Re-Examination Characterization and Screening of Stripe Rust Resistance Gene of Wheat TaPR1 Gene Family Based on the Transcriptome in Xinchun 32
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PR1 Family Identification
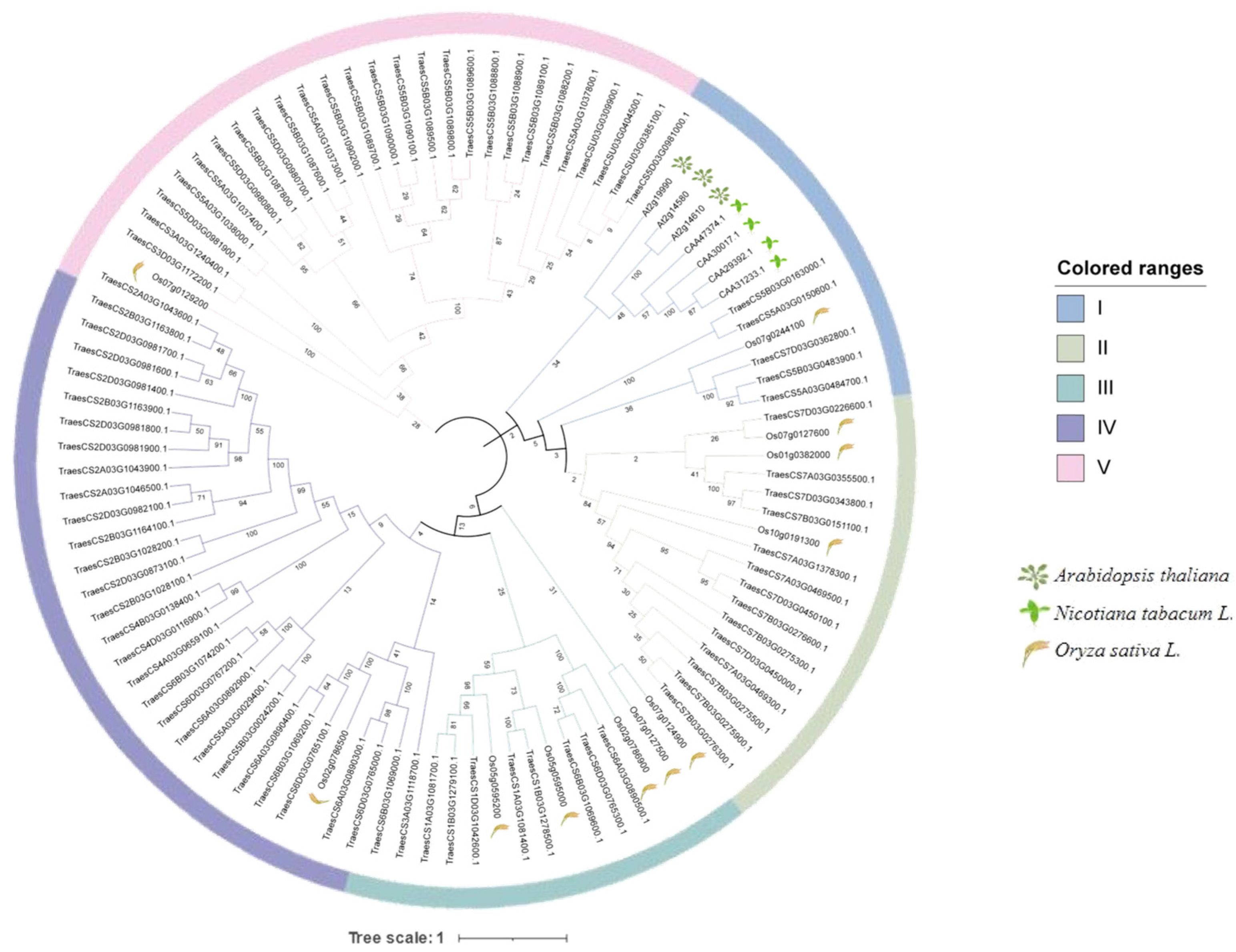
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of TaPR1 Genes
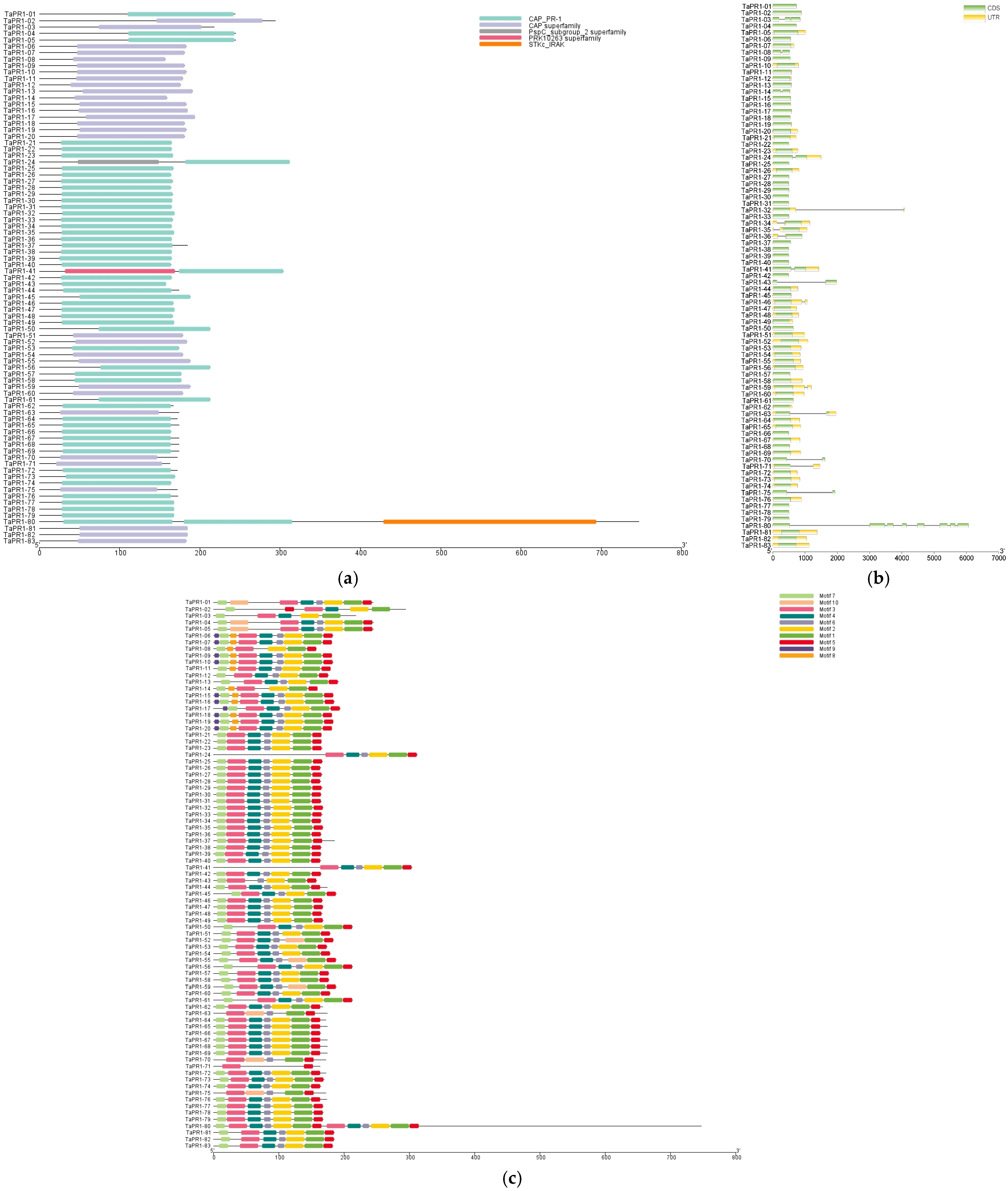
2.3. Structural Characteristics of the TaPR1 Gene Family
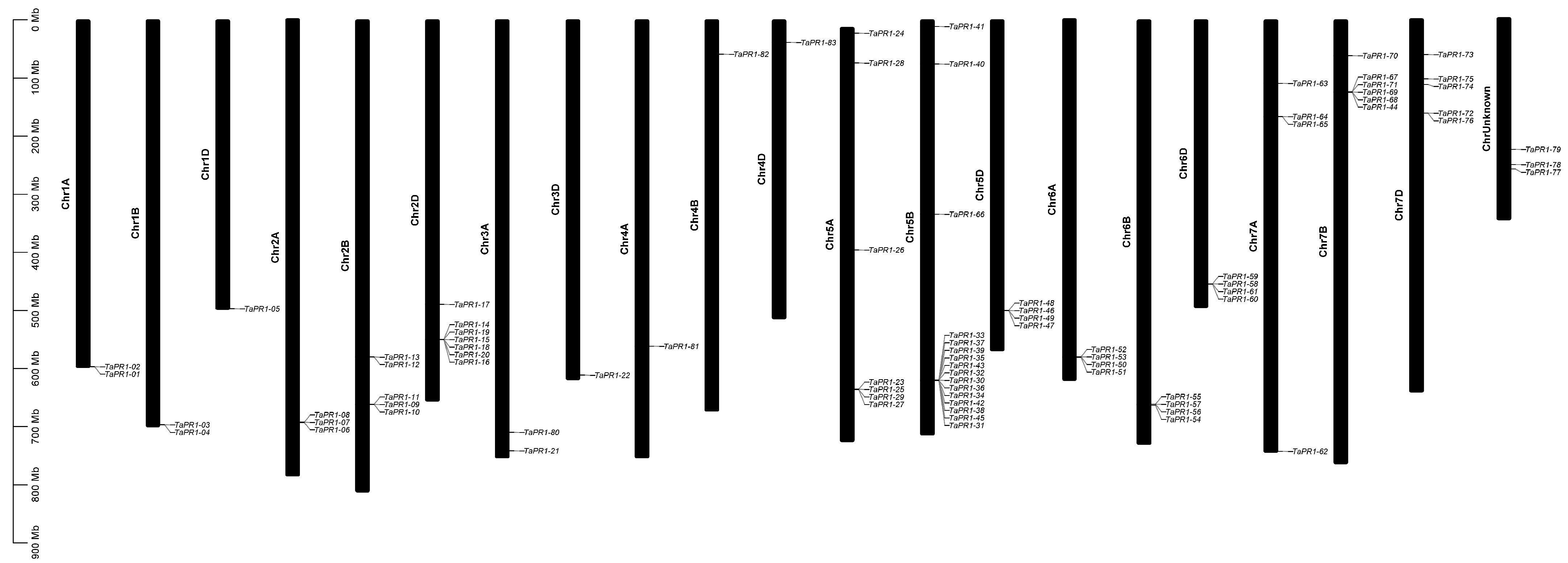
2.4. Chromosomal Distribution of TaPR1 Genes
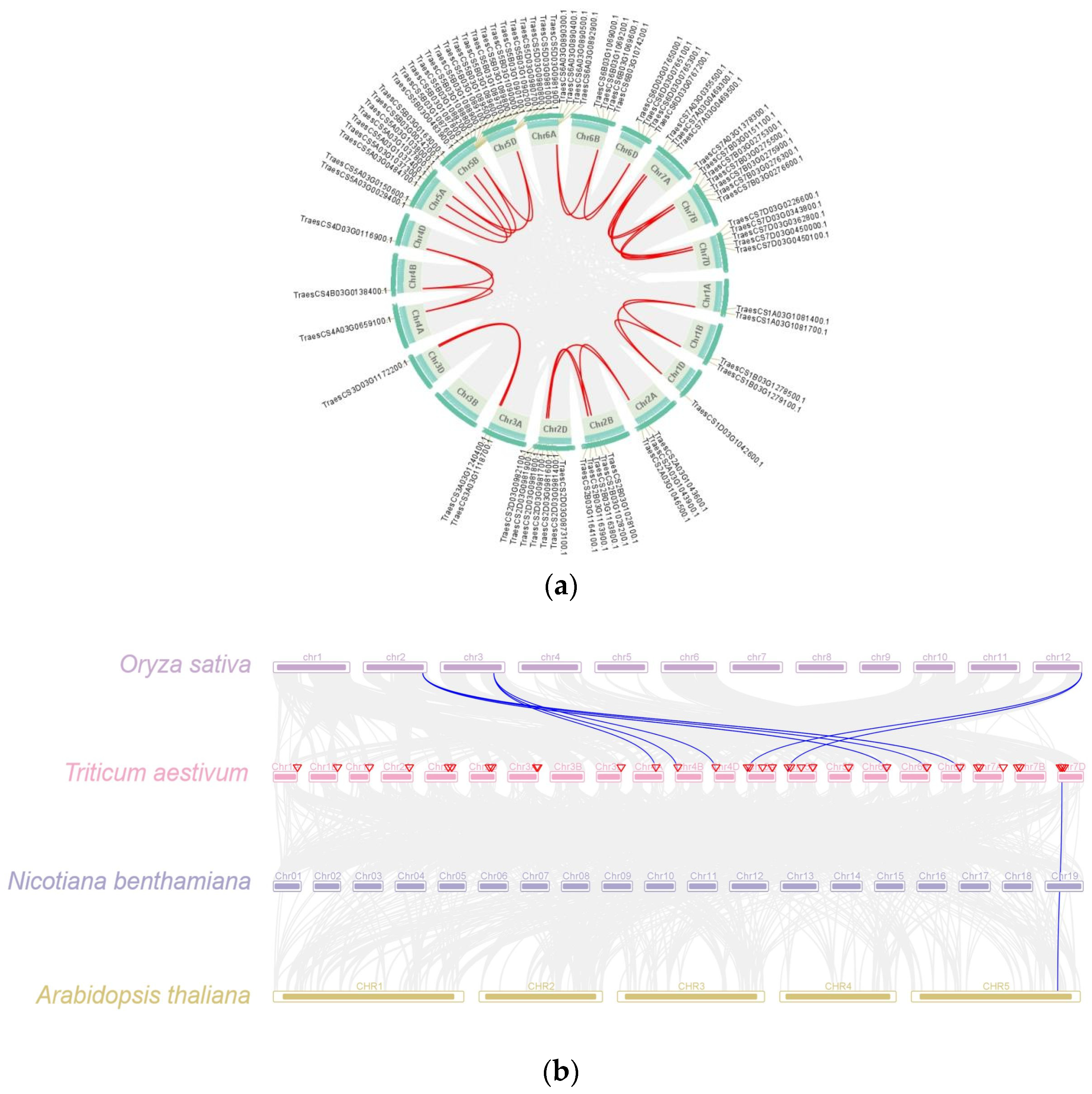
2.5. Collinearity Analysis of TaPR1 Gene Family
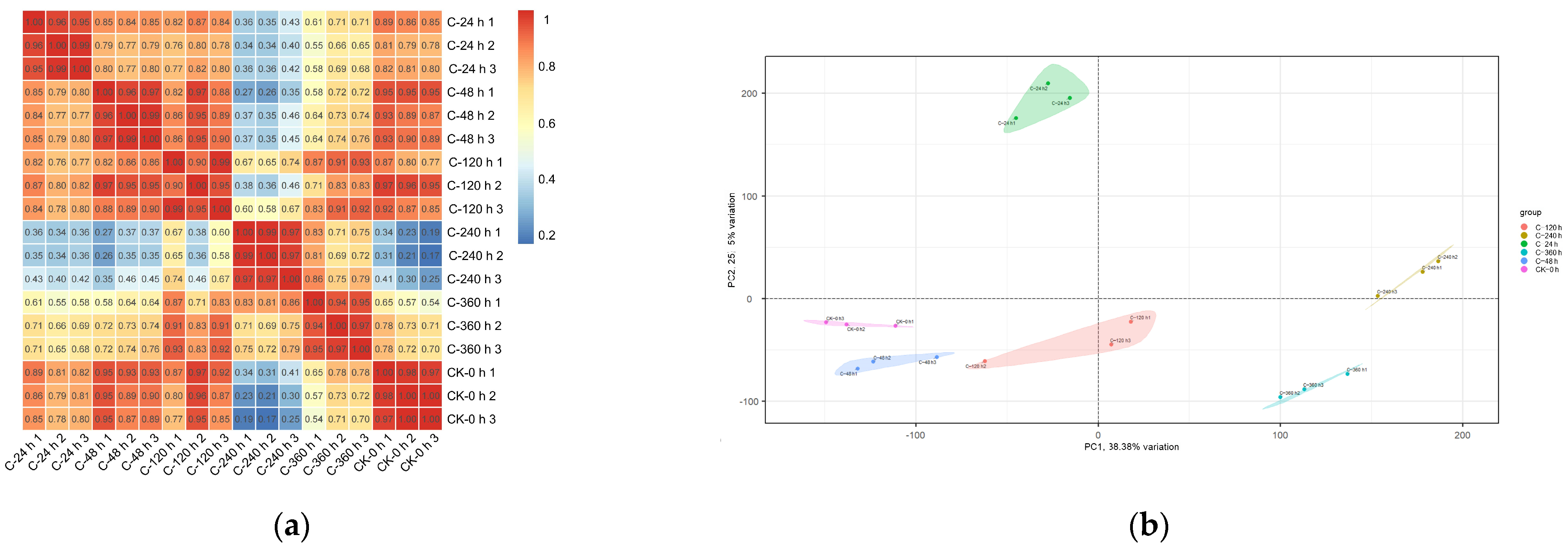
2.6. Analysis of RNA-Seq Data: Quality Assessment and Repeat Correlation
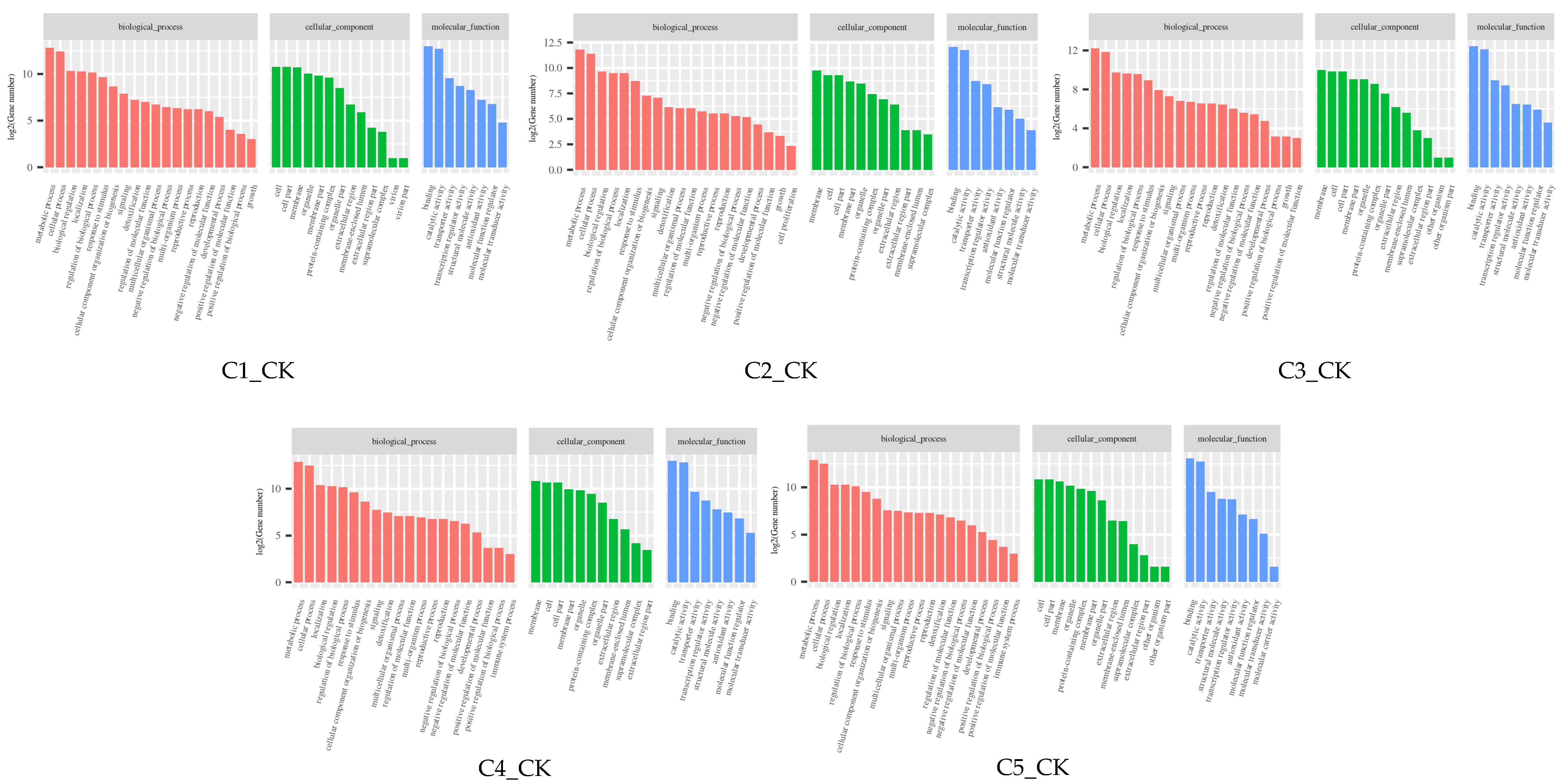
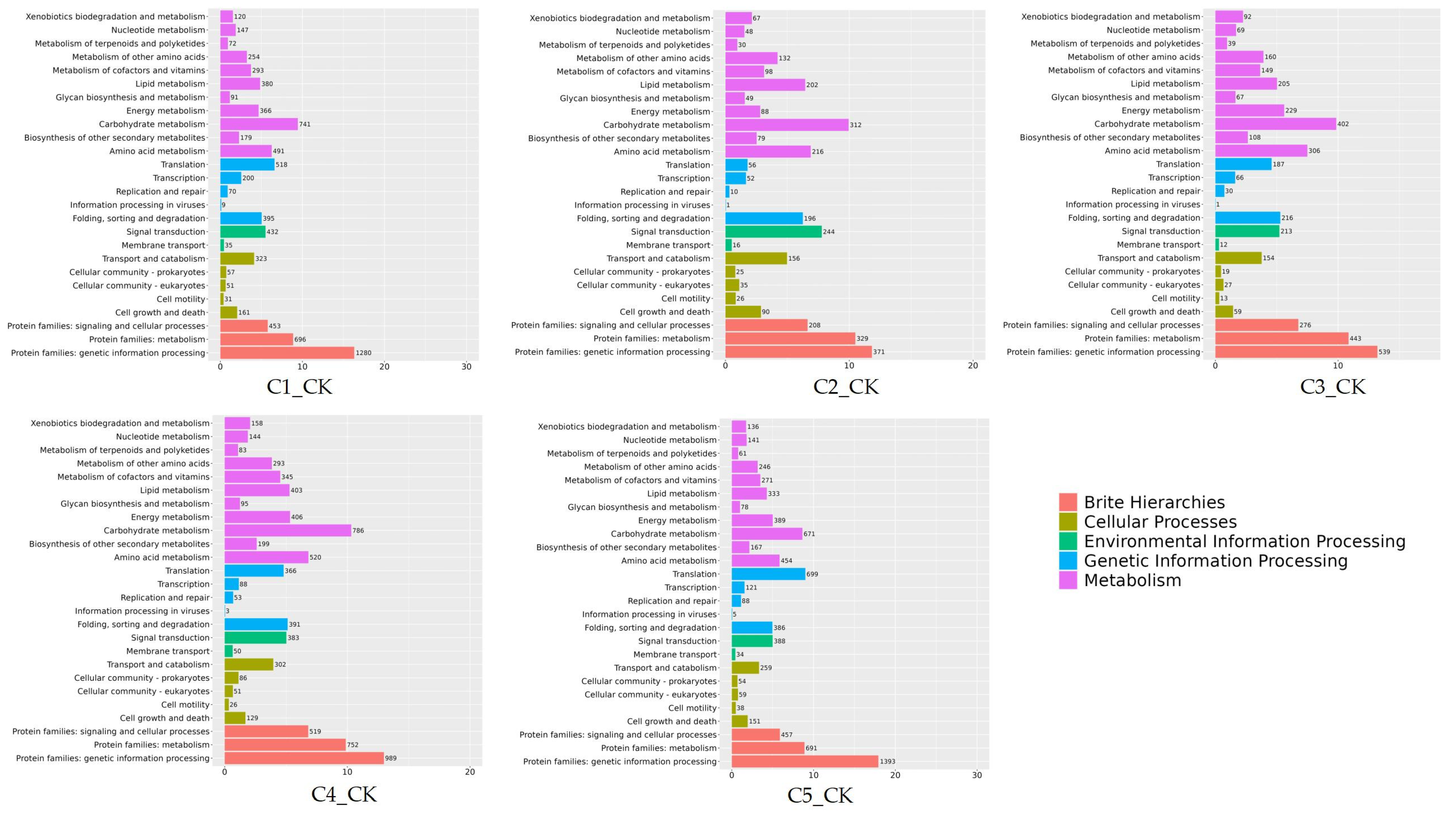
2.7. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
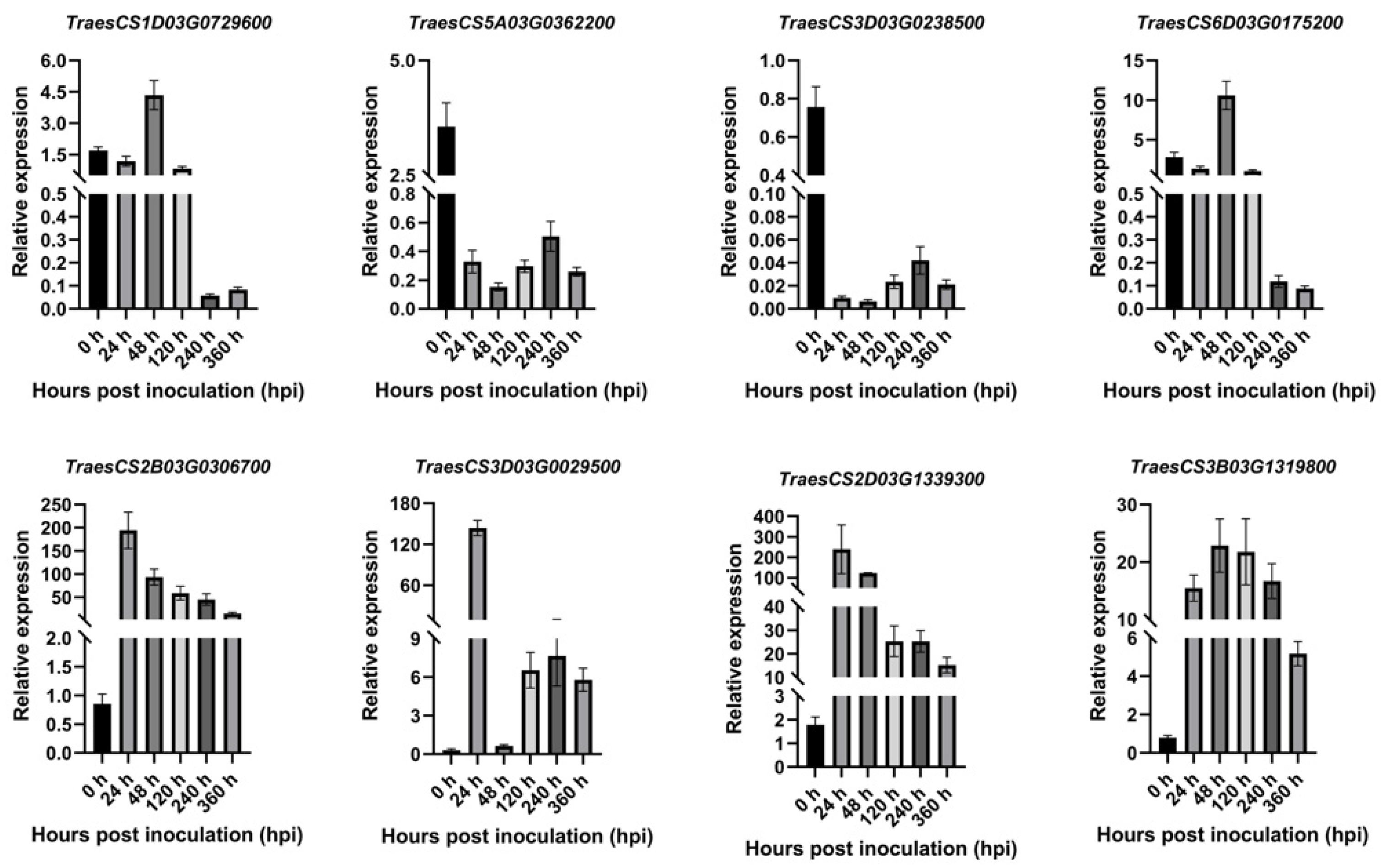
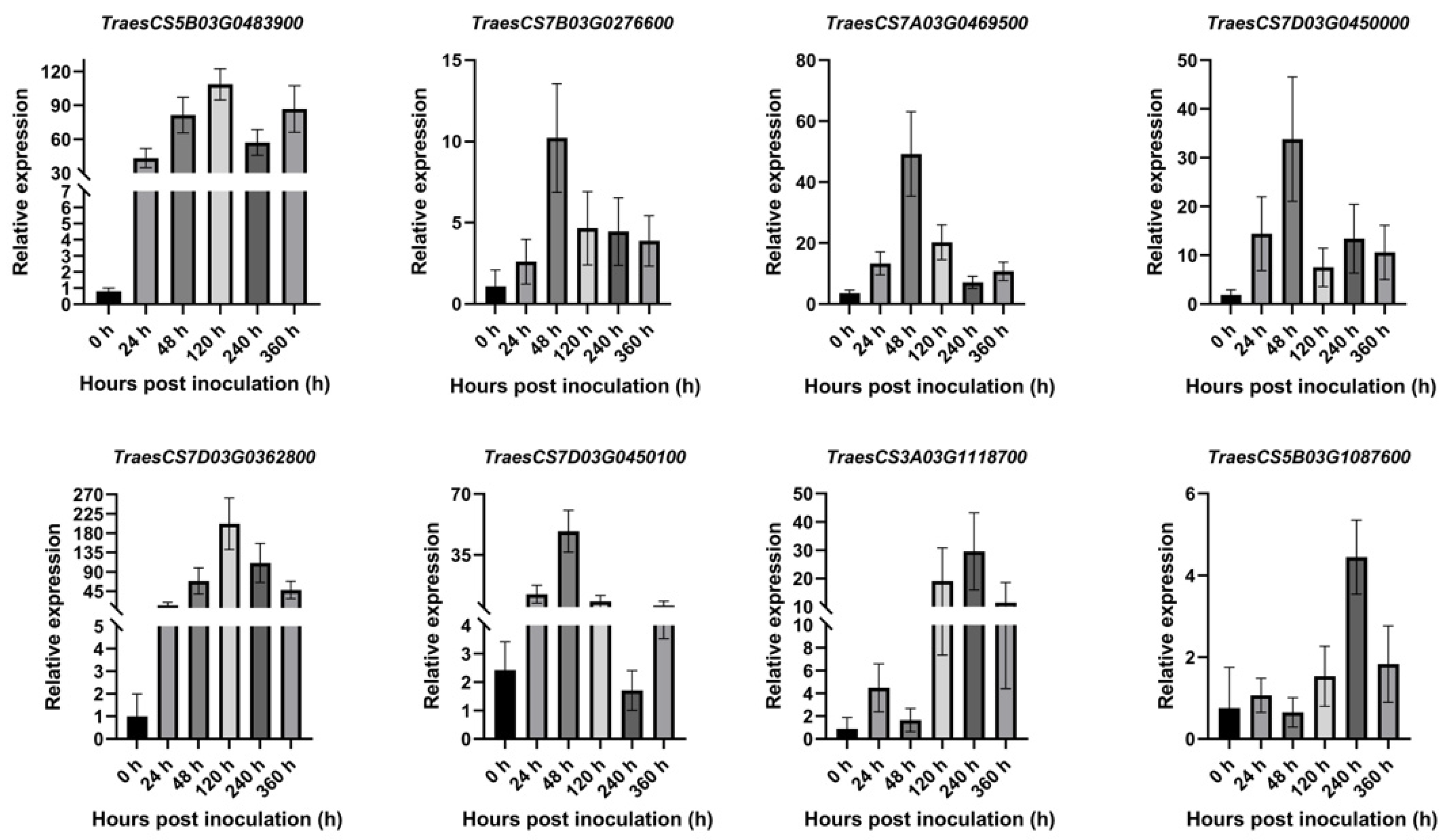
2.8. The Results of qRT-PCR Analysis
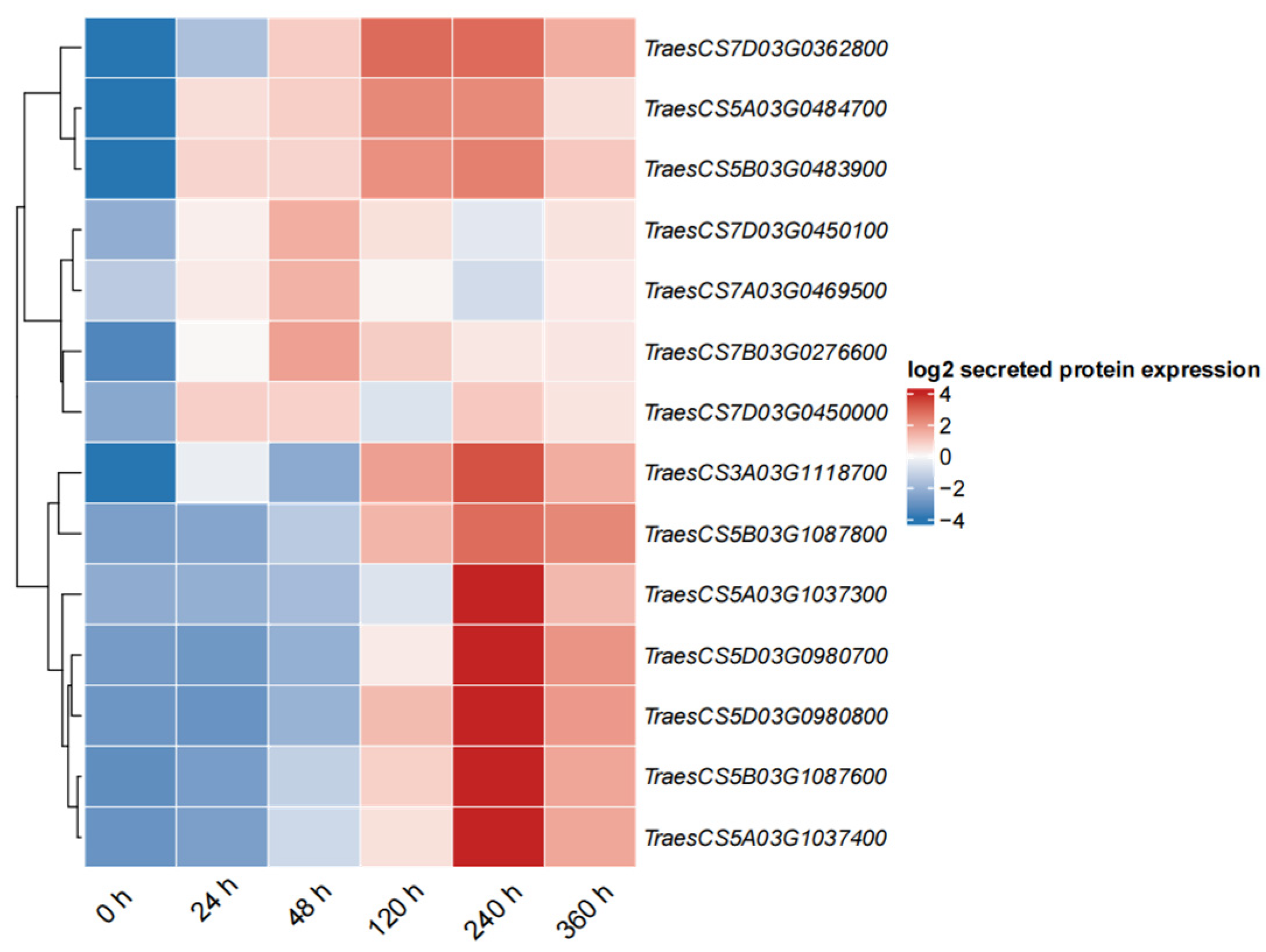
2.9. Expression Profiles of PR1 in Wheat in Response to Pst
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Comparison of PR1
4.2. Gene Structure and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Cis-Acting Element (CRE), Conserved Motif, and Conserved Domain Analysis
4.4. Chromosomal Localization and Collinearity Analysis
4.5. Plant and Fungal Materials
4.6. RNA-Sequencing, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes Analysis, and Gene Ontology Analysis
4.7. qRT-PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Saimi, A.; Liu, Q.; Ma, Z.; Chen, J. The Detection of Yr Genes in Xinjiang Wheat Cultivars Using Different Molecular Markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W.; Rosewarne, G.; Li, J.; Yang, E.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Tong, H.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of stripe rust resistance in modern Chinese wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X. Pathogens which threaten food security: Puccinia striiformis, the wheat stripe rust pathogen. Food Secur. 2020, 12, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddow, J.M.; Pardey, P.G.; Chai, Y.; Hurley, T.M.; Kriticos, D.J.; Braun, J.-C.; Park, R.F.; Cuddy, W.S.; Yonow, T. Research investment implications of shifts in the global geography of wheat stripe rust. Nat. Plants 2015, 1, 15132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Frick, M.; Huel, R.; Nykiforuk, C.L.; Wang, X.; Gaudet, D.A.; Eudes, F.; Conner, R.L.; Kuzyk, A.; Chen, Q.; et al. The stripe rust resistance gene Yr10 encodes an evolutionary-conserved and unique CC-NBS-LRR sequence in wheat. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1740–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Bin, B.A.I.; Jun, L.; Huang, L.; Zhibin, X.; YongXing, C.; Xu, L.; TingJie, C.; MiaoMiao, L.; et al. Current Status and Strategies for Utilization of StripeRust Resistance Genes in Wheat Breeding Program of China. Chin. J. Agric. Sci. 2024, 57, 34–51. [Google Scholar]
- Irigoyen, M.L.; Garceau, D.C.; Bohorquez-Chaux, A. Genome-wide analyses of cassava Pathogenesis-related (PR) gene families reveal core transcriptome responses to whitefly infestation, salicylic acid and jasmonic acid. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loon, L.C.; Van Kammen, A. Polyacrylamide disc electrophoresis of the soluble leaf proteins from Nicotiana tabacum var. ‘Samsun’ and ‘Samsun NN’: II. Changes in protein constitution after infection with tobacco mosaic virus. Virology 1970, 40, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loon, L.C.; Rep, M.; Pieterse, C.M. Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2006, 44, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fister, A.S.; Mejia, L.C.; Zhang, Y.; Herre, E.A.; Maximova, S.N.; Guiltinan, M.J. Theobroma cacao L. pathogenesis-related gene tandem array members show diverse expression dynamics in response to pathogen colonization. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 363. [Google Scholar]
- Manghwar, H.; Hussain, A.; Ullah, A.; Gul, S.; Shaban, M.; Khan, A.H.; Ali, M.; Sani, S.G.A.S.; Chaudhary, H.J.; Munis, M.F.H. Expression analysis of defense related genes in wheat and maize against Bipolaris sorokiniana. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 103, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlot, A.C.; Dempsey, D.A.; Ullah, A.; Gul, S.; Shaban, M.; Khan, A.H.; Ali, M.; Sani, S.G.A.S.; Chaudhary, H.J.; Munis, M.F.H. Salicylic Acid, a multifaceted hormone to combat disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Chen, Q.; Liu, C.H.; Lei, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wei, M.Q.; Guo, Z.R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, B.J.; et al. Fusarium graminearum FgCWM1 Encodes a Cell Wall Mannoprotein Conferring Sensitivity to Salicylic Acid and Virulence to Wheat. Toxins 2019, 11, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, L.; Rimbert, H.; Rodriguez, J.C.; Deal, K.R.; De Oliveira, R.; Choulet, F.; Keeble-Gagnère, G.; Tibbits, J.; Rogers, J.; et al. Optical maps refine the bread wheat Triticum aestivum cv. Chinese Spring genome assembly. Plant J. 2021, 107, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Lu, J.; Xing, J.; Xue, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L. Characterization and functional analyses of wheat TaPR1 genes in response to stripe rust fungal infection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, J.; Armengaud, P.; Giuntini, P.; Laval, V.; Milner, J.J. Inappropriate annotation of a key defence marker in Arabidopsis: Will the real PR-1 please stand up? Planta 2004, 219, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryals, J.; Lawton, K.A.; Delaney, T.P.; Friedrich, L.; Kessmann, H.; Neuenschwander, U.; Uknes, S.; Vernooij, B.; Weymann, K. Signal transduction in systemic acquired resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4202–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowling, S.A.; Clarke, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Klessig, D.F.; Dong, X. The cpr5 mutant of Arabidopsis expresses both NPR1-dependent and NPR1-independent resistance. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clarke, J.D.; Aarts, N.; Feys, B.J.; Dong, X.; Parker, J.E. Constitutive disease resistance requires EDS1 in the Arabidopsis mutants cpr1 and cpr6 and is partially EDS1-dependent in cpr5. Plant J. 2001, 26, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazebrook, J. Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritsch, C.; Muehlbauer, G.J.; Bushnell, W.R.; Somers, D.A.; Vance, C.P. Fungal Development and Induction of Defense Response Genes During Early Infection of Wheat Spikes by Fusarium graminearum. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2000, 13, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, D. Expression Profiles of Pathogenesis-Related Gene, TaLr35PR1, as it Relate to Lr35-Mediated Adult Plant Leaf Rust Resistance. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 34, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, J.E.; Sanchez, J.P.; Zumstein, K.; Gilchrist, D.G. Plant and animal PR1 family members inhibit programmed cell death and suppress bacterial pathogens in plant tissues. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 2111–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, P.; Rai, A.; Kumar, R.; Singh, M.; Sinha, B. Differential Expression of Pathogenesis Related Protein Genes in Tomato During Inoculation with A. Solani. J. Plant Pathol. Microb. 2014, 5, 217. [Google Scholar]
- Kazan, K.; Lyons, R. Intervention of Phytohormone Pathways by Pathogen Effectors. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2285–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrakh, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, X. Pathogenesis-related protein genes involved in race-specific all-stage resistance and non-race specific high-temperature adult-plant resistance to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in wheat. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2478–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhara, I.; Iwai, T.; Seo, S.; Yanagawa, Y.; Kawahigasi, H.; Hirose, S.; Ohkawa, Y.; Ohashi, Y. Characteristic expression of twelve rice PR1 family genes in response to pathogen infection, wounding, and defense-related signal compounds (121/180). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2008, 279, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Karim, H.; Li, Y.; Harwood, W.; Guzmán, C.; Lin, N.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Re-examination of the APETALA2/Ethylene-Responsive Factor Gene Family in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Indicates a Role in the Regulation of Starch Synthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 791584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Lu, S.; Anderson, J.B.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; DeWeese-Scott, C.; Fong, J.H.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; et al. CDD: A Conserved Domain Database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D225–D229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Ma, D.; Yin, J.; Yang, L.; He, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Tong, H.; Chen, L.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Characterization and Expression Profiling of Squamosa Promoter Binding Protein-Like (SBP) Transcription Factors in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Agronomy 2019, 9, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Luo, W.; Yang, C.; Ding, P.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, L.; Chang, Z.; Geng, H.; Wang, P.; et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the MADS-box gene family in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.-H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, T.; Yan, N.; Liu, Q.; Bai, T.; Gao, H.; Chen, J. Re-Examination Characterization and Screening of Stripe Rust Resistance Gene of Wheat TaPR1 Gene Family Based on the Transcriptome in Xinchun 32. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020640
Sun T, Yan N, Liu Q, Bai T, Gao H, Chen J. Re-Examination Characterization and Screening of Stripe Rust Resistance Gene of Wheat TaPR1 Gene Family Based on the Transcriptome in Xinchun 32. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020640
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Tingting, Niannian Yan, Qi Liu, Tingyu Bai, Haifeng Gao, and Jing Chen. 2025. "Re-Examination Characterization and Screening of Stripe Rust Resistance Gene of Wheat TaPR1 Gene Family Based on the Transcriptome in Xinchun 32" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020640
APA StyleSun, T., Yan, N., Liu, Q., Bai, T., Gao, H., & Chen, J. (2025). Re-Examination Characterization and Screening of Stripe Rust Resistance Gene of Wheat TaPR1 Gene Family Based on the Transcriptome in Xinchun 32. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020640






