Genome-Based Mexican Diet Bioactives Target Molecular Pathways in HBV, HCV, and MASLD: A Bioinformatic Approach for Liver Disease Prevention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review
2.1.1. Data Sources for the Literature Review
2.1.2. Search Strategy for Antiviral Nutrients
2.1.3. Search Strategy for Anti-MASLD Nutrients
2.1.4. Classification of the Biological Effect of Antiviral and Anti-MASLD Nutrients
2.2. Integrative Bioinformatic Analysis
2.2.1. Selection of Ingredients and Nutrients
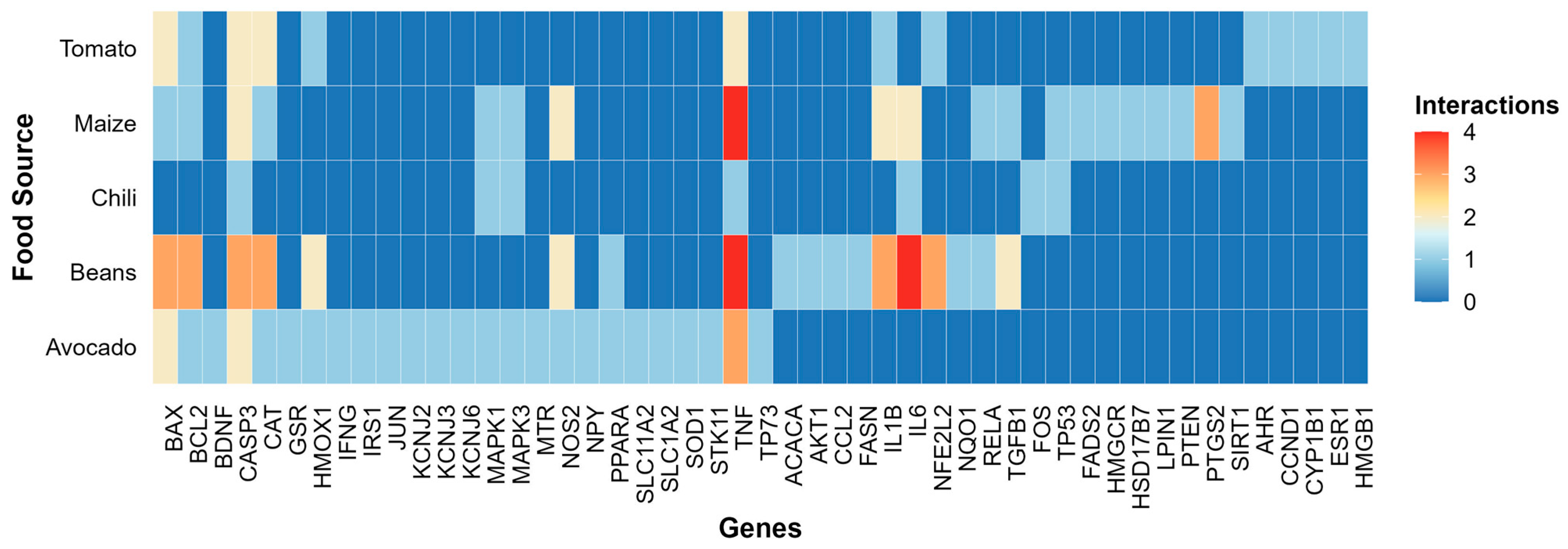
2.2.2. Identification of Gene Interactions with Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds
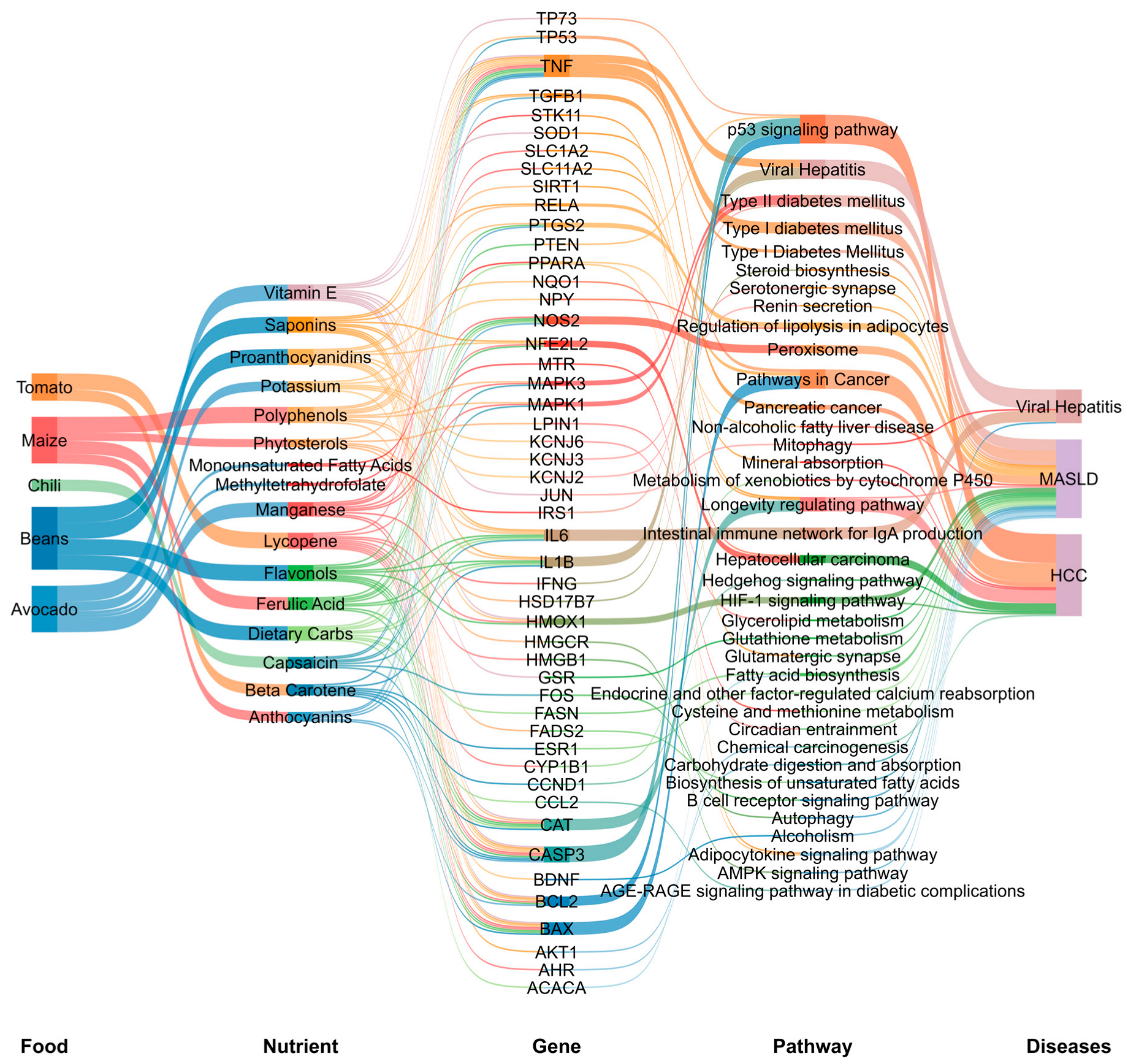
2.2.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis
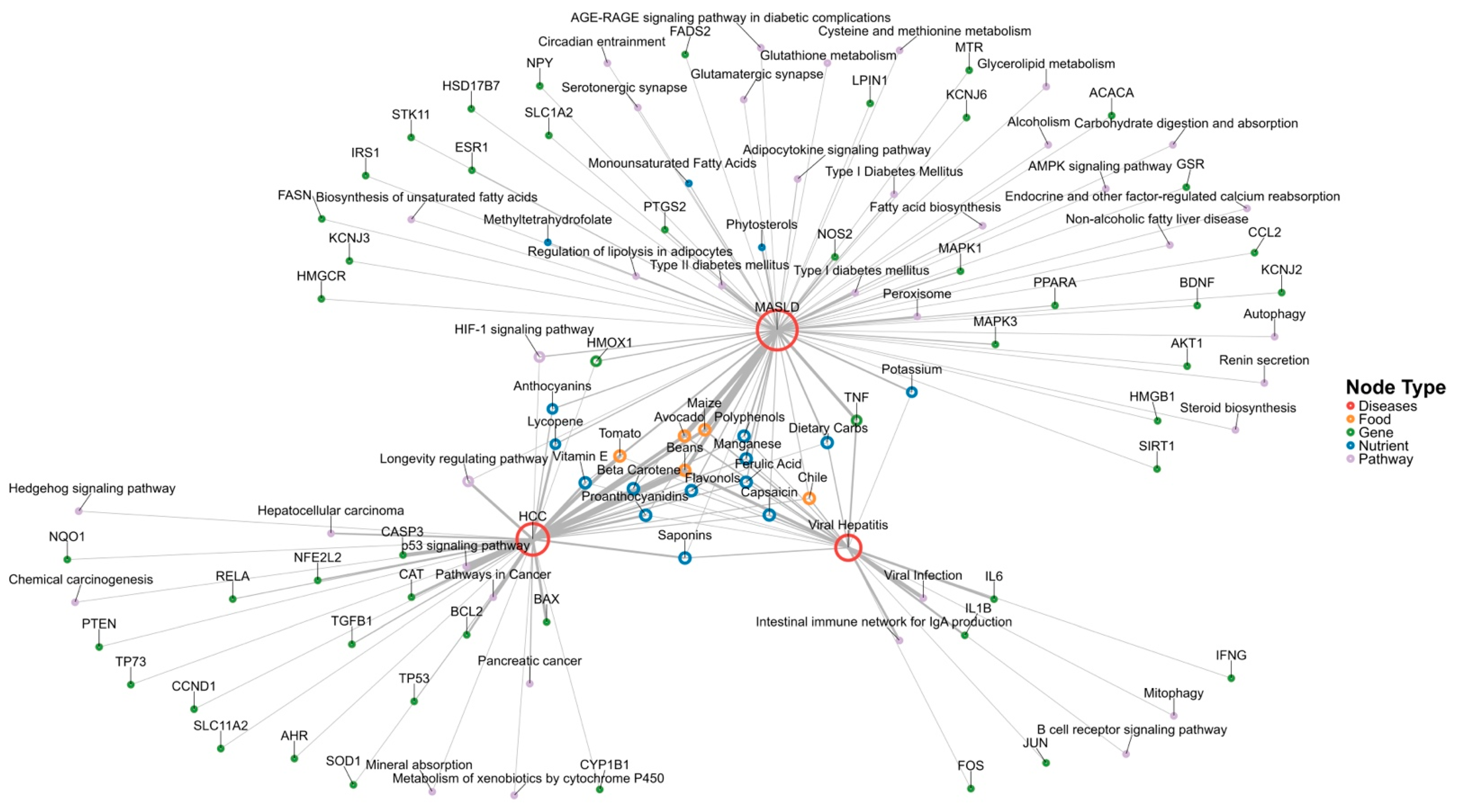
2.2.4. Data Visualization of the Integrative Bioinformatic Analysis
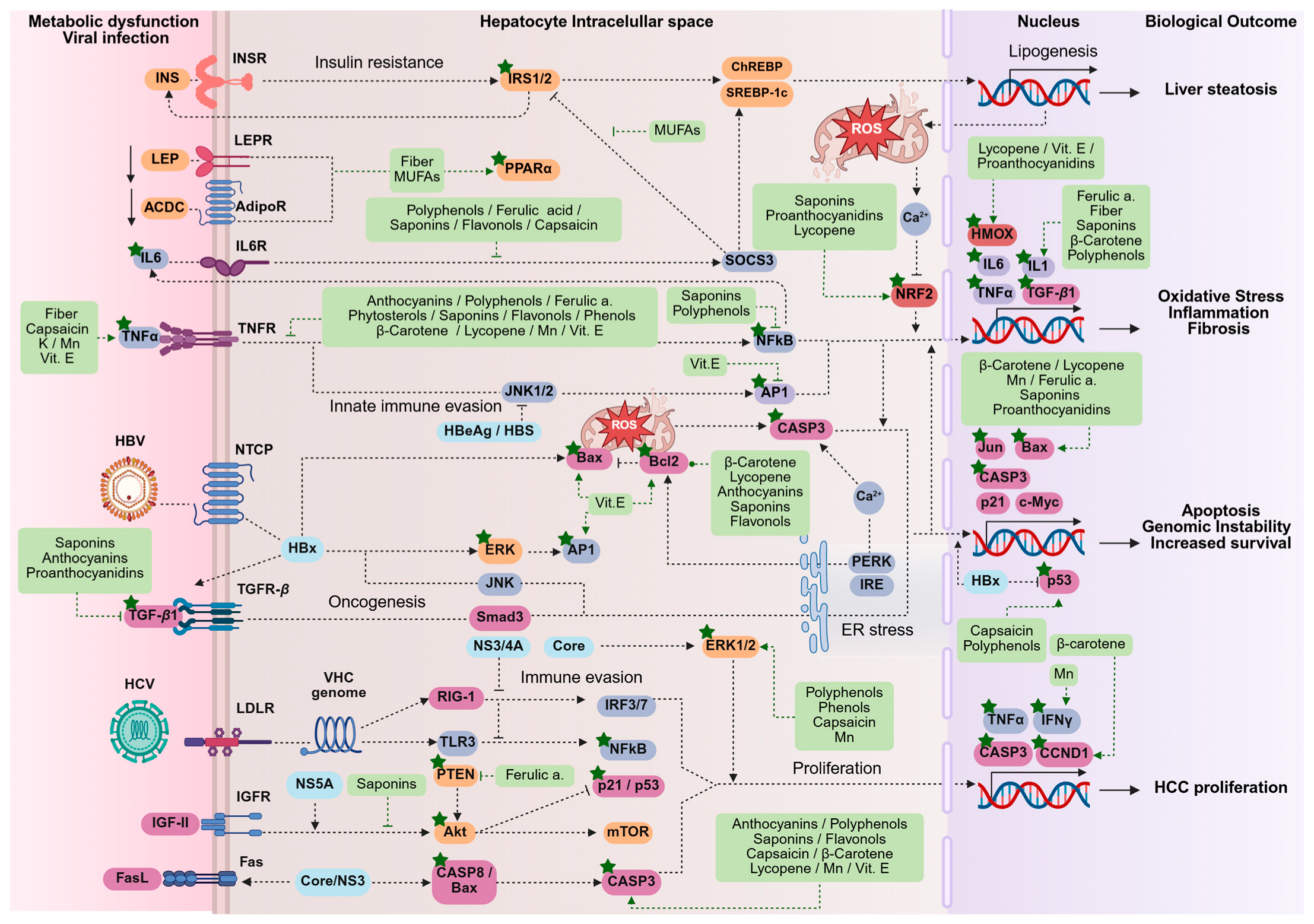
3. Results
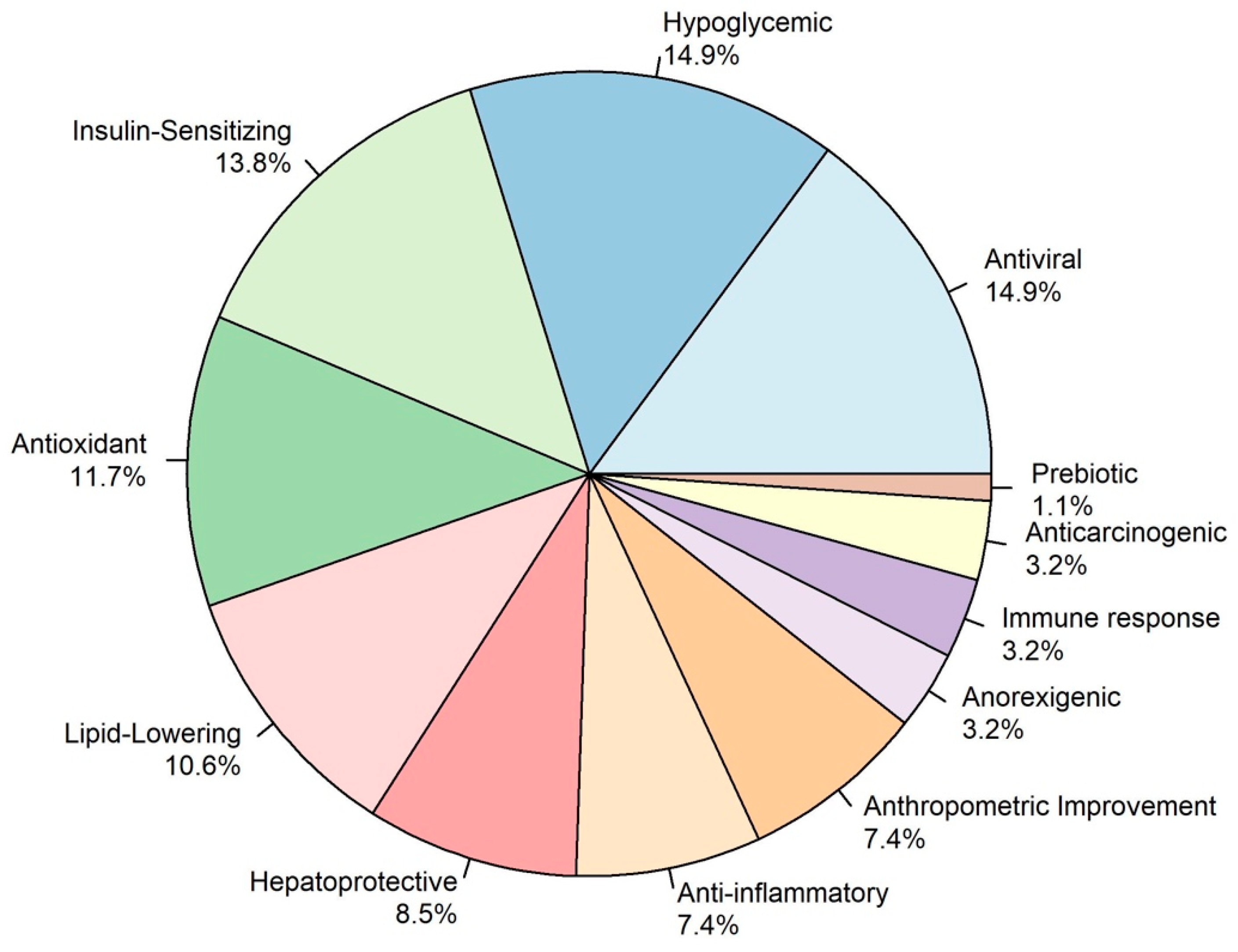
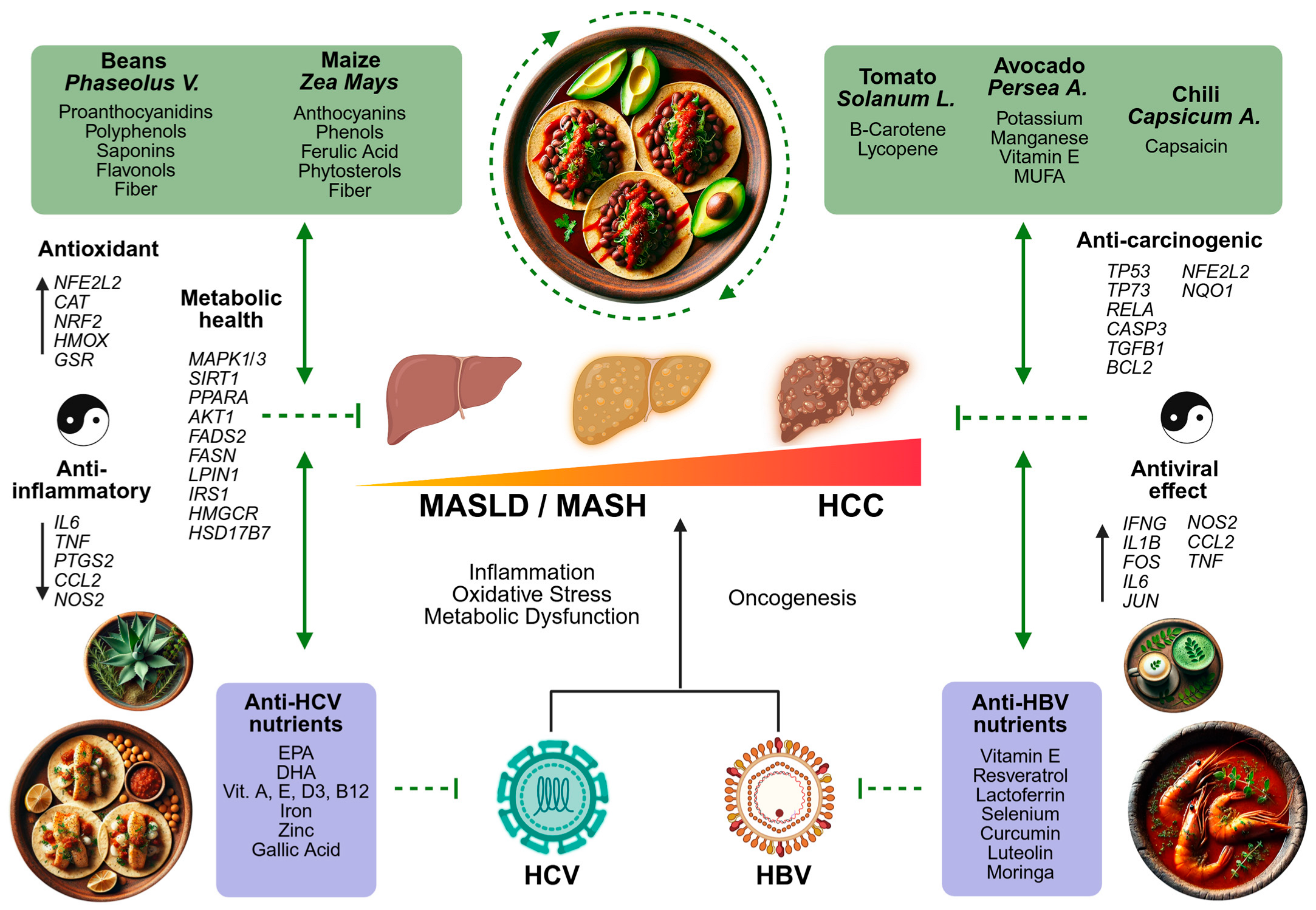
3.1. Literature Review of Nutrients in the Mexican Diet Against HBV, HCV, and MASLD
3.1.1. Antiviral Nutrients
3.1.2. Anti-MASLD Effect
Hypoglycemic and Insulin-Sensitizing Effect
Lipid-Lowering Effect
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Hepatoprotective and Potential Anti-Carcinogenic Effect
Gut Microbiota Modulation by Mexican Foods on Liver Health
3.2. Integrative Bioinformatic Analysis
3.2.1. Gene–Nutrient and Bioactive Compound Interactions
3.2.2. Functional Enrichment Analysis Visualization
3.2.3. Integration of Nutrigenomic Interactions of Traditional Mexican Foods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| MASH | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| GENOMEX | Genome-based Mexican (diet) |
| VLDL | Very-low-density lipoprotein |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| CTD | Comparative Toxicogenomic Database |
| HBsAg | Hepatitis B surface antigen |
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate |
| NTCP | Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| ALA | α-linolenic acid |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LPL | Lipoprotein lipase |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| ABCA1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 |
| LXRα | Liver X receptor alpha |
| CETP | Cholesterol ester transfer protein |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SOD1 | Superoxide dismutase |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-kappa B |
| MUFAs | Monounsaturated fatty acids |
References
- Saraceni, C.; Birk, J. A Review of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus Immunopathogenesis. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Hepatitis Report 2024: Action for Access in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240091672 (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Jose-Abrego, A.; Roman, S.; Laguna-Meraz, S.; Panduro, A. Host and HBV Interactions and Their Potential Impact on Clinical Outcomes. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.-D.; Shapiro, M.D.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Tilg, H.; Valenti, L.; Somers, V.K.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G.; Yang, W.; et al. Global Burden of Metabolic Diseases, 1990–2021. Metabolism 2024, 160, 155999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszewicz, J.; Flisiak, R. Metabolic Syndrome and Hepatitis C Infection—Brothers in Arms. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 1135–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarcuska, P.; Abdel-Razik, A.; Flisiak, R.; Singh, R.B. Chronic Viral Hepatitis and Metabolic Syndrome/Cardiovascular Risk. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 7369314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Cheng, P.-N.; Kao, J.-H. Systematic Review: Chronic Viral Hepatitis and Metabolic Derangement. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-C.; Liu, C.-J.; Kao, J.-H. Impact of Metabolic Disorders on Chronic Hepatitis B. Clin. Liver Dis. 2024, 23, e0130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhioub, M.; Khsiba, A.; Bachali, A.; Bibi, A.; Hamzaoui, L.; Azouz, M.M. Risk of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C. Tunis. Med. 2023, 101, 362–366. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.A. Metabolic Syndrome: A Warning Sign of Liver Fibrosis. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 31, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langness, J.A.; Tabano, D.; Wieland, A.; Tise, S.; Pratt, L.; Harrington, L.A.; Lin, S.; Ghuschcyan, V.; Nair, K.V.; Everson, G.T.; et al. Curing Chronic Hepatitis C: A Cost Comparison of the Combination Simeprevir Plus Sofosbuvir vs. Protease-Inhibitor-Based Triple Therapy. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose-Abrego, A.; Laguna-Meraz, S.; Roman, S.; Mariscal-Martinez, I.M.; Panduro, A. Hepatitis C Virus Resistance-Associated Substitutions in Mexico. Viruses 2025, 17, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, G.; Cruces, G. The Dynamics of Income Inequality in Mexico since NAFTA [with Comment]. Economía 2011, 12, 155–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna-Meraz, S.; Jose-Abrego, A.; Roman, S.; Leal-Mercado, L.; Panduro, A. Risk Factors Associated with Hepatitis C Subtypes and the Evolutionary History of Subtype 1a in Mexico. Viruses 2024, 16, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, G.; Dias, R.H.; Thomas, K.J.; Rivera, J.A.; Carvalho, N.; Barquera, S.; Hill, K.; Ezzati, M. Characterizing the Epidemiological Transition in Mexico: National and Subnational Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda-Villegas, M.; Roman, S.; Rivera-Iñiguez, I.; Ojeda-Granados, C.; Gonzalez-Aldaco, K.; Torres-Reyes, L.A.; Jose-Abrego, A.; Panduro, A. High Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Abnormal Liver Stiffness in a Young and Obese Mexican Population. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0208926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Nonato, I.; Galván-Valencia, Ó.; Hernández-Barrera, L.; Oviedo-Solís, C.I.; Barquera, S. Prevalencia de Obesidad y Factores de Riesgo Asociados En Adultos Mexicanos: Resultados de La Ensanut 2022. Inst. Nac. Salud Pública 2023, 65, s238–s247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panduro, A.; Roman, S.; Mariscal-Martinez, I.M.; Jose-Abrego, A.; Gonzalez-Aldaco, K.; Ojeda-Granados, C.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Torres-Reyes, L.A. Personalized Medicine and Nutrition in Hepatology for Preventing Chronic Liver Disease in Mexico. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1379364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.-H.; Wu, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-W.; Chang, C.-C. Prevalence, Trends, and Characteristics of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease among the US Population Aged 12–79 Years. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 36, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Lara, I.; Ortiz-López, M.G.; Bonilla-Delgado, J.; Pérez-Escobar, J.; Godínez-Aguilar, R.; Luévano-Contreras, C.; Espinosa-García, A.M.; Pérez-Durán, J.; García Alonso-Themann, P.; Nolasco-Quiroga, M.; et al. A Landscape of Liver Cirrhosis and Transplantation in Mexico: Changing Leading Causes and Transplant as Response. Ann. Hepatol. 2025, 30, 101562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INEGI. Estadísticas de Defunciones Registradas (EDR); INEGI 2023 Preliminar; INEGI: Aguascalientes, Mexico, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chávez-Manzanera, E.A.; Vera-Zertuche, J.M.; Kaufer-Horwitz, M.; Vázquez-Velázquez, V.; Flores-Lázaro, J.R.; Mireles-Zavala, L.; Calzada-León, R.; Garnica-Cuellar, J.C.; Sánchez-Muñoz, V.; Ramírez-Butanda, E.; et al. Mexican Clinical Practice Guidelines for Adult Overweight and Obesity Management. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 643–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centro Nacional para la Prevención y Control del VIH y el sida. Guía para la Prevención y Atención de las Hepatitis Virales en México 2023. Available online: http://www.gob.mx/censida/documentos/guia-para-la-prevencion-y-atencion-de-las-hepatitis-virales-en-mexico-2023 (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Uscanga Domínguez, L.; Bielsa Fernández, M.V.; Huerta Iga, F.; Lizardi Cervera, J.; Muñoz Espinosa, L.; López Tarabay, C.; Rodríguez Hernández, H.; Torre Delgadillo, A.; Lilia Tostado Ramos, C. Guías clínicas de diagnóstico y tratamiento de hepatopatía grasa no alcohólica. Generalidades. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2008, 73, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- IMSS. Diagnóstico y Tratamiento Farmacológico de la Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 2 en el Primer Nivel de Atención. In Guía de Evidencias y Recomendaciones: Guía de Práctica Clínica; IMSS: Mexico City, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda-Granados, C.; Panduro, A.; Gonzalez-Aldaco, K.; Sepulveda-Villegas, M.; Rivera-Iñiguez, I.; Roman, S. Tailoring Nutritional Advice for Mexicans Based on Prevalence Profiles of Diet-Related Adaptive Gene Polymorphisms. J. Pers. Med. 2017, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojeda-Granados, C.; Panduro, A.; Rivera-Iñiguez, I.; Sepúlveda-Villegas, M.; Roman, S. A Regionalized Genome-Based Mexican Diet Improves Anthropometric and Metabolic Parameters in Subjects at Risk for Obesity-Related Chronic Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose-Abrego, A.; Rivera-Iñiguez, I.; Torres-Reyes, L.A.; Roman, S. Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Activity of Food Nutrients and Potential Mechanisms of Action. Ann. Hepatol. 2023, 28, 100766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Aldaco, K.; Torres-Reyes, L.A.; Ojeda-Granados, C.; Leal-Mercado, L.; Roman, S.; Panduro, A. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection: From Basics to Clinical and Nutritional Management. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 2542–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, S.; Campos-Medina, L.; Leal-Mercado, L. Personalized Nutrition: The End of the One-Diet-Fits-All Era. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1370595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante-Araiza, F.; Gutiérrez-Salmeán, G. Traditional Mexican Foods as Functional Agents in the Treatment of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizondo-Solis, C.; Rojas-Gutiérrez, S.; Martínez-Canales, R.; Montoya-Rosales, A.; Hernández-García, M.; Salazar-Cepeda, C.; Ramírez, K.; Gelinas-Martín del Campo, M.; Salinas-Carmona, M.; Rosas-Taraco, A.; et al. Integrative Bioinformatics Analysis of Immune Activation and Gene Networks in Pediatric Septic Arthritis. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2025, 115, 108287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizumbo-Villarreal, D.; Flores-Silva, A.; Colunga-García Marín, P. The Archaic Diet in Mesoamerica: Incentive for Milpa Development and Species Domestication. Econ. Bot. 2012, 66, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.S.; Sood, S.; Broughton, A.; Cogan, G.; Hickey, M.; Chan, W.S.; Sudan, S.; Nicoll, A.J. The Association between Diet and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Wiegers, T.C.; Sciaky, D.; Barkalow, F.; Strong, M.; Wyatt, B.; Wiegers, J.; McMorran, R.; Abrar, S.; Mattingly, C.J. Comparative Toxicogenomics Database’s 20th Anniversary: Update 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1328–D1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Mering, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Snel, B.; Hooper, S.D.; Krupp, M.; Foglierini, M.; Jouffre, N.; Huynen, M.A.; Bork, P. STRING: Known and Predicted Protein-Protein Associations, Integrated and Transferred across Organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D433–D437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and Integrative Analysis of Large Gene Lists Using DAVID Bioinformatics Resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A Comprehensive Gene Set Enrichment Analysis Web Server 2016 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Matsuura, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG: Biological Systems Database as a Model of the Real World. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D672–D677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: The R Project for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Reshaping Data with the Reshape Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2; Use R! Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24275-0. [Google Scholar]
- Neuwirth, E. R Package RColorBrewer, version 1.1-3. ColorBrewer Palettes. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=RColorBrewer (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Sjoberg, D. Davidsjoberg/Ggsankey 2025. An Implementation of Grammar of Graphics for Graphs and Networks. Available online: https://ggraph.data-imaginist.com/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Csárdi, G.; Nepusz, T.; Traag, V.; Horvát, S.; Zanini, F.; Noom, D.; Müller, K.; Salmon, M.; Antonov, M. R Package, version 2.3. igraph: Network Analysis and Visualization. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025.
- Park, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, J.R.; Cho, S. Inhibitory Effects of Resveratrol on Hepatitis B Virus X Protein-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 18, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreone, P.; Fiorino, S.; Cursaro, C.; Gramenzi, A.; Margotti, M.; Di Giammarino, L.; Biselli, M.; Miniero, R.; Gasbarrini, G.; Bernardi, M. Vitamin E as Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis B: Results of a Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. Antivir. Res. 2001, 49, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorino, S.; Bacchi-Reggiani, M.L.; Leandri, P.; Loggi, E.; Andreone, P. Vitamin E for the Treatment of Children with Hepatitis B e Antigen-Positive Chronic Hepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Ikeda, M.; Saito, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Numata, K.; Kato, N.; Tanaka, K.; Sekihara, H. Lactoferrin Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Cultured Human Hepatocytes. Hepatol. Res. 2002, 24, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xiang, K.; Liu, J.; Song, J.; Feng, J.; Chen, J.; Dai, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Zhou, Y. Inhibition of In Vitro Infection of Hepatitis B Virus by Human Breastmilk. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Li, W.G. Protective Role of Selenium against Hepatitis B Virus and Primary Liver Cancer in Qidong. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1997, 56, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Yoo, H.S.; Kim, J.C.; Park, C.S.; Choi, M.S.; Kim, M.; Choi, H.; Min, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Yoon, S.W.; et al. Antiviral Effect of Curcuma longa Linn Extract against Hepatitis B Virus Replication. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 124, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waiyaput, W.; Payungporn, S.; Issara-Amphorn, J.; Panjaworayan, N.T.-T. Inhibitory Effects of Crude Extracts from Some Edible Thai Plants against Replication of Hepatitis B Virus and Human Liver Cancer Cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.-X.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.-J.; Rong, X.-Y.; Jing, S.; Xie, Y.-H.; Huang, D.-F.; Zhao, C. Luteolin-7-O-Glucoside Present in Lettuce Extracts Inhibits Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Production and Viral Replication by Human Hepatoma Cells In Vitro. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feustel, S.; Ayón-Pérez, F.; Sandoval-Rodriguez, A.; Rodríguez-Echevarría, R.; Contreras-Salinas, H.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J.; Sánchez-Orozco, L.V. Protective Effects of Moringa Oleifera on HBV Genotypes C and H Transiently Transfected Huh7 Cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 6063850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.A. Ameliorative Effects of Moringa Oleifera Lam Seed Extract on Liver Fibrosis in Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-F.; Shi, L.-P.; Ren, Y.-D.; Liu, Q.-F.; Liu, H.-F.; Zhang, R.-J.; Li, Z.; Zhu, F.-H.; He, P.-L.; Tang, W.; et al. Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Activity of Chlorogenic Acid, Quinic Acid and Caffeic Acid In Vivo and In Vitro. Antivir. Res. 2009, 83, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-L.; Chang, W.-C.; Yi, C.-H.; Hung, J.-S.; Liu, T.-T.; Lei, W.-Y.; Hsu, C.-S. Association of Coffee Consumption and Liver Fibrosis Progression in Patients with HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B: A 5-Year Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.S.; Jeong, S.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, S.H.; Ahn, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Park, Y.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, N.; et al. The Effect of Coffee Consumption on the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Hepatitis B Virus Endemic Area. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Tao, M.-H.; Hung, T.-M.; Chen, J.-C.; Lin, Z.-J.; Huang, C. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibits Entry of Hepatitis B Virus into Hepatocytes. Antivir. Res. 2014, 111, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamese, M.; Aydogdu, S.; Karamese, S.A.; Altoparlak, U.; Gundogdu, C. Preventive Effects of a Major Component of Green Tea, Epigallocathechin-3-Gallate, on Hepatitis-B Virus DNA Replication. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 4199–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Zhao, K.; Wang, J.; Ma, Z.; Xiao, X. Green Tea Polyphenol, Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate, Possesses the Antiviral Activity Necessary to Fight against the Hepatitis B Virus Replication In Vitro. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2014, 15, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Hu, J.; Shu, W.; Gao, B.; Xiong, S. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Opposes HBV-Induced Incomplete Autophagy by Enhancing Lysosomal Acidification, Which Is Unfavorable for HBV Replication. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, G.-Z.; Lin, T.-Y.; Hsu, J.T.A. Anti-HCV Activities of Selective Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 318, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, H.; Moriya, K.; Tsutsumi, T.; Shinzawa, S.; Fujie, H.; Shintani, Y.; Fujinaga, H.; Goto, K.; Todoroki, T.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Pathogenesis of Lipid Metabolism Disorder in Hepatitis C: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Counteract Lipid Alterations Induced by the Core Protein. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govea-Salas, M.; Rivas-Estilla, A.M.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Lozano-Sepúlveda, S.A.; Aguilar-Gonzalez, C.N.; Zugasti-Cruz, A.; Salas-Villalobos, T.B.; Morlett-Chávez, J.A. Gallic Acid Decreases Hepatitis C Virus Expression through Its Antioxidant Capacity. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunchorntavakul, C.; Wootthananont, T.; Atsawarungruangkit, A. Effects of Vitamin E on Chronic Hepatitis C Genotype 3: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2014, 97 (Suppl. 11), S31–S40. [Google Scholar]
- Hamamoto, S.; Fukuda, R.; Ishimura, N.; Rumi, M.A.K.; Kazumori, H.; Uchida, Y.; Kadowaki, Y.; Ishihara, S.; Kinoshita, Y. 9-Cis Retinoic Acid Enhances the Antiviral Effect of Interferon on Hepatitis C Virus Replication through Increased Expression of Type I Interferon Receptor. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2003, 141, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, A.; Kato, T. Inhibition of Hepatitis C Virus by Vitamin D. In Vitamins and Hormones; Litwack, G., Ed.; Hormones, Regulators and Viruses; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 117, Chapter 9; pp. 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Eltayeb, A.A.; Abdou, M.A.A.; Abdel-aal, A.M.; Othman, M.H. Vitamin D Status and Viral Response to Therapy in Hepatitis C Infected Children. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lott, W.B.; Martyn, J.; Haqshenas, G.; Gowans, E.J. Differential Effects on the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Internal Ribosome Entry Site by Vitamin B12 and the HCV Core Protein. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12075–12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillebeen, C.; Rivas-Estilla, A.M.; Bisaillon, M.; Ponka, P.; Muckenthaler, M.; Hentze, M.W.; Koromilas, A.E.; Pantopoulos, K. Iron Inactivates the RNA Polymerase NS5B and Suppresses Subgenomic Replication of Hepatitis C Virus. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9049–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, K.; Naganuma, A.; Sato, K.; Ikeda, M.; Kato, N.; Takagi, H.; Mori, M. Zinc Is a Negative Regulator of Hepatitis C Virus RNA Replication. Liver Int. 2006, 26, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, P.; Amelia, A.; Rahayu, R. Jicama (Pachyrhizus erosus) Fiber Prevents Excessive Blood Glucose and Body Weight Increase without Affecting Food Intake in Mice Fed with High-Sugar Diet. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2019, 6, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.J.; Lee, H.-A.; Han, J.-S. Jicama (Pachyrhizus erosus) Extract Increases Insulin Sensitivity and Regulates Hepatic Glucose in C57BL/Ksj-Db/Db Mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2016, 58, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ristic-Medic, D.; Perunicic-Pekovic, G.; Rasic-Milutinovic, Z.; Takic, M.; Popovic, T.; Arsic, A.; Glibetic, M. Effects of Dietary Milled Seed Mixture on Fatty Acid Status and Inflammatory Markers in Patients on Hemodialysis. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 563576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, D.L.; Eliasziw, M.; Chen, C.Y.O.; Blumberg, J.B. A Pecan-Rich Diet Improves Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, A.; Schwarzinger, B.; Stadlbauer, V.; Lanzerstorfer, P.; Iken, M.; Schwarzinger, C.; Kolb, P.; Schwarzinger, S.; Mörwald, K.; Brunner, S.; et al. Guava (Psidium guajava) Fruit Extract Prepared by Supercritical CO2 Extraction Inhibits Intestinal Glucose Resorption in a Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Jyothi, A.L.; Tejeswini, V.B.; Madhusudana, K.; Kumar, D.A.; Zehra, A.; Agawane, S.B. Mitigation of Starch and Glucose-Induced Postprandial Glycemic Excursion in Rats by Antioxidant-Rich Green-Leafy Vegetables’ Juice. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2013, 9, S66–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, U.; Oba, S. Nutritional and Bioactive Constituents and Scavenging Capacity of Radicals in Amaranthus hypochondriacus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Rodríguez, A.; de Mejía, E.G.; Dia, V.P.; Reyes-Moreno, C.; Milán-Carrillo, J. Extrusion Improved the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) Hydrolysates in LPS-Induced Human THP-1 Macrophage-like and Mouse RAW 264.7 Macrophages by Preventing Activation of NF-κB Signaling. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1028–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Campos, R.; Meza-Rios, A.; Rodriguez-Sanabria, J.S.; la Rosa-Bibiano, R.D.; Corona-Cervantes, K.; García-Mena, J.; Santos, A.; Sandoval-Rodriguez, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Dietary Supplementation with Mexican Foods, Opuntia ficus indica, Theobroma cacao, and Acheta domesticus: Improving Obesogenic and Microbiota Features in Obese Mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 987222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indrianingsih, A.W.; Wulanjati, M.P.; Windarsih, A.; Bhattacharjya, D.K.; Suzuki, T.; Katayama, T. In Vitro Studies of Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, and Antibacterial Activities of Theobroma cacao, Anonna muricata and Clitoria ternatea. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 33, 101995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Mazuka, M.; Yagi, N.; Sawazaki, A.; Koganei, M.; Natsume, M.; Kuriki, K.; Morimoto, T.; Asai, T.; et al. Effect of Cacao Polyphenol-Rich Chocolate on Postprandial Glycemia, Insulin, and Incretin Secretion in Healthy Participants. Nutrition 2021, 85, 111128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Jaimes, G.S.; Aguilar-Mora, F.A.; González-Ponce, H.A.; Avelar-González, F.J.; Saldaña, M.C.M.; Buist-Homan, M.; Moshage, H. Biocomponents from Opuntia Robusta and Opuntia Streptacantha Fruits Protect against Diclofenac-Induced Acute Liver Damage In Vivo and In Vitro. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 89, 104960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña-Cerino, J.M.; Guzmán, T.J.; Soto-Luna, I.C.; Betanzos-Cabrera, G.; Gurrola-Díaz, C.M. Cladodes from Nopalea cochenillifera (L.) Salm-Dyck (Cactaceae) attenuate postprandial glycaemia without markedly influencing α-glucosidase activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 1105–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, H.O.; Macedo, R.C.O. Cocoa-Induced (Theobroma cacao) Effects on Cardiovascular System: HDL Modulation Pathways. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 27, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña-Cerino, J.M.; Tiessen, A.; Soto-Luna, I.C.; Peniche-Pavía, H.A.; Vargas-Guerrero, B.; Domínguez-Rosales, J.A.; García-López, P.M.; Gurrola-Díaz, C.M. Consumption of Nixtamal from a New Variety of Hybrid Blue Maize Ameliorates Liver Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in a High-Fat Diet Rat Model. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 72, 104075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damián-Medina, K.; Salinas-Moreno, Y.; Milenkovic, D.; Figueroa-Yáñez, L.; Marino-Marmolejo, E.; Higuera-Ciapara, I.; Vallejo-Cardona, A.; Lugo-Cervantes, E. In Silico Analysis of Antidiabetic Potential of Phenolic Compounds from Blue Corn (Zea mays L.) and Black Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Heliyon 2020, 6, e03632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orona-Tamayo, D.; Valverde, M.E.; Paredes-López, O. Bioactive Peptides from Selected Latin American Food Crops—A Nutraceutical and Molecular Approach. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1949–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Xiong, Y.L. Antioxidant Activity of Zein Hydrolysates in a Liposome System and the Possible Mode of Action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6059–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, N.; Hira, T.; Yamada, N.; Hara, H. Oral Administration of Corn Zein Hydrolysate Stimulates GLP-1 and GIP Secretion and Improves Glucose Tolerance in Male Normal Rats and Goto-Kakizaki Rats. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3089–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Vital, D.A.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Anthocyanins from Purple Corn Activate Free Fatty Acid-Receptor 1 and Glucokinase Enhancing in Vitro Insulin Secretion and Hepatic Glucose Uptake. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nchanji, E.B.; Ageyo, O.C. Do Common Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Promote Good Health in Humans? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical and Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo, A.; Rivera-León, E.A.; Luévano-Contreras, C.; Urías-Silvas, J.E.; Luna-Vital, D.A.; Morales-Hernández, N.; Mojica, L. Common Bean Baked Snack Consumption Reduces Apolipoprotein B-100 Levels: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spadafranca, A.; Rinelli, S.; Riva, A.; Morazzoni, P.; Magni, P.; Bertoli, S.; Battezzati, A. Phaseolus vulgaris Extract Affects Glycometabolic and Appetite Control in Healthy Human Subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tao, L.; Hao, L.; Stanley, T.H.; Huang, K.-H.; Lambert, J.D.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. A Moderate-Fat Diet with One Avocado per Day Increases Plasma Antioxidants and Decreases the Oxidation of Small, Dense LDL in Adults with Overweight and Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Tcheng, M.; Roma, A.; Buraczynski, M.; Jayanth, P.; Rea, K.; Akhtar, T.A.; Spagnuolo, P.A. Avocatin B Protects Against Lipotoxicity and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Diet-Induced Obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bordi, P.L.; Fleming, J.A.; Hill, A.M.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Effect of a Moderate Fat Diet with and without Avocados on Lipoprotein Particle Number, Size and Subclasses in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orona-Tamayo, D.; Valverde, M.E.; Nieto-Rendón, B.; Paredes-López, O. Inhibitory Activity of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) Protein Fractions against Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme and Antioxidant Capacity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Martínez, E.; Lira-Islas, I.G.; Cariño-Cortés, R.; Soria-Jasso, L.E.; Pérez-Hernández, E.; Pérez-Hernández, N. Dietary Chia Seeds (Salvia hispanica) Improve Acute Dyslipidemia and Steatohepatitis in Rats. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuksan, V.; Jenkins, A.L.; Brissette, C.; Choleva, L.; Jovanovski, E.; Gibbs, A.L.; Bazinet, R.P.; Au-Yeung, F.; Zurbau, A.; Ho, H.V.T.; et al. Salba-Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) in the Treatment of Overweight and Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.-S.; Alqahtani, A.; Ojo, O.A.; Shaheen, H.M.; Wasef, L.; Elzeiny, M.; Ismail, M.; Shalaby, M.; Murata, T.; Zaragoza-Bastida, A.; et al. Biological Properties, Bioactive Constituents, and Pharmacokinetics of Some Capsicum spp. and Capsaicinoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, S.K.; Bliss, E.; Brown, L. Capsaicin in Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2018, 10, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Hwang, J.-T.; Park, H.S.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, M.-S. Capsaicin Stimulates Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Muscle Cells via the Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)/AMPK/P38 MAPK Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheau, C.; Badarau, I.A.; Caruntu, C.; Mihai, G.L.; Didilescu, A.C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. Capsaicin: Effects on the Pathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Molecules 2019, 24, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Velázquez, G.; Parra-Ortiz, M.; Mora, I.D.l.M.-D.l.; García-Torres, I.; Enríquez-Flores, S.; Alcántara-Ortigoza, M.A.; Angel, A.G.-D.; Velázquez-Aragón, J.; Ortiz-Hernández, R.; Cruz-Rubio, J.M.; et al. Effects of Fructans from Mexican Agave in Newborns Fed with Infant Formula: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8939–8951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Camberos, E.; Barragán-Álvarez, C.P.; Diaz-Martinez, N.E.; Rathod, V.; Flores-Fernández, J.M. Effects of Agave Fructans (Agave tequilana Weber var. azul) on Body Fat and Serum Lipids in Obesity. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2018, 73, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regalado-Rentería, E.; Aguirre-Rivera, J.R.; Godínez-Hernández, C.I.; García-López, J.C.; Oros-Ovalle, A.C.; Martínez-Gutiérrez, F.; Martinez-Martinez, M.; Ratering, S.; Schnell, S.; Ruíz-Cabrera, M.Á.; et al. Effects of Agave Fructans, Inulin, and Starch on Metabolic Syndrome Aspects in Healthy Wistar Rats. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 10740–10749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghan, P.; Pourghassem Gargari, B.; Asgharijafarabadi, M. Effects of High Performance Inulin Supplementation on Glycemic Status and Lipid Profile in Women with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Health Promot. Perspect. 2013, 3, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jones, J.B.; Provost, M.; Keaver, L.; Breen, C.; Ludy, M.J.; Mattes, R.D. A Randomized Trial on the Effects of Flavorings on the Health Benefits of Daily Peanut Consumption. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglio, C.; Peluso, I.; Raguzzini, A.; Villaño, D.V.; Cesqui, E.; Catasta, G.; Toti, E.; Serafini, M. Fruit Juice Drinks Prevent Endogenous Antioxidant Response to High-Fat Meal Ingestion. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto Calvache, J.; Cueto, M.; Farroni, A.; de Escalada Pla, M.; Gerschenson, L.N. Antioxidant Characterization of New Dietary Fiber Concentrates from Papaya Pulp and Peel (Carica papaya L.). J. Funct. Foods 2016, 27, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardina, K.P.; Pramaningtyas, M.D.; Hendrawati, A.; Adnan, L.; Adrian, H.; Agus, D.; Nariski, G.; Lucky, R. Effect of Administration of Avocado Juice (Persea americana Mill) on Rat-Induced Malondialdehid (Rattus norvegicus) Levels. Metab.-Clin. Exp. 2022, 128, 155098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.L.; Buana, R.L.; Cholili, D.A.; Sudarto, H.A.; Safitri, A.A.D.; Ramadhan, T.; Pramaningtyas, M.D. Body Weight Change in Hypercolestrolemic Rats Model After Intervention with Avocado (Persea americana Mill) Juice. Metab.-Clin. Exp. 2022, 128, 154996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Nitta, A.; Imai, S.; Kajiyama, S.; Miyawaki, T.; Ozasa, N.; Kajiyama, S.; Hashimoto, Y.; Fukui, M. Tomato Juice Preload Has a Significant Impact on Postprandial Glucose Concentration in Healthy Women: A Randomized Cross-over Trial. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 29, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitsimpikou, C.; Tsarouhas, K.; Kioukia-Fougia, N.; Skondra, C.; Fragkiadaki, P.; Papalexis, P.; Stamatopoulos, P.; Kaplanis, I.; Hayes, A.W.; Tsatsakis, A.; et al. Dietary Supplementation with Tomato-Juice in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Suggestion to Alleviate Detrimental Clinical Factors. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 74, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.; Sharma, A.; Singh, B.; Nagpal, A.K. Bioactivities of Phytochemicals Present in Tomato. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2833–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, S.-E.; Ferrell, J.M. Pathophysiological Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Ye, J.; Xu, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Updated Mechanisms of MASLD Pathogenesis. Lipids Health Dis. 2024, 23, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bril, F.; Berg, G.; Barchuk, M.; Nogueira, J.P. Practical Approaches to Managing Dyslipidemia in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2025, 14, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, I.S.; Medeiros, A.F.; Piuvezam, G.; Medeiros, G.C.B.S.; Maciel, B.L.L.; Morais, A.H.A. Insulin-Like Proteins in Plant Sources: A Systematic Review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 3421–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Simpson, B.K.; Sun, H.; Ngadi, M.O.; Ma, Y.; Huang, T. Phaseolus vulgaris Lectins: A Systematic Review of Characteristics and Health Implications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwärzler, J.; Grabherr, F.; Grander, C.; Adolph, T.E.; Tilg, H. The Pathophysiology of MASLD: An Immunometabolic Perspective. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 20, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpellini, E.; Scarcella, M.; Tack, J.F.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Zanetti, M.; Abenavoli, L. Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Gao, S.; Shi, J.; Wang, K. Gut-Liver Axis: The Role of Intestinal Microbiota and Their Metabolites in the Progression of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Gut Liver 2025, 19, 479–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, H.; Díaz, L.A.; Gil-Gómez, A.; Burton, J.; Bajaj, J.S.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Arrese, M.; Arab, J.P.; Khan, M.Q. Microbiome-Centered Therapies for the Management of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31, S94–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelnuovo, G.; Perez-Diaz-Del-Campo, N.; Guariglia, M.; Poggiolini, I.; Armandi, A.; Rosso, C.; Caviglia, G.P.; Bugianesi, E. Prebiotics Targeting Gut-Liver Axis to Treat Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Minerva Gastroenterol. 2024, 70, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashimada, M.; Honda, M. Effect of Microbiome on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Biogenics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, L.; Molinari, R.; Farinon, B.; Merendino, N. Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on the Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeler, M.; Ellero-Simatos, S.; Birkner, T.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Olsson, L.; Brolin, H.; Loeber, U.; Kraft, J.D.; Polizzi, A.; Martí-Navas, M.; et al. The Interplay between Dietary Fatty Acids and Gut Microbiota Influences Host Metabolism and Hepatic Steatosis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jm, P. Pathophysiology of Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Related Liver Disease. Trends Microbiol. 2004, 12, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, D.; Penin, F.; Rice, C.M. Replication of Hepatitis C Virus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazienza, V.; Clément, S.; Pugnale, P.; Conzelman, S.; Foti, M.; Mangia, A.; Negro, F. The Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein of Genotypes 3a and 1b Downregulates Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 through Genotype-specific Mechanisms. Hepatology 2007, 45, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi Pour, P.; Fakhri, S.; Asgary, S.; Farzaei, M.H.; Echeverría, J. The Signaling Pathways, and Therapeutic Targets of Antiviral Agents: Focusing on the Antiviral Approaches and Clinical Perspectives of Anthocyanins in the Management of Viral Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro-Landívar, M.F.; Tapia-Quirós, P.; Vecino, X.; Reig, M.; Valderrama, C.; Granados, M.; Cortina, J.L.; Saurina, J. Polyphenols and Their Potential Role to Fight Viral Diseases: An Overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, M.; Salavatiha, Z.; Gogoi, U.; Mohebbi, A. An Overview of Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Flavonoids and Their Mechanisms of Action. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1356003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieres-Castro, D.; Mora-Poblete, F. Saponins: Research Progress and Their Potential Role in the Post-COVID-19 Pandemic Era. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, M.; Ishida, Y.-I.; Akamatsu, E.; Ohmori, Y.; Sudoh, M.; Uto, H.; Tsubouchi, H.; Kataoka, H. Proanthocyanidin from Blueberry Leaves Suppresses Expression of Subgenomic Hepatitis C Virus RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 21165–21176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh-Madsen, R.; Plomgaard, P.; Møller, K.; Mittendorfer, B.; Pedersen, B.K. Influence of TNF-Alpha and IL-6 Infusions on Insulin Sensitivity and Expression of IL-18 in Humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 291, E108–E114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.K.; Bansal, M.B. Pathogenesis of MASLD and MASH—Role of Insulin Resistance and Lipotoxicity. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 59 (Suppl. S1), S10–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka, K.; Maciejewska-Markiewicz, D.; Sykulski, M.; Gruszczyńska, A.; Herman-Iżycka, J.; Wyleżoł, M.; Katarzyna Petriczko, K.; Palma, J.; Jakubczyk, K.; Janda-Milczarek, K.; et al. Gut Microbiome—How Does Two-Month Consumption of Fiber-Enriched Rolls Change Microbiome in Patients Suffering from MASLD? Nutrients 2024, 16, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhuiya, P.A.; Ahmed, A.; Dutta, P.P.; Sen, S.; Pathak, M.P. Mitigating Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): The Role of Bioactive Phytoconstituents in Indian Culinary Spices. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2025, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, J.W.; Tobin, J.D.; Rosa, R.M.; Andres, R. Effect of Experimental Potassium Deficiency on Glucose and Insulin Metabolism. Metabolism 1980, 29, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, S.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, J.; Na, L. Protective Effect of Manganese Treatment on Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Hepatocytes. Nutr. Hosp. 2023, 40, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asbaghi, O.; Nazarian, B.; Yousefi, M.; Anjom-Shoae, J.; Rasekhi, H.; Sadeghi, O. Effect of Vitamin E Intake on Glycemic Control and Insulin Resistance in Diabetic Patients: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutr. J. 2023, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliewer, S.A.; Sundseth, S.S.; Jones, S.A.; Brown, P.J.; Wisely, G.B.; Koble, C.S.; Devchand, P.; Wahli, W.; Willson, T.M.; Lenhard, J.M.; et al. Fatty Acids and Eicosanoids Regulate Gene Expression through Direct Interactions with Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors α and γ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4318–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, A.; Jump, D.B. Unsaturated Fatty Acid Regulation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α Activity in Rat Primary Hepatoctes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 35931–35939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, M.G.; Li, L.; Widenmaier, S.B. Protective Effects of Hepatocyte Stress Defenders, Nrf1 and Nrf2, against MASLD Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-M.; Desai, L.P. Reciprocal Regulation of TGF-β and Reactive Oxygen Species: A Perverse Cycle for Fibrosis. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, S.; ten Dijke, P. TGF-β in Progression of Liver Disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 347, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Topley, N.; Ito, T.; Phillips, A. Interleukin-6 Regulation of Transforming Growth Factor (TGF)-Beta Receptor Compartmentalization and Turnover Enhances TGF-Beta1 Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 12239–12245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, T.; Li, Y.; Zhou, G.; Miao, Z.; Shang, M.; He, J.; Ding, N.; et al. Duality of Interactions Between TGF-β and TNF-α During Tumor Formation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 810286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawish, R.A.; Samy, E.M.; Aziz, M.M. Ferulic Acid Protects against Gamma-Radiation Induced Liver Injury via Regulating JAK/STAT/Nrf2 Pathways. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 753, 109895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, N.M.; Mansour, A.M.; Allam, S. Lycopene Induces Insulin Signaling and Alleviates Fibrosis in Experimental Model of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Rats. PharmaNutrition 2020, 14, 100225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sario, A.; Candelaresi, C.; Omenetti, A.; Benedetti, A. Vitamin E in Chronic Liver Diseases and Liver Fibrosis. Vitam. Horm. 2007, 76, 551–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.A.; Othman, A.I.; EL-Missiry, M.A.; Farag, A.A.; Amer, M.E. Proanthocyanidins Attenuated Liver Damage and Suppressed Fibrosis in CCl4-Treated Rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 91127–91138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoolchund, A.G.S.; Khakoo, S.I. MASLD and the Development of HCC: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Challenges. Cancers 2024, 16, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeFort, K.R.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Song, B.-J. Contributing Roles of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Hepatocyte Apoptosis in Liver Diseases through Oxidative Stress, Post-Translational Modifications, Inflammation, and Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapaliya, S.; Wree, A.; Povero, D.; Inzaugarat, M.E.; Berk, M.; Dixon, L.; Papouchado, B.G.; Feldstein, A.E. Caspase 3 Inactivation Protects against Hepatic Cell Death and Ameliorates Fibrogenesis in a Diet Induced NASH Model. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeaupin, C.; Blanc, M.; Vallée, D.; Keller, H.; Bailly-Maitre, B. BAX Inhibitor-1: Between Stress and Survival. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 1722–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, L.W.; Hancock, A.R.; Chang, S.-F.; Wang, X.W.; Chang, S.; Callahan, C.P.; Geller, D.A.; Will, H.; Harris, C.C. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein and P53 Tumor Suppressor Interactions in the Modulation of Apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14707–14712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco Carcache, P.J.; Clinton, S.K.; Kinghorn, A.D. Discovery of Natural Products for Cancer Prevention. Cancer J. 2024, 30, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Guo, X.; Han, F.; He, Z.; Wang, Y. Emerging Role of Natural Products in Cancer Immunotherapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1163–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, E.R.; Gutierrez, E.A.; de Melo, F.C.S.A.; Novaes, R.D.; Gonçalves, R.V. Flavonoids Effects on Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Murine Models: A Systematic Review. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 6328970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, E.J.; Wankell, M.; Palamuthusingam, P.; McFarlane, C.; Hebbard, L. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. CCND1 Silencing Suppresses Liver Cancer Stem Cell Differentiation through Inhibiting Autophagy. Hum. Cell 2020, 33, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-López, G.; Panduro, A.; Sosa-Jurado, F.; Fierro, N.A.; Lira, R.; Márquez-Domínguez, L.; Cerbón, M.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Roman, S. Advances in the Elimination of Viral Hepatitis in Mexico: A Local Perspective on the Global Initiative. Pathogens 2024, 13, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistella, S.; D’Arcangelo, F.; Grasso, M.; Zanetto, A.; Gambato, M.; Germani, G.; Senzolo, M.; Russo, F.P.; Burra, P. Liver Transplantation for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Indications and Post-Transplant Management. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S286–S301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquera, S.; Rivera, J.A. Obesity in Mexico: Rapid Epidemiological Transition and Food Industry Interference in Health Policies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 746–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ortiz, N.A.; Unar-Munguía, M.; Bautista-Arredondo, S.; Shamah-Levy, T.; Colchero, M.A. Changes in Apparent Consumption of Staple Food in Mexico Associated with the Gradual Implementation of the NAFTA. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2022, 2, e0001144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Granados, C.; Barchitta, M.; La Rosa, M.C.; La Mastra, C.; Roman, S.; Panduro, A.; Agodi, A.; Maugeri, A. Evaluating Dietary Patterns in Women from Southern Italy and Western Mexico. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, S.; Ojeda-Granados, C.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Panduro, A. Genome-Based Nutrition: An Intervention Strategy for the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3449–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, J.J.; Lustig, R.H.; Howard, S.; Corkey, B.E. Obesogens: A Unifying Theory for the Global Rise in Obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astrup, A.; Dyerberg, J.; Selleck, M.; Stender, S. Nutrition Transition and Its Relationship to the Development of Obesity and Related Chronic Diseases. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2008, 9 (Suppl. S1), 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.C.; Sawaya, A.L.; Wibaek, R.; Mwangome, M.; Poullas, M.S.; Yajnik, C.S.; Demaio, A. The Double Burden of Malnutrition: Aetiological Pathways and Consequences for Health. Lancet 2020, 395, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B.M.; Adair, L.S.; Ng, S.W. Global Nutrition Transition and the Pandemic of Obesity in Developing Countries. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodirsky, B.L.; Dietrich, J.P.; Martinelli, E.; Stenstad, A.; Pradhan, P.; Gabrysch, S.; Mishra, A.; Weindl, I.; Le Mouël, C.; Rolinski, S.; et al. The Ongoing Nutrition Transition Thwarts Long-Term Targets for Food Security, Public Health and Environmental Protection. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojeda-Granados, C.; Abondio, P.; Setti, A.; Sarno, S.; Gnecchi-Ruscone, G.A.; González-Orozco, E.; De Fanti, S.; Jiménez-Kaufmann, A.; Rangel-Villalobos, H.; Moreno-Estrada, A.; et al. Dietary, Cultural, and Pathogens-Related Selective Pressures Shaped Differential Adaptive Evolution among Native Mexican Populations. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msab290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassington, L.; Arner, A.M.; Watowich, M.M.; Damstedt, J.; Ng, K.S.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Venkataraman, V.V.; Wallace, I.J.; Kraft, T.S.; Lea, A.J. Integrating the Thrifty Genotype and Evolutionary Mismatch Hypotheses to Understand Variation in Cardiometabolic Disease Risk. Evol. Med. Public Health 2024, 12, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lea, A.J.; Clark, A.G.; Dahl, A.W.; Devinsky, O.; Garcia, A.R.; Golden, C.D.; Kamau, J.; Kraft, T.S.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Martins, D.J.; et al. Applying an Evolutionary Mismatch Framework to Understand Disease Susceptibility. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, S.; Ojeda-Granados, C.; Panduro, A. Genética y evolución de la alimentación de la población en México. Rev. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2013, 21, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Corbett, S.; Courtiol, A.; Lummaa, V.; Moorad, J.; Stearns, S. The transition to modernity and chronic disease: Mismatch and natural selection. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, F.; Uribe, J.; Olvares, N.; Huerta, P.; Cabrera, D.; Romero-Gómez, M. The Janus of a Disease: Diabetes and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Manriquez, J.; Olivas-Martinez, A.; Chávez-García, L.C.; Fernández-Ramírez, A.; Moctezuma-Velazquez, C.; Kauffman-Ortega, E.; Castro-Narro, G.; Astudillo-García, F.; Escalona-Nandez, I.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; et al. Prevalence of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Mexico and Development of a Screening Tool: The MAFLD-S Score. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022, 1, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Granados, C.; Roman, S. Mediterranean Diet or Genome-Based Nutrition Diets in Latin America’s Clinical Practice Guidelines for Managing Chronic Liver Diseases? Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 20, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unar-Munguía, M.; Cervantes-Armenta, M.A.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, S.; Bonvecchio Arenas, A.; Fernández Gaxiola, A.C.; Rivera, J.A. Mexican National Dietary Guidelines Promote Less Costly and Environmentally Sustainable Diets. Nat. Food 2024, 5, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.T.; Wise, T.A.; Garvey, E. Achieving Mexico’s Maize Potential; Research in Agricultural & Applied Economics; Tufts University: Medford, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Buylla Roces, M.E.; Calderón, A.E.; Delgado Valerio, P.; Piñeyro Nelson, A.; Castro del Campo, N.; Consejo Nacional de Humanidades, Ciencias y Tecnologías (Conahcyt); Secretaría Ejecutiva de la Comisión Intersecretarial de Bioseguridad y Organismos Genéticamente Modificados (Cibiogem). Contaminación Transgénica en Maíz Para la Alimentación Humana del Pueblo de México; Secretaria de Ciencia, Humanidades, Tecnología e Innovación (SECIHTI): Ciudad de México, México; Available online: https://www.youtube.com/live/xnVd_1v2jak?si=lPt6FzCedLGLtAzv (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- Santillán-Fernández, A.; Salinas-Moreno, Y.; Valdez-Lazalde, J.R.; Carmona-Arellano, M.A.; Vera-López, J.E.; Pereira-Lorenzo, S. Relationship between Maize Seed Productivity in Mexico between 1983 and 2018 with the Adoption of Genetically Modified Maize and the Resilience of Local Races. Agriculture 2021, 11, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Vega-Rivera, A.; Merino-Pérez, L. Socio-Environmental Impacts of the Avocado Boom in the Meseta Purépecha, Michoacán, Mexico. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Iñiguez, I.; Panduro, A.; Villaseñor-Bayardo, S.J.; Sepulveda-Villegas, M.; Ojeda-Granados, C.; Roman, S. Influence of a Nutrigenetic Intervention on Self-Efficacy, Emotions, and Rewarding Behaviors in Unhealthy Eating among Mexicans: An Exploratory Pilot Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leal-Mercado, L.; Panduro, A.; José-Abrego, A.; Roman, S. Genome-Based Mexican Diet Bioactives Target Molecular Pathways in HBV, HCV, and MASLD: A Bioinformatic Approach for Liver Disease Prevention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188977
Leal-Mercado L, Panduro A, José-Abrego A, Roman S. Genome-Based Mexican Diet Bioactives Target Molecular Pathways in HBV, HCV, and MASLD: A Bioinformatic Approach for Liver Disease Prevention. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188977
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeal-Mercado, Leonardo, Arturo Panduro, Alexis José-Abrego, and Sonia Roman. 2025. "Genome-Based Mexican Diet Bioactives Target Molecular Pathways in HBV, HCV, and MASLD: A Bioinformatic Approach for Liver Disease Prevention" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188977
APA StyleLeal-Mercado, L., Panduro, A., José-Abrego, A., & Roman, S. (2025). Genome-Based Mexican Diet Bioactives Target Molecular Pathways in HBV, HCV, and MASLD: A Bioinformatic Approach for Liver Disease Prevention. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188977







