MicroRNA-200c in Cancer Generation, Invasion, and Metastasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biological Characteristics of MicroRNA-200c
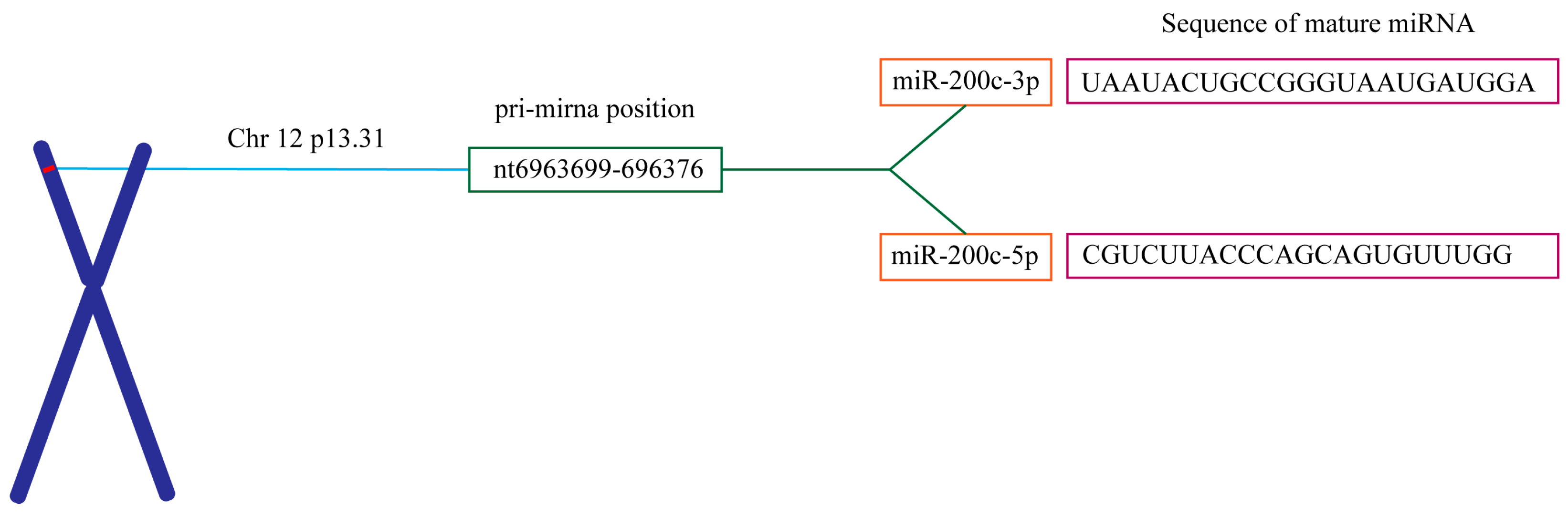
2.1. Biosynthesis and Regulatory Mechanisms of miR-200c
2.2. Target Genes and Functions of miR-200c
3. The Relationship Between MicroRNA-200c and Oncogenesis
3.1. Expression Patterns of miR-200c in Different Tumor Types
3.2. The Role of miR-200c in Tumor Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis
4. The Role of MicroRNA-200c in the Invasion Process
4.1. Regulation of EMT by miR-200c
4.2. Relationship Between miR-200c and Cell Migration and Invasion Capabilities
5. MicroRNA-200c and the Mechanisms of Tumor Metastasis
5.1. The Role of miR-200c in the Expression of Metastasis-Related Genes
5.2. The Interaction of miR-200c with the Tumor Microenvironment
6. Clinical Prospects of MicroRNA-200c
6.1. Potential of miR-200c as a Biomarker
6.2. Targeted Therapeutic Strategies Based on miR-200c
7. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nemeth, K.; Bayraktar, R.; Ferracin, M.; Calin, G.A. Non-coding RNAs in disease: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2024, 25, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slack, F.J.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. The Role of Non-coding RNAs in Oncology. Cell 2019, 179, 1033–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Jacob, L.S.; Slack, F.J. Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Kim, V.N. Small and long non-coding RNAs: Past, present, and future. Cell 2024, 187, 6451–6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravin, A.A.; Sachidanandam, R.; Girard, A.; Fejes-Toth, K.; Hannon, G.J. Developmentally regulated piRNA clusters implicate MILI in transposon control. Science 2007, 316, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss-László, Z.; Henry, Y.; Bachellerie, J.P.; Caizergues-Ferrer, M.; Kiss, T. Site-specific ribose methylation of preribosomal RNA: A novel function for small nucleolar RNAs. Cell 1996, 85, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, M.E.; Charenton, C.; Nagai, K. RNA Splicing by the Spliceosome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, R.; Lee, S.; Senavirathne, G.; Lai, E.C. microRNAs in action: Biogenesis, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 816–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viridiana, C.A.; Ángel, V.M.; Ruth, R.E. MicroRNAs: Beyond Post-transcriptional Regulation of mRNAs. Microrna 2021, 10, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.R.; Tang, L.J.; He, Y.; Garcia, R.C. An update on the role of miRNA-155 in pathogenic microbial infections. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Chen, G.; Liu, B.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xie, B.; Li, M.M.; Chen, J.X.; Chen, J.; Dai, Z. An intramolecular DNAzyme-based amplification for miRNA analysis with improving reaction kinetics and high sensitivity. Talanta 2022, 239, 123137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cobb, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev. Biol. 2007, 302, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjorgjieva, M.; Sobolewski, C.; Dolicka, D.; Correia de Sousa, M.; Foti, M. miRNAs and NAFLD: From pathophysiology to therapy. Gut 2019, 68, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. microRNAs: Master regulators as potential therapeutics in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 51, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhong, Q. MicroRNA-200c Inhibits the Metastasis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Targeting ZEB2, an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Regulator. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 50, 519–527. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, S.J.; Carter, J.V.; Burton, J.F.; Oxford, B.G.; Schmidt, M.N.; Hallion, J.C.; Galandiuk, S. The role of the miR-200 family in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer: A systematic review. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 2501–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, A.; Nieto, M.A. Non-coding RNAs take centre stage in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykxhoorn, D.M. MicroRNAs and metastasis: Little RNAs go a long way. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6401–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.L. Diagnostic potential of miR-200 family members in gingival crevicular fluid for chronic periodontitis: Correlation with clinical parameters and therapeutic implications. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zheng, J.; Li, R.; Tian, Y.; Lin, J.; Liang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Xu, A.; Zheng, R.; Liu, M.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC02582 acts downstream of miR-200c to promote radioresistance through CHK1 in breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Veronese, A.; Pichiorri, F.; Lee, T.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Volinia, S.; Pineau, P.; Marchio, A.; Palatini, J.; Suh, S.S.; et al. p53 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition through microRNAs targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Liu, L.Z.; Pei, X.Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Ye, F.; Xie, X.; Chen, J.; Tang, H.; Xie, X. miR-200c inhibits breast cancer proliferation by targeting KRAS. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34968–34978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Chen, G.; Xia, Q.; Shao, S.; Fang, H. Exosomal miR-200 family as serum biomarkers for early detection and prognostic prediction of cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 3870–3876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ljepoja, B.; Schreiber, C.; Gegenfurtner, F.A.; García-Roman, J.; Köhler, B.; Zahler, S.; Rädler, J.O.; Wagner, E.; Roidl, A. Inducible microRNA-200c decreases motility of breast cancer cells and reduces filamin A. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrba, L.; Jensen, T.J.; Garbe, J.C.; Heimark, R.L.; Cress, A.E.; Dickinson, S.; Stampfer, M.R.; Futscher, B.W. Role for DNA methylation in the regulation of miR-200c and miR-141 expression in normal and cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasabi, M.; Majidi, J.; Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Shomali, N.; Shirafkan, N.; Baghbani, E.; Kazemi, T.; Baradaran, B. The effect of combined miR-200c replacement and cisplatin on apoptosis induction and inhibition of gastric cancer cell line migration. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 22581–22592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsiani, C.; Bacalini, M.G.; Santoro, A.; Garagnani, P.; Collura, S.; D’Errico, A.; de Eguileor, M.; Grazi, G.L.; Cescon, M.; Franceschi, C.; et al. The peculiar aging of human liver: A geroscience perspective within transplant context. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 51, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Wang, J.; Shu, L.; Zhou, G. MiR-200c promotes papillary thyroid cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by downregulating PTEN. Tissue Cell 2021, 73, 101647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Chen, W.; Fan, X.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, L.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H. MicroRNA-200c inhibits apoptosis in pituitary adenoma cells by targeting the PTEN/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol. Res. 2013, 21, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Li, F.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-200c-5p Regulates Migration and Differentiation of Myoblasts via Targeting Adamts5 in Skeletal Muscle Regeneration and Myogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nag, A.; Mandal, C.C. A Comprehensive Review on miR-200c, A Promising Cancer Biomarker with Therapeutic Potential. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1381–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Messina, E.; Sanavia, T.; Labruna, V.; Ceccarelli, S.; Megiorni, F.; Gerini, G.; Pontecorvi, P.; Camero, S.; Perniola, G.; et al. Calcineurin Gamma Catalytic Subunit PPP3CC Inhibition by miR-200c-3p Affects Apoptosis in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Genes 2021, 12, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Ji, X.; Liu, K.; Shi, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; He, Y.; Xiang, M.; Zhao, R. Exosomal miR-200c-3p negatively regulates the migraion and invasion of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated colorectal cancer (CRC). BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, S.J.; Fiechter, C.; Burton, J.; Hallion, J.; Paas, M.; Patel, A.; Patel, A.; Rochet, A.; Scheurlen, K.; Gardner, S.; et al. Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 is a major regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through miR-200/ZEB1/E-cadherin, vimentin signaling in colon adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.F.; Du, M.F.; Fu, H.; Liu, J.; Xia, F.Y.; Du, H.N.; Liu, N. MiR-200c promotes proliferation of papillary thyroid cancer cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 5512–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Du, R.; Zhou, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, D.X.; Shao, Z.M.; Zhang, L.; et al. miR-200c/141 Regulates Breast Cancer Stem Cell Heterogeneity via Targeting HIPK1/β-Catenin Axis. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5801–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.D.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Kim, J.; Huang, S. Phosphodiesterase 7B/microRNA-200c relationship regulates triple-negative breast cancer cell growth. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1106–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Han, X.; Yu, K.; Sun, S.; Zhen, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, S. microRNA-200c downregulates XIAP expression to suppress proliferation and promote apoptosis of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, R.; Huang, N. MiR-200c-3p and miR-485-5p overexpression elevates cisplatin sensitivity and suppresses the malignant phenotypes of non-small cell lung cancer cells through targeting RRM2. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 1974–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Wang, D.H.; Wang, L.L.; Chen, Q.; Pan, L.L.; Xia, L. MicroRNA-200c suppressed cervical cancer cell metastasis and growth via targeting MAP4K4. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Qiu, M.; Tan, G.; Liang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, J. miR-200c inhibits invasion, migration and proliferation of bladder cancer cells through down-regulation of BMI-1 and E2F3. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoori, B.; Silvestris, N.; Mohammadi, A.; Khaze, V.; Baghbani, E.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Shanehbandi, D.; Derakhshani, A.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Baradaran, B. miR-34a and miR-200c Have an Additive Tumor-Suppressive Effect on Breast Cancer Cells and Patient Prognosis. Genes 2021, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, W.; Aimudula, A.; Lu, S.; Lu, P.; Aihaiti, R.; Bao, Y. Quaking I-5 protein inhibits invasion and migration of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma via inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition suppression through the regulation of microRNA 200c. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 3800–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Liu, G.S.; Zou, N.Z.; Zhang, H.; He, X.X.; Sun, P.L.; An, H.J.; Shen, H. microRNA-200c-3p suppresses proliferation and invasion of nephroblastoma cells by targeting EP300 and inactivating the AKT/FOXO1/p27 pathway. Neoplasma 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Jurmeister, S.; Baumann, M.; Balwierz, A.; Keklikoglou, I.; Ward, A.; Uhlmann, S.; Zhang, J.D.; Wiemann, S.; Sahin, Ö. MicroRNA-200c represses migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by targeting actin-regulatory proteins FHOD1 and PPM1F. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.L.; Liu, W.L.; Chang, J.M.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, Y.P.; Kuo, H.F.; Hsieh, C.C.; Ding, Y.S.; Chen, W.W.; Chong, I.W. MicroRNA-200c inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and migration of lung cancer by targeting HMGB1. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.; Kang, W.; Nan, Y.; Lei, Z.; Zhongdong, L.; Demin, L.; Lei, S.; Hairong, H. The Downregulation of miR-200c Promotes Lactate Dehydrogenase A Expression and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Fan, D.; Jiang, H. MicroRNA-200c binding to FN1 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, K.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Z. MiR-200c-3p aggravates gastric cell carcinoma via KLF6. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, P.; Mohr, A.M.; Grandgenett, P.M.; Steele, M.M.; Batra, S.K.; Hollingsworth, M.A. MicroRNA-200c modulates the expression of MUC4 and MUC16 by directly targeting their coding sequences in human pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.L.; Yu, C.C.; Chiou, G.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, P.I.; Chien, C.S.; Tseng, L.M.; Chu, P.Y.; Lu, K.H.; Chang, K.W.; et al. MicroRNA-200c attenuates tumour growth and metastasis of presumptive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma stem cells. J. Pathol. 2011, 223, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.Y.; Park, S.; Song, K.S.; Bae, S.W.; Lee, J.S.; Jang, K.J.; Park, Y.M. Anticancer Effects of 6-Gingerol Through Downregulating Iron Transport and PD-L1 Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Cells 2023, 12, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Gibbons, D.L.; Goswami, S.; Cortez, M.A.; Ahn, Y.H.; Byers, L.A.; Zhang, X.; Yi, X.; Dwyer, D.; Lin, W.; et al. Metastasis is regulated via microRNA-200/ZEB1 axis control of tumour cell PD-L1 expression and intratumoral immunosuppression. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Lan, P.; Han, Q.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, G.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Wei, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Oncofetal gene SALL4 reactivation by hepatitis B virus counteracts miR-200c in PD-L1-induced T cell exhaustion. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Dong, P.; Li, L.; Ma, X.; Xu, P.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, K.; Liu, J.; et al. MicroRNA-200c regulates cisplatin resistance by targeting ZEB2 in human gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, D.R.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Howe, E.N.; Nordeen, S.K.; Richer, J.K. MicroRNA-200c mitigates invasiveness and restores sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic agents. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, H.; Tian, J.; Yang, S. Roles of a TMPO-AS1/microRNA-200c/TMEFF2 ceRNA network in the malignant behaviors and 5-FU resistance of ovarian cancer cells. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 115, 104481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.Z.; Niu, Y.Q.; Li, Z.M.; Kou, D.; Zhang, L. MiR-200c inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of Wilms tumor cells by regulating akt signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 6623–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, D.; Yang, L.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, L. MicroRNA-200c-5p targets NIMA Related Kinase 7 (NEK7) to inhibit NOD-like receptor 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation, MODE-K cell pyroptosis, and inflammatory bowel disease in mice. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 146, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Chen, L.; He, X.; Ye, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, S. Atorvastatin Regulates MALAT1/miR-200c/NRF2 Activity to Protect Against Podocyte Pyroptosis Induced by High Glucose. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 1631–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yang, S.; Chen, G.; He, S. MiR-200c-3p regulates pyroptosis by targeting SLC30A7 in diabetic retinopathy. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 9603271221099589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, M.; Raza, U.; Saatci, Ö.; Eyüpoğlu, E.; Yurdusev, E.; Şahin, Ö. miR-200c: A versatile watchdog in cancer progression, EMT, and drug resistance. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Craene, B.; Berx, G. Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Ang, H.L.; Moghadam, E.R.; Mohammadi, S.; Zarrin, V.; Hushmandi, K.; Samarghandian, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Najafi, M.; Mohammadinejad, R.; et al. MicroRNAs and Their Influence on the ZEB Family: Mechanistic Aspects and Therapeutic Applications in Cancer Therapy. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, F.; Jonas, K.; Balihodzic, A.; Klec, C.; Reicher, A.; Barth, D.A.; Riedl, J.; Gerger, A.; Kiesslich, T.; Mayr, C.; et al. MicroRNA mimics can distort physiological microRNA effects on immune checkpoints by triggering an antiviral interferon response. RNA Biol. 2022, 19, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, K.; Toiyama, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Balaguer, F.; Nagasaka, T.; Koike, J.; Hemmi, H.; Koi, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. MicroRNA-200c modulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human colorectal cancer metastasis. Gut 2013, 62, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Sato, M.; Nishita, M. miR-200c-141 induces a hybrid E/M state and promotes collective cell migration in MDA-MB-231 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 709, 149829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.K.; Kim, H.S.; Jin, T.; Hwang, E.H.; Jung, M.; Moon, W.K. Overexpression of the miR-141/200c cluster promotes the migratory and invasive ability of triple-negative breast cancer cells through the activation of the FAK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways by secreting VEGF-A. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokmued, K.; Obeng, G.; Kawamoto, E.; Caidengbate, S.; Leangpanich, S.; Akama, Y.; Gaowa, A.; Shimaoka, M.; Park, E.J. miR-200c-3p regulates α4 integrin-mediated T cell adhesion and migration. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 440, 114146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Q.; He, H.Q.; Kang, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.K.; Zhu, X. MicroRNA-200c affects bladder cancer angiogenesis by regulating the Akt2/mTOR/HIF-1 axis. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 2713–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Cano, I.; Adam-Artigues, A.; Lameirinhas, A.; Blandez, J.F.; Candela-Noguera, V.; Lluch, A.; Bermejo, B.; Sancenón, F.; Cejalvo, J.M.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; et al. Delivery of miR-200c-3p Using Tumor-Targeted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Breast Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 38323–38334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Calin, G.A.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K. miRNA Deregulation in Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raue, R.; Frank, A.C.; Fuhrmann, D.C.; de la Cruz-Ojeda, P.; Rösser, S.; Bauer, R.; Cardamone, G.; Weigert, A.; Syed, S.N.; Schmid, T.; et al. MicroRNA-200c Attenuates the Tumor-Infiltrating Capacity of Macrophages. Biology 2022, 11, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Jin, T.; Li, C.; Zhang, S. miR-200c/PAI-2 promotes the progression of triple negative breast cancer via M1/M2 polarization induction of macrophage. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 81, 106028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, E.; Jung, S.C.; Nam, S.K.; Park, Y.; Seo, S.H.; Park, K.U.; Oh, H.K.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, S.B.; Lee, H.S. Tissue miR-200c-3p and circulating miR-1290 as potential prognostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishta, M.S.; Khamis, A.; Am, H.; Elshaar, A.H.; Gül, D. Exploring the tumor-suppressive role of miRNA-200c in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Potential and mechanisms of exosome-mediated delivery for therapeutic applications. Transl. Oncol. 2025, 51, 102216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katakura, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Hashimoto, H.; Kamimaki, C.; Tanaka, K.; Kubo, S.; Nakashima, K.; Teranishi, S.; Manabe, S.; Watanabe, K.; et al. MicroRNA-200b is a potential biomarker of the expression of PD-L1 in patients with lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 2975–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wen, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, C.; Wang, J.; Bao, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, L.; et al. MicroRNA-200a induces immunosuppression by promoting PTEN-mediated PD-L1 upregulation in osteosarcoma. Aging 2020, 12, 1213–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, C.C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, X.D. Regulation of PD-L1: A novel role of pro-survival signalling in cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phung, C.D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Choi, J.Y.; Pham, T.T.; Acharya, S.; Timilshina, M.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Ku, S.K.; et al. Reprogramming the T cell response to cancer by simultaneous, nanoparticle-mediated PD-L1 inhibition and immunogenic cell death. J. Control. Release 2019, 315, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; You, B.; Meng, J.; Huang, C.P.; Dong, G.; Wang, R.; Chou, F.; Gao, S.; Chang, C.; Yeh, S.; et al. Targeting the androgen receptor to enhance NK cell killing efficacy in bladder cancer by modulating ADAR2/circ_0001005/PD-L1 signaling. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 1988–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Qiu, X.; Teng, L.A.; Sriwastva, M.K.; Han, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, S.; Da, D.; et al. Rab1A-Mediated Exosomal Sorting of miR-200c Enhances Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis. Breast Cancer 2023, 15, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, N.; Cao, L.; Xiao, D.; Ye, X.; Luo, E.; Zhang, Z. Down-regulation of miR-200c associates with poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Chung Duong, T.; Nguyen, T.H.N.; Thi Ngoc Nguyen, T.; Huynh, L.H.; Ngo, H.P.; Thi Nguyen, H. Diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-200 family in breast cancer: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Cancer Epidemiol. 2022, 77, 102097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocia, C.; Dumitru, A.; Mateescu, B.; Negreanu, L.; State, M.; Cozaru, G.C.; Mitroi, A.F.; Brinzan, C.; Popescu, R.; Leopa, N.; et al. Tissue and Circulating MicroRNA-31, MicroRNA-200b, and MicroRNA-200c Reflects Disease Activity in Crohn’s Disease Patients: Results from the BIOMIR Study. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2023, 32, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Han, B. The Role of MicroRNAs in the Chemoresistance of Breast Cancer. Drug Dev. Res. 2015, 76, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Huo, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, W. MicroRNA-200c regulates the sensitivity of chemotherapy of gastric cancer SGC7901/DDP cells by directly targeting RhoE. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Men, X.; Zhao, R.; Han, J.; Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zuo, J.; Zhao, L.; Sang, M.; et al. miR-200c inhibits TGF-β-induced-EMT to restore trastuzumab sensitivity by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2 in gastric cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2018, 25, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, W.D.; Ye, X.M.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhu, H.Y.; Xi, W.J.; Huang, X.; Zhao, J.; Gu, B.; Zheng, G.X.; Yang, A.G.; et al. MiR-200c suppresses TGF-β signaling and counteracts trastuzumab resistance and metastasis by targeting ZNF217 and ZEB1 in breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1356–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, A.M.; Morais, C.M.; Sousa, M.; Rebelo, O.; Tão, H.; Barbosa, M.; Pedroso de Lima, M.C.; Jurado, A.S. MiR-200c-based metabolic modulation in glioblastoma cells as a strategy to overcome tumor chemoresistance. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 2315–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Phung, C.D.; Tran, T.H.; Pham, T.T.; Pham, L.M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Jeong, J.H.; Choi, H.G.; Ku, S.K.; Yong, C.S.; et al. Manipulating immune system using nanoparticles for an effective cancer treatment: Combination of targeted therapy and checkpoint blockage miRNA. J. Control Release 2021, 329, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Target Gene | Regulatory Function | Cancer Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZEB1 and ZEB2 | Migration, invasion, and metastasis | (TNBC) Breast cancer and colorectal cancer | [16,34,35] |
| KRAS | Proliferation | (TNBC) Breast cancer | [23] |
| c-Jun | Migration and invasion | (HR+ and TNBC) Breast cancer | [25] |
| VEGFR | Migration and invasion | Gastric cancer | [27] |
| MMP9 | Migration and invasion | Gastric cancer | [27] |
| RhoE | Cisplatin sensitivity | Gastric cancer | [27] |
| PTEN | Proliferation, migration, and invasion | Papillary thyroid cancer, gastric cancer, and pituitary adenoma | [29,30] |
| PPP3CC | Apoptosis | Epithelial ovarian cancer | [33] |
| DACH1 | Proliferation | papillary thyroid cancer | [36] |
| HIPK1 | Proliferation and metastasis | (HR+ and HER2+ and TNBC) Breast cancer | [37] |
| PDE7B | Proliferation | (TNBC) Breast cancer | [38] |
| XIAP | Proliferation | (TNBC) Breast cancer | [39] |
| RRM2 | Proliferation and cisplatin sensitivity | Non-small cell lung cancer | [40] |
| MAP4K4 | Proliferation, migration, and invasion | Cervical cancer | [41] |
| E2F3 | Proliferation, migration, and invasion | Bladder cancer | [42] |
| HIF1-α | Proliferation, migration, and invasion | (HR+ and TNBC) Breast cancer | [43] |
| QKI-5 | Migration and invasion | Renal clear cell cancer | [44] |
| EP300 | Proliferation, migration, and invasion | Wilms tumor | [45] |
| FHOD1 | Migration and invasion | (HR+ and TNBC) Breast cancer | [46] |
| PPM1F | Migration and invasion | (HR+ and TNBC) Breast cancer | [46] |
| HMGB1 | Migration and invasion | Non-small cell lung cancer | [47] |
| LDHA | Proliferation, migration, and invasion | Non-small cell lung cancer | [48] |
| FN1 | Proliferation, migration, and invasion | Gastric cancer | [49] |
| KLF6 | Migration and invasion | Gastric cancer | [50] |
| MUC4 and MUC16 | Metastasis | Pancreatic cancer | [51] |
| BMI1 | Proliferation and metastasis | Head and neck squamous cell cancer and bladder cancer | [52] |
| PD-L1 | Metastasis | Non-small cell lung cancer | [53,54,55] |
| ZEB2 | Cisplatin sensitivity | Gastric cancer | [56] |
| TUBB3 | Sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic agents | Endometrial cancer and ovarian cancer | [57] |
| TMEFF2 | Migration, invasion, metastasis, and 5-FU sensitivity | Ovarian cancer | [58] |
| Functional Category | Cancer Type | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor suppressor gene | Breast cancer | Downregulates ZEB1 and ZEB2, inhibiting EMT and reducing tumor cell invasiveness. | [16,22] |
| Downregulates CHK1 through the inhibition of long non-coding RNA LINC02582, increasing radiosensitivity. | [21] | ||
| Downregulates KRAS, suppressing breast cancer cell proliferation. | [23] | ||
| Downregulates filamin A, a cytoskeletal component, inhibiting breast cancer metastasis. | [25] | ||
| Regulates breast cancer stem cell heterogeneity, suppressing tumor metastasis. | [37] | ||
| Downregulates PDE7B, inhibiting tumor cell proliferation. | [38] | ||
| Downregulates XIAP, inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis. | [39] | ||
| Downregulates FHOD1 and PPM1F, inhibiting migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. | [46] | ||
| Gastric cancer | Downregulates RhoE, VEGFR, and MMP9, increasing cisplatin sensitivity. | [27] | |
| Downregulates FN1, inhibiting tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. | [49] | ||
| Downregulates ZEB2, enhancing cisplatin sensitivity. | [56] | ||
| Colorectal cancer | Downregulates ZEB1 and ZEB2, inhibiting EMT and reducing tumor cell invasiveness. | [34,68] | |
| Wilms tumor cells | Reduces Akt phosphorylation and its downstream protein GLUT1 expression, promoting apoptosis and inhibiting cell proliferation. | [59] | |
| Bladder cancer | Downregulates BMI-1 and E2F3, inhibiting EMT and reducing tumor cell invasion and proliferation. | [42] | |
| Inhibits Akt2/mTOR signaling pathway, affecting the expression of VEGF and HIF-1α, regulating tumor angiogenesis. | [72] | ||
| Non-small cell lung cancer | Downregulates RRM2, enhancing cisplatin sensitivity and inhibiting tumor proliferation. | [41] | |
| Downregulates HMGB1, inhibiting EMT, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells. | [47] | ||
| Downregulates LDHA, inhibiting NSCLC cell proliferation and migration. | [61] | ||
| Cervical cancer | Downregulates MAP4K4, inhibiting cervical cancer cell proliferation and progression. | [41] | |
| Clear cell renal carcinoma | Downregulates QKI-5, inhibiting EMT and reducing tumor cell invasiveness. | [44] | |
| Nephroblastoma cells | Downregulates EP300 and inactivates AKT/FOXO1/p27 pathway to suppress tumor cell proliferation and invasion. | [45] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | Downregulates MUC4 and MUC16, inhibiting tumor cell invasiveness. | [51] | |
| Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Downregulates BMI1/ZEB1, inhibiting EMT and reducing tumor cell invasiveness. | [52] | |
| HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma | Downregulates PD-L1, reversing antiviral CD8 T cell exhaustion. | [55] | |
| Ovarian cancer | Downregulates TMEFF2, inhibiting EMT, reducing tumor cell proliferation and invasion, and suppressing 5-FU resistance. | [58] | |
| Oncogene | Papillary thyroid cancer | Downregulates PTEN, promoting tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. | [29] |
| Pituitary adenoma cells | Downregulates PTEN, promoting tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. | [30] | |
| Ovarian cancer | Downregulates PPP3CC, inhibiting tumor cell apoptosis. | [33] | |
| Breast cancer | Promotes VEGF-A secretion, activating FAK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways, thereby enhancing cell migration and invasion. | [70] | |
| Promotes PAI-2 secretion and M2 macrophage polarization, facilitating tumor cell metastasis. | [76] | ||
| Gastric cancer | Downregulates KLF6, promoting tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. | [50] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, H.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Shen, N. MicroRNA-200c in Cancer Generation, Invasion, and Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020710
Guo H, Zhang N, Huang T, Shen N. MicroRNA-200c in Cancer Generation, Invasion, and Metastasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020710
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Honghao, Ning Zhang, Tao Huang, and Na Shen. 2025. "MicroRNA-200c in Cancer Generation, Invasion, and Metastasis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020710
APA StyleGuo, H., Zhang, N., Huang, T., & Shen, N. (2025). MicroRNA-200c in Cancer Generation, Invasion, and Metastasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020710






