Exploring CAR T-Cell Dynamics: Balancing Potent Cytotoxicity and Controlled Inflammation in CAR T-Cells Derived from Systemic Sclerosis and Myositis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
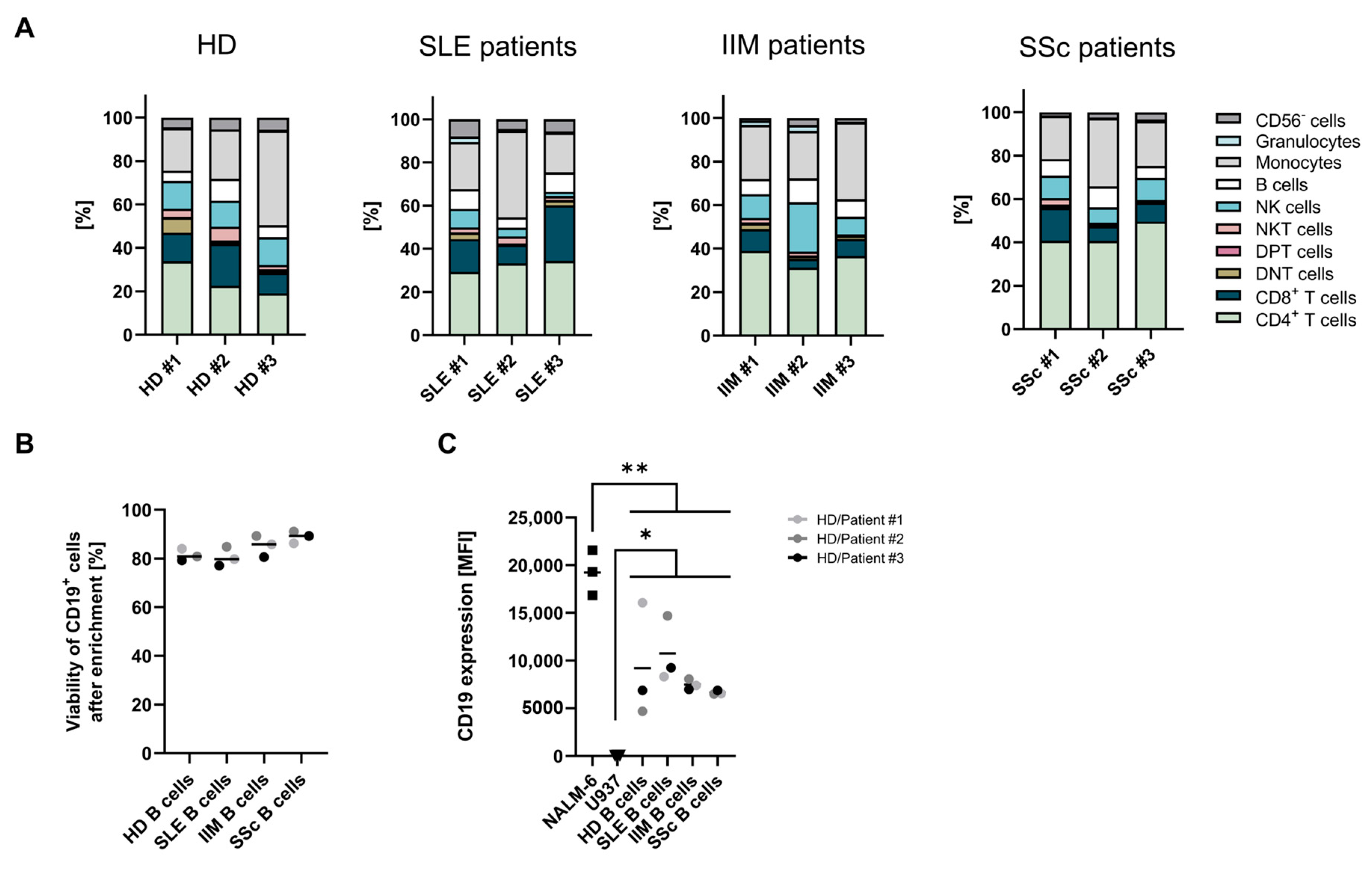
2.1. Starting Material and B-Cell Characterization
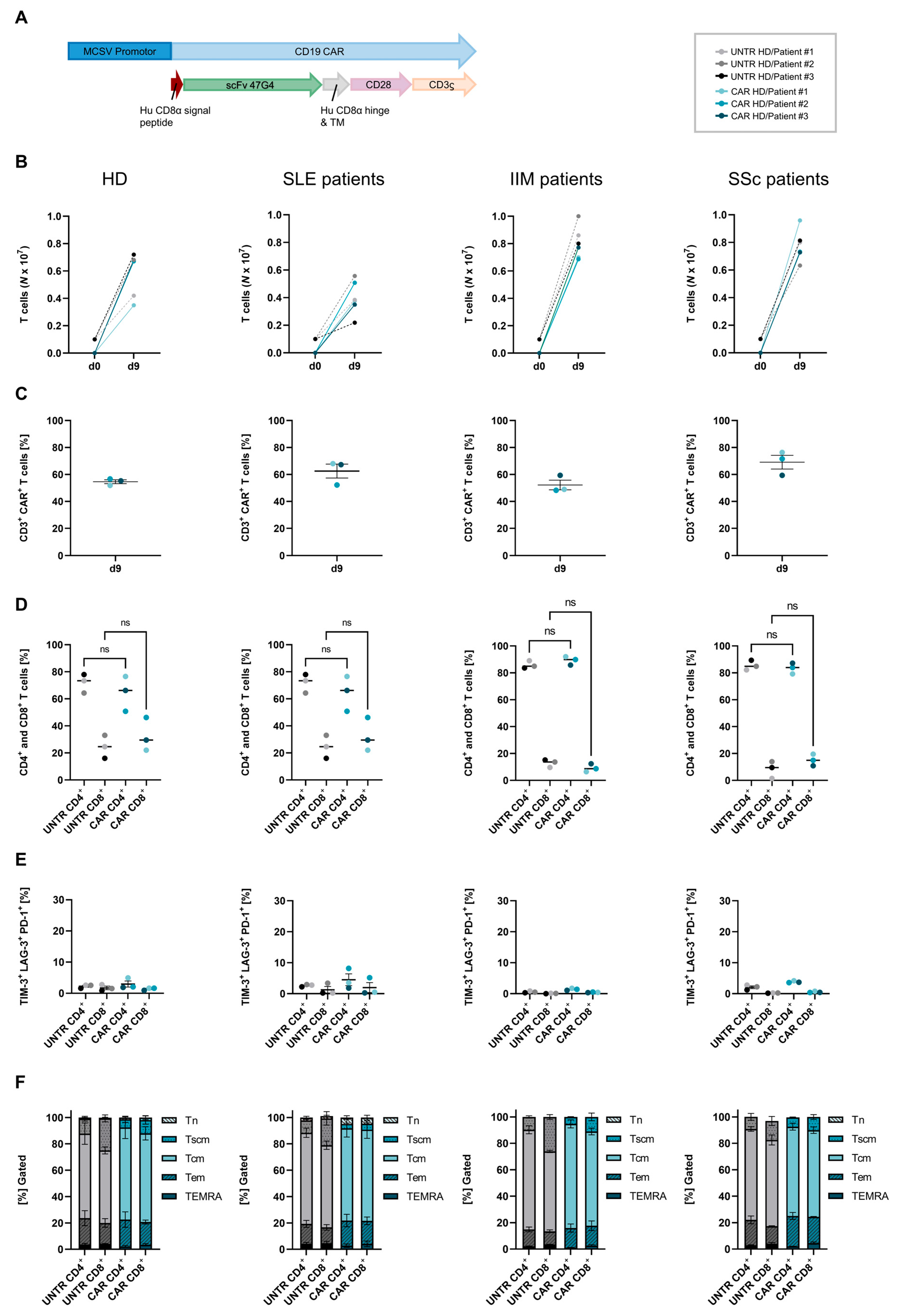
2.2. CAR T-Cell Manufacturing and Composition
2.3. Proliferation
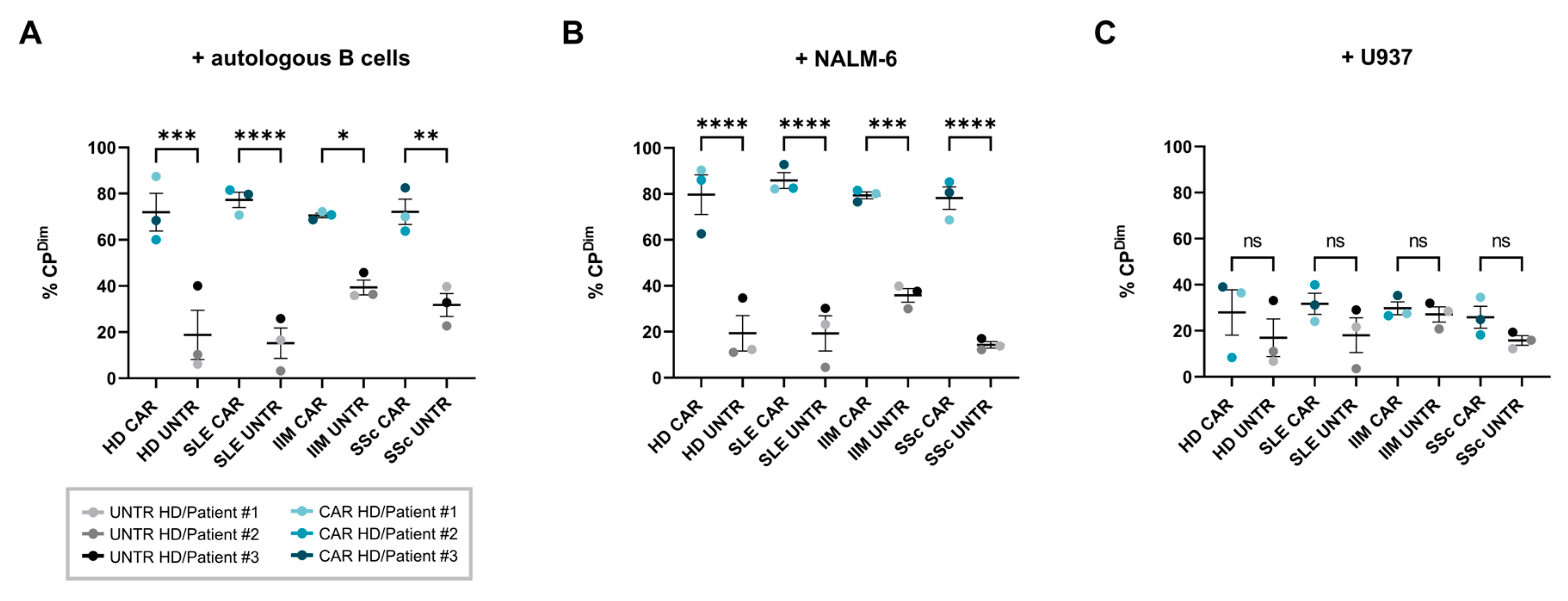
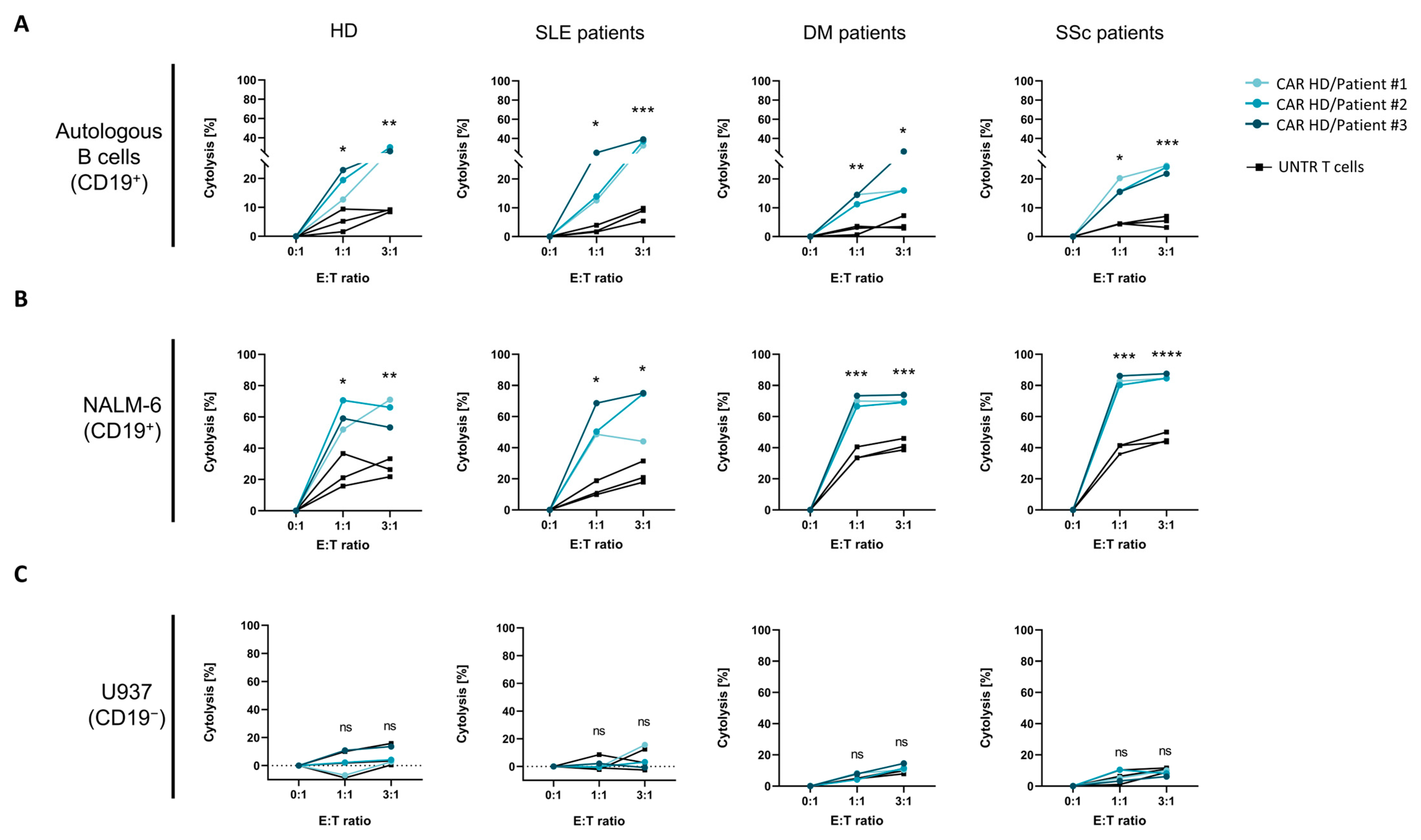
2.4. Cytotoxicity
2.5. Cytokine Release
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Material and Control Cell Lines
4.2. Description of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Vector
4.3. CAR T-Cell Generation
4.4. Flow Cytometric Analyses
4.5. B-Cell Isolation
4.6. Proliferation Assay
4.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
4.8. Cytokine Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- June, C.H.; O’Connor, R.S.; Kawalekar, O.U.; Ghassemi, S.; Milone, M.C. CAR T cell immunotherapy for human cancer. Science 2018, 359, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldini, C.R.; Ellis, G.I.; Riley, J.L. CAR T cells for infection, autoimmunity and allotransplantation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajanian, H.; Rurik, J.G.; Epstein, J.A. CAR-based therapies: Opportunities for immuno-medicine beyond cancer. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorner, T.; Furie, R. Novel paradigms in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 2019, 393, 2344–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, I.E.; Fujimoto, M.; Vencovsky, J.; Aggarwal, R.; Holmqvist, M.; Christopher-Stine, L.; Mammen, A.L.; Miller, F.W. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamburova, E.G.; Koenen, H.J.; Borgman, K.J.; ten Berge, I.J.; Joosten, I.; Hilbrands, L.B. A single dose of rituximab does not deplete B cells in secondary lymphoid organs but alters phenotype and function. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tur, C.; Eckstein, M.; Velden, J.; Rauber, S.; Bergmann, C.; Auth, J.; Bucci, L.; Corte, G.; Hagen, M.; Wirsching, A.; et al. CD19-CAR T-cell therapy induces deep tissue depletion of B cells. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 11, ard-2024-226142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, M.; Bornstein, G.G.; Suria, H. Biodistribution mechanisms of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies in health and disease. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szoor, A.; Toth, G.; Zsebik, B.; Szabo, V.; Eshhar, Z.; Abken, H.; Vereb, G. Trastuzumab derived HER2-specific CARs for the treatment of trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer: CAR T cells penetrate and eradicate tumors that are not accessible to antibodies. Cancer Lett. 2020, 484, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougiakakos, D.; Sengupta, R.; Gold, R.; Schroers, R.; Haghikia, A.; Lorente, M.; Pendleton, M.; Register, A.; Heesen, C.; Kroger, N.; et al. Successful generation of fully human, second generation, anti-CD19 CAR T cells for clinical use in patients with diverse autoimmune disorders. Cytotherapy 2024, in press. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingfelder, J.; Aigner, M.; Taubmann, J.; Minopoulou, I.; Park, S.; Kaplan, C.D.; Cheng, J.K.; Van Blarcom, T.; Schett, G.; Mackensen, A.; et al. Fully Human Anti-CD19 CAR T Cells Derived from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients Exhibit Cytotoxicity with Reduced Inflammatory Cytokine Production. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2024, 30, 582.e1–582.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmann, S.; Volkl, S.; Reimann, H.; Kronke, G.; Schett, G.; Achenbach, S.; Lutzny-Geier, G.; Muller, F.; Mougiakakos, D.; Dingfelder, J.; et al. Successful generation of CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells from patients with advanced Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Transplant. Cell Ther. 2023, 29, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougiakakos, D.; Kronke, G.; Volkl, S.; Kretschmann, S.; Aigner, M.; Kharboutli, S.; Boltz, S.; Manger, B.; Mackensen, A.; Schett, G. CD19-Targeted CAR T Cells in Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, F.; Boeltz, S.; Knitza, J.; Aigner, M.; Volkl, S.; Kharboutli, S.; Reimann, H.; Taubmann, J.; Kretschmann, S.; Rosler, W.; et al. CD19-targeted CAR T cells in refractory antisynthetase syndrome. Lancet 2023, 401, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecher, A.C.; Hensen, L.; Klein, R.; Schairer, R.; Lutz, K.; Atar, D.; Seitz, C.; Stanger, A.; Schneider, J.; Braun, C.; et al. CD19-Targeting CAR T Cells for Myositis and Interstitial Lung Disease Associated With Antisynthetase Syndrome. JAMA 2023, 329, 2154–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, C.; Muller, F.; Distler, J.H.W.; Gyorfi, A.H.; Volkl, S.; Aigner, M.; Kretschmann, S.; Reimann, H.; Harrer, T.; Bayerl, N.; et al. Treatment of a patient with severe systemic sclerosis (SSc) using CD19-targeted CAR T cells. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, J.; Nunez, D.; Mozaffar, T.; Stadanlick, J.; Werner, M.; Vorndran, Z.; Ellis, A.; Williams, J.; Cicarelli, J.; Lam, Q.; et al. Case study of CD19 CAR T therapy in a subject with immune-mediate necrotizing myopathy treated in the RESET-Myositis phase I/II trial. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 3821–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taubmann, J.; Knitza, J.; Muller, F.; Volkl, S.; Aigner, M.; Kleyer, A.; Gary, R.; Kretschmann, S.; Boeltz, S.; Atzinger, A.; et al. Rescue therapy of antisynthetase syndrome with CD19-targeted CAR-T cells after failure of several B-cell depleting antibodies. Rheumatology 2024, 63, e12–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghikia, A.; Hegelmaier, T.; Wolleschak, D.; Bottcher, M.; Pappa, V.; Motte, J.; Borie, D.; Gold, R.; Feist, E.; Schett, G.; et al. Clinical efficacy and autoantibody seroconversion with CD19-CAR T cell therapy in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and coexisting myasthenia gravis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 1597–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolai, R.; Merli, P.; Moran Alvarez, P.; Bracaglia, C.; Del Bufalo, F.; Marasco, E.; Caiello, I.; Prencipe, G.; Algeri, M.; Cefalo, M.G.; et al. Autologous CD19-Targeting CAR T Cells in a Patient With Refractory Juvenile Dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faissner, S.; Motte, J.; Sgodzai, M.; Geis, C.; Haghikia, A.; Mougiakakos, D.; Borie, D.; Schroers, R.; Gold, R. Successful use of anti-CD19 CAR T cells in severe treatment-refractory stiff-person syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2403227121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackensen, A.; Muller, F.; Mougiakakos, D.; Boltz, S.; Wilhelm, A.; Aigner, M.; Volkl, S.; Simon, D.; Kleyer, A.; Munoz, L.; et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, F.; Taubmann, J.; Bucci, L.; Wilhelm, A.; Bergmann, C.; Volkl, S.; Aigner, M.; Rothe, T.; Minopoulou, I.; Tur, C.; et al. CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy in Autoimmune Disease—A Case Series with Follow-Up. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabanza, L.; Pegues, M.; Geldres, C.; Shi, V.; Wiltzius, J.J.W.; Sievers, S.A.; Yang, S.; Kochenderfer, J.N. Function of Novel Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptors with Human Variable Regions Is Affected by Hinge and Transmembrane Domains. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 2452–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudno, J.N.; Lam, N.; Vanasse, D.; Shen, Y.W.; Rose, J.J.; Rossi, J.; Xue, A.; Bot, A.; Scholler, N.; Mikkilineni, L.; et al. Safety and feasibility of anti-CD19 CAR T cells with fully human binding domains in patients with B-cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghikia, A.; Hegelmaier, T.; Wolleschak, D.; Bottcher, M.; Desel, C.; Borie, D.; Motte, J.; Schett, G.; Schroers, R.; Gold, R.; et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T cells for refractory myasthenia gravis. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 1104–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischbach, F.; Richter, J.; Pfeffer, L.K.; Fehse, B.; Berger, S.C.; Reinhardt, S.; Kuhle, J.; Badbaran, A.; Rathje, K.; Gagelmann, N.; et al. CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in two patients with multiple sclerosis. Med 2024, 5, 550–558.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auth, J.; Muller, F.; Volkl, S.; Bayerl, N.; Distler, J.H.W.; Tur, C.; Raimondo, M.G.; Chenguiti Fakhouri, S.; Atzinger, A.; Coppers, B.; et al. CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy in patients with diffuse systemic sclerosis: A case series. Lancet Rheumatol. 2024, 11, S2665-9913(24)00282-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Santomasso, B.D.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Turtle, C.J.; Brudno, J.N.; Maus, M.V.; Park, J.H.; Mead, E.; Pavletic, S.; et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.J.; June, C.H. CAR T therapy extends its reach to autoimmune diseases. Cell 2022, 185, 4471–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patient | Diagnosis | Age (Years) | Sex (F/M) | Disease Duration (Years) | Organ Involvement | Treatments (CT/PT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus | ||||||
| SLE P#1 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | 23 | F | 2 | Skin, Joints, Lungs | CT: Hydroxychloroquine, Prednisolone, Anifrolumab |
| SLE P#2 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | 48 | F | 1 | Skin, Heart, Kidney (class III) | CT: Hydroxychloroquine, MMF, Marcumar PT: Prednisolone, Belimumab, Deucravacitinib |
| SLE P#3 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | 39 | F | 9 | Skin, Joints, HEM, Kidney (class IV) | CT: Quensyl, Azathioprine Prednisolone PT: Belimumab, Cyclophosphamide, Anifrolumab, Myfortic |
| Patients with systemic sclerosis | ||||||
| SSc P#1 | Systemic sclerosis | 69 | F | 5 | Skin, Raynaud, Esophagus, Lungs | CT: MMF |
| SSc P#2 | Systemic sclerosis | 68 | F | 3 | Skin, Raynaud, Esophagus, Lungs | CT: MMF |
| SSc P#3 | Systemic sclerosis | 66 | F | 12 | Skin, Joints, Lungs | CT: MMF, Nintedanib, Bosentan |
| Patients with idiopathic inflammatory myositis | ||||||
| IIM P#1 | Dermatomyositis (JO-1+) | 48 | F | 6 | Skin, Raynaud, Myositis, Fascitis, Lungs | CT: Filgotinib, MTX PT: MTX, Rituximab, Azathioprin, Prednisolone |
| IIM P#2 | Dermatomyositis (JO-1+) | 60 | M | 4 | Skin, Raynaud, Esophagus, Lungs | CT: MMF PT: Prednisolone, MMF |
| IIM P#3 | Dermatomyositis (JO-1+) | 52 | F | 5 | Skin, Raynaud, Joints, Lungs | CT: Nintedanib, Sildenafil, Hydroxychloroquine PT: MMF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dingfelder, J.; Taubmann, J.; von Heydebrand, F.; Aigner, M.; Bergmann, C.; Knitza, J.; Park, S.; Cheng, J.K.; Van Blarcom, T.; Schett, G.; et al. Exploring CAR T-Cell Dynamics: Balancing Potent Cytotoxicity and Controlled Inflammation in CAR T-Cells Derived from Systemic Sclerosis and Myositis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020467
Dingfelder J, Taubmann J, von Heydebrand F, Aigner M, Bergmann C, Knitza J, Park S, Cheng JK, Van Blarcom T, Schett G, et al. Exploring CAR T-Cell Dynamics: Balancing Potent Cytotoxicity and Controlled Inflammation in CAR T-Cells Derived from Systemic Sclerosis and Myositis Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020467
Chicago/Turabian StyleDingfelder, Janin, Jule Taubmann, Franziska von Heydebrand, Michael Aigner, Christina Bergmann, Johannes Knitza, Soo Park, Joseph K. Cheng, Thomas Van Blarcom, Georg Schett, and et al. 2025. "Exploring CAR T-Cell Dynamics: Balancing Potent Cytotoxicity and Controlled Inflammation in CAR T-Cells Derived from Systemic Sclerosis and Myositis Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020467
APA StyleDingfelder, J., Taubmann, J., von Heydebrand, F., Aigner, M., Bergmann, C., Knitza, J., Park, S., Cheng, J. K., Van Blarcom, T., Schett, G., Mackensen, A., & Lutzny-Geier, G. (2025). Exploring CAR T-Cell Dynamics: Balancing Potent Cytotoxicity and Controlled Inflammation in CAR T-Cells Derived from Systemic Sclerosis and Myositis Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020467






