and on Object-place Recognition Memory in Rats. Neuroscience 2019, 402, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.R.; Lin, Y.T.; Hwang, B.F. Ozone, particulate matter, and newly diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 44, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, A.; Tian, L.; Henderson, V.W.; Greicius, M.D.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative Investigators. Sex modifies the APOE-related risk of developing Alzheimer disease. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, B.C.; Thompson, P.M.; Brinton, R.D. Age, APOE and sex: Triad of risk of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 160, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, L.; Altmann, A.; Greicius, M.D. Apolipoprotein E, gender, and Alzheimer’s disease: An overlooked, but potent and promising interaction. Brain Imaging Behav. 2014, 8, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bour, A.; Grootendorst, J.; Vogel, E.; Kelche, C.; Dodart, J.C.; Bales, K.; Moreau, P.H.; Sullivan, P.M.; Mathis, C. Middle-aged human apoE4 targeted-replacement mice show retention deficits on a wide range of spatial memory tasks. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 193, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijpma, A.; Jansen, D.; Arnoldussen, I.A.; Fang, X.T.; Wiesmann, M.; Mutsaers, M.P.; Dederen, P.J.; Janssen, C.I.; Kiliaan, A.J. Sex Differences in Presynaptic Density and Neurogenesis in Middle-Aged ApoE4 and ApoE Knockout Mice. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 2013, 531326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris-Sampedro, F.; Reverte, I.; Basaure, P.; Cabre, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Colomina, M.T. Apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotype and the pesticide chlorpyrifos modulate attention, motivation and impulsivity in female mice in the 5-choice serial reaction time task. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 92, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaure, P.; Guardia-Escote, L.; Cabre, M.; Peris-Sampedro, F.; Sanchez-Santed, F.; Domingo, J.L.; Colomina, M.T. Postnatal chlorpyrifos exposure and apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotype differentially affect cholinergic expression and developmental parameters in transgenic mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 118, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belinson, H.; Michaelson, D.M. ApoE4-dependent Abeta-mediated neurodegeneration is associated with inflammatory activation in the hippocampus but not the septum. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, P.; Kuhn, H.; Ahmadian, S. Multiple Roles of Apolipoprotein E4 in Oxidative Lipid Metabolism and Ferroptosis During the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2024, 74, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.S.; Shetty, M.S.; Sajikumar, S.; Chen, C.; Soong, T.W.; Wong, B.S. ApoE4 expression accelerates hippocampus-dependent cognitive deficits by enhancing Abeta impairment of insulin signaling in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annese, A.; Manzari, C.; Lionetti, C.; Picardi, E.; Horner, D.S.; Chiara, M.; Caratozzolo, M.F.; Tullo, A.; Fosso, B.; Pesole, G.; et al. Whole transcriptome profiling of Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease patients provides insights into the molecular changes involved in the disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, K.E.; Hewes, A.A.; Garceau, D.T.; Kotredes, K.P.; Carter, G.W.; Sasner, M.; Howell, G.R. The APOE (epsilon3/epsilon4) Genotype Drives Distinct Gene Signatures in the Cortex of Young Mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 838436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathys, H.; Davila-Velderrain, J.; Peng, Z.; Gao, F.; Mohammadi, S.; Young, J.Z.; Menon, M.; He, L.; Abdurrob, F.; Jiang, X.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2019, 570, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren-Shaul, H.; Spinrad, A.; Weiner, A.; Matcovitch-Natan, O.; Dvir-Szternfeld, R.; Ulland, T.K.; David, E.; Baruch, K.; Lara-Astaiso, D.; Toth, B.; et al. A Unique Microglia Type Associated with Restricting Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell 2017, 169, 1276–1290.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Song, W.M.; Andhey, P.S.; Swain, A.; Levy, T.; Miller, K.R.; Poliani, P.L.; Cominelli, M.; Grover, S.; Gilfillan, S.; et al. Human and mouse single-nucleus transcriptomics reveal TREM2-dependent and TREM2-independent cellular responses in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghani, A.; Cacciottolo, M.; Doty, K.R.; D’Agostino, C.; Thorwald, M.; Safi, N.; Levine, M.E.; Sioutas, C.; Town, T.C.; Forman, H.J.; et al. Mouse brain transcriptome responses to inhaled nanoparticulate matter differed by sex and APOE in Nrf2-Nfkb interactions. Comput. Syst. Biol. 2020, 9, e54822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeser, A.C.; Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Lippmann, J.; Wagner, A.E.; Huebbe, P.; Storm, N.; Hoppner, W.; Wiswedel, I.; Gardemann, A.; Minihane, A.M.; et al. Nrf2-dependent gene expression is affected by the proatherogenic apoE4 genotype-studies in targeted gene replacement mice. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, T.; Lattanzio, F.; Calvo-Garrido, J.; Rimondini, R.; Rubio-Rodrigo, M.; Sundstrom, E.; Maioli, S.; Sandebring-Matton, A.; Cedazo-Minguez, A. Apolipoprotein E4 Elicits Lysosomal Cathepsin D Release, Decreased Thioredoxin-1 Levels, and Apoptosis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 56, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villasana, L.E.; Weber, S.; Akinyeke, T.; Raber, J. Genotype differences in anxiety and fear learning and memory of WT and ApoE4 mice associated with enhanced generation of hippocampal reactive oxygen species. J. Neurochem. 2016, 138, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramassamy, C.; Averill, D.; Beffert, U.; Theroux, L.; Lussier-Cacan, S.; Cohn, J.S.; Christen, Y.; Schoofs, A.; Davignon, J.; Poirier, J. Oxidative insults are associated with apolipoprotein E genotype in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2000, 7, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duits, F.H.; Kester, M.I.; Scheffer, P.G.; Blankenstein, M.A.; Scheltens, P.; Teunissen, C.E.; van der Flier, W.M. Increase in cerebrospinal fluid F2-isoprostanes is related to cognitive decline in APOE epsilon4 carriers. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 36, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glodzik-Sobanska, L.; Pirraglia, E.; Brys, M.; de Santi, S.; Mosconi, L.; Rich, K.E.; Switalski, R.; Saint Louis, L.; Sadowski, M.J.; Martiniuk, F.; et al. The effects of normal aging and ApoE genotype on the levels of CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrazi, H.; Vaisi-Raygani, A.; Rahimi, Z.; Tavilani, H.; Aminian, M.; Pourmotabbed, T. Association between enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant defense mechanism with apolipoprotein E genotypes in Alzheimer disease. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagne, A.; Barnes, S.R.; Sweeney, M.D.; Halliday, M.R.; Sagare, A.P.; Zhao, Z.; Toga, A.W.; Jacobs, R.E.; Liu, C.Y.; Amezcua, L.; et al. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in the aging human hippocampus. Neuron 2015, 85, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P. Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2004, 430, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, F.L.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Becher, B. Immune attack: The role of inflammation in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Landi, F.; Bernabei, R.; Marzetti, E. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Neuroinflammation: Intertwined Roads to Neurodegeneration. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Kulesza, R.J.; Mansour, Y.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, L.O.; Gonzalez-Maciel, A.; Reynoso-Robles, R.; Mukherjee, P.S. Alzheimer disease starts in childhood in polluted Metropolitan Mexico City. A major health crisis in progress. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.L.; Elder, A.; Auten, R.L.; Bilbo, S.D.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.C.; Cory-Slechta, D.A.; Costa, D.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Dorman, D.C.; et al. The outdoor air pollution and brain health workshop. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 972–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.; Tymianski, M. Glutamate receptors, neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Pflüg. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2010, 460, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlokovic, B.V. Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and other disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, M.A.; Banks, W.A. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction as a cause and consequence of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1500–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Avila-Ramirez, J.; Calderon-Garciduenas, A.; Gonzalez-Heredia, T.; Acuna-Ayala, H.; Chao, C.K.; Thompson, C.; Ruiz-Ramos, R.; Cortes-Gonzalez, V.; Martinez-Martinez, L.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Highly Exposed PM2.5 Urbanites: The Risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases in Young Mexico City Residents. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 54, 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform-extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.D.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. Thirteen years of clusterProfiler. Innovation 2024, 5, 100722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolde, R.; Vilo, J. GOsummaries: An R Package for Visual Functional Annotation of Experimental Data. F1000Research 2015, 4, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.H.; Chen, C.; Akyol, T.; Dusa, A.; Yu, G.; Cao, B.; Cai, P. ggVennDiagram: Intuitive Venn diagram software extended. iMeta 2024, 3, e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakamya, M.F.; Hu, K.; Jiang, C.; Chong, Z.; Liu, R.-M. Age- and ApoE Genotype-Dependent Transcriptomic Responses to O3 in the Hippocampus of Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062407
Nakamya MF, Hu K, Jiang C, Chong Z, Liu R-M. Age- and ApoE Genotype-Dependent Transcriptomic Responses to O3 in the Hippocampus of Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062407
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakamya, Mary F., Kaili Hu, Chunsun Jiang, Zechen Chong, and Rui-Ming Liu. 2025. "Age- and ApoE Genotype-Dependent Transcriptomic Responses to O3 in the Hippocampus of Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062407
APA StyleNakamya, M. F., Hu, K., Jiang, C., Chong, Z., & Liu, R.-M. (2025). Age- and ApoE Genotype-Dependent Transcriptomic Responses to O3 in the Hippocampus of Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062407





