Novel Organomineral Complex with Prolonged Antitumor Action
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
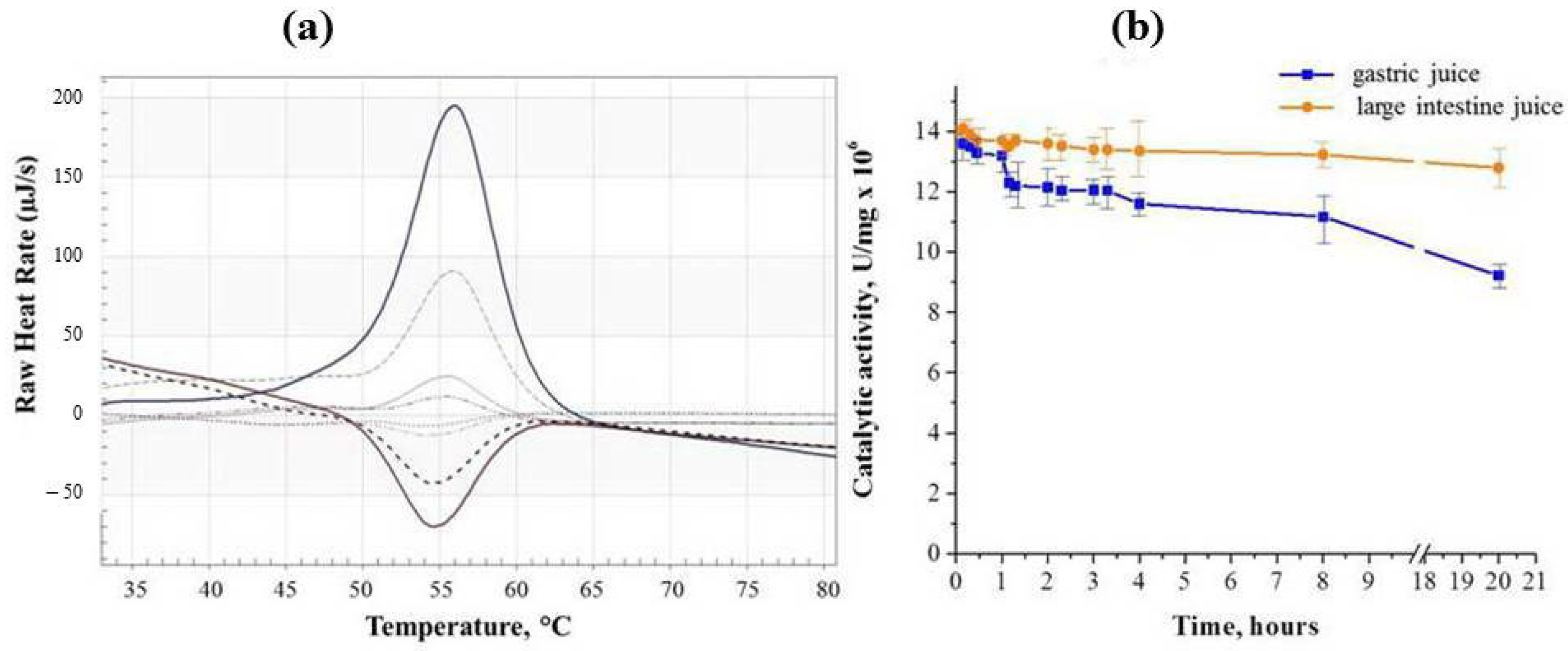
2.1. Binase Stability
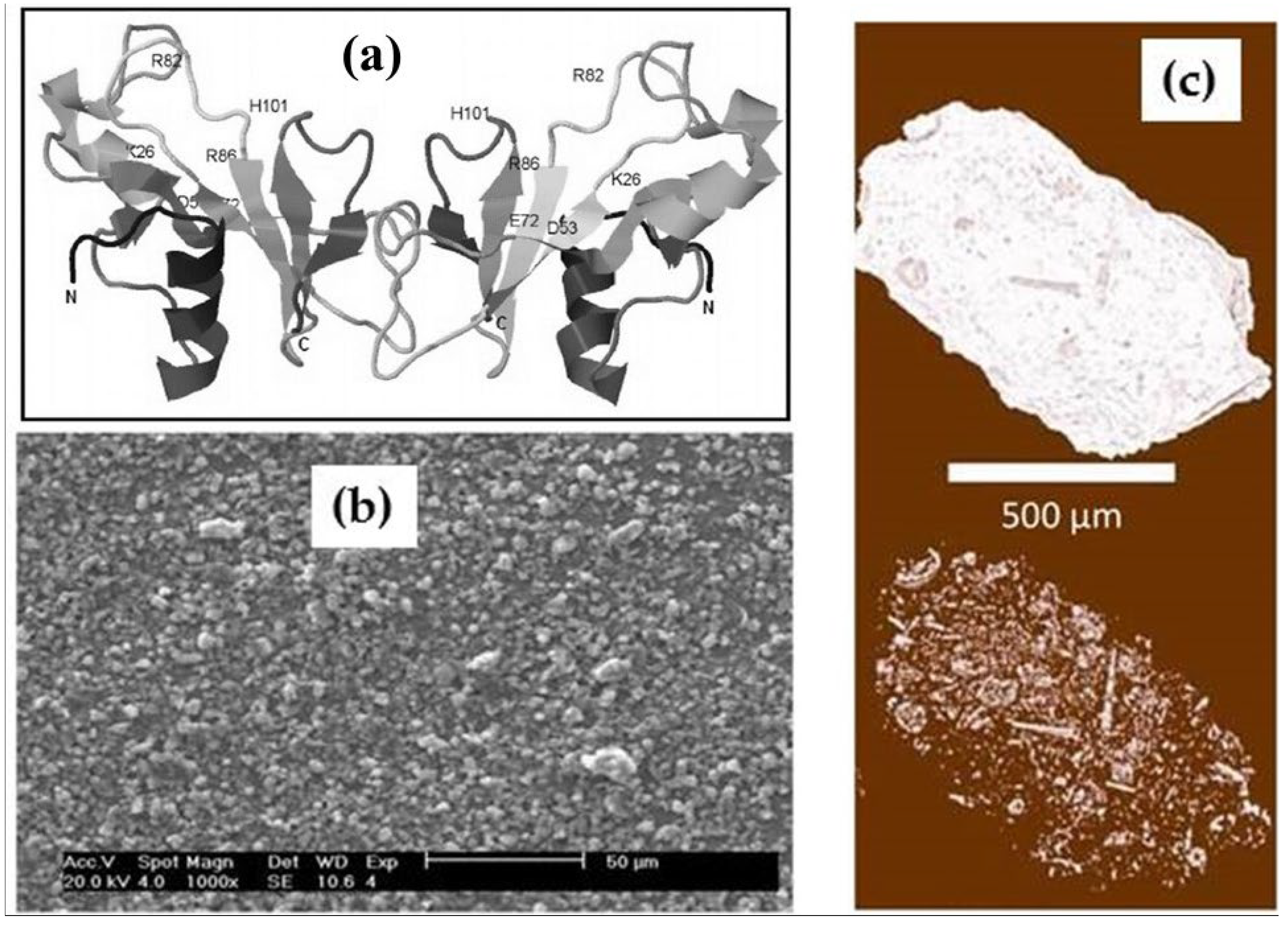
2.2. Correspondence Between Zeolite Porosity and Binase Size
2.3. Binase Loading and Release
2.4. Mechanism Supporting the Penetration of Binase into Zeolite
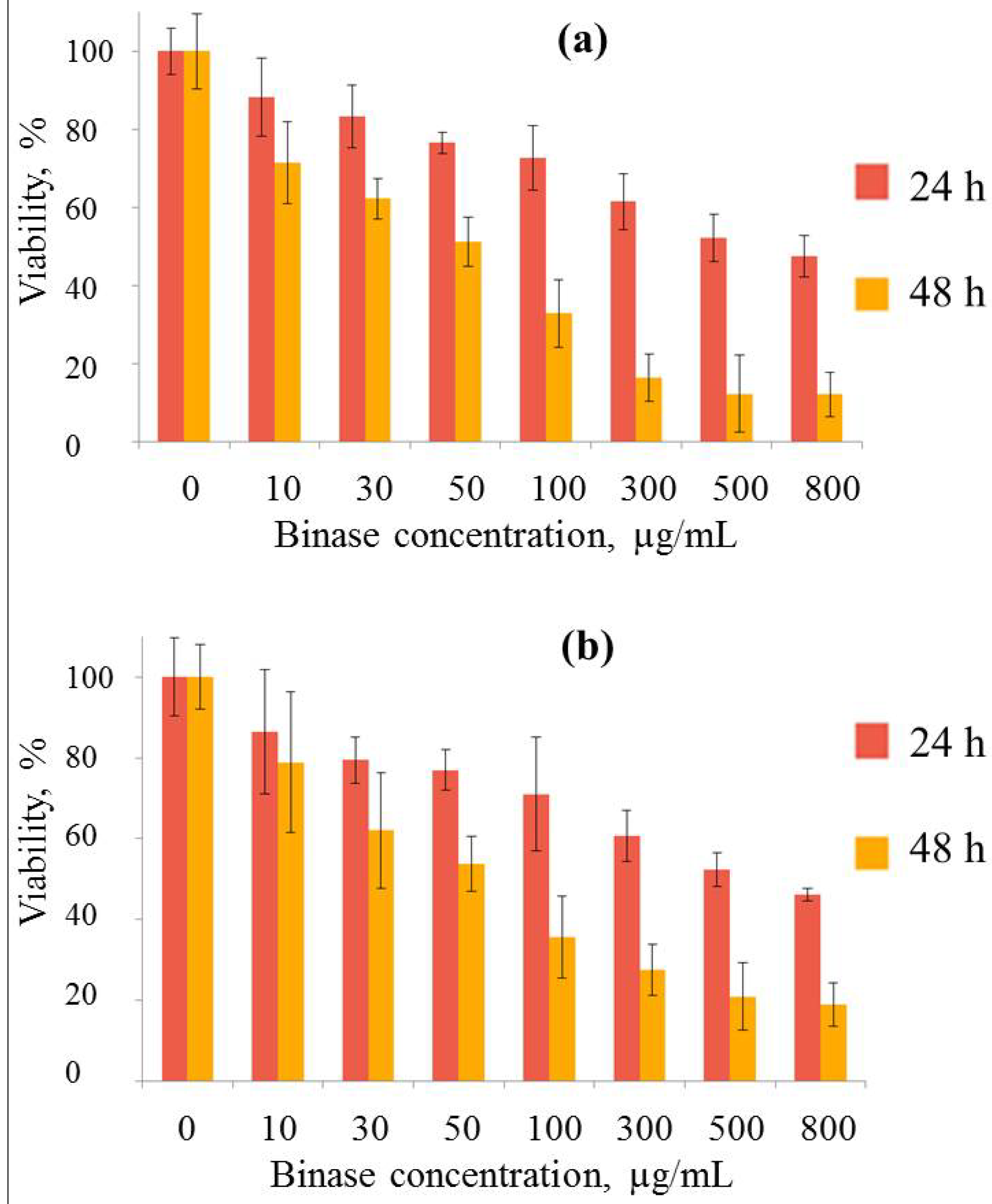
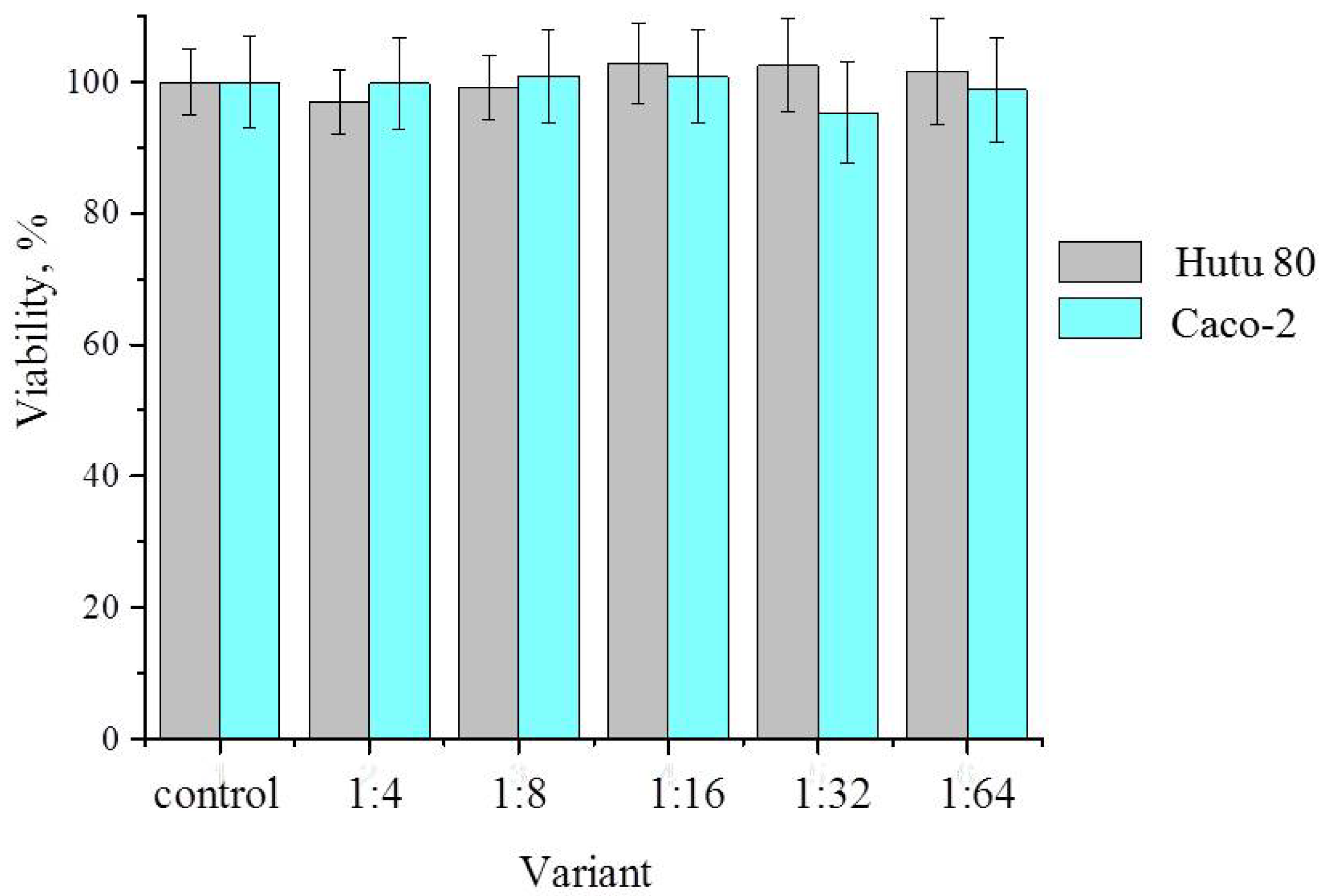
2.5. Binase and Zeolite Cytotoxicity Towards Human Adenocarcinoma Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. RNase
4.2. Zeolite
4.3. Zeolite Images
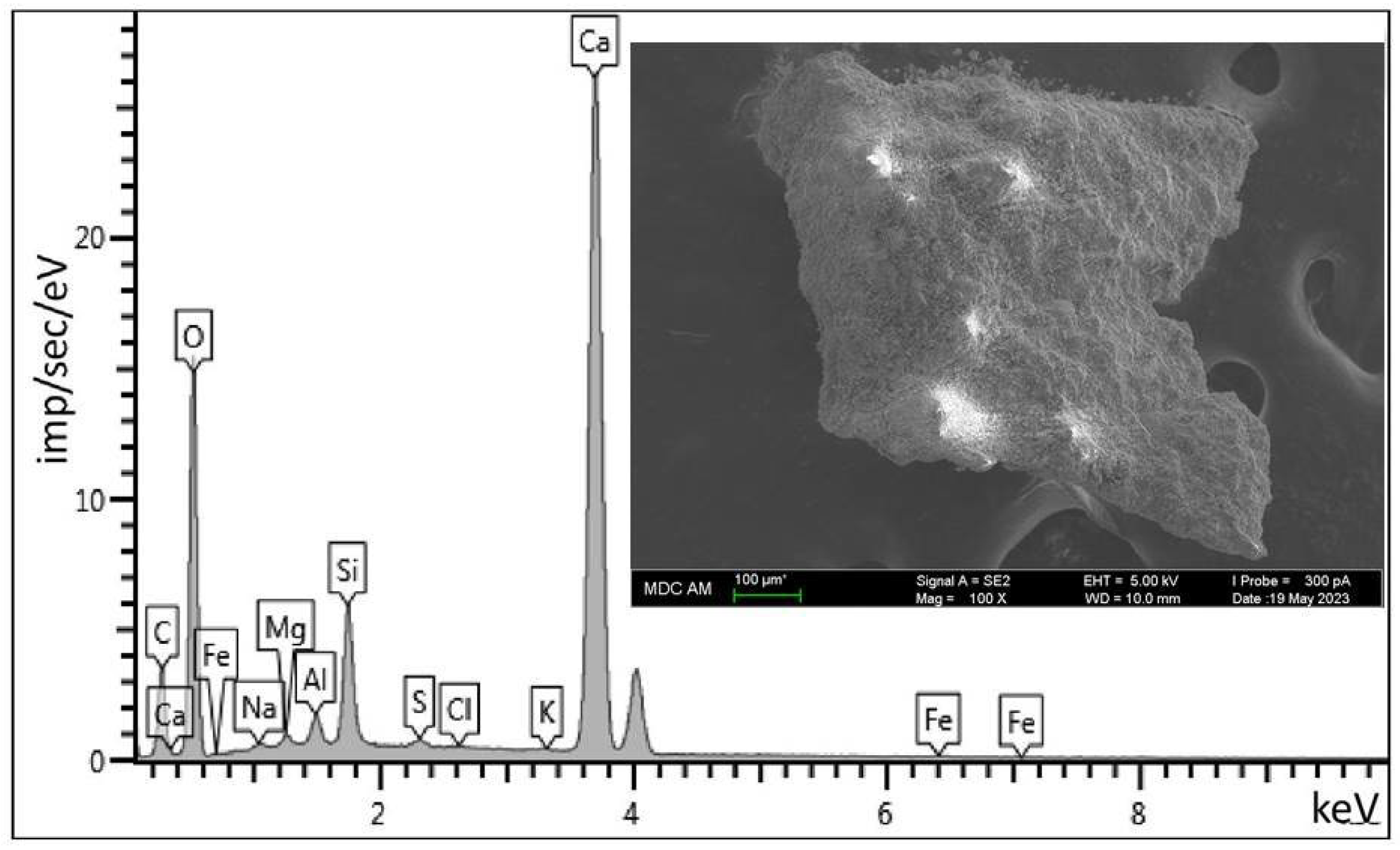
4.4. Elemental Composition of the Carrier
4.5. Zeolite Porosity Analyses
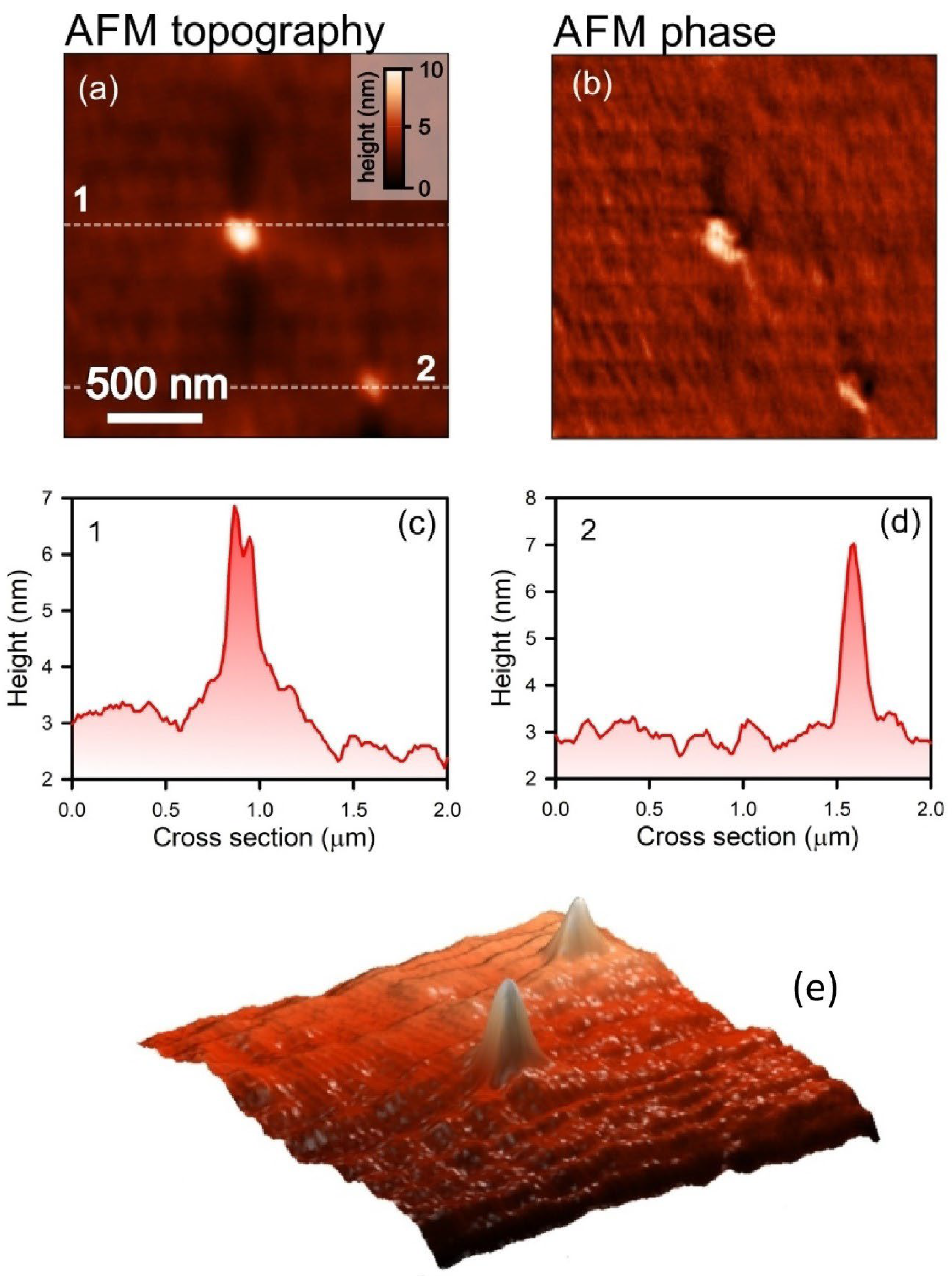
4.6. Atomic Force Microscopy
4.7. Enzyme Thermal Denaturation
4.8. Binase Sorption and Desorption
4.9. Model Fluids of the Gastrointestinal Tract
4.10. Cell Lines and Cytotoxicity Analysis
4.11. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| RAS | protein expressed from retrovirus-associated DNA sequences |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| DSC | differential scanning calorimetry |
| AFM | atomic force microscopy |
References
- Rybak, S.M.; Arndt, M.A.; Schirrmann, T.; Dübel, S.; Krauss, J. Ribonucleases and immunoRNases as anticancer drugs. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2665–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Sugawara, S.; Tatsuta, T.; Hosono, M.; Nitta, K.; Fujii, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Fujimura, T.; Taka, H.; Koide, Y.; et al. Sialyl-glycoconjugates in cholesterol-rich microdomains of P388 cells are the triggers for apoptosis induced by Rana catesbeiana oocyte ribonuclease. Glycoconj. J. 2014, 31, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antignani, A.; Naddeo, M.; Cubellis, M.V.; Russo, A.; D’Alessio, G. Antitumor action of seminal ribonuclease, its dimeric structure, and its resistance to the cytosolic ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 3492–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, T.; Kitazoe, M.; Tada, H.; de Llorens, R.; Salomon, D.S.; Ueda, M.; Yamada, H.; Seno, M. Growth inhibition of mammalian cells by eosinophil cationic protein. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelweiss, E.; Balandin, T.G.; Ivanova, J.L.; Lutsenko, G.V.; Leonova, O.G.; Popenko, V.I.; Sapozhnikov, A.M.; Deyev, S.M. Barnase as a new therapeutic agent triggering apoptosis in human cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnysheva, K.M.; Petrushanko, I.Y.; Spirin, P.V.; Prassolov, V.S.; Makarov, A.A.; Mitkevich, V.A. Ribonuclease binase induces death in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells by apoptosis. Mol. Biol. 2016, 50, 347–352. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironova, N.L.; Petrushanko, I.Y.; Patutina, O.A.; Sen’kova, A.V.; Simonenko, O.V.; Mitkevich, V.A.; Markov, O.; Zenkova, M.; Makarov, A.A. Ribonuclease binase inhibits primary tumor growth and metastases via apoptosis induction in tumor cells. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 2120–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilinskaya, O.N.; Singh, I.; Dudkina, E.; Ulyanova, V.; Kayumov, A.; Barreto, G. Direct inhibition of oncogenic KRAS by Bacillus pumilus ribonuclease (binase). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkoski, T.J.; Raines, R.T. Evasion of ribonuclease inhibitor as a determinant of ribonuclease cytotoxicity. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2008, 9, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.P.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.S.; Raines, R.T. Knockout of the ribonuclease inhibitor gene leaves human cells vulnerable to secretory ribonucleases. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 6359–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libonati, M.; Gotte, G.; Vottariello, F. A novel biological actions acquired by ribonuclease through oligomerization. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2008, 9, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokurenko, Y.; Nadyrova, A.; Ulyanova, V.; Ilinskaya, O. Extracellular ribonuclease from Bacillus licheniformis (Balifase), a new member of the N1/T1 RNase superfamily. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 4239375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudkina, E.; Ulyanova, V.; Shah Mahmud, R.; Khodzhaeva, V.; Dao, L.; Vershinina, V.; Kolpakov, A.; Ilinskaya, O. Three-step procedure for preparation of pure Bacillus altitudinis ribonuclease. FEBS Open Bio 2016, 6, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudkina, E.V.; Ulyanova, V.V.; Ilinskaya, O.N. Supramolecular organization as a factor of ribonuclease cytotoxicity. Acta Naturae 2020, 12, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudkina, E.; Ulyanova, V.; Asmandiyarova, V.; Vershinina, V.; Ilinskaya, O. Two main cancer biomarkers as molecular targets of binase antitumor activity. BioMed Res. Int. 2024, 8159893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilinskaya, O.N.; Koschinski, A.; Repp, H.; Mitkevich, V.A.; Dreyer, F.; Scholtz, J.M.; Pace, C.N.; Makarov, A.A. RNase-induced apoptosis: Fate of calcium-activated potassium channels. Biochimie 2008, 90, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Meng, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T. Application of ordered porous silica materials in drug delivery: A review. Molecules 2024, 29, 5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Gutiérrez, S.; Maiza-Razkin, E.; Pascual-Colino, J.; Araúzo-Bravo, M.J.; Beobide, G.; Castillo, O.; Castellanos-Rubio, A.; Gerovska, D.; Luque, A.; Pérez-Yáñez, S. Drug-delivery and biological activity in colorectal cancer of a supramolecular porous material assembled from heptameric chromium-copper-adenine entities. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 11156–11164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Șenilă, M.; Neag, E.; Tănăselia, C.; Șenilă, L. Removal of cesium and strontium ions from aqueous solutions by thermally treated natural zeolite. Materials 2023, 16, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, M.; Doszhanov, Y.; Saurykova, K.; Ahmadi, N.; Bolatova, D.; Kurmanbayeva, M.; Aydarbek, A.; Ihsas, R.; Seitzhanova, M.; Akhmetzhanova, D.; et al. Modification and application of natural clinoptilolite and mordenite from Almaty region for drinking water purification. Molecules 2025, 30, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgianos, P.; Pournara, A.D.; Andreou, E.K.; Armatas, G.S.; Manos, M.J. Composite materials based on a Zr4+ MOF and aluminosilicates for the simultaneous removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous media. Molecules 2023, 28, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarabi, A.; Nizet, S.; Röhrich, A.; Tschegg, C. Unveiling the broad-spectrum virucidal potential of purified clinoptilolite-tuff. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilinskaya, O.; Glukhov, M.; Yakovleva, G.; Galeeva, A.; Kurdy, W. Ribonuclease A-mineral carrier complex as a potential antitumor preparation. Eur. J. Biol. 2025, 84, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojaewa, V.; Lopatin, O.; Zelenikhin, P.; Ilinskaya, O. Zeolites as carriers of antitumor ribonuclease binase. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilinskaya, O.; Ulyanova, V.; Lisevich, I.; Dudkina, E.; Zakharchenko, N.; Kusova, A.; Faizullin, D.; Zuev, Y. The native monomer of Bacillus pumilus ribonuclease does not exist extracellularly. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4837623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khivantsev, K.; Derewinski, M.A.; Szanyi, J. Novel and emerging concepts related to cationic species in zeolites: Characterization, chemistry and catalysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2023, 358, 112378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Raines, R.T. Ribonucleases as novel chemotherapeutics: The ranpirnase example. BioDrugs 2008, 22, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenikhin, P.V.; Makeeva, A.V.; Nguen, T.N.; Siraj, Y.A.; Ilinskaya, O.N. Combined action of binase and bleomycin toward human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Biomed. Khim. 2016, 62, 279–282. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Proshkina, G.M.; Shramova, E.I.; Mirkasyimov, A.B.; Griaznova, O.Y.; Konovalova, E.V.; Schulga, A.A.; Deyev, S.M. The Barnase-Barstar-based pre-targeting strategy for enhanced antitumor therapy in vivo. Biochimie 2025, 228, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garipov, A.R.; Nesmelov, A.A.; Cabrera-Fuentes, H.A.; Ilinskaya, O.N. Bacillus intermedius ribonuclease (BINASE) induces apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells. Toxicon 2014, 92, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Fuentes, H.A.; Aslam, M.; Saffarzadeh, M.; Kolpakov, A.; Zelenikhin, P.; Preissner, K.T.; Ilinskaya, O.N. Internalization of Bacillus intermedius ribonuclease (BINASE) induces human alveolar adenocarcinoma cell death. Toxicon 2013, 69, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances Used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP). Scientific Opinion on the safety and efficacy of clinoptilolite of sedimentary origin for all animal species. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruchinkina, T.V. Evaluation of toxic properties of a preventive drug for normalization of mineral metabolism in cattle. Top. Issues Vet. Biol. 2023, 4, 76–79. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiev, B.I.; Aliev, A.A.; Shapieva, K.B.; Kanbulatova, Z.S.; Khalikov, A.S. Use of natural zeolites of Dagestan in medicine and veterinary science. Ecol. Med. 2018, 1, 87–92. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chernov, A.N.; Afordoani, D.M.; Prishchepenko, E.A. Characteristics of native zeolite cytotoxicity towards cattle epithelial cells. Agrar. Sci. 2022, 1, 40–43. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Online—Encyclopedia Tatarica. 2024. Available online: https://tatarica.org/ru/razdely/priroda/poleznye-iskopaemye/poleznye-iskopaemye/tatarsko-shatrashanskoe-mestorozhdenie (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Laurino, C.; Palmieri, B. Zeolite: “the magic stone”; main nutritional, environmental, experimental and clinical fields of application. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolanc, I.; Ferhatović Hamzić, L.; Orct, T.; Micek, V.; Šunić, I.; Jonjić, A.; Jurasović, J.; Missoni, S.; Čoklo, M.; Pavelić, S.K. The impact of long-term clinoptilolite administration on the concentration profile of metals in rodent organisms. Biology 2023, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, J.; Vasiljević, M.; Tassis, P.; Farkaš, H.; Bošnjak-Neumüller, J.; Männer, K. Effects of a modified clinoptilolite zeolite on growth performance, health status and detoxification of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A in male broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2021, 62, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atitlán-Gil, A.; Bretón-de la Loza, M.M.; Jiménez-Ortega, J.C.; Belefant-Miller, H.; Betanzos-Cabrera, G. Activated and micronized zeolite in the modulation of cellular oxidative stress in mexican smokers: A randomized clinical trial. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2017, 69, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrenović, J.; Rajić, N. Application of modified natural zeolite-clinoptilolite for bacterial control in the environment. Materials 2025, 18, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbein, T.; Dathe, W.; Deuerling, A.; Baum, R.P. Efficacy of Detoxsan® powder on diarrhea caused by gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiannidou, E.; Karavasili, C.; Kouskoura, M.G.; Filippousi, M.; Tendeloo, G.V.; Andreadis, I.I.; Eleftheriadis, G.K.; Kontopoulou, I.; Markopoulou, C.K.; Bouropoulos, N.; et al. In vitro and ex vivo assessment of microporous faujasite zeolite (NaX-FAU) as a carrier for the oral delivery of danazol. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutovic, M.; Lazovic, M.; Vukovic-Dejanovic, V.; Nikolic, D.; Petronic-Markovic, I.; Cirovic, D. Clinoptilolite for treatment of dyslipidemia: Preliminary efficacy study. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2017, 23, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.G.; Toan, N.T.; Cho, S.J.; Ko, J.H.; Jung, Y.K.; Lee, B.J. Dietary aluminosilicate supplement enhances immune activity in mice and reinforces clearance of porcine circovirus type 2 in experimentally infected pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 43, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amedlous, A.; Hélaine, C.; Dalena, F.; Anfray, C.; Ménard, T.; Blanchard, I.; Toutain, J.; Valable, S.; Mintova, S. Injectable biocompatible zeolite nanocrystals for enhanced tumor oxygenation and MRI Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 8003–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dernaika, F.; Halawy, L.; Zeaiter, J.; Kawrani, S.; Mroue, D.; Lteif, A.; Kourani, S.; Mehanna, M.; Abboud, C.; Mroueh, M.; et al. Development and characterization of a zeolite based drug delivery system: Application to cannabidiol oral delivery. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Shen, Q.H.; Xiong, Y.W.; Chen, J.W.; Hui, Q.; Zhou, R.; Luo, Y.F.; Cheng, B.; Tan, C.P.; Wu, T. Zinc-mediated metalloimmunotherapy with dual elimination of tumor and intratumoral bacteria in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biomaterials 2025, 323, 123439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Xue, J.; Liu, N.; Ren, X.; Tan, L.; Fu, C.; Wu, Q.; Niu, M.; Zou, J.; Meng, X. Apigenin and doxorubicin loaded zeolitic imidazole frameworks for triple-combination therapy of breast cancer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 697, 137979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasleem, M.W.; Rajpoot, S.R.; Zhang, H. Advances in cancer therapeutics with aptamer-functionalized ZIF-8 formulations for site-specific drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 681, 125816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, K. Heilung von Natur und Tierwelt Durch die Anwendung des Naturzeoliths; Spurbuchverlag: Baunach, Germany, 2017; 162p, ISBN 978-3-88778-502-4. [Google Scholar]
- Stylianou, M.A. Natural Zeolites in Medicine. In Book Handbook of Natural Zeolites; Inglezakis, V.J., Zorpas, A.A., Eds.; Bentham Science Publisher: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2012; pp. 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastinu, A.; Kumar, A.; Maccarinelli, G.; Bonini, S.A.; Premoli, M.; Aria, F.; Gianoncelli, A.; Memo, M. Zeolite clinoptilolite: Therapeutic virtues of an ancient mineral. Molecules 2019, 24, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Khosravi, S.; Ranjbar, A.; Mohammadi, M. Quercetin loaded-magnetic zeolite nano-composite material and evaluate its anti-cancer effect. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhrushina, E.O.; Belyavsky, N.O.; Kuzina, V.N.; Khodenok, A.I.; Demina, N.B.; Ramenskaya, G.V. Zeolites and zeolite imidazole frameworks in pharmacy (review). Drug Dev. Regist. 2025, 14, 193–221. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpakov, A.I.; Il’inskaia, O.N. The optimization of a method for determining RNAse activity by using high-polymer RNA. Klin. Lab. Diagn. 1999, 5, 14–16. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seitzhanova, M.A.; Doszhanov, E.O.; Kuldeev, E.I.; Mansurov, Z.A.; Taju, K.; Tanirbergenova, S.K.; Kanzharkan, E.; Tazhkenova, G.K. The influence of heat treatment on the sorption characteristics of zeolite used in the water purification process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 21, 173–179. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.R.S.; Loebenberg, R.; Almukainzi, M. Simulated biological fluids with possible application in dissolution testing. Dissolut. Technol. 2011, 18, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P.D.; Gahan, C.G.M.; Hill, C. A glutamate decarboxylase system protects Listeria monocytogenes in gastric fluid. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 40, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Binase Loading * | ||||||
| Time, h | 0.1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Loading solution, OD280 | 1.40 | 0.95 | 0.71 | 0.40 | ||
| RNase content in zeolite, % | 3.44 | 34.5 | 51.0 | 72.4 | ||
| Binase release ** | ||||||
| Time, h | 0.1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 20 | |
| Unloading solution, OD280 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.50 | |
| Σ(t) OD280 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.48 | 0.98 | |
| RNase release, % | 10.1 | 22.9 | 31.4 | 45.7 | 93.3 | |
| Element | Weight (%) | Atomic Mass (%) | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 60.60 | 78.33 | SiO2 |
| Na | 0.28 | 0.25 | Albite |
| Mg | 0.39 | 0.33 | MgO |
| Al | 0.90 | 0.69 | Al2O3 |
| Si | 3.95 | 2.91 | SiO2 |
| S | 0.21 | 0.13 | FeS2 |
| Cl | 0.05 | 0.03 | NaCl |
| K | 0.05 | 0.02 | KBr |
| Ca | 33.47 | 17.27 | Wollastonite |
| Fe | 0.12 | 0.04 | Fe |
| Sum | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilinskaya, O.; Yakovleva, G.; Zelenikhin, P.; Kolpakov, A.; Kurdy, W.; Glukhov, M.; Sedov, I.; Kharintsev, S. Novel Organomineral Complex with Prolonged Antitumor Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189205
Ilinskaya O, Yakovleva G, Zelenikhin P, Kolpakov A, Kurdy W, Glukhov M, Sedov I, Kharintsev S. Novel Organomineral Complex with Prolonged Antitumor Action. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):9205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189205
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlinskaya, Olga, Galina Yakovleva, Pavel Zelenikhin, Alexey Kolpakov, William Kurdy, Mikhail Glukhov, Igor Sedov, and Sergey Kharintsev. 2025. "Novel Organomineral Complex with Prolonged Antitumor Action" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 9205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189205
APA StyleIlinskaya, O., Yakovleva, G., Zelenikhin, P., Kolpakov, A., Kurdy, W., Glukhov, M., Sedov, I., & Kharintsev, S. (2025). Novel Organomineral Complex with Prolonged Antitumor Action. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 9205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189205








