Malignant Transformed and Non-Transformed Oral Leukoplakias Are Metabolically Different
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinicopathological Characterisation
2.2. Data Quality, Processing, and Treatment
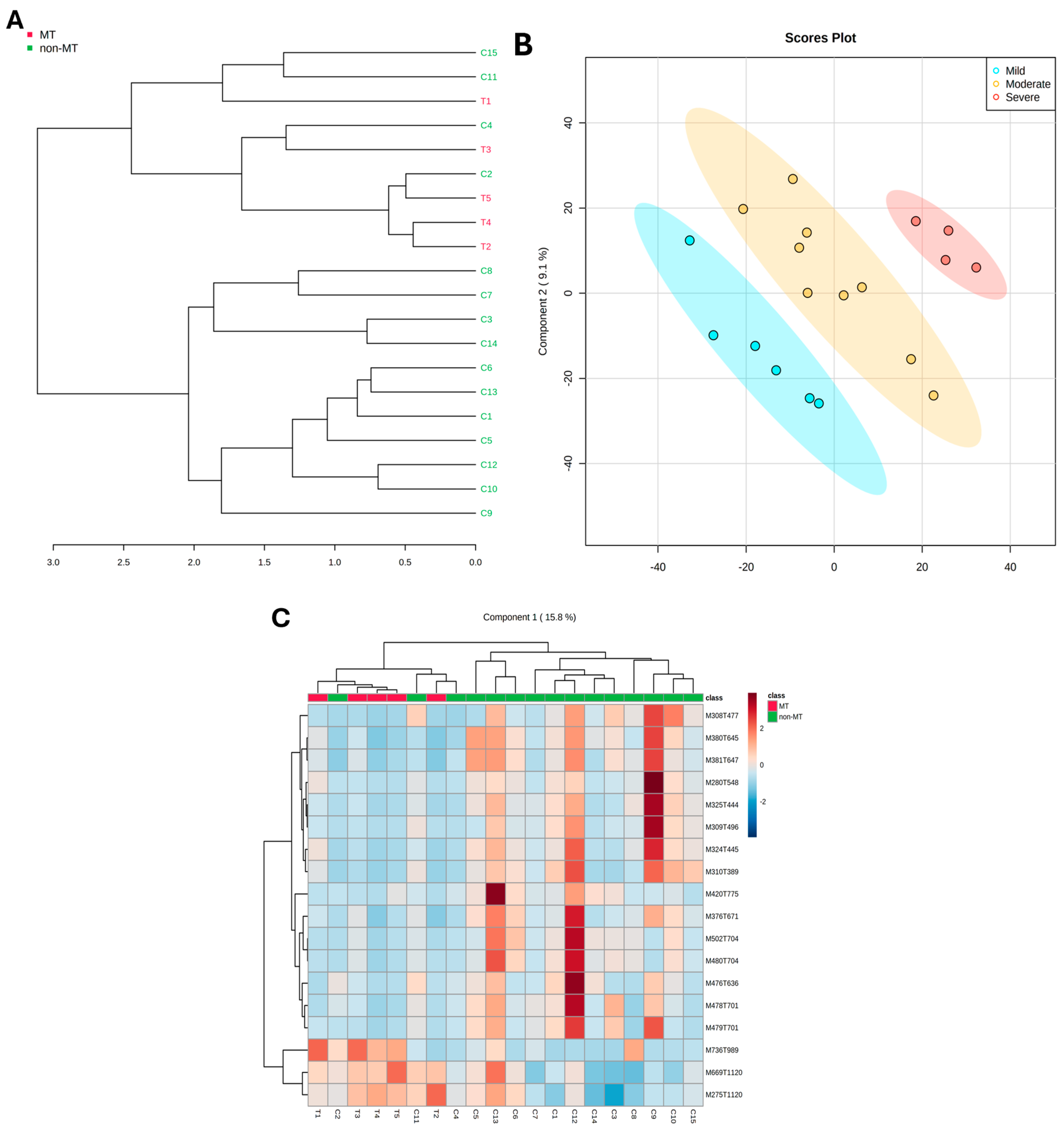
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Multivariate Modeling
2.5. Assessment of Key Molecular Features for Effective Group Discrimination
2.6. Metabolite Annotation and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics and Sample
4.2. Sample Preparation and Metabolite Extraction
4.3. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS)
4.4. Data Processing and Treatment
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. Recursive Selection of Discriminating Molecular Features
4.7. Assessment of the Discriminating Molecular Features Accuracy
4.8. Metabolite Annotation
4.9. Metabolic Pathway Enrichment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mello, F.W.; Miguel, A.F.P.; Dutra, K.L.; Porporatti, A.L.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Guerra, E.N.S.; Rivero, E.R.C. Prevalence of Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2018, 47, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evren, I.; Brouns, E.R.; Wils, L.J.; Poell, J.B.; Peeters, C.F.W.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Bloemena, E.; de Visscher, J.G.A.M. Annual Malignant Transformation Rate of Oral Leukoplakia Remains Consistent: A Long-Term Follow-up Study. Oral Oncol. 2020, 110, 105014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wils, L.J.; Poell, J.B.; Evren, I.; Koopman, M.S.; Brouns, E.R.E.A.; de Visscher, J.G.A.M.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Bloemena, E. Incorporation of Differentiated Dysplasia Improves Prediction of Oral Leukoplakia at Increased Risk of Malignant Progression. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, C.A.; Agaimy, A.; Wehrhan, F.; Weber, M.; Hille, V.; Brunner, K.; Wickenhauser, C.; Siebolts, U.; Nkenke, E.; Kesting, M.; et al. MAGE-A Expression in Oral and Laryngeal Leukoplakia Predicts Malignant Transformation. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhosale, P.G.; Cristea, S.; Ambatipudi, S.; Desai, R.S.; Kumar, R.; Patil, A.; Kane, S.; Borges, A.M.; Schäffer, A.A.; Beerenwinkel, N.; et al. Chromosomal Alterations and Gene Expression Changes Associated with the Progression of Leukoplakia to Advanced Gingivobuccal Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebers, T.J.H.; Bergshoeff, V.E.; Otte-Höller, I.; Kremer, B.; Speel, E.J.M.; Van Der Laak, J.A.W.M.; Merkx, M.A.W.; Slootweg, P.J. Chromosome Instability Predicts the Progression of Premalignant Oral Lesions. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperandio, M.; Brown, A.L.; Lock, C.; Morgan, P.R.; Coupland, V.H.; Madden, P.B.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Møller, H.; Odell, E.W. Predictive Value of Dysplasia Grading and DNA Ploidy in Malignant Transformation of Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders. Cancer Prev. Res. 2013, 6, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Wehrhan, F.; Baran, C.; Agaimy, A.; Büttner-Herold, M.; Öztürk, H.; Neubauer, K.; Wickenhauser, C.; Kesting, M.; Ries, J. Malignant Transformation of Oral Leukoplakia Is Associated with Macrophage Polarization. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, R.; Jiao, J.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, L.; Gong, Z. Transglutaminase 3 Contributes to Malignant Transformation of Oral Leukoplakia to Cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 104, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Silva, T.; Diniz, M.G.; de Sousa, S.F.; Gomez, R.S.; Gomes, C.C. Association between Histopathological Features of Dysplasia in Oral Leukoplakia and Loss of Heterozygosity. Histopathology 2016, 68, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, L.M.; Diniz, M.G.; Rogatto, S.R.; Gomez, R.S.; Gomes, C.C. The Genetic Basis of Oral Leukoplakia and Its Key Role in Understanding Oral Carcinogenesis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Lafuente-Ibáñez de Mendoza, I.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Malignant Transformation of Oral Leukoplakia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Last 5 Years. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1881–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Chung, M.; Jeong, H.S.; Baek, C.H.; Cho, J. Histological Features of Differentiated Dysplasia in the Oral Mucosa: A Review of Oral Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cases Diagnosed with Benign or Low-Grade Dysplasia on Previous Biopsies. Hum. Pathol. 2022, 126, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odell, E.; Kujan, O.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Sloan, P. Oral Epithelial Dysplasia: Recognition, Grading and Clinical Significance. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1947–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.S.; Holm, M.; Liese, J.; Engel, N.; Zimpfer, A.H. Diagnosis of Differentiated Dysplasia as a Variant of Oral Epithelial Dysplasia. Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 4185–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S. Emerging Applications of Metabolomics in Drug Discovery and Precision Medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinges, S.S.; Hohm, A.; Vandergrift, L.A.; Nowak, J.; Habbel, P.; Kaltashov, I.A.; Cheng, L.L. Cancer Metabolomic Markers in Urine: Evidence, Techniques and Recommendations. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2019, 16, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins-Chaves, R.R.; Silva, R.S.O.; Pereira, T.d.S.F.; Fonseca, F.P.; Gomez, R.S. Evolution Tumour Models Paving the Way for Understanding Oral Carcinogenesis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2023, 52, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Dutta, D.; Chaudhary, A.; Chandra Sing, B.; Banerjee, R.; Pal, M.; Paul, R.R.; Basak, A.; Das, A.K.; Ray, A.K.; et al. NanoLC MALDI MS/MS Based Quantitative Metabolomics Reveals the Alteration of Membrane Biogenesis in Oral Cancer. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 62420–62433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Gupta, S.; Mahdi, A.A. 1H NMR-Derived Serum Metabolomics of Leukoplakia and Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 441, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Jian, F.; Deng, P.; Li, W. Analysis of Plasma Metabolic Biomarkers in the Development of 4-Nitroquinoline-1-Oxide-Induced Oral Carcinogenesis in Rats. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Yang, X.; Narayanan, R.; Shankar, V.; Ethiraj, S.; Wang, X.; Duan, N.; Ni, Y.H.; Hu, Q.; Zare, R.N. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed from Saliva Metabolic Profiling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16167–16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, G.; Ramani, P.; Patankar, S. Serum Metabolomics in Oral Leukoplakia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2017, 14, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, G.; Ramani, P.; Patankar, S.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Evaluation of Salivary Metabolomics in Oral Leukoplakia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2019, 48, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Xie, G.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, P.; Qiu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Chen, T.; Su, M.; Zhao, A.; Jia, W. Salivary Metabolite Signatures of Oral Cancer and Leukoplakia. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.X.; Chen, T.L.; Qiu, Y.P.; Shi, P.; Zheng, X.J.; Su, M.M.; Zhao, A.H.; Zhou, Z.T.; Jia, W. Urine Metabolite Profiling Offers Potential Early Diagnosis of Oral Cancer. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, B.; Huang, J.; Jia, X.; Xue, J.; Shi, X.; Xiao, L.; Li, W. 1H NMR-Based Metabonomic and Pattern Recognition Analysis for Detection of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 401, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-De-La-Fuente, A.; Godzien, J.; Saugar, S.; Garcia-Carmona, R.; Badran, H.; Wishart, D.S.; Barbas, C.; Otero, A. CEU Mass Mediator 3.0: A Metabolite Annotation Tool. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.C.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueira, J.M.; Pontes, F.S.; Santos-Silva, A.R.; Almeida, O.P.; Costa, R.F.; Fonseca, F.P.; Gomez, R.S.; Neto, N.C.; Miyahara, L.A.; Rodrigues-Fernandes, C.I.; et al. Malignant Transformation of Oral Leukoplakia: A Multicentric Retrospective Study in Brazilian Population. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2020, 26, e292–e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubert, A.; Bagán, L.; Bagán, J.V. Oral Leukoplakia, a Clinical-Histopathological Study in 412 Patients. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2020, 12, e540–e546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speight, P.M.; Khurram, S.A.; Kujan, O. Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders: Risk of Progression to Malignancy. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2018, 125, 612–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldron, C.A.; Shafer, W.G. Leukoplakia Revisited. A Clinicopathologic Study 3256 Oral Leukoplakias. Cancer 1975, 36, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitório, J.G.; Duarte-Andrade, F.F.; dos Santos Fontes Pereira, T.; Fonseca, F.P.; Amorim, L.S.D.; Martins-Chaves, R.R.; Gomes, C.C.; Canuto, G.A.B.; Gomez, R.S. Metabolic Landscape of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, M.; Kazanietz, M.G. Overarching Roles of Diacylglycerol Signaling in Cancer Development and Antitumor Immunity. Sci. Signal. 2022, 15, eabo0264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, Y.; Kasamatsu, A.; Yamatoji, M.; Fushimi, K.; Ishigami, T.; Shimizu, T.; Kasama, H.; shiiba, M.; Tanzawa, H.; Uzawa, K. Diacylglycerol Lipase Alpha Promotes Tumorigenesis in Oral Cancer by Cell-Cycle Progression. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 367, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, A.; Saraswat, M.; Joenväärä, S.; Agarwal, R.; Jyllikoski, D.; Wilkman, T.; Mäkitie, A.; Silén, S. Mass Spectrometry–Based Lipidomics of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tissue Reveals Aberrant Cholesterol and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism—A Pilot Study. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.P.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Ateeq, B.; Asangani, I.A.; Athanikar, J.N.; Yocum, A.K.; Mehra, R.; Siddiqui, J.; Palapattu, G.; Wei, J.T.; et al. The Role of Sarcosine Metabolism in Prostate Cancer Progression. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernei, N.; Heger, Z.; Gumulec, J.; Zitka, O.; Masarik, M.; Babula, P.; Eckschlager, T.; Stiborova, M.; Kizek, R.; Adam, V. Sarcosine as a Potential Prostate Cancer Biomarker—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13893–13908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasim, M.; Shaheen, S.; Fatima, B.; Hussain, D.; Hassan, F.; Tahreem, S.; Riaz, M.M.; Yar, A.; Majeed, S.; Najam-ul-Haq, M. Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Detection of Sarcosine in Serum of Prostate Cancer Patients by CoNiWBO/RGO Nanocomposite. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markin, P.A.; Brito, A.; Moskaleva, N.; Fodor, M.; Lartsova, E.V.; Shpot, Y.V.; Lerner, Y.V.; Mikhajlov, V.Y.; Potoldykova, N.V.; Enikeev, D.V.; et al. Plasma Sarcosine Measured by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Distinguishes Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Prostate Cancer from Benign Prostate Hyperplasia. Lab. Med. 2021, 51, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polachini, G.M.; de Castro, T.B.; Smarra, L.F.S.; Henrique, T.; de Paula, C.H.D.; Severino, P.; López, R.V.M.; Carvalho, A.L.; de Mattos Zeri, A.C.; Silva, I.D.C.G.; et al. Plasma Metabolomics of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Based on NMR and MS Approaches Provides Biomarker Identification and Survival Prediction. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Rosén, J.; Landberg, R.; Brunius, C. Variable Selection and Validation in Multivariate Modelling. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filzmoser, P.; Liebmann, B.; Varmuza, K. Repeated Double Cross Validation. J. Chemom. 2009, 23, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Wei, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Feng, H. Association between 35 Blood and Urine Biomarkers and Oral Leukoplakia: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1437493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Qian, B.; Xu, J.; Yang, J.; Wu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Fan, Y.; Li, H. Clinical Relevance of Serum Lipids in the Carcinogenesis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisel, P.; Dau, M.; Sümnig, W.; Holtfreter, B.; Houshmand, M.; Nauck, M.; Kocher, T. Association between Glycemia, Serum Lipoproteins, and the Risk of Oral Leukoplakia: The Population-Based Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP). Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1230–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Finck, B.N.; Hall, A.M. Does Diacylglycerol Accumulation in Fatty Liver Disease Cause Hepatic Insulin Resistance? Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 104132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.; Hatch, G.M.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F.; Wang, M. The Relationship between Phospholipids and Insulin Resistance: From Clinical to Experimental Studies. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, D.; Saltiel, A.R. Phosphoinositides in Insulin Action and Diabetes. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 362, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Yang, J.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. The Role of Oxidized Phospholipids in the Development of Disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 76, 100909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Aftabizadeh, M.; Zhao, Q.; Tripathi, S.C.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Ann, D.; Hanash, S.; Yu, H. Fatty Acid Oxidation Protects Cancer Cells from Apoptosis by Increasing Mitochondrial Membrane Lipids. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, K.C.; Shrivastava, D. Analysis of Plasma Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant Enzymes Status in Patients of Oral Leukoplakia: A Case Control Study. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2016, 6, S213–S218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somashekar, B.S.; Kamarajan, P.; Danciu, T.; Kapila, Y.L.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Ramamoorthy, A. Magic Angle Spinning NMR-Based Metabolic Profiling of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tissues. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 5232–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senghore, T.; Li, Y.F.; Sung, F.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Hua, C.H.; Liu, C.S.; Huang, R.J.; Yeh, C.C. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress Associated with the Risk of Potentially Malignant Oral Disorders. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 5211–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goicoechea, L.; Conde de la Rosa, L.; Torres, S.; García-Ruiz, C.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Mitochondrial Cholesterol: Metabolism and Impact on Redox Biology and Disease. Redox Biol. 2023, 61, 102643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, M.R.; Tugnoli, V. Cholesteryl Esters in Malignancy. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 359, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devasahayam Arokia Balaya, R.; Sen, P.; Grant, C.W.; Zenka, R.; Sappani, M.; Lakshmanan, J.; Athreya, A.P.; Kandasamy, R.K.; Pandey, A.; Byeon, S.K. An Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals a Multi-Analyte Signature of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma in Serum. J. Gastroenterol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Huang, H.; Zou, M.; Luo, H.; Liu, T.; Zhu, S.; Ye, B. Identification of Circulating Metabolites Linked to the Risk of Breast Cancer: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1442723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohe, V.K.; Degwekar, S.S.; Bhowate, R.R.; Kadu, R.P.; Dangore, S.B. Evaluation of Correlation of Serum Lipid Profile in Patients with Oral Cancer and Precancer and Its Association with Tobacco Abuse. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2010, 39, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganavi, B.S.; Patil, S.; Rao, R.S. Evaluation of Serum Lipids and Lipoproteins as Prognosticators in Leukoplakia. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2015, 15, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukumaran, D.; Kumar Vadivel, J.; Thirupambaram Nataraja, U.; Jayaraman, S. Comparative Assessment of Lipid Peroxidase in Oral Cancer and Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders. Cureus 2024, 16, e66474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecka, J.; Trouillas, P.; Gašparović, A.Č.; Gazzano, E.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Riganti, C. Phospholipids and Cholesterol: Inducers of Cancer Multidrug Resistance and Therapeutic Targets. Drug Resist. Updates 2020, 49, 100670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadfield, L.A.; Pane, A.A.; Talebi, A.; Swinnen, J.V.; Fendt, S.M. Lipid Metabolism in Cancer: New Perspectives and Emerging Mechanisms. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1363–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Liu, R.; Meng, Y.; Xing, D.; Xu, D.; Lu, Z. Lipid Metabolism and Cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20201606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Geng, F.; Cheng, X.; Guo, D. Lipid Metabolism Reprogramming and Its Potential Targets in Cancer. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimenta-Barros, L.A.; Ramos-García, P.; González-Moles, M.Á.; Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: Systematic review and comprehensive meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2025, 31, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamleh, M.A.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Spagou, K.; Masson, P.; Want, E.J. Optimizing the Use of Quality Control Samples for Signal Drift Correction in Large-Scale Urine Metabolic Profiling Studies. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2670–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Comprehensive and Integrative Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| #ID | Sex | Age | Ethnicity | Anatomic Location | Evolution (Months) | OED Grade | Malignant Transformation (Months) | Recurrence (Months) | Follow-Up (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | F | 43 | NW | Soft palate and oropharynx | 24 | Severe | 36 | No | NI |
| T2 | M | 72 | W | Floor of the mouth | 12 | Moderate | 24 | Yes (2 and 7) | NI |
| T3 | M | 73 | NW | Tongue (posterior border) | NI | Moderate | NI | Yes (9) | 12 |
| T4 | F | NI | NI | Tongue (posterior border) | NI | Moderate | NI | NI | NI |
| T5 | F | 31 | NW | Tongue (posterior border) | 2 | Moderate | NI | Yes (3, 4, 7, 32) | 72 |
| C1 | M | 54 | W | Hard palate | 60 | Moderate | - | Yes (2 and 2) | 48 |
| C2 | F | 76 | NI | Buccal mucosa | NI | Severe | - | NI | NI |
| C3 | M | 40 | W | Tongue (posterior border) | 2 | Severe | - | Yes (1) | 12 |
| C4 | M | 73 | W | Tongue (posterior border and belly) | NI | Mild | - | NI | NI |
| C5 | M | 53 | W | Worda antero-posterior de língua | NI | Mild | - | No | 24 |
| C6 | M | 38 | W | Tongue (belly) | 1 | Mild | - | NI | NI |
| C7 | M | 69 | W | Buccal mucosa | 36 | Moderate | - | No | 72 |
| C8 | F | 87 | W | Fornix | 8 | Moderate | - | NI | 108 |
| C9 | F | 34 | NW | Buccal mucosa | 5 | Mild | - | Yes (72) | 144 * |
| C10 | M | 49 | W | Tongue (posterior border) | 3 | Moderate | - | No | 60 * |
| C11 | M | 69 | NW | Buccal mucosa | NI | Mild | - | No | 36 |
| C12 | M | 59 | W | Tongue (posterior border and belly) | 1 | Mild | - | No | 24 |
| C13 | F | 39 | NW | Fornix | 36 | Moderate | - | Yes (6) | 84 |
| C14 | F | 40 | NW | Tongue (posterior border and belly) | NI | Severe | - | No | 48 |
| C15 | M | 68 | NW | Gingival mucosa | 60 | Absent | - | No | 72 |
| Molecular Feature | p. Value * | Fold Change | SAM (p. Value) | SAM (q. Value) | MUVR (PLS p. Value) | MUVR (RF p. Value) | AUC | Ionization Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M669T1120 | 0.004 | 3.2 | 0.000 | 0.1 | 0.08 | 0.03 * | 0.96 | Positive |
| M275T1120 | 0.003 | 2.8 | 0.002 | 0.4 | 0.08 | 0.03 * | 0.96 | Positive |
| M736T989 | 0.005 | 0.6 | 0.002 | 0.4 | 0.08 | 0.03 * | 0.95 | Positive |
| M376T671 | 0.007 | 0.8 | 0.003 | 0.4 | 0.08 | - | 0.75 | Positive |
| M324T445 | 0.007 | −0.4 | 0.004 | 0.4 | 0.08 | - | 0.85 | Positive |
| M380T645 | 0.006 | 0.7 | 0.005 | 0.4 | 0.08 | - | 0.6 | Positive |
| M476T636 | 0.014 | −3.5 | 0.005 | 0.2 | 0.003 * | 0.002 * | 0.68 | Negative |
| M325T444 | 0.005 | 0.0 | 0.007 | 0.5 | 0.08 | - | 0.72 | Positive |
| M308T477 | 0.003 | −2.6 | 0.007 | 0.5 | 0.08 | - | 0.68 | Positive |
| M478T701 | 0.013 | −3.8 | 0.007 | 0.5 | 0.03 * | 0.002 * | 0.68 | Negative |
| M310T389 | 0.009 | 0.7 | 0.012 | 0.5 | 0.08 | - | 0.72 | Positive |
| M420T775 | 0.019 | 0.4 | 0.013 | 0.5 | 0.08 | 0.03 * | 0.69 | Positive |
| M280T548 | 0.005 | −0.9 | 0.013 | 0.5 | 0.08 | - | 0.64 | Positive |
| M309T496 | 0.013 | 1.0 | 0.016 | 0.5 | 0.08 | - | 0.72 | Positive |
| M502T704 | 0.019 | 0.3 | 0.016 | 0.5 | 0.08 | - | 0.67 | Positive |
| M480T704 | 0.021 | −3.7 | 0.016 | 0.5 | 0.08 | - | 0.61 | Positive |
| M479T701 | 0.015 | −2.3 | 0.025 | 0.5 | 0.03 * | 0.002 * | 0.63 | Negative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins-Chaves, R.R.; Bastos, V.C.; Vitório, J.G.; Duarte-Andrade, F.F.; Pereira, T.d.S.F.; Leite-Lima, F.; Gomes, T.E.C.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; Moreira, V.R.; França, M.S.; et al. Malignant Transformed and Non-Transformed Oral Leukoplakias Are Metabolically Different. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051802
Martins-Chaves RR, Bastos VC, Vitório JG, Duarte-Andrade FF, Pereira TdSF, Leite-Lima F, Gomes TEC, Lebron YAR, Moreira VR, França MS, et al. Malignant Transformed and Non-Transformed Oral Leukoplakias Are Metabolically Different. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051802
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins-Chaves, Roberta Rayra, Victor Coutinho Bastos, Jéssica Gardone Vitório, Filipe Fideles Duarte-Andrade, Thaís dos Santos Fontes Pereira, Flávia Leite-Lima, Thaís Ellen Chaves Gomes, Yuri Abner Rocha Lebron, Victor Rezende Moreira, Monique Sedlmaier França, and et al. 2025. "Malignant Transformed and Non-Transformed Oral Leukoplakias Are Metabolically Different" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051802
APA StyleMartins-Chaves, R. R., Bastos, V. C., Vitório, J. G., Duarte-Andrade, F. F., Pereira, T. d. S. F., Leite-Lima, F., Gomes, T. E. C., Lebron, Y. A. R., Moreira, V. R., França, M. S., Santos, L. V. d. S., Lange, L. C., Macedo, A. N. d., Picossi, C. R. C., Pontes, H. A. R., Diniz, M. G., Gomes, C. C., Castro, W. H. d., Canuto, G. A. B., & Gomez, R. S. (2025). Malignant Transformed and Non-Transformed Oral Leukoplakias Are Metabolically Different. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051802








