Human Induced Lung Organoids: A Promising Tool for Cystic Fibrosis Drug Screening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
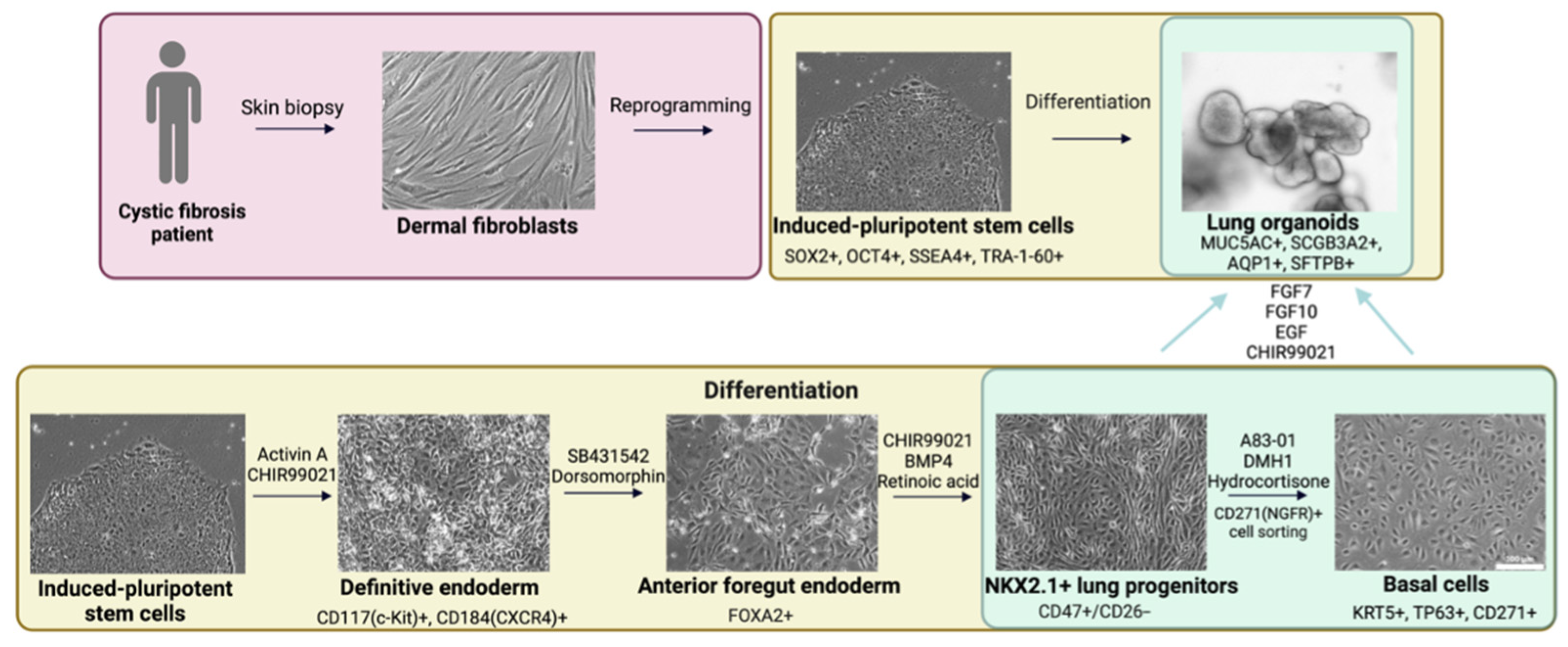
2.1. Derivation of Cell Cultures
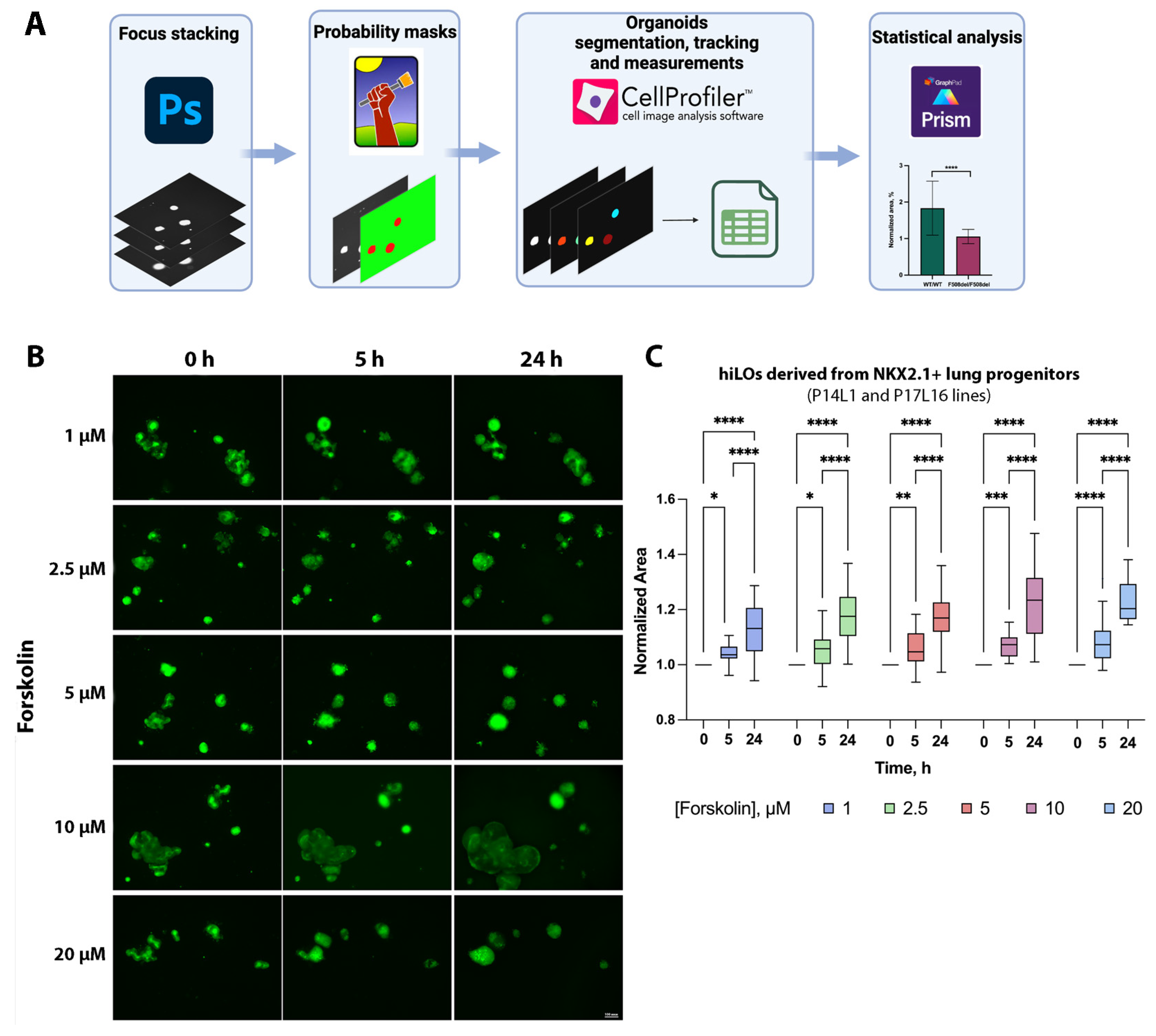
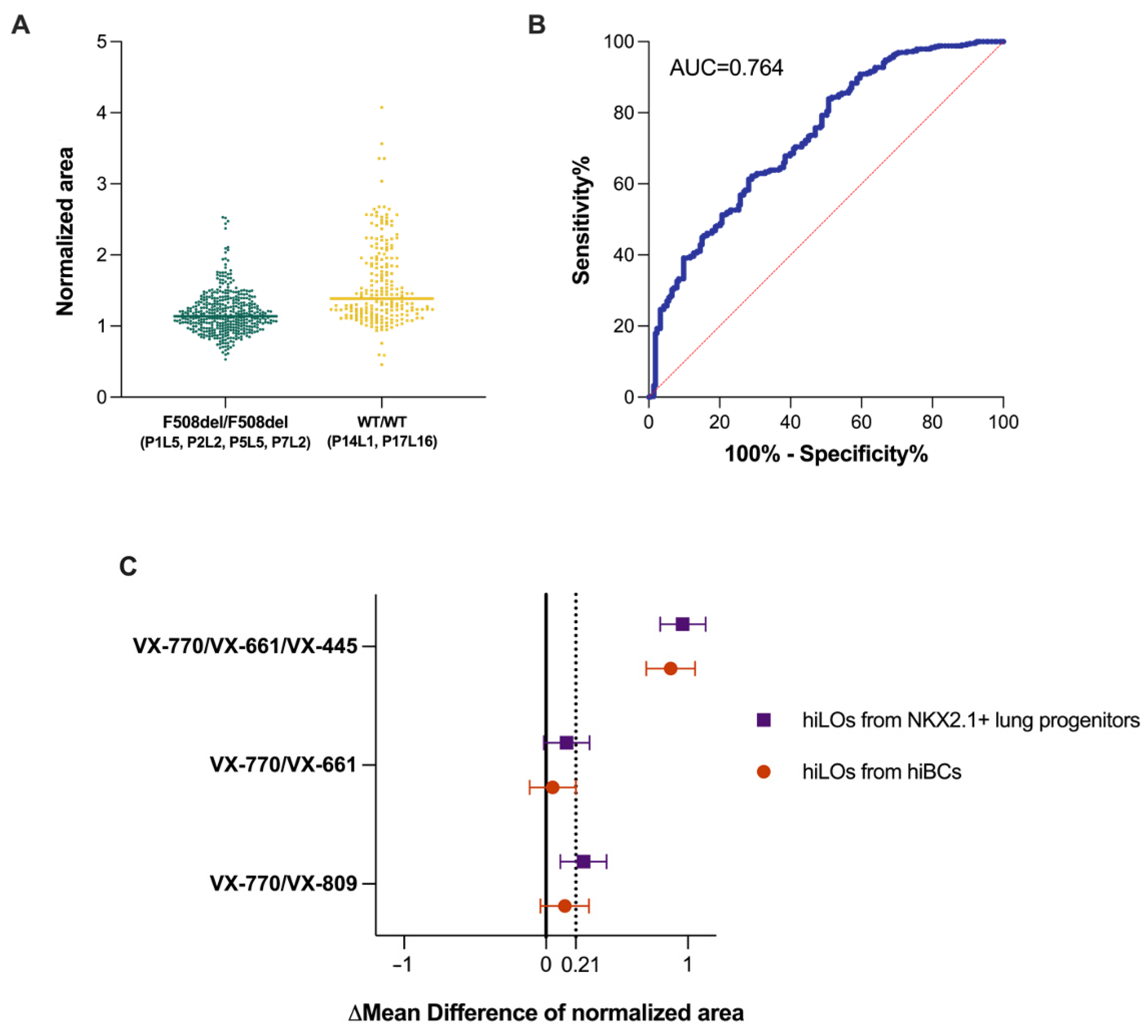
2.2. FIS Assay on Non-CF hiLOs
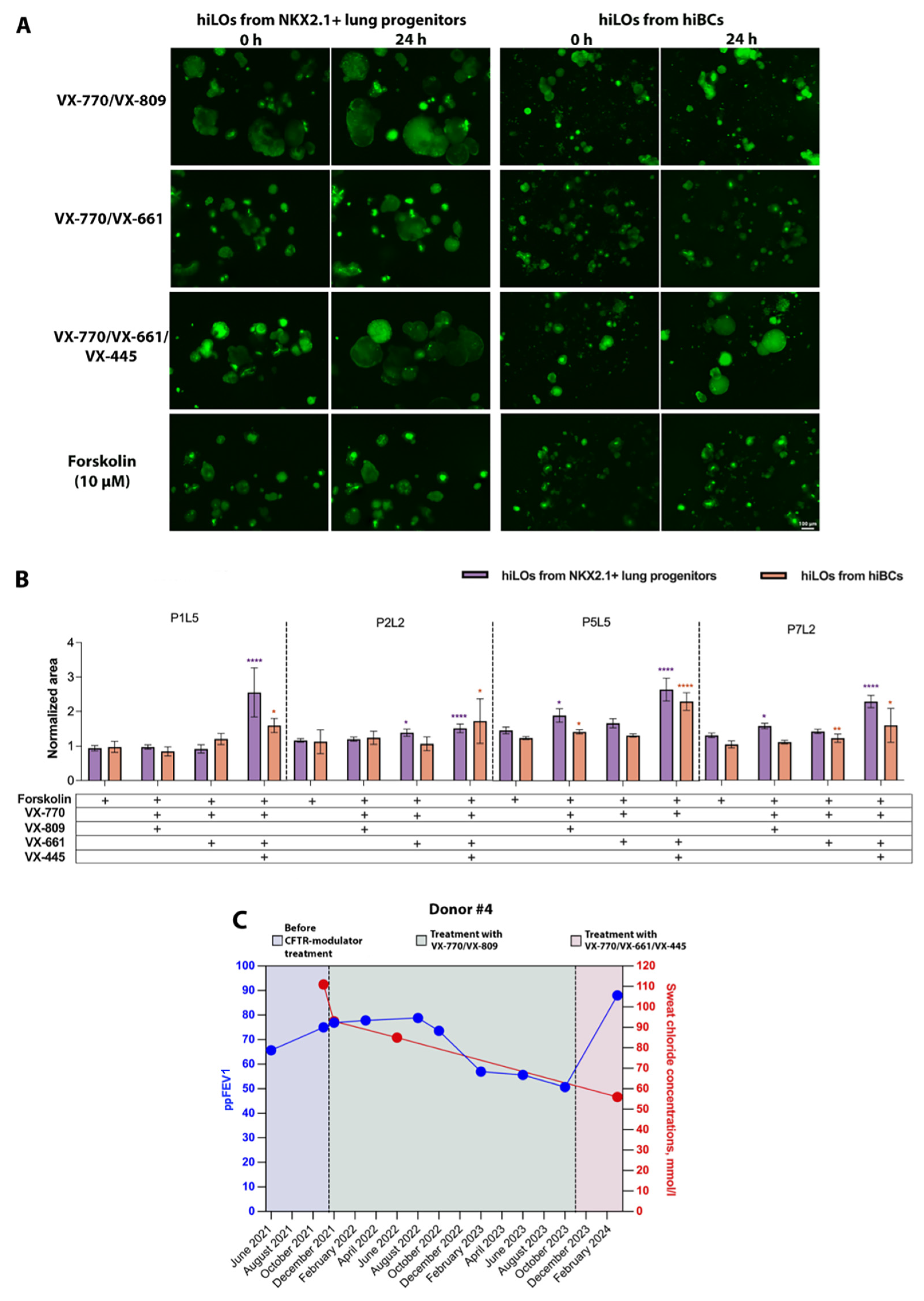
2.3. FIS Assay with Modulators on CF hiLOs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. FIS Assay of hiLOs
4.4. Statistical Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Boeck, K. Cystic fibrosis in the year 2020: A disease with a new face. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinha, C.M.; Callebaut, I. Molecular mechanisms of cystic fibrosis-how mutations lead to misfunction and guide therapy. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20212006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaques, R.; Shakeel, A.; Hoyle, C. Novel therapeutic approaches for the management of cystic fibrosis. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2020, 15, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajac, I.; Sermet, I. Therapeutic approaches for patients with cystic fibrosis not eligible for current CFTR modulators. Cells 2021, 10, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Goor, F.; Yu, H.; Burton, B.; Hoffman, B.J. Effect of ivacaftor on CFTR forms with missense mutations associated with defects in protein processing or function. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2014, 13, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gecili, E.; Su, W.; Brokamp, C.; Andrinopoulou, E.-R.; III, F.J.L.; Pestian, T.; Clancy, J.P.; Solomon, G.M.; Brewington, J.J.; Szczesniak, R.D. Rapid cystic fibrosis lung-function decline and in-vitro CFTR modulation. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, e69–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, J.F.; Berkers, G.; Kruisselbrink, E.; Vonk, A.; de Jonge, H.R.; Janssens, H.M.; Bronsveld, I.; van de Graaf, E.A.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E.S.; Houwen, R.H.J.; et al. Characterizing responses to CFTR-modulating drugs using rectal organoids derived from subjects with cystic fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 344ra84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcios, N.L. Cystic fibrosis lung disease: An overview. Respir. Care 2019, 65, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.; Rao, M.S. A review of the methods for human iPSC derivation. In Pluripotent Stem Cells: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Li, Q.; Shu, Y.; Wang, H.; Thomas, B.; Maxwell, J.T.; Zhang, Y. Exploiting urine-derived induced pluripotent stem cells for advancing precision medicine in cell therapy, disease modeling, and drug testing. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 31, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boj, S.F.; Vonk, A.M.; Statia, M.; Su, J.; Dekkers, J.F.; Vries, R.R.; Beekman, J.M.; Clevers, H. Forskolin-induced Swelling in Intestinal Organoids: An In Vitro Assay for Assessing Drug Response in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 120, 55159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, J.F.; Wiegerinck, C.L.; De Jonge, H.R.; Bronsveld, I.; Janssens, H.M.; De Winter-de Groot, K.M.; Brandsma, A.M.; de Jong, N.W.; Bijvelds, M.J.; Scholte, B.J.; et al. A functional CFTR assay using primary cystic fibrosis intestinal organoids. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laselva, O.; Conese, M. Three-Dimensional Airway Spheroids and Organoids for Cystic Fibrosis Research. J. Respir. 2021, 1, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, V.M.; Schulzke, J.-D.; Seidler, U.E. Chapter 58—Ion Channels of the Gastrointestinal Epithelial Cells. In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract, 6th ed.; Said, H.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 1363–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Zomer-van Ommen, D.D.; de Poel, E.; Kruisselbrink, E.; Oppelaar, H.; Vonk, A.M.; Janssens, H.M.; van der Ent, C.K.; Hagemeijer, M.C.; Beekman, J.M. Comparison of ex vivo and in vitro intestinal cystic fibrosis models to measure CFTR-dependent ion channel activity. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2018, 17, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, J.P.; Cotton, C.U.; Donaldson, S.H.; Solomon, G.M.; VanDevanter, D.R.; Boyle, M.P.; Gentzsch, M.; Nick, J.A.; Illek, B.; Wallenburg, J.C.; et al. CFTR modulator theratyping: Current status, gaps and future directions. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2019, 18, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Anderson, J.D.; Deng, L.; Mackay, S.; Bailey, J.; Kersh, L.; Rowe, S.M.; Guimbellot, J.S. Human Nasal Epithelial Organoids for Therapeutic Development in Cystic Fibrosis. Genes 2020, 11, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, N.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Zomer-van Ommen, D.D.; Heo, I.; Böttinger, L.; Klay, D.; Weeber, F.; Huelsz-Prince, G.; Iakobachvili, N.; Amatngalim, G.D.; et al. Long-term expanding human airway organoids for disease modeling. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sette, G.; Cicero, S.L.; Blaconà, G.; Pierandrei, S.; Bruno, S.M.; Salvati, V.; Castelli, G.; Falchi, M.; Fabrizzi, B.; Cimino, G.; et al. Theratyping cystic fibrosis in vitro in ALI culture and organoid models generated from patient-derived nasal epithelial conditionally reprogrammed stem cells. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2100908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berical, A.; Lee, R.E.; Lu, J.; Beermann, M.L.; Le Suer, J.A.; Mithal, A.; Thomas, D.; Ranallo, N.; Peasley, M.; Stuffer, A.; et al. A multimodal iPSC platform for cystic fibrosis drug testing. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huch, M.; Koo, B.-K. Modeling mouse and human development using organoid cultures. Development 2015, 142, 3113–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, A.A.; Sinha, I.P.; Southern, K.W. Ataluren and similar compounds (specific therapies for premature termination codon class I mutations) for cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchenko, A.; Kondrateva, E.; Tabakov, V.; Efremova, A.; Salikhova, D.; Bukharova, T.; Goldshtein, D.; Balyasin, M.; Bulatenko, N.; Amelina, E.; et al. Airway and Lung Organoids from Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Can Be Used to Assess CFTR Conductance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, F.J.; Suzuki, S.; Beermann, M.L.; Barillà, C.; Wang, R.; Villacorta-Martin, C.; Berical, A.; Jean, J.; Le Suer, J.; Matte, T.; et al. Derivation of airway basal stem cells from human pluripotent stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 28, 79–95.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchenko, A.; Belova, L.; Balyasin, M.; Kochergin-Nikitsky, K.; Kondrateva, E.; Voronina, E.; Pozhitnova, V.; Tabakov, V.; Salikhova, D.; Bukharova, T.; et al. Airway basal cells from human-induced pluripotent stem cells: A new frontier in cystic fibrosis research. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1336392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalho, A.S.; Fürstová, E.; Vonk, A.M.; Ferrante, M.; Verfaillie, C.; Dupont, L.; Boon, M.; Proesmans, M.; Beekman, J.M.; Sarouk, I.; et al. Correction of CFTR function in intestinal organoids to guide treatment of cystic fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 57, 1902426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, K.B.; Hawkins, F.; Serra, M.; Thomas, D.C.; Jacob, A.; Kotton, D.N. Efficient Derivation of Functional Human Airway Epithelium from Pluripotent Stem Cells via Temporal Regulation of Wnt Signaling. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 20, 844–857.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awatade, N.T.; Wong, S.L.; Hewson, C.K.; Fawcett, L.K.; Kicic, A.; Jaffe, A.; Waters, S.A. Human Primary Epithelial Cell Models: Promising Tools in the Era of Cystic Fibrosis Personalized Medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondratyeva, E.; Efremova, A.; Melyanovskaya, Y.; Voronkova, A.; Polyakov, A.; Bulatenko, N.; Adyan, T.; Sherman, V.; Kovalskaia, V.; Petrova, N.; et al. Evaluation of the complex p.[Leu467Phe; Phe508del] CFTR allele in the intestinal organoids model: Implications for therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondo, E.; Cresta, F.; Pastorino, C.; Tomati, V.; Capurro, V.; Pesce, E.; Lena, M.; Iacomino, M.; Baffico, A.M.; Coviello, D.; et al. The L467F-F508del complex allele hampers pharmacological rescue of mutant CFTR by elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor in cystic fibrosis patients: The value of the ex vivo nasal epithelial model to address nonresponders to CFTR-modulating drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahm, F.S. Receiver operating characteristic curve: Overview and practical use for clinicians. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2022, 75, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Mourik, P.; Beekman, J.M.; van der Ent, C.K. Intestinal organoids to model cystic fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1802379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, J.R.; Onaitis, M.W.; Rawlins, E.L.; Lu, Y.; Clark, C.P.; Xue, Y.; Randell, S.H.; Hogan, B.L. Basal cells as stem cells of the mouse trachea and human airway epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12771–12775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djidrovski, I.; Georgiou, M.; Hughes, G.L.; Patterson, E.I.; Casas-Sanchez, A.; Pennington, S.H.; Biagini, G.A.; Moya-Molina, M.; Bor, J.; Smit, M.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects an upper airway model derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 2021, 39, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, S.M.; Daines, C.; Ringshausen, F.C.; Kerem, E.; Wilson, J.; Tullis, E.; Nair, N.; Simard, C.; Han, L.; Ingenito, E.P.; et al. Tezacaftor–ivacaftor in residual-function heterozygotes with cystic fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2024–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, C.E.; Elborn, J.S.; Ramsey, B.W.; Marigowda, G.; Huang, X.; Cipolli, M.; Colombo, C.; Davies, J.C.; De Boeck, K.; Flume, P.A.; et al. Lumacaftor–Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Homozygous for Phe508del CFTR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tice, J.A.; Kuntz, K.M.; Wherry, K.; Seidner, M.; Rind, D.M.; Pearson, S.D. The effectiveness and value of novel treatments for cystic fibrosis. J. Manag. Care Spéc. Pharm. 2021, 27, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkers, G.; van Mourik, P.; Vonk, A.M.; Kruisselbrink, E.; Dekkers, J.F.; Groot, K.M.d.W.-D.; Arets, H.G.; der Wilt, R.E.M.-V.; Dijkema, J.S.; Vanderschuren, M.M.; et al. Rectal organoids enable personalized treatment of cystic fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1701–1708.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, A.; Sherman, V.; Melyanovskaya, Y.; Mokrousova, D.; Krasnova, M.; Bulatenko, N.; Bukharova, T.; Makhnach, O.; Alimov, A.; Goldshtein, D.; et al. Personalized assessment of the effectiveness of targeted drugs for the treatment of cystic fibrosis in a patient with c.264_268delATATT and c.3139+1G>C rare variants of the CFTR gene. Genes Cells 2024, 19, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierlaagh, M.C.; Ramalho, A.S.; Silva, I.A.; Vonk, A.M.; Bor, R.M.v.D.; van Mourik, P.; Pott, J.; Suen, S.W.; Boj, S.F.; Vries, R.G.; et al. Repeatability and reproducibility of the Forskolin-induced swelling (FIS) assay on intestinal organoids from people with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2024, 23, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacalhau, M.; Camargo, M.; Lopes-Pacheco, M. Laboratory tools to predict CFTR modulator therapy effectiveness and to monitor disease severity in cystic fibrosis. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elviro, C.F.; Blanchon, S.; Hoehnel, S.; Schumacher, U.; Sauty, A.; Brandenberg, N.; Regamey, N. Diagnostic tools and CFTR functional assays in cystic fibrosis: Utility and availability in Switzerland. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2021, 151, w20496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muilwijk, D.; de Poel, E.; van Mourik, P.; Suen, S.W.; Vonk, A.M.; Brunsveld, J.E.; Kruisselbrink, E.; Oppelaar, H.; Hagemeijer, M.C.; Berkers, G.; et al. Forskolin-induced organoid swelling is associated with long-term cystic fibrosis disease progression. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2100508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatngalim, G.D.; Rodenburg, L.W.; Aalbers, B.L.; Raeven, H.H.; Aarts, E.M.; Sarhane, D.; Spelier, S.; Lefferts, J.W.; AL Silva, I.; Nijenhuis, W.; et al. Measuring cystic fibrosis drug responses in organoids derived from 2D differentiated nasal epithelia. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202101320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondrateva, E.; Demchenko, A.; Slesarenko, Y.; Pozhitnova, V.; Yasinovsky, M.; Amelina, E.; Tabakov, V.; Voronina, E.; Lavrov, A.; Smirnikhina, S. Generation of two induced pluripotent stem cell lines (RCMGi004-A and -B) from human skin fibroblasts of a cystic fibrosis patient with compound heterozygous F508del/W1282X mutations in CFTR gene. Stem Cell Res. 2021, 52, 102232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondrateva, E.; Adilgereeva, E.; Amelina, E.; Tabakov, V.; Demchenko, A.; Ustinov, K.; Yasinovsky, M.; Voronina, E.; Lavrov, A.; Smirnikhina, S. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cell line (RCMGi001-A) from human skin fibroblasts of a cystic fibrosis patient with p.F508del mutation. Stem Cell Res. 2020, 48, 101933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchuk, I.; Kondrateva, E.; Demchenko, A.; Grigorieva, O.; Erofeeva, A.; Amelina, E.; Tabakov, V.; Orlova, M.; Voronina, E.; Pozhitnova, V.; et al. Generation of two induced pluripotent stem cell lines (RCMGi005-A/B) from human skin fibroblasts of a cystic fibrosis patient with homozygous F508del mutation in CFTR gene. Stem Cell Res. 2022, 64, 102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondrateva, E.; Demchenko, A.; Slesarenko, Y.; Yasinovsky, M.; Amelina, E.; Tabakov, V.; Voronina, E.; Lavrov, A.; Smirnikhina, S. Derivation of iPSC line (RCMGi002-A) from dermal fibroblasts of a cystic fibrosis female patient with homozygous F508del mutation. Stem Cell Res. 2021, 53, 102251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, A.E.; Jones, T.R.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Clarke, C.; Kang, I.H.; Friman, O.; Guertin, D.A.; Chang, J.H.; Lindquist, R.A.; Moffat, J.; et al. CellProfiler: Image analysis software for identifying and quantifying cell phenotypes. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, S.; Kutra, D.; Kroeger, T.; Straehle, C.N.; Kausler, B.X.; Haubold, C.; Schiegg, M.; Ales, J.; Beier, T.; Rudy, M.; et al. Ilastik: Interactive machine learning for (bio) image analysis. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Donor | Age (Years, Taking Clinical Characteristics) | Age (Years, Sampling Skin Biopsy) | Sex | CFTR Genotype | SCC, mmol/L (Method) | ppFEV1 | Microbiology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 28 | 27 | M | F508del/ F508del | 66 (Gibson) | 24 | SA AX MA |
| 2 | 3 for SCC 26 for ppFEV1 | 20 | M | F508del/ F508del | 75 (Gibson) | 58 | PA AF |
| 3 | 33 | 29 | M | F508del/ F508del | 82 (Nanoduct) | 20.8 | BC |
| 4 | 26 | 22 | F | F508del/ F508del | 111 (Nanoduct) | 75 | SA CA KO |
| 5 | - | 14 | M | WT/WT | - | - | - |
| 6 | - | 7 | F | WT/WT | - | - | - |
| Donor | Cell Line | CFTR Genotype | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P1L5 | F508del/F508del | [46] |
| 2 | P2L2 | F508del/F508del | https://hpscreg.eu/cell-line/RCMGi013-A, accessed on 5 December 2024 |
| 3 | P5L5 | F508del/F508del | [47] |
| 4 | P7L2 | F508del/F508del | [48] |
| 5 | P14L1 | WT/WT | https://hpscreg.eu/cell-line/RCMGi014-A, accessed on 5 December 2024 |
| 6 | P17L16 | WT/WT | https://hpscreg.eu/cell-line/RCMGi016-A, accessed on 5 December 2024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demchenko, A.; Balyasin, M.; Nazarova, A.; Grigorieva, O.; Panchuk, I.; Kondrateva, E.; Tabakov, V.; Schagina, O.; Amelina, E.; Smirnikhina, S. Human Induced Lung Organoids: A Promising Tool for Cystic Fibrosis Drug Screening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020437
Demchenko A, Balyasin M, Nazarova A, Grigorieva O, Panchuk I, Kondrateva E, Tabakov V, Schagina O, Amelina E, Smirnikhina S. Human Induced Lung Organoids: A Promising Tool for Cystic Fibrosis Drug Screening. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(2):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020437
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemchenko, Anna, Maxim Balyasin, Aleksandra Nazarova, Olga Grigorieva, Irina Panchuk, Ekaterina Kondrateva, Vyacheslav Tabakov, Olga Schagina, Elena Amelina, and Svetlana Smirnikhina. 2025. "Human Induced Lung Organoids: A Promising Tool for Cystic Fibrosis Drug Screening" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 2: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020437
APA StyleDemchenko, A., Balyasin, M., Nazarova, A., Grigorieva, O., Panchuk, I., Kondrateva, E., Tabakov, V., Schagina, O., Amelina, E., & Smirnikhina, S. (2025). Human Induced Lung Organoids: A Promising Tool for Cystic Fibrosis Drug Screening. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(2), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26020437







