The Effect of Escin on the Plasma Membrane of Human Red Blood Cells
Abstract
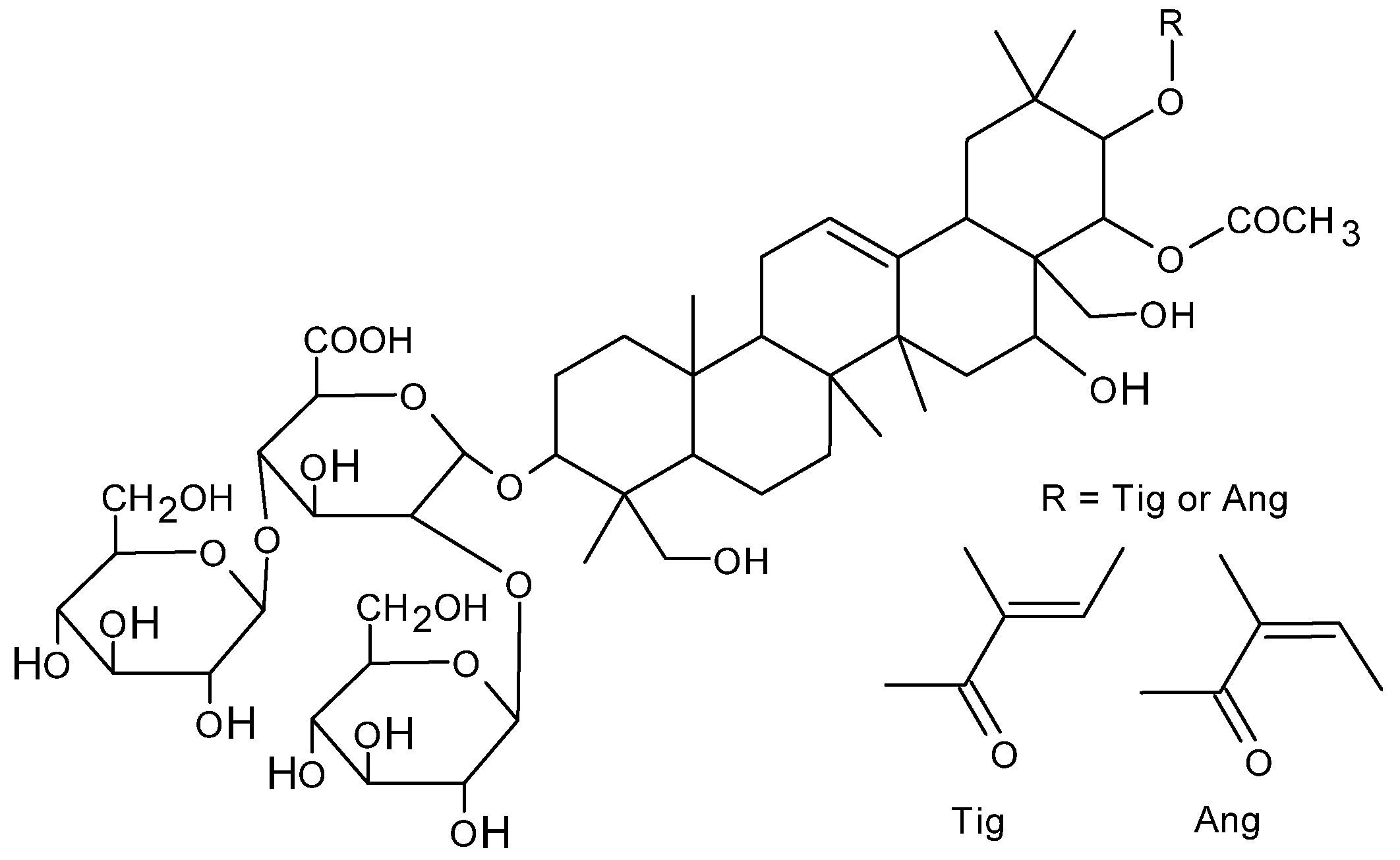
1. Introduction
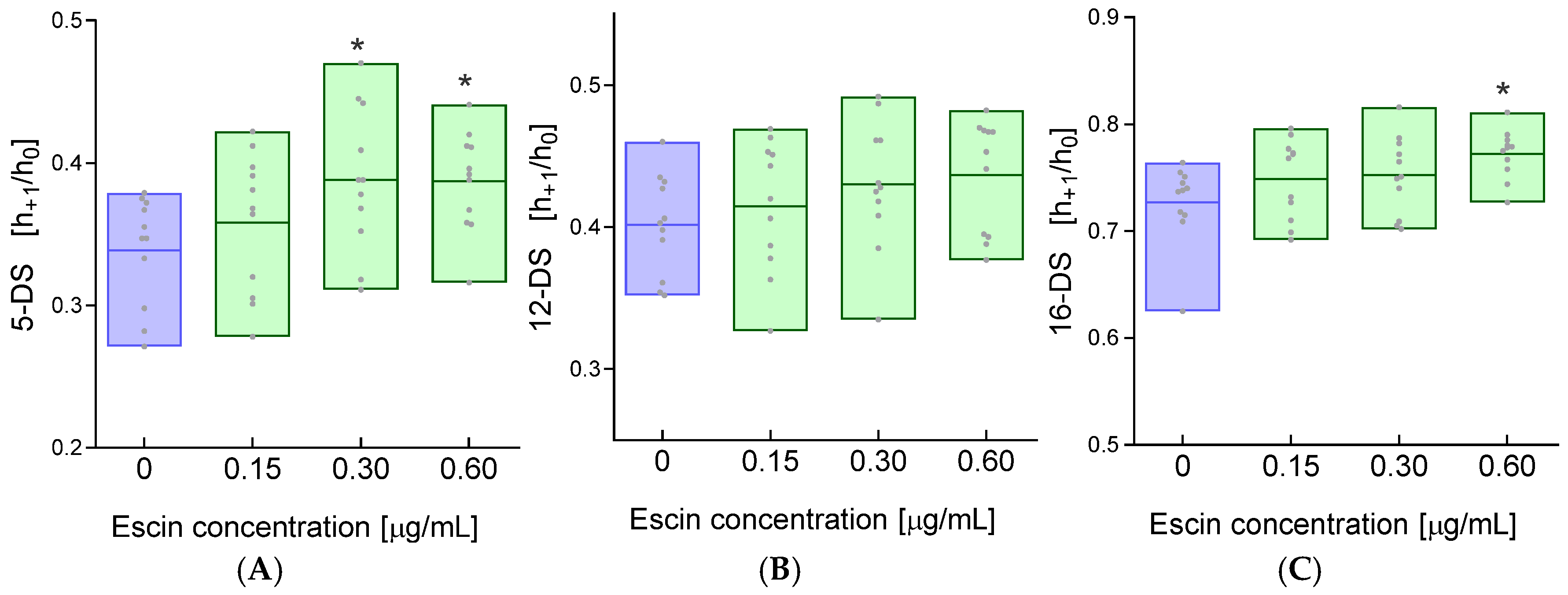
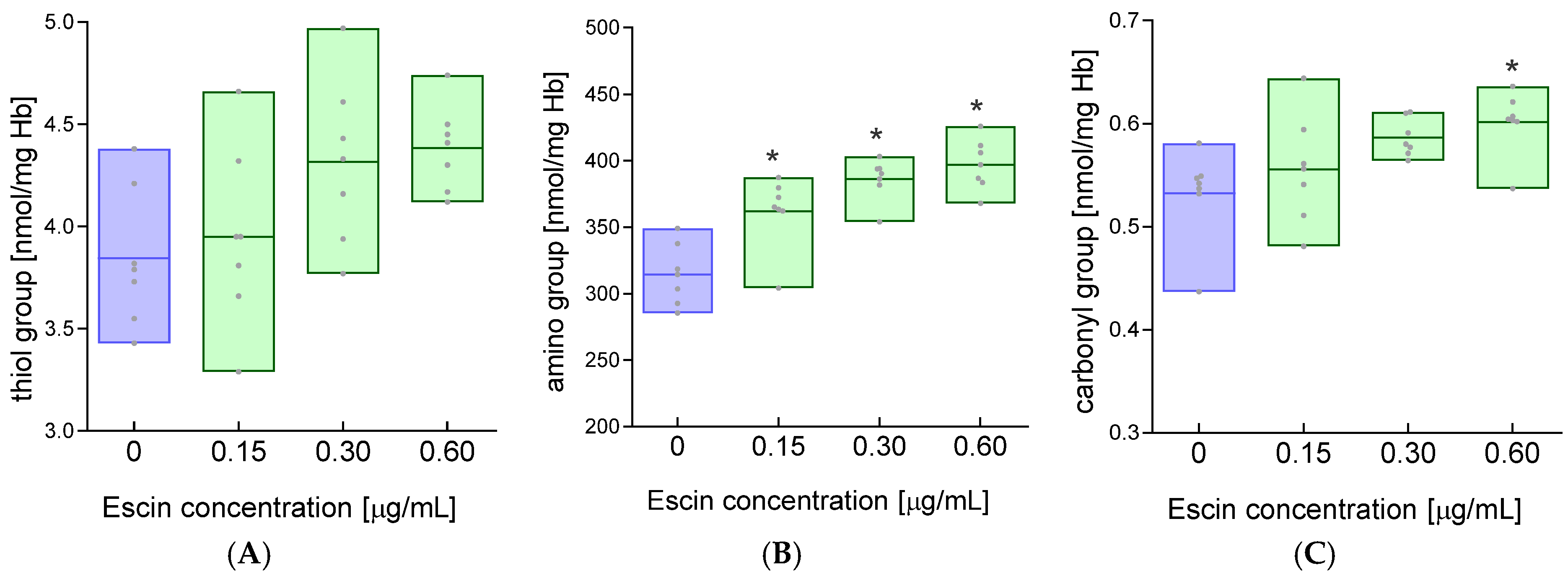
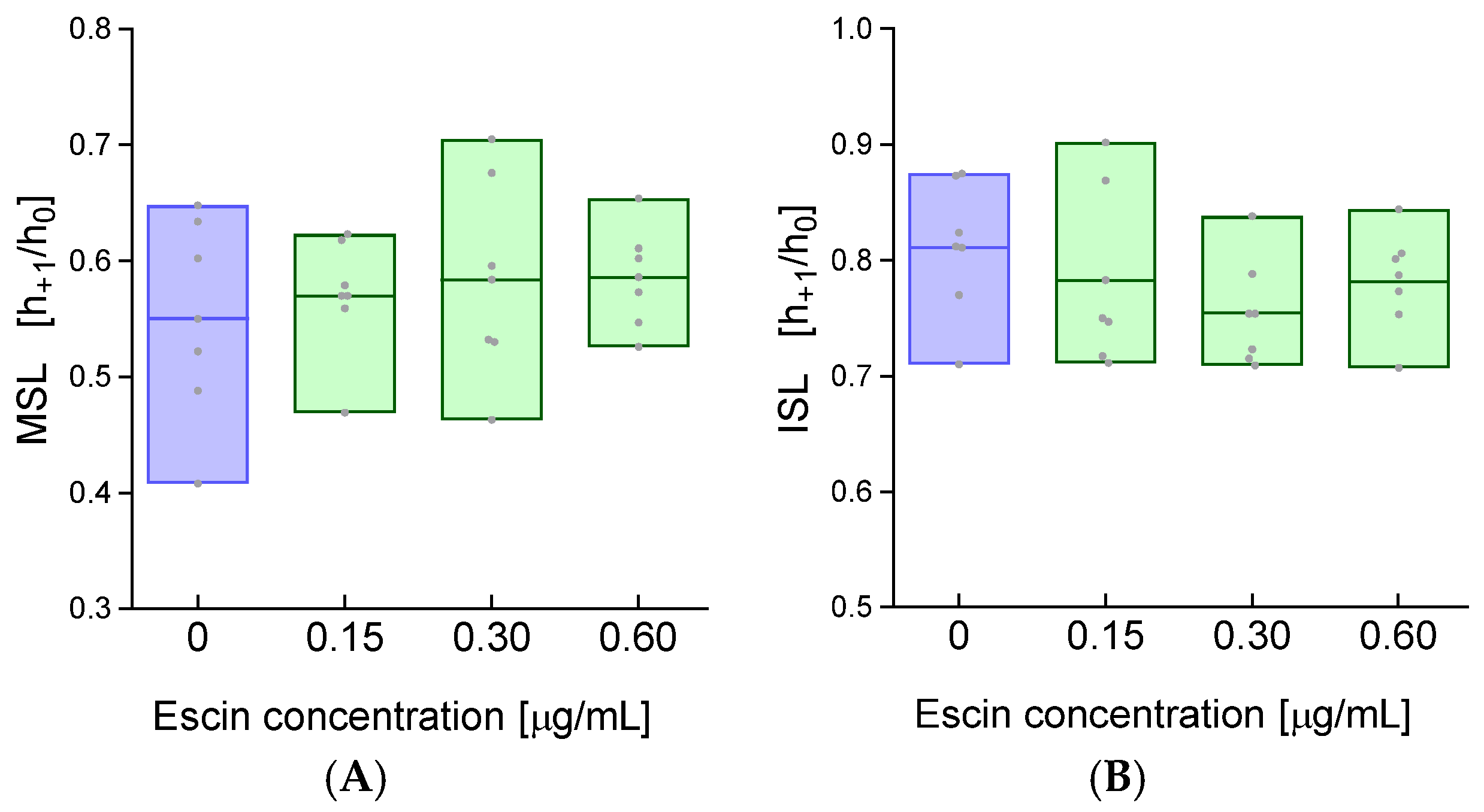
2. Results
3. Disscussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Experimental Protocol
4.3. Determination of the Degree of Hemolysis
4.4. Determination of Cell Membrane Fluidity
4.5. Determination of the Conformational State of Membrane Proteins
4.6. Measurement of the Concentration of Free Thiol Groups
4.7. Measurement of the Concentration of Amino Groups
4.8. Measurement of Carbonyl Group Concentration
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheok, C.Y.; Salman, H.A.K.; Sulaiman, R. Extraction and quantification of saponins: A review. Food Res. Int. 2014, 59, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netala, V.R.; Ghosh, S.B.; Bobbu, P.; Anitha, D.; Tartte, V. Triterpenoid saponins: A review on biosynthesis, Applications and mechanism of their action. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 59, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Geisler, R.; Dargel, C.; Hellweg, T. The Biosurfactant β-Aescin: A Review on the Physico-Chemical Properties and Its Interaction with Lipid Model Membranes and Langmuir Monolayers. Molecules 2019, 25, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirtori, C.R. Aescin: Pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic profile. Pharmacol. Res. 2001, 44, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, P.A.; Alves, M.C.; Polonini, H.C.; Dutra, L.S.; Leite, M.N.; Raposo, N.R.B.; Ferreira, A.D.O.; Brandão, M.A.F. New HPLC method for quality control of β-Escin in Aesculus hippocastanum L. Hydroalcohol. Extr. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2013, 32, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.-J.; Zhang, M.-L.; Cui, X.-Y.; Gao, F.; He, Q.; Li, X.-J.; Zhang, J.-W.; Fawcett, J.P.; Gu, J.-K. Comparative pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of escin Ia and isoescin Ia after administration of escin and of pure escin Ia and isoescin Ia in rat. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, A.S.; Ahmed, A.M.; Tariq, M.R. Study of saponins in methanol extract of the leaves of acacia etbaica subspecies etbaica. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 803–810. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Laval, S.; Yu, B. Chemical synthesis of saponins. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 2014, 71, 137–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarino, P.; Colson, E.; André, J.; Gerbaux, P. Horse Chestnut Saponins-Escins, Isoescins, Transescins, and Desacylescins. Molecules 2023, 28, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hien, H.M.; Le Hien, P.; Hung, T.V. New HPLC pattern-oriented approach for quality control of enteric coated tablets containing aescin from Aesculus hippocastanum. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 222, 115106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Li, Y.; Murakami, T.; Ninomiya, K.; Yamahara, J.; Yoshikawa, M. Effects of escins Ia, Ib, IIa, and IIb from horse chestnut, the seeds of Aesculus hippocastanum L., on acute inflammation in animals. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 20, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jiang, N.; Xin, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Fan, H.; Du, Y.; Li, C.; Fu, F. Protective effect of aescin from the seeds of Aesculus hippocastanum on liver injury induced by endotoxin in mice. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.-Q.; Xu, S.-Q.; Cheng, J.; Cao, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.-P.; Huang, Y.-J.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.-M. Anti-inflammatory effect of external use of escin on cutaneous inflammation: Possible involvement of glucocorticoids receptor. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, D.H.J.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G.; Wang, L.; Hui, K.M.; Kumar, A.P.; Tran, T. Molecular targets and anti-cancer potential of escin. Cancer Lett. 2018, 422, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Lao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Niu, J.; Xiao, Z.; Arulselvan, P.; Shen, J. Escin induces apoptosis in ovarian cancer cell line by triggering S-phase cell cycle arrest and p38 MAPK/ERK pathway inhibition. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 101644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.R. The post-thrombotic syndrome. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2010, 2010, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.R. The post thrombotic syndrome. Thromb. Res. 2011, 127 (Suppl. S3), S89–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek-Makuch, M.; Studzińska-Sroka, E. Horse chestnut—Efficacy and safety in chronic venous insufficiency: An overview. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2015, 25, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittler, M.H.; Ernst, E. Horse chestnut seed extract for chronic venous insufficiency. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 11, CD003230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patlolla, J.M.R.; Rao, C.V. Anti-inflammatory and Anti-cancer Properties of β-Escin, a Triterpene Saponin. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 1, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, F.; Wink, M. Synergistic interactions of saponins and monoterpenes in HeLa cells, Cos7 cells and in erythrocytes. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallelli, L. Escin: A review of its anti-edematous, anti-inflammatory, and venotonic properties. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 3425–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreij, R.; Dargel, C.; Moleiro, L.H.; Monroy, F.; Hellweg, T. Aescin Incorporation and Nanodomain Formation in DMPC Model Membranes. Langmuir 2017, 33, 12351–12361, Erratum in Langmuir 2017, 33, 14527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorent, J.H.; Quetin-Leclercq, J.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.-P. The amphiphilic nature of saponins and their effects on artificial and biological membranes and potential consequences for red blood and cancer cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8803–8822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleiro, L.H.; Martín-Romero, M.T.; Herráez-Aguilar, D.; Santiago, J.A.; Caselli, N.; Dargel, C.; Geisler, R.; Hellweg, T.; Monroy, F. Dual mechanical impact of β-escin on model lipid membranes. Front. Soft Matter 2023, 3, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharmakognosie—Phytopharmazie, 8th ed.; überarbeitete und aktualisierte Auflage; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; ISBN 9783540342816.
- van Wyk, B.-E.; Wink, M. Medicinal Plants of the World: An Illustrated Scientific Guide to Important Medicinal Plants and Their Uses; Briza Pub: Pretoria, South Africa, 2004; ISBN 1875093443. [Google Scholar]
- Wink, M. Bioprospecting: The Search for Bioactive Lead Structures from Nature. In Medicinal Plant Biotechnology; Kayser, O., Quax, W.J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 97–116. ISBN 9783527314430. [Google Scholar]
- Wink, M. Evolutionary advantage and molecular modes of action of multi-component mixtures used in phytomedicine. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, C.; Legault, J.; Girard-Lalancette, K.; Mshvildadze, V.; Pichette, A. Haemolytic activity, cytotoxicity and membrane cell permeabilization of semi-synthetic and natural lupane- and oleanane-type saponins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, L.W.; Simpson, M.J. Topology of a protein spin label in erythrocyte membranes. FEBS Lett. 1979, 108, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masullo, M.; Pizza, C.; Piacente, S. Ruscus Genus: A Rich Source of Bioactive Steroidal Saponins. Planta Medica 2016, 82, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, S.J.; Nicolson, G.L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science 1972, 175, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Meer, G.; Voelker, D.R.; Feigenson, G.W. Membrane lipids: Where they are and how they behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, R.; Ursell, T.; Wiggins, P.; Sens, P. Emerging roles for lipids in shaping membrane-protein function. Nature 2009, 459, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorent, J.H.; Levental, K.R.; Ganesan, L.; Rivera-Longsworth, G.; Sezgin, E.; Doktorova, M.; Lyman, E.; Levental, I. Plasma membranes are asymmetric in lipid unsaturation, packing and protein shape. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 644–652, Erratum in Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Gallot, G. Dynamics of Cell Membrane Permeabilization by Saponins Using Terahertz Attenuated Total Reflection. Biophys. J. 2020, 119, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, E.; Stoya, G.; Völkner, A.; Richter, W.; Lemke, C.; Linss, W. Hemolysis of human erythrocytes with saponin affects the membrane structure. Acta Histochem. 2000, 102, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwozdzinski, L.; Bernasinska-Slomczewska, J.; Hikisz, P.; Wiktorowska-Owczarek, A.; Kowalczyk, E.; Pieniazek, A. The Effect of Diosmin, Escin, and Bromelain on Human Endothelial Cells Derived from the Umbilical Vein and the Varicose Vein-A Preliminary Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domanski, D.; Zegrocka-Stendel, O.; Perzanowska, A.; Dutkiewicz, M.; Kowalewska, M.; Grabowska, I.; Maciejko, D.; Fogtman, A.; Dadlez, M.; Koziak, K. Molecular Mechanism for Cellular Response to β-Escin and Its Therapeutic Implications. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, J.T.; Mitchell, C.; Hanahan, D.J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1963, 100, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Iwakiri, Y.; Tokuhiro, S.; Fukushima, S.; Takeuchi, Y. Protective effects of some neutral amino acids against hypotonic hemolysis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowell, E.A.; Ough, C.S.; Bakalinsky, A. Determination of Alpha Amino Nitrogen in Musts and Wines by TNBS Method. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1985, 36, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.L.; Garland, D.; Oliver, C.N.; Amici, A.; Climent, I.; Lenz, A.G.; Ahn, B.W.; Shaltiel, S.; Stadtman, E.R. Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gwozdzinski, L.; Pieniazek, A.; Gwozdzinski, K. The Effect of Escin on the Plasma Membrane of Human Red Blood Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188923
Gwozdzinski L, Pieniazek A, Gwozdzinski K. The Effect of Escin on the Plasma Membrane of Human Red Blood Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188923
Chicago/Turabian StyleGwozdzinski, Lukasz, Anna Pieniazek, and Krzysztof Gwozdzinski. 2025. "The Effect of Escin on the Plasma Membrane of Human Red Blood Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188923
APA StyleGwozdzinski, L., Pieniazek, A., & Gwozdzinski, K. (2025). The Effect of Escin on the Plasma Membrane of Human Red Blood Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188923




