Salivary Amylase Gene Copy Number Relates with BMI Z-Score and with Response to Lifestyle Intervention for Children with Overweight and Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study and Participants
4.2. Anthropometric Parameters
4.3. Dietary Assessment
4.4. Saliva Sample Collection
4.5. DNA Extraction and Gene Copy Number Analysis Through qPCR
4.6. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- World Health Organization. Charts and Tables: WHO Child Growth Standards for Children Aged Under 5 Years. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/child-growth-standards (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Charts and Tables: WHO Growth Reference for Children Aged Between 5–19 Years. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/growth-reference-data-for-5to19-years (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- de Bont, J.; Bennett, M.; León-Muñoz, L.M.; Duarte-Salles, T. The Prevalence and Incidence Rate of Overweight and Obesity among 2.5 Million Children and Adolescents in Spain. Rev. Española Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 75, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Muniesa, P.; Mártinez-González, M.A.; Hu, F.B.; Després, J.P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Loos, R.J.F.; Moreno, L.A.; Bray, G.A.; Martinez, J.A. Obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.S.; Ge, B.; Petroski, G.; Kruse, R.L.; McElroy, J.A.; Koopman, R.J. Socioeconomic Status and Other Factors Associated with Childhood Obesity. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2018, 31, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdz, D.; Alvarez-Pitti, J.; Wójcik, M.; Borghi, C.; Gabbianelli, R.; Mazur, A.; Herceg-čavrak, V.; Lopez-Valcarcel, B.G.; Brzeziński, M.; Lurbe, E.; et al. Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: From Childhood to Adulthood. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gato-Moreno, M.; Martos-Lirio, M.F.; Leiva-Gea, I.; Bernal-López, M.R.; Vegas-Toro, F.; Fernández-Tenreiro, M.C.; López-Siguero, J.P. Early Nutritional Education in the Prevention of Childhood Obesity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, D.S.; Goodwin Davies, A.J.; Phan, T.L.T.; Cole, F.S.; Pajor, N.; Rao, S.; Eneli, I.; Kompaniyets, L.; Lange, S.J.; Christakis, D.A.; et al. Measuring BMI Change among Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. 2022, 17, e12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, D.C.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Curry, S.J.; Barry, M.J.; Davidson, K.W.; Doubeni, C.A.; Epling, J.W.; Kemper, A.R.; Krist, A.H.; Kurth, A.E.; et al. Screening for Obesity in Children and Adolescents: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2017, 317, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, D.S.; Hu, F.B.; Tappy, L.; Brand-Miller, J. Dietary Carbohydrates: Role of Quality and Quantity in Chronic Disease. BMJ 2018, 361, k2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erta, G.; Gersone, G.; Jurka, A.; Tretjakovs, P. The Link between Salivary Amylase Activity, Overweight, and Glucose Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrot des Gachons, C.; Breslin, P.A.S. Salivary Amylase: Digestion and Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, E.; Santos, V.; Barrambana, S.; Simões, C.; Carreira, L.; Infante, P.; Capela e Silva, F. Saliva Protein Composition Relates with Interindividual Variations in Bread Sensory Ratings. Starch-Stärke 2021, 73, 2000052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.; Costa, G.; Cordeiro, C.; Pinheiro, C.; Amado, F.; Lamy, E. Salivary Proteome and Glucose Levels Are Related with Sweet Taste Sensitivity in Young Adults. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1389208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, M.; El-Sayed Moustafa, J.S.; Takousis, P.; Pesce, F.; Bonnefond, A.; Andersson-Assarsson, J.C.; Sudmant, P.H.; Dorajoo, R.; Al-Shafai, M.N.; Bottolo, L.; et al. Low Copy Number of the Salivary Amylase Gene Predisposes to Obesity. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraju, V.; Venkatapoorna, C.M.K.; Babu, J.R.; Geetha, T. Salivary Amylase Gene Copy Number Is Associated with the Obesity and Inflammatory Markers in Children. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejía-Benítez, M.A.; Bonnefond, A.; Yengo, L.; Huyvaert, M.; Dechaume, A.; Peralta-Romero, J.; Klünder-Klünder, M.; García Mena, J.; El-Sayed Moustafa, J.S.; Falchi, M.; et al. Beneficial Effect of a High Number of Copies of Salivary Amylase AMY1 Gene on Obesity Risk in Mexican Children. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, R.Y.Y.; Mustaffa, S.B.; Wasan, P.S.; Sheng, L.; Marshall, C.R.; Scherer, S.W.; Teo, Y.Y.; Yap, E.P.H. Complex Copy Number Variation of AMY1 Does Not Associate with Obesity in Two East Asian Cohorts. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher, C.L.; Handsaker, R.E.; Esko, T.; Tuke, M.A.; Weedon, M.N.; Hastie, A.R.; Cao, H.; Moon, J.E.; Kashin, S.; Fuchsberger, C.; et al. Structural Forms of the Human Amylase Locus and Their Relationships to SNPs, Haplotypes and Obesity. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Akl, N.; Thompson, R.I.; Arredouani, A. High plasma salivary α-amylase, but not high AMY1 copy number, associated with low obesity rate in Qatari adults: Cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Moreno, M.; Mejía-Benítez, A.; Sharma, T.; Peralta-Romero, J.; Locia-Morales, D.; Klünder-Klünder, M.; National Obesity Network Mexico; Cruz, M.; Meyre, D. Association of AMY1A/AMY2A copy numbers and AMY1/AMY2 serum enzymatic activity with obesity in Mexican children. Pediatr. Obes. 2020, 8, e12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajic, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Dean, K.; Neznanova, L.; Romano, R.A.; Garneau, D.; Daugherity, E.; Globig, A.; Ruhl, S.; Gokcumen, O. Independent Amylase Gene Copy Number Bursts Correlate with Dietary Preferences in Mammals. eLife 2019, 8, e44628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, G.H.; Dominy, N.J.; Claw, K.G.; Lee, A.S.; Fiegler, H.; Redon, R.; Werner, J.; Villanea, F.A.; Mountain, J.L.; Misra, R.; et al. Diet and the Evolution of Human Amylase Gene Copy Number Variation. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.L.; Saus, E.; Smalley, S.V.; Cataldo, L.R.; Alberti, G.; Parada, J.; Gratacòs, M.; Estivill, X. Copy Number Polymorphism of the Salivary Amylase Gene: Implications in Human Nutrition Research. J. Nutr. Nutr. 2012, 5, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.M.; Byrne, S.; Thompson, A.; Ratnam, N.; Blair, E.; Bulsara, M.; Jones, T.W.; Davis, E.A. Increasing Body Mass Index Z-Score Is Continuously Associated with Complications of Overweight in Children, even in the Healthy Weight Range. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Peltzer, C.; Kahar, P.; Parmar, M.S. Body Mass Index (BMI): A Screening Tool Analysis. Cureus 2022, 14, e22119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillie, L.S.; Wang, D.; Popkin, B.M. Snacking Is Longitudinally Associated with Declines in Body Mass Index z Scores for Overweight Children, but Increases for Underweight Children. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozafarinia, M.; Heidari-Beni, M.; Abbasi, B.; Kelishadi, R. Association between Dietary Fat Quality Indices with Anthropometric Measurements in Children and Adolescents. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shay, C.M.; Van Horn, L.; Stamler, J.; Dyer, A.R.; Brown, I.J.; Chan, Q.; Miura, K.; Zhao, L.; Okuda, N.; Daviglus, M.L.; et al. Food and Nutrient Intakes and Their Associations with Lower BMI in Middle-Aged US Adults: The International Study of Macro-/Micronutrients and Blood Pressure (INTERMAP). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Cristobal, R.; Navas-Carretero, S.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Ordovas, J.M.; Martínez, J.A. Contribution of Macronutrients to Obesity: Implications for Precision Nutrition. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatapoorna, C.M.K.; Ayine, P.; Parra, E.P.; Koenigs, T.; Phillips, M.; Babu, J.R.; Sandey, M.; Geetha, T. Association of Salivary Amylase (AMY1) Gene Copy Number with Obesity in Alabama Elementary School Children. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcovecchio, M.L.; Florio, R.; Verginelli, F.; De Lellis, L.; Capelli, C.; Verzilli, D.; Chiarelli, F.; Mohn, A.; Cama, A. Low AMY1 Gene Copy Number Is Associated with Increased Body Mass Index in Prepubertal Boys. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukh, G.; Ericson, U.; Andersson-Assarsson, J.; Orho-Melander, M.; Sonestedt, E. Dietary starch intake modifies the relation between copy number variation in the salivary amylase gene and BMI. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Lee, K.W. Dietary Carbohydrates Interact with AMY1 Polymorphisms to Influence the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Korean Adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Children. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2013, 16, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.K.; Collins, C.; May, C.; Brain, K.; Wong See, D.; Burrows, T. Effectiveness of Family-Based Weight Management Interventions for Children with Overweight and Obesity: An Umbrella Review. JBI Evid. Synth. 2019, 17, 1341–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyberg, G.; Norman, Å.; Sundblom, E.; Zeebari, Z.; Elinder, L.S. Effectiveness of a Universal Parental Support Programme to Promote Health Behaviours and Prevent Overweight and Obesity in 6-Year-Old Children in Disadvantaged Areas, the Healthy School Start Study II, a Cluster-Randomised Controlled Trial. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Park, J.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, M.N.; Ham, O.K. Parent Involvement Intervention in Developing Weight Management Skills for Both Parents and Overweight/Obese Children. Asian Nurs. Res. 2016, 10, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjansdottir, A.G.; Johannsson, E.; Thorsdottir, I. Effects of a School-Based Intervention on Adherence of 7-9-Year-Olds to Food-Based Dietary Guidelines and Intake of Nutrients. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 13, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirasa, F.; Mitchell, L.; Azhar, A.; Chandrasekara, A.; Harris, N. A 6-Week Healthy Eating Intervention with Family Engagement Improves Food Knowledge and Preferences but Not Dietary Diversity among Urban Preschool Children in Sri Lanka. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 4328–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, S.F.; Lavelle, F.; Moore, S.E.; Dean, M.; McKinley, M.C.; McCole, P.; Hunter, R.F.; Dunne, L.; O’Connell, N.E.; Cardwell, C.R.; et al. Food Environment Intervention Improves Food Knowledge, Wellbeing and Dietary Habits in Primary School Children: Project Daire, a Randomised-Controlled, Factorial Design Cluster Trial. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, O.Y. Macronutrients Modified Dietary Intervention in the Management of Overweight/Obese Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2024, 67, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.A.; Truby, H.; Lee, A.; Harper, C.; Abbott, R.A.; Davies, P.S.W. Associations of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference with: Energy Intake and Percentage Energy from Macronutrients, in a Cohort of Australian Children. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stea, T.H.; Vettore, M.V.; Øvrebø, B.; Abildsnes, E. Changes in Dietary Habits and BMI Z-Score after a 6-Month Non-Randomized Cluster-Controlled Trial among 6-12 Years Old Overweight and Obese Norwegian Children. Food Nutr. Res. 2023, 67, 10–29219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heianza, Y.; Zhou, T.; Yuhang, C.; Huang, T.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. Starch Digestion–Related Amylase Genetic Variants, Diet, and Changes in Adiposity: Analyses in Prospective Cohort Studies and a Randomized Dietary Intervention. Diabetes 2020, 69, 1917–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.J.; Lobstein, T. Extended International (IOTF) Body Mass Index Cut-Offs for Thinness, Overweight and Obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Overweight and Obesity in Preschoolers. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03800823?cond=NCT03800823&rank=1 (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Ek, A.; Delisle Nyström, C.; Chirita-Emandi, A.; Tur, J.A.; Nordin, K.; Bouzas, C.; Argelich, E.; Martínez, J.A.; Frost, G.; Garcia-Perez, I.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial for Overweight and Obesity in Preschoolers: The More and Less Europe Study—An Intervention within the STOP Project. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, D.A.; Landry, D.; Little, J.; Minelli, C. Systematic Review of Statistical Approaches to Quantify, or Correct for, Measurement Error in a Continuous Exposure in Nutritional Epidemiology. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2017, 17, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, S.; Ródenas-Munar, M.; Argelich, E.; Mateos, D.; Ugarriza, L.; Tur, J.A.; Bouzas, C. Dietary Lipid Profile in Spanish Children with Overweight or Obesity: A Longitudinal Study on the Impact of Children’s Eating Behavior and Sedentary Habits. Nutrients 2025, 17, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing Real-Time PCR Data by the Comparative C(T) Method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
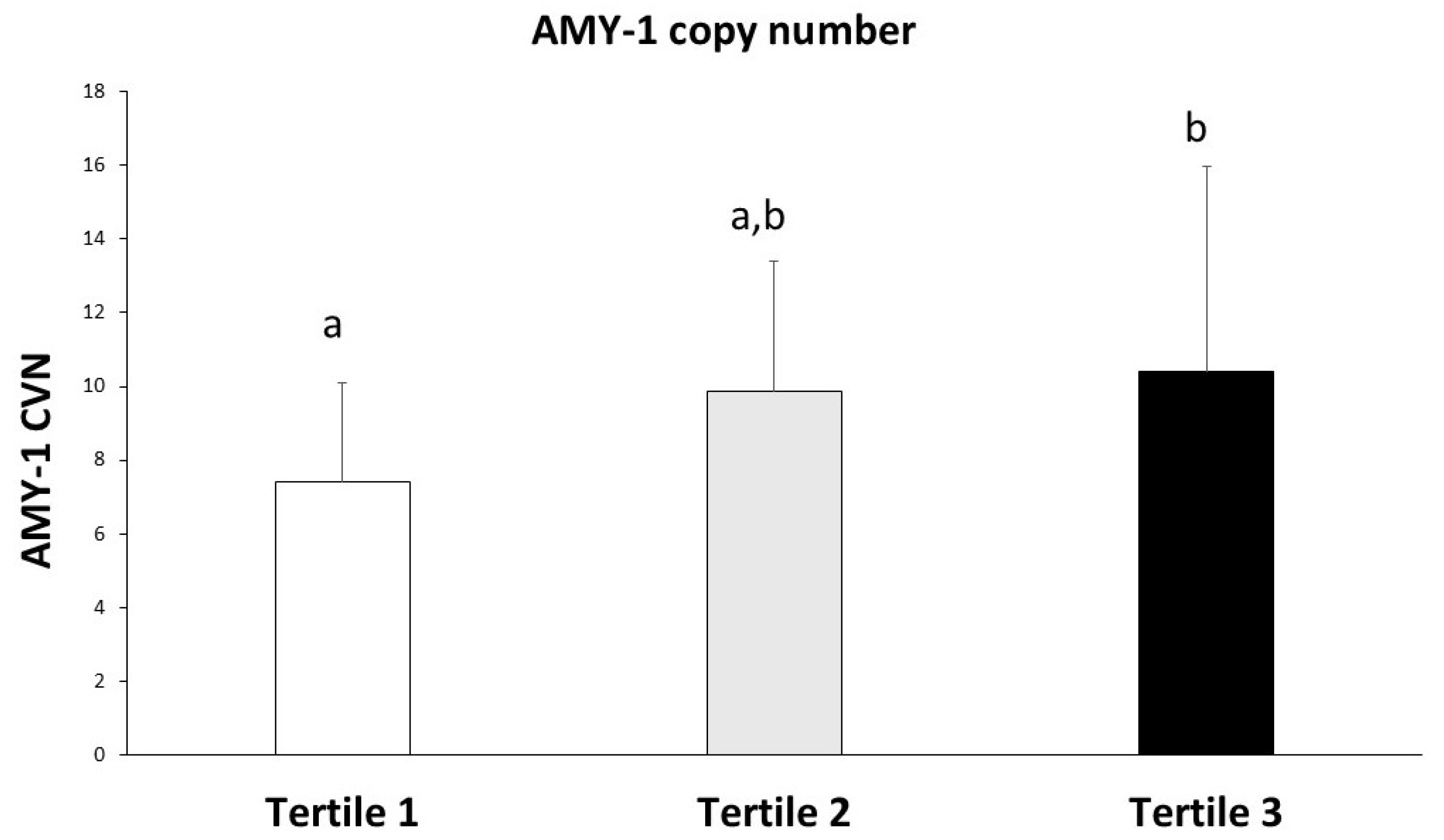

| Tertile 1 (<3.08) n = 30 | Tertile 2 (3.08 to 3.77) n = 30 | Tertile 3 (>3.77) n = 30 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Boys | 10 (31.0) | 11 (36.7) | 9 (30.0) | 0.351 |
| Girls | 20 (69.0) | 19 (63.3) | 21 (70.0) | |
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||
| Age (years) | 5.3 (1.5) | 5.7 (1.1) | 5.1 (1.4) | 0.185 |
| Weight (kg) | 27.0 (6.8) a | 34.8 (7.4) b | 37.6 (1.9) b | <0.001 |
| Height (cm) | 116.1 (12.5) | 120.8 (10.7) | 116.6 (12.2) | 0.240 |
| Waist (cm) | 66.5 (8.3) a | 74.0 (7.1) b | 79.0 (9.2) c | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 19.8 (1.8) a | 23.5 (1.2) b | 27.1 (2.9) c | <0.001 |
| z-score BMI | 2.2 (0.6) a | 3.4 (0.2) b | 4.3 (0.5) c | <0.001 |
| Energy (kcal) | 1461.3 (368.4) | 1678.2 (342.1) | 1704.8 (434.0) | 0.108 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 167.7 (52.2) | 193.4 (37.6) | 196.3 (61.7) | 0.197 |
| Protein (g) | 60.1 (14.7) | 68.5 (14.4) | 71.5 (26.7) | 0.186 |
| Fat (g) | 54.7 (14.8) | 60.6 (16.6) | 61.4 (20.0) | 0.423 |
| SFA (g) | 21.9 (7.0) | 23.6 (7.5) | 24.3 (6.2) | 0.398 |
| MUFA (g) | 18.7 (3.1) | 19.2 (3.9) | 19.5 (4.1) | 0.812 |
| PUFA (g) | 8.17 (3.6) | 9.94 (3.8) | 10.2 (4.0) | 0.206 |
| r | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Anthropometry (n = 90) | ||
| Weight | 0.002 | 0.989 |
| Waist | 0.005 | 0.969 |
| BMI | 0.146 | 0.238 |
| BMI z-score | 0.253 * | 0.039 |
| Food intake (n = 90) | ||
| Energy | 0.226 | 0.116 |
| Carbohydrates | 0.125 | 0.374 |
| Protein | 0.146 | 0.298 |
| Fat | 0.258 | 0.063 |
| SFA | 0.232 | 0.094 |
| MUFA | 0.254 | 0.078 |
| PUFA | 0.291 * | 0.034 |
| Standard Care (Control) (n = 22) | Parent Support Program (n = 25) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | |||
| Weight (kg) | Baseline | 31.5 (6.2) | 33.4 (10.0) | 0.462 |
| 9 months | 36.3 (7.9) | 37.6 (11.9) | 0.337 | |
| Δ | 4.8 (1.7) | 4.2 (1.9) | 0.070 | |
| Height (cm) | Baseline | 118.4 (11.0) | 118.4 (12.3) | 0.477 |
| 9 months | 124.1 (10.5) | 127.8 (10.9) | 0.134 | |
| Δ | 5.7 (1.6) | 9.4 (2.7) | 0.115 | |
| Waist (cm) | Baseline | 71.5 (7.2) | 70.5 (10.0) | 0.278 |
| 9 months | 72.6 (9.5) | 69.8 (11.6) | 0.215 | |
| Δ | 1.1 (2.3) | −0.07 (1.6) | 0.307 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | Baseline | 22.5 (2.9) | 23.3 (3.6) | 0.586 |
| 9 months | 23.5 (3.9) | 22.9 (4.1) | 0.298 | |
| Δ | 1.06 (2.1) | −0.446 (1.4) | 0.003 * | |
| BMI z-score | Baseline | 3.11 (1.0) | 3.34 (1.0) | 0.832 |
| 9 months | 3.34 (1.1) | 3.14 (1.3) | 0.277 | |
| Δ | 0.231 (0.4) | −0.203 (0.5) | <0.001 * | |
| Energy (kcal) | Baseline | 1620.9 (377.3) | 1698.3 (481.5) | 0.345 |
| 9 months | 1733.6 (393.1) | 1443.8 (316.1) | 0.022 * | |
| Δ | 112.7 (46.6) | −254.5 (33.5) | 0.032 * | |
| Carbohydrates (g) | Baseline | 185.2 (54.1) | 204.5 (64.6) | 0.326 |
| 9 months | 208.9 (61.0) | 187.1 (50.3) | 0.066 | |
| Δ | 23.7 (89.1) | −17.4 (68.6) | 0.039 * | |
| Protein (g) | Baseline | 66.8 (20.1) | 76.7 (33.0) | 0.129 |
| 9 months | 70.5 (14.7) | 63.8 (16.8) | 0.264 | |
| Δ | 3.7 (33.9) | −12.9 (35.0) | 0.079 | |
| Fat (g) | Baseline | 66.0 (21.0) | 61.7 (19.0) | 0.372 |
| 9 months | 65.1 (21.9) | 47.4 (13.4) | 0.026 * | |
| Δ | −0.9 (5.5) | −14.3 (6.1) | 0.045 * | |
| SFA (g) | Baseline | 24.3 (8.60 | 24.9 (8.1) | 0.150 |
| 9 months | 23.2 (6.2) | 18.6 (5.4) | 0.130 | |
| Δ | −1.1 (2.6) | −6.3 (3.6) | 0.044 * | |
| MUFA (g) | Baseline | 20.1 (6.9) | 20.9 (5.6) | 0.237 |
| 9 months | 23.4 (9.2) | 16.9 (6.1) | 0.036 * | |
| Δ | 3.3 (6.6) | −4.3 (5.9) | 0.075 | |
| PUFA (g) | Baseline | 10.8 (5.5) | 8.95 (3.7) | 0.036 * |
| 9 months | 9.7 (4.4) | 7.09 (2.7) | 0.027 * | |
| Δ | −1.13 (7.0) | −1.86 (3.0) | 0.260 | |
| r | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Anthropometry (n = 25) | ||
| Δ Weight (kg) | 0.038 | 0.885 |
| Δ Waist (cm) | 0.381 | 0.161 |
| Δ BMI (kg/m2) | 0.037 | 0.875 |
| Δ BMI z-score | −0.008 | 0.972 |
| Food intake (n = 25) | ||
| Δ Energy (kcal) | −0.175 | 0.461 |
| Δ Carbohydrates (g) | −0.124 | 0.604 |
| Δ Protein (g) | −0.170 | 0.474 |
| Δ Fat (g) | −0.421 | 0.064 |
| Δ SFA (g) | −0.219 | 0.353 |
| Δ MUFA (g) | −0.135 | 0.581 |
| Δ PUFA (g) | −0.448 | 0.047 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Bouzas, C.; Cardoso, H.; García, S.; Argelich, E.; Mateos, D.; Marques, M.; Campos, C.; Lamy, E.; Tur, J.A. Salivary Amylase Gene Copy Number Relates with BMI Z-Score and with Response to Lifestyle Intervention for Children with Overweight and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189059
Monserrat-Mesquida M, Bouzas C, Cardoso H, García S, Argelich E, Mateos D, Marques M, Campos C, Lamy E, Tur JA. Salivary Amylase Gene Copy Number Relates with BMI Z-Score and with Response to Lifestyle Intervention for Children with Overweight and Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189059
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonserrat-Mesquida, Margalida, Cristina Bouzas, Hélia Cardoso, Silvia García, Emma Argelich, David Mateos, Monica Marques, Catarina Campos, Elsa Lamy, and Josep A. Tur. 2025. "Salivary Amylase Gene Copy Number Relates with BMI Z-Score and with Response to Lifestyle Intervention for Children with Overweight and Obesity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189059
APA StyleMonserrat-Mesquida, M., Bouzas, C., Cardoso, H., García, S., Argelich, E., Mateos, D., Marques, M., Campos, C., Lamy, E., & Tur, J. A. (2025). Salivary Amylase Gene Copy Number Relates with BMI Z-Score and with Response to Lifestyle Intervention for Children with Overweight and Obesity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 9059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189059











