The Combination Empagliflozin/Metformin Attenuates the Progression of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in a Diet-Induced Experimental Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
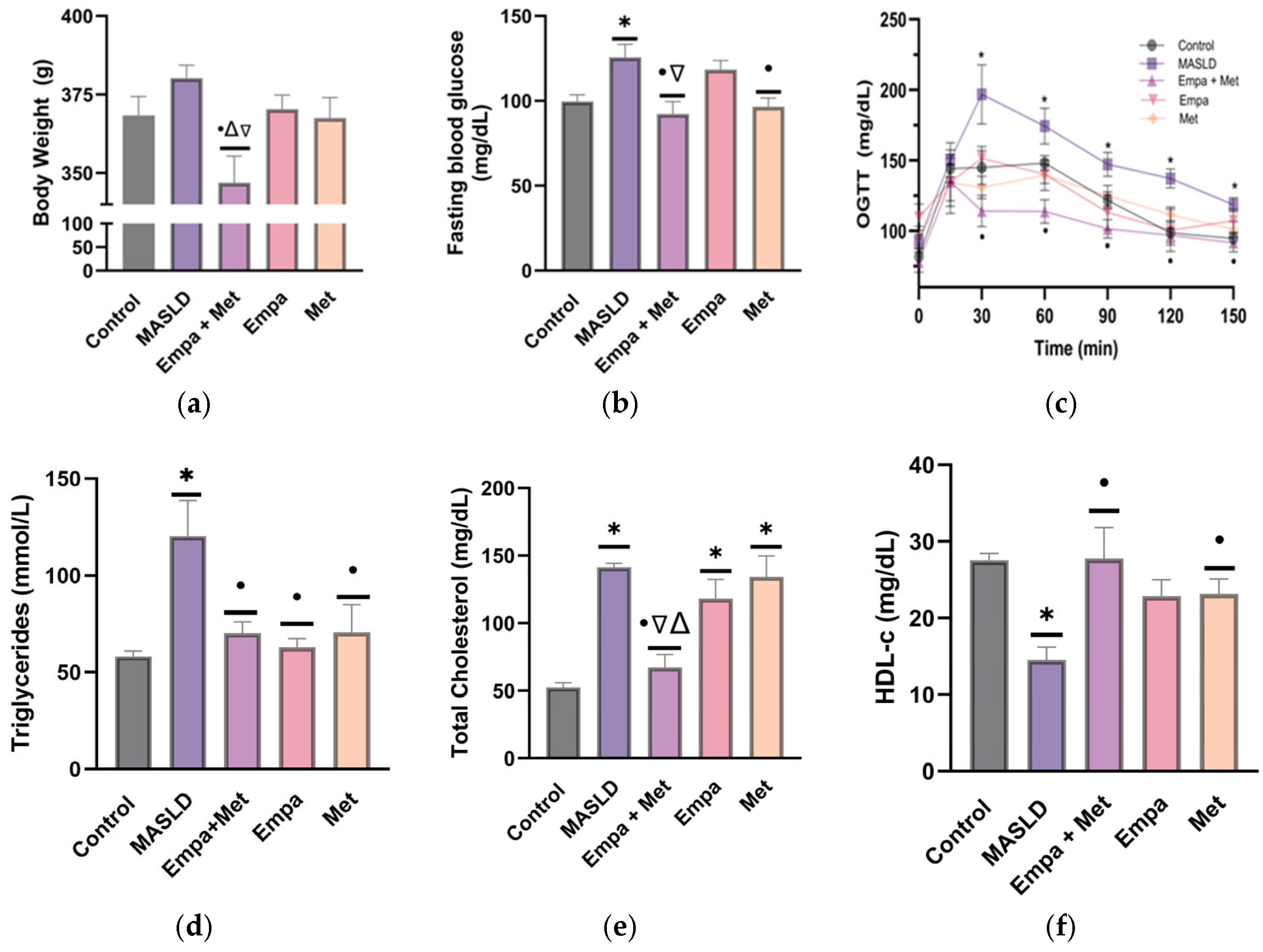
2.1. Validation of the Model of Metabolic Syndrome and Liver Damage
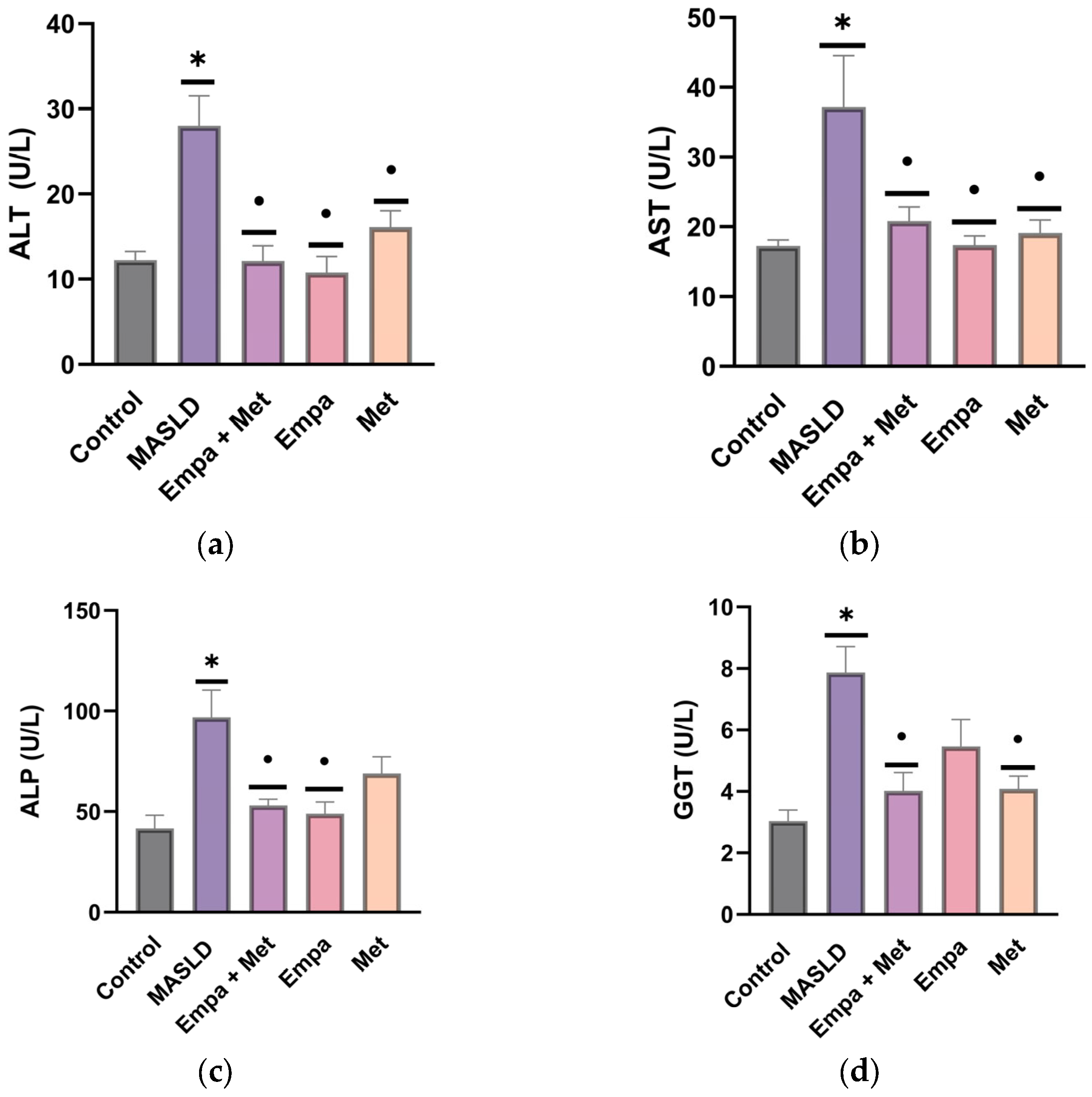
2.2. Plasma Markers of Liver Function
2.3. Effect of Empagliflozin/Metformin Combination on Risk Factors Associated with MASLD Progression
2.4. Effect of the Combination Empagliflozin/Metformin on the Markers of Liver Damage in MASLD
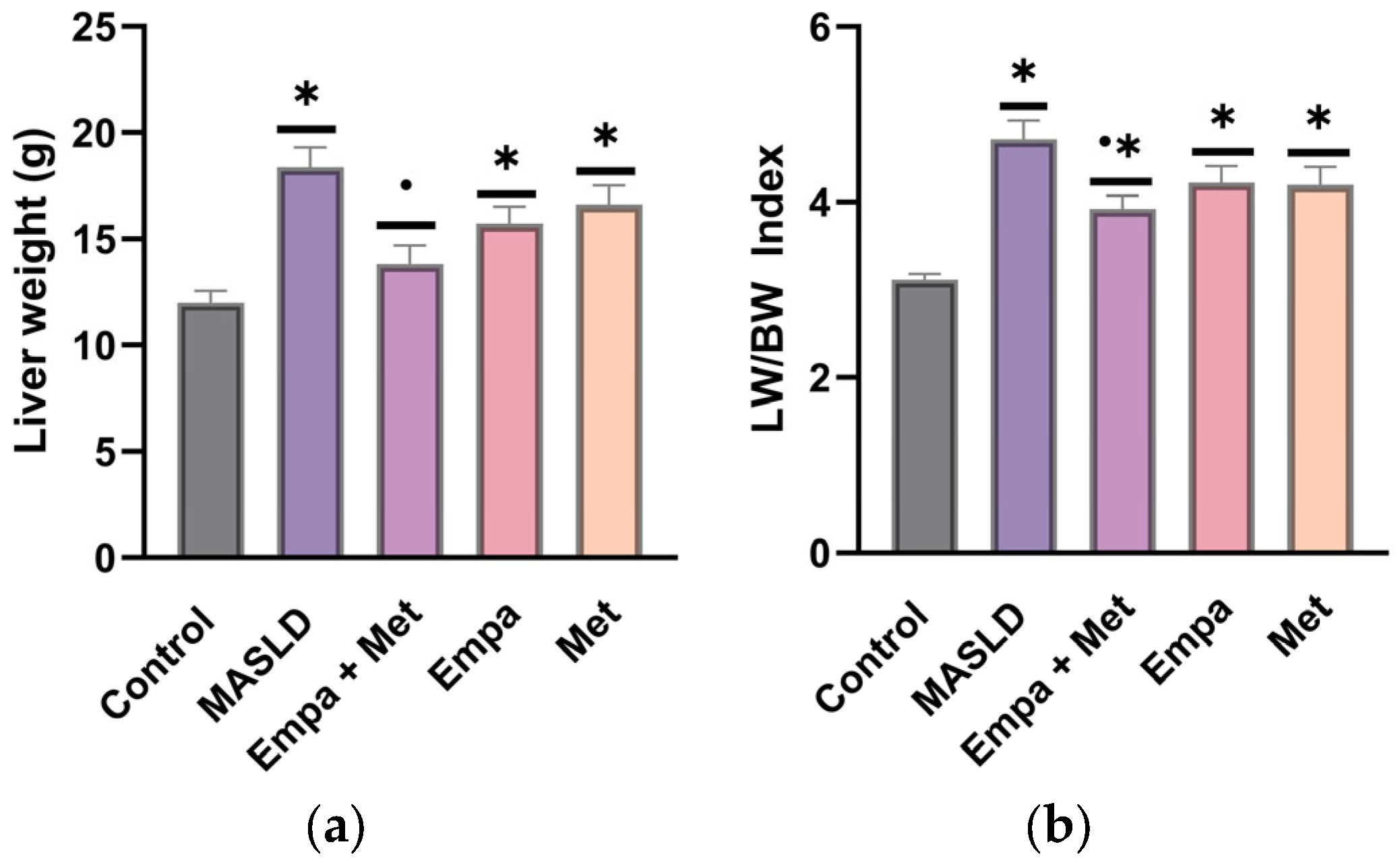
2.5. Liver Hypertrophy
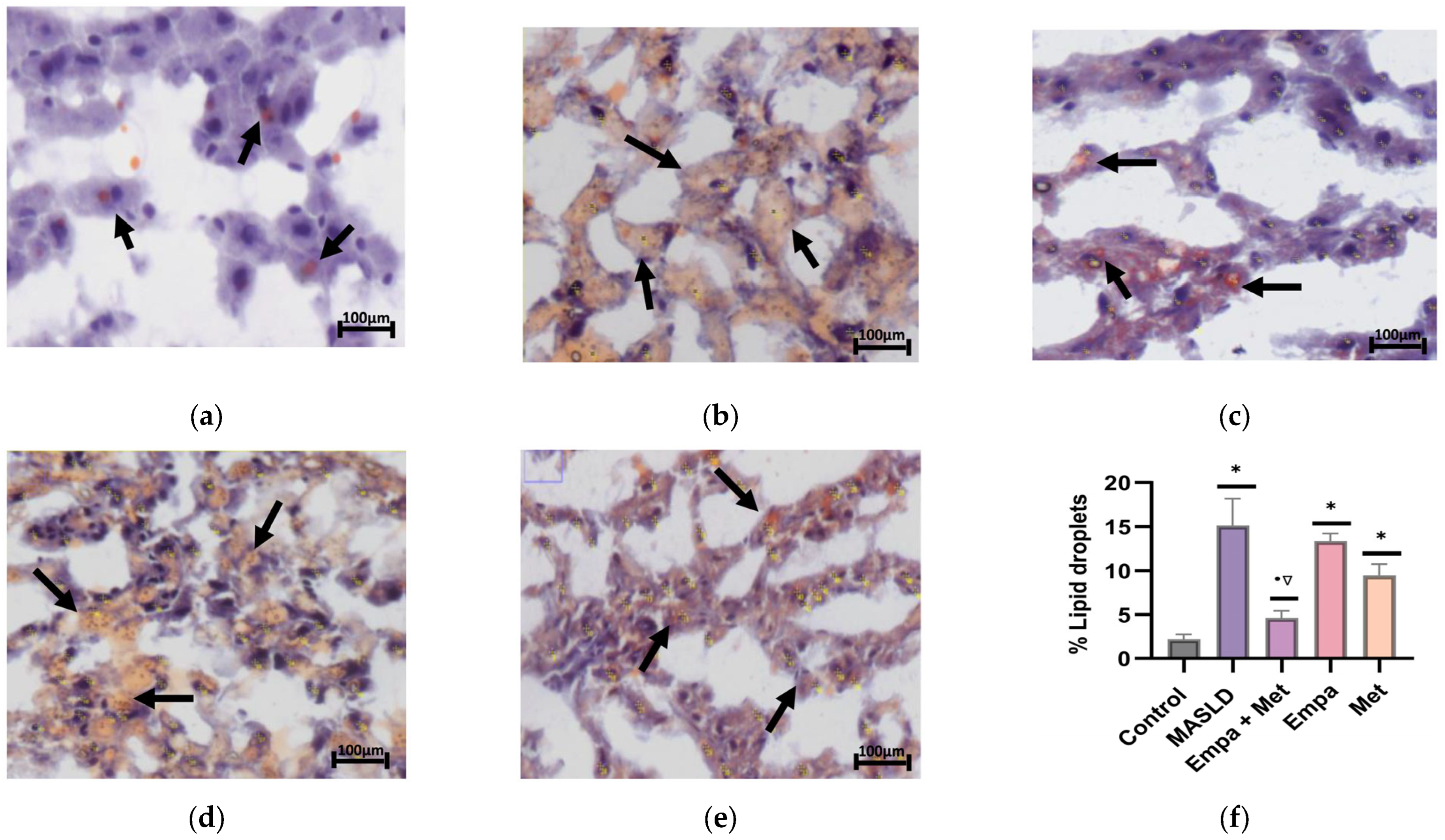
2.6. The Combination Empa + Met Alleviates Liver Damage and Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
2.7. Effect of the Empagliflozin/Metformin Combination on Oxidative Stress in Liver Tissue
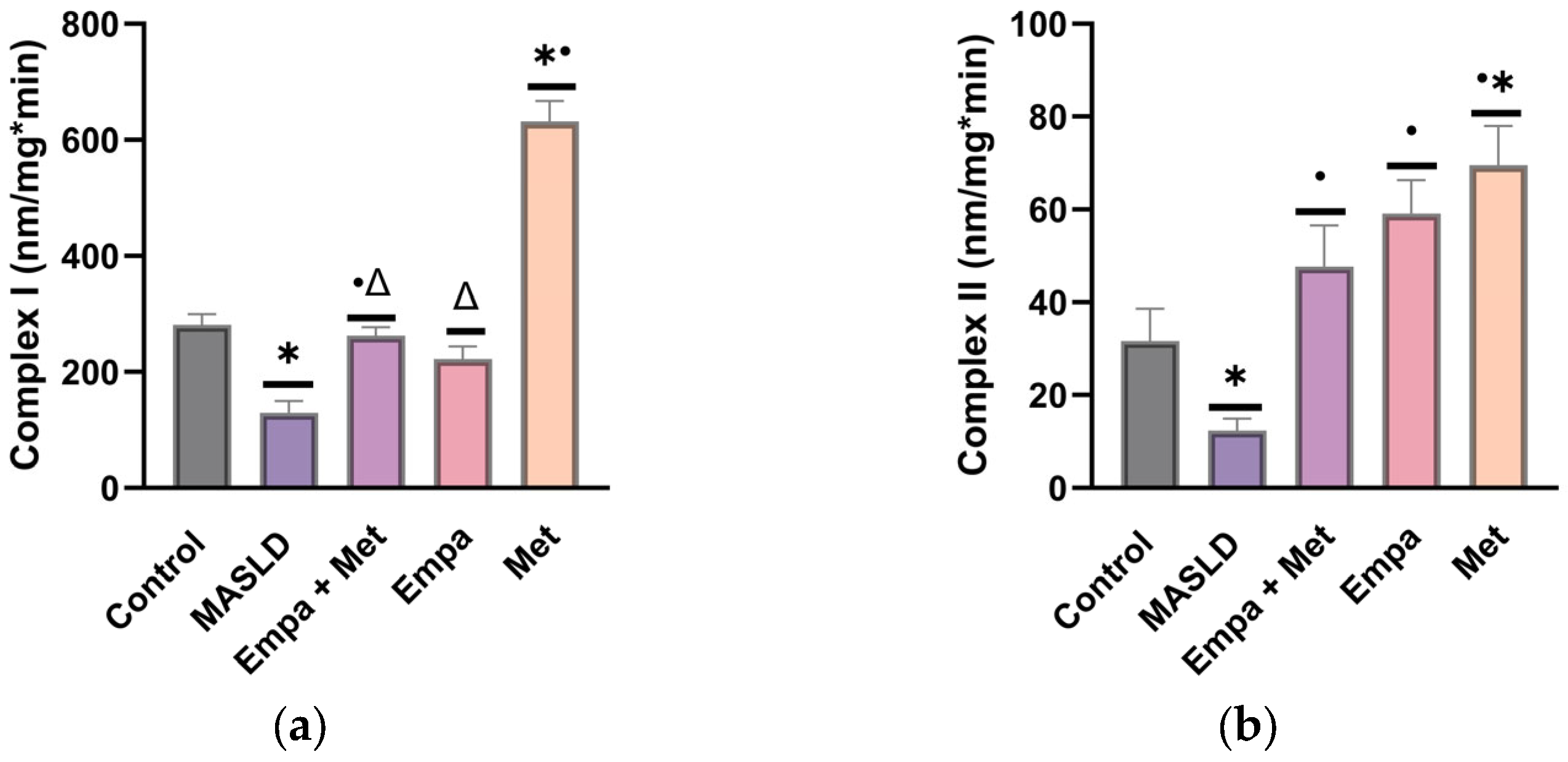
2.8. Effect of Empagliflozin/Metformin Combination on Mitochondrial Complexes I and II Activity
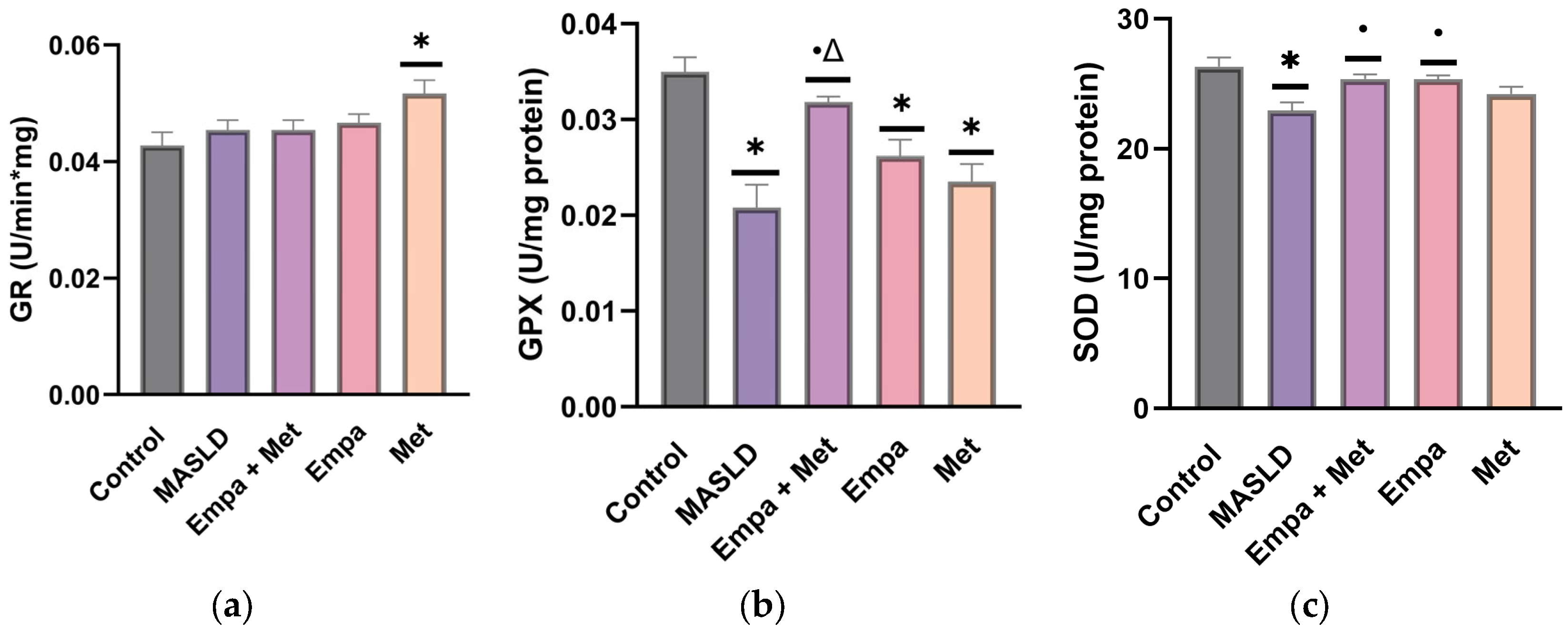
2.9. Effect of the Combination Empagliflozin/Metformin on the Endogenous Antioxidant Enzymes in the Liver
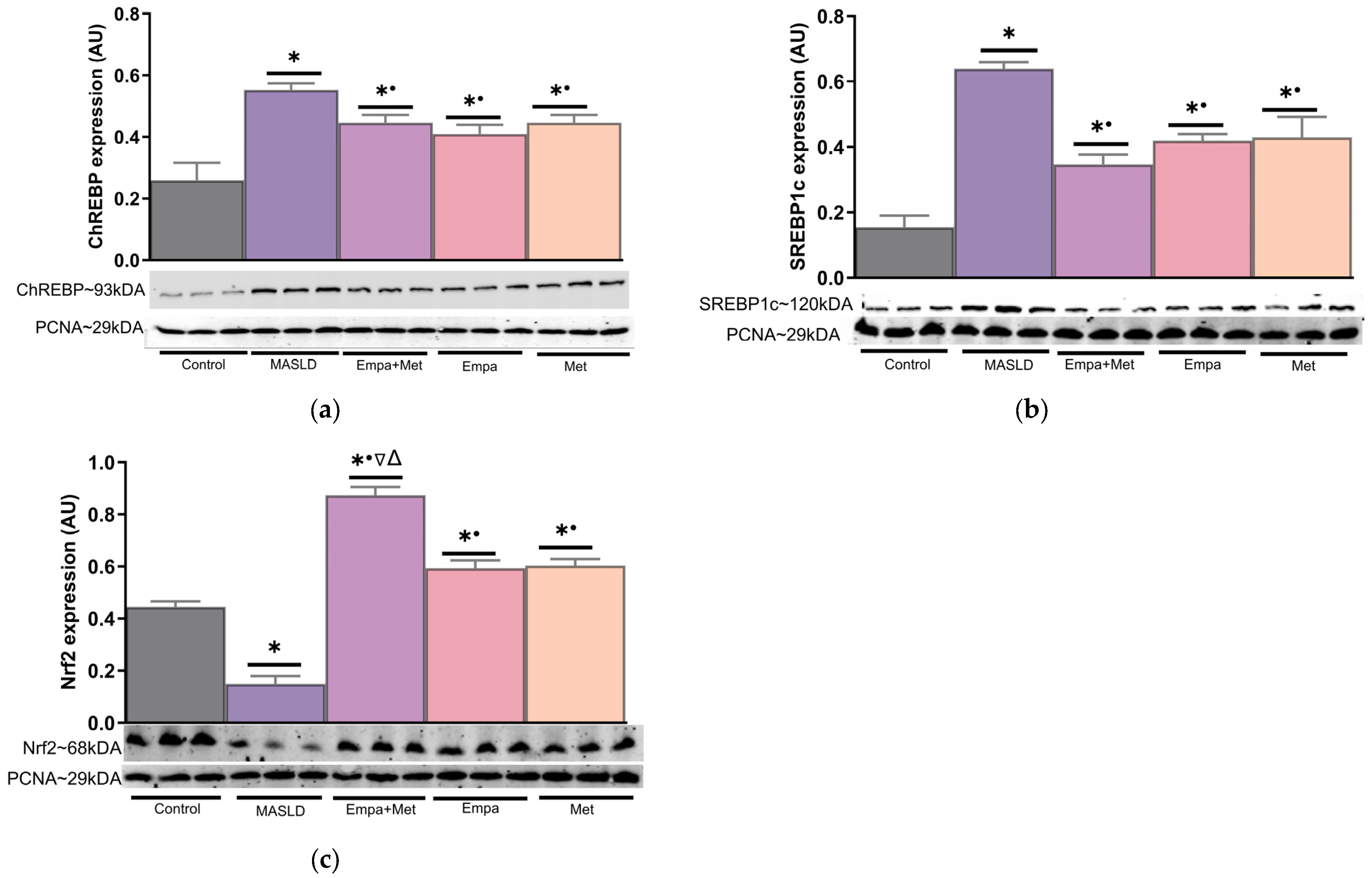
2.10. Expression of Transcription Factors Involved in Lipid Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in the Liver
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Blood Samples
4.4. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
4.5. Determination of Lipid Profile in Plasma
4.6. Markers of Liver Function in Plasma
4.7. Histological Analysis
4.7.1. Hematoxylin/Eosin (H&E) Staining
4.7.2. Red Oil Staining
4.7.3. Assessment of the Liver Content of Triglycerides and Cholesterol
4.8. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress
4.8.1. Assessment of the Activity of the Mitochondrial Respiratory Complexes
4.8.2. Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes in Liver
4.8.3. Determination of Concentrations of Malondialdehyde
4.8.4. Determination of Oxidized Proteins
4.9. Analysis of Protein Expression of Nuclear Transcription Factors
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine transaminase |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| AMPK | (AMP)-activated protein kinase alpha |
| BT | Bilirubin total |
| ChREBP | Carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein |
| DB | Direct bilirubin |
| DNL | De novo lipogenesis |
| DNPH | 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine |
| FFAs | Free fatty acids |
| FGB | Fasting blood glucose |
| GLP-1 | Agonists, glucagon-like peptide 1 |
| GGT | γ-Glutamyl transferase |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| GR | Glutathione reductase |
| HDL-c | high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IR | Insulin resistance |
| LXR | Liver X receptor alpha |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MS | Metabolic syndrome |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| NLRP3 | Nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich repeat-containing family, pyrin domain containing 3 |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor-erythroid 2 p45-related factor 2 (Nrf2) |
| OGTT | Oral glucose tolerance test |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| PUFAs | Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| SGLT2i | Sodium-glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitor |
| SREBP-1c | Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| TNF-alpha | Tumour necrosis factor-alpha |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| VLDL | Very low-density lipoproteins |
References
- Shaaban, H.H.; Alzaim, I.; El-Mallah, A.; Aly, R.G.; El-Yazbi, A.F.; Wahid, A. Metformin, pioglitazone, dapagliflozin and their combinations ameliorate manifestations associated with NAFLD in rats via anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, anti-oxidant and anti-apoptotic mechanisms. Life Sci. 2022, 308, 120956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Hong, W.; Lu, S.; Li, Y.; Guan, Y.; Weng, X.; Feng, Z. The NLRP3 Inflammasome in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis: Therapeutic Targets and Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 780496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchay, M.S.; Krishan, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Farooqui, K.J.; Singh, M.K.; Wasir, J.S.; Bansal, B.; Kaur, P.; Jevalikar, G.; Gill, H.K.; et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Liver Fat in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial (E-LIFT Trial). Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouwels, S.; Sakran, N.; Graham, Y.; Leal, A.; Pintar, T.; Yang, W.; Kassir, R.; Singhal, R.; Mahawar, K.; Ramnarain, D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiki, N.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Mantzoros, C.S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and dyslipidemia: An update. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Boursier, J.; de Ledinghen, V.; Anty, R.; Costentin, C.; Bureau, C. Confirmatory biomarker diagnostic studies are not needed when transitioning from NAFLD to MASLD. J. Hepatol. 2023, 80, e51–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tao, X.; Zeng, M.; Mi, Y.; Xu, L. Clinical and histological features under different nomenclatures of fatty liver disease: NAFLD, MAFLD, MASLD and MetALD. J. Hepatol. 2023, 80, e64–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.J. Epidemiology of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and alcohol-related liver disease (ALD). Metab. Target Organ. Damage 2024, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Kalligeros, M.; Henry, L. Epidemiology of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31, S32–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remus, P.A.; Fratila, O.; Rus, M.; Anca, C.A.R.; Mihai, V.C.; Pantis, C.; Diaconu, C.C.; Bratu, O.; Bungau, S.; Nemeth, S. Risk factors for adiposity in the urban population and influence on the prevalence of overweight and obesity. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Guo, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, L.; Auger, C.; Konoeda, H.; Sadri, A.-R.; Amini-Nik, S.; Jeschke, M.G. Hepatic steatosis associated with decreased β-oxidation and mitochondrial function contributes to cell damage in obese mice after thermal injury. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosavljevic, T.; Brankovic, M.; Samardzic, J.; Djuretić, J.; Vukicevic, D.; Vucevic, D.; Jakovljevic, V. Altered Mitochondrial Function in MASLD: Key Features and Promising Therapeutic Approaches. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzurović, E.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Mantzoros, C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and their association with vascular risk. Metabolism 2021, 119, 154770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Chai, J. In-depth analysis of de novo lipogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Mechanism and pharmacological interventions. Liver Res. 2023, 7, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Bi, Y.; Li, P.; Yin, T.; Gao, C.; Shen, S.; Gao, L.; Yang, D.; Zhu, D. Effects of liraglutide, metformin and gliclazide on body composition in patients with both type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized trial. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 10, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, H.; Malek, M.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Zamani, F.; Sohrabi, M.; Babaei, M.R.; Khamseh, M.E. Effect of Empagliflozin on Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Without Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 4697–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.; Sanyal, A. Breakthroughs in therapies for NASH and remaining challenges. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntikoudi, A.; Papachristou, A.; Tsalkitzi, A.; Margari, N.; Evangelou, E.; Vlachou, E. Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) and Type 2 Diabetes: Mechanisms, Diagnostic Approaches, and Therapeutic Interventions. Diabetology 2025, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doycheva, I.; Loomba, R. Effect of Metformin on Ballooning Degeneration in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): When to Use Metformin in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Adv. Ther. 2014, 31, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viollet, B.; Guigas, B.; Sanz, G.N.; Leclerc, J.; Foretz, M.; Andreelli, F. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: An overview. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gkiourtzis, N.; Michou, P.; Moutafi, M.; Glava, A.; Cheirakis, K.; Christakopoulos, A.; Vouksinou, E.; Fotoulaki, M. The benefit of metformin in the treatment of pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 4795–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Nikolopoulou, C.; Papoutsi, K.; Kyrou, I.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Kalotychou, V.; Randeva, M.S.; Chatha, K.; et al. Empagliflozin Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in High Fat Diet Fed ApoE(-/-) Mice by Activating Autophagy and Reducing ER Stress and Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.-C.; Stoica, R.A.; Salmen, T.; Janež, A.; Volčanšek, Š.; Popovic, D.; Muzurovic, E.; Rizzo, M.; Stoian, A.P. The Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2-Inhibitors on Steatosis and Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease or Steatohepatitis and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicina 2023, 59, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Ren, Q.; Chen, S.; Pan, X.; Yue, L.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Zhen, R. Metabolic and Hepatic Effects of Empagliflozin on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Mice. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 2549–2560, Erratum in: Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 2833–2834. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S439882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Tiniakos, D.G. Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5286–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arroyo, F.E.; Gonzaga-Sánchez, G.; Tapia, E.; Muñoz-Jiménez, I.; Manterola-Romero, L.; Osorio-Alonso, H.; Arellano-Buendía, A.S.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Roncal-Jiménez, C.A.; Lanaspa, M.A.; et al. Osthol Ameliorates Kidney Damage and Metabolic Syndrome Induced by a High-Fat/High-Sugar Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arroyo, F.E.; Gonzaga-Sánchez, G.; Silva-Palacios, A.; Roldán, F.J.; Loredo-Mendoza, M.L.; Alvarez-Alvarez, Y.Q.; Coyotl, J.A.d.L.S.; Orozco, K.A.V.; Tapia, E.; Osorio-Alonso, H.; et al. Osthole Prevents Heart Damage Induced by Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome: Role of Fructokinase (KHK). Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendia, A.S.A.; Rojas, J.G.J.; García-Arroyo, F.; Trejo, O.E.A.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F.; Argüello-García, R.; Sánchez-Lozada, L.G.; Bojalil, R.; Osorio-Alonso, H. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of allicin in the kidney of an experimental model of metabolic syndrome. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, I.C.M.; Karkucinska-Wieckowska, A.; Janikiewicz, J.; Szymanska, S.; Pronicki, M.; Dobrzyn, P.; Dabrowski, M.; Dobrzyn, A.; Oliveira, P.J.; Zischka, H.; et al. Western Diet Causes Obesity-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Development by Differentially Compromising the Autophagic Response. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, E.S.; Makri, E.; Goulas, A.; Xanthopoulos, K.; Polyzos, S.A. Animal studies of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2024, 37, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bence, K.K.; Birnbaum, M.J. Metabolic drivers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Sullivan, S.; Nadeau, K.J.; Green, M.; Roncal, C.; Nakagawa, T.; Kuwabara, M.; Sato, Y.; Kang, D.-H.; et al. Fructose and sugar: A major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caturano, A.; Galiero, R.; Loffredo, G.; Vetrano, E.; Medicamento, G.; Acierno, C.; Rinaldi, L.; Marrone, A.; Salvatore, T.; Monda, M.; et al. Effects of a Combination of Empagliflozin Plus Metformin vs. Metformin Monotherapy on NAFLD Progression in Type 2 Diabetes: The IMAGIN Pilot Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, A.; Takasu, T. Therapeutic Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitor Ipragliflozin and Metformin on NASH in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Endocr. Res. 2020, 45, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Azar, R.P.; Hosseiniazar, M.M.; Gharabagh, L.H. Empagliflozin add-on therapy is superior to metformin monotherapy in diabetic patients with NAFLD: An open-label, single-center, pilot clinical trial. J. Gen. Fam. Med. 2024, 25, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.-L.; Vethakkan, S.R.; Mustapha, N.R.N.; Mahadeva, S.; Chan, W.-K. Empagliflozin for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 65, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romera, I.; Ampudia-Blasco, F.J.; Pérez, A.; Ariño, B.; Pfarr, E.; Kis, S.G.; Naderali, E. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin in combination with other oral hypoglycemic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol. Nutr. Eng. Ed. 2016, 63, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirne, C.; Croce, E.; Di Benedetto, D.; Cantaluppi, V.; Comi, C.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Minisini, R.; Grossini, E.; Pirisi, M. Oxidative Stress in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Livers 2022, 2, 30–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Sun, P.; Zhang, W.; Xin, Q.; Wang, N.; Niu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luo, J.; Lu, J.; et al. Empagliflozin-Enhanced Antioxidant Defense Attenuates Lipotoxicity and Protects Hepatocytes by Promoting FoxO3a- and Nrf2-Mediated Nuclear Translocation via the CAMKK2/AMPK Pathway. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.K.; Marcinko, K.; Desjardins, E.M.; Lally, J.S.; Ford, R.J.; Steinberg, G.R. Treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Role of AMPK. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2016, 311, E730–E740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrese, M.; Cabrera, D.; Kalergis, A.M.; Feldstein, A.E. Innate Immunity and Inflammation in NAFLD/NASH. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Fukusato, T. Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15539–15548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Okanoue, T.; Bzowej, N.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Younes, Z.; Kohli, A.; Sarin, S.; Caldwell, S.H.; Alkhouri, N.; et al. Selonsertib for patients with bridging fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis due to NASH: Results from randomized phase III STELLAR trials. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albhaisi, S.; Noureddin, M. Current and Potential Therapies Targeting Inflammation in NASH. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 767314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janić, M.; Janež, A.; Šabović, M.; El-Tanani, M.; Rangraze, I.; Rizzo, M.; Lunder, M. Glucometabolic Efficacy of the Empagliflozin/Metformin Combination in People with Type 1 Diabetes and Increased Cardiovascular Risk: A Sub-Analysis of a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janić, M.; Cankar, M.; Šmid, J.; Štiglic, A.F.; Jerin, A.; Šabovič, M.; Janež, A.; Lunder, M.; Sasso, F.C. Empagliflozin-Metformin Combination Has Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Properties that Correlate with Vascular Protection in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Qiao, Q.; et al. Effect of dapagliflozin on liver and pancreatic fat in patients with type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2023, 37, 108610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milder, J.B.; Liang, L.-P.; Patel, M. Acute oxidative stress and systemic Nrf2 activation by the ketogenic diet. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 40, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na Kim, M.; Moon, J.H.; Cho, Y.M. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition reduces cellular senescence in the diabetic kidney by promoting ketone body-induced NRF2 activation. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 2561–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lin, J.; Yang, N.; Chen, M. Sugary Kefir Strain Lactobacillus mali APS1 Ameliorated Hepatic Steatosis by Regulation of SIRT-1/Nrf-2 and Gut Microbiota in Rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1700903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhry, S.; Nazmy, M.H.; Meakin, P.J.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Walsh, S.V.; Tsujita, T.; Dillon, J.F.; Ashford, M.L.; Hayes, J.D. Loss of Nrf2 markedly exacerbates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, W.; Wu, M.; Pan, H.; Lei, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, Q.; Ouyang, X.; Liang, Z. The SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin attenuates the activity of ROS-NLRP3 inflammasome axis in steatohepatitis with diabetes mellitus. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, W.; Zhong, J.; Lei, F.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W. Canagliflozin exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting intracellular glucose metabolism and promoting autophagy in immune cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 152, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Jia, Y.; Ma, A.; He, J.; Shao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, B.; Zhou, H. Dapagliflozin protects against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in db/db mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 934136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukeland, J.W.; Konopski, Z.; Eggesbø, H.B.; von Volkmann, H.L.; Raschpichler, G.; Bjøro, K.; Haaland, T.; Løberg, E.M.; Birkeland, K. Metformin in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, controlled trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Rahimlou, M.; Mahmoodi, M.; Moosavian, S.P.; Symonds, M.E.; Jalali, R.; Zare, M.; Imanieh, M.H.; Stasi, C. The effects of metformin administration on liver enzymes and body composition in non-diabetic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and/or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: An up-to date systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, M.D.; Galic, S.; Marcinko, K.; Sikkema, S.; Pulinilkunnil, T.; Chen, Z.-P.; O’NEill, H.M.; Ford, R.J.; Palanivel, R.; O’BRien, M.; et al. Single phosphorylation sites in Acc1 and Acc2 regulate lipid homeostasis and the insulin-sensitizing effects of metformin. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Rah, S.-Y.; An, H.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Roh, G.S.; Ryter, S.W.; Park, J.W.; Yang, C.H.; Surh, Y.-J.; Kim, U.-H.; et al. Metformin-induced TTP mediates communication between Kupffer cells and hepatocytes to alleviate hepatic steatosis by regulating lipophagy and necroptosis. Metabolism 2023, 141, 155516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, F.; Craddock, L.; Yang, J. Mechanism of AMPK suppression of LXR-dependent Srebp-1c transcription. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.J.; Dai, W.; Scott, M.J.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.Z.; Huang, X.S. Metformin improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese mice via down-regulation of apolipoprotein A5 as part of the AMPK/LXRα signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 108802–108809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, A.M.; Youssef, M.E.; El-Fattah, E.E.A.; Gobba, N.A.; Gaafar, A.G.A.; Girgis, S.; Shata, A.; Hafez, A.-M.; El-Ahwany, E.; Amin, N.A.; et al. Blunting p38 MAPKα and ERK1/2 activities by empagliflozin enhances the antifibrotic effect of metformin and augments its AMPK-induced NF-κB inactivation in mice intoxicated with carbon tetrachloride. Life Sci. 2021, 286, 120070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arefin, A.; Gage, M.C. Metformin, Empagliflozin, and Their Combination Modulate Ex-Vivo Macrophage Inflammatory Gene Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, L.; Zou, J.; Ran, W.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, H.; Guo, J. Advancements in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1087260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascolo, A.; Di Napoli, R.; Balzano, N.; Cappetta, D.; Urbanek, K.; De Angelis, A.; Scisciola, L.; Di Meo, I.; Sullo, M.G.; Rafaniello, C.; et al. Safety profile of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: A brief summary. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1010693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, K.; Takeda, K.; Maeda, M.; Ogawa, W.; Sato, T.; Okada, S.; Ohnishi, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Kashiwagi, A. Glucose area under the curve during oral glucose tolerance test as an index of glucose intolerance. Diabetol. Int. 2015, 7, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.-K.; Dai, W.; Zheng, Y.-W.; Zhao, S.-P. miR-122 promotes hepatic lipogenesis via inhibiting the LKB1/AMPK pathway by targeting Sirt1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifante, J.; de la Fuente-Fernández, M.; Román-Carmena, M.; Fernandez, N.; García, D.J.; Granado, M.; Ximendes, E. In vivo grading of lipids in fatty liver by near-infrared autofluorescence and reflectance. J. Biophotonics 2022, 16, e202200208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitler, K.M.; Shetty, S.K.; Cushing, E.M.; Sylvers-Davie, K.L.; Davies, B.S.J. Regulation of plasma triglyceride partitioning by adipose-derived ANGPTL4 in mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados-Castro, L.F.; Rodríguez-Rangel, D.S.; Montaño, M.; Ramos, C.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. Wood smoke exposure induces a decrease in respiration parameters and in the activity of respiratory complexes I and IV in lung mitochondria from guinea pigs. Environ. Toxicol. 2013, 30, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela-López, E.; del Valle-Mondragón, L.; Castrejón-Téllez, V.; Pérez-Torres, I.; Arenas, A.P.; Rojas, F.M.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Vargas-González, A.; Pastelín-Hernández, G.; Torres-Narváez, J.C.; et al. Role of the Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Type 1 (TRPV1) in the Regulation of Nitric Oxide Release in Wistar Rat Aorta. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8531975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Western Diet and Sugary Drink | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Control | MASLD | Empa/Met | Empa | Met |
| BW (g) | 314.3 ± 12.71 | 344.7 ± 5.09 * | 350.50 ± 9.86 * | 335.5 ± 9.97 | 324.73 ± 5.59 * |
| FBG (mg/dL) | 88.83 ± 2.10 | 102.3 ± 2.08 * | 97.83 ± 2.71 * | 106.8 ± 6.34 * | 102.2 ± 3.09 * |
| TC (mg/dL) | 59.62 ± 3.31 | 157.3 ± 6.75 * | 176.9 ± 14.03 * | 135.4 ± 9.60 * | 163.4 ± 13.09 * |
| TG (mmol/L) | 47.95 ± 5.69 | 166.2 ± 16.85 * | 192.7 ± 28.59 * | 152.1 ± 27.74 * | 179.5 ± 48.39 * |
| HDL-c (mg/dL) | 30.15 ± 1.58 | 20.99 ± 1.70 * | 21.37 ± 3.64 | 23.07 ± 3.47 * | 25.33 ± 4.18 * |
| OGTT [AUC (mg/dL/h)] | 6630 ± 422.3 | 8512 ± 448.1 * | 8349 ± 193.2 * | 8676 ± 144.5 * | 8481 ± 303.2 * |
| ALT (U/L) | 8.47 ± 0.70 | 17.52 ± 1.96 * | 14.79 ± 1.55 * | 10.63 ± 1.58 * | 10.85 ± 1.92 * |
| AST (U/L) | 17.01 ± 0.99 | 29.16 ± 3.91 * | 29.23 ± 3.37 * | 28.74 ± 3.52 * | 21.19 ± 2.85 * |
| ALP (U/L) | 51.21 ± 5.45 | 124.5 ± 11.52 * | 102.9 ± 4.44 * | 112.4 ± 8.22 * | 128.2 ± 13.18 * |
| GGT (U/L) | 2.75 ± 0.21 | 7.65 ± 0.75 * | 10.58 ± 1.36 * | 7.67 ± 1.1 * | 8.48 ± 1.12 * |
| DB (mg/dL) | 0.77 ± 0.11 | 2.83 ± 0.46 * | 3.06 ± 0.62 * | 3.38 ± 0.53 * | 2.85 ± 0.87 * |
| TB (mg/dL) | 0.14 ± 0.007 | 1.15 ± 0.25 * | 1.0 ± 0.26 * | 1.15 ± 0.26 * | 1.12 ± 0.20 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zambrano-Vásquez, O.R.; Cortes-Camacho, F.; Cabrera-Angeles, J.C.; Hernández-Alba, A.L.; García-Arroyo, F.E.; Castañeda-Sánchez, J.I.; Aréchaga-Ocampo, E.; Aparicio-Trejo, O.E.; Valle-Mondragón, L.D.; Martínez-Olivares, C.E.; et al. The Combination Empagliflozin/Metformin Attenuates the Progression of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in a Diet-Induced Experimental Rat Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189010
Zambrano-Vásquez OR, Cortes-Camacho F, Cabrera-Angeles JC, Hernández-Alba AL, García-Arroyo FE, Castañeda-Sánchez JI, Aréchaga-Ocampo E, Aparicio-Trejo OE, Valle-Mondragón LD, Martínez-Olivares CE, et al. The Combination Empagliflozin/Metformin Attenuates the Progression of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in a Diet-Induced Experimental Rat Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):9010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189010
Chicago/Turabian StyleZambrano-Vásquez, Oscar René, Fernando Cortes-Camacho, Juan Carlos Cabrera-Angeles, Ana Lilia Hernández-Alba, Fernando Enrique García-Arroyo, Jorge Ismael Castañeda-Sánchez, Elena Aréchaga-Ocampo, Omar Emiliano Aparicio-Trejo, Leonardo Del Valle-Mondragón, Constanza Estefanía Martínez-Olivares, and et al. 2025. "The Combination Empagliflozin/Metformin Attenuates the Progression of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in a Diet-Induced Experimental Rat Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 9010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189010
APA StyleZambrano-Vásquez, O. R., Cortes-Camacho, F., Cabrera-Angeles, J. C., Hernández-Alba, A. L., García-Arroyo, F. E., Castañeda-Sánchez, J. I., Aréchaga-Ocampo, E., Aparicio-Trejo, O. E., Valle-Mondragón, L. D., Martínez-Olivares, C. E., Hernández-Pando, R., Sánchez-Lozada, L. G., & Osorio-Alonso, H. (2025). The Combination Empagliflozin/Metformin Attenuates the Progression of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in a Diet-Induced Experimental Rat Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 9010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189010







