Cortical White and Grey Matter Volume Differences Associated with Plasma Cytokine and Chemokine Levels in PLWH in Cape Town
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics
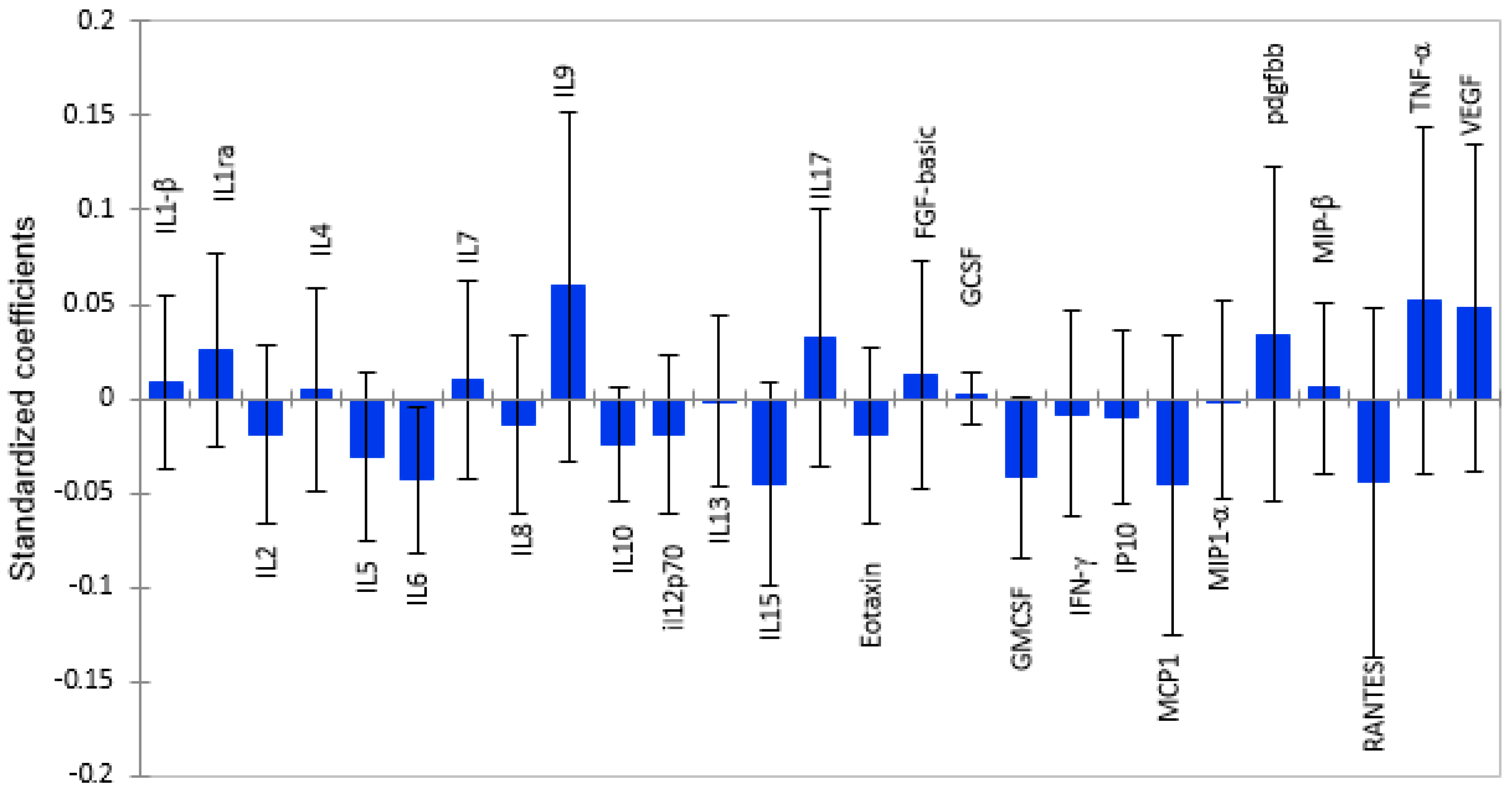
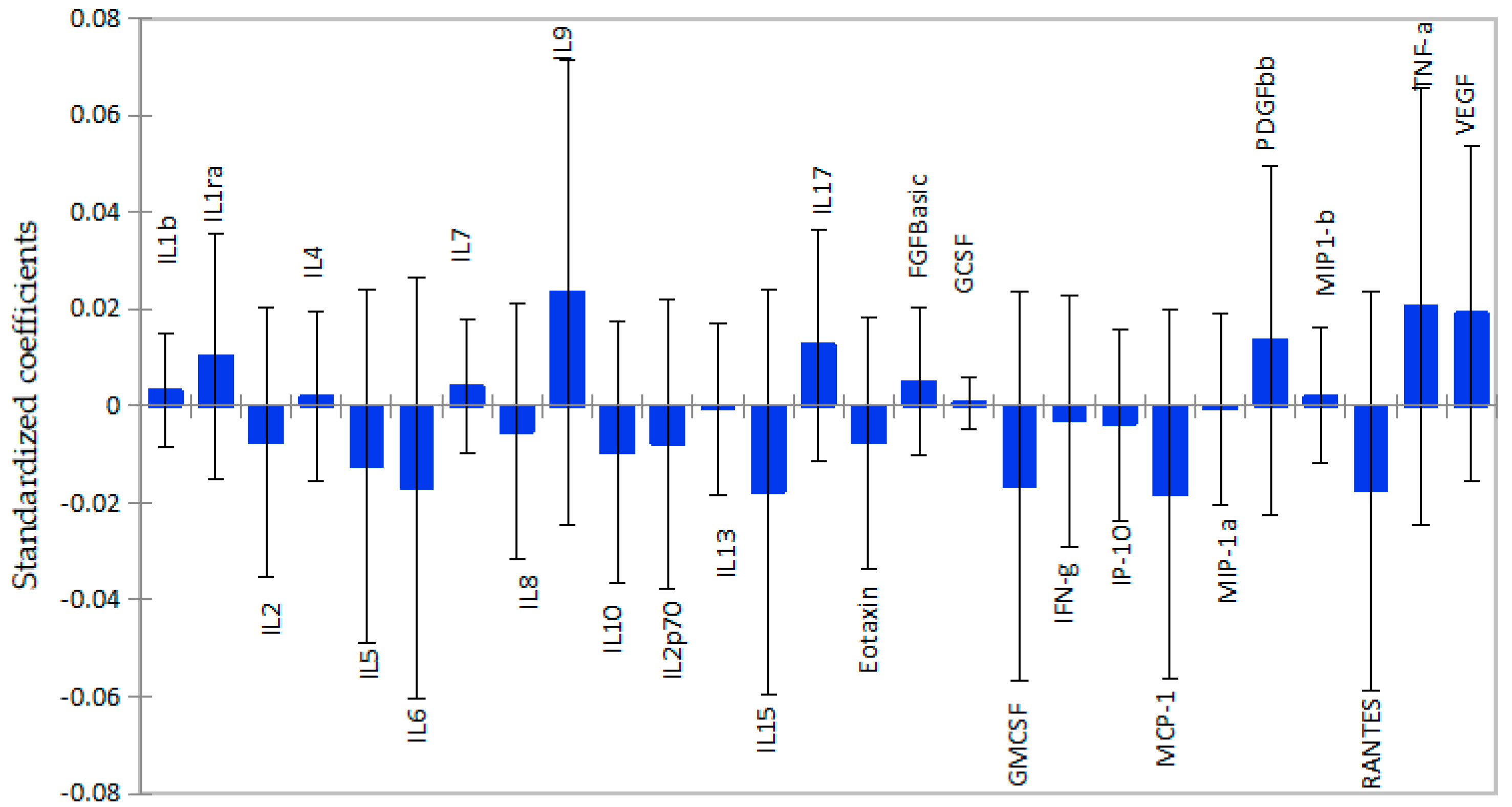
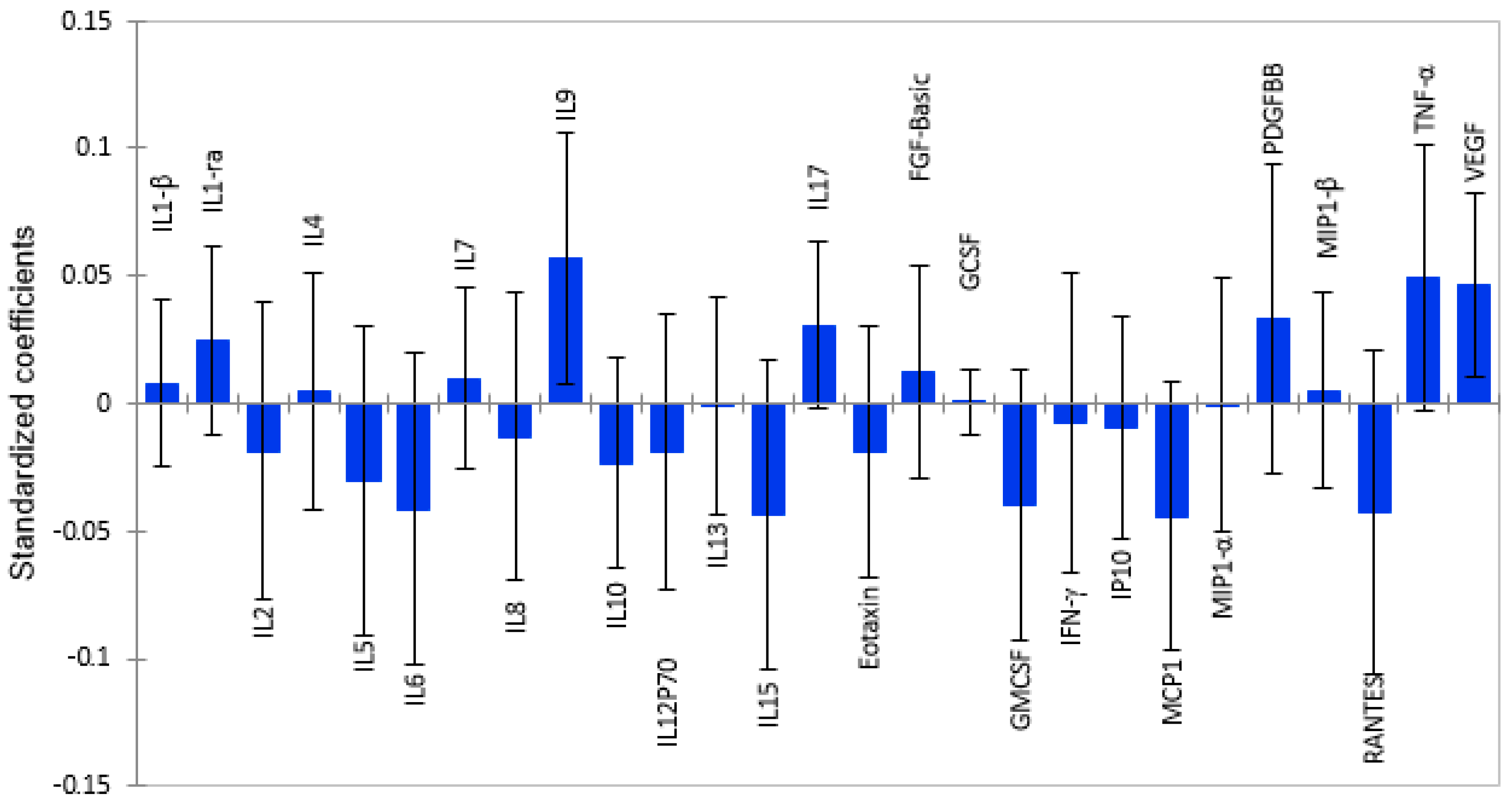
2.2. White Matter Volume as a Function of Plasma Cytokine Levels
2.3. Subcortical Grey Matter Volume as a Function of Cytokine Levels
2.4. Total Grey Matter Volume as a Function of Plasma Cytokines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Participants
4.2. Plasma Cytokine Quantification by Multiplex Assay
4.3. Structural Neuroimaging and Volumetric Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simioni, S.; Cavassini, M.; Annoni, J.M.; Abraham, R.A.; Bourquin, I.; Schiffer, V.; Calmy, A.; Chave, J.P.; Giacobini, E.; Hirschel, B.; et al. Cognitive dysfunction in HIV patients despite long-standing suppression of viremia. AIDS 2010, 24, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, V.R.; Ruiz, A.P.; Prasad, V.R. Viral and cellular factors underlying neuropathogenesis in HIV associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). AIDS Res. Ther. 2014, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Banks, W.A. Role of immune system in neuroinflammation and neurocognitive implications. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everall, I.; Vaida, F.; Khanlou, N.; Lazzaretto, D.; Achim, C.; Letendre, S.; Moore, D.; Ellis, R.; Cherner, M.; Gelman, B.; et al. Cliniconeuropathologic correlates of human immunodeficiency virus in the era of antiretroviral therapy. J. Neurovirol. 2009, 15, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohgu, S.; A Banks, W. Brain pericytes increase the lipopolysaccharide-enhanced transcytosis of HIV-1 free virus across the in vitro blood-brain barrier: Evidence for cytokine-mediated pericyte-endothelial cell cross talk. Fluids Barriers CNS 2013, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Stone, K.P.; Hsuchou, H.; Manda, V.K.; Zhang, Y.; Kastin, A.J. Cytokine signaling modulates blood-brain barrier function. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 3729–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A.; Plotkin, S.R.; Kastin, A.J. Permeability of the blood-brain barrier to soluble cytokine receptors. Neuroimmunomodulation 1995, 2, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A. Blood-brain barrier transport of cytokines: A mechanism for neuropathology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Sinclair, E.; Peterson, J.; Lee, E.; Kyriakides, T.C.; Li, F.Y.; Hagberg, L.; Fuchs, D.; Price, R.W.; Gisslen, M.; et al. Progressive increase in central nervous system immune activation in untreated primary HIV-1 infection. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampa, J.; Westman, M.; Kadetoff, D.; Agréus, A.N.; Le Maître, E.; Gillis-Haegerstrand, C.; Andersson, M.; Khademi, M.; Corr, M.; Christianson, C.A.; et al. Peripheral inflammatory disease associated with centrally activated IL-1 system in humans and mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12728–12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, M.C.; Ances, B.M. Role of neuroimaging in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Semin. Neurol. 2014, 34, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakkas, A.; Ellis, R.J.; Watson, C.W.; Umlauf, A.; Heaton, R.K.; Letendre, S.; Collier, A.; Marra, C.; Clifford, D.B.; Gelman, B.; et al. White matter damage, neuroinflammation, and neuronal integrity in HAND. J. Neurovirol. 2019, 25, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, J.; Hana, G.; Russell, T.; Price, J.; McCaffrey, D.; Harezlak, J.; Sem, E.; Anyanwu, J.C.; Guttmann, C.R.; Navia, B.; et al. Reliability and validity of MRI-based automated volumetry software relative to auto-assisted manual measurement of subcortical structures in HIV-infected patients from a multisite study. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jernigan, T.L.; Archibald, S.L.; Fennema-Notestine, C.; Taylor, M.J.; Theilmann, R.J.; Julaton, M.D.; Notestine, R.J.; Wolfson, T.; Letendre, S.L.; Ellis, R.J.; et al. Clinical factors related to brain structure in HIV: The CHARTER study. J. Neurovirol. 2011, 17, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennema-Notestine, C.; Ellis, R.J.; Archibald, S.L.; Jernigan, T.L.; Letendre, S.L.; Notestine, R.J.; Taylor, M.J.; Theilmann, R.J.; Julaton, M.D.; Croteau, D.J.; et al. Increases in brain white matter abnormalities and subcortical gray matter are linked to CD4 recovery in HIV infection. J. Neurovirology 2013, 19, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fjell, A.M.; Walhovd, K.B.; Fennema-Notestine, C.; McEvoy, L.K.; Hagler, D.J.; Holland, D.; Brewer, J.B.; Dale, A.M. One-year brain atrophy evident in healthy aging. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 15223–15231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ances, B.M.; Hammoud, D.A. Neuroimaging of HIV associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2014, 9, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcour, V.; van Griensven, F.; de Souza, M.; Kim, J.; Ananworanich, J.; RV254/SEARCH 010 Study Group. Central nervous system viral invasion and inflammation during acute HIV infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.M.; Jahanshad, N. Novel Neuroimaging Methods to Understand How HIV Affects the Brain. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015, 12, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.M.; Dutton, R.A.; Hayashi, K.M.; Toga, A.W.; Lopez, O.L.; Aizenstein, H.J.; Becker, J.T. Thinning of the cerebral cortex visualized in HIV/AIDS reflects CD4+ T lymphocyte decline. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15647–15652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ances, B.M.; Ortega, M.; Vaida, F.; Heaps, J.; Paul, R. Independent effects of HIV, aging, and HAART on brain volumetric measures. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2012, 59, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zoest, R.A.; Underwood, J.; De Francesco, D.; Sabin, C.A.; Cole, J.H.; Wit, F.W.; Caan, M.W.A.; Kootstra, N.A.; Fuchs, D.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Structural Brain Abnormalities in Successfully Treated HIV Infection: Associations with Disease and Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 217, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongvatana, A.; Correia, S.; Dunsiger, S.; Gauthier, L.; Devlin, K.N.; Ross, S.; Navia, B.; Tashima, K.T.; DeLaMonte, S.; Cohen, R.A. Plasma cytokine levels are related to brain volumes in HIV-infected individuals. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Catts, V.S.; Sheedy, D.; McCrossin, T.; Kril, J.J.; Weickert, C.S. Cortical grey matter volume reduction in people with schizophrenia is associated with neuro-inflammation. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarrey, A.C.; Pacheco, J.; Carlson, O.D.; Egan, J.M.; Thambisetty, M.; An, Y.; Ferrucci, L.; Resnick, S.M. Interleukin-6 is linked to longitudinal rates of cortical thinning in aging. Transl. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spudich, S.; González-Scarano, F. HIV-1-related central nervous system disease: Current issues in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a007120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Chong, L.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Hou, C.; Li, R. Correlation between serum RANTES levels and the severity of Parkinson’s disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 208408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhai, Q.; Luo, Y.; Dorf, M.E. RANTES-mediated chemokine transcription in astrocytes involves activation and translocation of p90 ribosomal S6 protein kinase (RSK). J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 19042–19048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Conant, K.; Garzino-Demo, A.; Nath, A.; McArthur, J.C.; Halliday, W.; Power, C.; Gallo, R.C.; Major, E.O. Induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in HIV-1 Tat-stimulated astrocytes and elevation in AIDS dementia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3117–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, N.K.; Williams, R.; Callen, S.; Zien, C.; Narayan, O.; Buch, S. Roles of MCP-1 in development of HIV-dementia. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 3913–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatovic, S.M.; Shakui, P.; Keep, R.F.; Moore, B.B.; Kunkel, S.L.; Van Rooijen, N.; Andjelkovic, A.V. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2005, 25, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Ernst, T.; St Hillaire, C.; Conant, K. Antiretroviral treatment alters relationship between MCP-1 and neurometabolites in HIV patients. Antivir. Ther. 2004, 9, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Liao, Y.C.; Wang, Y.F.; Lin, I.F.; Wang, S.J.; Fuh, J.L. Plasma MCP-1 and cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: A two-year tollow-up study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menza, M.; Dobkin, R.D.; Marin, H.; Mark, M.H.; Gara, M.; Bienfait, K.; Dicke, A.; Kusnekov, A. The role of inflammatory cytokines in cognition and other non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Psychosomatics 2010, 51, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, L.; Williams, K.C.; Uhlmann, A.A.; Temmingh, H.; Burger, A.; Stein, D.J.; Naudé, P.J.W. Subcortical volumes, frontal cortical thickness, and pro-inflammatory cytokines in schizophrenia versus methamphetamine-induced psychosis. Brain Imaging Behav. 2025, 19, 874–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Vorburger, R.; Scarmeas, N.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Manly, J.J.; Schupf, N.; Mayeux, R.; Brickman, A.M. Circulating inflammatory biomarkers in relation to brain structural measurements in a non-demented elderly population. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 65, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArthur, J.C.; Johnson, T.P. Chronic inflammation mediates brain injury in HIV infection: Relevance for cure strategies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2020, 33, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, A.; Mackie, P.M.; Phan, L.T.; Tansey, M.G.; Khoshbouei, H. The complex role of inflammation and gliotransmitters in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 176, 105940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Gutierrez, J.; Meier, I.B.; Guzman, V.A.; Manly, J.J.; Schupf, N.; Brickman, A.M.; Mayeux, R. Circulating inflammatory biomarkers are related to cerebrovascular disease in older adults. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 6, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbert, L.C.; Lahna, D.; Promjunyakul, N.; Boespflug, E.; Ohya, Y.; Higashiuesato, Y.; Nishihira, J.; Katsumata, Y.; Tokashiki, T.; Dodge, H.H. Risk Factors Associated with Cortical Thickness and White Matter Hyperintensities in Dementia Free Okinawan Elderly. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 63, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Zuleta, W.G.; Sanchez, E. IL-9: Function, Sources, and Detection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1585, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.L.; Mao, X.O.; Greenberg, D.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor: Direct neuroprotective effect in in vitro ischemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10242–10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporer, B.I.; Koedel, U.; Paul, R.; Eberle, J.; Arendt, G.; Pfister, H.W. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is increased in serum, but not in cerebrospinal fluid in HIV associated CNS diseases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matsuzaki, H.; Tamatani, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Namikawa, K.; Kiyama, H.; Vitek, M.P.; Mitsuda, N.; Tohyama, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor rescues hippocampal neurons from glutamate-induced toxicity: Signal transduction cascades. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 1218–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Hu, G.; Cai, Y.; Liao, K.; Buch, S. Mechanisms of platelet-derived growth factor-BB in restoring HIV Tat-cocaine-mediated impairment of neuronal differentiation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 6377–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertoff, M.; Di Paolo, N.; Schoeneberg, A.; Depino, A.; Ferrari, C.; Wurst, W.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Eisel, U.; Pitossi, F. Neuroprotective and neurodegenerative effects of the chronic expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic circuit of adult mice. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 227, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Christakos, S.; Mattson, M.P. Tumor necrosis factors protect neurons against metabolic-excitotoxicity insults and promote maintenance of calcium homeostasis. Neuron 1994, 12, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, L.; Klein, M.; Schlett, K.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Eisel, U.L. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) -mediated neuroprotection against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity is enhanced by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation. Essential role of a TNF receptor 2-mediated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent NF-kappa B pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 32869–32881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, G.; Marcuzzi, A.; Zanin, V.; Monasta, L.; Zauli, G. Cytokine Levels in the Serum of Healthy Subjects. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 434010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhanya, V.; Jacobs, G.B.; Paul, R.H.; Joska, J.A.; Seedat, S.; Nyandoro, G.; Engelbrecht, S.; Glashoff, R.H. Plasma Cytokine Biomarker Cutoff Values for HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Impairment in Adults. Viral Immunol. 2021, 34, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, S.; Cohen, R.; Gongvatana, A.; Ross, S.; Olchowski, J.; Devlin, K.; Tashima, K.; Navia, B.; Delamonte, S. Relationship of plasma cytokines and clinical biomarkers to memory performance in HIV. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 265, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M.; Hapel, A.J. Concordant and Discordant Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Cytokine and Chemokine Responses in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Early-Stage Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhanya, V.; Jacobs, G.B.; Naidoo, S.; Paul, R.H.; Joska, J.; Seedat, S.; Nyandoro, G.; Engelbrecht, S.; Glashoff, R.H. Plasma Cytokine Levels As Predictors of Global and Domain-Specific Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Associated Neurocognitive Impairment in Treatment-Naive Individuals. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2021, 41, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhanya, V.; Jacobs, G.B.; Naidoo, S.; Paul, R.H.; Joska, J.; Seedat, S.; Nyandoro, G.; Engelbrecht, S.; Glashoff, R. Impact of plasma IP-10/CXCL10 and RANTES/CCL5 levels on neurocognitive function in HIV treatment naïve patients. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2021, 37, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, R.H.; Phillips, S.; Hoare, J.; Laidlaw, D.H.; Cabeen, R.; Olbricht, G.R.; Su, Y.; Stein, D.J.; Engelbrecht, S.; Seedat, S.; et al. Neuroimaging abnormalities in clade C HIV are independent of Tat genetic diversity. J. Neurovirol. 2017, 23, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaps-Woodruff, J.M.; Joska, J.; Cabeen, R.; Baker, L.M.; Salminen, L.E.; Hoare, J.; Laidlaw, D.H.; Wamser-Nanney, R.; Peng, C.Z.; Engelbrecht, S.; et al. White matter fiber bundle lengths are shorter in cART naive HIV: An analysis of quantitative diffusion tractography in South Africa. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017, 12, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gender | Frequency (Freq) (n) | Percent (%) | Cumulative (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 115 | 73.72 | 73.72 | |||
| Male | 41 | 26.28 | 100.00 | |||
| Total | 156 | 100.00 | ||||
| Diagnosis | ||||||
| Not impaired | 98 | 63.24 | 63.24 | |||
| Impaired | 58 | 36.76 | 100.00 | |||
| Total | 156 | 100.00 | ||||
| Treatment status | ||||||
| No | 112 | 82.96 | 82.96 | |||
| Yes | 23 | 17.04 | 100.00 | |||
| Total | 135 | 100.00 | ||||
| Variable | Freq (n) | Mean | Std. Dev. | Median | Lower quartile (p25) | Upper quartile (p75) |
| Age | 155 | 31.658 | 5.337 | 31.000 | 28 | 35 |
| Viral load | 107 | 124,750.27 | 292,383.8 | 21,515.000 | 3684 | 99,999 |
| CD4 absolute | 155 | 241.748 | 174.24 | 204.000 | 129 | 325 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) |
| (1) Proviral load | 1.000 | ||||||||
| (2) THS ratio | −0.096 | 1.000 | |||||||
| (0.264) | |||||||||
| (3) CD 45 Absolute | −0.046 | −0.140 | 1.000 | ||||||
| (0.593) | (0.103) | ||||||||
| (4) CD 348 absolute | −0.120 | 0.207 * | 0.437 * | 1.000 | |||||
| (0.163) | (0.016) | (0.000) | |||||||
| (5) plasma viral load | 0.364 * | −0.203 * | −0.137 | −0.145 | 1.000 | ||||
| (0.000) | (0.018) | (0.110) | (0.091) | ||||||
| (6) Subcortical grey matter | 0.092 | 0.012 | 0.050 | −0.045 | 0.105 | 1.000 | |||
| (0.392) | (0.913) | (0.606) | (0.642) | (0.330) | |||||
| (7) Cortical white matter | −0.030 | 0.222 * | −0.020 | 0.014 | −0.002 | 0.505 * | 1.000 | ||
| (0.784) | (0.038) | (0.836) | (0.886) | (0.985) | (0.000) | ||||
| (8) Total grey matter | 0.083 | 0.127 | 0.006 | −0.019 | 0.079 | 0.752 * | 0.704 * | 1.000 | |
| (0.443) | (0.238) | (0.947) | (0.846) | (0.466) | (0.000) | (0.000) | |||
| (9) Whole_dti_mdm~n | −0.013 | −0.254 * | −0.075 | −0.133 | 0.184 | −0.036 | −0.294 * | −0.153 | 1.000 |
| (0.909) | (0.021) | (0.459) | (0.189) | (0.096) | (0.720) | (0.003) | (0.129) |
| Cytokine | Coefficient | Std. Err. | z | p > |z| | 95% Conf. Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortical white matter volume | ||||||
| IL-1β | 0.0020477 | 0.0009955 | 2.06 | 0.040 | 0.0000966 | 0.0039988 |
| IL-1α | 4.44 × 10−6 | 1.67 × 10−6 | 2.66 | 0.008 | 1.17 × 10−6 | 7.70 × 10−6 |
| IL-7 | 0.0010158 | 0.000482 | 2.11 | 0.035 | 0.000071 | 0.0019606 |
| IL-9 | 1.42 × 10−6 | 6.33 × 10−7 | 2.24 | 0.025 | 1.80 × 10−7 | 2.66 × 10−6 |
| MCP-1 | −0.0009288 | 0.0003753 | −2.47 | 0.013 | −0.0016643 | −0.0001933 |
| PDGFBBB | 3.57 × 10−7 | 1.42 × 10−7 | 2.52 | 0.012 | 7.89 × 10−8 | 6.36 × 10−7 |
| RANTES | −1.52 × 10−6 | 4.82 × 10−7 | −3.16 | 0.002 | −2.47 × 10−6 | −5.77 × 10−7 |
| VEGF | 1.57 × 10−6 | 4.93 × 10−7 | 3.19 | 0.001 | 6.07 × 10−7 | 2.54 × 10−6 |
| Subcortical grey volume | ||||||
| IL-1α | 7.88 × 10−6 | 2.47 × 10−6 | 3.19 | 0.001 | 3.04 × 10−6 | 0.0000127 |
| IL-6 | −0.0021455 | 0.000831 | −2.58 | 0.010 | −0.0037743 | −0.0005167 |
| Total grey volume | ||||||
| IL-1α | 3.16 × 10−6 | 1.57 × 10−6 | 2.01 | 0.045 | 7.61 × 10−8 | 6.25 × 10−6 |
| IL-6 | −0.0020823 | 0.0005579 | −3.73 | 0.000 | −0.0031758 | −0.0009888 |
| IL-8 | −0.0014577 | 0.0006186 | −2.36 | 0.018 | −0.0026701 | −0.0002453 |
| IL-10 | −0.0035407 | 0.0013919 | −2.54 | 0.011 | −0.0062688 | −0.0008126 |
| IL-12p70 | −0.0020964 | 0.0008961 | −2.34 | 0.019 | −0.0038527 | −0.0003402 |
| IL-15 | −0.0001525 | 0.0000626 | −2.44 | 0.015 | −0.0002751 | −0.0000298 |
| GM-CSF | −0.003109 | 0.0010898 | −2.85 | 0.004 | −0.0052449 | −0.0009732 |
| GCSF | −0.0059812 | 0.0031477 | −1.90 | 0.057 | −0.0121505 | 0.0001881 |
| MCP-1 | −0.0024353 | 0.0008448 | −2.88 | 0.004 | −0.0040912 | −0.0007795 |
| RANTES | −2.54 × 10−6 | 1.04 × 10−6 | −2.44 | 0.015 | −4.57 × 10−6 | −5.02 × 10−7 |
| TNF-α | 5.11 × 10−6 | 2.52 × 10−6 | 2.03 | 0.042 | 1.75 × 10−7 | 0.00001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruhanya, V.; Engelbrecht, S.; Williams, M.E.; Paul, R.H.; Manasa, J.; Nyandoro, G.; Joska, J.A.; Seedat, S.; Glashoff, R.H. Cortical White and Grey Matter Volume Differences Associated with Plasma Cytokine and Chemokine Levels in PLWH in Cape Town. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 12000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412000
Ruhanya V, Engelbrecht S, Williams ME, Paul RH, Manasa J, Nyandoro G, Joska JA, Seedat S, Glashoff RH. Cortical White and Grey Matter Volume Differences Associated with Plasma Cytokine and Chemokine Levels in PLWH in Cape Town. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(24):12000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412000
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuhanya, Vurayai, Susan Engelbrecht, Monray E. Williams, Robert H. Paul, Justen Manasa, George Nyandoro, John A. Joska, Soraya Seedat, and Richard Helmuth Glashoff. 2025. "Cortical White and Grey Matter Volume Differences Associated with Plasma Cytokine and Chemokine Levels in PLWH in Cape Town" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 24: 12000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412000
APA StyleRuhanya, V., Engelbrecht, S., Williams, M. E., Paul, R. H., Manasa, J., Nyandoro, G., Joska, J. A., Seedat, S., & Glashoff, R. H. (2025). Cortical White and Grey Matter Volume Differences Associated with Plasma Cytokine and Chemokine Levels in PLWH in Cape Town. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(24), 12000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412000





