Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analyses of Odorant-Binding Proteins in Hoverfly Eupeodes corollae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of OBP Genes in E. corollae
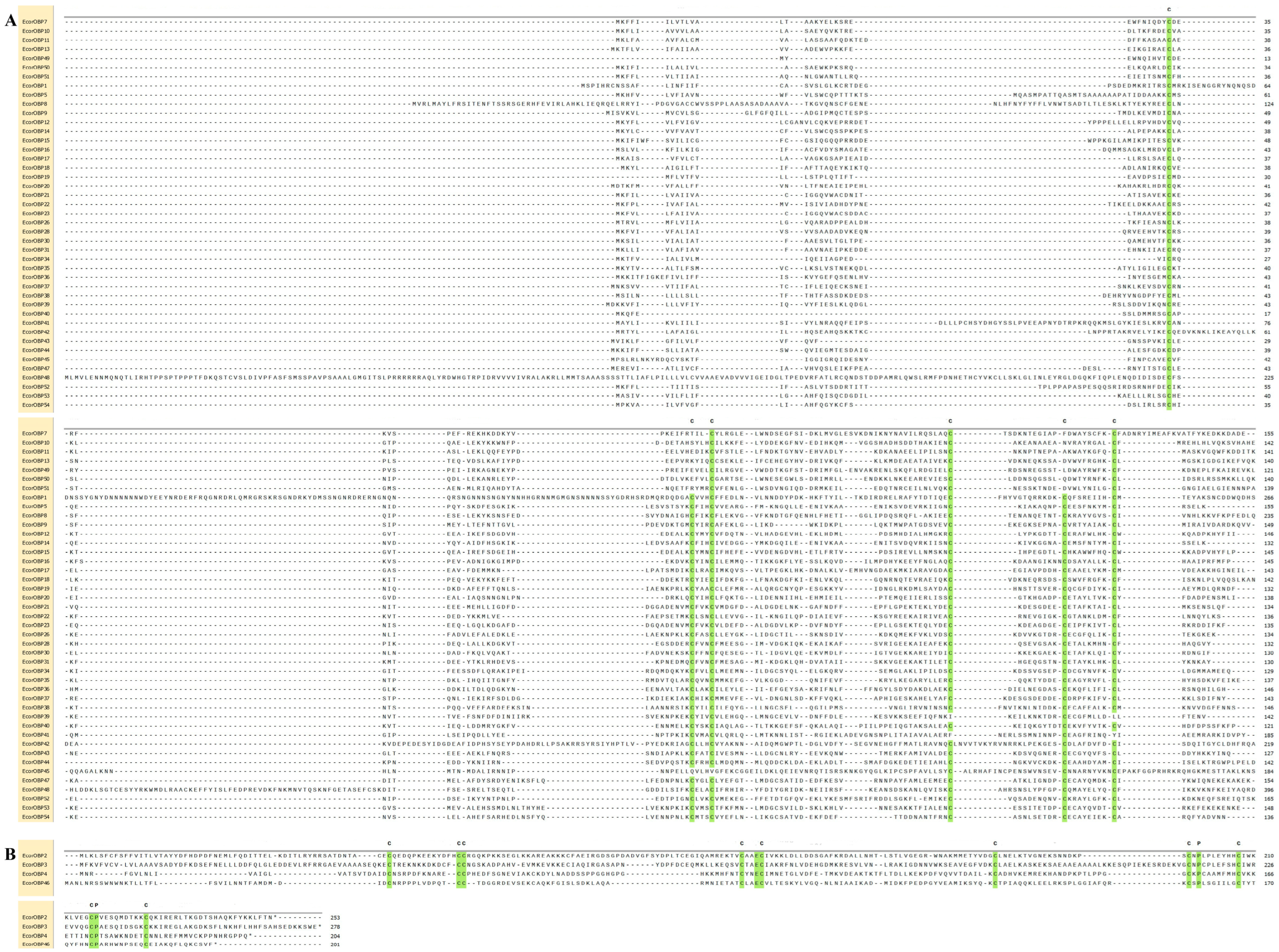
2.2. Motif Compositions and Gene Structure of EcorOBP Genes
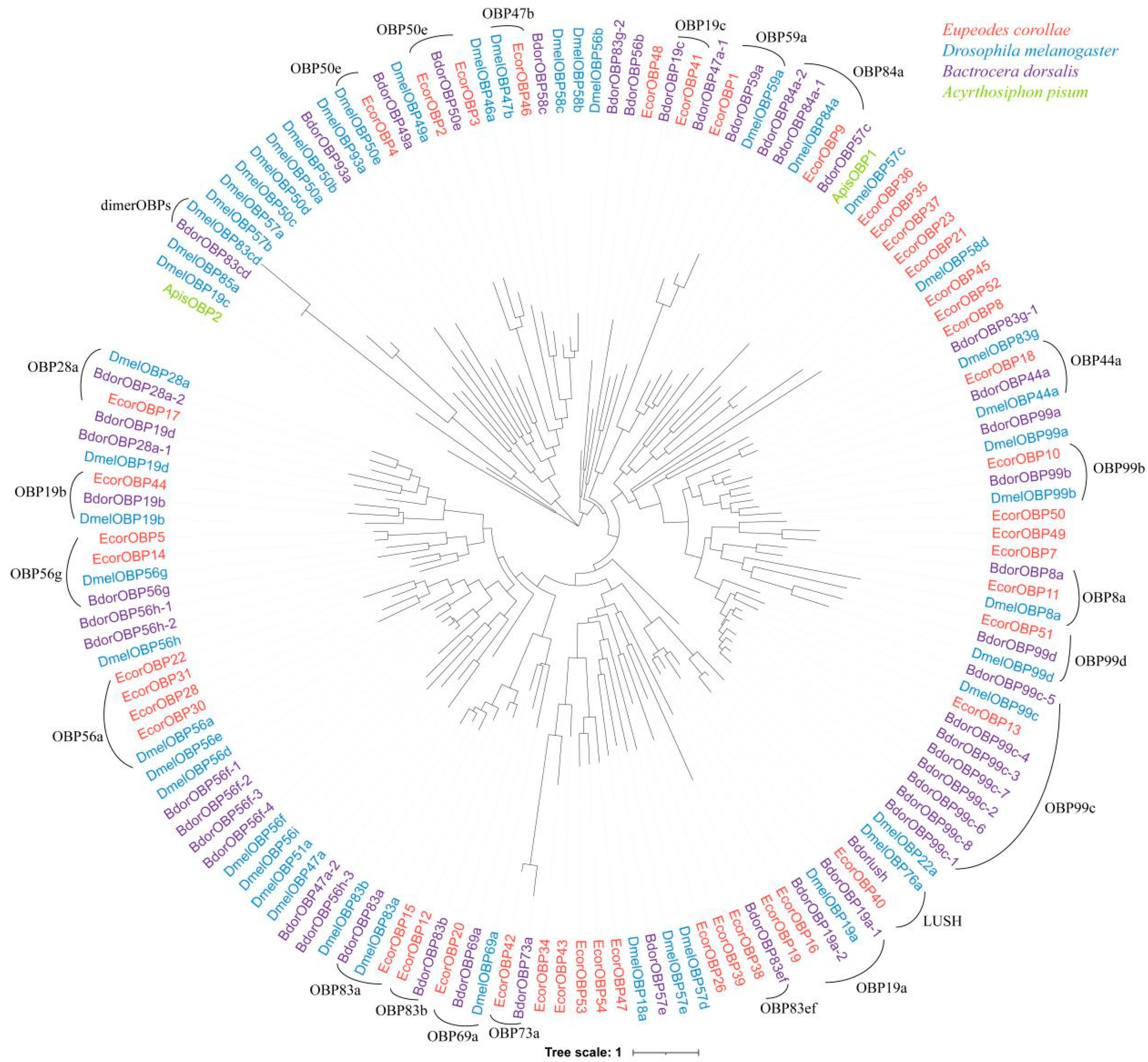
2.3. Evolutionary Analyses of OBP Family
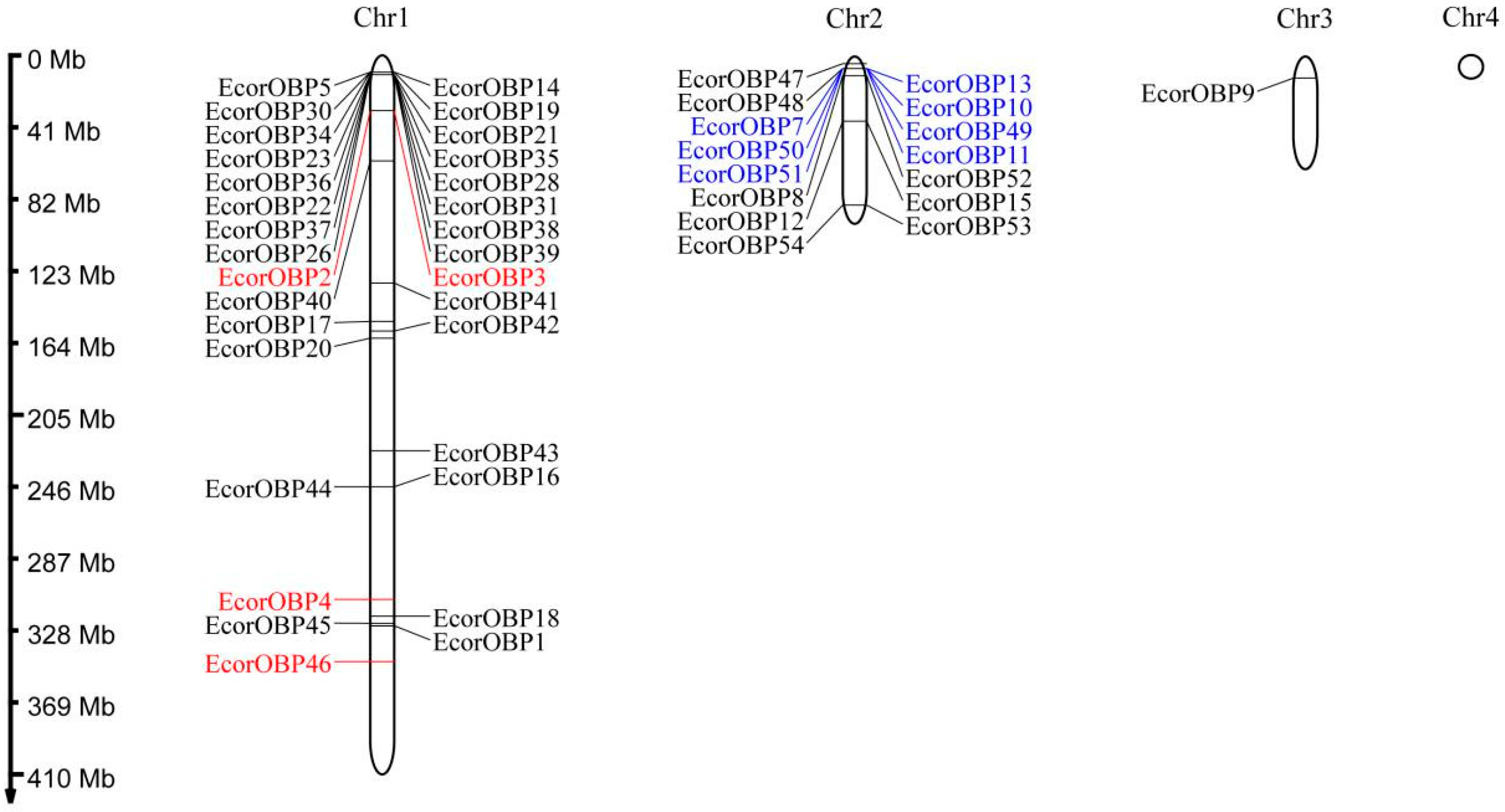
2.4. Chromosomal Locations
2.5. Evolution Analysis of OBP Orthologs
2.6. Synteny Analysis of OBP Genes in E. corollae and Other Hoverfly Species
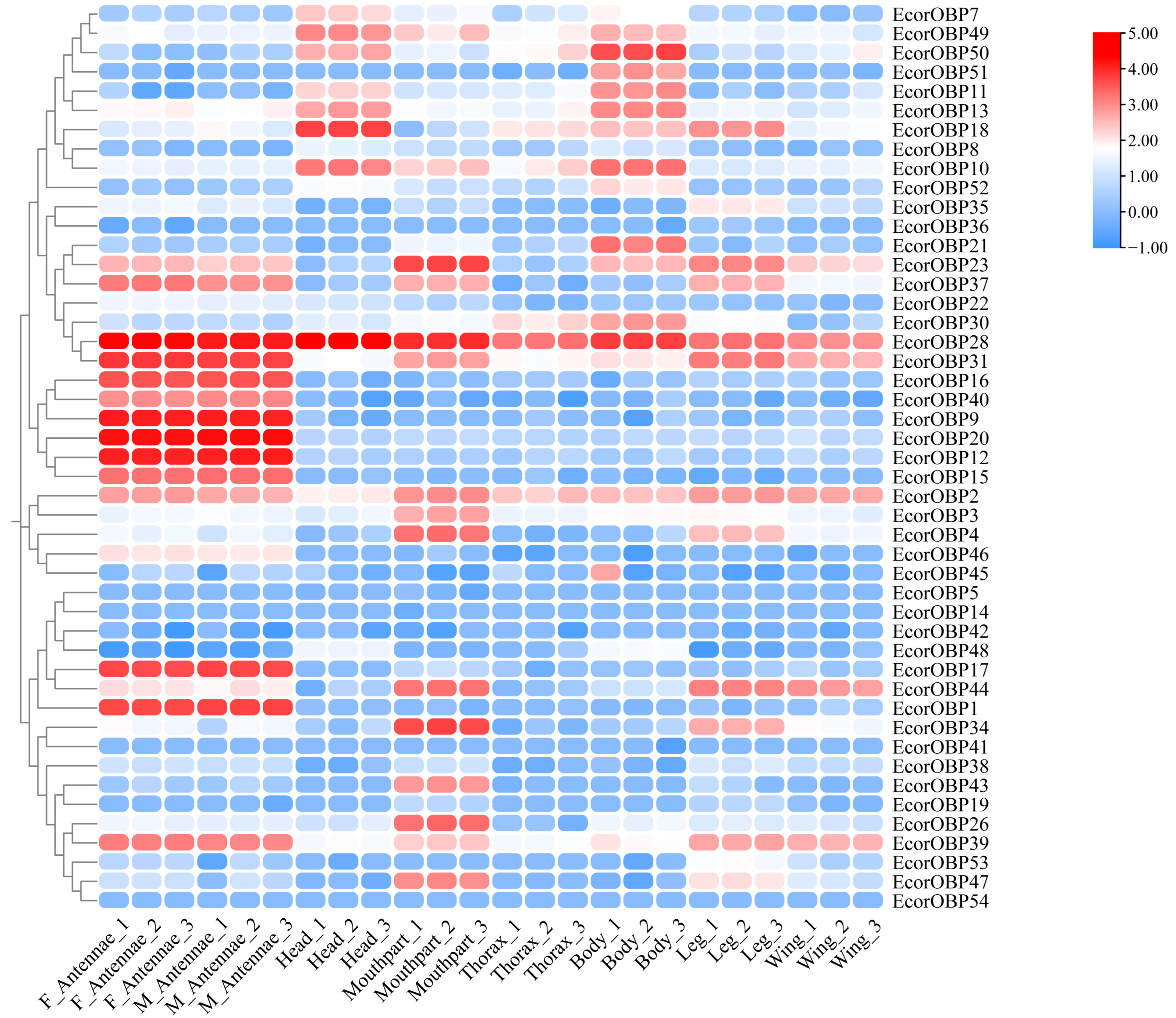
2.7. Expression Profiles of EcorOBPs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Transcriptomic Analysis
4.2. Identification and Physicochemical Properties of OBPs
4.3. Gene Structure and Conserved Motif Analysis
4.4. Evolutionary Analyses of OBP Genes
4.5. Chromosomal Localization and Synteny Analysis
4.6. Ka/Ks Calculation
4.7. Insect Rearing and Tissue Collection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brito, N.F.; Oliveira, D.S.; Santos, T.C.; Moreira, M.F.; Melo, A.C.A. Current and potential biotechnological applications of odorant-binding proteins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8631–8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruyne, M.; Foster, K.; Carlson, J.R. Odor coding in the Drosophila antenna. Neuron 2001, 30, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Dani, F.R. Beyond chemoreception: Diverse tasks of soluble olfactory proteins in insects. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, B.S.; Stensmyr, M.C. Evolution of insect olfaction. Neuron 2011, 72, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larter, N.K.; Sun, J.S.; Carlson, J.R. Organization and function of Drosophila odorant binding proteins. eLife 2016, 5, e20242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Felicioli, A.; Dani, F.R. Soluble proteins of chemical communication: An overview across arthropods. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.J. Odorant-binding proteins in insects. Vitam. Horm. 2010, 83, 241–272. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, R.G.; Große-Wilde, E.; Zhou, J.J. The Lepidoptera odorant binding protein gene family: Gene gain and loss within the GOBP/PBP complex of moths and butterflies. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 62, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, M.N.R.; Naga, K.C.; Nebapure, S.M.; Subramanian, S. Unravelling the genomic landscape reveals the presence of six novel odorant-binding proteins in whitefly Bemisia tabaci Asia II-1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279 Pt 1, 135140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Zhou, J.J.; Ban, L.P.; Calvello, M. Soluble proteins in insect chemical communication. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1658–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihani, K.; Ferveur, J.F.; Briand, L. The 40-year mystery of insect odorant-binding proteins. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J.; Huang, W.; Zhang, G.A.; Pickett, J.A.; Field, L.M. “Plus-C” odorant-binding protein genes in two Drosophila species and the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Gene 2004, 327, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Xie, J.; Liu, J.; Khashaveh, A.; Liu, X.; Yi, C.; Zhao, D.; He, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. Odorant-binding protein HvarOBP5 in ladybird Hippodamia variegata regulates the perception of semiochemicals from preys and habitat plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.G.; Riddiford, L.M. Pheromone binding and inactivation by moth antennae. Nature 1981, 293, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, N.N.; Yang, A.J.; Wu, C.; Xiao, H.Y.; Guo, Y.R.; Liu, N.Y. Genome-wide analysis of odorant-binding proteins in Papilio xuthus with focus on the perception of two PxutGOBPs to host odorants and insecticides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 10747–10761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Arena, S.; Spinelli, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Wei, R.; Cambillau, C.; Scaloni, A.; Wang, G.; Pelosi, P. Reverse chemical ecology: Olfactory proteins from the giant panda and their interactions with putative pheromones and bamboo volatiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9802–E9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Ye, Z.; Tikhe, C.V.; Tu, Z.J.; Zwiebel, L.J.; Dimopoulos, G. Pleiotropic odorant-binding proteins promote Aedes aegypti reproduction and flavivirus transmission. mBio 2021, 12, e0253121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Shan, S.; Song, X.; Khashaveh, A.; Wang, S.; Yin, Z.; Lu, Z.; Dhiloo, K.H.; Zhang, Y. Plant volatile ligands for male-biased MmedOBP14 stimulate orientation behavior of the parasitoid wasp Microplitis mediator. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 223 Pt A, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, R.; Du, Y.; Gao, B.; Gui, F.; Lu, K. Olfactory perception of herbicide butachlor by GOBP2 elicits ecdysone biosynthesis and detoxification enzyme responsible for chlorpyrifos tolerance in Spodoptera litura. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Minter, M.; Homem, R.A.; Michaelson, L.V.; Venthur, H.; Lim, K.S.; Withers, A.; Xi, J.; Jones, C.M.; Zhou, J.J. Odorant binding proteins promote flight activity in the migratory insect, Helicoverpa armigera. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 3795–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mao, K.; Ren, Z.; Jin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, T.; He, S.; Li, J.; Wan, H. Odorant binding protein 3 is associated with nitenpyram and sulfoxaflor resistance in Nilaparvata lugens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209 Pt A, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhu, R.; Yao, W.C.; Xu, J.W.; Wang, M.; Ren, J.Y.; Xu, C.Z.; Huang, Z.R.; Zhang, X.W.; et al. Computational and experimental approaches to decipher the binding mechanism of general odorant-binding protein 2 from Athetis lepigone to chlorpyrifos and phoxim. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, L.; Lequerica, M.; Reid, C.R.; Latty, T. Dual ecosystem services of syrphid flies (Diptera: Syrphidae): Pollinators and biological control agents. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 1973–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotton, K.R.; Gao, B.; Menz, M.H.M.; Morris, R.K.A.; Ball, S.G.; Lim, K.S.; Reynolds, D.R.; Hu, G.; Chapman, J.W. Mass seasonal migrations of hoverflies provide extensive pollination and crop protection services. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 2167–2173.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.R.; Sun, Y.F.; Luo, S.P.; Wu, K.M. Characterization of antennal chemosensilla and associated odorant binding as well as chemosensory proteins in the Eupeodes corollae (Diptera: Syrphidae). J. Insect Physiol. 2019, 113, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.R.; Niu, L.L.; Sun, Y.F.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wu, K.M. Odorant binding proteins and chemosensory proteins in Episyrphus balteatus (Diptera: Syrphidae): Molecular cloning, expression profiling, and gene evolution. J. Insect Sci. 2020, 20, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.R. Chemosensory genes in the antennal transcriptome of two syrphid species, Episyrphus balteatus and Eupeodes corollae (Diptera: Syrphidae). BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dong, W.; Li, H.; D’Onofrio, C.; Bai, P.; Chen, R.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; et al. Molecular basis of (E)-β-farnesene-mediated aphid location in the predator Eupeodes corollae. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 951–962.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Nakano-Baker, O.; Godin, D.; MacKenzie, D.; Sarikaya, M. iOBPdb A database for experimentally determined functional characterization of insect odorant binding proteins. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hekmat-Scafe, D.S.; Scafe, C.R.; McKinney, A.J.; Tanouye, M.A. Genome-wide analysis of the odorant-binding protein gene family in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Gao, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, K.; Li, D.; Li, B.; Chen, L.; Gao, M.; Huangfu, N.; Elumalai, P.; et al. Chromosome-level genome assembly of marmalade hoverfly Episyrphus balteatus (Diptera: Syrphidae). Sci. Data 2024, 11, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Du, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, H.; Song, L.; Chen, Q.; Ren, B. An expanded odorant-binding protein mediates host cue detection in the parasitic wasp Baryscapus dioryctriae basis of the chromosome-level genome assembly analysis. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Duan, H.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, Q.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y. Key amino residues determining binding activities of the odorant binding protein AlucOBP22 to two host plant terpenoids of Apolygus lucorum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5949–5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.Q.; Chen, J.T.; Pan, Y.J.; Li, H.L. A sublethal dose of neonicotinoid imidacloprid precisely sensed and detoxified by a C-minus odorant-binding protein 17 highly expressed in the legs of Apis cerana. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.Y.; Li, G.C.; Wang, Z.Q.; Guo, Y.R.; Liu, N.Y. Combined transcriptomic, proteomic and genomic analysis identifies reproductive-related proteins and potential modulators of female behaviors in Spodoptera litura. Genomics 2021, 113, 1876–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Xu, K.; Ma, W.; Su, W.; Tai, M.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X. Contact chemosensory genes identified in leg transcriptome of Apis cerana cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2015–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Ishibashi, J.; Leal, W.S. Fatty acid solubilizer from the oral disk of the blowfly. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e51779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frerot, B.; Leppik, E.; Groot, A.T.; Unbehend, M.; Holopainen, J.K. Chemical signatures in plant: Insect interactions. Adv. Bot. Res. 2016, 81, 139–177. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; Clark, R.E.; Fu, Z.; Lee, B.W.; Crowder, D.W. Insect alarm pheromones in response to predators: Ecological trade-offs and molecular mechanisms. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 128, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Li, Z.X. Biosynthesis of aphid alarm pheromone is modulated in response to starvation stress under regulation by the insulin, glycolysis and isoprenoid pathways. J. Insect Physiol. 2021, 128, 104174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.F.; De Biasio, F.; Qiao, H.L.; Iovinella, I.; Yang, S.X.; Ling, Y.; Riviello, L.; Battaglia, D.; Falabella, P.; Yang, X.L.; et al. Two odorant-binding proteins mediate the behavioural response of aphids to the alarm pheromone (E)-ß-farnesene and structural analogues. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, C.; Yang, Z.K.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.P.; Li, F.Q.; Yang, X.L.; Luo, C. Binding affinity characterization of four antennae-enriched odorant-binding proteins from Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 829766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, J.T.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, J.L.; Li, X.C.; Liang, P.; Gao, X.W.; Zhou, J.J.; Gu, S.H. Coordinative mediation of the response to alarm pheromones by three odorant binding proteins in the green peach aphid Myzus persicae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 130, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.S.; Larter, N.K.; Chahda, J.S.; Rioux, D.; Gumaste, A.; Carlson, J.R. Humidity response depends on the small soluble protein Obp59a in Drosophila. eLife 2018, 7, e39249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, G.H.; Weber, A.L.; Wang, P.; Magwire, M.M.; Negron, Y.L.; Mackay, T.F.; Anholt, R.R. Natural variation, functional pleiotropy and transcriptional contexts of odorant binding protein genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2010, 186, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.C.; Gordon, B.; McDonough-Goldstein, C.E.; Misra, S.; Findlay, G.D.; Clark, A.G.; Wolfner, M.F. The seminal odorant binding protein Obp56g is required for mating plug formation and male fertility in Drosophila melanogaster. eLife 2023, 12, e86409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Gao, B.; Wu, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, K. Genome of the hoverfly Eupeodes corollae provides insights into the evolution of predation and pollination in insects. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.Q.; Wang, J.; Wong, G.K.; Yu, J. KaKs_Calculator: Calculating Ka and Ks through model selection and model averaging. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2006, 4, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Dai, L. ParaAT: A parallel tool for constructing multiple protein-coding DNA alignments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 419, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Accession Number | ORF (bp) | SP (aa) | MM (kDa) | pI | Class | Best Blastp Hit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene Annotation | E-Value | Identity % | |||||||
| EcorOBP1 | MT585316 | 351 | 1–19 | 14.02 | 7.66 | Classic | EcorOBP1 | 0.0 | 99.63 |
| EcorOBP2 | MT585317 | 759 | 1–18 | 28.94 | 7.86 | Plus-C | EcorOBP2 | 0.0 | 96.83 |
| EcorOBP3 | MT585318 | 570 | –– | 21.14 | 6.6 | Plus-C | EcorOBP3 | 6 × 10−131 | 98.19 |
| EcorOBP4 | MT585319 | 612 | 1–23 | 22.61 | 6.23 | Plus-C | EcorOBP4 | 6 × 10−148 | 99.51 |
| EcorOBP5 n | PQ284629 | 468 | 1–19 | 17.18 | 8.45 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129943204 [Eupeodes corollae] | 1 × 10−106 | 97.42 |
| EcorOBP7 | MT585321 | 468 | 1–16 | 18.44 | 5.59 | Minus-C | EcorOBP7 | 2 × 10−108 | 98.71 |
| EcorOBP8 | MT585322 | 456 | 1–19 | 17.46 | 5.73 | Classic | EcorOBP8 | 6 × 10−92 | 92.31 |
| EcorOBP9 | MT585323 | 450 | 1–18 | 16.53 | 4.88 | Classic | EcorOBP9 | 3 × 10−104 | 99.33 |
| EcorOBP10 | MT585324 | 447 | 1–16 | 16.94 | 6.09 | Minus-C | EcorOBP10 | 8 × 10−105 | 100 |
| EcorOBP11 | MT585325 | 444 | 1–18 | 16.40 | 5.07 | Minus-C | EcorOBP11 | 7 × 10−102 | 100 |
| EcorOBP12 | MT585326 | 441 | 1–20 | 16.49 | 5.52 | Classic | EcorOBP12 | 7 × 10−104 | 100 |
| EcorOBP13 | MT585327 | 441 | 1–16 | 16.61 | 6.32 | Minus-C | EcorOBP13 | 3 × 10−101 | 100 |
| EcorOBP14 n | PQ284630 | 399 | 1–19 | 14.69 | 5.67 | Classic | general odorant-binding protein 57c [Eupeodes corollae] | 1 × 10−91 | 100 |
| EcorOBP15 | MT585328 | 438 | 1–21 | 16.78 | 5.44 | Classic | EcorOBP15 | 2 × 10−102 | 99.31 |
| EcorOBP16 | MT585329 | 438 | 1–23 | 16.28 | 7.5 | Classic | EcorOBP16 | 3 × 10−99 | 97.93 |
| EcorOBP17 | MT585330 | 432 | 1–24 | 15.40 | 5.2 | Classic | EcorOBP17 | 3 × 10−97 | 100 |
| EcorOBP18 | MT585331 | 429 | 1–18 | 16.66 | 9.11 | Classic | EcorOBP18 | 6 × 10−98 | 100 |
| EcorOBP19 n | PQ284651 | 399 | 1–21 | 15.21 | 4.71 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129919207 [Episyrphus balteatus] | 7 × 10−48 | 58.02 |
| EcorOBP20 | MT585332 | 411 | 1–21 | 15.80 | 5.13 | Classic | EcorOBP20 | 1 × 10−96 | 99.28 |
| EcorOBP21 n | PQ284631 | 405 | 1–20 | 14.87 | 4.04 | Classic | general odorant-binding protein 56h-like [Eupeodes corollae] | 2 × 10−89 | 99.25 |
| EcorOBP22 | MT585333 | 411 | 1–20 | 15.37 | 5.53 | Classic | EcorOBP22 | 2 × 10−93 | 100 |
| EcorOBP23 n | PQ284632 | 408 | 1–20 | 15.13 | 4.14 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129939419 [Eupeodes corollae] | 8 × 10−91 | 100 |
| EcorOBP26 | MT585336 | 405 | 1–19 | 15.12 | 5.54 | Classic | EcorOBP26 | 9 × 10−86 | 94.78 |
| EcorOBP28 | MT585338 | 399 | 1–18 | 14.71 | 5.83 | Classic | EcorOBP28 | 5 × 10−89 | 99.24 |
| EcorOBP30 | MT585340 | 393 | 1–20 | 14.63 | 5.12 | Classic | EcorOBP30 | 1 × 10−86 | 98.46 |
| EcorOBP31 | MT585341 | 393 | 1–18 | 14.79 | 5.96 | Classic | EcorOBP31 | 1 × 10−89 | 99.23 |
| EcorOBP34 | MT585344 | 390 | 1–18 | 14.59 | 4.51 | Classic | EcorOBP34 | 2 × 10−86 | 99.22 |
| EcorOBP35 n | PQ284633 | 414 | 1–21 | 15.97 | 8.12 | Classic | general odorant-binding protein 56a-like [Eupeodes corollae] | 3 × 10−39 | 44.85 |
| EcorOBP36 n | PQ284634 | 441 | 1–23 | 16.89 | 4.98 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129940025 [Eupeodes corollae] | 8 × 10−96 | 96.58 |
| EcorOBP37 n | PQ284635 | 432 | 1–25 | 16.46 | 5.13 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129939358 [Eupeodes corollae] | 7 × 10−97 | 99.30 |
| EcorOBP38 n | PQ284636 | 441 | 1–19 | 16.50 | 4.65 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129940488 [Eupeodes corollae] | 3 × 10−101 | 100 |
| EcorOBP39 n | PQ284637 | 429 | 1–22 | 16.76 | 5.03 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129938798 [Eupeodes corollae] | 1 × 10−90 | 97.18 |
| EcorOBP40 n | PQ284638 | 366 | 5′missing | 13.71 | 8.18 | Classic | general odorant-binding protein lush [Eupeodes corollae] | 4 × 10−84 | 100 |
| EcorOBP41 n | PQ284639 | 558 | 1–20 | 21.05 | 7.59 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129946411 [Eupeodes corollae] | 8 × 10−128 | 97.30 |
| EcorOBP42 n | PQ284640 | 660 | 1–19 | 25.27 | 5.91 | Classic | general odorant-binding protein 70 [Eupeodes corollae] | 1 × 10−162 | 100 |
| EcorOBP43 n | PQ284641 | 384 | 1–19 | 14.68 | 4.91 | Classic | general odorant-binding protein 56d-like [Eupeodes corollae] | 3 × 10−87 | 98.43 |
| EcorOBP44 n | PQ284642 | 438 | 1–20 | 16.40 | 4.55 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129939463 [Eupeodes corollae] | 3 × 10−102 | 100 |
| EcorOBP45 n | PQ284652 | 561 | –– | 21.07 | 9.34 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129952676 [Eupeodes corollae] | 4 × 10−133 | 98.39 |
| EcorOBP46 n | PQ284643 | 603 | 1–29 | 22.47 | 6.70 | Plus-C | uncharacterized protein LOC129952205 [Eupeodes corollae] | 2 × 10−147 | 99.50 |
| EcorOBP47 n | PQ284644 | 465 | 1–20 | 17.84 | 4.45 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129939928 [Eupeodes corollae] | 5 × 10−106 | 97.40 |
| EcorOBP48 n | PQ846003 | 1209 | –– | 45.96 | 7.47 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129942694 [Eupeodes corollae] | 0.0 | 98.76 |
| EcorOBP49 n | PQ284645 | 399 | 1–19 | 15.94 | 5.62 | Minus-C | EcorOBP6 | 1 × 10−80 | 88.64 |
| EcorOBP50 n | PQ284646 | 429 | 1–15 | 16.61 | 6.38 | Minus-C | general odorant-binding protein 99a-like [Eupeodes corollae] | 4 × 10−95 | 99.30 |
| EcorOBP51 n | PQ284647 | 429 | 1–19 | 16.21 | 4.65 | Minus-C | uncharacterized protein LOC129942711 [Eupeodes corollae] | 7 × 10−96 | 97.18 |
| EcorOBP52 n | PQ284648 | 504 | 1–19 | 19.25 | 5.18 | Classic | general odorant-binding protein 99a-like [Eupeodes corollae] | 5 × 10−116 | 97.61 |
| EcorOBP53 n | PQ284649 | 447 | 1–22 | 16.76 | 5.22 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129940557 [Eupeodes corollae] | 9 × 10−102 | 99.32 |
| EcorOBP54 n | PQ284650 | 411 | 1–19 | 15.63 | 5.01 | Classic | uncharacterized protein LOC129941715 [Eupeodes corollae] | 1 × 10−93 | 99.26 |
| Gene Pair Compared | Ka | Ks | Pairwise Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|
| EcorOBP1-EbalOBP2 | 0.10131 | 1.05918 | 0.09565 |
| EcorOBP2-EbalOBP1 | 0.24240 | 1.19253 | 0.20327 |
| EcorOBP4-EbalOBP3 | 0.23683 | 0.95730 | 0.24740 |
| EcorOBP7-EbalOBP18 | 0.34741 | 1.07076 | 0.32445 |
| EcorOBP8-EbalOBP26 | 0.61546 | 1.44500 | 0.42592 |
| EcorOBP9-EbalOBP13 | 0.09568 | 0.68299 | 0.14009 |
| EcorOBP10-EbalOBP12 | 0.20224 | 0.70834 | 0.28552 |
| EcorOBP11-EbalOBP14 | 0.29320 | 0.80486 | 0.36429 |
| EcorOBP12-EbalOBP20 | 0.00877 | 0.26438 | 0.03320 |
| EcorOBP13-EbalOBP21 | 0.21247 | 1.11337 | 0.19083 |
| EcorOBP15-EbalOBP23 | 0.02958 | 0.29025 | 0.10191 |
| EcorOBP16-EbalOBP22 | 0.03274 | 1.46490 | 0.02235 |
| EcorOBP17-EbalOBP24 | 0.19724 | 0.90357 | 0.21829 |
| EcorOBP18-EbalOBP25 | 0.03152 | 0.62774 | 0.05021 |
| EcorOBP20-EbalOBP31 | 0.06263 | 0.90399 | 0.06928 |
| EcorOBP23-EbalOBP32 | 0.31054 | 0.70558 | 0.44013 |
| EcorOBP37-EbalOBP29 | 0.26758 | 1.12227 | 0.23843 |
| EcorOBP40-EbalOBP17 | 0.09451 | 1.08560 | 0.08705 |
| EcorOBP44-EbalOBP19 | 0.19349 | 0.95005 | 0.20366 |
| EcorOBP46-EbalOBP4 | 0.12787 | 0.86276 | 0.14822 |
| EcorOBP48-EbalOBP26 | 0.89590 | 2.20138 | 0.40697 |
| EcorOBP49-EbalOBP8 | 0.34413 | 0.85256 | 0.40364 |
| EcorOBP52-EbalOBP45 | 0.66046 | 1.06255 | 0.62157 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, H.; Jia, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Wu, C.; Wu, K. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analyses of Odorant-Binding Proteins in Hoverfly Eupeodes corollae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188956
Yuan H, Jia H, Zhou X, Li H, Wu C, Wu K. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analyses of Odorant-Binding Proteins in Hoverfly Eupeodes corollae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188956
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, He, Huiru Jia, Xianyong Zhou, Hui Li, Chao Wu, and Kongming Wu. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analyses of Odorant-Binding Proteins in Hoverfly Eupeodes corollae" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188956
APA StyleYuan, H., Jia, H., Zhou, X., Li, H., Wu, C., & Wu, K. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analyses of Odorant-Binding Proteins in Hoverfly Eupeodes corollae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188956






