Low-Molecular-Weight Bovine Collagen Peptides Reduce Fat Accumulation in C. elegans and Ameliorate Obesity-Related Metabolic Dysfunction and Microbiota Diversity in C57BL/6 Male Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
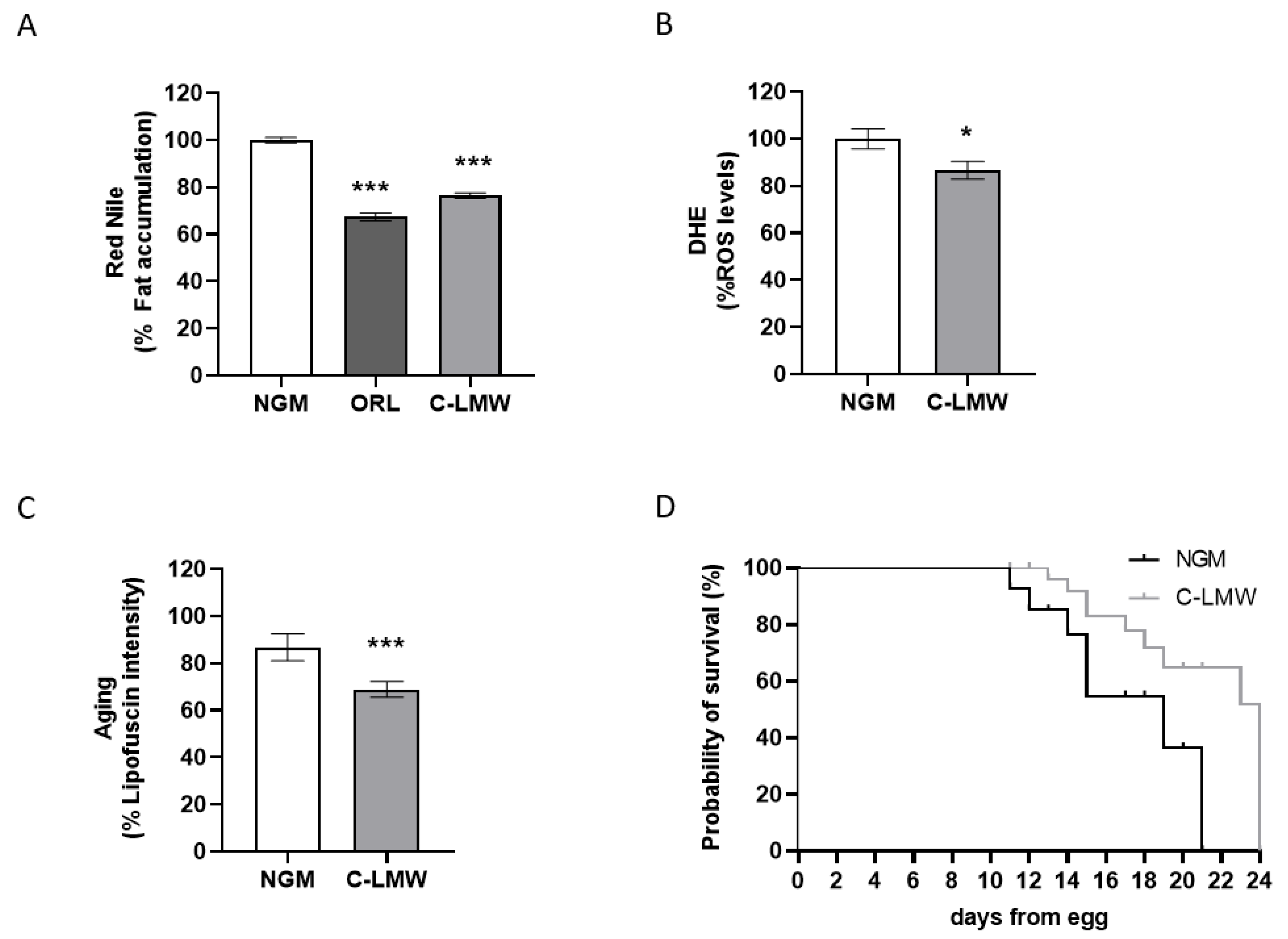
2.1. Collagen Hydrolysate C-LMW Improves Healthspan in C. elegans
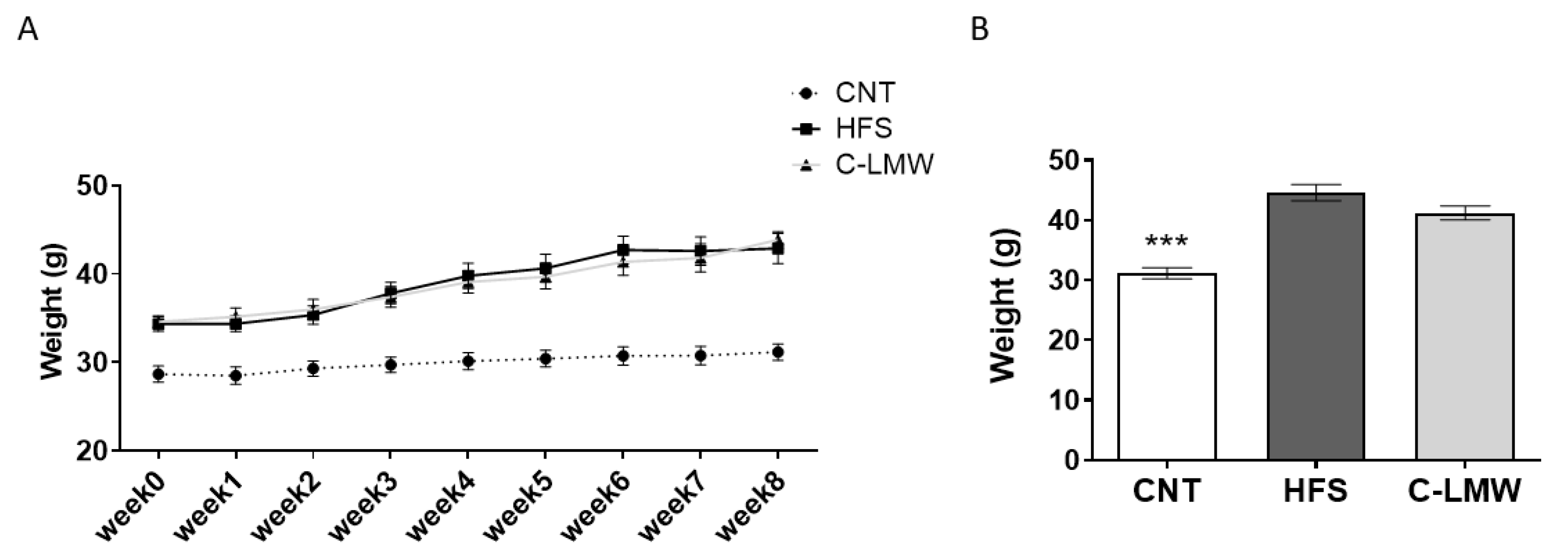
2.2. Body Weight Evolution and Final Body Weight in Mice
2.3. Supplementation with C-LMW Reduces Adiposity in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
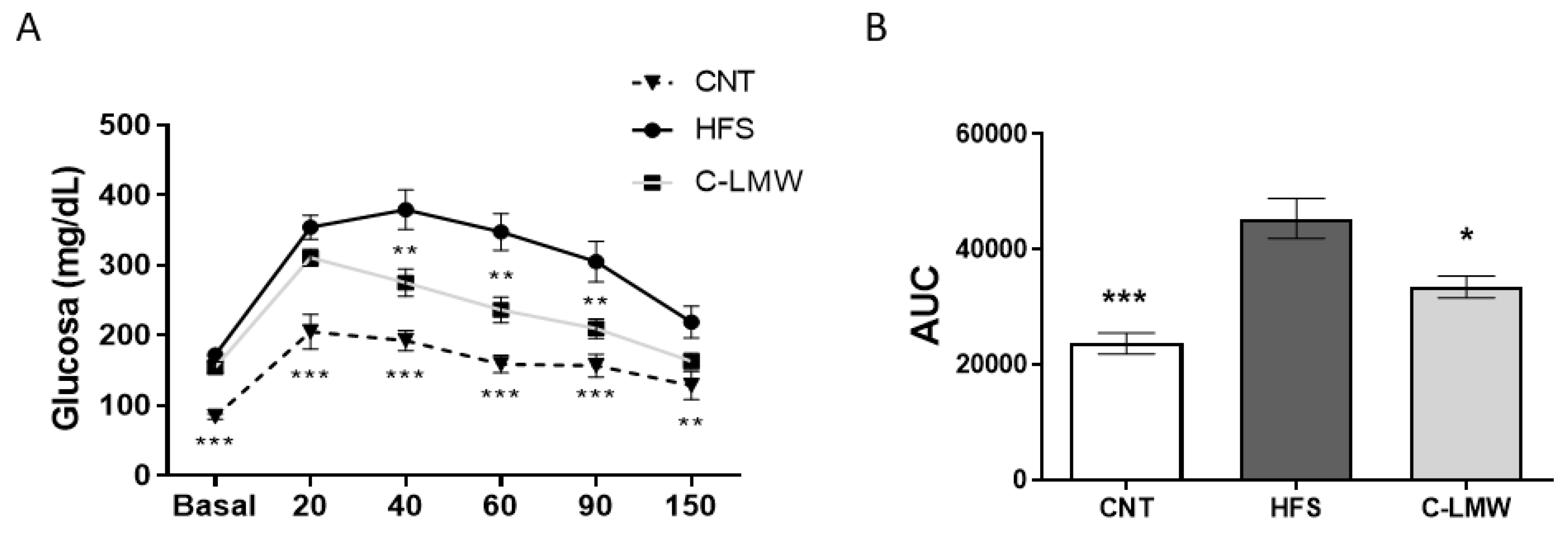
2.4. Supplementation with C-LMW Ameliorates Glucose Metabolism in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
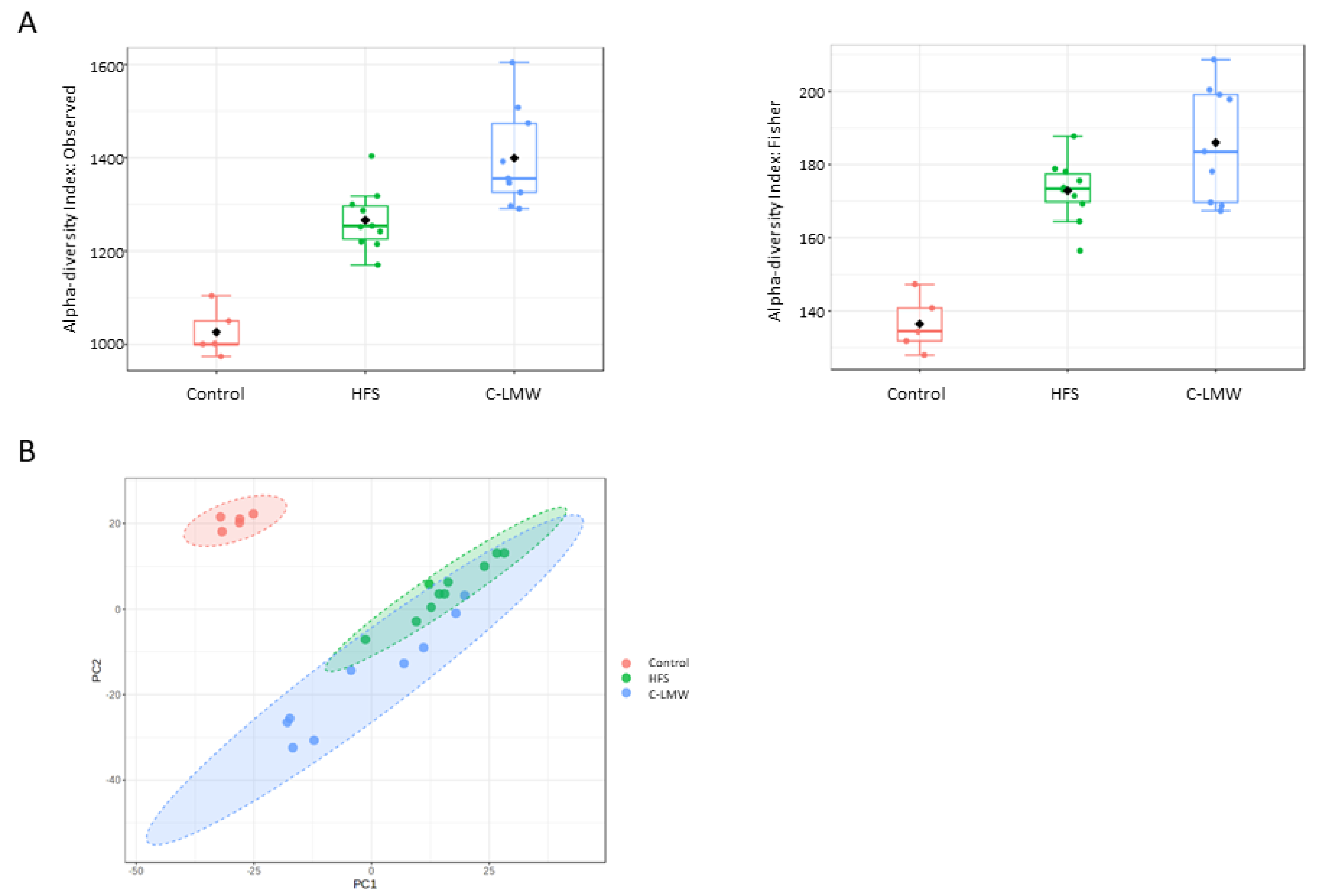
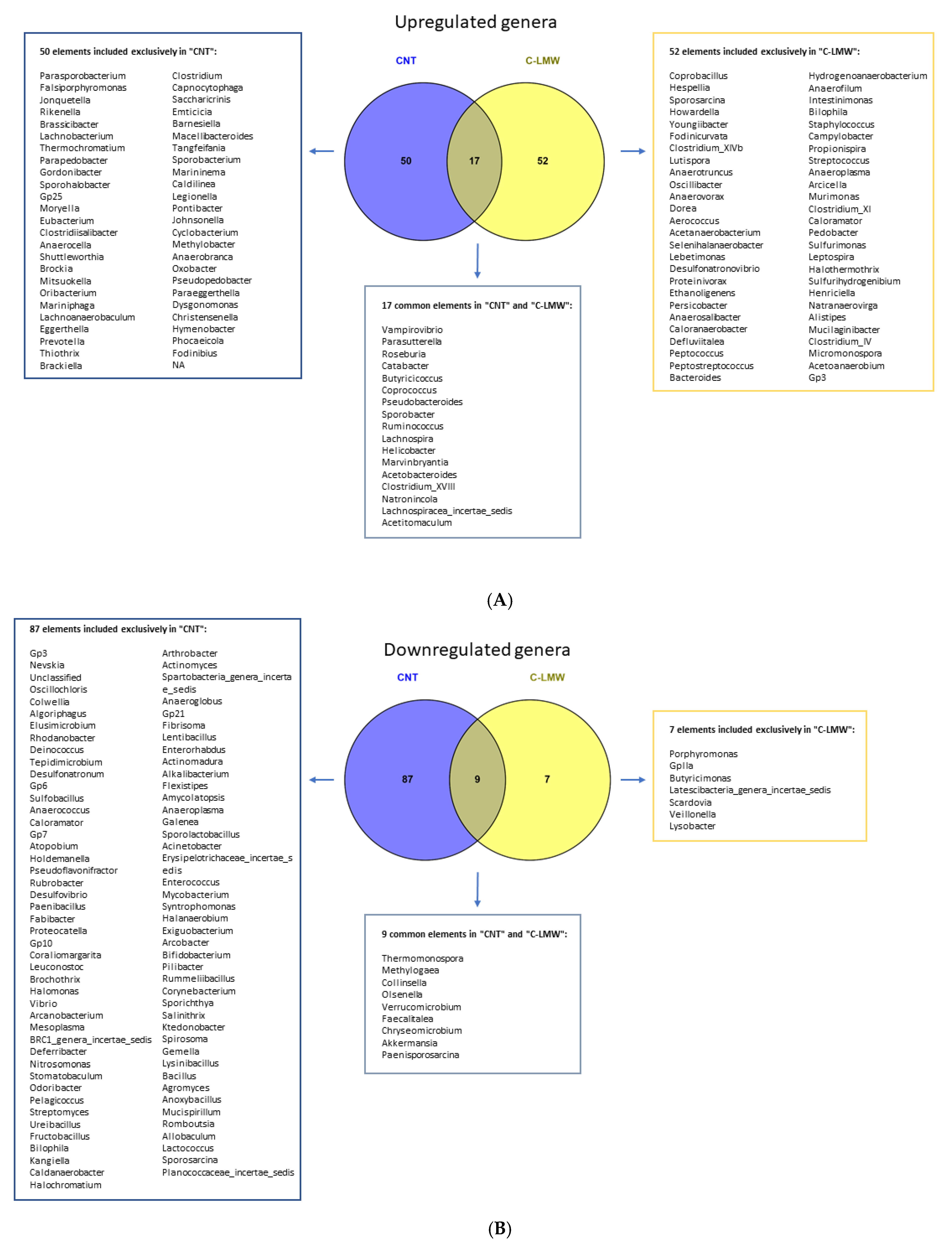
2.5. C-LMW Modulates Fecal Microbiota Increasing Alpha Diversity and the Abundance of Beneficial Bacteria in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Production Process and Amino Acid Composition of Collagen Peptides from Bovine Sources
4.2. C. elegans Experimental Design
4.3. Nile Red and DHE Staining Methods
4.4. Estimation of Aging in C. elegans
4.5. Lifespan Analysis
4.6. Image Acquisition and Quantification
4.7. Experimental Design in Mice
4.8. Intraperitoneal Glucose Tolerance Test (ipGTT)
4.9. Biochemical Analyses
4.10. Fecal Microbiota Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boutari, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. A 2022 Update on the Epidemiology of Obesity and a Call to Action: As Its Twin COVID-19 Pandemic Appears to Be Receding, the Obesity and Dysmetabolism Pandemic Continues to Rage On. Metabolism 2022, 133, 155217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitch, A.K.; Bays, H.E. Obesity Definition, Diagnosis, Bias, Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), and Telehealth: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement (CPS) 2022. Obes. Pillars 2022, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Davarci, O.; Chaftari, P.; Avenatti, E. Obesity as a Disease: A Primer on Clinical and Physiological Insights. Methodist. Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2025, 21, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.N.; Barber, T.; Renshaw, D.; Farnaud, S.; Oduro-Donkor, D.; Turner, M.C. Associations between the Gut Microbiome and Metabolic, Inflammatory, and Appetitive Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi Abdolmaleky, H.; Zhou, J.R. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Epigenetic Alterations in Metabolic Diseases. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakir, S.K.; Jawed, B.; Esposito, J.E.; Kanwal, R.; Pulcini, R.; Martinotti, R.; Ceci, E.; Botteghi, M.; Gaudio, F.; Toniato, E.; et al. The Role of Peptides in Nutrition: Insights into Metabolic, Musculoskeletal, and Behavioral Health: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara, T.; Abeyrathne, E.D.N.S.; Ahn, D.U. Effect of Bioactive Peptides on Gut Microbiota and Their Relations to Human Health. Foods 2024, 13, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajomiwe, N.; Boland, M.; Phongthai, S.; Bagiyal, M.; Singh, J.; Kaur, L. Protein Nutrition: Understanding Structure, Digestibility, and Bioavailability for Optimal Health. Foods 2024, 13, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Yamaguchi, M.; Watanabe, K.; Shimizu, M.; Azusa, T.; Sone, H.; Kamiyama, S. Effects of Collagen Peptide Administration on Visceral Fat Content in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2021, 67, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, M.; Shin, H.; Ahn, H.; Park, Y.K. Low-Molecular Collagen Peptide Supplementation and Body Fat Mass in Adults Aged 50 Years: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2023, 12, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raksha, N.; Halenova, T.; Vovk, T.; Kostyuk, O.; Synelnyk, T.; Andriichuk, T.; Maievska, T.; Savchuk, O.; Ostapchenko, L. Anti-obesity effect of collagen peptides obtained from Diplulmaris antarctica, a jellyfish of the Antarctic region. Croat. Med. J. 2023, 64, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Jiang, D.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Fu, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. Elucidating the modulatory role of dietary hydroxyproline on the integrity and functional performance of the intestinal barrier in early-weaned piglets: A comprehensive analysis of its interplay with the gut microbiota and metabolites. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 134, 112268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Huimin, D.W. Antioxidant activity in vitro of hydroxyproline peptides. Shipin Kexue Food Sci. 2021, 42, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Brunk, U.T.; Terman, A. Lipofuscin: Mechanisms of Age-Related Accumulation and Influence on Cell Function. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 611–619. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, M.; Noh, J.S. Regulatory Effects of Skate Skin-Derived Collagen Peptides with Different Molecular Weights on Lipid Metabolism in the Liver and Adipose Tissue. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Free Radicals, Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Stress and Its Classification. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, P.; Braeckman, B.P.; Matthijssens, F. ROS in Aging Caenorhabditis elegans: Damage or Signaling? Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2012, 2012, 608478. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, B.; Fu, Y. Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Yak Bones Collagen Enhanced the Capacities of Antiaging and Antioxidant in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 89, 104933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudirman, S.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, C.K.; Felim, J.; Kuo, H.P.; Kong, Z.L. Fermented Jellyfish (Rhopilema esculentum) Collagen Enhances Antioxidant Activity and Cartilage Protection on Surgically Induced Osteoarthritis in Obese Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1117893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G. Marine Peptides as Potential Anti-Aging Agents: Preparation, Characterization, Mechanisms of Action, and Future Perspectives. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, C.; Li, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhuang, J.; Shen, F.; Wang, Q.; Feng, F.; et al. Sea Cucumber (Acaudina leucoprocta) Peptides Extended the Lifespan and Enhanced Antioxidant Capacity via DAF-16/DAF-2/SOD-3/OLD-1/PEPT-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1065145. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Hu, X.; Zheng, H.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Guo, Z.; Huang, W.; Yu, R.; Song, L.; Zhu, J. Two Novel Antioxidant Peptides Derived from Arca subcrenata against Oxidative Stress and Extend Lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 81, 104462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.T.; McCarroll, S.A.; Bargmann, C.I.; Fraser, A.; Kamath, R.S.; Ahringer, J.; Li, H.; Kenyon, C. Genes That Act Downstream of DAF-16 to Influence the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2003, 424, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The Hallmarks of Aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, N.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Duan, R. Anti-Aging Effects and Mechanisms of Cod Collagen Peptides (CCPs) in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tometsuka, C.; Koyama, Y.I.; Ishijima, T.; Toyoda, T.; Teranishi, M.; Takehana, K.; Abe, K.; Nakai, Y. Collagen Peptide Ingestion Alters Lipid Metabolism-Related Gene Expression and the Unfolded Protein Response in Mouse Liver. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.; Song, Y.O.; Kang, K.H.; Noh, J.S. Anti-Obesity Effects of Collagen Peptide Derived from Skate (Raja Kenojei) Skin Through Regulation of Lipid Metabolism. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Nishime, Y.; Yuba, R.; Himeno, A.; Koizumi, S. Reduced Visceral Fat Weight and Body Weight Due to Ingestion of Fermented Collagen Peptide in High-Fat Diet-Fed Obese Mice. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2022, 68, 533–539. [Google Scholar]
- López-Yoldi, M.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Abete, I.; Ibero-Baraibar, I.; Aranaz, P.; González-Salazar, I.; Izco, J.M.; Recalde, J.I.; González-Navarro, C.J.; Milagro, F.I.; et al. Anti-Obesity Effects of a Collagen with Low Digestibility and High Swelling Capacity: A Human Randomized Control Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelo, X.S.; Luck, H.; Winer, S.; Winer, D.A. Morphological and Inflammatory Changes in Visceral Adipose Tissue during Obesity. Endocr. Pathol. 2014, 25, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, G.H.; Yoo, K.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Chung, H.; Jung, S.C.; Park, S.K.; Kim, J.S. Collagen Peptide Exerts an Anti-Obesity Effect by Influencing the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Gut. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Bang, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Jun, W.; Lee, Y.H. Anti-Obesity Effect of Porcine Collagen Peptide in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice by Regulating Adipogenesis. J. Med. Food 2022, 25, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Hur, J.; Ham, S.A.; Jo, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, M.J.; Seo, H.G. Fish Collagen Peptide Inhibits the Adipogenic Differentiation of Preadipocytes and Ameliorates Obesity in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Deza, D.; García-López, S.; Bernal-Monterde, V.; Polo-Cuadro, C.; Yagüe-Caballero, C.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M. Obesity-Mediated Inflammation and Its Influence on Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathophysiology, Clinical Impact, and Therapeutic Implications. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Gao, Y.; Ju, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Duan, Y. Collagen Peptides Alleviate Hyperglycemia in Mice by Modulating Insulin Resistance, Glucose Metabolism and Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 301, 140498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasset, E.; Briand, F.; Virgilio, N.; Schön, C.; Wilhelm, M.; Cudennec, B.; Ravallec, R.; Aboubacar, H.; Vleminckx, S.; Prawitt, J.; et al. A Specific Collagen Hydrolysate Improves Postprandial Glucose Tolerance in Normoglycemic and Prediabetic Mice and in a First Proof of Concept Study in Healthy, Normoglycemic and Prediabetic Humans. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 9607–9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; He, S.; Chen, Y.; Jin, H. Antidiabetic Effect of Collagen Peptides from Harpadon Nehereus Bones in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mice by Regulating Oxidative Stress and Glucose Metabolism. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in Health and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X. Regulation of the Gut Microbiota by Diet and Exercise: Improvements in Cognition and Emotion. Future Foods 2023, 8, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Zhang, C.; Song, W.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y. Jellyfish Collagen Hydrolysate Alleviates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress and Improves Gut Microbe Composition in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 5628702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampanelli, E.; Romp, N.; Troise, A.D.; Ananthasabesan, J.; Wu, H.; Gül, I.S.; De Pascale, S.; Scaloni, A.; Bäckhed, F.; Fogliano, V.; et al. Gut Bacterium Intestinimonas butyriciproducens Improves Host Metabolic Health: Evidence from Cohort and Animal Intervention Studies. Microbiome 2025, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhong, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Pi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Luo, J.; Xu, W. Bacteroides acidifaciens and Its Derived Extracellular Vesicles Improve DSS-Induced Colitis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1304232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Almela, I.; Romaní-Pérez, M.; Bullich-Vilarrubias, C.; Benítez-Páez, A.; Gómez Del Pulgar, E.M.; Francés, R.; Liebisch, G.; Sanz, Y. Bacteroides uniformis Combined with Fiber Amplifies Metabolic and Immune Benefits in Obese Mice. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1865706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Ryu, S.; Fukuda, S.; Hase, K.; Yang, C.S.; Lim, H.S.; Kim, M.S.; et al. Gut Commensal Bacteroides acidifaciens Prevents Obesity and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivière, A.; Selak, M.; Lantin, D.; Leroy, F.; De Vuyst, L. Bifidobacteria and Butyrate-Producing Colon Bacteria: Importance and Strategies for Their Stimulation in the Human Gut. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 206602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Jin, C.; Hao, L.; Mehal, W.Z.; Strowig, T.; Thaiss, C.A.; Kau, A.L.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Inflammasome-Mediated Dysbiosis Regulates Progression of NAFLD and Obesity. Nature 2012, 482, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, N.; Katagiri, S.; Komazaki, R.; Watanabe, K.; Maekawa, S.; Shiba, T.; Udagawa, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Ohtsu, A.; Kohda, T.; et al. Endotoxemia by Porphyromonas gingivalis Injection Aggravates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Disrupts Glucose/Lipid Metabolism, and Alters Gut Microbiota in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 406192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Katagiri, S.; Takahashi, H.; Sasaki, N.; Maekawa, S.; Komazaki, R.; Hatasa, M.; Kitajima, Y.; Maruyama, Y.; Shiba, T.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis Impairs Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle Associated with Altering Gut Microbiota. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21171. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, M.K.; Boudry, G.; Lemay, D.G.; Raybould, H.E. Changes in Intestinal Barrier Function and Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats Are Dynamic and Region Dependent. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G840–G851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmody, R.N.; Gerber, G.K.; Luevano, J.M.; Gatti, D.M.; Somes, L.; Svenson, K.L.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Diet Dominates Host Genotype in Shaping the Murine Gut Microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astbury, S.; Atallah, E.; Vijay, A.; Aithal, G.P.; Grove, J.I.; Valdes, A.M. Lower Gut Microbiome Diversity and Higher Abundance of Proinflammatory Genus Collinsella Are Associated with Biopsy-Proven Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Yu, Q.; Tang, J.; Xiang, J.; Kendall, M.M. Unraveling the Gut Microbiota’s Role in Obesity: Key Metabolites, Microbial Species, and Therapeutic Insights. J. Bacteriol. 2025, 207, e0047924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, K.M.; Hansell, E.J.; Thorley, J.; Funnell, M.P.; Thackray, A.E.; Stensel, D.J.; Bailey, S.J.; James, L.J.; Prawitt, J.; Virgilio, N.; et al. The effects of collagen peptide supplementation on appetite and post-exercise energy intake in females: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Norte, J.A.; García-Mir, B.; Quintana, L.; Buracchio, B.; Guerrero-Bonmatty, R. Anti-Aging Effects of Low-Molecular-Weight Collagen Peptide Supplementation on Facial Wrinkles and Skin Hydration: Outcomes from a Six-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Norte, J.A.; Gervasini-Rodríguez, G.; Santiago-Triviño, M.Á.; García-López, V.; Guerrero-Bonmatty, R. Oral administration of hydrolyzed collagen alleviates pain and enhances functionality in knee osteoarthritis: Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2024, 43, 101424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, P.; Navarro-Herrera, D.; Zabala, M.; Romo-Hualde, A.; López-Yoldi, M.; Vizmanos, J.L.; Milagro, F.I.; González-Navarro, C.J. Phenolic Compounds Reduce the Fat Content in Caenorhabditis elegans by Affecting Lipogenesis, Lipolysis, and Different Stress Responses. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavorov-Dayliev, D.; Milagro, F.I.; Ayo, J.; Oneca, M.; Goyache, I.; López-Yoldi, M.; Aranaz, P. Glucose-lowering effects of a synbiotic combination containing Pediococcus acidilactici in C. elegans and mice. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 2117–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis Model Assessment: Insulin Resistance and β-Cell Function from Fasting Plasma Glucose and Insulin Concentrations in Man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cuevillas, B.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Abete, I.; Zulet, M.A.; Galarregui, C.; Gonzalez-Navarro, C.J.; Milagro, F.I.; Martínez, J.A.; Navas-Carretero, S. Possible Metabolic Interplay between Quality of Life and Fecal Microbiota in a Presenior Population: Preliminary Results. Nutrition 2022, 103–104, 111841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavorov-Dayliev, D.; Milagro, F.I.; López-Yoldi, M.; Clemente, I.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Ayo, J.; Oneca, M.; Aranaz, P. Pediococcus acidilactici (PA1c®) Alleviates Obesity-Related Dyslipidemia and Inflammation in Wistar Rats by Activating Beta-Oxidation and Modulating the Gut Microbiota. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10855–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xia, J. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for Comprehensive Statistical, Functional, and Meta-Analysis of Microbiome Data. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CNT | HFS | C-LMW | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epididymal fat (g) | 0.54 ± 0.09 *** | 1.85 ± 0.16 | 1.90 ± 0.11 |
| Retroperitoneal fat (g) | 0.25 ± 0.05 *** | 0.86 ± 0.06 | 0.70 ± 0.09 |
| Subcutaneous fat (g) | 0.32 ± 0.05 *** | 2.22 ± 0.25 | 1.70 ± 0.20 |
| Mesenteric fat (g) | 0.32 ± 0.06 *** | 1.37 ± 0.12 | 0.99 ± 0.11 * |
| Visceral fat (g) | 1.11 ± 0.19 *** | 4.20 ± 0.18 | 3.59 ± 0.20 * |
| Total fat (g) | 1.43 ± 0.23 *** | 6.42 ± 0.34 | 5.29 ± 0.39 * |
| Liver (g) | 1.10 ± 0.05 ** | 1.50 ± 0.11 | 1.24 ± 0.07 |
| Gastrocnemius muscle (g) | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.01 |
| Spleen (g) | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| CNT | HFS | C-LMW | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 105.9 ± 14.7 *** | 219.5 ± 7.44 | 190.5 ± 9.2 * |
| Insulin (µg/L) | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) *** | 2.8 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.3 * |
| HOMA | 2.4 ± 0.7 *** | 37.9 ± 4.8 | 19.0 ± 3.4 ** |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 116.6 ± 3.1 *** | 187.8 ± 10.6 | 160.1 ± 10.2 |
| HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 60.7 ± 5.4 * | 76.1 ± 3.2 | 70.28 ± 3.6 |
| Cholesterol/HDL-Cholesterol | 2.0 ± 0.1 * | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 2.2 (2.0–2.3) |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 90.7 ± 4.8 | 91.7 ± 4.9 | 84.1 ± 6.9 |
| ALT (U/L) | 60.1 ± 5.0 | 91.5 ± 13.1 | 88.9 ± 11.4 |
| AST (U/L) | 372.3 ± 49.3 | 340.6 ± 32.4 | 374.4 ± 39.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Yoldi, M.; Aranaz, P.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; González-Salazar, I.; Izco, J.M.; Recalde, J.I.; González-Navarro, C.J.; Milagro, F.I. Low-Molecular-Weight Bovine Collagen Peptides Reduce Fat Accumulation in C. elegans and Ameliorate Obesity-Related Metabolic Dysfunction and Microbiota Diversity in C57BL/6 Male Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189149
López-Yoldi M, Aranaz P, Riezu-Boj JI, González-Salazar I, Izco JM, Recalde JI, González-Navarro CJ, Milagro FI. Low-Molecular-Weight Bovine Collagen Peptides Reduce Fat Accumulation in C. elegans and Ameliorate Obesity-Related Metabolic Dysfunction and Microbiota Diversity in C57BL/6 Male Diet-Induced Obese Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):9149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189149
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Yoldi, Miguel, Paula Aranaz, José I. Riezu-Boj, Itxaso González-Salazar, Jesús M. Izco, José I. Recalde, Carlos J. González-Navarro, and Fermín I. Milagro. 2025. "Low-Molecular-Weight Bovine Collagen Peptides Reduce Fat Accumulation in C. elegans and Ameliorate Obesity-Related Metabolic Dysfunction and Microbiota Diversity in C57BL/6 Male Diet-Induced Obese Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 9149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189149
APA StyleLópez-Yoldi, M., Aranaz, P., Riezu-Boj, J. I., González-Salazar, I., Izco, J. M., Recalde, J. I., González-Navarro, C. J., & Milagro, F. I. (2025). Low-Molecular-Weight Bovine Collagen Peptides Reduce Fat Accumulation in C. elegans and Ameliorate Obesity-Related Metabolic Dysfunction and Microbiota Diversity in C57BL/6 Male Diet-Induced Obese Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 9149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189149








