Copper Dysregulation in Major Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analytic Evidence for a Putative Trait Marker
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
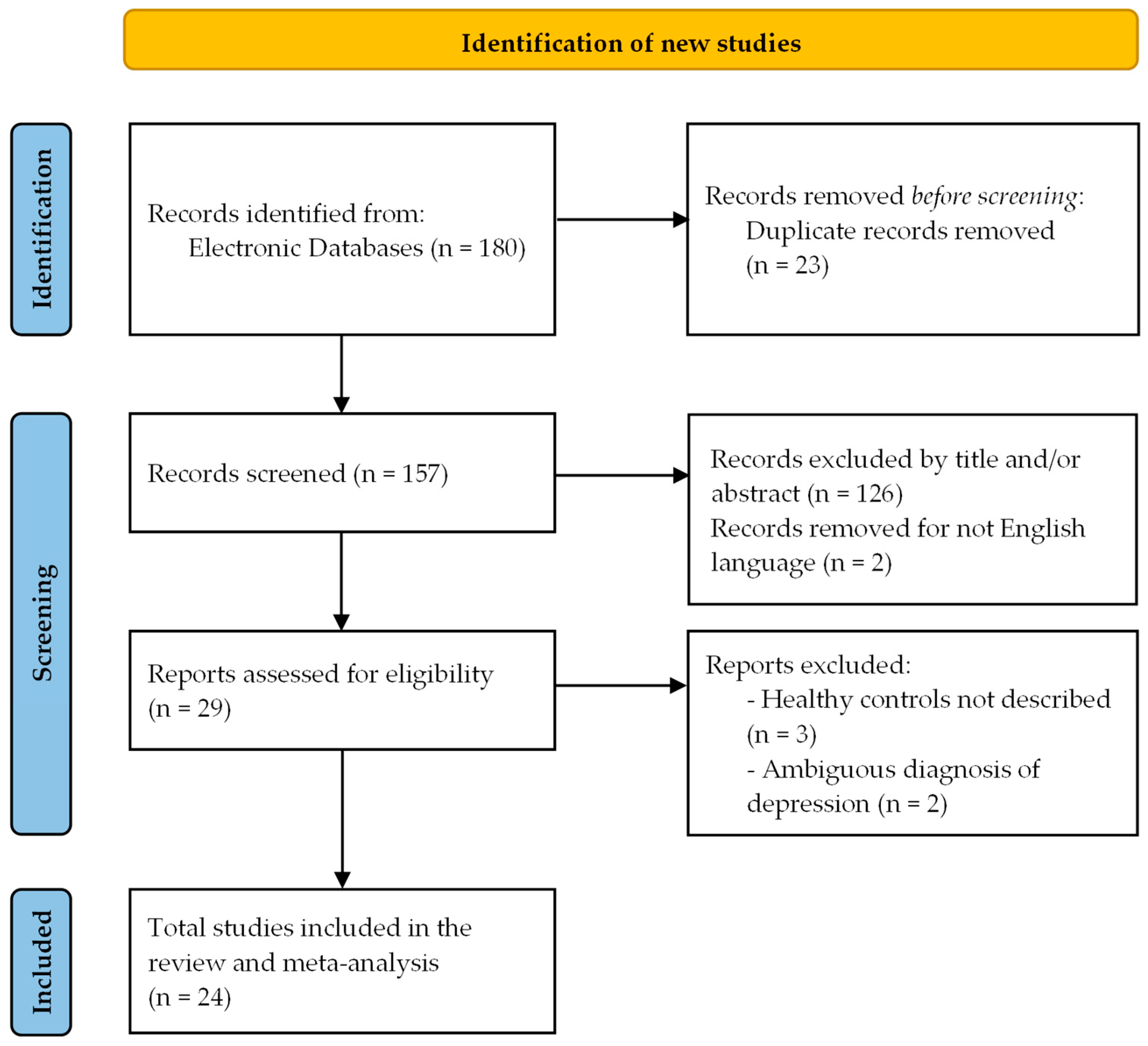
2.1. Prisma Guidelines
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.4. Selection of Studies
2.5. Data Extraction and Management
2.6. Assessment of Risk of Bias in Included Studies
- -
- Good quality with 3 or 4 stars in the selection domain AND 1 or 2 stars in the comparability domain AND 2 or 3 stars in the outcome/exposure domain;
- -
- Fair quality with 2 stars in the selection domain AND 1 or 2 stars in the comparability domain AND 2 or 3 stars in the outcome/exposure domain;
- -
- Poor quality with 0 or 1 star in the selection domain OR 0 stars in the comparability domain OR 0 or 1 stars in the outcome/exposure domain.
2.7. Effect Measures
2.8. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
2.9. Sensitivity Analyses
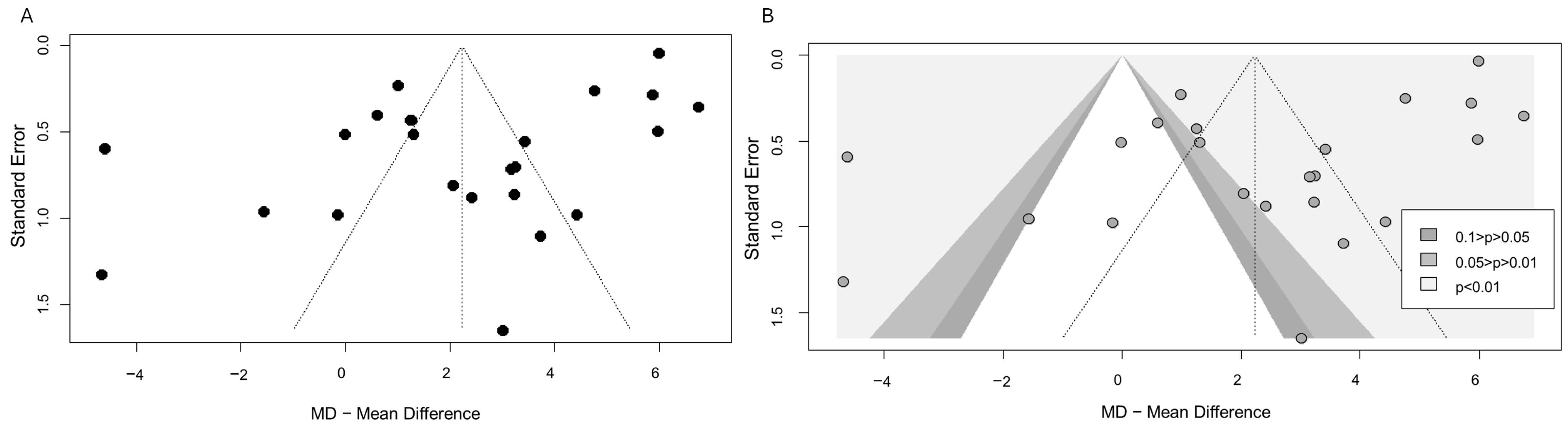
2.10. Publication Bias
3. Results
3.1. Selection and Characteristics of the Studies
| Study | Country | Sample Size | Gender F (%) | Age [Years (SD)] | Cu [µmol/L (SD)] | Diagnostic Criteria | Biological Matrix | Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author (Year) | MDD | CTRL | MDD | CTRL | MDD | CTRL | MDD | CTRL | ||||
| Manser 1989 [34] | Pakistan | 31 | 62 | 51.6 | 46.8 | NA | NA | 17.9 (3.7) | 14.7 (1.8) | NA | whole blood | AAS |
| Narang 1991 [6] | Indian | 35 | 35 | 40 | 40 | matched | matched | 19.2 (4.5) | 16.8 (2.6) | HDRS | plasma | AAS |
| Maes 1997 [20] | Belgium | 31 | 15 | 45.20 | 33 | 51.4 (13.5) | 47.5 (15) | 18.6 (4.7) | 18.7 (1.9) | HDRS | serum | AAS |
| Yu 1997 [18] | China | 22 | 26 | 63.6 | NA | 27.6 (9.2) | 29.4 (8.7) | 15.5 (4.7) | 11.8 (2.3) | CCMD-2R | serum | AAS |
| Fernandez-Gonzales 1998 [23] | Spain | 24 | 33 | 87.5 | 60.6 | NA | NA | 16.4 (3.8) | 21.1 (6.1) | DSM-IV | serum | AAS |
| Schlegel-Zawadzka 1999 [13] | Poland | 19 | 16 | 63.2 | 37.5 | 42.2 (10.6) | 37 (9.1) | 18.1 (2.7) | 14.9 (1.4) | HDRS | serum | AAS |
| Chang 2001 [29] | China | 68 | 66 | 51.5 | 50.0 | 32.0 (11.6) | 31.5 (10.5) | 19.0 (2.1) | 17.8 (2.8) | CCMD-2R | serum | DCP-AES |
| Ma 2006 [30] | China | 60 | 40 | 73.3 | 55 | 39.8 (14.2) | 36.4 (2.1) | 17.0 (2.6) | 15.8 (1.7) | CCMD-3/HAMD | serum | AAS |
| Crayton 2007 [11] | USA | 813 | 54 | 59.7 | 51.8 | 30–60 | 45.7 (7.0) | 15.3 (4.6) | 16.1 (2.7) | DSM-IV | serum | AAS |
| Wan 2008 [31] | China | 70 | 64 | 25.7 | 23.4 | 23.2 (8.4) | 30.9 (9.2) | 22.2 (1.0) | 16.3 (2.0) | CCMD-3/HAMD | blood | Polarography |
| Liu 2008 [17] | China | 41 | 21 | 58.5 | 57.1 | 35.2 (12.8) | 36.8 (11.3) | 19.8 (3.3) | 17.8 (2.8) | CCMD-3/ICD-10 | serum | DCP-AES |
| Salustri 2010 [35] | Italy | 13 | 13 | 84.6 | 84.6 | 54.2 (13.5) | 55.9 (19.3) | 16.5 (4.3) | 13.5 (4.1) | DSM-IV/MADRS | serum | Colorimetry |
| Li 2014 [33] | China | 65 | 65 | 55.4 | 53.8 | 38.5 (7.5) | 38.7 (7.1) | 20.1 (1.7) | 15.3 (1.2) | HDRS | serum | Polarography |
| Alghadir 2015 [10] | Egypt | 73 | 77 | 45.2 | 35.1 | 7–18 | 7–18 | 25.6 (3.4) | 19.7 (2.5) | CDI | serum | AAS |
| Styczen 2016 [21] | Poland | 114 | 50 | 75.4 | 72 | 49.4 (10.7) | 45.8 (12.4) | 12.7 (4.2) | 14.3 (6.1) | MADRS-HDRS | serum | ETAAS |
| Skzup 2017 [36] | Poland | 70 | 128 | 100 | 100 | 56.3 (5.5) | 56.3 (5.6) | 18.2 (1.2) | 16.8 (3.5) | Beck | serum | AAS |
| Islam 2018 [14] | Bangladesh | 247 | 248 | 63 | 59 | 33.0 (0.7) | 33.5 (0.6) | 21.9 (0.5) | 15.9 (0.3) | DSM-IV | serum | AAS |
| Al-Fartusie 2019 [37] | Iraq | 60 | 60 | NA | NA | 40–60 | 39–58 | 24.4 (1.8) | 17.6 (2.1) | NA | serum | FAAS |
| Tanvir 2020 [38] | Pakistan | 185 | 185 | 55.7 | 64.9 | 37.75 (11.5) | 39.4 (12.6) | 19.1 (6.2) | 15.7 (4.2) | ICD10 | serum | FAAS |
| Liao 2021 [15] | China | 41 | 41 | 63.4 | 51.2 | 28.07 (10.1) | 26.5 (7.9) | 16.9 (4.7) | 13.7 (2.8) | HDRS-YMRS | serum | AAS |
| Fu 2023 [22] | China | 72 | 75 | 50 | 49 | 39.3 (15.5) | 41.9 (6.9) | 15.6 (1.8) | 20.2 (3.3) | HAMD | serum | ICP-MS |
| Liu 2024 [16] | China | 429 | 4418 | 59.4 | 49.0 | 49.47 (17.2) | 47.4 (18.6) | 19.6 (4.5) | 18.6 (4.5) | PHQ-9 | serum | ICP-DRC-MS |
| Zhong 2024 [19] | China | 108 | 44 | 56.5 | 50 | 25.85 (7.4) | 25.9 (3.8) | 12.1 (2.3) | 13.5 (2.8) | HDRS-YMRS | serum | AAS |
| Abd Rab El Rasool & Farghal 2024 [32] | Egypt | 45 | 45 | 71.1 | 66.7 | 31.1 (5.5) | 28.3 (6.3) | 19.7 (6.1) | 15.3 (2.2) | HDRS-YMRS | serum | AAS |
3.2. Overall Analysis
3.3. Publication Bias
3.4. Meta-Analysis in Female Subjects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates. 2017. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/254610 (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Walker, E.R.; McGee, R.E.; Druss, B.G. Mortality in mental disorders and global disease burden implications: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuijpers, P.; Smit, F. Excess mortality in depression: A meta-analysis of community studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2002, 72, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Milaneschi, Y.; Lamers, F.; Vogelzangs, N. Understanding the somatic consequences of depression: Biological mechanisms and the role of depression symptom profile. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, R.L.; Gupta, K.R.; Narang, A.P.; Singh, R. Levels of copper and zinc in depression. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1991, 35, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lutsenko, S.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Hubbard, A.L. Copper handling machinery of the brain. Metallomics 2010, 2, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, K.; Ralle, M.; Schaffer, T.; Jayakanthan, S.; Bari, B.; Muchenditsi, A.; Lutsenko, S. ATP7A and ATP7B copper transporters have distinct functions in the regulation of neuronal dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 20085–20098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.F. (Ed.) Chapter 7—Copper: Basic Physiological and Nutritional Aspects. In Molecular, Genetic, and Nutritional Aspects of Major and Trace Minerals; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Alghadir, A.H.; Gabr, S.A.; Al-Eisa, E. Effects of Physical Activity on Trace Elements and Depression Related Biomarkers in Children and Adolescents. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 172, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crayton, J.W.; Walsh, W.J. Elevated serum copper levels in women with a history of post-partum depression. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2007, 21, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; You, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L. Copper in depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 267, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel-Zawadzka, M.; Zieba, A.; Dudek, D.; Zak-Knapik, J.; Nowak, G. Is serum copper a “trait marker” of unipolar depression? A preliminary clinical study. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 51, 535–538. Available online: http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/10817533 (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Islam, M.R.; Islam, M.R.; Shalahuddin Qusar, M.M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Kabir, M.H.; Mustafizur Rahman, G.K.M.; Islam, M.S.; Hasnat, A. Alterations of serum macro-minerals and trace elements are associated with major depressive disorder: A case-control study. BMC Psychiatry 2018, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Lai, S.; Zhong, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Huang, H.; Chen, G.; Chen, F.; Jia, Y. Interaction of Serum Copper and Neurometabolites on Executive Dysfunction in Unmedicated Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 564375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Jiang, C. Independent and combined effect of serum copper and folate on depression: Cross-sectional data from the NHANES 2011–2016. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1389480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.B. The Study of the Association Between Trace Element and Senile Dementia/Depressive Disorder. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.Y.; Cui, S.; Wang, Y.Z.; Liu, L.L.; He, B.P.; Zhao, D.S.; Sun, J.; et al. Determination of trace elements in serum and erythrocyte of depression. Hebei Ment. Health 1997, 10, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Q.; Lai, S.; He, J.; Zhong, S.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Yan, S.; Jia, Y. Gender-related alterations of serum trace elements and neurometabolism in the anterior cingulate cortex of patients with major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 360, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Vandoolaeghe, E.; Neels, H.; Demedts, P.; Wauters, A.; Meltzer, H.Y.; Altamura, C.; Desnyder, R. Lower serum zinc in major depression is a sensitive marker of treatment resistance and of the immune/inflammatory response in that illness. Biol. Psychiatry 1997, 42, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styczeń, K.; Sowa-Kućma, M.; Siwek, M.; Dudek, D.; Reczyński, W.; Misztak, P.; Szewczyk, B.; Topór-Mądry, R.; Opoka, W.; Nowak, G. Study of the Serum Copper Levels in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 174, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, N.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, F.; He, L.; Xia, S.; et al. Serum and urinary essential trace elements in association with major depressive disorders: A case-control study. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1297411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-González, M.D.; García-Unzueta, M.T.; Herrán, A.; Vázquez-Barquero, J.L.; Díez-Manrique, J.F.; Álvarez, C. Trace elements in serum of psychiatric outpatients. Quim. Clin. 1998, 17, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Squitti, R.; Rongioletti, M.; Fostinelli, S.; Severino, A.; Bonvicini, C.; Geviti, A.; Martinelli, A.; Tura, G.B.; Ghidoni, R. Copper excess in psychiatric disorders: A focus on mood spectrum disorders and sex. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 86, 127532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squitti, R.; Bonvicini, C.; Fostinelli, S.; Rongioletti, M.; Severino, A.; Geviti, A.; Fiorenza, A.; Bellini, S.; Martinelli, A.; Tura, G.B.; et al. The serum trace metal signature distinguishes patients with psychiatric disorders from healthy controls. Biometals 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 74, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.R.; Wang, H.M.; Li, X.H.; Dai, Z.S.; Zhao, Y.H. Determination of 14 kinds of trace elements in the serum of patients with depression. Chin. J. Behav. Med. Sci. 2001, 6, 589–590. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.J.; Guo, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.P.; Lei, Y.X.; Li, L. Study on correlation between three trace elements and syndrome of depression. Shanxi Tradit. Chin. Med. 2006, 27, 815–816. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.H.; Wang, X.J.; Mao, B.F.; Jia, X.D. Study on the changes of 8 trace elements in the whole blood of patients with depression. Contempor. Med. 2008, 142, 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Rab El Rasool, A.O.; Farghal, E.E.E. Serum Copper and Zinc Levels in Bipolar and Major Depressive Disorders. SVU-Int. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 7, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Study on the change of serum CRP, BDNF and trace elements of patients with depression. China Mod. Med. 2014, 21, 99–100. [Google Scholar]
- Manser, W.W.; Khan, M.A.; Hasan, K.Z. Trace element studies on Karachi population. Part IV: Blood copper, zinc, magnesium and lead levels in psychiatric patients with depression, mental retardation and seizure disorders. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 1989, 39, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Salustri, C.; Squitti, R.; Zappasodi, F.; Ventriglia, M.; Bevacqua, M.G.; Fontana, M.; Tecchio, F. Oxidative stress and brain glutamate-mediated excitability in depressed patients. J. Affect. Disord. 2010, 127, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkup, M.; Jurczak, A.; Brodowska, A.; Brodowska, A.; Noceń, I.; Chlubek, D.; Laszczyńska, M.; Karakiewicz, B.; Grochans, E. Analysis of Relations Between the Level of Mg, Zn, Ca, Cu, and Fe and Depressiveness in Postmenopausal Women. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 176, 64, Erratum in Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 176, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fartusie, F.S.; Al-Bairmani, H.K.; Al-Garawi, Z.S.; Yousif, A.H. Evaluation of Some Trace Elements and Vitamins in Major Depressive Disorder Patients: A Case-Control Study. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 189, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanvir, S.; Asif, N.; Qayyum, R.; Ijaz, A.; Hafeez, A.; Ali, S. Trace metal profiling in patients with depression in Pakistani population. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2020, 70, 1883–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, L.; Carvalho, L.A.; Birkenhager, T.K.; Hoogendijk, W.J.; Kushner, S.A.; Drexhage, H.A.; Bergink, V. Circulating cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells as potential predictors for antidepressant response in melancholic depression. Restoration of T regulatory cell populations after antidepressant therapy. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandley, M.J.; Szebeni, A.; Szebeni, K.; Wang-Heaton, H.; Garst, J.; Stockmeier, C.A.; Lewis, N.H.; Ordway, G.A. Markers of elevated oxidative stress in oligodendrocytes captured from the brainstem and occipital cortex in major depressive disorder and suicide. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 117, 110559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Egger, M. Investigating and dealing with publication bias and other reporting biases in meta-analyses of health research: A review. Res. Synth. Methods 2021, 12, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroll, J.B.; Moustgaard, R.; Gotzsche, P.C. Dealing with substantial heterogeneity in Cochrane reviews. Cross-sectional study. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2011, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insel, T.R. The NIMH Research Domain Criteria (RDoC) Project: Precision medicine for psychiatry. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study | Adequate Definition of Cases | Representativeness of Cases | Selection of Controls | Definition of Controls | Comparability | Exposure Assessment | Same Method | Non-Response Rate | Total Quality Scores | AHRQ Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manser 1989 [34] | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | Fair |
| Narang 1991 [6] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 | Good |
| Maes 1997 [20] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | Good |
| Yu 1997 [18] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good |
| Fernandez-Gonzales 1998 [23] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good |
| Schlegel-Zawadzka 1999 [13] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | Poor |
| Chang 2001 [29] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | Fair |
| Ma 2006 [30] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good |
| Crayton 2007 [11] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | Poor |
| Wan 2008 [31] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good |
| Liu 2008 [17] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | Fair |
| Salustri 2010 [35] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 | Good |
| Li 2014 [33] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | Fair |
| Alghadir 2015 [10] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good |
| Styczeń 2016 [21] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good |
| Szkup 2017 [36] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good |
| Islam 2018 [14] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good |
| Al-Fartusie 2019 [37] | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | Fair |
| Tanvir 2020 [38] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good |
| Liao 2021 [15] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good |
| Fu 2023 [22] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 | Good |
| Liu 2024 [16] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | Fair |
| Zhong 2024 [19] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good |
| Abd Rab El Rasool & Farghal 2024 [32] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 | Good |
| Sensitivity Analyses | Number of Studies | MD | 95% CI | p | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excluding Salustri et al., 2010 and Szkup et al., 2017 [35,36] | 22 | 2.23 | 0.86–3.61 | 0.003 | 98.7% |
| Excluding Manser et al., 1989 and Alghadir et al., 2015 [10,34] | 22 | 2.00 | 0.67–3.33 | 0.005 | 98.7% |
| Excluding studies with AHRQ standards equal to poor [11,13] | 22 | 2.26 | 0.88–3.63 | 0.003 | 98.6% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Squitti, R.; Ventriglia, M.; Simonelli, I.; Bonvicini, C.; Crescenti, D.; Borroni, B.; Rongioletti, M.; Ghidoni, R. Copper Dysregulation in Major Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analytic Evidence for a Putative Trait Marker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189247
Squitti R, Ventriglia M, Simonelli I, Bonvicini C, Crescenti D, Borroni B, Rongioletti M, Ghidoni R. Copper Dysregulation in Major Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analytic Evidence for a Putative Trait Marker. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):9247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189247
Chicago/Turabian StyleSquitti, Rosanna, Mariacarla Ventriglia, Ilaria Simonelli, Cristian Bonvicini, Daniela Crescenti, Barbara Borroni, Mauro Rongioletti, and Roberta Ghidoni. 2025. "Copper Dysregulation in Major Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analytic Evidence for a Putative Trait Marker" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 9247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189247
APA StyleSquitti, R., Ventriglia, M., Simonelli, I., Bonvicini, C., Crescenti, D., Borroni, B., Rongioletti, M., & Ghidoni, R. (2025). Copper Dysregulation in Major Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analytic Evidence for a Putative Trait Marker. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 9247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189247







