Integrative Analysis of miR-21, PTEN, and Immune Signatures in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
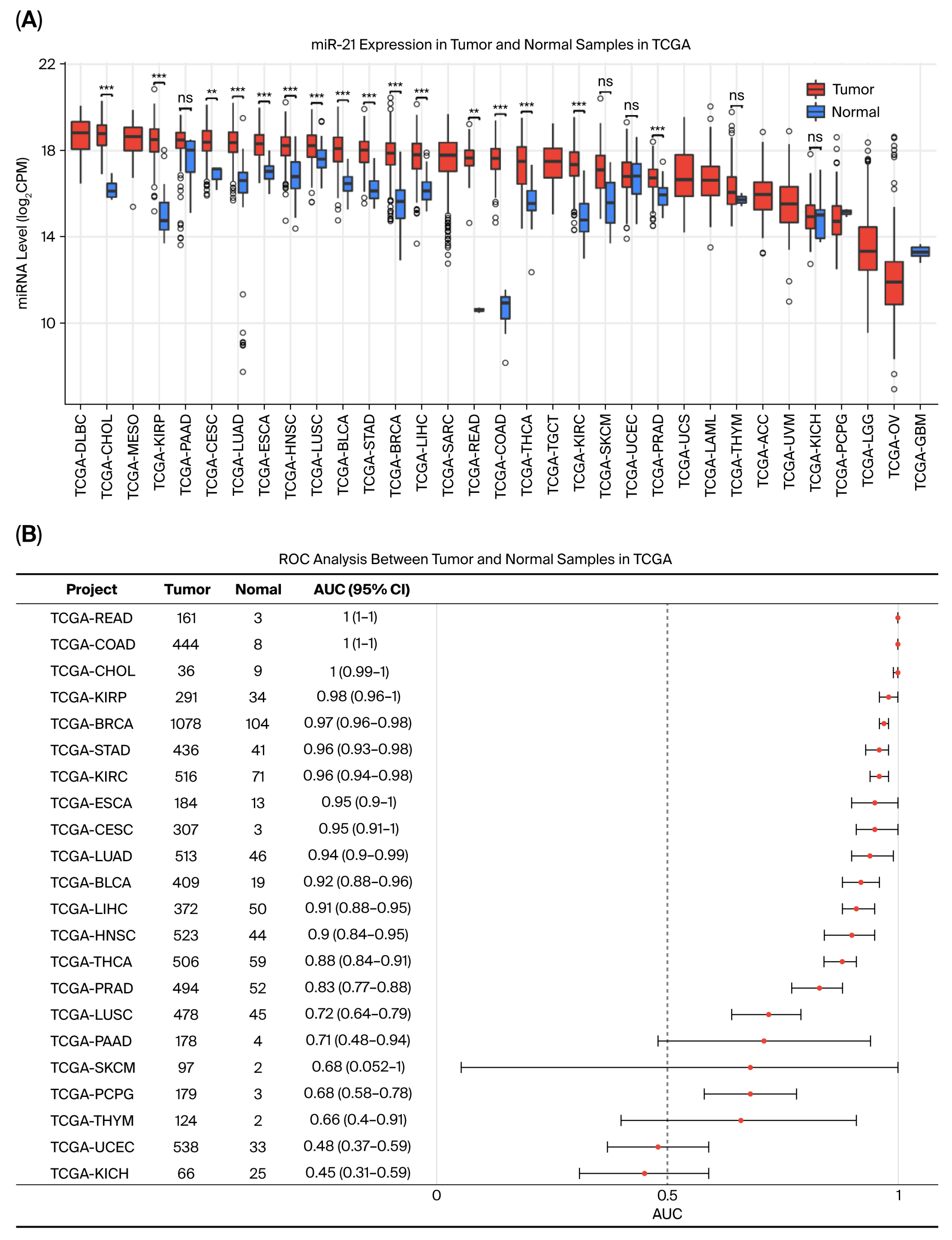
2.1. miR-21-5p Is Highly Expressed in Colorectal Cancer and Exhibits Strong Diagnostic Performance
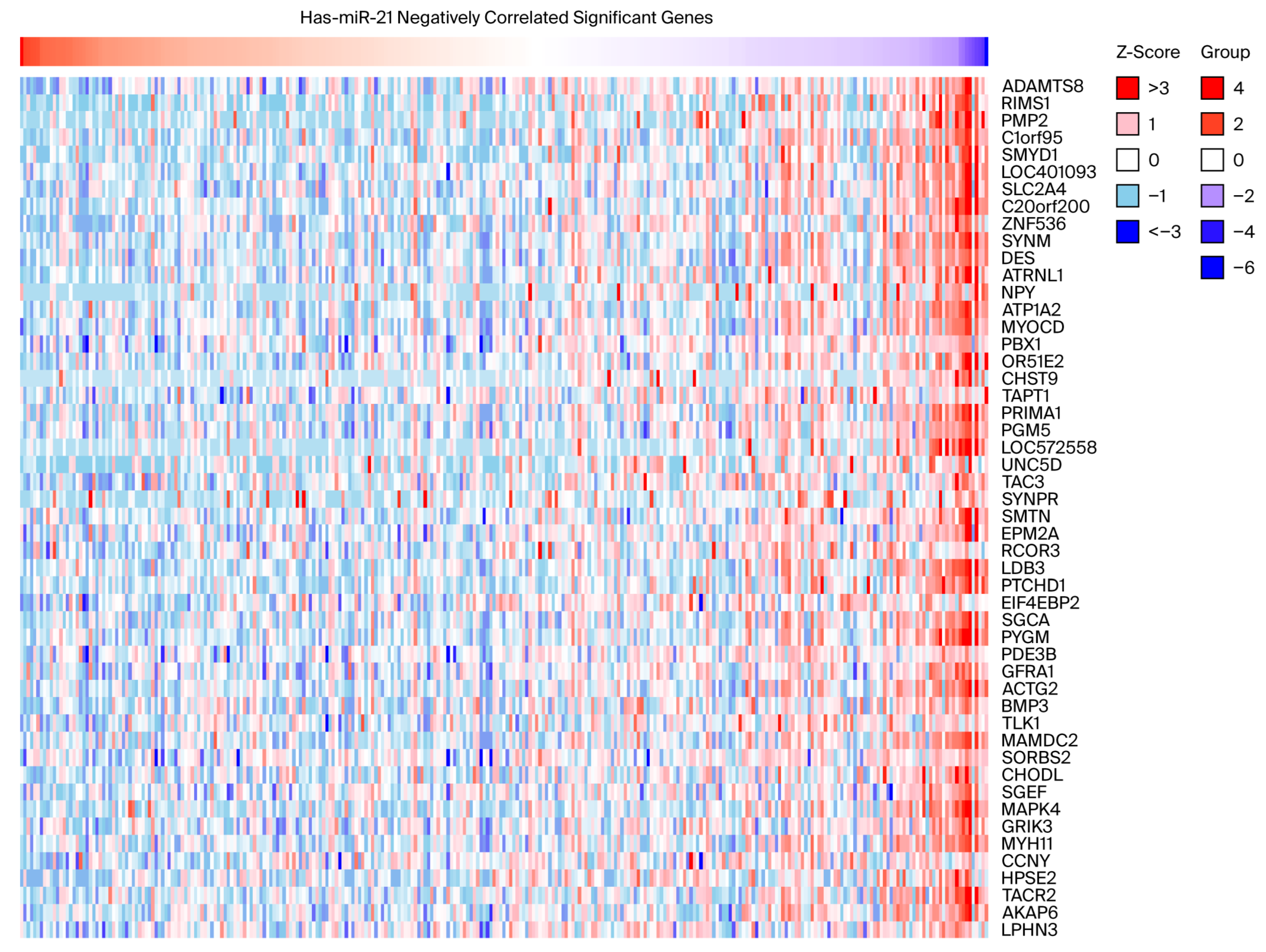
2.2. miR-21-5p Is Inversely Associated with Tumor Suppressor Gene Expression and Immune-Related Pathways
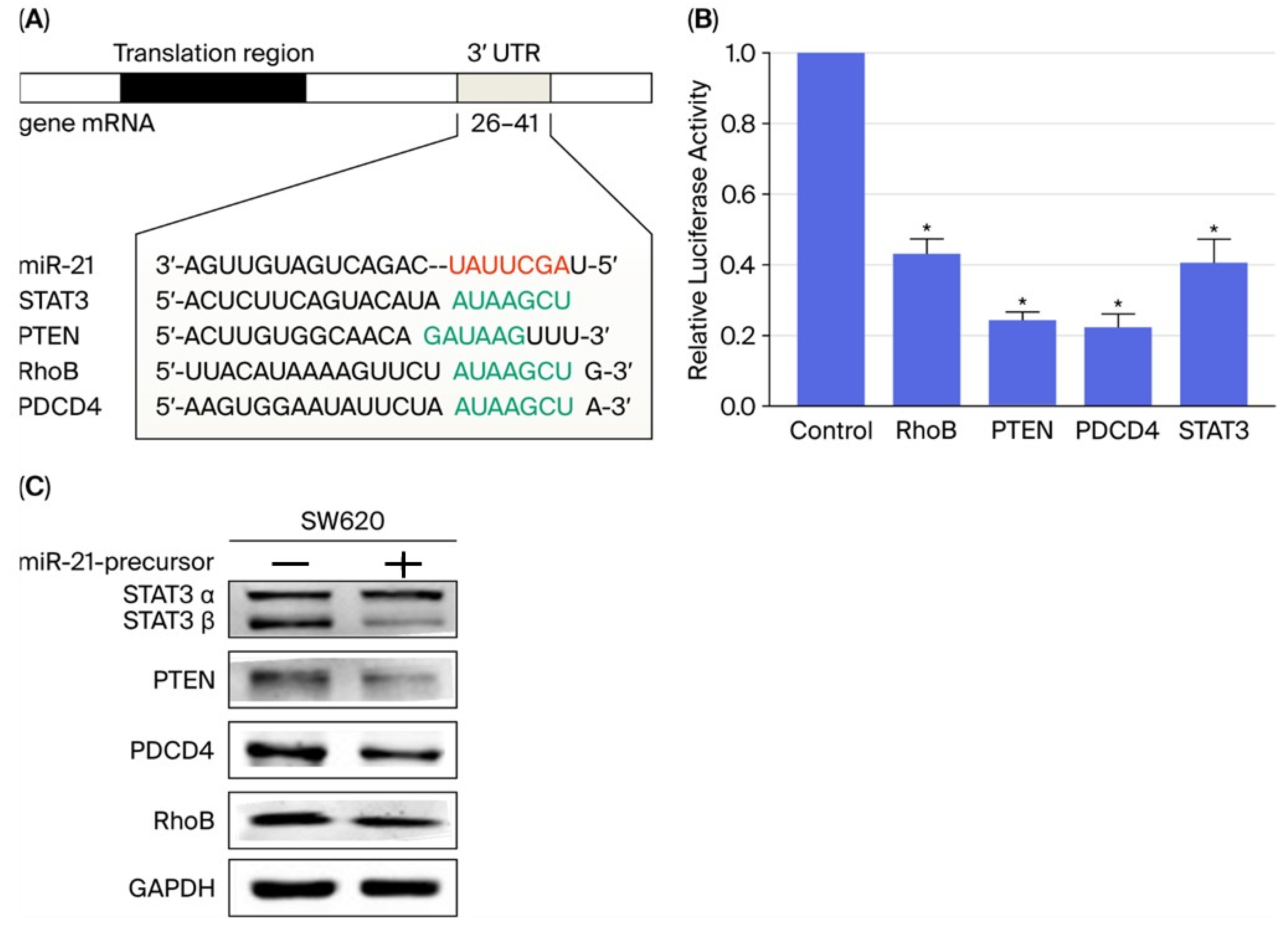
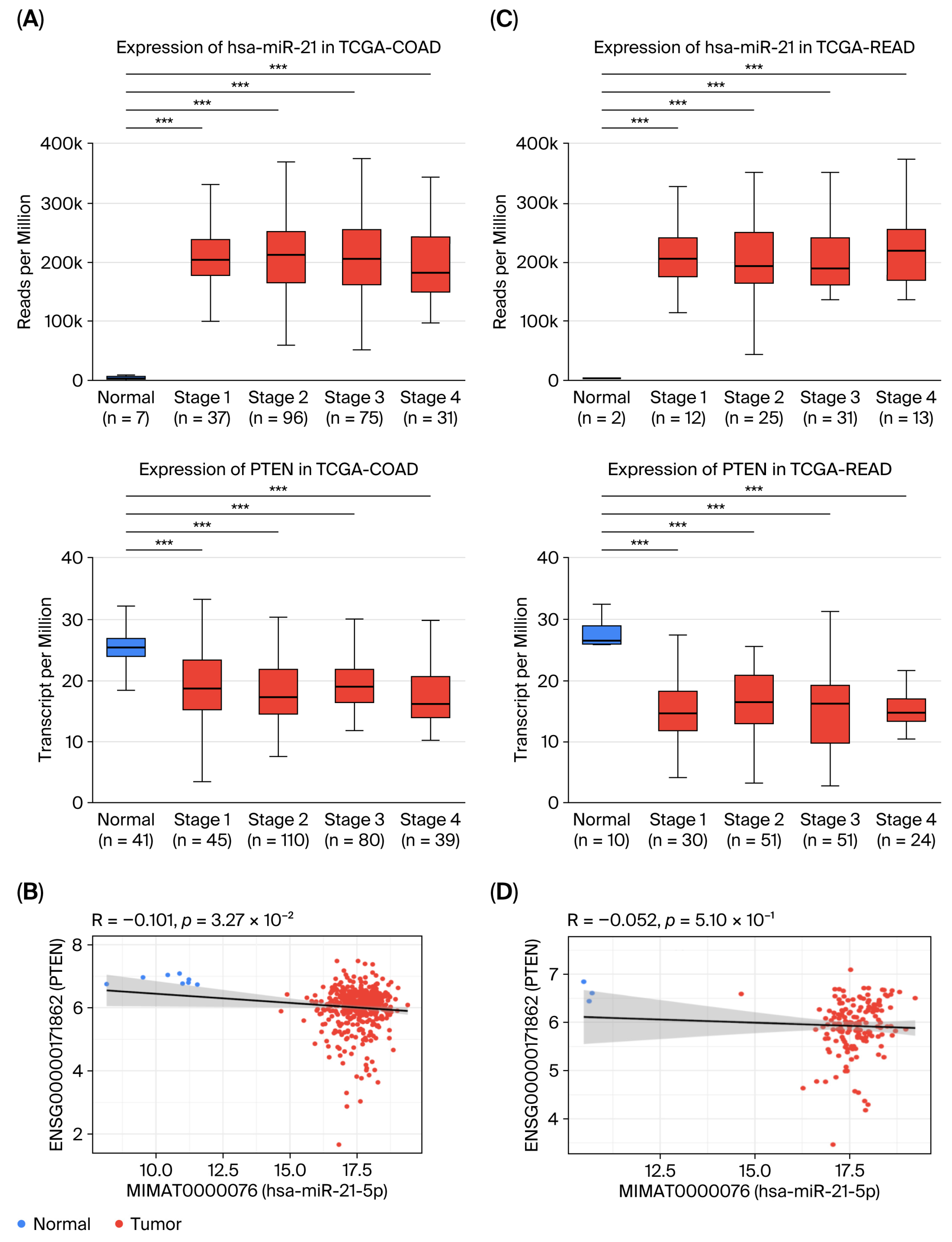
2.3. PTEN Is a Direct Target of miR-21-5p and Is Downregulated in CRC
2.4. High miR-21-5p and Low PTEN Expression Are Associated with Impaired Immune Activation and Unfavorable Prognosis
2.5. PTEN Expression Positively Correlates with Immune Cell Infiltration
2.6. Proposed Model of miR-21-5p-Mediated Immune Evasion in CRC
3. Discussion
3.1. Tumor-Intrinsic Immune Suppression Mediated by miR-21-5p in Colorectal Cancer
3.2. Exosomal miR-21-5p and Systemic Immune Modulation
3.3. Therapeutic Implications for CRC
3.4. Future Perspectives and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection and Bioinformatics Analysis
- Public data acquisition
4.2. miRNA and mRNA Expression Analysis
4.3. LinkedOmics Analysis
4.4. UALCAN Expression and Prognostic Analysis
4.5. Immune Infiltration Analysis
4.6. Survival Analysis
4.7. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.8. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.9. Western Blot
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brenner, H.; Kloor, M.; Pox, C.P. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2014, 383, 1490–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, E.; Arnold, M.; Gini, A.; Lorenzoni, V.; Cabasag, C.J.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Murphy, N.; Bray, F. Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut 2023, 72, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.L. Current Microsatellite Instability Testing in Management of Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Color. Cancer 2021, 20, e12–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabeti Touchaei, A.; Vahidi, S. Unraveling the interplay of CD8 + T cells and microRNA signaling in cancer: Implications for immune dysfunction and therapeutic approaches. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahadi, A. The significance of microRNA deregulation in colorectal cancer development and the clinical uses as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker and therapeutic agent. Noncoding RNA Res. 2020, 5, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, M.I.; Taylor, K.; Pringle, J.H.; Jameson, J.S. MicroRNAs are novel biomarkers of colorectal cancer. Br J. Surg. 2009, 96, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriely, G.; Wurdinger, T.; Kesari, S.; Esau, C.C.; Burchard, J.; Linsley, P.S.; Krichevsky, A.M. MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 5369–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Lang, M.; Wehbe, H.; Maheshwari, S.; Mendell, J.T.; Jiang, J.; Schmittgen, T.D.; Patel, T. Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 2113–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawra, H.S.; Agarwal, M.; Mishra, A.; Chandel, S.S.; Singh, R.P.; Dubey, G.; Kukreti, N.; Singh, M. MicroRNA-21′s role in PTEN suppression and PI3K/AKT activation: Implications for cancer biology. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 254, 155091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carissimi, C.; Carucci, N.; Colombo, T.; Piconese, S.; Azzalin, G.; Cipolletta, E.; Citarella, F.; Barnaba, V.; Macino, G.; Fulci, V. miR-21 is a negative modulator of T-cell activation. Biochimie 2014, 107, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Yang, Q. MiR-21 modulates the polarization of macrophages and increases the effects of M2 macrophages on promoting the chemoresistance of ovarian cancer. Life Sci. 2020, 242, 117162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.H.; Choi, J.; Jang, H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.W.; Ryu, Y.; Choi, J.; Choi, Y.; Chi, S.G.; Kwon, I.C.; et al. Targeted delivery of anti-miRNA21 sensitizes PD-L1(high) tumor to immunotherapy by promoting immunogenic cell death. Theranostics 2024, 14, 3777–3792. [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa, T.; Baba, Y.; Yamauchi, M.; Kuchiba, A.; Nosho, K.; Shima, K.; Tanaka, N.; Huttenhower, C.; Frank, D.A.; Fuchs, C.S.; et al. STAT3 expression, molecular features, inflammation patterns, and prognosis in a database of 724 colorectal cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nail, H.M.; Chiu, C.C.; Leung, C.H.; Ahmed, M.M.M.; Wang, H.D. Exosomal miRNA-mediated intercellular communications and immunomodulatory effects in tumor microenvironments. J. Biomed Sci. 2023, 30, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Shi, C.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Zou, Z.; Ran, X.; Su, Y. TGF-beta-induced miR-21 negatively regulates the antiproliferative activity but has no effect on EMT of TGF-beta in HaCaT cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 44, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, S.; Aazzane, O.; Guendaoui, S.; Tawfiq, N.; Sahraoui, S.; Guessous, F.; Karkouri, M. A miRNA Signature for Non-Invasive Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis in Morocco: miR-21, miR-29a and miR-92a. Noncoding RNA 2025, 11, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X. Expressions of miR-21 and miR-210 in Breast Cancer and Their Predictive Values for Prognosis. Iran. J. Public Health 2020, 49, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Diao, M.; Tan, S.; Huang, S.; Cheng, Y.; You, T. MicroRNA-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20211653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. A comprehensive review of miR-21 in liver disease: Big impact of little things. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 134, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.X.; Hartner, J.; Lim, E.J.; Fabry, V.; Mingler, M.K.; Cole, E.T.; Orkin, S.H.; Aronow, B.J.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA-21 limits in vivo immune response-mediated activation of the IL-12/IFN-gamma pathway, Th1 polarization, and the severity of delayed-type hypersensitivity. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 3362–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.W.; Zeng, H.S. Regulation of JAK/STAT signal pathway by miR-21 in the pathogenesis of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. World J. Pediatr. 2020, 16, 502–513, Correction in World J. Pediatr. 2021, 17, 676–679.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.H.; Yue, J.; Fan, M.; Pfeffer, L.M. IFN induces miR-21 through a signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-dependent pathway as a suppressive negative feedback on IFN-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8108–8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, B.; Yu, J.; Zhang, A.; Qin, L.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y. miR-21-5p inhibits inflammation injuries in LPS-treated H9c2 cells by regulating PDCD4. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 11450–11460. [Google Scholar]
- Asangani, I.A.; Rasheed, S.A.; Nikolova, D.A.; Leupold, J.H.; Colburn, N.H.; Post, S.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, D.; Rane, S.; Lypowy, J.; He, M.; Chen, I.Y.; Vashistha, H.; Yan, L.; Malhotra, A.; Vatner, D.; Abdellatif, M. MicroRNA-21 targets Sprouty2 and promotes cellular outgrowths. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 3272–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, K.; Han, B.; Bai, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L. MicroRNA-21 (Mir-21) Promotes Cell Growth and Invasion by Repressing Tumor Suppressor PTEN in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Pan, J.; Zheng, S.; Cai, D.; Luo, A.; Xia, Z.; Huang, J. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-21-5p Induces Macrophage M2 Polarization by Targeting RhoB. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.; Deng, Q.; Kumar, M.; Zhou, Z.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.; Young, K.H.; et al. miR-21 depletion in macrophages promotes tumoricidal polarization and enhances PD-1 immunotherapy. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3151–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Hu, B.; Jadhav, R.R.; Jin, J.; Zhang, H.; Cavanagh, M.M.; Akondy, R.S.; Ahmed, R.; Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Activation of miR-21-Regulated Pathways in Immune Aging Selects against Signatures Characteristic of Memory T Cells. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 2148–2162 e2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Xie, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Zou, Z.; Xiong, L. Exosomal miRNAs assist in the crosstalk between tumor cells and immune cells and its potential therapeutics. Life Sci. 2023, 329, 121934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedaeinia, R.; Sharifi, M.; Avan, A.; Kazemi, M.; Rafiee, L.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Salehi, R. Locked nucleic acid anti-miR-21 inhibits cell growth and invasive behaviors of a colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line: LNA-anti-miR as a novel approach. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurj, A.; Fontana, B.; Varani, G.; Calin, G.A. Small molecules targeting microRNAs: New opportunities and challenges in precision cancer therapy. Trends Cancer 2024, 10, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Jia, W.; Lu, L.; Han, R. MicroRNAs with Multiple Targets of Immune Checkpoints, as a Potential Sensitizer for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Breast Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2023, 15, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista-Sanchez, D.; Arriaga-Canon, C.; Pedroza-Torres, A.; De La Rosa-Velazquez, I.A.; Gonzalez-Barrios, R.; Contreras-Espinosa, L.; Montiel-Manriquez, R.; Castro-Hernandez, C.; Fragoso-Ontiveros, V.; Alvarez-Gomez, R.M.; et al. The Promising Role of miR-21 as a Cancer Biomarker and Its Importance in RNA-Based Therapeutics. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, Y.T.; Yang, J.C.; Chang, J.B.; Tsai, S.C. Down-Regulation of miR-194-5p for Predicting Metastasis in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Fan, J.; Wang, B.; Traugh, N.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER: A Web Server for Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e108–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.C.; Huang, S.F.; Chiang, J.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Huang, C.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Tsai, F.J.; Kao, M.C.; Yang, J.S. The differential regulation of microRNAs is associated with oral cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Description | Size | Leading Edge Number | ES | NES | p Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antigen processing and presentation | 68 | 40 | 0.74072 | 2.4975 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | 93 | 49 | 0.67393 | 2.4705 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 96 | 38 | 0.66632 | 2.4394 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Osteoclast differentiation | 126 | 47 | 0.63476 | 2.4287 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Phagosome | 144 | 51 | 0.6074 | 2.3955 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 157 | 61 | 0.60571 | 2.3663 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | 55 | 26 | 0.70094 | 2.2973 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity | 117 | 52 | 0.61234 | 2.2788 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Proteasome | 44 | 33 | 0.70113 | 2.2401 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction | 274 | 96 | 0.52239 | 2.1771 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Insulin secretion | 85 | 26 | −0.60735 | −1.9731 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| Circadian entrainment | 94 | 31 | −0.60202 | −1.9738 | <2.2 × 10−16 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| cAMP signaling pathway | 193 | 46 | −0.52073 | −1.8511 | <2.2 × 10−16 | 0.0024103 |
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | 160 | 59 | −0.51717 | −1.7921 | <2.2 × 10−16 | 0.0039441 |
| Description | Size | Leading Edge Number | ES | NES | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th17 cell differentiation | 105 | 55 | 0.61623 | 2.0455 | 0.005937 |
| Intestinal immune network for IgA production | 45 | 32 | 0.68539 | 2.0104 | 0.007037 |
| Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 90 | 47 | 0.61978 | 1.984 | 0.007751 |
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | 152 | 58 | 0.56912 | 1.9477 | 0.010027 |
| Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction | 275 | 114 | 0.53498 | 1.9211 | 0.010005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yen, Y.-T.; Hsu, C.-I.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tsai, S.-C. Integrative Analysis of miR-21, PTEN, and Immune Signatures in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412118
Yen Y-T, Hsu C-I, Chen Y-C, Tsai S-C. Integrative Analysis of miR-21, PTEN, and Immune Signatures in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(24):12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412118
Chicago/Turabian StyleYen, Yu-Ting, Chen-I Hsu, Yee-Chun Chen, and Shih-Chang Tsai. 2025. "Integrative Analysis of miR-21, PTEN, and Immune Signatures in Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 24: 12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412118
APA StyleYen, Y.-T., Hsu, C.-I., Chen, Y.-C., & Tsai, S.-C. (2025). Integrative Analysis of miR-21, PTEN, and Immune Signatures in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(24), 12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412118







