BDNF Val66Met Genotype, DNA Methylation, mRNA, and Protein Levels as Potential Blood-Based Biomarkers for Dementia and Cognitive Decline
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Participant’s Demographic and Clinical Data
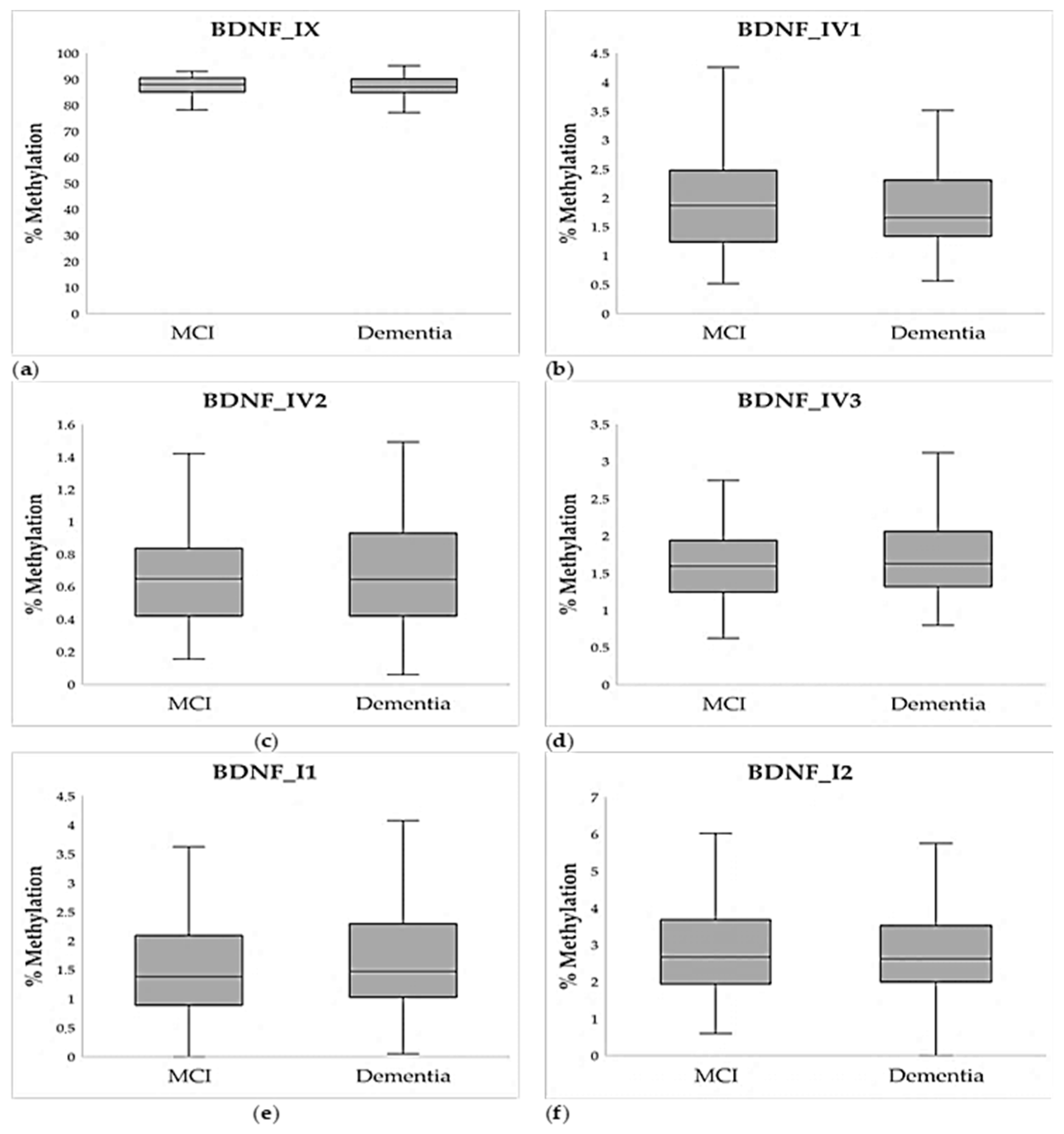
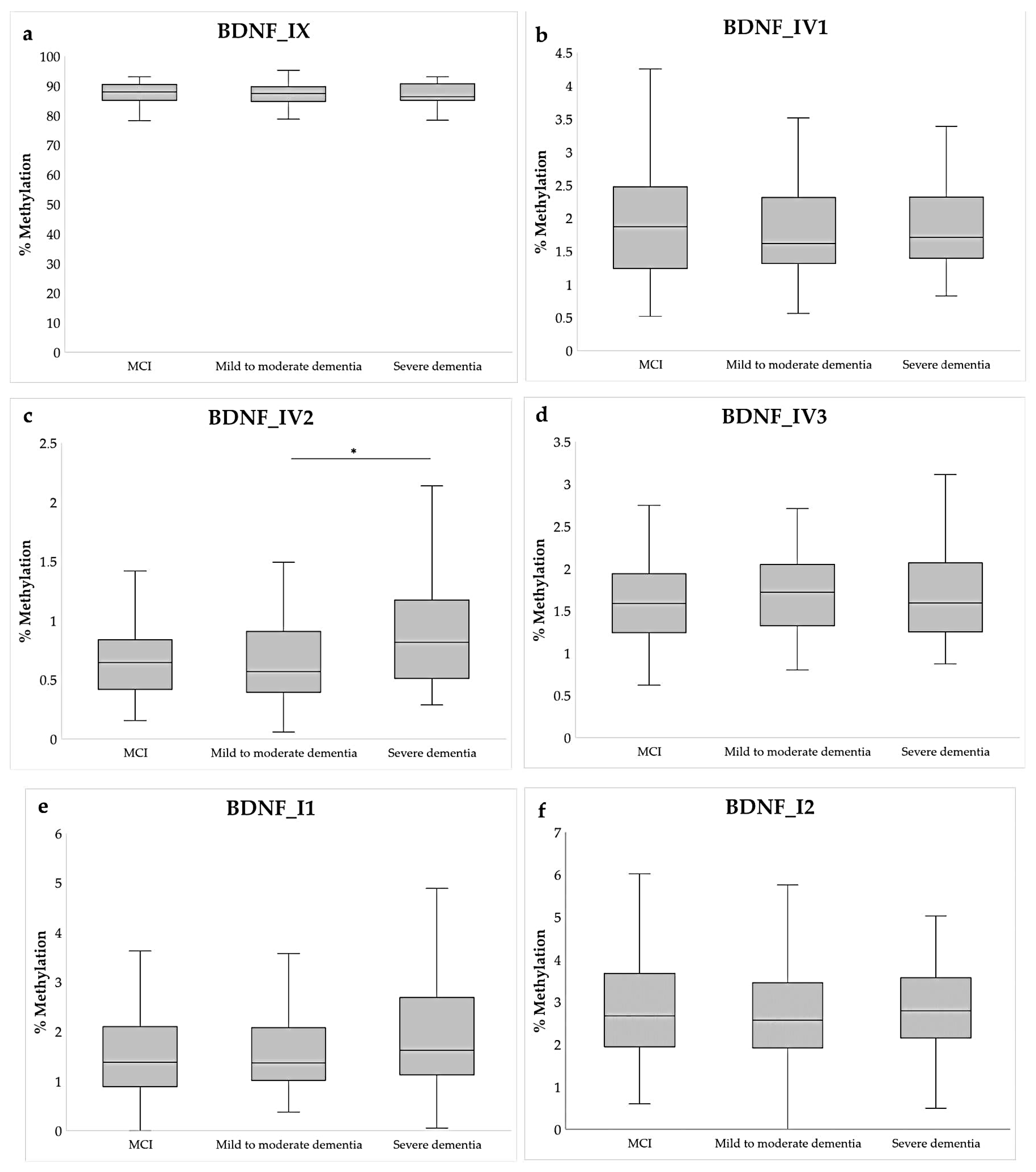
2.2. Methylation Analysis
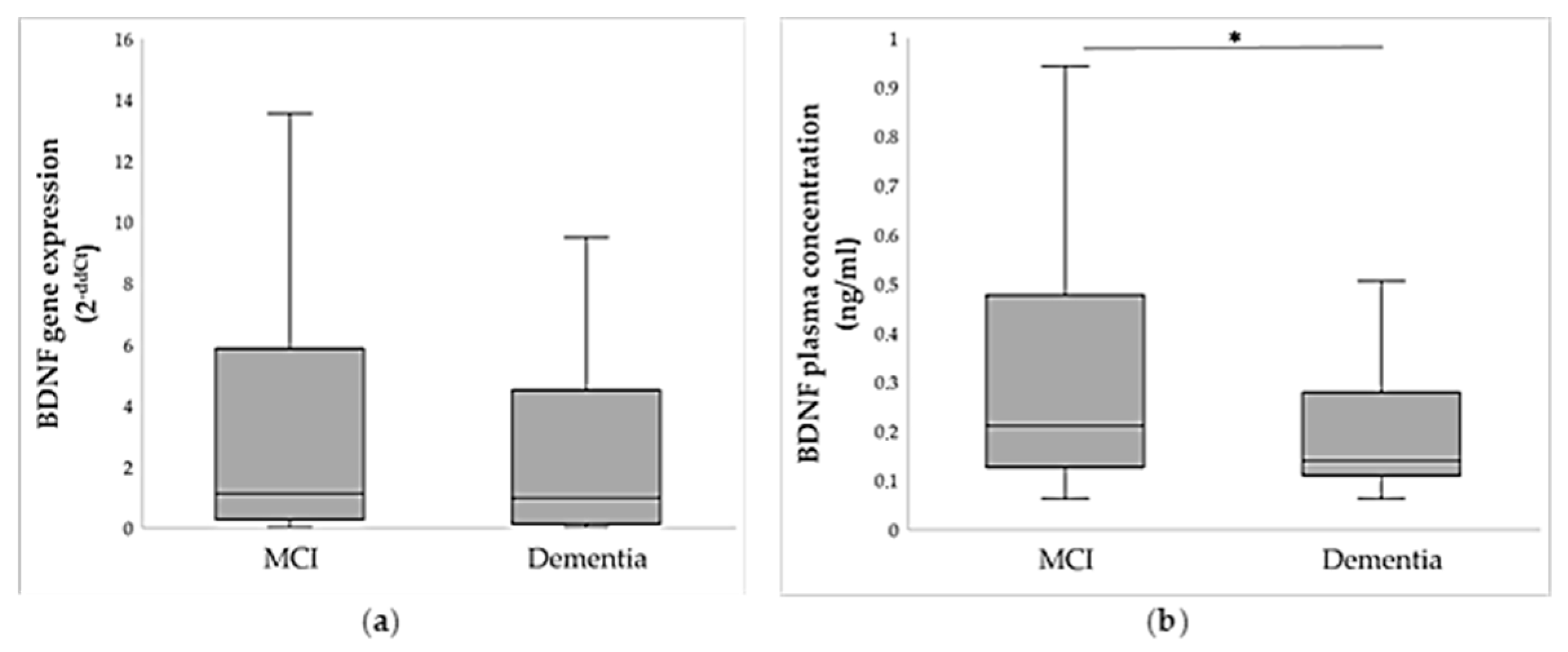
2.3. BDNF Gene and Protein Expression Analysis
2.4. Association of BDNF Methylation and Expression with Cognitive Scales
2.5. Association of BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism with BDNF Methylation and Expression
2.6. Association of BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism with Dementia and Cognitive Scores
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Blood Collection
4.3. Methylation Analysis
4.3.1. DNA Isolation and Bisulfite Conversion
4.3.2. Primer Design
4.3.3. Amplicon Generation
4.3.4. Library Preparation and Next-Generation Sequencing
4.4. Gene Expression
4.4.1. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription
4.4.2. Real-Time PCR and Comparative Ct (ΔΔCt) Method
4.5. Determination of BDNF Plasma Concentration
4.6. Genotyping
4.7. Biostatistical and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDNF | Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| CDT | Clock Drawing Test |
| MCI | Mild Cognitive Impairment |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
References
- Arvanitakis, Z.; Shah, R.C.; Bennett, D.A. Diagnosis and Management of Dementia: Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 1589–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Dementia. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Wilbur, J. Dementia: Dementia Types. FP Essent. 2023, 534, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farias, S.T.; Mungas, D.; Reed, B.R.; Harvey, D.; DeCarli, C. Progression of mild cognitive impairment to dementia in clinic- vs community-based cohorts. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Nagappan, G.; Lu, Y. BDNF and synaptic plasticity, cognitive function, and dysfunction. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 220, pp. 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sterling, K.; Song, W. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Alzheimer’s disease and its pharmaceutical potential. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Poo, M.M. Neurotrophin Regulation of Neural Circuit Development and Function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 14, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, D.K.; Scharfman, H.E. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. Growth Factors 2004, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, C.; Heese, K.; Hulette, C.; Rosenberg, C.; Otten, U. Region-Specific Neurotrophin Imbalances in Alzheimer Disease: Decreased Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Increased Levels of Nerve Growth Factor in Hippocampus and Cortical Areas. Arch. Neurol. 2000, 57, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wuu, J.; Mufson, E.J.; Fahnestock, M. Precursor Form of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Mature Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Are Decreased in the Pre-Clinical Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ji, H.; Dai, D.; Xu, X.; Jiang, D.; Hong, Q.; Ye, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; et al. Elevation of Peripheral BDNF Promoter Methylation Links to the Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Ishii, J.; Shinagawa, S.; Nakayama, R.; Shibata, N.; Kuerban, B.; Ohnuma, T.; Kondo, K.; Arai, H.; et al. Association between DNA Methylation of the BDNF Promoter Region and Clinical Presentation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Dis. Extra 2015, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransquet, P.D.; Ritchie, K.; Januar, V.; Saffery, R.; Ancelin, M.L.; Ryan, J. Is Peripheral BDNF Promoter Methylation a Preclinical Biomarker of Dementia? J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 73, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, M.F.; Kojima, M.; Callicott, J.H.; Goldberg, T.E.; Kolachana, B.S.; Bertolino, A.; Zaitsev, E.; Gold, B.; Goldman, D.; Dean, M.; et al. The BDNF Val66met Polymorphism Affects Activity-Dependent Secretion of BDNF and Human Memory and Hippocampal Function. Cell 2003, 112, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mill, J.; Tang, T.; Kaminsky, Z.; Khare, T.; Yazdanpanah, S.; Bouchard, L.; Jia, P.; Assadzadeh, A.; Flanagan, J.; Schumacher, A.; et al. Epigenomic Profiling Reveals DNA-Methylation Changes Associated with Major Psychosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 82, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakusic, J.; Vrieze, E.; Ghosh, M.; Pizzagalli, D.A.; Bekaert, B.; Claes, S.; Godderis, L. Interplay of Val66Met and BDNF Methylation: Effect on Reward Learning and Cognitive Performance in Major Depression. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouter, K.; Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Nedic Erjavec, G.; Milos, T.; Tudor, L.; Uzun, S.; Mimica, N.; Pivac, N.; Videtic Paska, A. Difference in Methylation and Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheleznyakova, G.Y.; Cao, H.; Schiöth, H.B. BDNF DNA Methylation Changes as a Biomarker of Psychiatric Disorders: Literature Review and Open Access Database Analysis. Behav. Brain Funct. 2016, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, V.; Sinibaldi, L.; Fiorentino, A.; Parisi, C.; Catalanotto, C.; Pasini, A.; Cogoni, C.; Pizzuti, A. Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Expression Is Regulated by MicroRNAs MiR-26a and MiR-26b Allele-Specific Binding. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, G.; Cavalleri, T.; Fazio, L.; Angrisano, T.; Iacovelli, L.; Porcelli, A.; Maddalena, G.; Punzi, G.; Mancini, M.; Gelao, B.; et al. BDNF Rs6265 Methylation and Genotype Interact on Risk for Schizophrenia. Epigenetics 2016, 11, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lommatzsch, M.; Zingler, D.; Schuhbaeck, K.; Schloetcke, K.; Zingler, C.; Schuff-Werner, P.; Virchow, J.C. The Impact of Age, Weight and Gender on BDNF Levels in Human Platelets and Plasma. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, H.; Altar, C.A.; Chen, R.; Nakamura, T.; Nakahashi, T.; Kambayashi, J.I.; Sun, B.; Tandon, N.N. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Is Stored in Human Platelets and Released by Agonist Stimulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 87, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Banks, W.A.; Fasold, M.B.; Bluth, J.; Kastin, A.J. Transport of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor across the Blood-Brain Barrier. Neuropharmacology 1998, 37, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Dalla Nora, E.; Morieri, M.L.; Soavi, C.; Sanz, J.M.; Zurlo, A.; Fellin, R.; Zuliani, G. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor plasma levels: Relationship with dementia and diabetes in the elderly population. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2015, 70, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, E.M.; Duarte, J.A.; Bristot, G.; Scotton, E.; Camozzato, A.L.; Chaves, M.L. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Serum Levels and Hippocampal Volume in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia due to Alzheimer Disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Dis. Extra 2016, 6, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.K.S.; Ho, C.S.H.; Tam, W.W.S.; Kua, E.H.; Ho, R.C. Decreased Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease (AD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, Y.; Yao, H.; Imamura, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Monji, A. Lower brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels are associated with age-related memory impairment in community-dwelling older adults: The Sefuri study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, J.D.; Strobl, E.V.; Shelly, W.B.; Karydas, A.M.; Robin Ketelle, R.N.; Wolkowitz, O.M.; Miller, B.L.; Rankin, K.P. BDNF serum concentrations show no relationship with diagnostic group or medication status in neurodegenerative disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2012, 9, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelucci, F.; Spalletta, G.; di Iulio, F.; Ciaramella, A.; Salani, F.; Colantoni, L.; Varsi, A.E.; Gianni, W.; Sancesario, G.; Caltagirone, C.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) patients are characterized by increased BDNF serum levels. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2010, 7, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Bryant, S.E.; Hobson, V.L.; Hall, J.R.; Barber, R.C.; Zhang, S.; Johnson, L.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Texas Alzheimer’s Research Consortium. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels are specifically associated with memory performance among Alzheimer’s disease cases. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2011, 31, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.C.; Gonçalves, G.S.; Rocha, N.P.; Moraes, E.N.; Bicalho, M.A.; Gualberto Cintra, M.T.; Jardim de Paula, J.; José Ravic de Miranda, L.F.; Clayton de Souza Ferreira, A.; Teixeira, A.L.; et al. Increased plasma levels of BDNF and inflammatory markers in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 53, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laske, C.; Stransky, E.; Leyhe, T.; Eschweiler, G.W.; Wittorf, A.; Richartz, E.; Bartels, M.; Buchkremer, G.; Schott, K. Stage-dependent BDNF serum concentrations in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2006, 113, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balietti, M.; Giuli, C.; Conti, F. Peripheral Blood Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor as a Biomarker of Alzheimer’s Disease: Are There Methodological Biases? Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6661–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Graham, P.L.; Angelucci, F.; Lucia, A.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Leyhe, T.; Turana, Y.; Lee, I.R.; Yoon, J.H.; et al. Peripheral Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7297–7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.K.S.; Coughlan, C.; Heyn, P.C.; Tagawa, A.; Carollo, J.J.; Kua, E.H.; Mahendran, R. Increased plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) as a potential biomarker for and compensatory mechanism in mild cognitive impairment: A case-control study. Aging 2021, 13, 22666–22689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Borovecki, F.; Filipcic, I.; Vuic, B.; Milos, T.; Nedic Erjavec, G.; Konjevod, M.; Tudor, L.; Mimica, N.; Uzun, S.; et al. Relationship between Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Cognitive Decline in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, A.; Labad, J.; Salvat-Pujol, N.; Barrachina, M.; Costas, J.; Urretavizcaya, M.; de Arriba-Arnau, A.; Crespo, J.M.; Soriano-Mas, C.; Carracedo, Á.; et al. BDNF Genetic Variants and Methylation: Effects on Cognition in Major Depressive Disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Stewart, R.; Park, M.S.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, I.S.; Kim, H.R.; Shin, M.G.; Cho, K.H.; Yoon, J.S. Associations of BDNF Genotype and Promoter Methylation with Acute and Long-Term Stroke Outcomes in an East Asian Cohort. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, H.S.; Hains, J.M.; Armanini, M.; Laramee, G.R.; Johnson, S.A.; Winslow, J.W. BDNF MRNA Is Decreased in the Hippocampus of Individuals with Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 1991, 7, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.S.; Keleshian, V.L.; Klein, S.; Rapoport, S.I. Epigenetic Modifications in Frontal Cortex from Alzheimer’s Disease and Bipolar Disorder Patients. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaras, M.; Hill, R.; Van Den Buuse, M. The BDNF Gene Val66Met Polymorphism as a Modifier of Psychiatric Disorder Susceptibility: Progress and Controversy. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; You, Y.; Joseph, C.; Mirzaei, M.; Klistorner, A.; Graham, S.L.; Gupta, V. BDNF Polymorphism: A Review of Its Diagnostic and Clinical Relevance in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, Y.L.; Ng, T.; Tan, M.; Tan, A.; Chan, A. Impact of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Genetic Polymorphism on Cognition: A Systematic Review. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e01009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havelka Mestrovic, A.; Tudor, L.; Nedic Erjavec, G.; Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Svob Strac, D.; Kovacic Petrovic, Z.; Pivac, N. The Impact of BDNF Val66Met on Cognitive Skills in Veterans with Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 735, 135235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincheva, I.; Glatt, C.E.; Lee, F.S. Impact of the BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism on Cognition: Implications for Behavioral Genetics. Neuroscientist 2012, 18, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Chicherio, C.; Nyberg, L.; Von Oertzen, T.; Nagel, I.E.; Papenberg, G.; Sander, T.; Heekeren, H.R.; Lindenberger, U.; Bäckman, L. Ebbinghaus Revisited: Influences of the BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism on Backward Serial Recall Are Modulated by Human Aging. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2010, 22, 2164–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.S.; Shin, W.J.; Lee, J.E.; Do, J.T. CpG and Non-CpG Methylation in Epigenetic Gene Regulation and Brain Function. Genes 2017, 8, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affinito, O.; Palumbo, D.; Fierro, A.; Cuomo, M.; De Riso, G.; Monticelli, A.; Miele, G.; Chiariotti, L.; Cocozza, S. Nucleotide distance influences co-methylation between nearby CpG sites. Genomics 2020, 112, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780890425541. [Google Scholar]
- Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Smailagic, N.; Roquéi Figuls, M.; Ciapponi, A.; Sanchez-Perez, E.; Giannakou, A.; Pedraza, O.L.; Bonfill Cosp, X.; Cullum, S. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias in People with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD010783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, K.I. Clock-Drawing: Is It the Ideal Cognitive Screening Test? Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2000, 15, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James Kent, W.; Sugnet, C.W.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Pringle, T.H.; Zahler, A.M.; Haussler, D. The Human Genome Browser at UCSC. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illumina Inc. 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation-Preparing 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Amplicons for the Illumina MiSeq System. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/documents/documentation/chemistry_documentation/16s/16s-metagenomic-library-prep-guide-15044223-b.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Nedic Erjavec, G.; Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Tudor, L.; Uzun, S.; Kovacic Petrovic, Z.; Konjevod, M.; Sagud, M.; Kozumplik, O.; Svob Strac, D.; Peraica, T.; et al. Moderating Effects of BDNF Genetic Variants and Smoking on Cognition in PTSD Veterans. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. Babraham Bioinformatics. FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Available online: https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Krueger, F.; Andrews, S.R. Bismark: A Flexible Aligner and Methylation Caller for Bisulfite-Seq Applications. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1571–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akalin, A.; Kormaksson, M.; Li, S.; Garrett-Bakelman, F.E.; Figueroa, M.E.; Melnick, A.; Mason, C.E. MethylKit: A Comprehensive R Package for the Analysis of Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Profiles. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Demographic Data | MCI | Dementia | Statistics * |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (Male) | 153 (61.0%) | 76 (49.0%) | χ2 = 5.541; p = 0.011 |
| N (Female) | 98 (39.0%) | 79 (51.0%) | |
| Age | 68 (64; 71) | 70 (65; 72) | U = 15,622.5; p = 0.001 |
| Neurocognitive clinical scales | |||
| MMSE | 27 (26; 29) | 22 (20; 23) | U = 0.0; p < 0.001 |
| CDT | 4 (4; 5) | 3 (2; 5) | U = 11,845.0; p < 0.001 |
| Base Model | Test Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplicon | β | 95% CI | p-Value | β | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age | 1.066 | 1.012–1.123 | 0.016 | 1.074 | 1.014–1.139 | 0.016 |
| Sex (male) | 0.464 | 0.238–0.903 | 0.024 | 0.413 | 0.202–0.841 | 0.015 |
| BDNF_IX | 0.931 | 0.849–1.022 | 0.133 | |||
| BDNF_IV1 | 0.512 | 0.309–0.847 | 0.009 | |||
| BDNF_IV2 | 0.802 | 0.313–2.056 | 0.646 | |||
| BDNF_IV3 | 1.527 | 0.822–2.835 | 0.180 | |||
| BDNF_I1 | 1.508 | 0.914–2.486 | 0.108 | |||
| BDNF_I2 | 0.950 | 0.737–1.223 | 0.689 | |||
| Model statistics | χ2 = 10.784; p = 0.005 −2 Log Likelihood = 202.4. R2 = 0.090 | χ2 = 25.282; p = 0.001 −2 Log Likelihood = 187.7; R2 = 0.201 | ||||
| Amplicon | MMSE | CDT |
|---|---|---|
| BDNF_IX | ρ = 0.072; p = 0.313 | ρ = 0.068; p = 0.341 |
| BDNF_IV1 | ρ = 0.070; p = 0.330 | ρ = −0.015; p = 0.829 |
| BDNF_IV2 | ρ = −0.027; p = 0.708 | ρ = 0.168; p = 0.019 |
| BDNF_IV3 | ρ = −0.006; p = 0.936 | ρ = −0.066; p = 0.372 |
| BDNF_I1 | ρ = −0.014; p = 0.843 | ρ = 0.073; p = 0.312 |
| BDNF_I2 | ρ = −0.018; p = 0.815 | ρ = 0.031; p = 0.679 |
| BDNF gene expression | ρ = 0.095; p = 0.284 | ρ = 0.205; p = 0.019 |
| BDNF protein expression | ρ = 0.211; p < 0.001 | ρ = 0.061; p = 0.243 |
| BDNF Val66Met Genotypes | BDNF Val66Met Carriers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | GA | GG | Statistics * | A carriers | GG | Statistics ** | |
| BDNF_IX | 82.263 (77.201; 89.935) | 85.035 (82.749; 86.069) | 89.115 (87.026; 90.782) | H = 60.29; p < 0.001 | 85.035 (82.371; 86.208) | 89.115 (87.026; 90.782) | U = 1400.0; p < 0.001 |
| BDNF_IV1 | 3.279 (2.888; 3.793) | 1.683 (1.240; 2.314) | 1.811 (1.351; 2.273) | H = 5.83; p = 0.054 | 1.694 (1.246; 2.591) | 1.811 (1.351; 2.273) | U = 4239.0; p = 0.824 |
| BDNF_IV2 | 0.765 (0.698; 1.084) | 0.611 (0.438; 1.089) | 0.644 (0.411; 0.873) | H = 1.20; p = 0.550 | 0.647 (0.444; 1.087) | 0.644 (0.411; 0.873) | U = 3896.0; p = 0.423 |
| BDNF_IV3 | 1.630 (1.386; 2.066) | 1.731 (1.404; 2.047) | 1.558 (1.249; 1.972) | H = 1.88; p = 0.391 | 1.724 (1.403; 2.048) | 1.558 (1.249; 1.972) | U = 3456.0; p = 0.172 |
| BDNF_I1 | 2.179 (1.685; 3.322) | 1.426 (1.017; 2.114) | 1.451 (0.947; 2.113) | H = 3.21; p = 0.201 | 1.493 (1.058; 2.248) | 1.451 (0.947; 2.113) | U = 3998.5; p = 0.601 |
| BDNF_I2 | 4.954 (1.878; 5.339) | 2.662 (2.186; 3.538) | 2.524 (1.952; 3.436) | H = 3.67; p = 0.160 | 2.684 (2.112; 3.786) | 2.524 (1.952; 3.436) | U = 3157.0; p = 0.133 |
| BDNF gene expression | - | 3.693 (0.180; 6.720) | 0.795 (0.263; 4.611) | - | 3.693 (0.180; 6.720) | 0.795 (0.263; 4.611) | U = 1405.0; p = 0.296 |
| BDNF protein expression | 0.222 (0.145; 0.708) | 0.191 (0.127; 0.448) | 0.164 (0.113; 0.412) | H = 3.491; p = 0.175 | 0.195 (0.127; 0.451) | 0.166 (0.113; 0.408) | U = 14428.0; p = 0.099 |
| Amplicon | Location (hg19) | Statistics * |
|---|---|---|
| IX_CpG1 | chr11: 27,679,840 | p = 0.260; p = 0.001 |
| IX_CpG2 | chr11: 27,679,854 | p = 0.083; p = 0.286 |
| IX_CpG3 | chr11: 27,679,880 | p = 0.076; p = 0.289 |
| IX_CpG4 | chr11: 27,679,917 | p = 0.503; p = 5.571 × 10−13 |
| IX_CpG5 (rs6265) | chr11: 27,679,923 | - |
| IX_CpG6 | chr11: 27,679,977 | p = 0.437; p = 4.666 × 10−10 |
| IX_CpG7 | chr11: 27,680,000 | p = 0.256; p = 0.001 |
| IX_CpG8 | chr11: 27,680,033 | p = 0.233; p = 0.001 |
| BDNF_IX | chr11: 27,679,766–27,680,064 | p = 0.621; p = 1.459 × 10−21 |
| BDNF_IV1 | chr11: 27,721,638–27,721,854 | p = −0.259; p = 0.001 |
| BDNF_IV2 | chr11: 27,722,209–27,722,487 | p = −0.091; p = 0.296 |
| BDNF_IV3 | chr11: 27,723,104–27,723,373 | p = −0.245; p = 0.002 |
| BDNF_I1 | chr11: 27,743,454–27,743,762 | p = −0.210; p = 0.006 |
| BDNF_I2 | chr11: 27,744,260–27,744,605 | p = 0.027; p = 0.844 |
| BDNF Val66Met Genotypes | BDNF Val66Met Carriers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | GA | GG | Statistics * | A Carriers | GG | Statistics ** | ||
| Diagnosis | MCI | 10 (76.9%) | 74 (60.7%) | 149 (62.1%) | χ2 = 1.322 p = 0.516 | 84 (62.2%) | 149 (62.1%) | χ2 = 0.001 p = 0.979 |
| Dementia | 3 (23.1%) | 48 (39.3%) | 91 (37.9%) | 51 (37.8%) | 91 (37.9%) | |||
| Severity of cognitive decline | MCI | 10 (76.9%) | 74 (60.7%) | 149 (62.1%) | χ2 = 2.800 p = 0.592 | 84 (62.2%) | 149 (62.1%) | χ2 = 1.472 p = 0.479 |
| Mild to moderate | 2 (15.4%) | 35 (28.7%) | 74 (30.8%) | 37 (27.4%) | 74 (30.8%) | |||
| Severe | 1 (7.7%) | 13 (10.7%) | 17 (7.1%) | 14 (10.4%) | 17 (7.1%) | |||
| Scores on cognitive scales | MMSE | 26 (25; 27) | 26 (22; 27) | 25 (23; 27) | H = 0.02; p = 0.990 | 26 (23; 27) | 25 (23; 27) | U = 16192.5; p = 0.994 |
| SAT | 4 (3; 5) | 4 (3; 5) | 4 (3; 5) | H = 1.37; p = 0.505 | 4 (3; 5) | 4 (3; 5) | U = 15023.0; p = 0.243 | |
| Amplicon | Chromosome | Start Position | End Position | Location | Strand, Length | Number of CpGs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDNF_IX | chr11 | 27679766 | 27680064 | Exon IX (coding) | (−), 299 | 8 |
| BDNF_IV1 | chr11 | 27721638 | 27721854 | Promoter of the exon IV | (−), 217 | 19 |
| BDNF_IV2 | chr11 | 27722209 | 27722487 | Promoter of the exon IV | (−), 279 | 23 |
| BDNF_IV3 | chr11 | 27723104 | 27723373 | Promoter of the exon IV | (−), 270 | 15 |
| BDNF_I1 | chr11 | 27743454 | 27743762 | Promoter of the exon I | (−), 309 | 20 |
| BDNF_I2 | chr11 | 27744260 | 27744605 | Promoter of the exon I | (−), 346 | 22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tudor, L.; Videtic Paska, A.; Konjevod, M.; Balic, N.; Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Uzun, S.; Vuic, B.; Milos, T.; Nedic Erjavec, G.; Mimica, N.; et al. BDNF Val66Met Genotype, DNA Methylation, mRNA, and Protein Levels as Potential Blood-Based Biomarkers for Dementia and Cognitive Decline. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188987
Tudor L, Videtic Paska A, Konjevod M, Balic N, Nikolac Perkovic M, Uzun S, Vuic B, Milos T, Nedic Erjavec G, Mimica N, et al. BDNF Val66Met Genotype, DNA Methylation, mRNA, and Protein Levels as Potential Blood-Based Biomarkers for Dementia and Cognitive Decline. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188987
Chicago/Turabian StyleTudor, Lucija, Alja Videtic Paska, Marcela Konjevod, Nikola Balic, Matea Nikolac Perkovic, Suzana Uzun, Barbara Vuic, Tina Milos, Gordana Nedic Erjavec, Ninoslav Mimica, and et al. 2025. "BDNF Val66Met Genotype, DNA Methylation, mRNA, and Protein Levels as Potential Blood-Based Biomarkers for Dementia and Cognitive Decline" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188987
APA StyleTudor, L., Videtic Paska, A., Konjevod, M., Balic, N., Nikolac Perkovic, M., Uzun, S., Vuic, B., Milos, T., Nedic Erjavec, G., Mimica, N., Kouter, K., Pivac, N., & Svob Strac, D. (2025). BDNF Val66Met Genotype, DNA Methylation, mRNA, and Protein Levels as Potential Blood-Based Biomarkers for Dementia and Cognitive Decline. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188987








