Metabolically Healthy Obesity Is Characterized by a Distinct Proteome Signature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Cohort
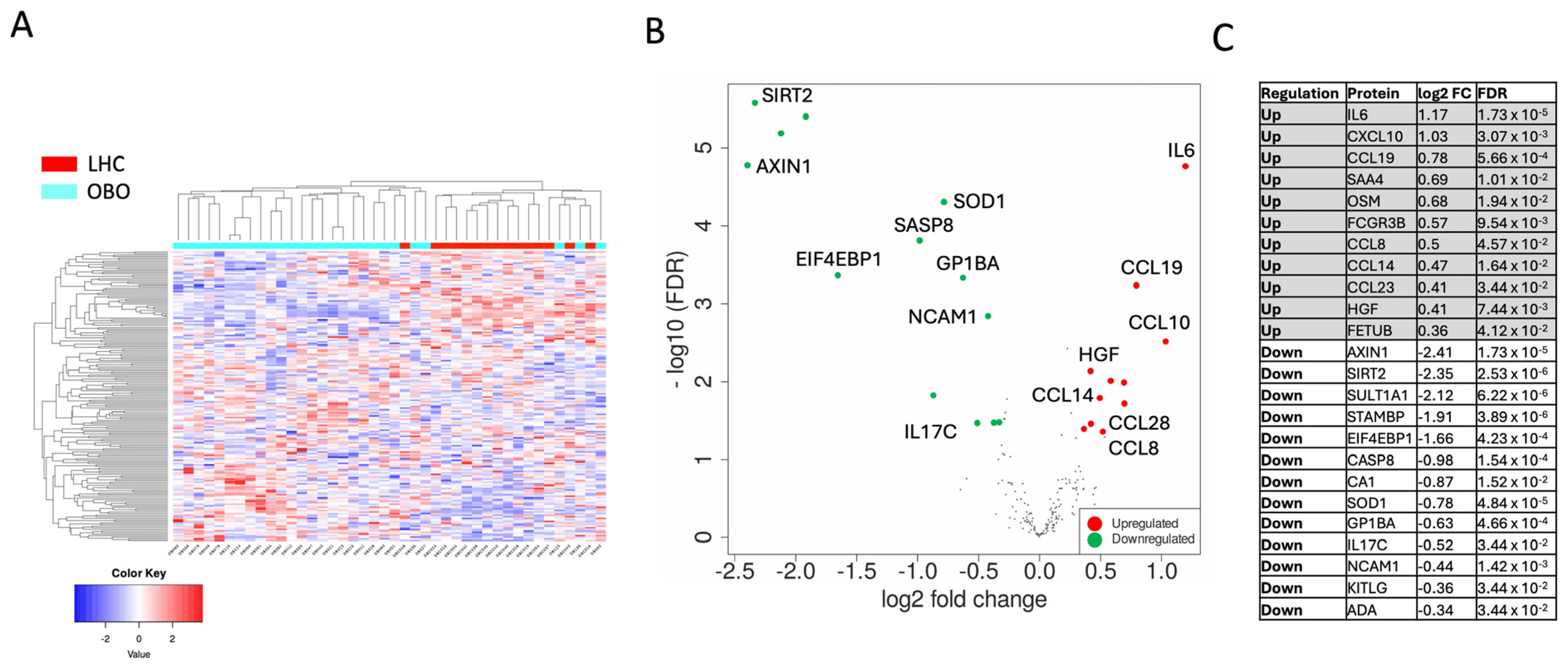
2.2. Proteomic Analysis Revealed a Differential Plasma Protein Profile in Obesity
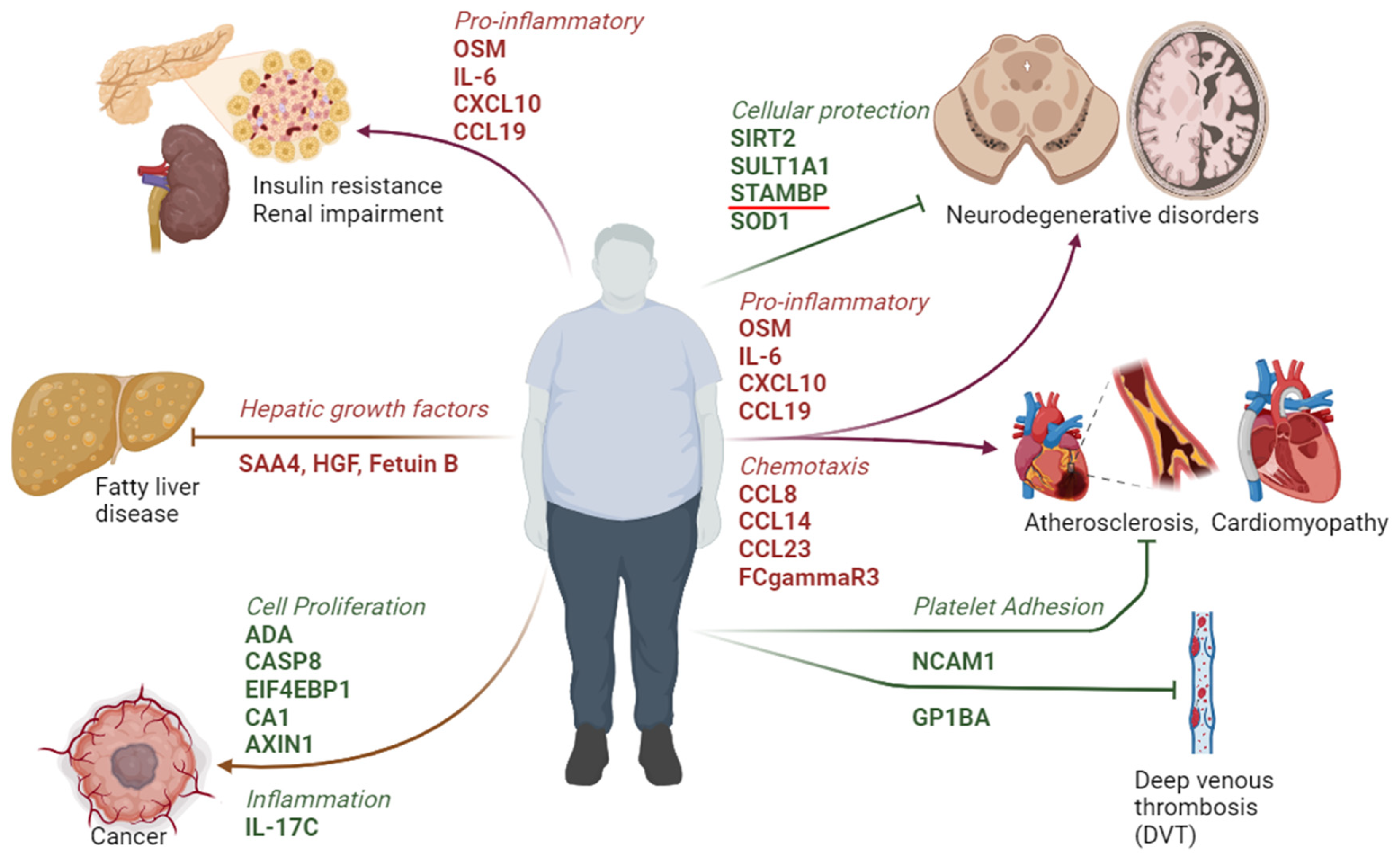
2.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis of DEPs Revealed Immunological Pathways in Obesity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Measurements and Assays
4.3. Baseline Statistical Analysis
4.4. Proteomic Assay
4.5. Bioinformatics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Altas; World Obesity Federation: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, A.; Fernandes, A.; Barateiro, A. The complex relationship between obesity and neurodegenerative diseases: An updated review. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1294420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Cordero, J.A.; Perez-Perez, A.; Jimenez-Cortegana, C.; Alba, G.; Flores-Barragan, A.; Sanchez-Margalet, V. Obesity as a Risk Factor for Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: The Role of Leptin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, K.; Karssiens, T.; Kumar, V.; Pandit, H. Obesity and osteoarthritis. Maturitas 2016, 89, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aune, D.; Norat, T.; Vatten, L.J. Body mass index, abdominal fatness and the risk of gallbladder disease. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, J.R.; Jenkins, T.G.; Carrell, D.T.; Hotaling, J.M. Obesity, male infertility, and the sperm epigenome. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 107, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, N.B.; Baur, L.A.; Felix, J.F.; Hill, A.J.; Marcus, C.; Reinehr, T.; Summerbell, C.; Wabitsch, M. Child and adolescent obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Balasundaram, P. Public Health Considerations Regarding Obesity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- De Frel, D.L.; Atsma, D.E.; Pijl, H.; Seidell, J.C.; Leenen, P.J.M.; Dik, W.A.; van Rossum, E.F.C. The Impact of Obesity and Lifestyle on the Immune System and Susceptibility to Infections Such as COVID-19. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 597600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildman, R.P.; Muntner, P.; Reynolds, K.; McGinn, A.P.; Rajpathak, S.; Wylie-Rosett, J.; Sowers, M.R. The obese without cardiometabolic risk factor clustering and the normal weight with cardiometabolic risk factor clustering: Prevalence and correlates of 2 phenotypes among the US population (NHANES 1999–2004). Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, F.A.; Abdesselem, H.B.; Cyprian, F.; Iskandarani, A.; Doudin, A.; Samra, T.A.; Alkasem, M.; Abdalhakam, I.; Taheri, S.; Abou-Samra, A.B. Inflammatory protein signatures in individuals with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, F.A.; Mall, R.; Iskandarani, A.; Ullah, E.; Samra, T.A.; Cyprian, F.; Parray, A.; Alkasem, M.; Abdalhakam, I.; Farooq, F.; et al. Characteristic MicroRNAs Linked to Dysregulated Metabolic Pathways in Qatari Adult Subjects With Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 937089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, F.A.; Mall, R.; Ullah, E.; Iskandarani, A.; Cyprian, F.; Samra, T.A.; Alkasem, M.; Abdalhakam, I.; Farooq, F.; Taheri, S.; et al. An integrated multi-omic approach demonstrates distinct molecular signatures between human obesity with and without metabolic complications: A case-control study. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, F.A.; Ullah, E.; Mall, R.; Iskandarani, A.; Samra, T.A.; Cyprian, F.; Parray, A.; Alkasem, M.; Abdalhakam, I.; Farooq, F.; et al. Dysregulated Metabolic Pathways in Subjects with Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajik, S.; Mirzababaei, A.; Ghaedi, E.; Kord-Varkaneh, H.; Mirzaei, K. Risk of type 2 diabetes in metabolically healthy people in different categories of body mass index: An updated network meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Res. 2019, 11, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Haring, H.U.; Hu, F.B.; Schulze, M.B. Metabolically healthy obesity: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and clinical implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C.M. Metabolically healthy obesity: Definitions, determinants and clinical implications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2013, 14, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongraw-Chaffin, M.; Foster, M.C.; Anderson CA, M.; Burke, G.L.; Haq, N.; Kalyani, R.R.; Ouyang, P.; Sibley, C.T.; Tracy, R.; Woodward, M.; et al. Metabolically Healthy Obesity, Transition to Metabolic Syndrome, and Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Pan, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, G.P. Applications of multi-omics analysis in human diseases. MedComm 2023, 4, e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.B.; Maranville, J.C.; Peters, J.E.; Stacey, D.; Staley, J.R.; Blackshaw, J.; Burgess, S.; Jiang, T.; Paige, E.; Surendran, P.; et al. Genomic atlas of the human plasma proteome. Nature 2018, 558, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.; Emsley, J. Gene of the issue: GP1BA gene mutations associated with bleeding. Platelets 2017, 28, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.M.; Wu, H.F.; Wang, K.F.; Yu, D.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Ren, Q.; Chen, W.Z.; Lin, F.; Yu, Z.; Zhuang, C.L. Transcriptome profiling of fast/glycolytic and slow/oxidative muscle fibers in aging and obesity. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wueest, S.; Konrad, D. The controversial role of IL-6 in adipose tissue on obesity-induced dysregulation of glucose metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, E607–E613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Devalaraja, M.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Engelmann, M.D.M.; Hovingh, G.K.; Ivkovic, M.; Lo, L.; Kling, D.; Pergola, P.; Raj, D.; et al. IL-6 inhibition with ziltivekimab in patients at high atherosclerotic risk (RESCUE): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2060–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedell-Neergaard, A.S.; Lang Lehrskov, L.; Christensen, R.H.; Legaard, G.E.; Dorph, E.; Larsen, M.K.; Launbo, N.; Fagerlind, S.R.; Seide, S.K.; Nymand, S.; et al. Exercise-Induced Changes in Visceral Adipose Tissue Mass Are Regulated by IL-6 Signaling: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 844–855.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotak, M.; Clark, M.; Suur, B.E.; Borgeson, E. Inflammation and resolution in obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2025, 21, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.E.; Park, C.Y.; Sweeney, G. Biomarkers of insulin sensitivity and insulin resistance: Past, present and future. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 52, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Bachmann, R.A.; Chen, J. Interleukin-6 and insulin resistance. Vitam. Horm. 2009, 80, 613–633. [Google Scholar]
- Ellingsgaard, H.; Hauselmann, I.; Schuler, B.; Habib, A.M.; Baggio, L.L.; Meier, D.T.; Eppler, E.; Bouzakri, K.; Wueest, S.; Muller, Y.D.; et al. Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from L cells and alpha cells. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueck, P.J.; Morris, J.K.; Stanford, J.A. Current Perspectives: Obesity and Neurodegeneration—Links and Risks. Degener. Neurol. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2023, 13, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Edison, P. Cardiometabolic risk factors and neurodegeneration: A review of the mechanisms underlying diabetes, obesity and hypertension in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2024, 95, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochumon, S.; Al-Rashed, F.; Abu-Farha, M.; Devarajan, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Ahmad, R. Adipose tissue expression of CCL19 chemokine is positively associated with insulin resistance. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso, L.; Ortega, R.; Selles, F.; Wu-Xiong, N.Y.; Ortega, J.; Civera, M.; Ascaso, J.F.; Sanz, M.J.; Real, J.T.; Piqueras, L. Upregulation of angiostatic chemokines IP-10/CXCL10 and I-TAC/CXCL11 in human obesity and their implication for adipose tissue angiogenesis. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, E.; Gesta, S.; Kahn, C.R. SIRT2 regulates adipocyte differentiation through FoxO1 acetylation/deacetylation. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, T. Chemokine systems link obesity to insulin resistance. Diabetes Metab. J. 2013, 37, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomino, D.C.; Marti, L.C. Chemokines and immunity. Einstein 2015, 13, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Hartigh, L.J.; May, K.S.; Zhang, X.S.; Chait, A.; Blaser, M.J. Serum amyloid A and metabolic disease: Evidence for a critical role in chronic inflammatory conditions. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1197432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.D.; Kip, K.E.; Marroquin, O.C.; Ridker, P.M.; Kelsey, S.F.; Shaw, L.J.; Pepine, C.J.; Sharaf, B.; Bairey Merz, C.N.; Sopko, G.; et al. Serum amyloid A as a predictor of coronary artery disease and cardiovascular outcome in women: The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute-Sponsored Women’s Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE). Circulation 2004, 109, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzi, C.; Huth, C.; Herder, C.; Baumert, J.; Thorand, B.; Rathmann, W.; Meisinger, C.; Wichmann, H.E.; Roden, M.; Peters, A.; et al. Acute-phase serum amyloid A protein and its implication in the development of type 2 diabetes in the KORA S4/F4 study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, A.I.; Rothenberg, L.S.; DeBeer, F.C.; Cantor, R.M.; Rotter, J.I.; Lusis, A.J. Association between serum amyloid A proteins and coronary artery disease: Evidence from two distinct arteriosclerotic processes. Circulation 1997, 96, 2914–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, T.; Kolehmainen, M.; Schwab, U.; Pulkkinen, L.; Laaksonen, D.E.; Rauramaa, R.; Uusitupa, M.; Gylling, H. Serum concentrations and expressions of serum amyloid A and leptin in adipose tissue are interrelated: The Genobin Study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 158, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Z.; Lee, M.J.; Hu, H.; Pollin, T.I.; Ryan, A.S.; Nicklas, B.J.; Snitker, S.; Horenstein, R.B.; Hull, K.; Goldberg, N.H.; et al. Acute-phase serum amyloid A: An inflammatory adipokine and potential link between obesity and its metabolic complications. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, J.; Considine, R.V.; Bovenkerk, J.E.; Li, J.; Slavens, C.A.; Jones, R.M.; March, K.L. Obesity is associated with increased levels of circulating hepatocyte growth factor. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Lin, M.; Shi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, X. Hepatokine Fetuin B expression is regulated by leptin-STAT3 signalling and associated with leptin in obesity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elks, C.M.; Zhao, P.; Grant, R.W.; Hang, H.; Bailey, J.L.; Burk, D.H.; McNulty, M.A.; Mynatt, R.L.; Stephens, J.M. Loss of Oncostatin M Signaling in Adipocytes Induces Insulin Resistance and Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 17066–17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Hu, F.; Wang, D.; Kang, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, B.; Liu, S.; Yuan, G. Sirtuin 2 Prevents Liver Steatosis and Metabolic Disorders by Deacetylation of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4alpha. Hepatology 2021, 74, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Shigenaga, J.; Moser, A.; Grunfeld, C.; Feingold, K.R. Suppression of DHEA sulfotransferase (Sult2A1) during the acute-phase response. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 287, E731–E738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghose, R.; Omoluabi, O.; Gandhi, A.; Shah, P.; Strohacker, K.; Carpenter, K.C.; McFarlin, B.; Guo, T. Role of high-fat diet in regulation of gene expression of drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, S.; Paltser, G.; Chan, Y.; Tsui, H.; Engleman, E.; Winer, D.; Dosch, H.M. Obesity predisposes to Th17 bias. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 2629–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumarac-Dumanovic, M.; Stevanovic, D.; Ljubic, A.; Jorga, J.; Simic, M.; Stamenkovic-Pejkovic, D.; Starcevic, V.; Trajkovic, V.; Micic, D. Increased activity of interleukin-23/interleukin-17 proinflammatory axis in obese women. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Goodrich, J.A.; Chen, W.; Qiu, C.; Chen, J.C.; Costello, E.; Alderete, T.L.; Chatzi, L.; Gilliland, F.; Chen, Z. Cardiometabolic profiles and proteomics associated with obesity phenotypes in a longitudinal cohort of young adults. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, L.; Nordberg, N.; Broberg, J.; Bjorkesten, J.; Assarsson, E.; Henriksson, S.; Grundberg, I.; Pettersson, E.; Westerberg, C.; Liljeroth, E.; et al. Proximity Extension Assay in Combination with Next-Generation Sequencing for High-throughput Proteome-wide Analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2021, 20, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Son, E.W.; Yao, R. iDEP: An integrated web application for differential expression and pathway analysis of RNA-Seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
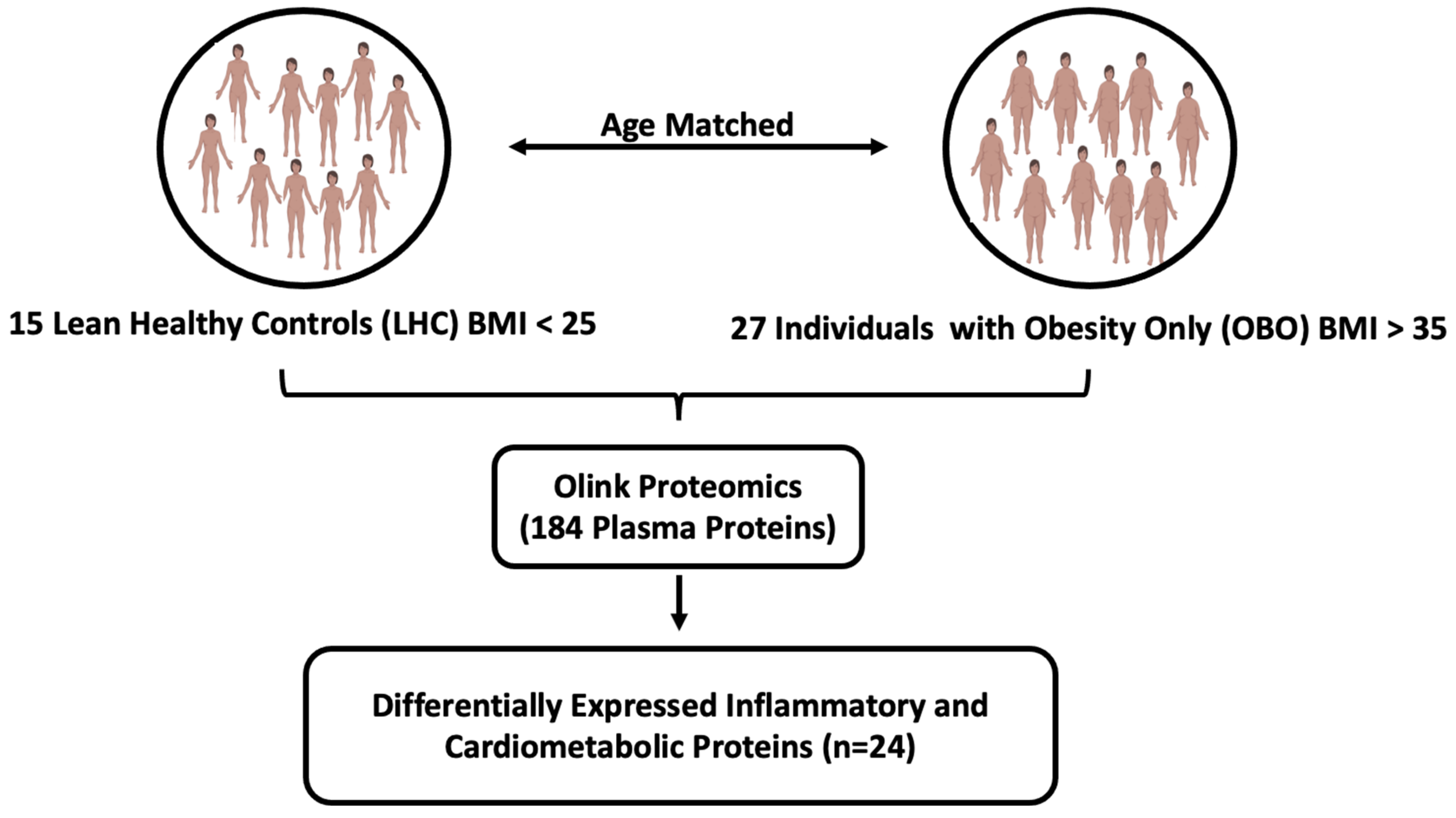

| Feature | OBO (n = 27) | LHC (n = 15) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 36.4 ± 5.5 | 38.8 ± 4.3 | 0.23 |
| Gender (number) | 17 (F) 10 (M) | 7 (F) 8 (M) | 0.004 |
| Height (cm) | 167.7 ± 11.3 | 172.2 ± 8.9 | 0.203 |
| Weight (kg) | 115.8 ± 21.5 | 73.6 ± 8.6 | 0.0004 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 41.2 ± 4.9 | 24.8 ± 2.2 | 0.0002 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 118.0 ± 12.7 | 112.8 ± 10.7 | 0.197 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 67.95 ± 13.2 | 68.0 ± 5.8 | 0.990 |
| HbA1c (mmol/L) | 35.7 ± 2.41 | 33.9 ± 1.86 | 0.069 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.19 ± 0.45 | 0.96 ± 0.35 | 0.143 |
| Total Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.62 ± 1.05 | 4.77 ± 0.99 | 0.665 |
| Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) (mmol/L) | 2.69 ± 1.07 | 2.96 ± 0.93 | 0.415 |
| High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) (mmol/L) | 1.40 ± 0.59 | 1.35 ± 0.19 | 0.647 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 5.2 ± 0.7 | 4.7 ± 0.5 | 0.006 |
| Creatinine (mmol/L) | 65.9 ± 12.2 | 74.5 ± 13.3 | 0.041 |
| Insulin (mIU/L) | 20.0 ± 14.2 | 2.9 ± 1.7 | 0.0003 |
| C-reactive Protein (CRP) (mg/L) | 5.8 ± 1.8 | 1.3 ± 1.1 | 0.002 |
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) (U/L) | 26.8 ± 18.5 | 23.5 ± 15.1 | 0.554 |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) (U/L) | 20.5 ± 9.4 | 21.1 ± 7.4 | 0.845 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mir, F.A.; Abdesselem, H.B.; Cyprian, F.; Iskandarani, A.; Doudin, A.; Shraim, M.A.; Alkhalaf, B.M.; Alkasem, M.; Abdalhakam, I.; Bensmail, I.; et al. Metabolically Healthy Obesity Is Characterized by a Distinct Proteome Signature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052262
Mir FA, Abdesselem HB, Cyprian F, Iskandarani A, Doudin A, Shraim MA, Alkhalaf BM, Alkasem M, Abdalhakam I, Bensmail I, et al. Metabolically Healthy Obesity Is Characterized by a Distinct Proteome Signature. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052262
Chicago/Turabian StyleMir, Fayaz Ahmad, Houari B. Abdesselem, Farhan Cyprian, Ahmad Iskandarani, Asmma Doudin, Mutasem AbdelRahim Shraim, Bader M. Alkhalaf, Meis Alkasem, Ibrahem Abdalhakam, Ilham Bensmail, and et al. 2025. "Metabolically Healthy Obesity Is Characterized by a Distinct Proteome Signature" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052262
APA StyleMir, F. A., Abdesselem, H. B., Cyprian, F., Iskandarani, A., Doudin, A., Shraim, M. A., Alkhalaf, B. M., Alkasem, M., Abdalhakam, I., Bensmail, I., Al Halabi, H. A., Taheri, S., & Abou-Samra, A.-B. (2025). Metabolically Healthy Obesity Is Characterized by a Distinct Proteome Signature. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052262






